Temperature Field Optimization for Multi-Microwave Sources Based on Collaborative Switching under Uncertain Communication
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- A microwave heating distributed architecture using multiple magnetrons is designed to reduce heating time, and a collaborative switching heating strategy for multi-microwave sources is constructed.
- (2)
- Using an event-triggered strategy to reduce the frequency of communication between intelligent agents.
- (3)
- Establishing stability conditions for a multi-microwave sources cooperative switching system under DoS attacks.
- (4)
- Developing a numerical heating model for multi-microwave sources using finite element analysis and evaluating the optimal collaborative switching heating strategy under various time-frequency distributions.
2. Materials and Methods
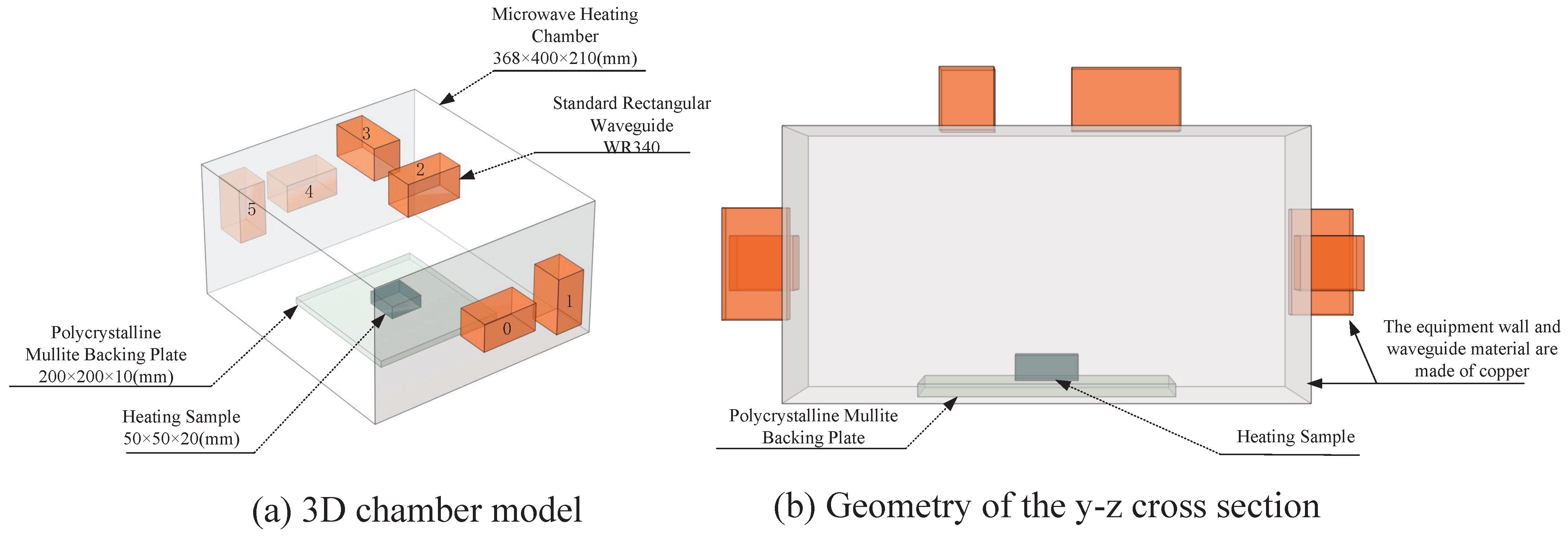
2.1. Multi-Microwave Sources Heating Model
2.2. Experimental Material Selection
3. Theory
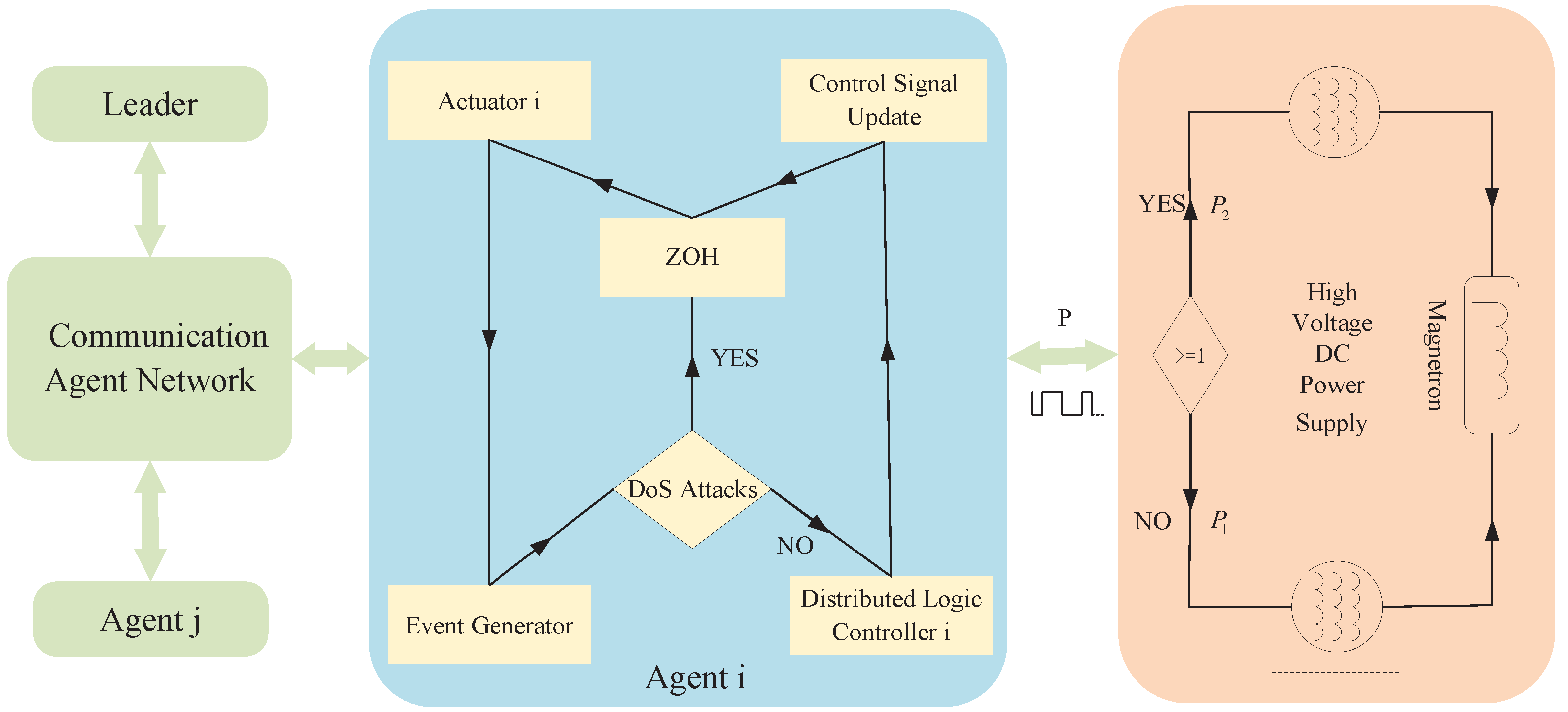
3.1. Theory of Consistency by Multi-Microwave Sources Event-Triggered
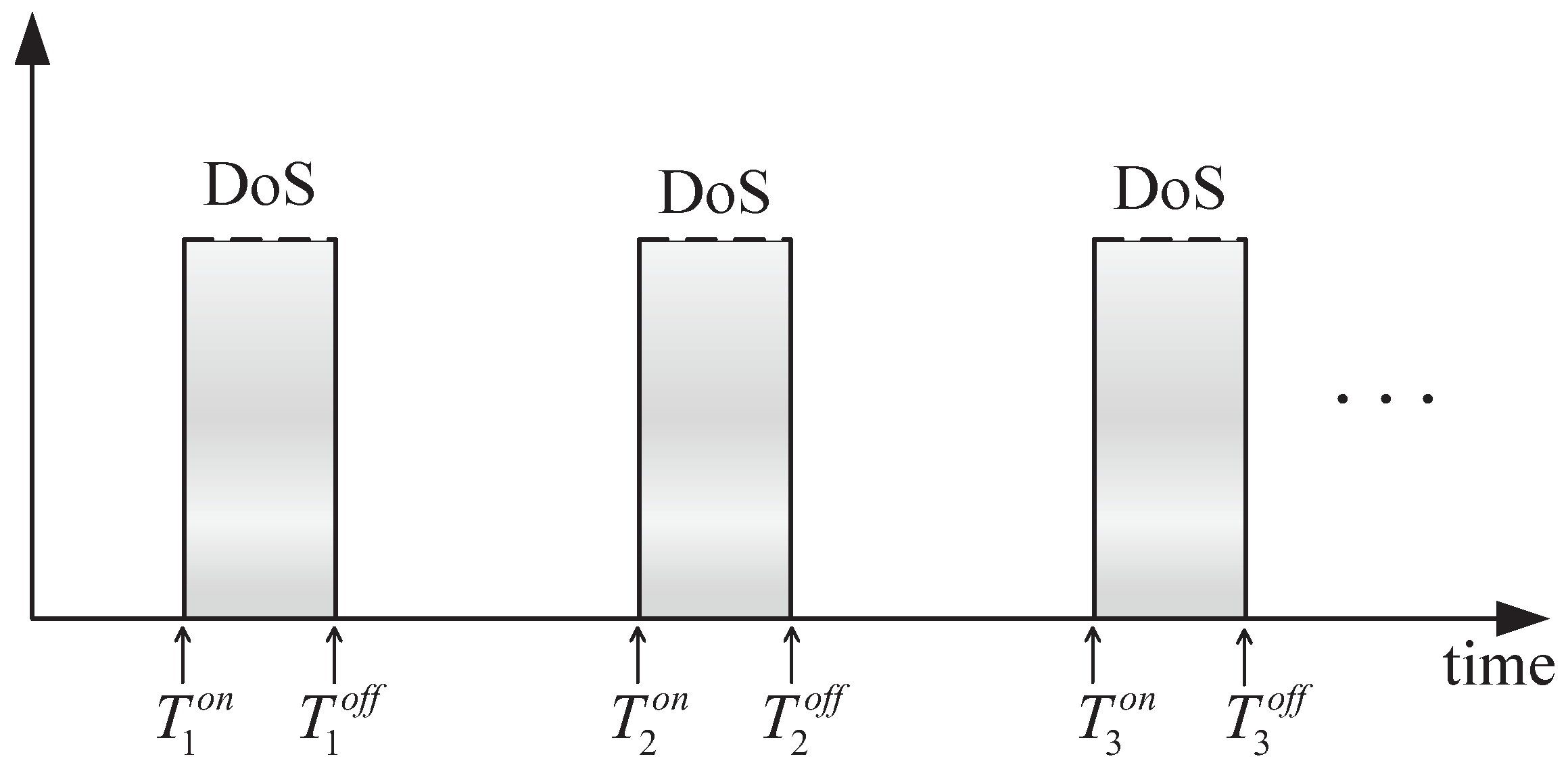
