Deep Eutectic Solvent Pretreatment and Green Separation of Lignocellulose
Abstract
:1. Introduction
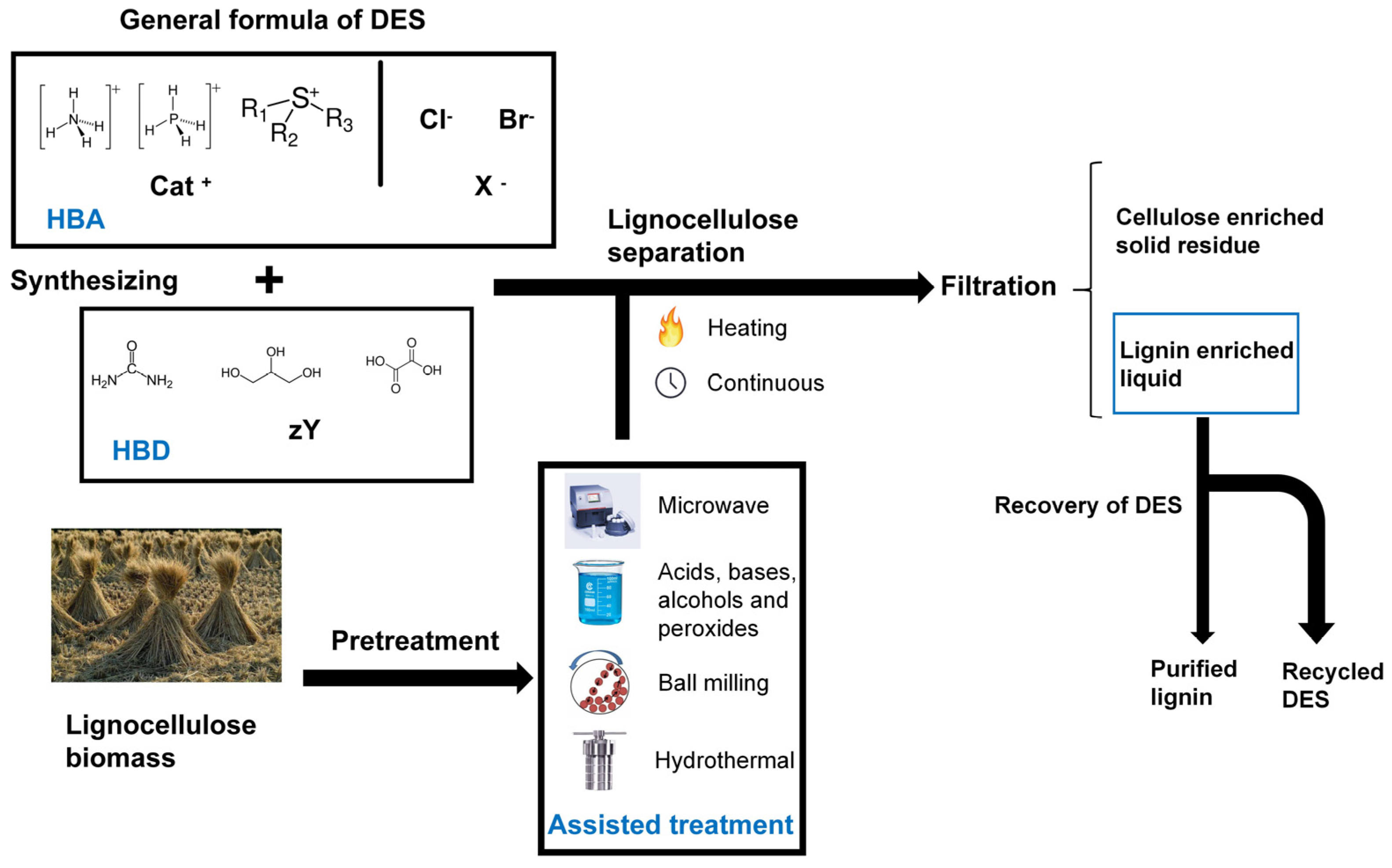
2. Deep Eutectic Solvent in Separation of Lignocellulose
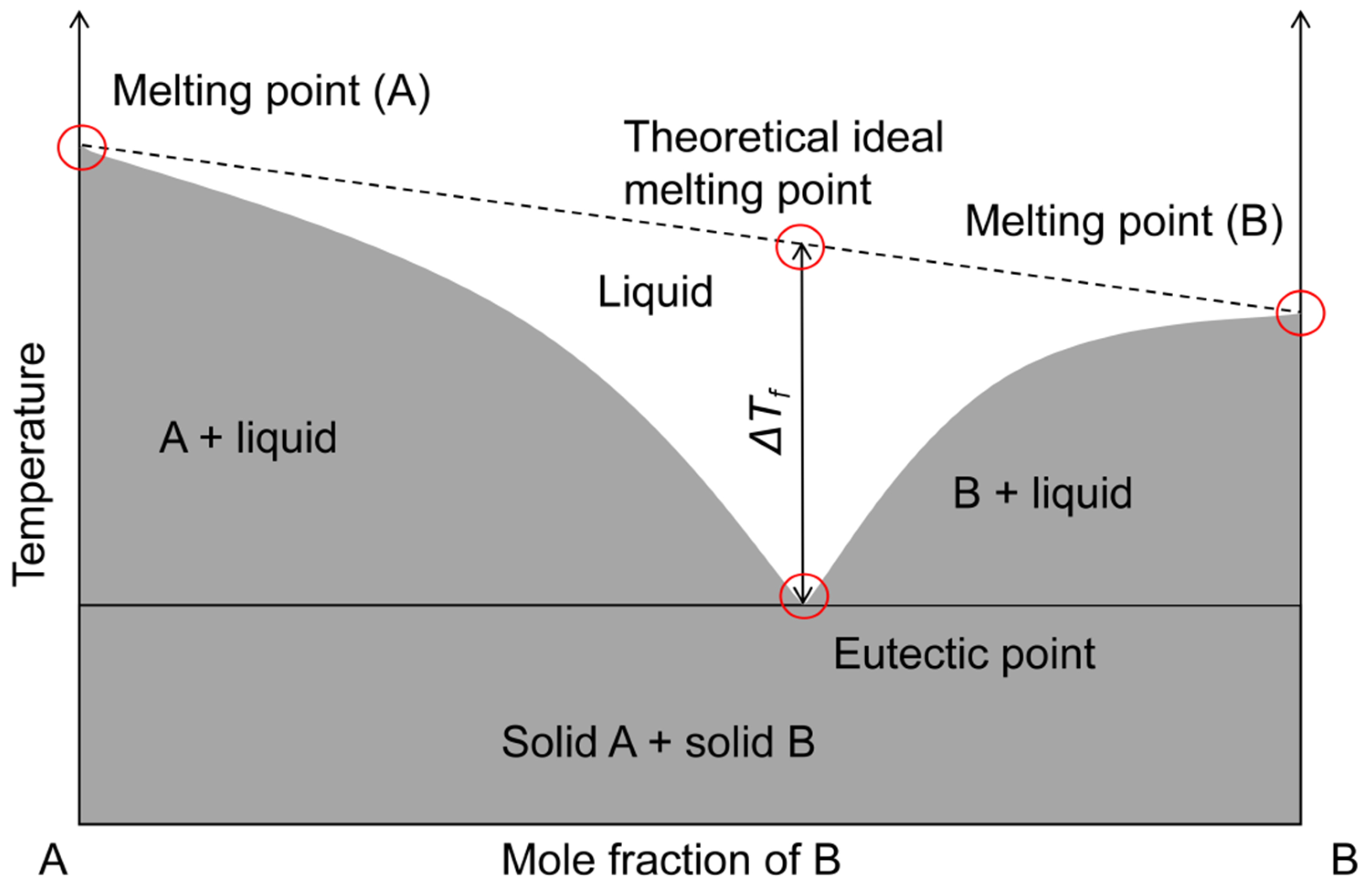
3. Definition of Deep Eutectic Solvent Effects
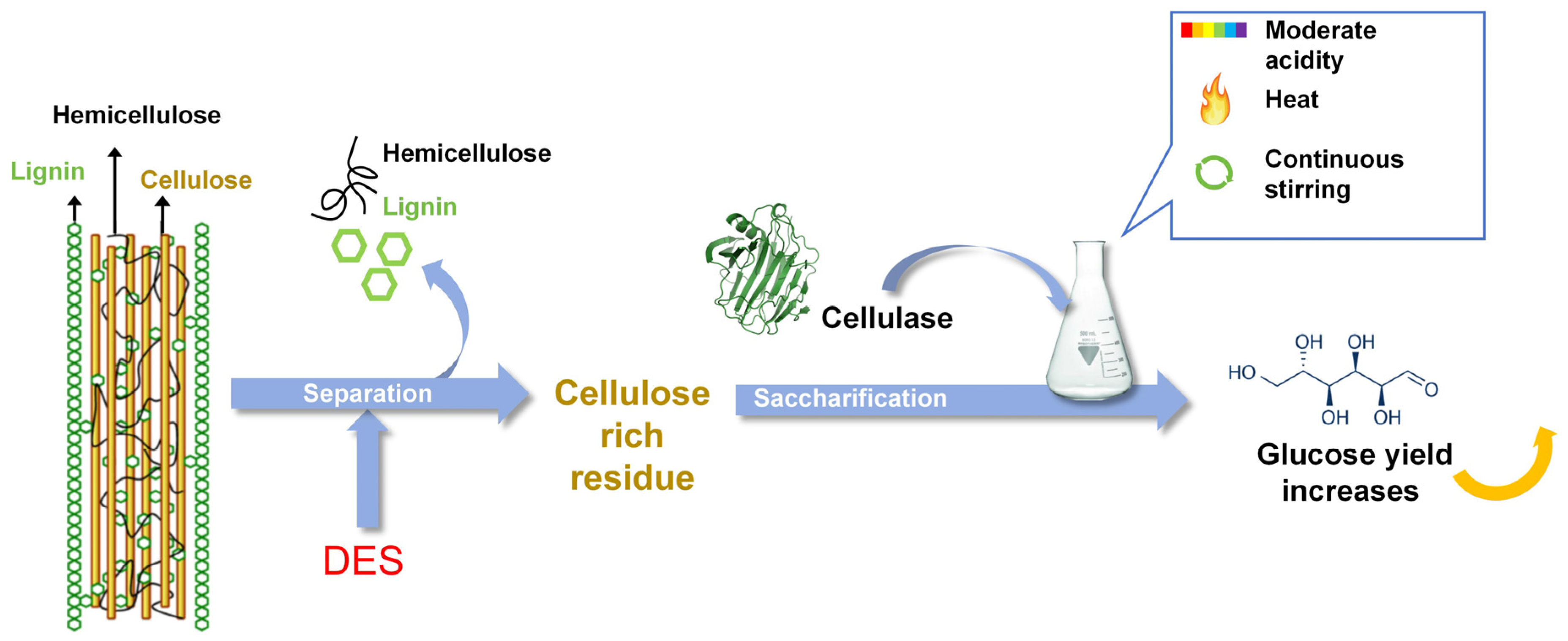
4. Effect of DES on Sugar Conversion of Substrate
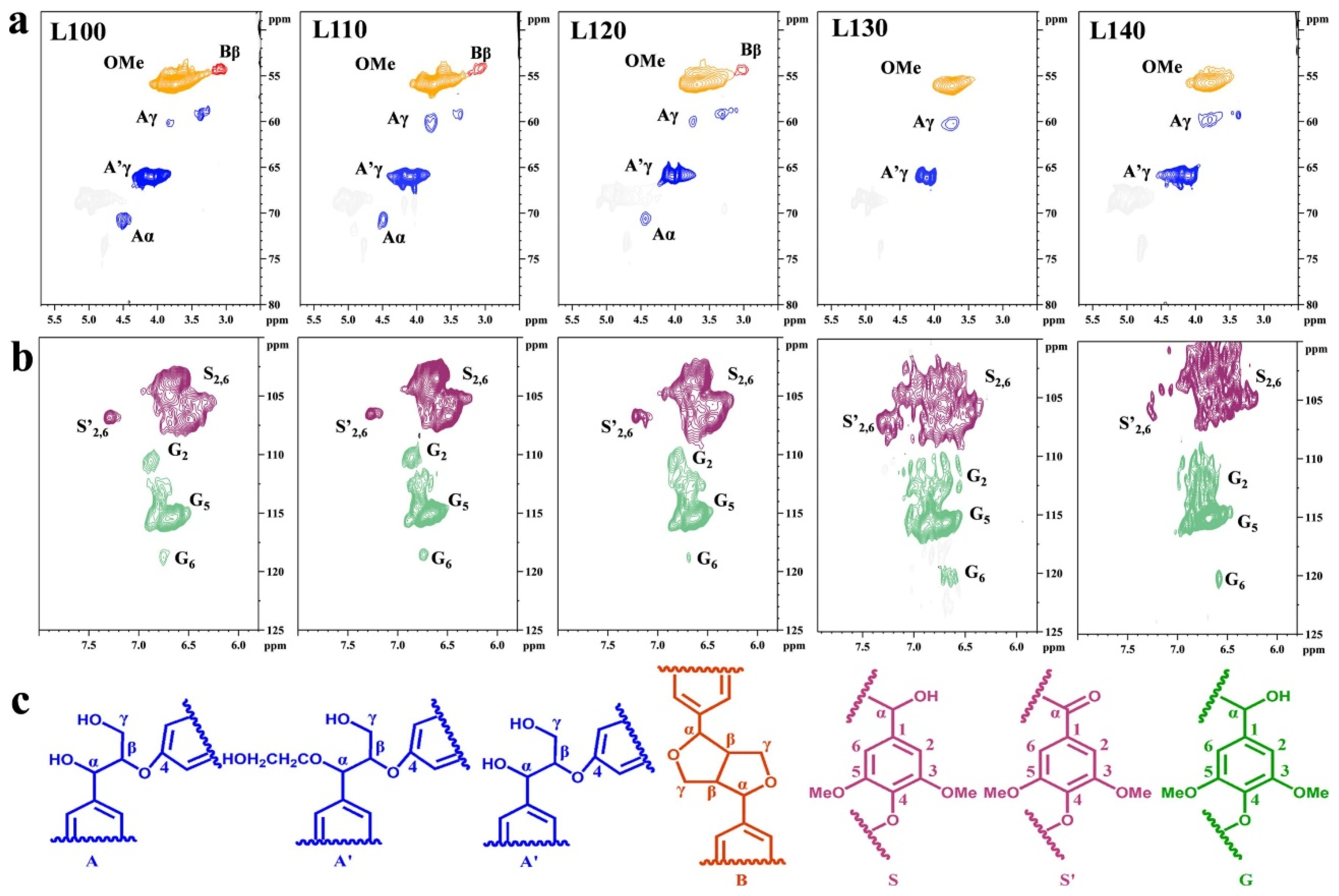
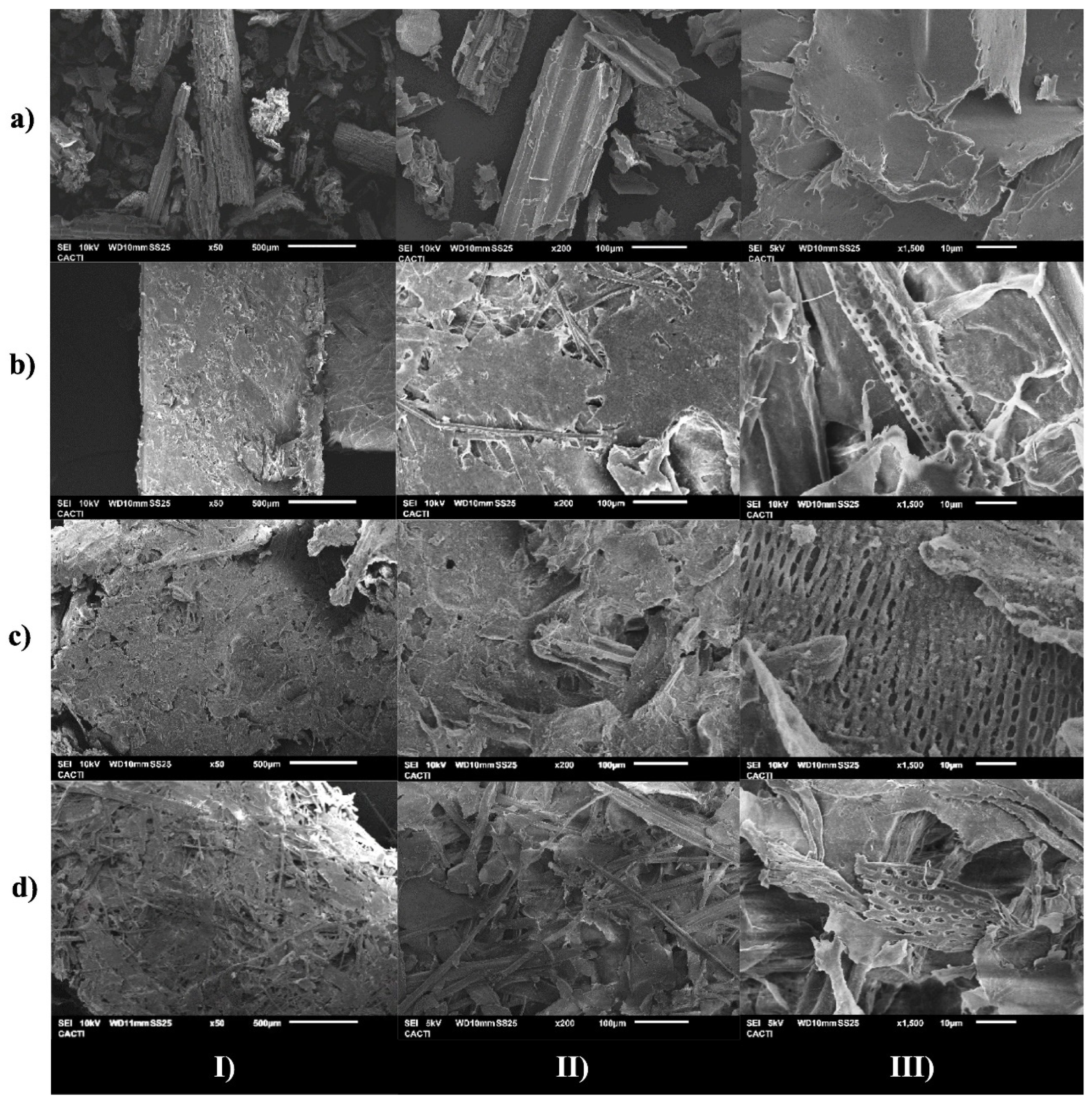
5. Effect of DES Treatment on the Chemical Structure of Lignocellulosic Separation Products
6. Conclusions
- Prior to DES pretreatment, fat-soluble components in biomass can be eliminated through organic solvent or supercritical fluid extraction to enhance the efficiency of DES treatment.
- Variations in the separation effect between different types of DESs and biomass have been observed, which are generally attributed to differences in their physical and chemical properties, including solvent polarity, proton-providing capacity, hydrogen bonding capacity, and electrical conductivity. The specific impacts of these properties require systematic exploration.
- While the DES processing temperature has gradually decreased in previous studies, further investigation is needed to explore the potential for lower temperatures or even room temperature separation.
- Attention should be given to assessing the impact of DES treatment on the chemical structure and crystallinity of lignin products as this influence can guide lignin towards meeting specific deep processing requirements.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DES | Deep eutectic solvent |
| CAGR | Compound annual growth rate |
| ILs | Ionic liquids |
| HBD | Hydrogen bond donor |
| HBA | Hydrogen bond acceptor |
| HMF | 5-hydroxymethylfurfural |
| F | 2-furfural |
| BHMF | 2,5-Bishydroxymethylfuran |
| ChCl | Choline chloride |
| LA | Lactic acid |
| p-TsOH | p-Toluenesulfonic Acid |
| MEA | Monoethanolamine |
| GL | Glycerol |
| AA | Acetic acid |
| BTEAC | Benzyltriethylammonium chloride |
| FA | Formic acid |
| GndHCl | Guanidine hydrochloride |
| 4-CSA | 4-chlorobenzene sulfonic acid |
| OA | Oxalic acid |
| EG | Ethylene glycol |
| CA | Citric acid |
| HES | Hydroxyethyl sulfonic acid |
| IPA | Isopropanolamine |
| PTA | Phosphotungstic acid |
| CTAB | Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide |
| BET | Brunauer-Emmett-Teller |
| AHP | Alkaline hydrogen peroxide |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| FT-IR | Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy |
| LCC | Lignin-carbohydrate complex |
| G unit | Guaiacol |
| S unit | Syringyl |
| 2D-HSQC | 2D-Heteronuclear Single Quantum Coherence |
| SCB | Sugarcane bagasse |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
References
- Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Liang, H.; Gao, L.; Zhao, J.; Liu, G.; Qu, Y. A closed-loop strategy for on-site production of saccharolytic enzymes for lignocellulose biorefinery using internal lignocellulosic hydrolysates. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 480, 148–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Singhania, R.R.; Nigam, P.S.; Dong, C.-D.; Patel, A.K.; Puri, M. Global status of lignocellulosic biorefinery: Challenges and perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 344, 126–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.M.; Greco, A.; Rajabimashhadi, Z.; Corcione, C.E. Efficient and environmentally friendly techniques for extracting lignin from lignocellulose biomass and subsequent uses: A review. Clean. Mater. 2024, 13, 100–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoghlami, A.; Paës, G. Lignocellulosic Biomass: Understanding Recalcitrance and Predicting Hydrolysis. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Fridrich, B.; de Santi, A.; Elangovan, S.; Barta, K. Bright Side of Lignin Depolymerization: Toward New Platform Chemicals. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 614–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wu, S.; Liu, Y. Structural changes of poplar lignin during the ternary deep eutectic solvent (DES) treatment and synergetic alkali-DES treatment. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 208, 117782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, K.; Drielak, E.; Sudarshan Varma, V.; Muthusamy, S.; Kumar, G. Updates on the pretreatment of lignocellulosic feedstocks for bioenergy production—A review. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2018, 8, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Takkellapati, S. The current and emerging sources of technical lignins and their applications. Biofuel Bioprod. Biorefin. 2018, 12, 756–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez, D.; Urueña, A.; Piñero, R.; Barrio, A.; Tamminen, T. Determination of Hemicellulose, Cellulose, and Lignin Content in Different Types of Biomasses by Thermogravimetric Analysis and Pseudocomponent Kinetic Model (TGA-PKM Method). Processes 2020, 8, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, J.Y.; Pen, K.M.; Poi, J.V.; Ooi, K.M.; Yee, K.F. Upcycling of biomass waste from durian industry for green and sustainable applications: An analysis review in the Malaysia context. Energy Nexus 2023, 10, 100203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, P.; Yang, G.; Hu, L.; Sun, J.; Shi, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J. Recent advances in the valorization of plant biomass. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2021, 14, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, P.; Bajpai, P. Pretreatment of Lignocellulosic Biomass; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; p. 17. [Google Scholar]
