Analytical Model of Mechanical Responses of Circular Tunnels Considering Rheological Behavior of Surrounding Rock and Functionally Graded Lining
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Problem Statement
- (1)
- The horizontal and vertical pressure are equal.
- (2)
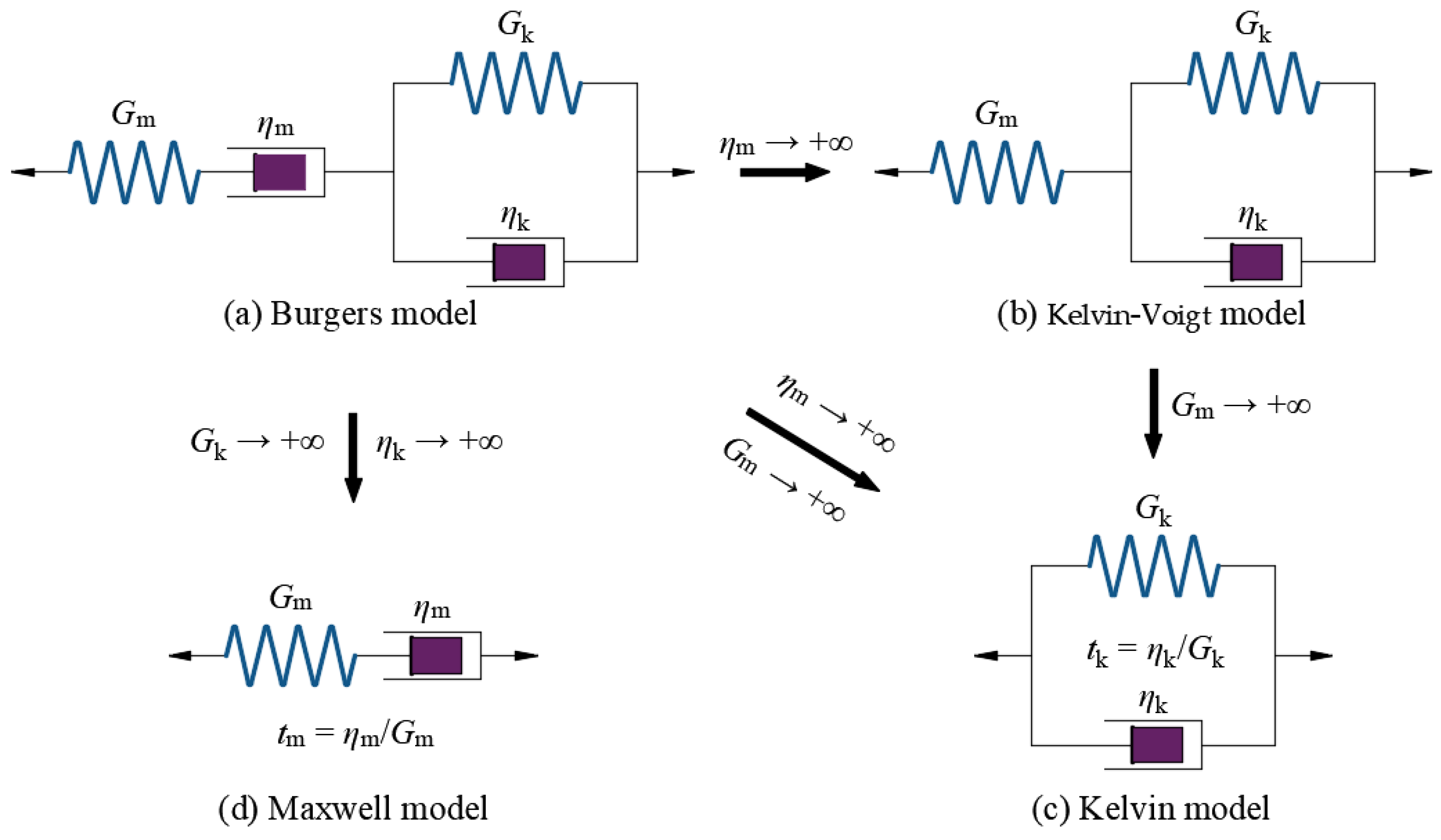
- The rock mass is a homogeneous, isotropic, and viscoelastic material [10].
- (3)
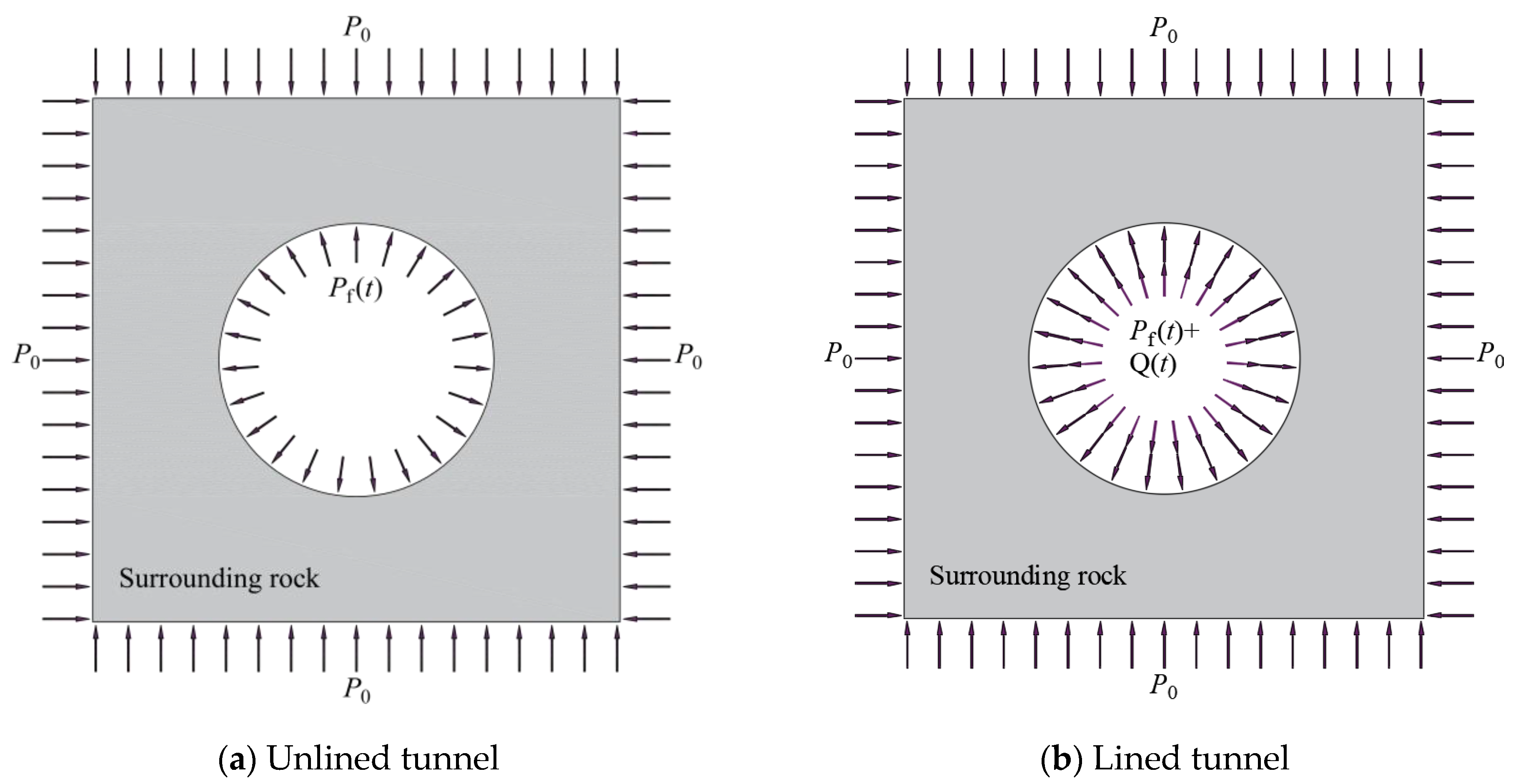
- The excavation radius of the circular tunnel is R2.