3.2. Event-Triggered Consistency Theory of Multi-Microwave Sources under DoS Attacks
4. Results and Discussion
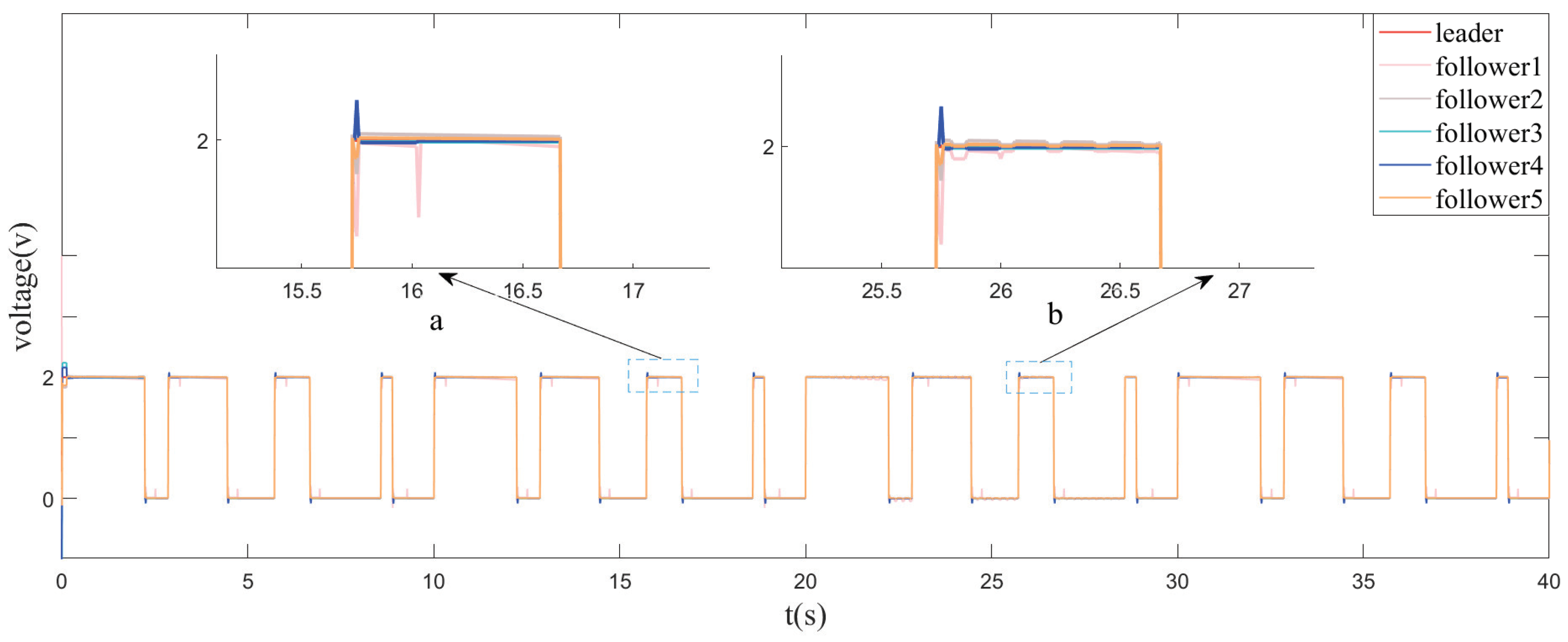
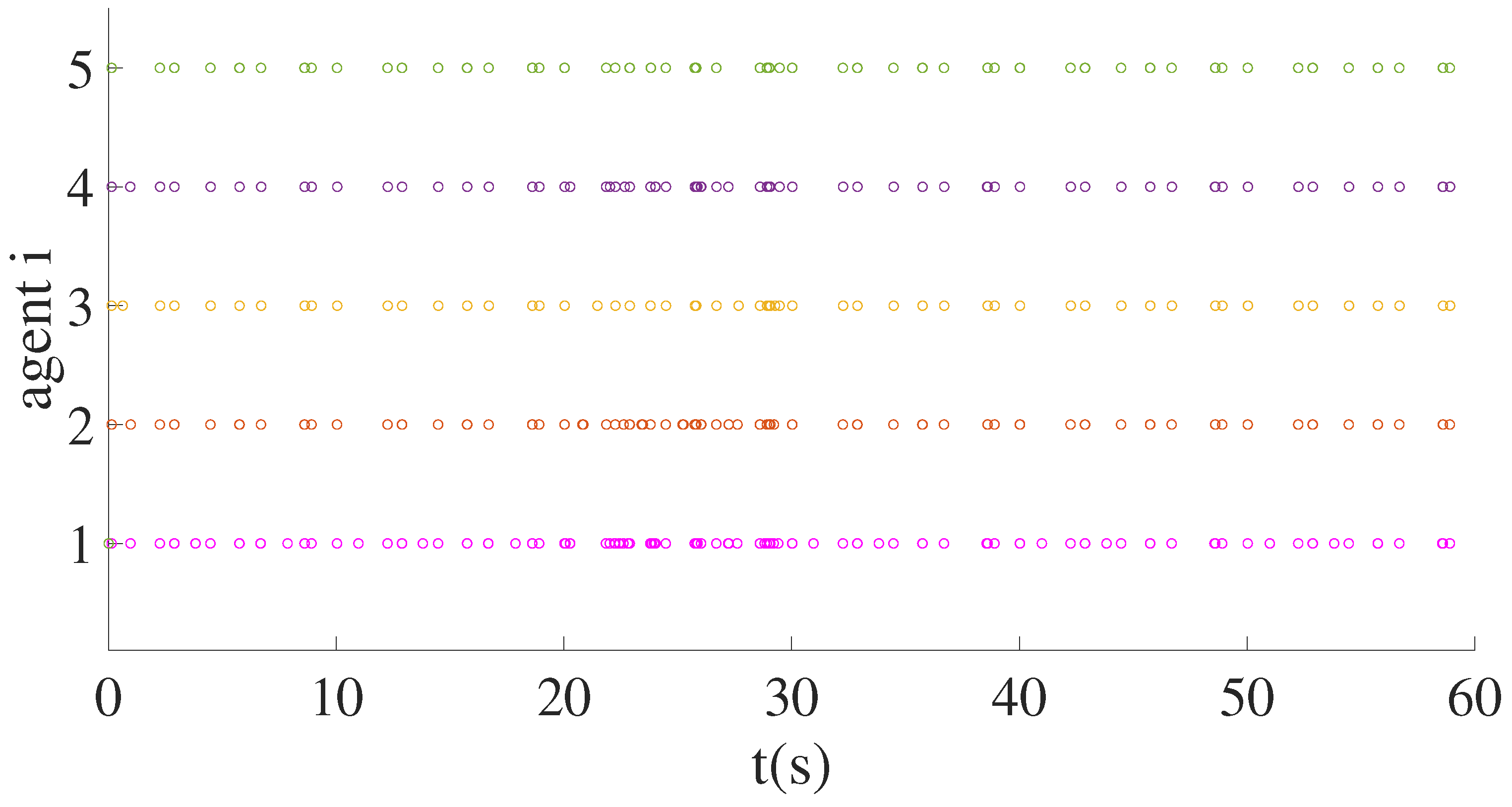
4.1. Event-Triggered Collaborative Switching of Multi-Microwave Agents under DoS Attacks
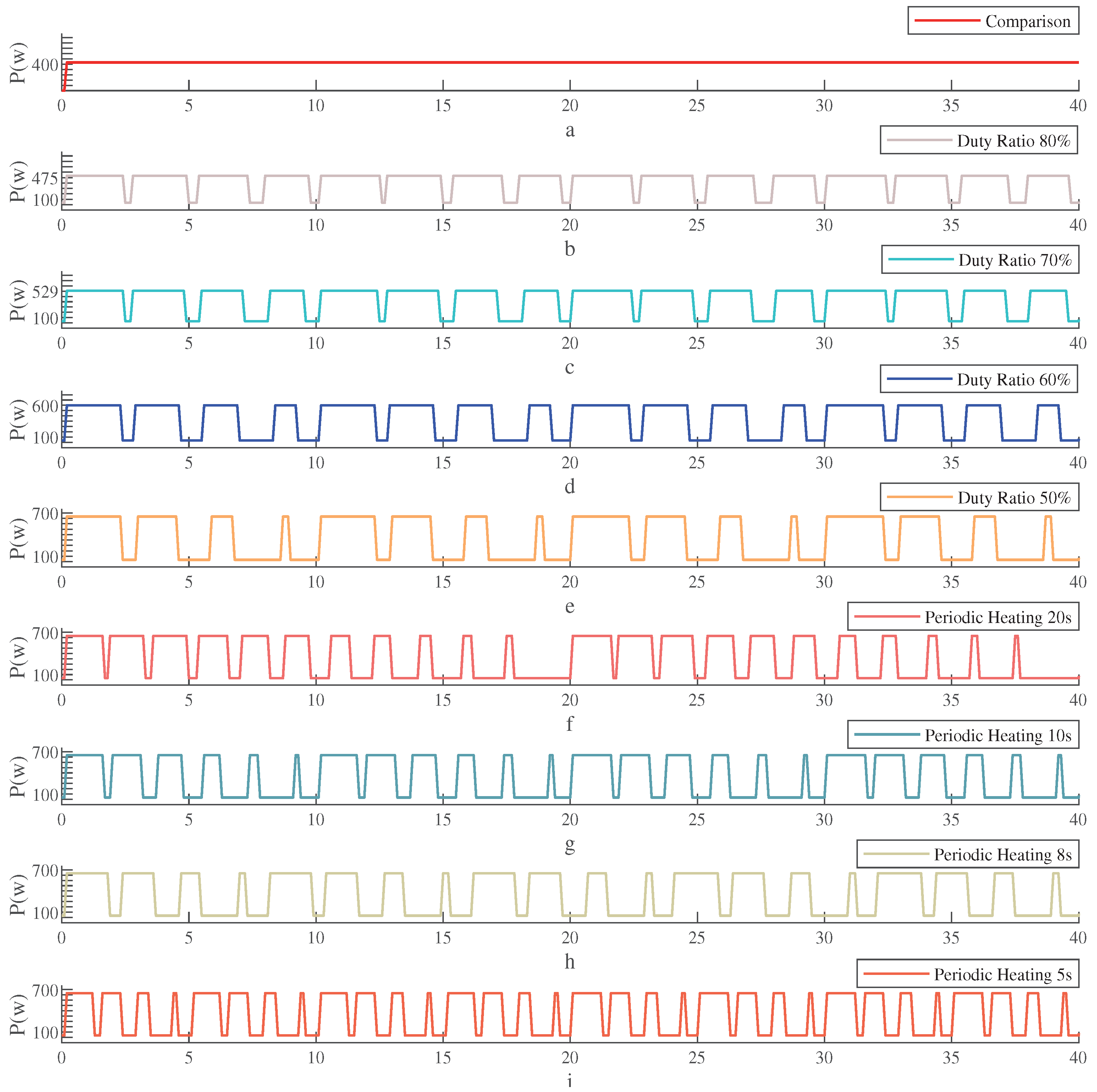