- Okur, M.; Eslek Koyuncu, D.D. Investigation of pretreatment parameters in the delignification of paddy husks with deep eutectic solvents. Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 142, 105811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velmurugan, R.; Kuhad, R.C.; Gupta, R.; Chakraborty, S.; Ashokkumar, V.; Incharoensakdi, A. Ionic liquid under alkaline aqueous conditions improves corncob delignification, polysaccharide recovery, enzymatic hydrolysis and ethanol fermentation. Biomass Bioenergy 2023, 178, 106980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Chen, B.; Koo, Y.-M.; MacFarlane, D.R. Introduction: Ionic Liquids. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6633–6635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.-Y.; Sun, Q.; Zuo, C.; Xu, L.-H.; Sun, S.-N.; Wen, J.-L.; Yuan, T.-Q. Efficient fractionation and targeted valorization of industrial xylose residue by synergistic and mild alkaline deep eutectic solvent-hydrogen peroxide pretreatment. Fuel Process. Technol. 2023, 241, 107591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, M.; Niu, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Li, S.; Jia, W.; Zhou, Z.; Zeng, X.; Lin, L. Biochar catalysts for efficiently 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) synthesis in aqueous natural deep eutectic solvent (A-NADES). Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 192, 115953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhamarnah, Y.; Qiblawey, H.; Nasser, M. A review on Deep eutectic solvents as the emerging class of green solvents for membrane fabrication and separations. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 398, 124250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgharbawy, A.A.M.; Hayyan, M.; Hayyan, A.; Basirun, W.J.; Salleh, H.M.; Mirghani, M.E.S. A grand avenue to integrate deep eutectic solvents into biomass processing. Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 137, 105550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Qi, X. Deep eutectic solvents for synthesis of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. Curr. Opin. Green. Sustain. 2024, 47, 100924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Liu, Y.; Meng, J.; Cheng, W.; Chen, W.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Yu, H. Multiple hydrogen bond coordination in three-constituent deep eutectic solvents enhances lignin fractionation from biomass. Green. Chem. 2018, 20, 2711–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.-J.; Chen, T.; Wang, H.-M.; Mei, Q.; Yue, F.; Sun, S.; Wen, J.-L.; Yuan, T.-Q.; Sun, R.-C. Structural and Morphological Transformations of Lignin Macromolecules during Bio-Based Deep Eutectic Solvent (DES) Pretreatment. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 2130–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.-Y.; Xu, L.-H.; Sun, Q.; Sun, S.-N.; Cao, X.-F.; Wen, J.-L.; Yuan, T.-Q. Ultrafast alkaline deep eutectic solvent pretreatment for enhancing enzymatic saccharification and lignin fractionation from industrial xylose residue. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 352, 127065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homan, T.; Shahbaz, K.; Farid, M.M. Improving the production of propyl and butyl ester-based biodiesel by purification using deep eutectic solvents. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 174, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majid, Q.; Richu; Kumar, A. Effect of choline chloride and urea based deep eutectic solvent on the physicochemical properties of salicylic acid and salicylamide at T = (288.15 to 313.15) K. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 334, 116500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijardar, S.P.; Singh, V.; Gardas, R.L. Revisiting the Physicochemical Properties and Applications of Deep Eutectic Solvents. Molecules 2022, 27, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, K.A.; Sadeghi, R. Database of deep eutectic solvents and their physical properties: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 384, 121899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, K.; Jin, Y.; Wu, W. DES: Their effect on lignin and recycling performance. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 3241–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arevalo-Gallegos, A.; Ahmad, Z.; Asgher, M.; Parra-Saldivar, R.; Iqbal, H.M. Lignocellulose: A sustainable material to produce value-added products with a zero waste approach—A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 99, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luterbacher, J.; Alonso, D.M.; Dumesic, J. Targeted chemical upgrading of lignocellulosic biomass to platform molecules. Green. Chem. 2014, 16, 4816–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallezot, P. Conversion of biomass to selected chemical products. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 1538–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabushita, M.; Kobayashi, H.; Fukuoka, A. Catalytic transformation of cellulose into platform chemicals. Appl. Catal. B 2014, 145, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istasse, T.; Richel, A. Mechanistic aspects of saccharide dehydration to furan derivatives for reaction media design. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 23720–23742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulignati, S.; Licursi, D.; Di Fidio, N.; Antonetti, C.; Raspolli Galletti, A.M. Novel Challenges on the Catalytic Synthesis of 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) from Real Feedstocks. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wei, J.; Feng, Y.; Liu, H.; Tang, X.; Zeng, X.; Sun, Y.; Lei, T.; Lin, L. Efficient synthesis of bio-based monomer 2,5-bishydroxymethylfuran by the solvent-free hydrogenation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural-based deep eutectic mixture. J. Chem. Technol. 2020, 95, 1748–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jung, D.; Park, K. Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents for the extraction of organic and inorganic analytes from aqueous environments. TrAC 2019, 118, 853–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andruch, V.; Várfalvyová, A.; Halko, R.; Jatkowska, N.; Płotka-Wasylka, J. Application of deep eutectic solvents in bioanalysis. TrAC 2022, 154, 116660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Yang, C.; Jiang, Z.; Jin, Y.; Wu, W. Lignocellulose pretreatment by deep eutectic solvents and related technologies: A review. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2023, 8, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabed, H.; Sahu, J.N.; Boyce, A.N.; Faruq, G. Fuel ethanol production from lignocellulosic biomass: An overview on feedstocks and technological approaches. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 66, 751–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.T.; Chua, A.S.M.; Ngoh, G.C. Deep eutectic solvent for lignocellulosic biomass fractionation and the subsequent conversion to bio-based products—A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297, 122522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, M.C.; Wu, T.Y. Sequential pretreatment with alkaline hydrogen peroxide and choline chloride:copper (II) chloride dihydrate—Synergistic fractionation of oil palm fronds. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 301, 122684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Fakayode, O.A.; Ren, M.; Li, H.; Liang, J.; Yagoub, A.E.A.; Fan, Z.; Zhou, C. Laccase-catalyzed lignin depolymerization in deep eutectic solvents: Challenges and prospects. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2023, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.-T.; Wang, C.; Guo, M.F.; Aprà, E.; Ma, R.; Ragauskas, A.J.; Zhang, X. Lignin with controlled structural properties by N-heterocycle-based deep eutectic solvent extraction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2307323120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Li, X.; You, T.; Li, D.; Nawaz, H.; Zhang, X.; Xu, F. Insights into alkaline choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvents pretreatment for Populus deltoides: Lignin structural features and modification mechanism. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Zhao, G.; Ding, C.; Wu, B.; Lian, Z.; Lian, H. Physicochemical transformation of rice straw after pretreatment with a deep eutectic solvent of choline chloride/urea. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 176, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, N.; Jiang, B.; Hu, J.; Huang, M.; He, J.; Jiang, Q.; Zhao, L.; Shen, F.; Tian, D. The coupling effects between acid-catalyzed hydrothermal pretreatment and acidic/alkaline deep eutectic solvent extraction for wheat straw fractionation. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 386, 129579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Yu, X.; Yagoub, A.E.-G.A.; Chen, L.; Zhou, C. Efficient removal of lignin from vegetable wastes by ultrasonic and microwave-assisted treatment with ternary deep eutectic solvent. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 149, 112357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Yu, X.; Yagoub, A.E.A.; Chen, L.; Mustapha, A.T.; Zhou, C. Enhancement of lignin removal and enzymolysis of sugarcane bagasse by ultrasound-assisted ethanol synergized deep eutectic solvent pretreatment. Renew. Energy 2021, 172, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, T.; Yao, S.; Tang, Y. Comparison of polyol-based deep eutectic solvents (DESs) on pretreatment of moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens) for enzymatic hydrolysis. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 189, 115767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, R.; Kuang, Y.; Wang, J.; Xiao, W.; Lin, J.; Liu, Z. Improved glucose yield and concentration of sugarcane bagasse by the pretreatment with ternary deep eutectic solvents and recovery of the pretreated liquid. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 366, 128186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Jiang, J.; Jiang, H.; Liu, C.; Dong, Y.; Chen, X.; Xiao, L.-P. Acid/alkali-catalyzed deep eutectic solvent pretreatment of corn straw for enhanced biohydrogen production. Fuel 2023, 348, 128521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Huang, T.; Liu, J.; Gao, H.; Bian, H.; Wang, R.; Huang, C.; Sha, J.; Dai, H. Recyclable deep eutectic solvent coupling sodium hydroxide post-treatment for boosting woody/herbaceous biomass conversion at mild condition. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 320, 124327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, X.; Zhan, Y.; Bian, H.; Wu, S.; Dai, H.; Liang, F.; Meng, X.; Huang, C.; Fang, G.; et al. A tailored deep eutectic solvent for high-yield conversion of poplar residues to bio-based building blocks at mild conditions. J. Chem. Eng. 2024, 487, 150407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhou, Z.; Tian, D.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, J.; Deng, P.; Zou, H.; Lu, C. Acidic deep eutectic solvent assisted mechanochemical delignification of lignocellulosic biomass at room temperature. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 234, 123593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Gong, L.; Ma, C.; He, Y.-C. Enhanced enzymatic saccharification of sorghum straw by effective delignification via combined pretreatment with alkali extraction and deep eutectic solvent soaking. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 340, 125695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Wan, C. Ultrafast fractionation of lignocellulosic biomass by microwave-assisted deep eutectic solvent pretreatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 250, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gundupalli, M.P.; Tantayotai, P.; Panakkal, E.J.; Chuetor, S.; Kirdponpattara, S.; Thomas, A.S.S.; Sharma, B.K.; Sriariyanun, M. Hydrothermal pretreatment optimization and deep eutectic solvent pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass: An integrated approach. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2022, 17, 100957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-W.; Xia, S.-Q.; Ma, P.-S. Facile pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass using deep eutectic solvents. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 219, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.-L.; Yue, Z.; Sun, S.-C.; Sun, S.-N.; Cao, X.-F.; Yuan, T.-Q.; Wen, J.-L. Exploration of deep eutectic solvent-based biphasic system for furfural production and enhancing enzymatic hydrolysis: Chemical, topochemical, and morphological changes. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 352, 127074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.T.; Ngoh, G.C.; Chua, A.S.M. Evaluation of fractionation and delignification efficiencies of deep eutectic solvents on oil palm empty fruit bunch. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 123, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Yu, X.; Yagoub, A.E.-G.A.; Chen, L.; Fakayode, O.A.; Zhou, C. Synergism of sweeping frequency ultrasound and deep eutectic solvents pretreatment for fractionation of sugarcane bagasse and enhancing enzymatic hydrolysis. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 73, 105470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zheng, T.; Yang, L.; Li, J.; Yao, J. Using deep eutectic solvents to pretreat corncob for the fabrication of sustainable lignocellulose hydrogels. Biomass Bioenergy 2023, 174, 106824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Yang, Q.; Hu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Hui, L. Solid acid facilitated deep eutectic solvents extraction of high-purity and antioxidative lignin production from poplar wood. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, B.; Hou, S.; Jia, Y.; Yang, C.; Su, Y.; Ling, Z.; Huang, C.; Lai, C.; Yong, Q. Synergistic effects of hydrothermal and deep eutectic solvent pretreatment on co-production of xylo-oligosaccharides and enzymatic hydrolysis of poplar. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 341, 125787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, D.; Guo, Y.; Hu, J.; Yang, G.; Zhang, J.; Luo, L.; Xiao, Y.; Deng, S.; Deng, O.; Zhou, W.; et al. Acidic deep eutectic solvents pretreatment for selective lignocellulosic biomass fractionation with enhanced cellulose reactivity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 142, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Wang, K.; Zhou, M.; Xu, J.; Jiang, J. Efficient fractionation of moso bamboo by synergistic hydrothermal-deep eutectic solvents pretreatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 328, 124873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, J.; Xie, J.; Zhu, S.; Wang, B.; Li, J.; Chen, K. Physicochemical transformation and enzymatic hydrolysis promotion of reed straw after pretreatment with a new deep eutectic solvent. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 290, 119472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Chen, J.; Cheng, Z.; Zhu, S.; Xu, J. Pretreatment of pine lignocelluloses by recyclable deep eutectic solvent for elevated enzymatic saccharification and lignin nanoparticles extraction. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 269, 118321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, X.; Qureshi, N. High-efficient cellulosic butanol production from deep eutectic solvent pretreated corn stover without detoxification. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 162, 113258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.; Park, S.; Jung, D.; Oh, K.K.; Lee, S.H. Effect of hydrogen bond donor on the choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvent-mediated extraction of lignin from pine wood. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Song, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X. Culturing rhodotorula glutinis in fermentation-friendly deep eutectic solvent extraction liquor of lignin for producing microbial lipid. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 337, 125475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Eberhardt, T.L.; Meng, F.; Xu, C.; Pan, H. Efficient extraction of lignin from moso bamboo by microwave-assisted ternary deep eutectic solvent pretreatment for enhanced enzymatic hydrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 400, 130666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.; Mittal, N.; Dhukia, S.; Atri, A.K.; Singh, V. Novel ternary based natural deep eutectic solvents (NADES) for sustainable extraction of lignin nanoparticles from waste Pinus roxburghii needles: A green approach. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2024, 39, 101518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Yuan, X.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, S.; Xu, Z.; Jin, M. Densification pretreatment with a limited deep eutectic solvent triggers high-efficiency fractionation and valorization of lignocellulose. Green. Chem. 2023, 25, 8026–8039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Yu, D.; Yuan, J.; Wu, H.; Luo, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Yang, S. Efficient delignification of wheat straw for microbial lipid production enabled by a novel ternary deep eutectic solvent containing ethylene glycol. Fuel 2023, 347, 128485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zhang, X.-F.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, T.; Yao, J. Deep eutectic solvent with bifunctional Brønsted-Lewis acids for highly efficient lignocellulose fractionation. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 347, 126723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Fan, B.; Tang, W.; He, Y.-C.; Ma, C. Comprehensive understanding of co-producing fermentable sugar, furfural, and xylo-oligosaccharides through the pretreatment with CTAB-based deep eutectic solvent containing Brønsted and Lewis acid. J. Chem. Eng. 2024, 488, 150637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Zhuang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Xie, D.; Yoo, C.G.; Yang, Q. Fractionation of Poplar Wood Using a Bifunctional Aromatic Acid under Mild Conditions. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 5364–5376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, E.S.; Da Costa Lopes, A.M.; Freire, M.G.; Freire, C.S.R.; Silvestre, A.J.D. Unveiling Modifications of Biomass Polysaccharides during Thermal Treatment in Cholinium Chloride : Lactic Acid Deep Eutectic Solvent. ChemSusChem 2021, 14, 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Cheng, J.; Zhan, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Yoo, C.G.; Fang, G.; Meng, X.; Ragauskas, A.J.; et al. Utilization of guaiacol-based deep eutectic solvent for achieving a sustainable biorefinery. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 362, 127771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muryanto, M.; Sudiyani, Y.; Darmawan, M.A.; Handayani, E.M.; Gozan, M. Simultaneous Delignification and Furfural Production of Palm Oil Empty Fruit Bunch by Novel Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvent. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2023, 48, 16359–16371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharska, K.; Rybarczyk, P.; Hołowacz, I.; Łukajtis, R.; Glinka, M.; Kamiński, M. Pretreatment of Lignocellulosic Materials as Substrates for Fermentation Processes. Molecules 2018, 23, 2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jančíková, V.; Jablonský, M. Exploiting Deep Eutectic Solvent-like Mixtures for Fractionation Biomass, and the Mechanism Removal of Lignin: A Review. Sustainability 2024, 16, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Vasco, C.; Ma, R.; Quintero, M.; Guo, M.; Geleynse, S.; Ramasamy, K.K.; Wolcott, M.; Zhang, X. Unique low-molecular-weight lignin with high purity extracted from wood by deep eutectic solvents (DES): A source of lignin for valorization. Green. Chem. 2016, 18, 5133–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonyeam, J.; Chaipanya, R.; Suksomboon, S.; Khan, M.J.; Amatariyakul, K.; Wibowo, A.; Posoknistakul, P.; Charnnok, B.; Liu, C.G.; Laosiripojana, N.; et al. Process design for acidic and alcohol based deep eutectic solvent pretreatment and high pressure homogenization of palm bunches for nanocellulose production. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 7550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Huang, C.; Zhan, Y.; Han, S.; Wang, J.; Meng, X.; Yoo, C.G.; Fang, G.; Ragauskas, A.J. Effective biomass fractionation and lignin stabilization using a diol DES system. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 443, 136395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajardo-Parra, N.F.; Cotroneo-Figueroa, V.P.; Aravena, P.; Vesovic, V.; Canales, R.I. Viscosity of Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents: Experiments and Modeling. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2020, 65, 5581–5592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.J.; Alabdrabalameer, H.A.; Skoulou, V. Choosing Physical, Physicochemical and Chemical Methods of Pre-Treating Lignocellulosic Wastes to Repurpose into Solid Fuels. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirhan, H.; Fauzi, A.; Skoulou, V.K.; Haywood, S.H.; Zein, S.H. Wheat straw bio-refining. part I: Optimization of the microwave radiation process with sulphuric acid pre-treatment. Curr. Microw. Chem. 2017, 4, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, T.; Zhang, X.; Gu, X.; Han, L.; Ji, G.; Chen, X.; Xiao, W. Ball milling for biomass fractionation and pretreatment with aqueous hydroxide solutions. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 7733–7742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martina, K.; Cravotto, G.; Varma, R.S. Impact of Microwaves on Organic Synthesis and Strategies toward Flow Processes and Scaling Up. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 86, 13857–13872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gude, V.G.; Martinez-Guerra, E. Green Chemistry of Microwave-Enhanced Biodiesel Production. Prod. Biofuels Chem. Microw. 2015, 3, 225–250. [Google Scholar]
- Maiti, S.; Gallastegui, G.; Suresh, G.; Pachapur, V.L.; Brar, S.K.; Le Bihan, Y.; Drogui, P.; Buelna, G.; Verma, M.; Galvez-Cloutier, R. Microwave-assisted one-pot conversion of agro-industrial wastes into levulinic acid: An alternate approach. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 265, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, R.; Zhou, X.; Qian, M.; Wang, C.; Boldor, D.; Lei, H.; Zhang, X. Advancements and applications of microwave-assisted deep eutectic solvent (MW-DES) lignin extraction: A comprehensive review. Green. Chem. 2024, 26, 1153–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratishko, V.; Shulga, S.; Achkevych, O.; Tigunova, O. Ultrasonic cavitation of lignocellulosic raw materials as effective method of preparation for butanol production. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Scientific Conference Engineering for Rural Development Proceedings, Jelgava, Latvia, 24–26 May 2023; Faculty of Engineering, Latvia University of Life Sciences and Technologies: Jelgava, Latvia, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.M.; Quek, J.D.; Tey, W.Y.; Lim, S.; Kang, H.S.; Quen, L.K.; Mahmood, W.A.W.; Jamaludin, S.I.S.; Teng, K.H.; Khoo, K.S. Biomass valorization by integrating ultrasonication and deep eutectic solvents: Delignification, cellulose digestibility and solvent reuse. Biochem. Eng. J. 2022, 187, 108587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaei-Rad, Z.; Pazouki, M.; Fooladi, J.; Azin, M.; Gummadi, S.N.; Allahverdi, A. Investigation of a robust pretreatment technique based on ultrasound-assisted, cost-effective ionic liquid for enhancing saccharification and bioethanol production from wheat straw. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, Q.; Feng, Y.; Xuan, J. Composition of Lignocellulose Hydrolysate in Different Biorefinery Strategies: Nutrients and Inhibitors. Molecules 2024, 29, 2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Tang, P.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, G. An environmentally friendly bleaching process for cotton fabrics: Mechanism and application of UV/H2O2 system. Cellulose 2020, 27, 1071–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Peng, L.; Fang, Z.; Lin, X.; Sun, C.; Qiu, X. Dispersing boron nitride nanosheets with carboxymethylated cellulose nanofibrils for strong and thermally conductive nanocomposite films with improved water-resistance. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 321, 121250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; An, X.; Yang, S. The Effect of Ball Milling Time on the Isolation of Lignin in the Cell Wall of Different Biomass. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 807625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitotaw, Y.W.; Habtu, N.G.; Gebreyohannes, A.Y.; Nunes, S.P.; Van Gerven, T. Ball milling as an important pretreatment technique in lignocellulose biorefineries: A review. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2023, 13, 15593–15616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, C.; Dixit, P.; Momayez, F.; Jönsson, L.J. Hydrothermal Pretreatment of Lignocellulosic Feedstocks to Facilitate Biochemical Conversion. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 846592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosal, K.; Ghosh, S. Biodegradable polymers from lignocellulosic biomass and synthetic plastic waste: An emerging alternative for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2023, 156, 100761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scapini, T.; dos Santos, M.S.N.; Bonatto, C.; Wancura, J.H.C.; Mulinari, J.; Camargo, A.F.; Klanovicz, N.; Zabot, G.L.; Tres, M.V.; Fongaro, G.; et al. Hydrothermal pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for hemicellulose recovery. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 342, 126033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Wang, A.; Yan, C.; Liu, S.; Li, L.; Wu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Nie, G.; Nie, S.; et al. Study on the Solubility of Industrial Lignin in Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abolore, R.S.; Jaiswal, S.; Jaiswal, A.K. Green and sustainable pretreatment methods for cellulose extraction from lignocellulosic biomass and its applications: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2024, 7, 100396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Shao, X.; Jiang, R.; Ma, Z.; Wang, H. Effects of ultrasonic/microwave-assisted treatment on the properties of corn distarch phosphate/corn straw cellulose films and structure characterization. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 1467–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amesho, K.; Lin, Y.-C.; Venkata Mohan, S.; Halder, S.; Ponnusamy, V.K.; Jhang, S.-R. Deep eutectic solvents in the transformation of biomass into biofuels and fine chemicals: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 21, 183–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isci, A.; Kaltschmitt, M. Recovery and recycling of deep eutectic solvents in biomass conversions: A review. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2022, 12, 197–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kim, K.H.; Jeong, K.; Kim, N.-K.; Yoo, C.G. Sustainable biorefinery processes using renewable deep eutectic solvents. Curr. Opin. Green. Sustain. 2021, 27, 100396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yan, C.; Xue, Z. Deep eutectic solvents for fractionation and valorization of lignocellulose. Green. Chem. Eng. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panić, M.; Gunjević, V.; Cravotto, G.; Radojčić Redovniković, I. Enabling technologies for the extraction of grape-pomace anthocyanins using natural deep eutectic solvents in up-tOHalf-litre batches extraction of grape-pomace anthocyanins using NADES. Food Chem. 2019, 300, 125185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, K.; Zuo, M.; Song, X.; Zeng, X.; Tang, X.; Sun, Y.; Lei, T.; Lin, L. An effective pathway for 5-brominemethylfurfural synthesis from biomass sugars in deep eutectic solvent. J. Chem. Technol. 2017, 92, 2929–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.K.; Parikh, B.S.; Pravakar, M. Natural deep eutectic solvent mediated pretreatment of rice straw: Bioanalytical characterization of lignin extract and enzymatic hydrolysis of pretreated biomass residue. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 9265–9275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiner, B.; Fleischer, P.; Schörken, U. Biocatalytic synthesis of biodiesel utilizing deep eutectic solvents: A two-step-one-pot approach with free lipases suitable for acidic and used oil processing. Process Biochem. 2016, 51, 1808–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayyan, A.; Hashim, M.A.; Hayyan, M.; Mjalli, F.S.; AlNashef, I.M. A novel ammonium based eutectic solvent for the treatment of free fatty acid and synthesis of biodiesel fuel. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 46, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamilla, J.L.K.; Novak, U.; Grilc, M.; Likozar, B. Natural deep eutectic solvents (DES) for fractionation of waste lignocellulosic biomass and its cascade conversion to value-added bio-based chemicals. Biomass Bioenergy 2019, 120, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grillo, G.; Gunjević, V.; Radošević, K.; Redovniković, I.R.; Cravotto, G. Deep Eutectic Solvents and Nonconventional Technologies for Blueberry-Peel Extraction: Kinetics, Anthocyanin Stability, and Antiproliferative Activity. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza, A.; Tapia, X.; Yañez, C.; Vilches, F.; Candia, O.; Cabezas, R.; Romero, J. Obtaining Hydroxytyrosol from Olive Mill Waste Using Deep Eutectic Solvents and Then Supercritical CO2. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 6273–6284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Meng, X.; Jeong, K.; Li, S.; Leem, G.; Kim, K.H.; Pu, Y.; Ragauskas, A.J.; Yoo, C.G. Investigation of a Lignin-Based Deep Eutectic Solvent Using p-Hydroxybenzoic Acid for Efficient Woody Biomass Conversion. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 12542–12553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, E.S.; Freire, M.G.; Freire, C.S.R.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Silvestre, A.J.D. Enhanced Conversion of Xylan into Furfural using Acidic Deep Eutectic Solvents with Dual Solvent and Catalyst Behavior. ChemSusChem 2020, 13, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Mu, T. Revisiting greenness of ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents. Green. Chem. Eng. 2021, 2, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Dutta, T.; Sun, J.; Simmons, B.; Singh, S. Biomass pretreatment using deep eutectic solvents from lignin derived phenols. Green. Chem. 2018, 20, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, C.; Romero, L.; Rintoul, I.; Branco, L.C.; Marrucho, I.M. From Phase Change Materials to Green Solvents: Hydrophobic Low Viscous Fatty Acid—Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 3888–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Y. A novel poly(deep eutectic solvent)-based magnetic silica composite for solid-phase extraction of trypsin. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 946, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Mou, H.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Mu, T. Eutectic Molecular Liquids Based on Hydrogen Bonding and π–π Interaction for Exfoliating Two-dimensional Materials and Recycling Polymers. Chem. Asian J. 2019, 14, 3350–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Xiong, D.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J. Miscible–Immiscible Transition of Deep Eutectic Solvents in Water Switched by CO2. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 17882–17887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Chen, W.; Zhou, L.; Qin, J.; Meng, Y.; Mu, T. Vaporization enthalpy, long-term evaporation and evaporation mechanism of polyethylene glycol-based deep eutectic solvents. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 9493–9501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Bai, X.; Lusi, A.; Wan, C. High-Solid Lignocellulose Processing Enabled by Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent for Lignin Extraction and Industrially Relevant Production of Renewable Chemicals. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 12205–12216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhu, P.; Luo, L.; Lin, H.; Tao, Y.; Ruan, L.; Wang, L.; Qing, Q. p-Toluenesulfonic acid enhanced neutral deep eutectic solvent pretreatment of soybean straw for efficient lignin removal and enzymatic hydrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 395, 130338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, T.; Singh, V. Natural deep eutectic solvents (NADES) assisted deconstruction of oilcane bagasse for high lipid and sugar recovery. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 210, 118127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, D.; Sun, Y.