- (4)
- The lining is an inhomogeneous, isotropic, and elastic material.
- (5)
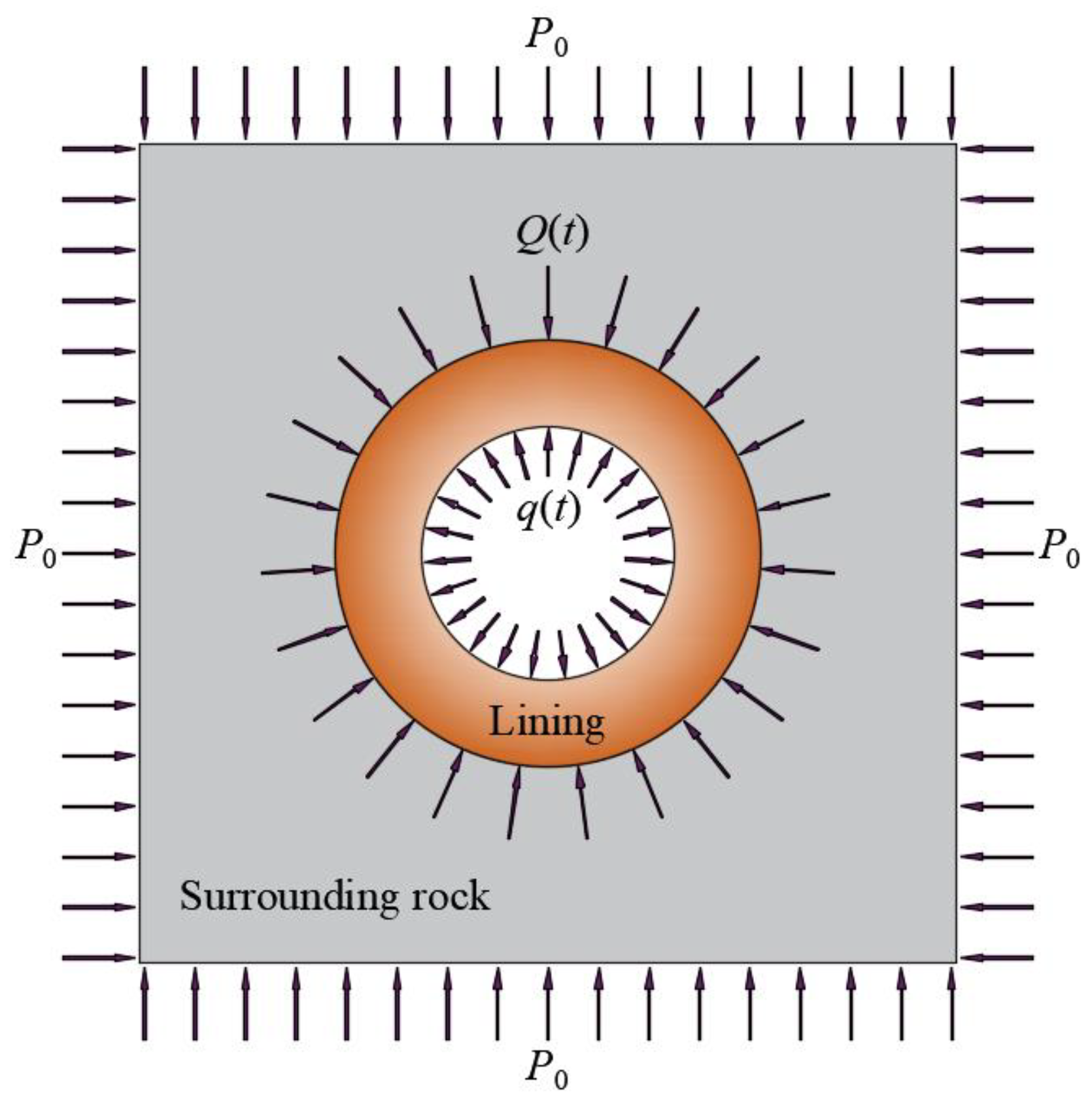
- The inner and outer radii of the lining are R1 and R2, respectively.
- (6)
- The thickness of the lining is d.
- (7)
- The mechanical property (such as elastic modulus) of the lining varies only along the radial direction as a power function.
- (8)
- The inner surface of the lining is subjected to the pressure q(t) in the radial direction.
