A New Approach for Deepfake Detection with the Choquet Fuzzy Integral
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Deepfake Video Creation
2.1.1. Reenactment
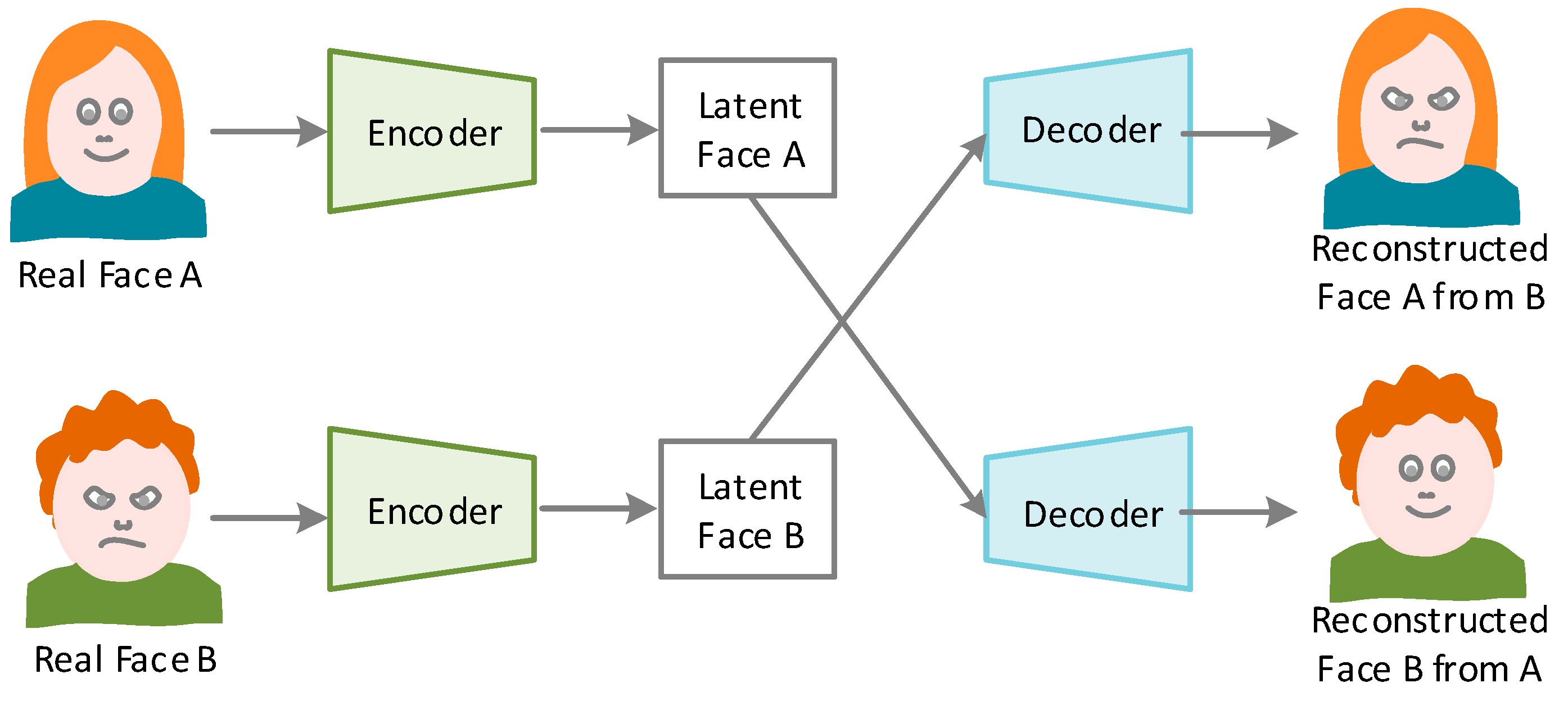
2.1.2. Replacement
2.1.3. Editing
2.1.4. Synthesis
2.2. Deepfake Video Detection
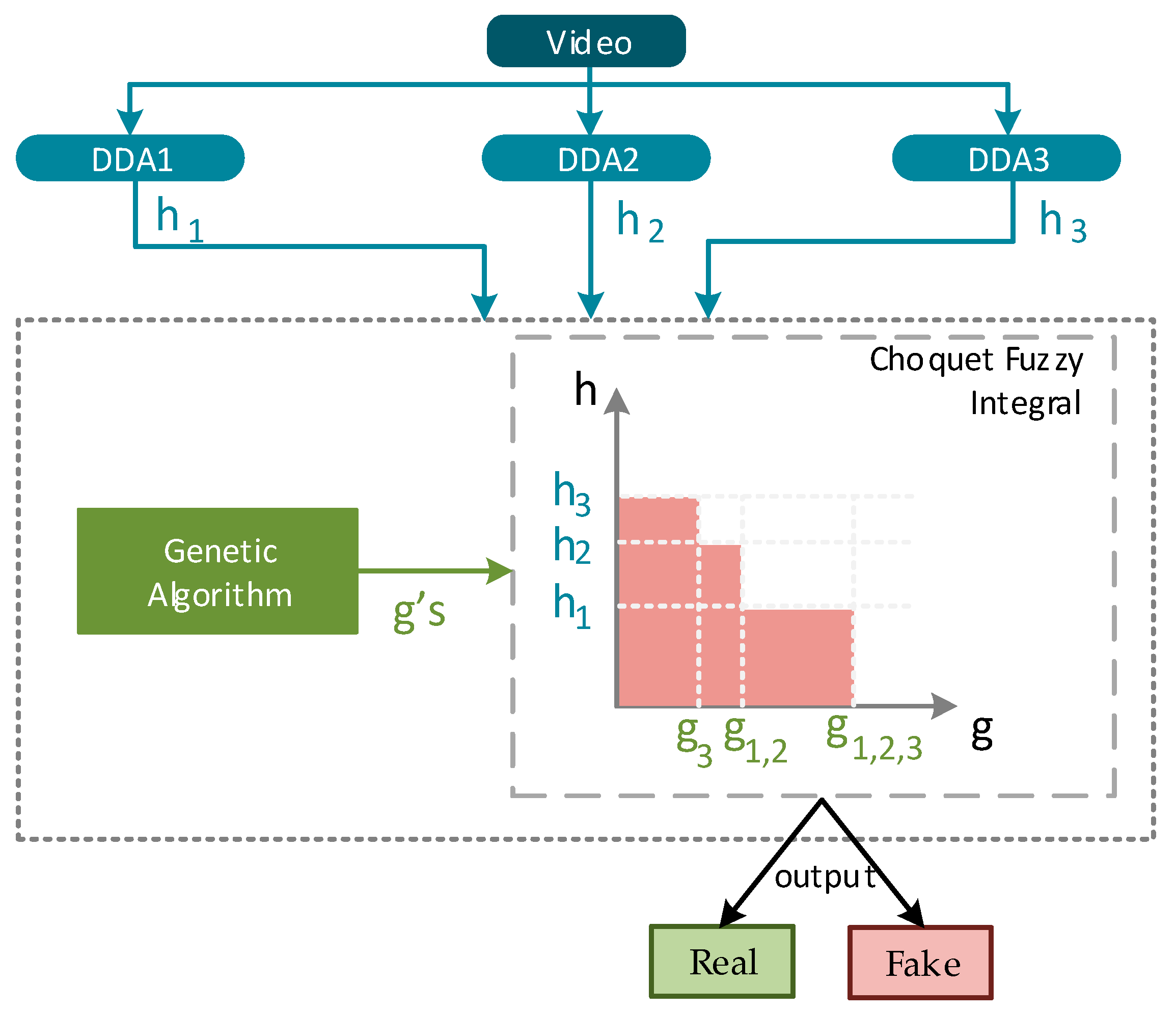
3. Proposed Method
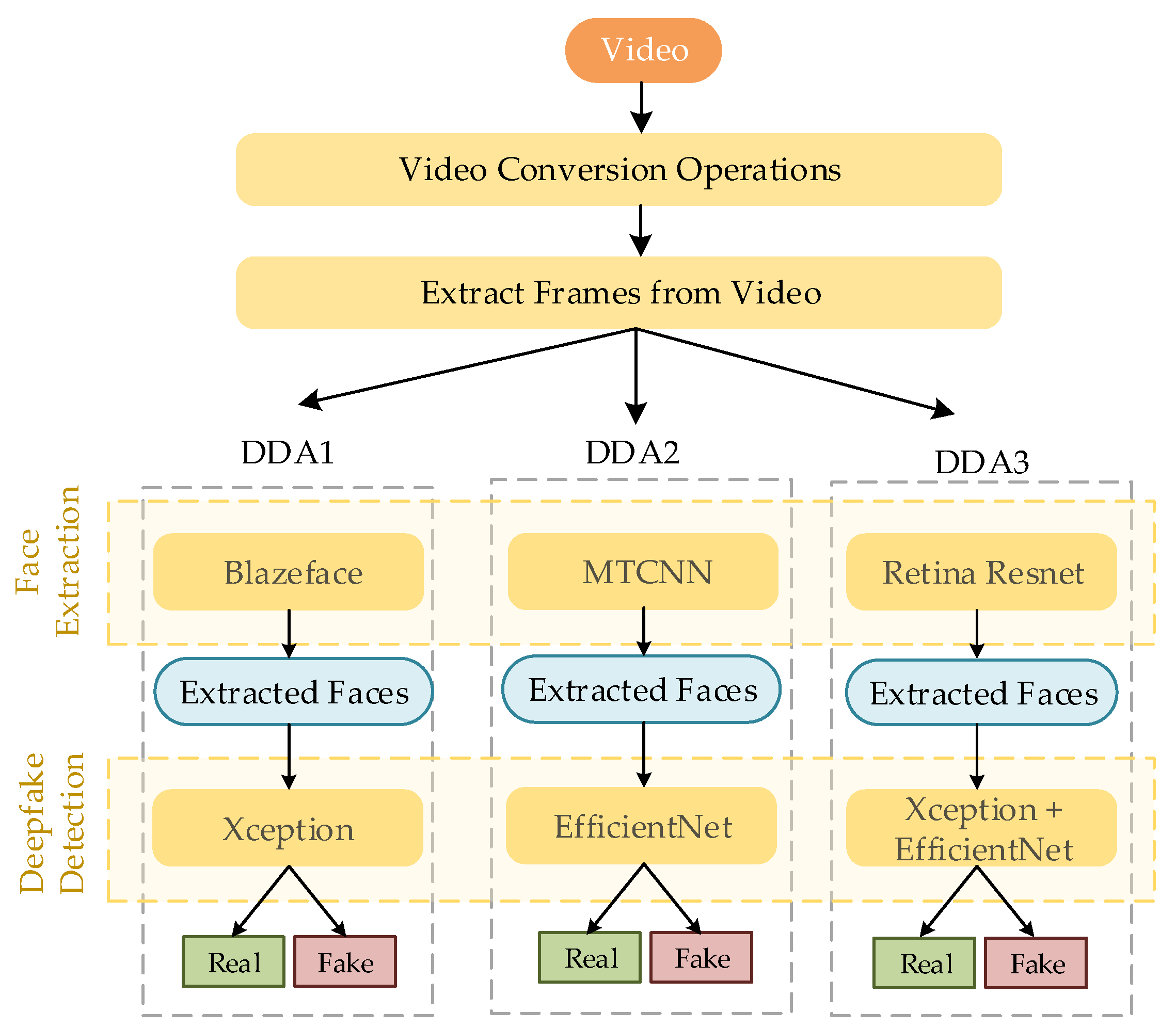
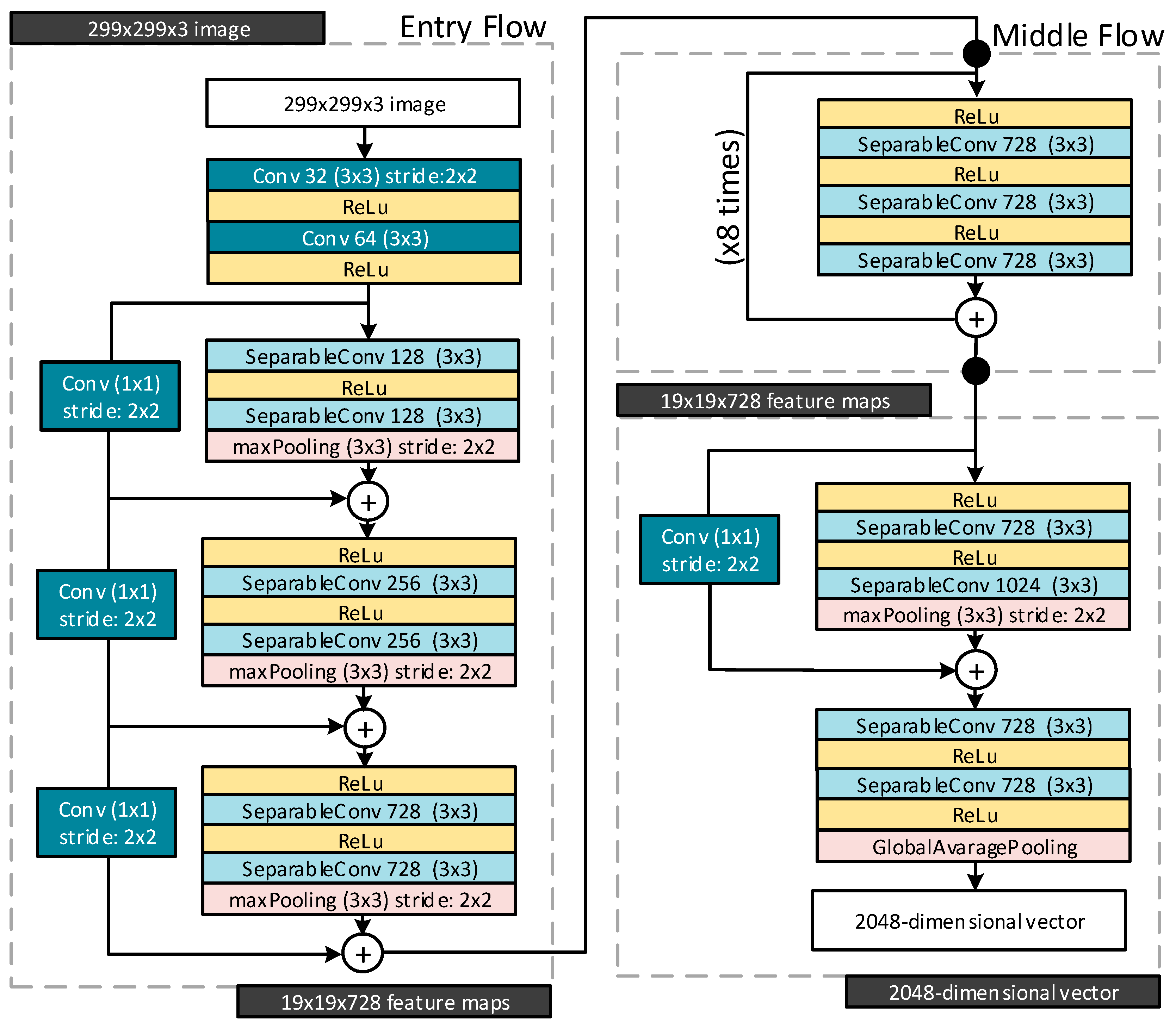
3.1. Deepfake Detection Algorithm 1 (DDA 1)
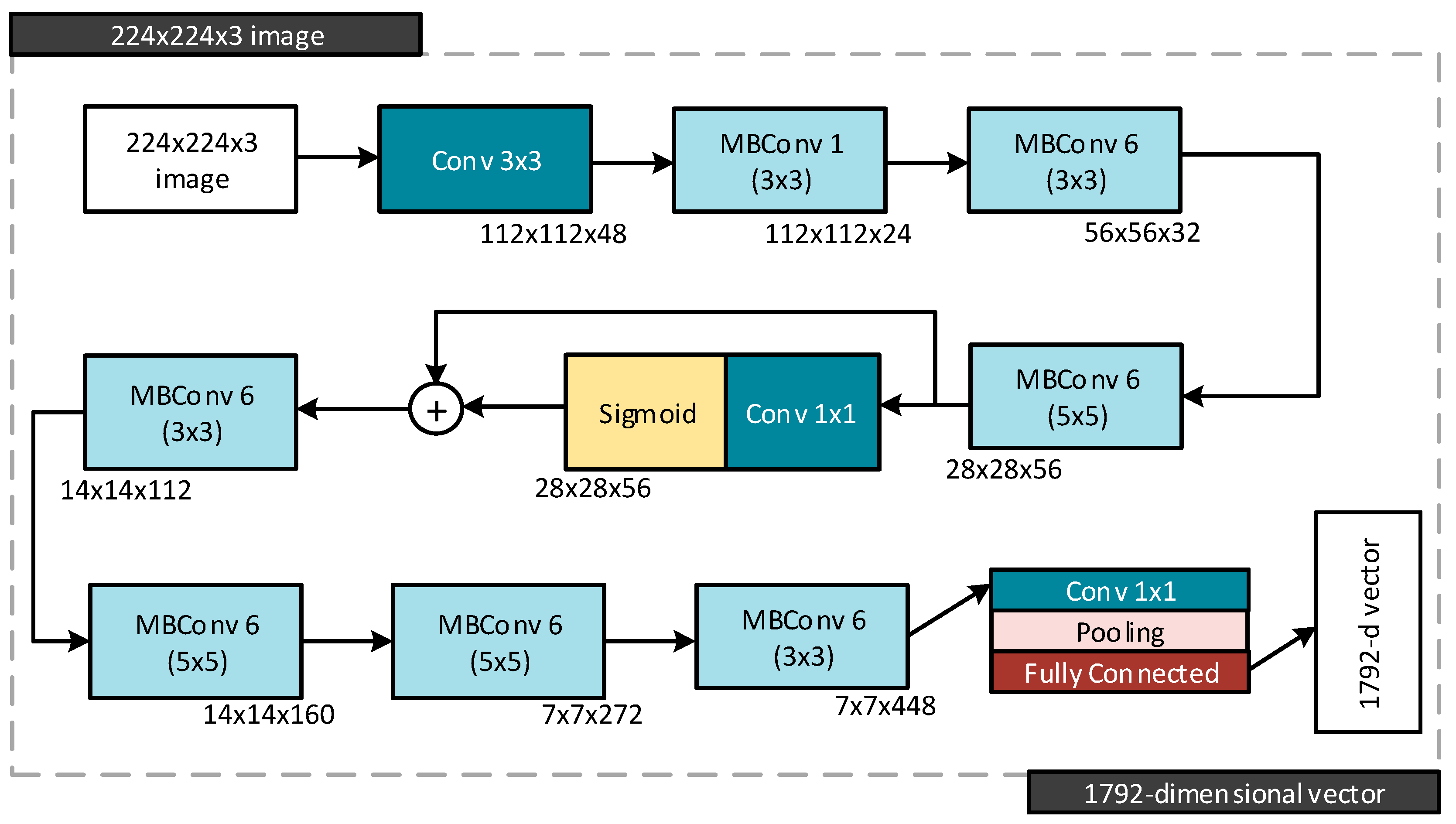
3.2. Deepfake Detection Algorithm 2 (DDA 2)
3.3. Deepfake Detection Algorithm 3 (DDA 3)
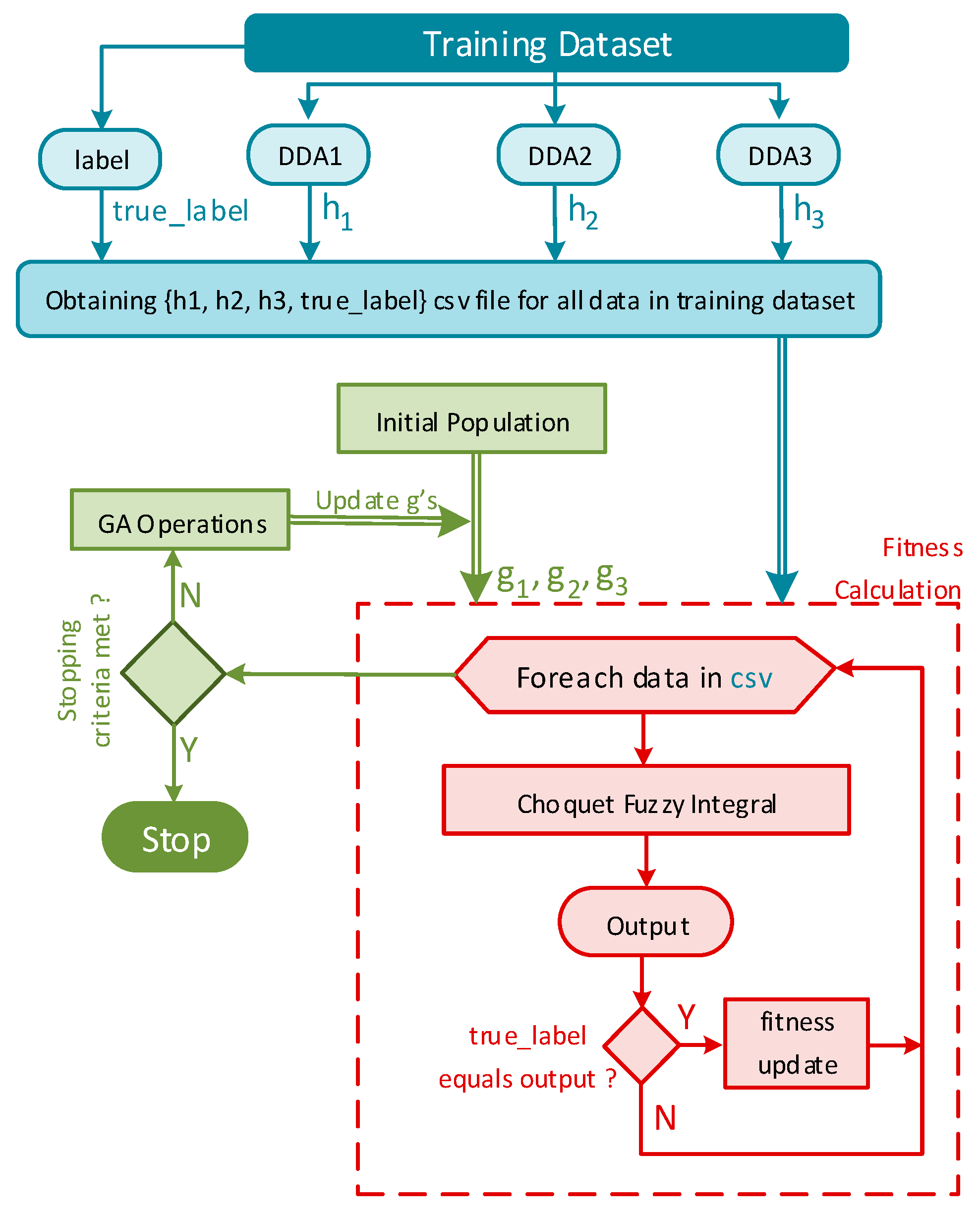
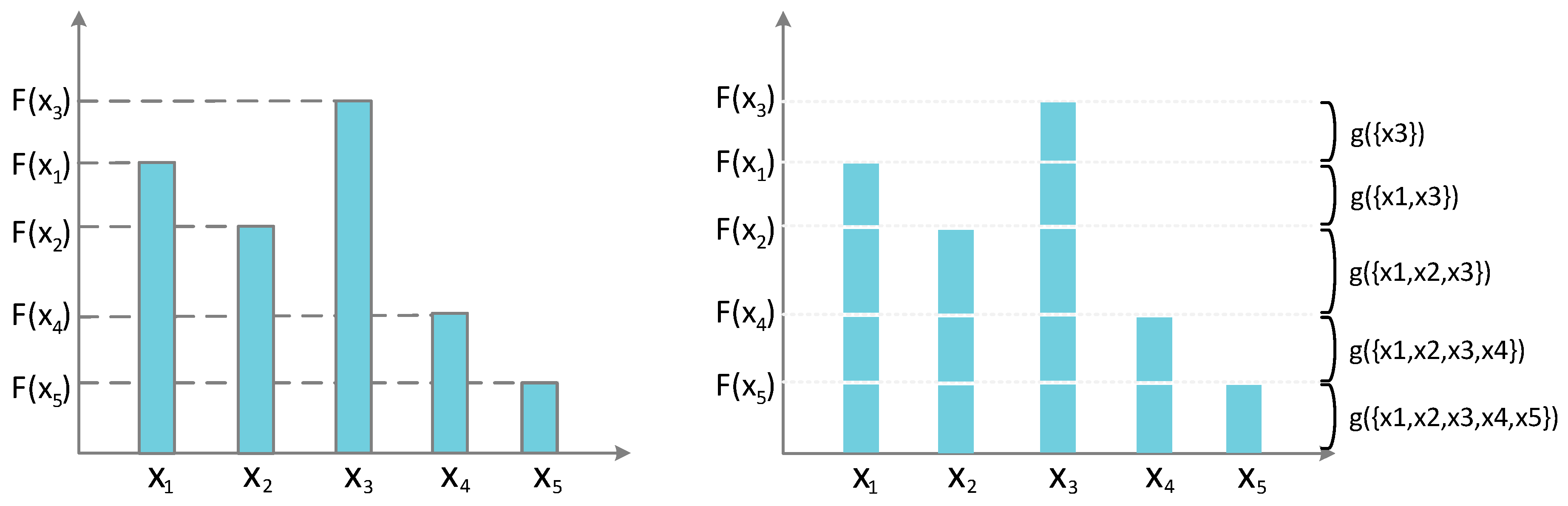
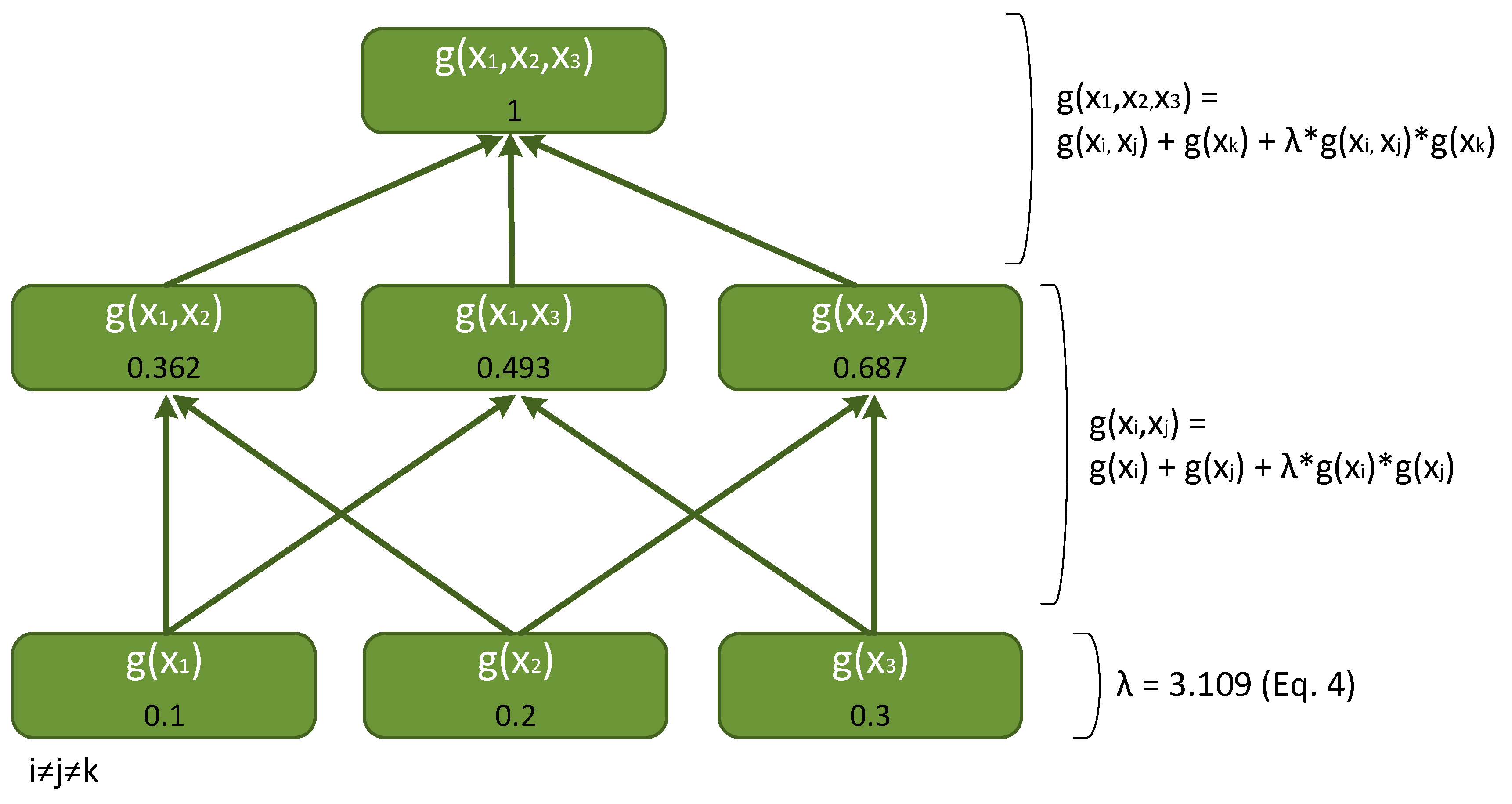
3.4. The Choquet Fuzzy Integral
4. Experimental Results
5. Discussions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berrahal, M.; Boukabous, M.; Idrissi, I. A Comparative Analysis of Fake Image Detection in Generative Adversarial Networks and Variational Autoencoders. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Decision Aid Sciences and Applications (DASA), Annaba, Algeria, 16–17 September 2023; pp. 223–230. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, H.; Kaur, K.; Mohan Nahak, F.; Singh, S.K.; Kumar, S. Deepfake as an Artificial Intelligence tool for VFX Films. In Proceedings of the 2023 7th International