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, F.; Fang, G.; Zhu, H.; Liu, Y. Selective degradation of hemicellulose and lignin for improving enzymolysis efficiency via pretreatment using deep eutectic solvents. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 376, 128937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, J.; Xu, H.; Liu, H.; He, Y.-C. Improving saccharification efficiency of corn stover through ferric chloride-deep eutectic solvent pretreatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 399, 130579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemalatha, M.; Lakshmi, B. Valorization of fruit waste using DES pretreatment and hydrolysis over a heterogeneous catalyst for bioethanol production. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2021, 13, 5731–5741. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, P.; Ji, Z.; Ling, Z.; Yong, Q. Microwave-assisted fast co-production of fermentable sugar and nanocellulose via tunable zinc acetate based deep eutectic solvents treatments. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 191, 115965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Xu, B.; Wang, X.; Lang, J.; Zhang, H. Chemical and Structural Elucidation of Lignin and Cellulose Isolated Using DES from Bagasse Based on Alkaline and Hydrothermal Pretreatment. Polymers 2022, 14, 2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tang, W.; He, Y.-C. Integrated understanding of acidic deep eutectic solvent choline chloride: Oxalic acid pretreatment to enhance the enzymatic hydrolysis of rape straw. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 206, 117691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.; Lv, Y.; Liu, M. Research on lignin-modified flexible polyurethane foam and its application in sound absorption. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2024, 137, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Hou, X.; Sun, J.; Sun, D.; Gao, Z. Efficacy and Functional Mechanisms of a Two-Stage Pretreatment Approach Based on Alkali and Ionic Liquid for Bioconversion of Waste Medium-Density Fiberboard. Molecules 2024, 29, 2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Lyu, G.; Liu, Y.; Lou, R.; Lucia, L.A.; Yang, G.; Chen, J.; Saeed, H.A.M. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) for the Isolation of Willow Lignin (Salix matsudana cv. Zhuliu). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Jiang, B.; Chen, H.; Wu, W.; Wu, S.; Jin, Y.; Xiao, H. Recent advances in understanding the effects of lignin structural characteristics on enzymatic hydrolysis. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2021, 14, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.-Y.; Xu, L.-H.; Sun, Q.; Shen, X.-J.; Wen, J.-L.; Yuan, T.-Q. Tailored one-pot lignocellulose fractionation to maximize biorefinery toward controllable producing lignin nanoparticles and facilitating enzymatic hydrolysis. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 450, 138315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Pan, Y.; Ma, X.; Yin, S.; Zhu, M. Efficient separation and production of high-quality rubber, lignin nanoparticles and fermentable sugars from Eucommia ulmoides pericarp via deep eutectic solvent pretreatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.-j.; Wen, J.-L.; Mei, Q.; Chen, X.; Sun, D.; Yuan, T.-Q.; Sun, R.-C. Facile fractionation of lignocelluloses by biomass-derived deep eutectic solvent (DES) pretreatment for cellulose enzymatic hydrolysis and lignin valorization. Green. Chem. 2018, 21, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morán-Aguilar, M.G.; Calderón-Santoyo, M.; de Souza Oliveira, R.P.; Aguilar-Uscanga, M.G.; Domínguez, J.M. Deconstructing sugarcane bagasse lignocellulose by acid-based deep eutectic solvents to enhance enzymatic digestibility. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 298, 120097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.U.; Kim, J.W.; Seo, S.; Jae, J. Hydrolysis of regenerated cellulose from ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvent over sulfonated carbon catalysts. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 8153–8162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, M.-K.; Zuo, C.; Yang, Y.-T.; Liu, Y.-H.; Ma, C.-Y.; Wen, J.-L. Green Fractionation and Structural Characterization of Lignin Nanoparticles via Carboxylic-Acid-Based Deep Eutectic Solvent (DES) Pretreatment. Fermentation 2023, 9, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Xing, S.; Jin, Y.; Lu, X.; Huang, C.; Yong, Q. Insight into understanding the performance of deep eutectic solvent pretreatment on improving enzymatic digestibility of bamboo residues. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 306, 123163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Peng, J.; Kong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Su, Z.; Li, B.; Song, X.; Liu, S.; Tian, W. Key process parameters for deep eutectic solvents pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass materials: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 310, 123416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Wu, S.; Huang, M.; Zhao, L.; He, J.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, S.; Hu, J.; Tian, D.; Shen, F. Integration of lignin microcapsulated pesticide production into lignocellulose biorefineries through FeCl3-mediated deep eutectic solvent pretreatment. Green. Chem. 2022, 24, 5242–5254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kłosowski, G.; Mikulski, D. Changes in various lignocellulose biomasses structure after microwave-assisted hydrotropic pretreatment. Renew. Energy 2023, 219, 119387. [Google Scholar]
| Substrate | Solvent (mol) | Assisted Treatment | Condition | Delignification Rate (%) | Lignin in Solid Residue (%) | Cellulose in Solid Residue (%) | Hemicellulose in Solid Residue (%) | Cellulose Preservation (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alkaline DESs | |||||||||
| Industrial xylose residue | ChCl: MEA (1:6) | Microwave-assisted | 80 °C, 10 min | 91.95 | 3.59 | 95.60 | 0.42 | 98.73 | [23] |
| Wheat straw | LA: Pyrazole (1:1) | - | 145 °C, 9 h | 93.70 | 2.15 | - | - | 51.17 | [43] |
| Populus | ChCl: Imidazole (3:7) | - | 150 °C, 0.67 h | 75.50 | 6.50 | 29.90 | 2.90 | 69.25 | [44] |
| Rice straw | ChCl: Urea (1:2) | - | 130 °C, 6 h | 43.19 | 8.43 | 25.06 | 11.55 | 70.61 | [45] |
| Wheat straw | GL: Urea (1:2) | Hydrothermal pretreatment | 90 °C, 3 h | 75.60 | 19.80 | 76.13 | nd | 99.20 | [46] |
| Neutral DESs | |||||||||