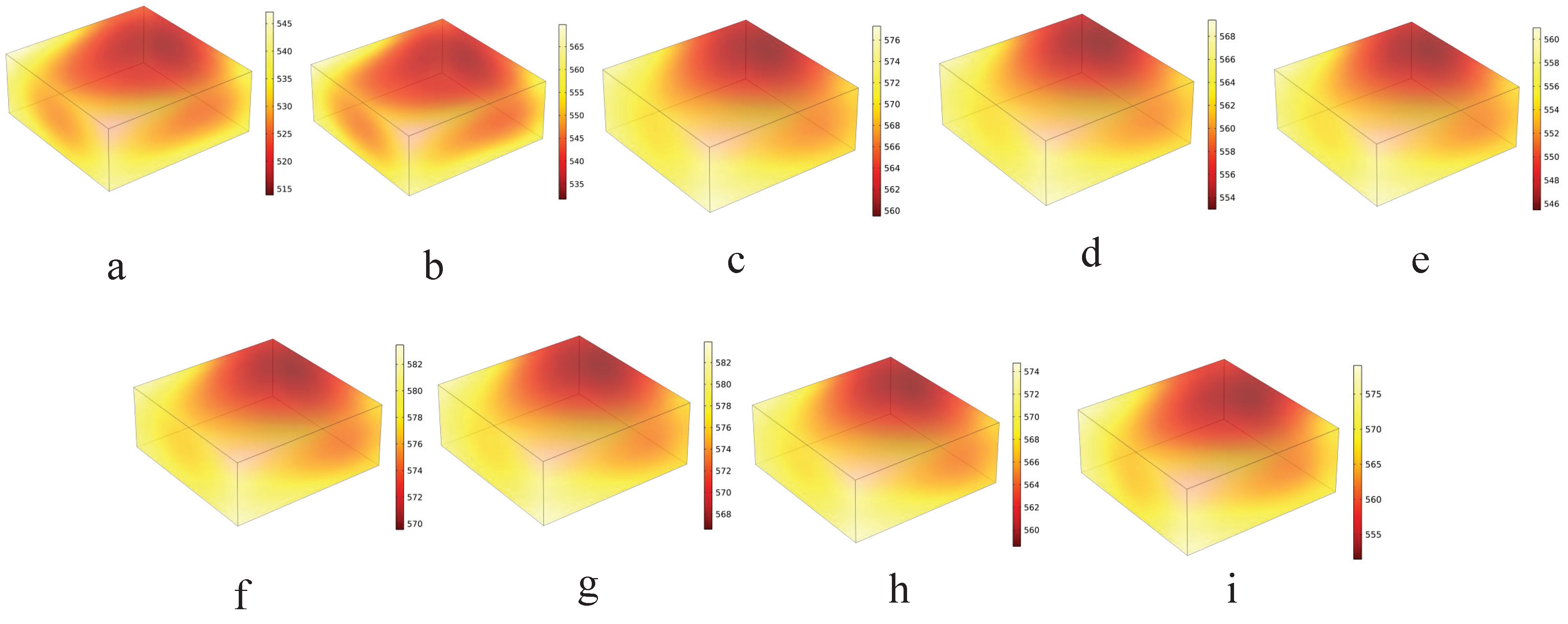
4.2. Multi-Microwave Sources Collaborative Switching Heating
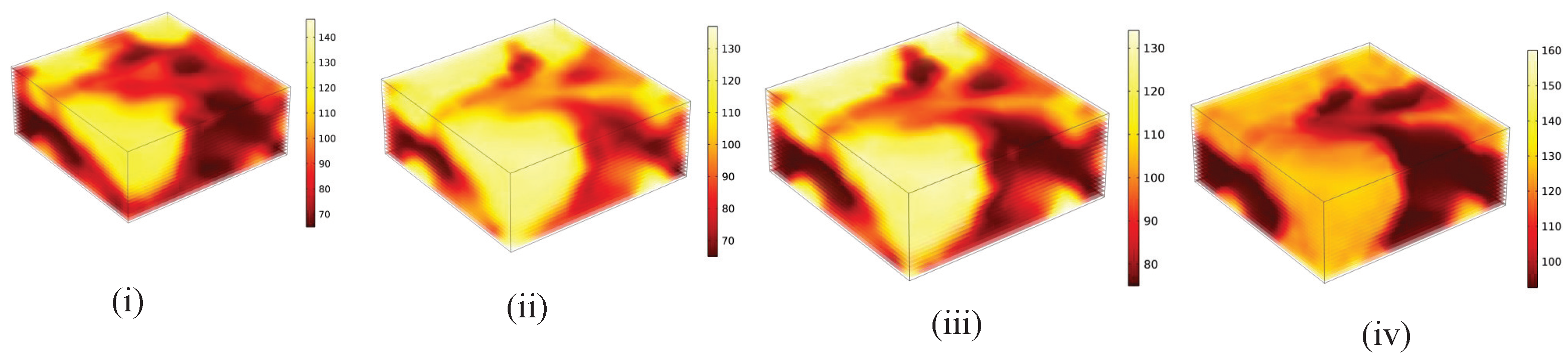
- (i)
- Multi-microwave sources constant power strategy. The output power of six microwave sources in the experiment was set at 200 W.