Conference on Computation System and Information Technology for Sustainable Solutions (CSITSS), Bangalore, India, 2–4 November 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Seymour, M.; Riemer, K.; Yuan, L.; Dennis, A.R. Beyond Deep Fakes. Commun. ACM 2023, 66, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshed, M.A.; Mumtaz, S.; Ibrahim, M.; Dewi, C.; Tanveer, M.; Ahmed, S. Multiclass AI-Generated Deepfake Face Detection Using Patch-Wise Deep Learning Model. Computers 2024, 13, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, A.; Munir, K.; Almutairi, M. A Novel Deep Learning Approach for Deepfake Image Detection. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afchar, D.; Nozick, V.; Yamagishi, J.; Echizen, I. Mesonet: A compact facial video forgery detection network. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Workshop on Information Forensics and Security (WIFS), Hong Kong, China, 11–13 December 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–7. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8630761/ (accessed on 27 February 2024).
- Korshunov, P.; Marcel, S. DeepFakes: A New Threat to Face Recognition? Assessment and Detection. arxiv 2018, arXiv:1812.08685. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1812.08685 (accessed on 23 February 2024).
- Ismail, A.; Elpeltagy, M.; Zaki, M.S.; Eldahshan, K. A new deep learning-based methodology for video deepfake detection using XGBoost. Sensors 2021, 21, 5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, A.; Mohanty, S.P.; Corcoran, P.; Kougianos, E. A Machine Learning Based Approach for Deepfake Detection in Social Media Through Key Video Frame Extraction. SN Comput. Sci. 2021, 2, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, D.; Kumar, Y.J.; Goh, O.S.; Ye, Z.; Chi, W. DeepfakeNet, an efficient deepfake detection method. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2021, 12, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almars, A.M. Deepfakes detection techniques using deep learning: A survey. J. Comput. Commun. 2021, 9, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T. Deepfake generation and detection, a survey. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 6259–6276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İlhan, İ.; Karaköse, M. A Comparison Study for The Detection and Applications of Deepfake Videos. Adıyaman Üniversitesi Mühendislik Bilim. Derg. 2021, 8, 47–60. [Google Scholar]
- AtaŞ, S.; İlhan, İ.; KarakÖse, M. An Efficient Deepfake Video Detection Approach with Combination of EfficientNet and Xception Models Using Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2022 26th International Conference on Information Technology (IT), Zabljak, Montenegro, 16–19 February 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 1–4. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9743542/ (accessed on 27 February 2024).