3. Analytical Model
3.1. Mechanical Analysis of Surrounding Rock
- (1)
- Unlined tunnel
- (2)
- Lined tunnel
3.2. Mechanical Analysis of Lining
3.3. Deformation Compatibility on Rock–Lining Interface
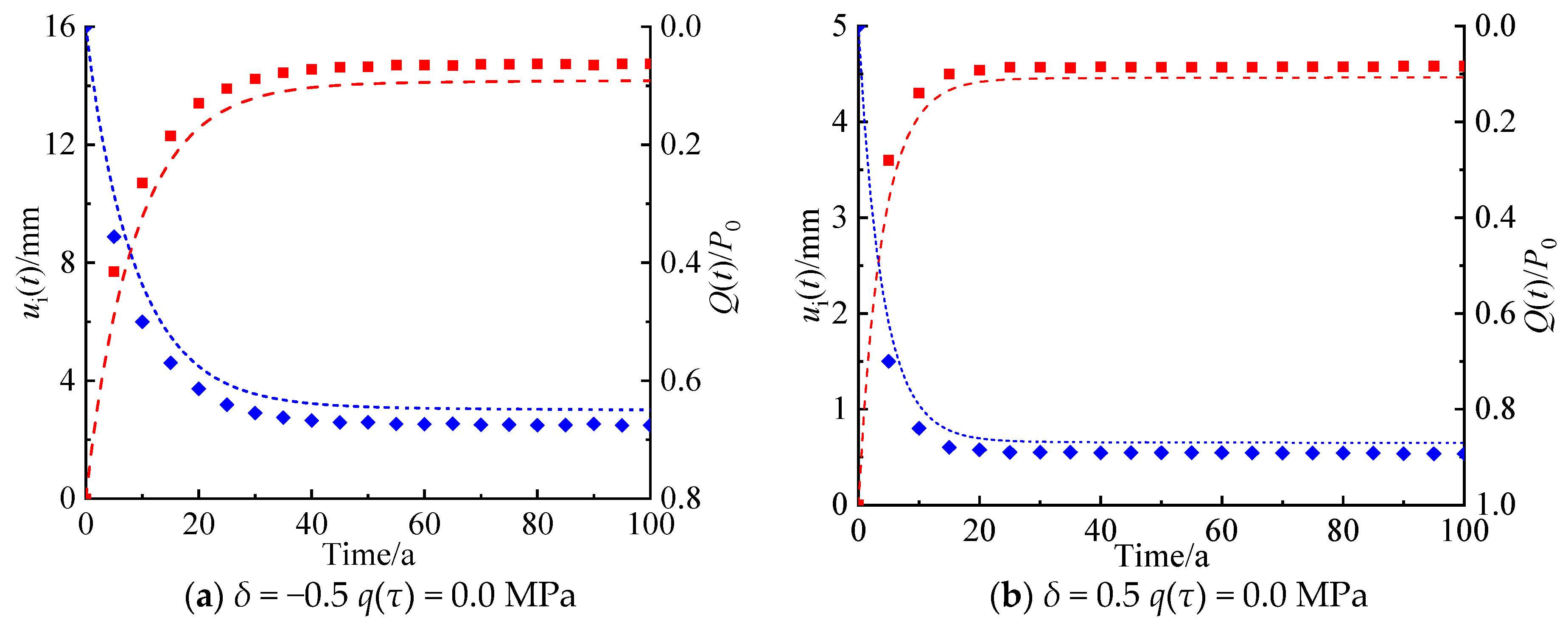
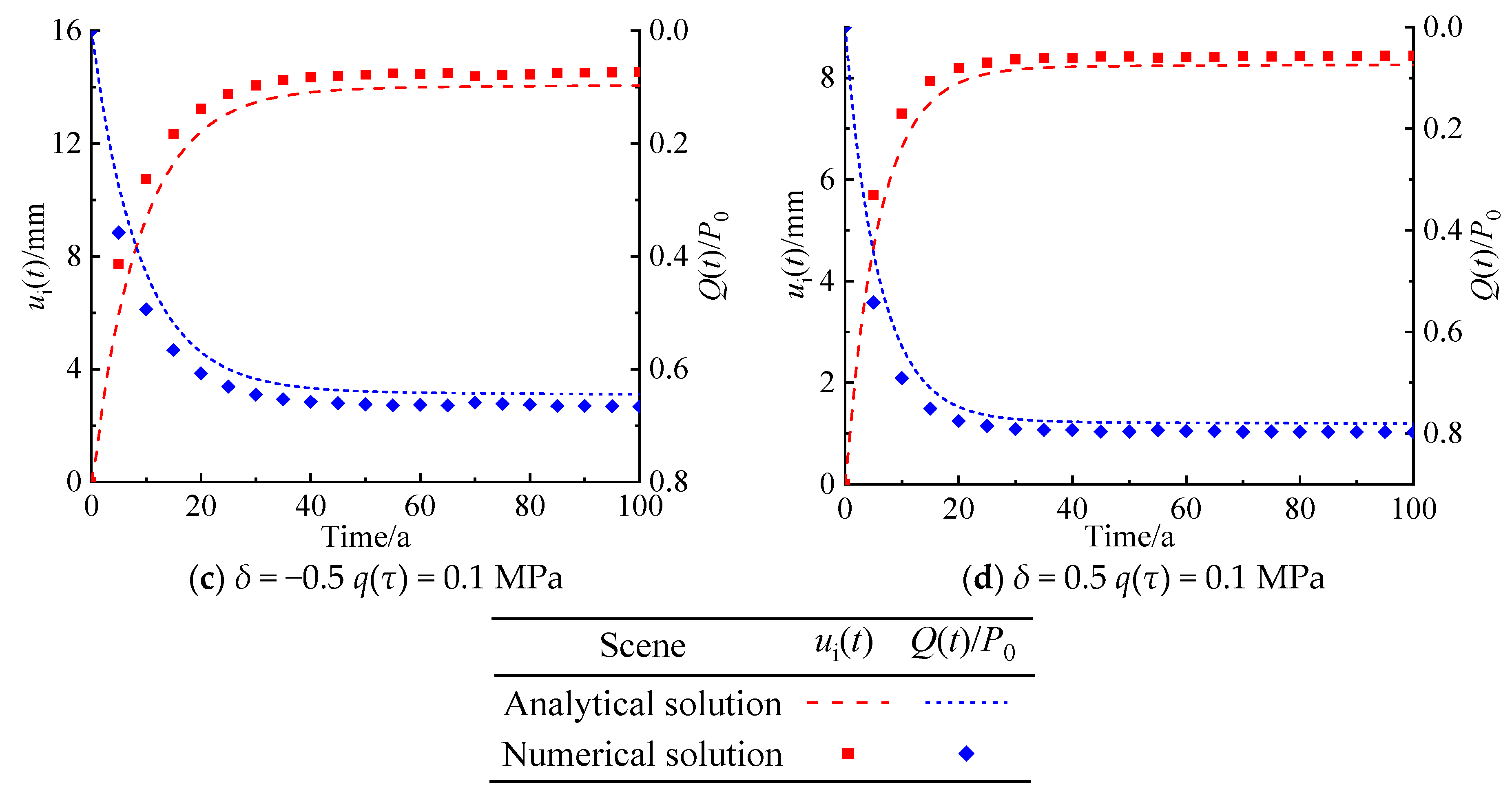
4. Validation
4.1. Comparison with Existing Analytical Solution
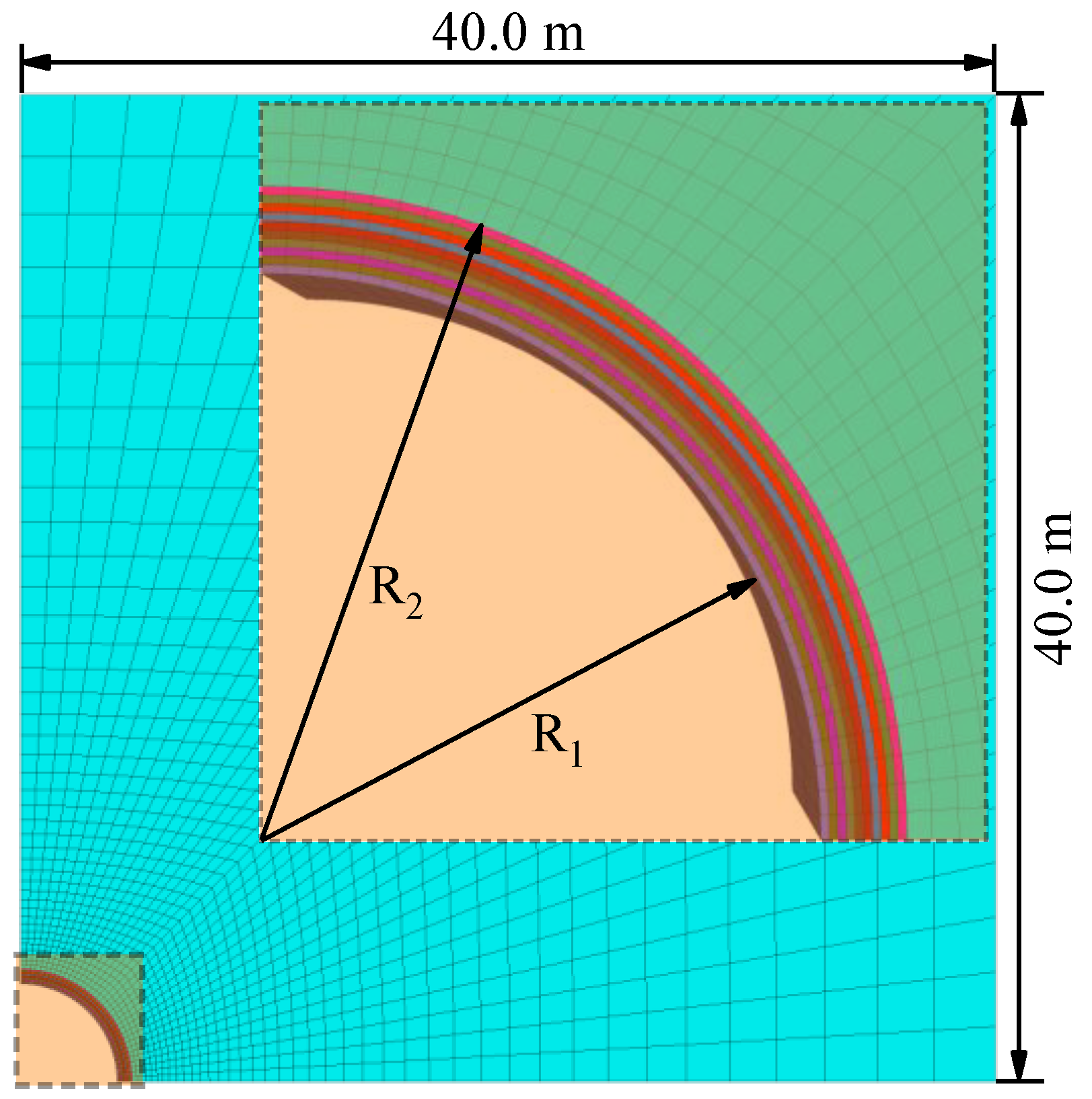
4.2. Comparison with Numerical Simulation
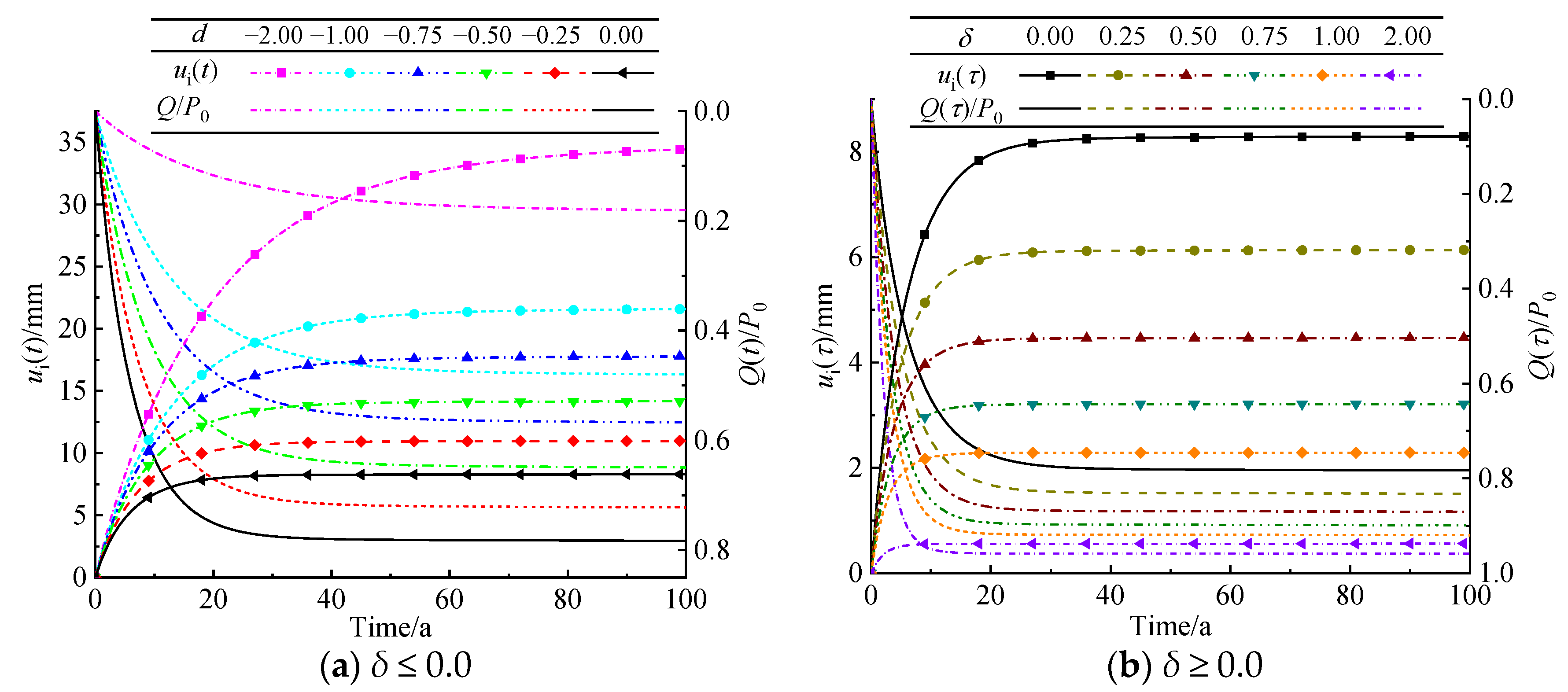
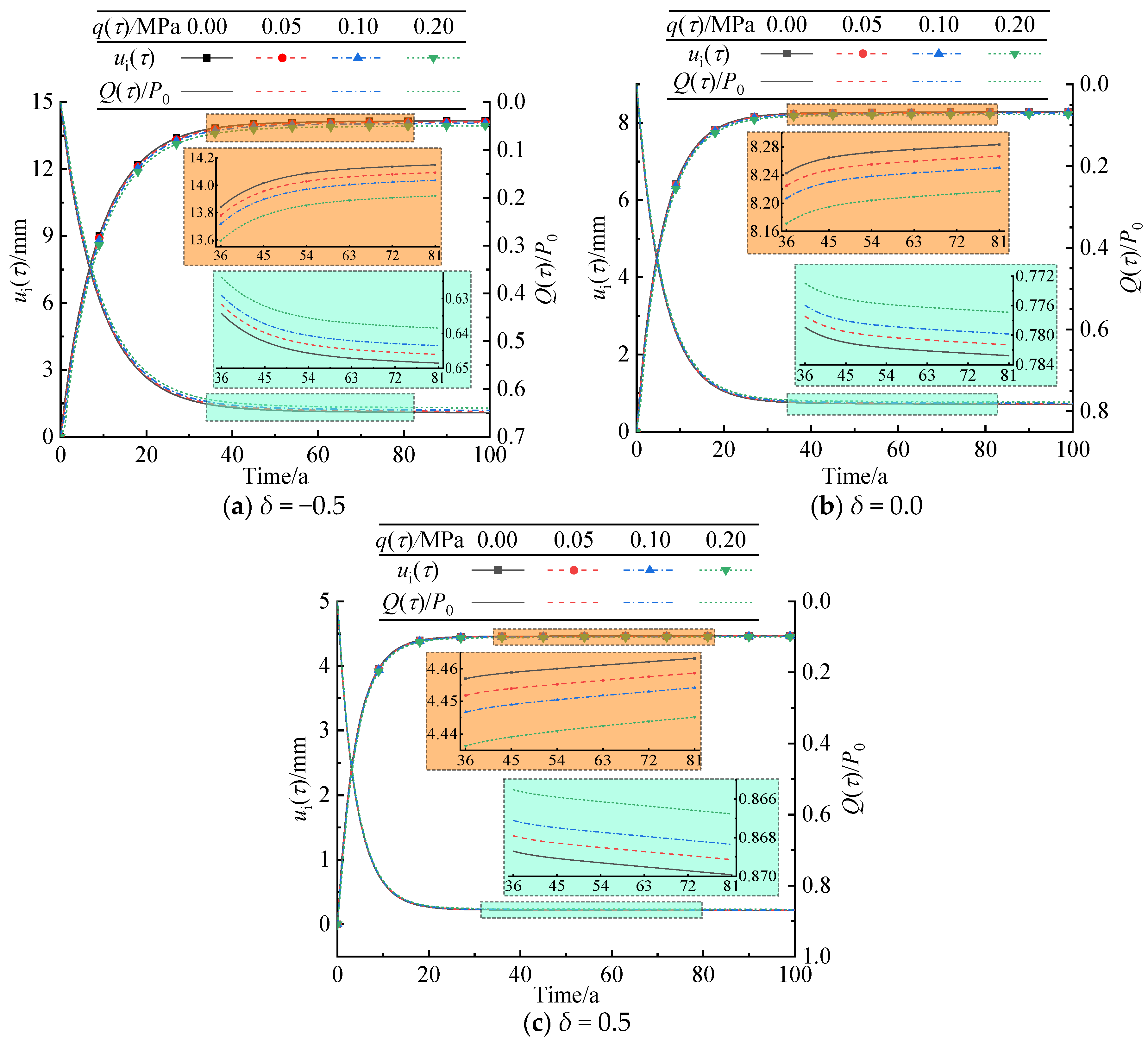
5. Parametric Analysis
5.1. Radially Inhomogeneous Coefficient of Lining
5.2. Radially Inner Surface Pressure of Lining
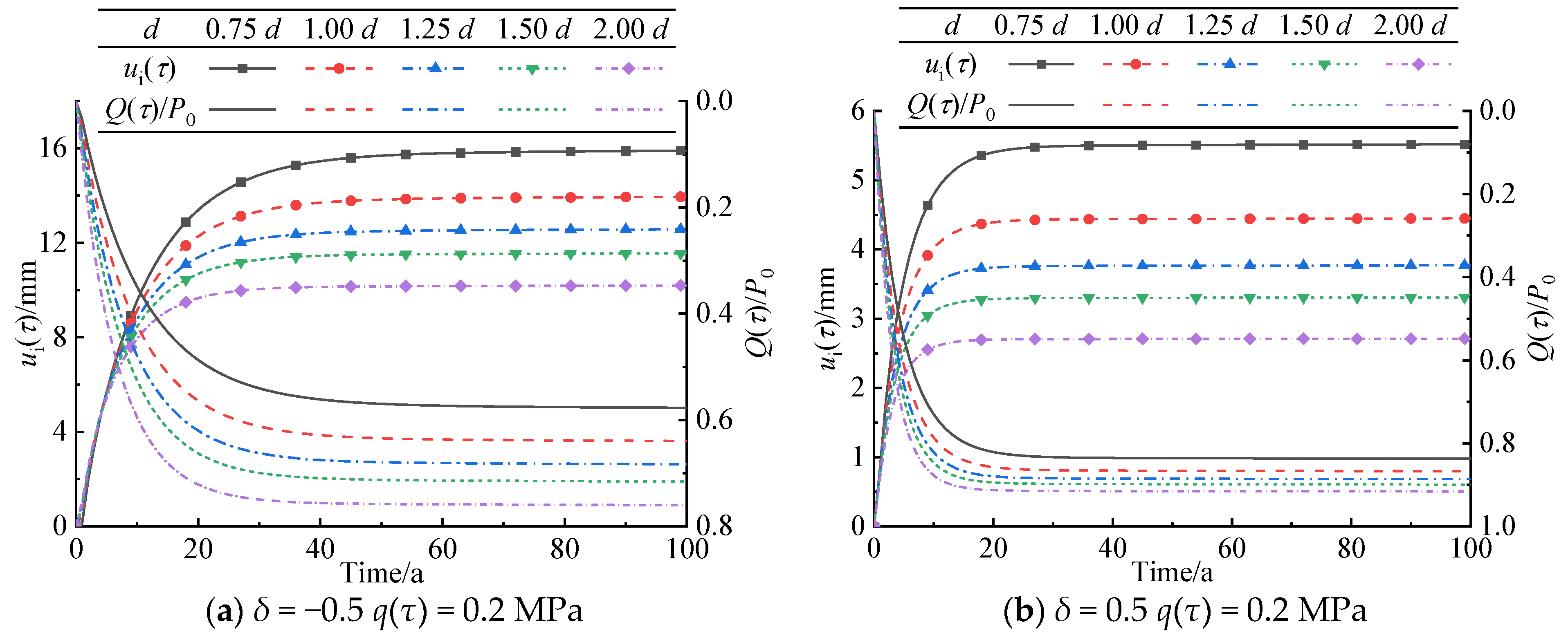
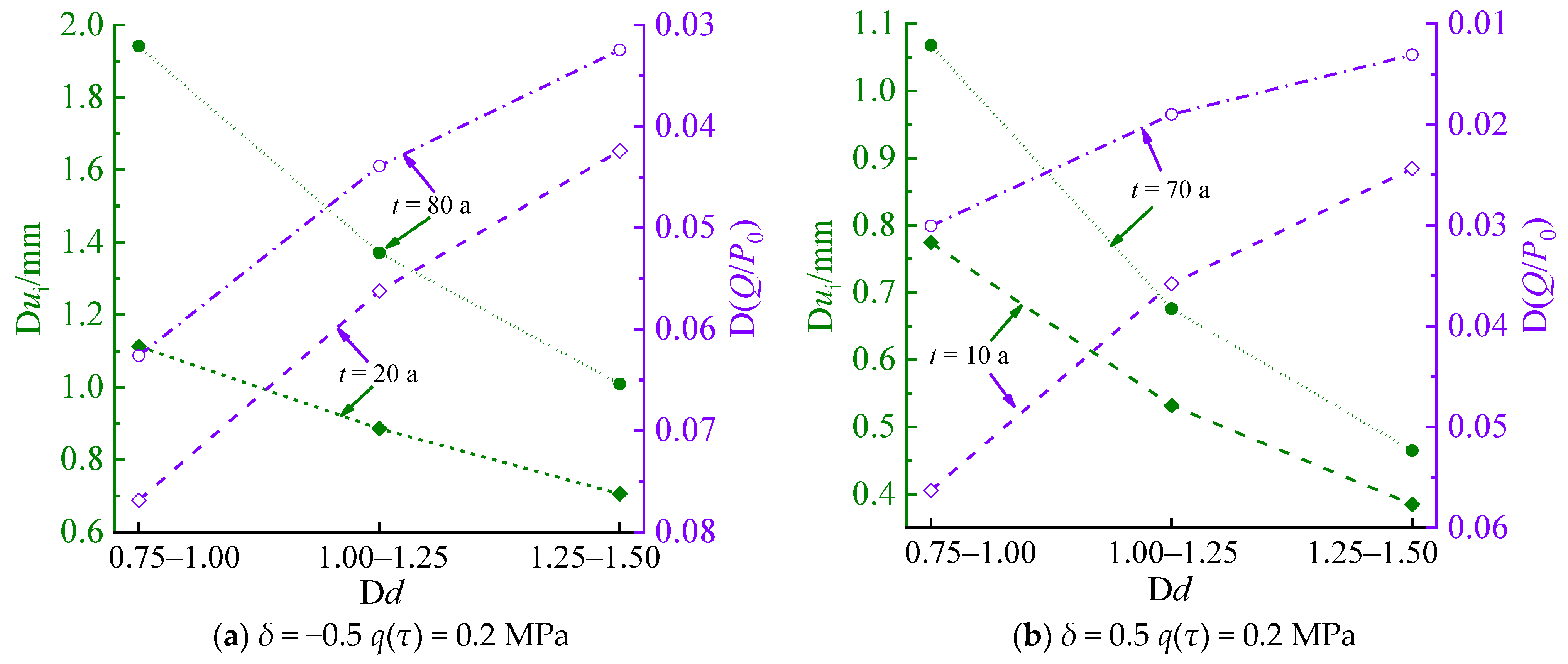
5.3. Lining Thickness
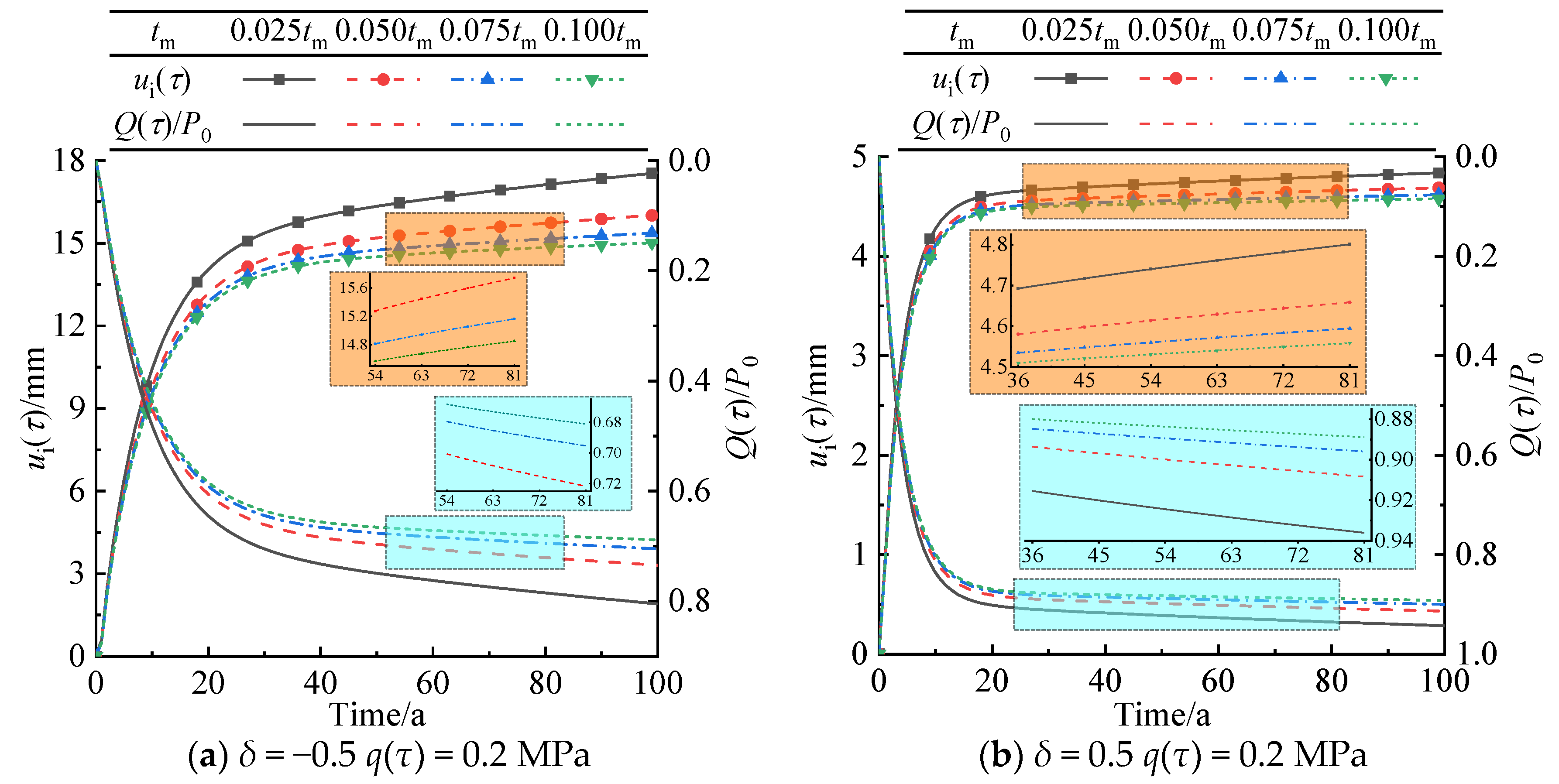
5.4. Relaxation Time of Maxwell Model
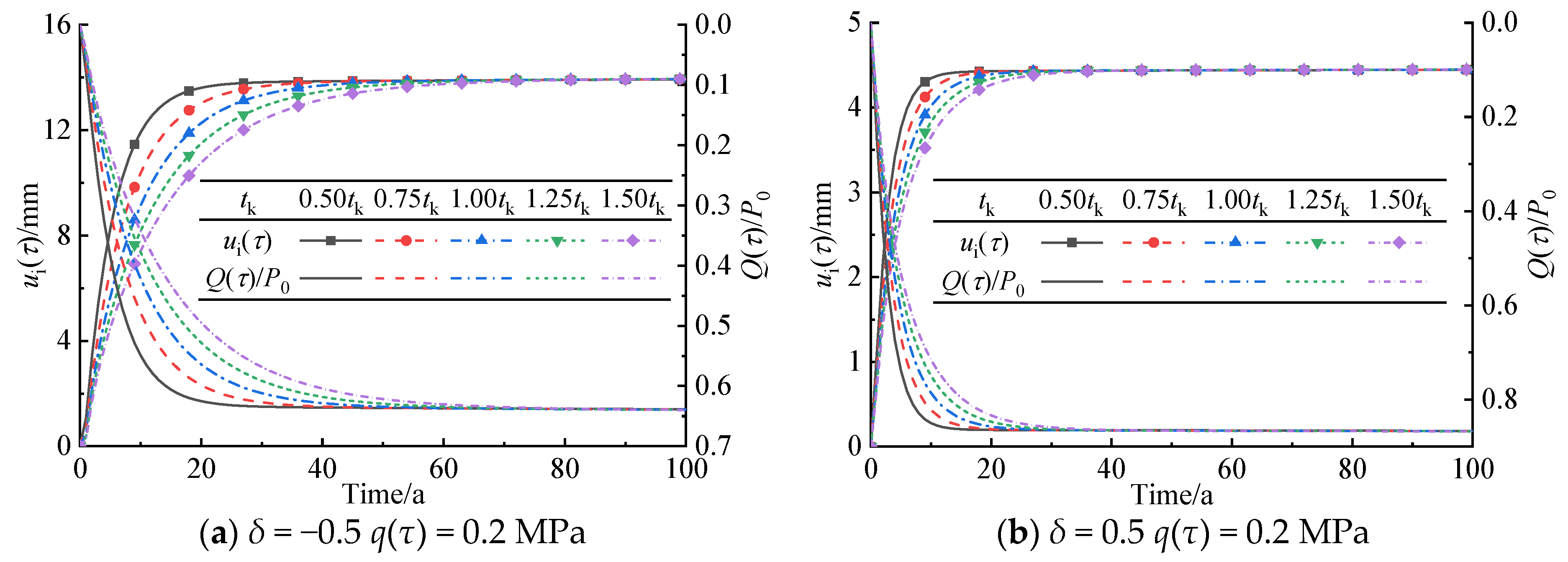
5.5. Retardation Time of Kelvin Model
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fang, Q.; Zhang, D.L.; Li, Q.Q.; Wong, L.N.Y. Effects of twin tunnels construction beneath existing shield-driven twin tunnels. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2014, 45, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revesz, A.; Chaer, I.; Thompson, J.; Mavroulidou, M.; Gunn, M.; Maidment, G. Ground source heat pumps and their interactions with underground railway tunnels in an urban environment: A review. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 93, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, W.Q.; Li, L.C.; Chen, D.Z.; Wang, S.X.; Xiao, F.K. Long-term deformation and control structure of rheological tunnels based on numerical simulation and on-site monitoring. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2020, 118, 104928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.M.; Fang, Q.; Wang, J.; Wang, G. Influences of high-speed train speed on tunnel aerodynamic pressures. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.M.; Fang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.L. Aerodynamic effect associated with tunnel length. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2024, 28, 2997–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.H.; Shi, Y.; Sun, R.; Yang, J.S. Damage behavior and maintenance design of tunnel lining based on numerical evaluation. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2020, 109, 104209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namli, M. Evaluation of the effect of using fiber reinforcement in tunnel linings for metro projects. Undergr. Space 2021, 6, 732–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.L. Elasto-plastic solution for a circular lined tunnel considering yield criteria for surrounding rock and functionally graded lining in cold-region tunnels. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.N.; Utili, S.; Jiang, M.J. An analytical approach for the sequential excavation of axisymmetric lined tunnels in viscoelastic rock. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2014, 68, 85–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Z.F.; Wu, Z.J.; Liu, B.G.; Liu, Q.S. Coupled analytical solutions for deep-buried circular lined tunnels considering tunnel face advancement and soft rock rheology effects. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2019, 94, 103111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.M.; Fang, Q.; Wang, G.; Wang, J. Analytical solution of a circular lined tunnel with alterable mechanical property under hydrostatic stress and internal pressure. J. Central South Univ. 2022, 29, 2757–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shao, J.F.; Xu, W.Y.; Jia, Y.; Zhao, H.B. Creep behaviour and permeability evolution of cataclastic sandstone in triaxial rheological tests. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2015, 19, 496–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Q.; He, C.; Wang, J.; Ma, C.C. Time-dependent squeezing deformation mechanism of tunnels in layered soft-rock stratum under high geo-stress. J. Mt. Sci. 2021, 18, 1371–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaheri, M.; Ranjbarnia, M.; Oreste, P. Reliability analysis of deep pressurized tunnels excavated in the rock mass with rheological behavior. Transp. Geotech. 2024, 45, 101212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.C.; Jiang, Y.J.; Tanabashi, Y. Rheological parameter estimation for the prediction of long-term deformations in conventional tunnelling. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2009, 24, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonini, M.; Barla, G. The Saint Martin La Porte access adit (Lyon–Turin Base Tunnel) revisited. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2012, 30, 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifzadeh, M.; Daraei, R.; Broojerdi, M.S. Design of sequential excavation tunneling in weak rocks through findings obtained from displacements based back analysis. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2012, 28, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.N.; Guo, Z.B.; Qiao, X.B.; Fan, J.Y.; Li, W.; Mi, M.; Tao, Z.G.; He, M.C. Large deformation mechanism of thin-layered carbonaceous slate and energy coupling support technology of NPR anchor cable in Minxian Tunnel: A case study. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2021, 117, 104151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.G.; Ren, S.L.; Li, G.; Xu, H.T.; Luo, S.L.; He, M.C. Model test on support scheme for carbonaceous slate tunnel in high geostress zone at high depth. J. Mt. Sci. 2021, 18, 764–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Fang, F.; Han, W.; Jiang, Y.J.; Zhang, X.D.; Xu, F.; Zhang, S.B. Coupled rheological behavior of tunnel rock masses reinforced by rock bolts based on the non-hydrostatic stress field. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2023, 137, 105112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Li, S.C.; Zhao, S.S.; Liu, R.C. Rheological characterization of the conditioned sandy soil under gas-loading pressure for earth pressure balance shield tunnelling. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2024, 146, 105658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, K.; Gutierrez, M.; Hedayat, A. Physical model simulation of rock-support interaction for the tunnel in squeezing ground. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2022, 14, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.D.; Li, X.G.; Fang, Y.F.; Jin, D.L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, H.Z. Investigation into the pregelatinized starch additive alleviated the deterioration in rheological properties of slurries induced by high-temperature environment and seawater intrusion during submarine slurry shield tunneling. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2024, 147, 105693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.W.; Gutierrez, M. Study on the damage evolution in secondary tunnel lining under the combined actions of corrosion degradation of preliminary support and creep deformation of surrounding rock. Transp. Geotech. 2021, 27, 100501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.S.; Wang, H.N.; Song, F.; Rodriguez-Dono, A. Time-dependent analytical solutions for tunnels excavated in anisotropic rheological rock masses. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2024, 152, 105890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.G.; Huang, M.H.; Pan, Y.T.; Jiang, K.M.; Li, Z.N.; Ma, S.K.; Zhang, Y.N. Analytical prediction of time-dependent behavior for tunneling-induced ground movements and stresses subjected to surcharge loading based on rheological mechanics. Comput. Geotech. 2021, 129, 103858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, D.L.; Zhang, S.L.; Fang, Q.; Sun, Z.Y. Long-term mechanical analysis of tunnel structures in rheological rock considering the degradation of primary lining. Undergr. Space 2023, 10, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carranza-Torres, C.; Rysdahl, B.; Kasim, M. On the elastic analysis of a circular lined tunnel considering the delayed installation of the support. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2013, 61, 57–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.M.; Fang, Q.; Wang, G.; Zhang, D.L.; Chen, T.L. Fatigue damage and residual life of secondary lining of high-speed railway tunnel under aerodynamic pressure wave. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2021, 111, 103851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.Y.; Zhang, D.L.; Fang, Q.; Wang, J.C.; Chu, Z.F.; Hou, Y.J. Analysis of interaction between tunnel support system and surrounding rock for underwater mined tunnels considering the combined effect of blasting damage and seepage pressure. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2023, 141, 105314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.P.; Jia, L.L.; Wang, M.N.; Wang, F. Displacement prediction of tunnels based on a generalised Kelvin constitutive model and its application in a subsea tunnel. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2016, 54, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Sheng, Q.; Dong, Y.K.; Miao, C.X.; Huang, J.H.; Zhang, A.J. Two-stage analysis of interaction between strain-softening rock mass and liner for circular tunnels considering delayed installation of liner. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2020, 26, 1492–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargar, A.R. An analytical solution for circular tunnels excavated in rock masses exhibiting viscous elastic-plastic behavior. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2019, 124, 104128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.C.; Wang, M.B. Elastic analysis of stress–displacement field for a lined circular tunnel at great depth due to ground loads and internal pressure. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2008, 23, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.Z.; Zhang, L.Q.; Zhang, N. Analytic stress solutions for a circular pressure tunnel at pressure and great depth including support delay. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2011, 48, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, D.L.; Zhang, S.L.; Fang, Q.; Fang, H.C. Analytical solution of long-term service performance of tunnel considering lining deterioration in rheological surrounding rock. Rock Soil Mech. 2021, 42, 2795–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.L.; Yuan, J.; Liu, X.M.; Li, J.G.; Zhang, P.; Niu, Z.R. Burgers viscoelastic model-based variable stiffness design of compliant clamping mechanism for leafy greens harvesting. Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 208, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomikos, P.; Rahmannejad, R.; Sofianos, A. Supported axisymmetric tunnels within linear viscoelastic Burgers rocks. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2011, 44, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertrich, J.; Neumayer, S.; Steidl, G. Convolutional proximal neural networks and plug-and-play algorithms. Linear Algebra Its Appl. 2021, 631, 203–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaskov, P. On pathwise Riemann–Stieltjes integrals. Stat. Probab. Lett. 2019, 150, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, N.; He, J.H. Laplace transform: Making the variational iteration method easier. Appl. Math. Lett. 2019, 92, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campagna, R.; Conti, C.; Cuomo, S. Computational error bounds for Laplace transform inversion based on smoothing splines. Appl. Math. Comput. 