| Garlic skin | ChCl: GL: AlCl3·6H2O (1:2:0.2) | Ultrasound + microwave assisted | Room temperature, 30 min; 80 °C, 20 min | 90.14 | 5.15 | 48.52 | 29.44 | 79.75 | [47] |
| Sugarcane bagasse | ChCl: GL: FeCl3·6H2O (1:1:0.3) | Ultrasound ethanol pretreatment | 240 W, 1 h; DES: 120 °C, 3 h | 86.39 | 9.04 | 66.17 | - | - | [48] |
| Bamboo | ChCl: Xylitol (1:2) | 1 wt% H2SO4 | 120 °C, 4 h | 84.91 | 10.72 | 73.30 | 1.82 | 72.68 | [49] |
| Sugarcane bagasse | ChCl: PEG 600 (1:4) | 1 wt% HES | 170 °C, 2 h | 83.23 | 11.41 | 75.66 | nd | 73.63 | [50] |
| Corn straw | ChCl: 1,4-butanediol (1:2) | NaOH assisted | 100 °C, 3 h | 81.30 | - | - | - | 71.50 | [51] |
| Industrial xylose residue | ChCl: IPA (1:6) | Hydrogen peroxide assisted | 60 °C, 2 h | 97.11 | 1.31 | 91.88 | 2.52 | - | [16] |
| Acid DESs | |||||||||
| Poplar sawdust | ChCl: p-TsOH (1:2) | NaOH treatment | 100 °C, 40 min | 92.20 | 4.69 | 87.50 | 1.61 | 92.98 | [52] |
| Poplar residues | ChCl: p-TsOH (1:2) | Ethanol | 90 °C, 1 h | 90.99 | - | - | - | 90.47 | [53] |
| Poplar wood chips | ChCl: p-TsOH (1:2) | Ball milling | Room temperature, 3 h | 99.78 | - | - | - | 82.19 | [54] |
| Sorghum straw | ChCl: LA (1:1) | NaOH 0.75 wt% pretreatment | NaOH:121 °C, 1 h DES:140 °C, 0.67 h | 79.30 | 11.20 | 53.40 | 29.30 | 79.67 | [55] |
| Corn stover | ChCl: LA (1:2) | Microwave-assisted | 800 W, 45 s | 79.60 | 9.22 | 65.78 | 5.03 | 75.11 | [56] |
| Sugarcane bagasse | ChCl: LA (1:2) | Hydrothermal pretreatment | 130 °C, 1.5 h | 84.30 | 3.50 | 78.50 | 10.60 | 56.76 | [57] |
| Corncob | ChCl: LA (1:2) | - | 110 °C, 24 h | 95.50 | - | 77.80 | - | - | [58] |
| Eucalyptus grandis | ChCl: LA (1:2) | - | 150 °C, 1.5 h | 93.00 | 8.90 | 78.4 | nd | 49.47 | [59] |
| Oil palm empty fruit bunch | ChCl: LA (1:5) | - | 120 °C, 8 h | 88.00 | 4.70 | 71.40 | nd | - | [60] |
| Sugarcane bagasse | ChCl: LA (1:10) | Ultrasound | 40 kHz, 1.5 h DES:120 °C, 3 h | 86.82 | 6.89 | 65.62 | 4.47 | 67.57 | [61] |
| Corncob | ChCl: LA (1:10) | - | 130 °C, 4 h | 95.90 | 1.5 0 | 74.90 | 7.00 | 89.03 | [62] |
| Poplar | ChCl: LA (1:10) | PTA | 120 °C, 4 h | 82.20 | - | - | - | - | [63] |
| Poplar sawdust | ChCl: LA (1:10) | Hydrothermal pretreatment | 130 °C, 1.5 h | 84.40 | 7.80 | 79.20 | 10.20 | 86.10 | [64] |
| Poplar | ChCl: acetic acid (AA) (1:2) | - | 130 °C, 3 h | 76.50 | 9.50 | 85.40 | 6.90 | 99.00 | [65] |
| Bamboo | ChCl: acetic acid (1:2) | - | 140 °C, 6 h | 80.10 | 7.30 | - | - | 92.70 | [66] |
| Reed straw | BTEAC: FA (1:6) | 1,4-dioxane/water (96:4 v/v) | 130 °C, 3 h | 94.10 | 9.00 | 89.32 | 1.68 | 88.57 | [67] |
| Radiata pine | BTEAC: FA (1:2) | - | 150 °C, 2 h | 87.00 | 7.41 | 82.69 | 6.02 | 88.23 | [68] |
| Corn stover | BTEAC: LA (1:7) | - | 140 °C, 1.5 h | 83.51 | 9.47 | 67.07 | 4.66 | 87.71 | [69] |
| Pine wood powder | ChCl:LA: FA (1:1:1) | - | 130 °C, 6 h | 72.00 | 15.20 | 63.40 | 10.30 | 83.84 | [70] |
| R. glutinis | ChCl: GL: Acetic acid (1:2:1.5) | - | 140 °C, 4 h | 63.76 | 7.29 | 55.6 | 23.91 | 78.00 | [71] |
| Bamboo | GL: GndHCl: FeCl3·6H2O (2:1:0.2,) | Microwave-assisted | 120 °C, 10 min | 81.17 | 11.13 | 74.37 | 6.03 | 90.96 | [72] |
| Poplar | ChCl: EG: 4-CSA (1:2:0.7) | KOH pretreatment | 90 °C, 0.5 h | 97.01 | 1.05 | 93.33 | 4.38 | 95.02 | [6] |
| Pine needles | LA: Oxalic acid: ChCl (4:1:1) | Toluene-ethanol pretreatment | 120 °C, 3 h | 95.80 | - | - | - | - | [73] |
| Corn stover | ChCl: Oxalic acid: EG (1:0.2:2) | Densification pretreatment | 130 °C, 1 h | 75.27 | 7.85 | 59.43 | 11.09 | 88.75 | [74] |
| Wheat straw | ChCl: CA: EG (1:1:2, mol) | - | 100 °C, 12 h | 92.37 | 5.71 | 89.12 | 3.04 | 89.18 | [75] |
| Paddy husks | EG: CA (1:2) | - | 90 °C, 16 h | 52.35 | 15.25 | 44.00 | 17.37 | - | [13] |
| Poplar sawdust | ZnCl2: LA (1:10) | - | 140 °C, 3 h | 97.50 | 2.20 | 92.50 | 2.70 | 93.84 | [76] |
| Canola straw | CTAB: LA: FeCl3 (1:4:0.012) | - | 180 °C, 2 h | 87.40 | 8.70 | 59.40 | 2.10 | 53.89 | [77] |
| Substrate | DES | Condition | Untreated Glucose Yield (%) | DES-Treated Glucose Yield (%) | Increase Rate (100×%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Switchgrass | ChCl: lactic acid 1:2 | Solid loading 1.5 wt%, 20 mg protein/g solid, CTec2:HTec2 = 1:9 (vol%) | 13.61 | 75.0 | 4.51 | [56] |
| Industrial xylose residue | ChCl: monoethanolamine 1:6 | Solid loading, 5 wt%, 10 FPU/g CTec2 | 15.97 | 90.12 | 4.64 | [23] |
| Industrial xylose residue | ChCl: monoethanolamine 1:6 | 10 FPU/g CTec2 | 34.95 | 95.89 | 1.74 | [16] |
| Sugarcane | ChCl: lactic acid 1:2 | Solid loading, 10 wt%, 15 mg protein/g solid, cellulase enzymes NS22257 | 19.74 | 93.99 | 3.76 | [132] |
| Corn stover | FeCl3/ChCl: N-(2-hydroxyethyl) Ethylenediamine 1:4 | Solid loading, 5 wt%, 30 FPU/g CTec2 | 16.54 | 98.6 | 4.96 | [134] |
| Soybean straw | p-TsOH/BTEAC: glycerol 1:12 | Solid loading, 5 wt%, 10 FPU/g, CTec2 | 9.17 | 90.18 | 8.83 | [131] |
| Eucalyptus wood chips | AlCl3/Betaine: lactic acid 1:2 | 30 FPU/g, CTec2 | 13.20 | 96.00 | 6.27 | [133] |
| Substrate | DES | Chemical Bonds | Absorption Peaks (cm−1) | Trend | Affected Component | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moso bamboo | ChCl: zinc acetate = 1:6 | OH/C-H | 3331/2891 | Almost disappeared | Hydrogen bonds | [136] |
| C=O | 1734 | Decreased | Hemicellulose | |||
| Rape straw | ChCl: oxalic acid = 3:1 | CO | 1625 | Significantly reduced | Lignin | [138] |
| CO stretching | 1050 | Reduced | Hemicellulose-cellulose-lignin polymers | |||
| CH or CH2 bending | 896 | Reduced | β-glucoside bond | |||
| Willow | ChCl: lactic acid = 1:10 | CH bending vibration of aliphatic compounds | 1373 | Not present | Carbohydrates | [141] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, Z.; Chong, G.; Guo, H. Deep Eutectic Solvent Pretreatment and Green Separation of Lignocellulose. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7662. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177662
Yao Z, Chong G, Guo H. Deep Eutectic Solvent Pretreatment and Green Separation of Lignocellulose. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(17):7662. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177662
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Zhengyuan, Gunhean Chong, and Haixin Guo. 2024. "Deep Eutectic Solvent Pretreatment and Green Separation of Lignocellulose" Applied Sciences 14, no. 17: 7662. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177662
APA StyleYao, Z., Chong, G., & Guo, H. (2024). Deep Eutectic Solvent Pretreatment and Green Separation of Lignocellulose. Applied Sciences, 14(17), 7662. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177662