- Dey, S.; Bhattacharya, R.; Malakar, S.; Mirjalili, S.; Sarkar, R. Choquet fuzzy integral-based classifier ensemble technique for COVID-19 detection. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 135, 104585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taha, A.; Barukab, O.; Malebary, S. Fuzzy integral-based multi-classifiers ensemble for android malware classification. Mathematics 2021, 9, 2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadha, A.; Kumar, V.; Kashyap, S.; Gupta, M. Deepfake: An Overview. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Computing, Communications, and Cyber-Security, Ghaziabad, India, 3–4 October 2020; Singh, P.K., Wierzchoń, S.T., Tanwar, S., Ganzha, M., Rodrigues, J.J.P.C., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems. Springer: Singapore, 2021; Volume 203, pp. 557–566, ISBN 9789811607325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirsky, Y.; Lee, W. The Creation and Detection of Deepfakes: A Survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2022, 54, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yu, Y. Face Transfer with Generative Adversarial Network. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1710.06090. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1710.06090 (accessed on 25 May 2024).
- Kietzmann, J.; Lee, L.W.; McCarthy, I.P.; Kietzmann, T.C. Deepfakes: Trick or treat? Bus. Horiz. 2020, 63, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thies, J.; Zollhofer, M.; Stamminger, M.; Theobalt, C.; Nießner, M. Face2face: Real-time face capture and reenactment of rgb videos. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 2387–2395. Available online: http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_cvpr_2016/html/Thies_Face2Face_Real-Time_Face_CVPR_2016_paper.html (accessed on 27 February 2024).
- Nguyen, T.T.; Nguyen, Q.V.H.; Nguyen, D.T.; Nguyen, D.T.; Huynh-The, T.; Nahavandi, S.; Nguyen, T.T.; Pham, Q.-V.; Nguyen, C.M. Deep learning for deepfakes creation and detection: A survey. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2022, 223, 103525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chang, M.-C.; Lyu, S. In ictu oculi: Exposing ai created fake videos by detecting eye blinking. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Workshop on Information Forensics and Security (WIFS), Hong Kong, China, 11–13 December 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–7. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8630787/ (accessed on 27 February 2024).