2020, 383, 125376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barla, G.; Bonini, M.; Semeraro, M. Analysis of the behaviour of a yield-control support system in squeezing rock. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2011, 26, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran-Manhl, H.; Sulem, J.; Subrin, D. Progressive degradation of rock properties and time-dependent behavior of deep tunnels. Acta Geotech. 2016, 11, 693–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| P0 | MPa | 5.89 |
| R1 | m | 3.96 (constant) |
| R2 | m | 4.57 |
| d | m | 0.61 |
| EL0 | GPa | 16.55 |
| vL | - | 0.2 |
| δ | - | −0.50 (0.50) |
| α | - | 0.68 |
| β | - | 0.60 |
| t0 | a | 0.00 |
| ηm | GPa·a | 1590 |
| Gm | MPa | 3447 (constant) |
| tm | a | 461.27 |
| ηk | GPa·a | 7.98 |
| Gk | MPa | 345 (constant) |
| tk | a | 23.13 |
| q(τ) | MPa | 0.00 (0.10) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, J.; Zhang, X. Analytical Model of Mechanical Responses of Circular Tunnels Considering Rheological Behavior of Surrounding Rock and Functionally Graded Lining. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7434. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177434
Du J, Zhang X. Analytical Model of Mechanical Responses of Circular Tunnels Considering Rheological Behavior of Surrounding Rock and Functionally Graded Lining. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(17):7434. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177434
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Jianming, and Xuan Zhang. 2024. "Analytical Model of Mechanical Responses of Circular Tunnels Considering Rheological Behavior of Surrounding Rock and Functionally Graded Lining" Applied Sciences 14, no. 17: 7434. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177434
APA StyleDu, J., & Zhang, X. (2024). Analytical Model of Mechanical Responses of Circular Tunnels Considering Rheological Behavior of Surrounding Rock and Functionally Graded Lining. Applied Sciences, 14(17), 7434. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177434