- (ii)
- (iii)
- Group switching consistent variable power (method of [16]). The power output of the microwave varies over time. Following the example in reference [16], the power output curves for microwave sources 0, 3, and 5 are set to W, while the power output curves for microwave sources 1, 2, and 4 are set to W.
- (iv)
- The multi-microwave sources collaborative switching heating strategy (our method). The power output trajectory of the microwave source is denoted as , with a heating cycle of 20 s and duty cycle of ; the time-frequency distribution of the output power aligns with the switching strategy (f), as shown in Figure 8. Excessive microwave power can cause changes in material properties due to the differences between SiC and potato, therefore, let W, W. The heating effects of potatoes are shown in Figure 10.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gulisano, F.; Crucho, J.; Gallego, J.; Picado-Santos, L. Microwave healing performance of asphalt mixture containing electric arc furnace (EAF) slag and graphene nanoplatelets (GNPs). Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Yang, B.; Xiao, Q. Hierarchical Coordinated Predictive Control of Multiagent Systems for Process Industries. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Fan, X.; Yu, S.; Xia, H.; Nong, Y.; Bian, J.; Sun, M.; Zi, W. Microwave heating of biomasswaste residues for sustainable bioenergy and biomass materials preparation: A parametric simulation study. Energy 2023, 274, 127347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ye, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, H. Double-ridged waveguide for efficiently heating ultrafine filament fibers. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2023, 200, 123543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Su, J.; Yang, F.; Wu, Y.; Ye, J.; Huang, K.; Yang, Y. Effect of lossy thin-walled cylindrical food containers on microwave heating performance. J. Food Eng. 2023, 337, 111232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, J.; Zhu, H.; Yang, Y. Study of multi-frequency heating based on the nonlinear response characteristics of magnetron to improve uniformity. J. Microw. Power Electromagn. Energy 2023, 57, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo, L.; Ferreira, G.; López-Sabirón, A.M. Exergy transfer principles of microwavable materials under electromagnetic effects. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 27, 102313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Song, C.; Fu, P. Regulating n-doping strategies to construct 3d interconnected abundant porous n-doped carbon for polarization loss-enhanced microwave absorbers: Theory, design, and experiments. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 140118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radoiu, M.; Mello, A. Technical advances, barriers, and solutions in microwaveassisted technology for industrial processing. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2022, 181, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Huang, K.; Liu, Y.; Gou, D. Multidirectional polarization impacts on microwave heating efficiency: A molecular dynamics research of microwave heating of common solvents. J. Phys. Chem. B 2023, 127, 970–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghian Dinani, S.; Jenn, A.; Kulozik, U. Effect of vertical and horizontal sample orientations on uniformity of microwave heating produced by magnetron and solid-state generators. Foods 2022, 10, 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Gu, H.; Zhu, H.; Yang, Y. Multi-physics field computation for microwave heating of multi-mobile components based on transformation optics and implicit function. Appl. Sci. 2023, 14, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, P.; Jin, G.; Nie, G.; Song, C.; Cui, Z. Multi-physical simulation of stirring effect on heating uniformity in a microwave reactor with an interlayer. J. Therm. Sci. Eng. Appl. 2022, 14, 011002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Qiu, Y. Double pendulum mode stirrer for improved multimode microwave heating performance. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput.-Aided Eng. 2021, 31, e22866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, C.; Zhan, L.; Yao, S. Finite element simulation and experimental research on uniformity regulation of microwave heating of composite materials. Polymers 2022, 14, 3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Wu, Z.; Gao, H.; Shi, Y.; Peng, F.; Huang, H.; Han, Z. Temperature field optimization for distributed combined heat of multi-microwave sources based on group consistency under time-varying communication topology. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2024, 241, 122302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S. Effect of metal slots on the heating uniformity of multisource cavity microwave. Front. Energy Res. 2023, 10, 1007566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; He, W.; Sun, J.; Wang, G.; Chen, J. Event-triggered control of switched nonlinear time-delay systems with asynchronous switching. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2024, 54, 4348–4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Hua, C. Leader-following consensus of multiagent systems via asynchronous sampled-data control: A hybrid system approach. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2022, 67, 2568–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Jin, X.Z.; Wu, Z.G.; Che, W.W. Data-driven-based cooperative resilient learning method for nonlinear mass under dos attacks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2024, 1–10, early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Yue, D.; Chen, X.; Cheng, Z.; Xie, X. Resilient h filtering for event-triggered networked systems under nonperiodic dos jamming attacks. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2019, 51, 1392–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-W.; Zeng, Z.-H.; Liu, X.-K.; Liu, Z.-W. Input-to-state stability of switched linear systems with unstabilizable modes under dos attacks. Automatica 2022, 146, 110607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, M.; Basak, T. A review on the susceptor assisted microwave processing of materials. Energy 2016, 97, 306–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, M.; Basak, T. Role of metal inserts for targeted, uniform or controlled microwave heating objectives involving generalized sets of dielectrics (Group 1–4). Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2024, 222, 125133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, Z.; Liu, S.; Yang, Y.; Liu, B. Research on the optimisation of the temperature field distribution of a multi-source microwave agent system based on event-triggered. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2024, 109727. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, P.; Deng, F.; Liu, X.; Gao, X. Event-triggered resilientl control for markov jump systems subject to denial-of-service jamming attacks. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2021, 52, 10240–10252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.-H.; Kan, Z.; Klotz, J.R.; Shea, J.M.; Dixon, W.E. Event-triggered control of multiagent systems for fixed and time-varying network topologies. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2017, 62, 5365–5371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, P.; Deng, F.; Gao, X.; Liu, X. Eventtriggered and self-triggered l control for markov jump stochastic nonlinear systems under dos attacks. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2021, 53, 1170–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wu, Z.; Gao, H.; Zhou, L.; Sun, J. Research on the optimisation of the temperature field distribution of a multi microwave source agent system based on group consistency. High Temp. Mater. Process. 2022, 41, 650–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Group | Material Type |
|---|---|
| Carrot, Apple, Potato, Radish, Beef, Lamb | |
| Bread, Pizza, Alumina, Zirconia, PET | |
| White pudding, Ham, Tomato sauce, SiC | |
| Almonds, Walnut and peanut butter |
| Material Properties | SiC a | Copper b,c | Potato a | Air a,b,c |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relative permittivity (real part) | 1 | 1 | ||
| Loss tangent | - | - | - | |
| Electrical conductivity [S/m] | - | 5.998 × 107 | 0 | 0 |
| Thermal conductivity [W/(m K)] | 0.648 | 0.648 | 0 | |
| Density(kg·) | 3100 | 8700 | 1050 | - |
| Heat capacity at constant pressure [J/(kg K)] | 3600 | 3640 | - |
| Agent i | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exist DoS attacks | 118 | 116 | 112 | 105 | 106 |
| Absent DoS attacks (method of [25]) | 94 | 101 | 90 | 88 | 95 |
| Switching Strategies (Group) | (°C) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Constant power heating group a | 0.4981 | 0.0117 | 33.900 |
| Experimental group b | 0.4769 | 0.0087 | 30.120 |
| Experimental group c | 0.4630 | 0.0076 | 17.816 |
| Experimental group d | 0.4660 | 0.0069 | 16.424 |
| Experimental group e | 0.4768 | 0.0066 | 15.502 |
| Experimental group f | 0.4449 | 0.0072 | 17.273 |
| Experimental group g | 0.4669 | 0.0073 | 17.335 |
| Experimental group h | 0.4561 | 0.0069 | 16.206 |
| Experimental group i | 0.4739 | 0.0076 | 17.693 |
| Heating Strategies | ||
|---|---|---|
| (i) Multi-microwave sources constant power strategy | 0.4502 | 0.2435 |
| (ii) Multi-microwave sources consistent variable power (method of [29]) | 0.1209 | 0.3801 |
| (iii) Group switching consistent variable power (method of [16]) | 0.1454 | 0.3729 |
| (iv) Multi-microwave sources collaborative switching heating strategy | 0.3587 | 0.1928 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, B.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X. Temperature Field Optimization for Multi-Microwave Sources Based on Collaborative Switching under Uncertain Communication. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7474. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177474
Yang B, Zhao Z, Zhang H, Chen Y, Chen X. Temperature Field Optimization for Multi-Microwave Sources Based on Collaborative Switching under Uncertain Communication. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(17):7474. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177474
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Biao, Zhongwei Zhao, Haoran Zhang, Yang Chen, and Xiucai Chen. 2024. "Temperature Field Optimization for Multi-Microwave Sources Based on Collaborative Switching under Uncertain Communication" Applied Sciences 14, no. 17: 7474. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177474
APA StyleYang, B., Zhao, Z., Zhang, H., Chen, Y., & Chen, X. (2024). Temperature Field Optimization for Multi-Microwave Sources Based on Collaborative Switching under Uncertain Communication. Applied Sciences, 14(17), 7474. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177474