- de Lima, O.; Franklin, S.; Basu, S.; Karwoski, B.; George, A. Deepfake Detection using Spatiotemporal Convolutional Networks. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.14749. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/2006.14749 (accessed on 23 February 2024).
- Sabir, E.; Cheng, J.; Jaiswal, A.; AbdAlmageed, W.; Masi, I.; Natarajan, P. Recurrent convolutional strategies for face manipulation detection in videos. Interfaces 2019, 3, 80–87. [Google Scholar]
- Güera, D.; Delp, E.J. Deepfake video detection using recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 15th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance (AVSS), Auckland, New Zealand, 27–30 November 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–6. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8639163/ (accessed on 25 May 2024).
- Li, Y.; Lyu, S. Exposing deepfake videos by detecting face warping artifacts. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.00656. Available online: http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_CVPRW_2019/papers/Media%20Forensics/Li_Exposing_DeepFake_Videos_By_Detecting_Face_Warping_Artifacts_CVPRW_2019_paper.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2024).
- Khalil, S.S.; Youssef, S.M.; Saleh, S.N. iCaps-Dfake: An integrated capsule-based model for deepfake image and video detection. Future Internet 2021, 13, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Lyu, S. Exposing deep fakes using inconsistent head poses. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2019–2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 8261–8265. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8683164/ (accessed on 27 February 2024).
- Dang, H.; Liu, F.; Stehouwer, J.; Liu, X.; Jain, A.K. On the detection of digital face manipulation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 5781–5790. Available online: http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_CVPR_2020/html/Dang_On_the_Detection_of_Digital_Face_Manipulation_CVPR_2020_paper.html (accessed on 23 February 2024).
- Nguyen, H.H.; Fang, F.; Yamagishi, J.; Echizen, I. Multi-task learning for detecting and segmenting manipulated facial images and videos. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 10th International Conference on Biometrics Theory, Applications and Systems (BTAS), Tampa, FL, USA, 23–26 September 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–8. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9185974/ (accessed on 25 May 2024).
- Korshunov, P.; Marcel, S. Speaker inconsistency detection in tampered video. In Proceedings of the 2018 26th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Roma, Italy, 3–7 September 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 2375–2379. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8553270/ (accessed on 25 May 2024).
- Korshunov, P.; Halstead, M.; Castan, D.; Graciarena, M.; McLaren, M.; Burns, B.; Lawson, A.; Marcel, S. Tampered speaker inconsistency detection with phonetically aware audio-visual features. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 10–15 June 2019; Available online: https://publications.idiap.ch/attachments/papers/2019/Korshunov_AVFAKESICML_2019.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2024).
- Chen, T.; Kumar, A.; Nagarsheth, P.; Sivaraman, G.; Khoury, E. Generalization of Audio Deepfake Detection. In Proceedings of the Odyssey, Tokyo, Japan, 1–5 November 2020; pp. 132–137. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Avrosh-Kumar/publication/345141913_Generalization_of_Audio_Deepfake_Detection/links/600cb38945851553a0678e07/Generalization-of-Audio-Deepfake-Detection.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2024).
- Chintha, A.; Thai, B.; Sohrawardi, S.J.; Bhatt, K.; Hickerson, A.; Wright, M.; Ptucha, R. Recurrent convolutional structures for audio spoof and video deepfake detection. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2020, 14, 1024–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1251–1258. Available online: http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_cvpr_2017/html/Chollet_Xception_Deep_Learning_CVPR_2017_paper.html (accessed on 25 May 2024).
- Yasrab, R.; Jiang, W.; Riaz, A. Fighting deepfakes using body language analysis. Forecasting 2021, 3, 303–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, D.; Salmani, S. Deepfake: A survey on facial forgery technique using generative adversarial network. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems (ICCS), Madurai, India, 15–17 May 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 852–857. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9065881/ (accessed on 25 May 2024).
- Matern, F.; Riess, C.; Stamminger, M. Exploiting visual artifacts to expose deepfakes and face manipulations. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Winter Applications of Computer Vision Workshops (WACVW), Waikoloa Village, HI, USA, 7–11 January 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 83–92. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8638330/ (accessed on 25 May 2024).
- Amerini, I.; Galteri, L.; Caldelli, R.; Del Bimbo, A. Deepfake video detection through optical flow based cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27–28 October 2019; pp. 1205–1207. Available online: http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_ICCVW_2019/html/HBU/Amerini_Deepfake_Video_Detection_through_Optical_Flow_Based_CNN_ICCVW_2019_paper.html?ref=https://githubhelp.com (accessed on 25 May 2024).
- Rossler, A.; Cozzolino, D.; Verdoliva, L.; Riess, C.; Thies, J.; Nießner, M. Faceforensics++: Learning to detect manipulated facial images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1–11. Available online: http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_ICCV_2019/html/Rossler_FaceForensics_Learning_to_Detect_Manipulated_Facial_Images_ICCV_2019_paper.html (accessed on 23 February 2024).
- Dolhansky, B.; Bitton, J.; Pflaum, B.; Lu, J.; Howes, R.; Wang, M.; Ferrer, C.C. The DeepFake Detection Challenge (DFDC) Dataset. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.07397. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/2006.07397 (accessed on 25 May 2024).
- Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Sun, P.; Qi, H.; Lyu, S. Celeb-df: A large-scale challenging dataset for deepfake forensics. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 3207–3216. Available online: http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_CVPR_2020/html/Li_Celeb-DF_A_Large-Scale_Challenging_Dataset_for_DeepFake_Forensics_CVPR_2020_paper.html (accessed on 23 February 2024).
- Lu, X.; Firoozeh Abolhasani Zadeh, Y.A. Deep Learning-Based Classification for Melanoma Detection Using XceptionNet. J. Healthc. Eng. 2022, 2022, e2196096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remi Cadene/Pretrained-Models. Pytorch 2024. Available online: https://github.com/Cadene/pretrained-models.pytorch (accessed on 25 May 2024).
- Tan, M.; Le, Q. Efficientnet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 10–15 June 2019; PMLR: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 6105–6114. Available online: http://proceedings.mlr.press/v97/tan19a.html?ref=jina-ai-gmbh.ghost.io (accessed on 25 May 2024).
- GitHub—AITTSMD/MTCNN-Tensorflow: Reproduce MTCNN Using Tensorflow. Available online: https://github.com/AITTSMD/MTCNN-Tensorflow (accessed on 25 May 2024).
- Xiang, J.; Zhu, G. Joint face detection and facial expression recognition with MTCNN. In Proceedings of the 2017 4th International Conference on Information Science and Control Engineering (ICISCE), Changsha, China, 21–23 July 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 424–427. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8110322/ (accessed on 25 May 2024).
- Geetha, A.; Prakash, N. Classification of Glaucoma in Retinal Images Using EfficientnetB4 Deep Learning Model. CSSE 2022, 43, 1041–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallah Tehrani, A.; Cheng, W.; Dembczyński, K.; Hüllermeier, E. Learning monotone nonlinear models using the Choquet integral. Mach Learn. 2012, 89, 183–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goztepe, K. A Study on OS Selection Using ANP Based Choquet Integral in Terms of Cyber Threats. IJISS 2012, 1, 67–78. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, P.; Ball, J.E.; Anderson, D.T. Fusion of an Ensemble of Augmented Image Detectors for Robust Object Detection. Sensors 2018, 18, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Ebrahimi, T. Assessment framework for deepfake detection in real-world situations. J. Image Video Process. 2024, 2024, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Luo, W.; Wei, K.; Liu, M. Improved Xception with Dual Attention Mechanism and Feature Fusion for Face Forgery Detection. In Proceedings of the 2022 4th International Conference on Data Intelligence and Security (ICDIS), Shenzhen, China, 24–26 August 2022; pp. 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayadibi, I.; Güraksın, G.E.; Ergün, U.; Özmen Süzme, N. An Eye State Recognition System Using Transfer Learning: AlexNet-Based Deep Convolutional Neural Network. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2022, 15, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Hybrid CNN-LSTM model for Video Deepfake Detection by Leveraging Optical Flow Features|IEEE Conference Publication|IEEE Xplore. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9892905 (accessed on 25 May 2024).
- Kshirsagar, M.; Suratkar, S.; Kazi, F. Deepfake video detection methods using deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2022 Third International Conference on Intelligent Computing Instrumentation and Control Technologies (ICICICT), Kannur, India, 11–12 August 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 27–34. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9917701/ (accessed on 13 August 2024).
- Rana, M.S.; Sung, A.H. Deepfakestack: A deep ensemble-based learning technique for deepfake detection. In Proceedings of the 2020 7th IEEE International Conference on Cyber Security and Cloud Computing (CSCloud)/2020 6th IEEE International Conference on Edge Computing and Scalable Cloud (EdgeCom), New York, NY, USA, 1–3 August 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 70–75. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9171002/ (accessed on 13 August 2024).
- Bonettini, N.; Cannas, E.D.; Mandelli, S.; Bondi, L.; Bestagini, P.; Tubaro, S. Video face manipulation detection through ensemble of cnns. In Proceedings of the 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Milan, Italy, 10–15 January 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 5012–5019. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9412711/ (accessed on 13 August 2024).
- Silva, S.H.; Bethany, M.; Votto, A.M.; Scarff, I.H.; Beebe, N.; Najafirad, P. Deepfake forensics analysis: An explainable hierarchical ensemble of weakly supervised models. Forensic Sci. Int. Synerg. 2022, 4, 100217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Concas, S.; La Cava, S.M.; Orrù, G.; Cuccu, C.; Gao, J.; Feng, X.; Marcialis, G.L.; Roli, F. Analysis of score-level fusion rules for deepfake detection. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Year | Method Name | Neural Network Model | Method Type | Mouth | Expression | Pose | Gaze | Body | Source | Target | Dataset |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | FT-GAN | LSTM, CNN, GAN | FR | + | + | + | * | P | P | SCUText2face | |
| 2018 | Recycle-GAN | GAN | IS | + | + | + | P | - | Viper | ||
| 2018 | DeepFaceLab | GAN | FS | + | + | + | PV | - | FaceForensics++ | ||
| 2017 | Syth. Obama | LSTM | FR | + | + | S | PV | Obama video | |||
| 2018 | ReenactGAN | GAN | FR | + | + | + | P | P | Celebrity Video/ Boundary Estimation Dataset, DISFA | ||
| 2018 | Vid2vid | Autoencoders | SP | + | + | + | * | + | PV | - | YouTube dancing videos, Street-scene videos, Face videos |
| 2019 | Everybody DN | GAN | SP | + | + | + | G | - | YouTube short videos | ||
| 2019 | Few-shot Vid2Vid | - | SP | + | + | + | * | + | PG | PG | YouTube dancing videos, Street-scene videos, Face videos |
| 2018 | paGAN | GAN | FR (Real-time) | + | + | + | + | P | P | Chicago Face Dataset, Compound facial expressions (CFE), Radbound Faces | |
| 2018 | X2Face | U-Net, pix2pix | FR | + | + | + | P | P | VoxCeleb video | ||
| 2018 | FaceID-GAN | GAN | FR | + | + | + | P | P | CASIA-WebFace, CelebA, IJB-A, LFW | ||
| 2019 | wg-GAN | GAN | FR (Real-time) | + | + | P | P | MMI Facial Expression, MUG | |||
| 2019 | FSGAN | GAN, CNN, U-Net, Pix2pixHD | FR/FS | + | + | + | P | P | IJB-C | ||
| 2019 | FaceSwapNet | pix2pix | FR | + | + | P | P | RaFD | |||
| 2019 | FusionNet | U-Net | FR | + | + | + | * | P | P | EOTT, CelebA, RAF-DB, FFHQ | |
| 2019 | Speech2Vid | CNN | FR | + | S | PV | VGG Face, VoxCeleb2, LRS2 | ||||
| 2020 | MarioNETte | Autoencoders | FR | + | + | + | P | P | VoxCeleb1, CelebV | ||
| 2016 | Face2Face | Graphical based | FS (Real-time) | P | P | YouTube | |||||
| 2018 | FaceSwap GAN | GAN | FS | - | P | YouTube | |||||
| 2018 | DeepFaceLab | GAN, TrueFace | FS | - | P | FaceForensics++ | |||||
| 2017 | Fast Face Swap | FS | P | P | FaceForensics | ||||||
| 2018 | RSGAN | GAN, Separator networks | FS | P | P | CelebA | |||||
| 2019 | FS Face Trans. | GAN | FS | P | P | CelebA | |||||
| 2019 | FaceShifter | GAN | FS | P | P | FaceForensics++ |
| Methods | Model | Content | Source | Dataset/ACC–EE–AUC | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feature | Face | Image | Image | Video | Sound | FF-DF | UADFV | Celeb-DF | DF-TIMIT | DFD | DFDC | Other | ||
| Eye blinking [23] | LRCN (LSTM + CNN) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 0.99 | |||||||||
| Using space–temporal properties [25] | RCN (CNN + RNN) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 96.9 | |||||||||
| In-frame and temporal inconsistencies [26] | CNN + RNN | ✓ | ✓ | 97.1 | ||||||||||
| Face warping artifacts [27] | CNN | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 93.0 | 97.7 | 64.6 | 99.9 | 93.0 | 75.5 | ||||
| MesoNet [6] | CNN | ✓ | ✓ | 95.23 | 82.1 | 53.6 | 87.8 | |||||||
| Capsule forensics [28] | Capsule CNN | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 99.33 | |||||||||
| Head poses [29] | SVM | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 47.3 | 89.0 | 54.6 | 53.2 | 55.9 | ||||
| Face manipulation [30] | CNN | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 98.4 | ||||||||
| Multi-task learning [31] | CNN + DE | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 36.5 | 62.2 | ||||||||
| Voice inconsistency [32] | LSTM | ✓ | ✓ | 24.74 | ||||||||||
| Voice inconsistency [33] | LSTM + DNN | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 17.6 | |||||||||
| Audio features [34] | DNN | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 1.26 | |||||||||
| Video and audio features [35] | LSTM | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 100 | 99.6 | |||||||
| XceptionNet [36] | CNN | 99.26 | 38.7 | 56.7 | ||||||||||
| Forgery detection by body analysis [37] | DNN-LSTM | ✓ | ✓ | 94.39 | ||||||||||
| Head pose estimation [24] | LBP + CNN | ✓ | ✓ | 91.70 | ||||||||||
| Time and space analysis [25] | CNN + RNN | ✓ | ✓ | 96.90 | ||||||||||
| Using a f2f counterfeiting technique [38] | CNN + LSTM | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 95 | ||||||||
| Use of visual artifacts [39] | MLP | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 84 | 84 | |||||||
| Optical flow [40] | CNN | ✓ | ✓ | 81.61 | ||||||||||
| Dataset | Real | Fake | Year | Resolution | Method | Source | Actor | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Video | Frame | Video | Frame | ||||||
| DeepFake-TIMIT-LQ (DF-TIMIT) [7] | 320 | 34.0 k | 320 | 34.0 k | 2018 | 64 | faceswap-GAN | VidTIMITDataset | 32 |
| DeepFake-TIMIT-HQ [7] | 320 | 34.0 k | 320 | 34.0 k | 2018 | 128 | faceswap-GAN | VidTIMITDataset | 32 |
| FaceForensics++ (FF-DF) [41] | 1000 | 509.9 k | 1000 | 509.9 k | 2019 | 480, 720, 1080 | Deepfakes, Face2Face, FaceSwap, NeuralTextures | YouTube | 977 |
| Facebook DeepFake Detection Challenge Dataset (DFDC) [42] | 1131 | 488.4 k | 4119 | 1783.3 k | 2019 | 480, 720, 1080 | 8 different methods: FSGAN, StyleGAN, MM/NN, DF-256 | Volunteer Actors | 960 |
| CELEB-DF [43] | 590 | 225.4 k | 5639 | 2116.8 k | 2019 | 256 | DeepFake synthesis algorithm | YouTube | 59 |
| Set | Fuzzy Measure Values | Set | Fuzzy Measure Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.7173912 | ||
| 0.0833336 | 0.9444430 | ||
| 0.0175454 | 0.8823529 | ||
| 0.3000000 | 1.0 |
| Dataset | DDA 1 | DDA 2 | DDA 3 | Proposed Method | ||||
| ACC | F1 | ACC | F1 | ACC | F1 | ACC | F1 | |
| Custom dataset | 65.08 | 71.67 | 56.91 | 65.56 | 72.91 | 84.15 | 75.91 | 85.28 |
| Input Description | Elapsed Time (sec) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resolution | Length (sec) | FPS | File Size | DDA 1 | DDA 2 | DDA 3 | Proposed Method |
| 1080 × 1920 | 10.02 | 30 | 13 Mb | 2.42 | 4.13 | 2.57 | 4.52 |
| 942 × 500 | 15.47 | 30 | 4.4 Mb | 3.25 | 5.54 | 3.21 | 5.95 |
| 432 × 500 | 13.63 | 30 | 592 kB | 2.73 | 4.86 | 2.82 | 5.03 |
| 942 × 500 | 10.47 | 30 | 1.68 Mb | 2.20 | 3.61 | 2.28 | 3.98 |
| 512 × 384 | 5.40 | 25 | 290 kB | 0.82 | 1.52 | 0.85 | 1.80 |
| Study | Method | Dataset | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|
| DDA (Model) 1 | XceptionNet | DFDC-P | 78.64 |
| CELEB-DF | 77.45 | ||
| FF-DF | 95.50 | ||
| DF-TIMIT | 73.75 | ||
| DDA (Model) 2 | EfficientNet + XceptionNet | DFDC-P | 86.5 |
| CELEB-DF | 75.2 | ||
| FF-DF | 95.3 | ||
| DF-TIMIT | 74.1 | ||
| DDA (Model) 3 | EfficientNet | DFDC-P | 87.98 |
| CELEB-DF | 72.09 | ||
| FF-DF | 93.4 | ||
| DF-TIMIT | 63.47 | ||
| [39] | MLP | FF-DF | 86.6 |
| LogReg | 82.3 | ||
| [28] | iCaps-Dfake | CELEB-DF | 96.9 |
| DFDC-P | 87.8 | ||
| [53] | CapsuleNet | FF-DF | 94.52 |
| CELEB-DF | 99.14 | ||
| [54] | XceptionNet variant | FF-DF (LQ) | 98.1 |
| [55] | DCNN | ZJU | 99.4 |
| CEW | 99.69 | ||
| [56] | OF + RNN + CNN combinations | FF-DF | 91.0 |
| DFDC | 68.0 | ||
| CELEB-DF | 83.0 | ||
| [57] | Combination of 6 different ResNet versions (50, 50V2, 101, 101V2, 152, and 152V2) | Google + FF-DF | 95.5 |
| [58] | DFC—Combination of 7 different classifiers (XceptionNet, InceptionV3, Inception v2, MobilNet, ResNet101, DenseNet121, and DenseNet169) | FF-DF | 100.0 |
| [59] | Combination of EfficientNet B4, B4ST, B4Att, B4AttST | FF-DF | 94.4 |
| DFDC | 87.8 | ||
| [60] | Combination of 3 different classifiers (Xception, Xception with Attention, and Efficient-NetB3 with Attention) | DFDC | 97.5 |
| CELEB-DF | 98.4 | ||
| [61] | MLP—Combination of 6 different classifiers (EfficientNetAttB4ST, AttB4, B4ST, B4, Xception, and ResNet) | FF-DF | 98.4 |
| Proposed Method | Choquet fuzzy integral | DFDC-P | 95.3 |
| CELEB-DF | 92.6 | ||
| FF-DF | 99.8 | ||
| DF-TIMIT | 89.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karaköse, M.; İlhan, İ.; Yetiş, H.; Ataş, S. A New Approach for Deepfake Detection with the Choquet Fuzzy Integral. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7216. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14167216
Karaköse M, İlhan İ, Yetiş H, Ataş S. A New Approach for Deepfake Detection with the Choquet Fuzzy Integral. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(16):7216. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14167216
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaraköse, Mehmet, İsmail İlhan, Hasan Yetiş, and Serhat Ataş. 2024. "A New Approach for Deepfake Detection with the Choquet Fuzzy Integral" Applied Sciences 14, no. 16: 7216. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14167216
APA StyleKaraköse, M., İlhan, İ., Yetiş, H., & Ataş, S. (2024). A New Approach for Deepfake Detection with the Choquet Fuzzy Integral. Applied Sciences, 14(16), 7216. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14167216







