Biodegradation and Detoxification of Some Dyes by Crude Lignin Peroxidase Complex Produced by Escherichia coli Accession No: LR0250096.1 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa Accession No: CP031449.2
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Isolation and Characterization of the Organisms
2.3. Enzyme Production
2.4. Dye Decoloration
2.5. Dye Toxicity in Bacteria Study
2.6. Enzyme Decolorization Kinetics
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Dye Decolorization Study
3.2. Effect of Key Factors on Dye Decolorization
3.2.1. Effect of Enzyme Concentration
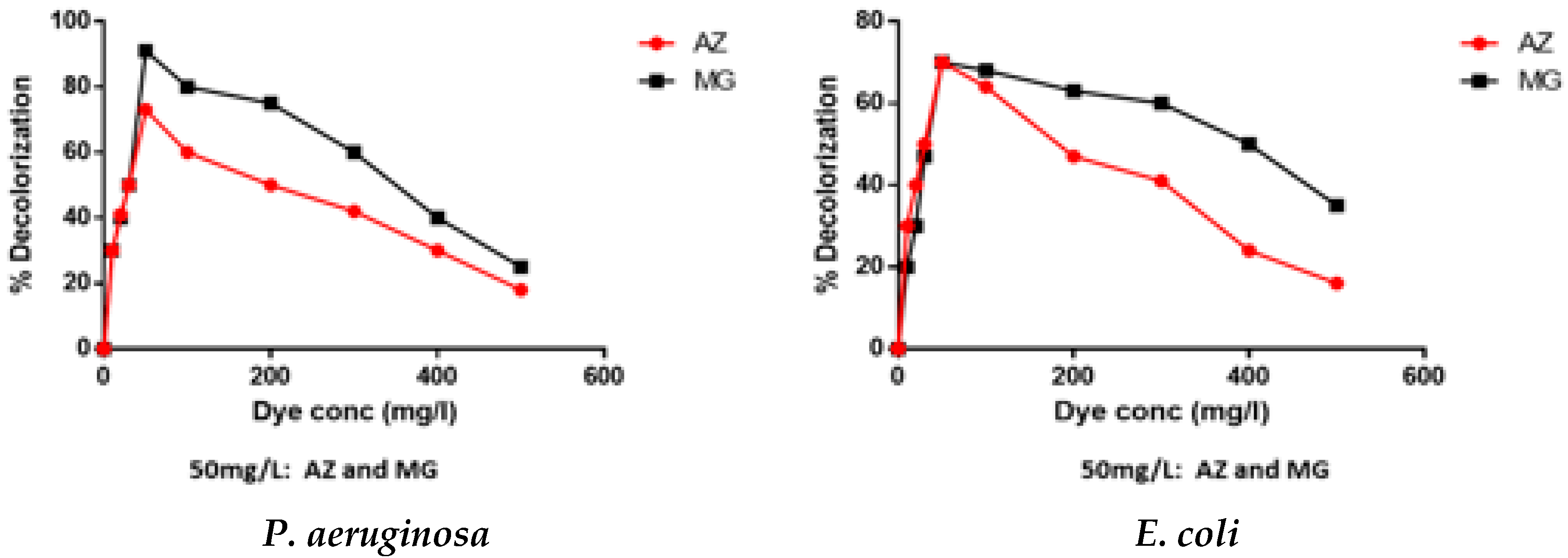
3.2.2. Effect of Dye Concentrations
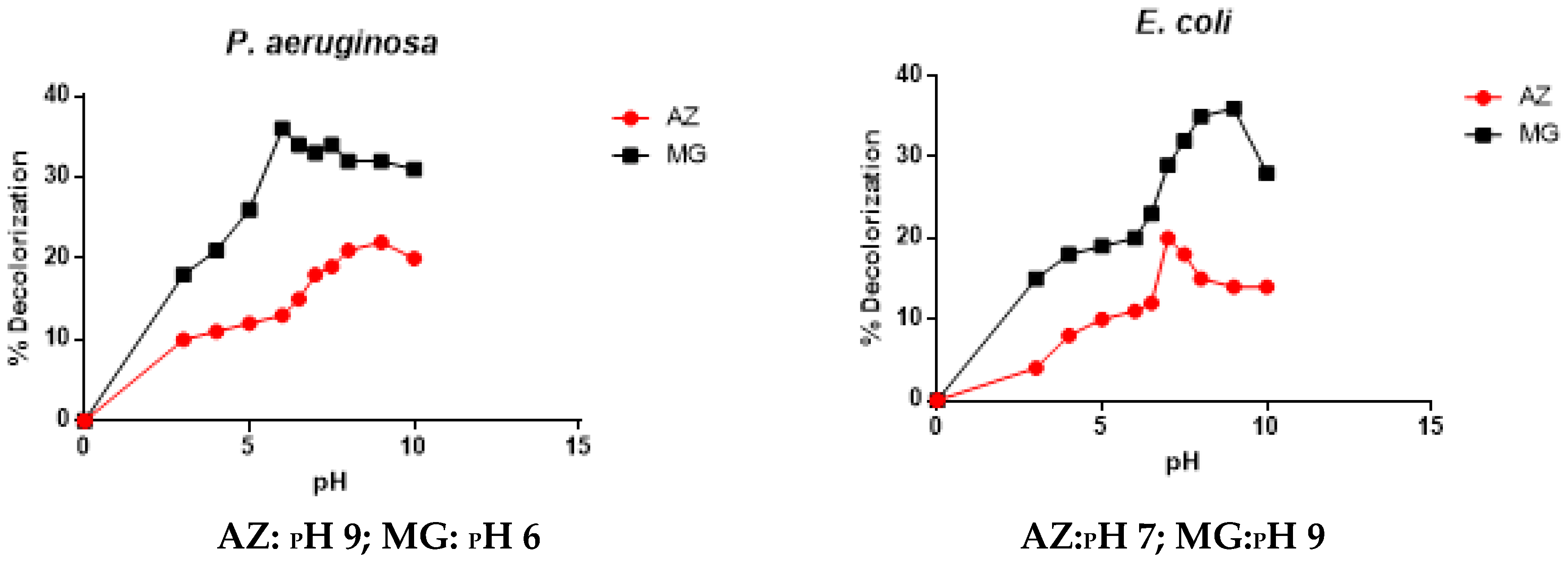
3.2.3. Effect of pH
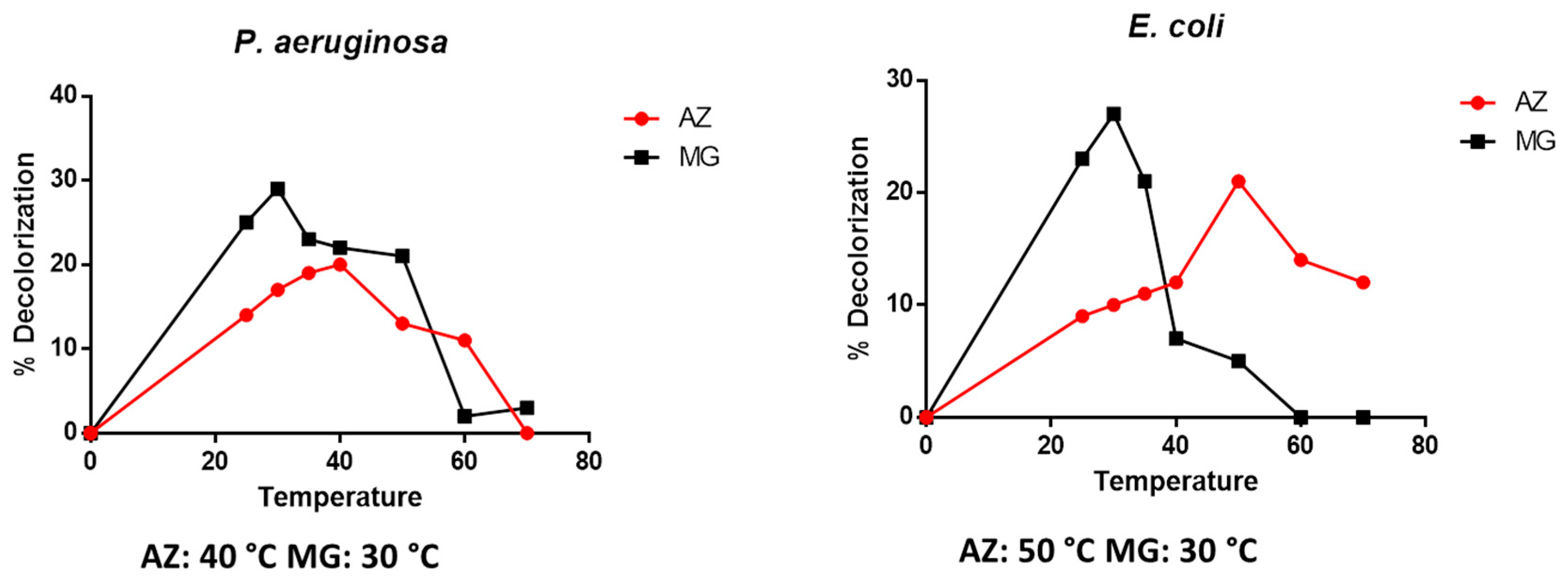
3.2.4. Effect of Temperature
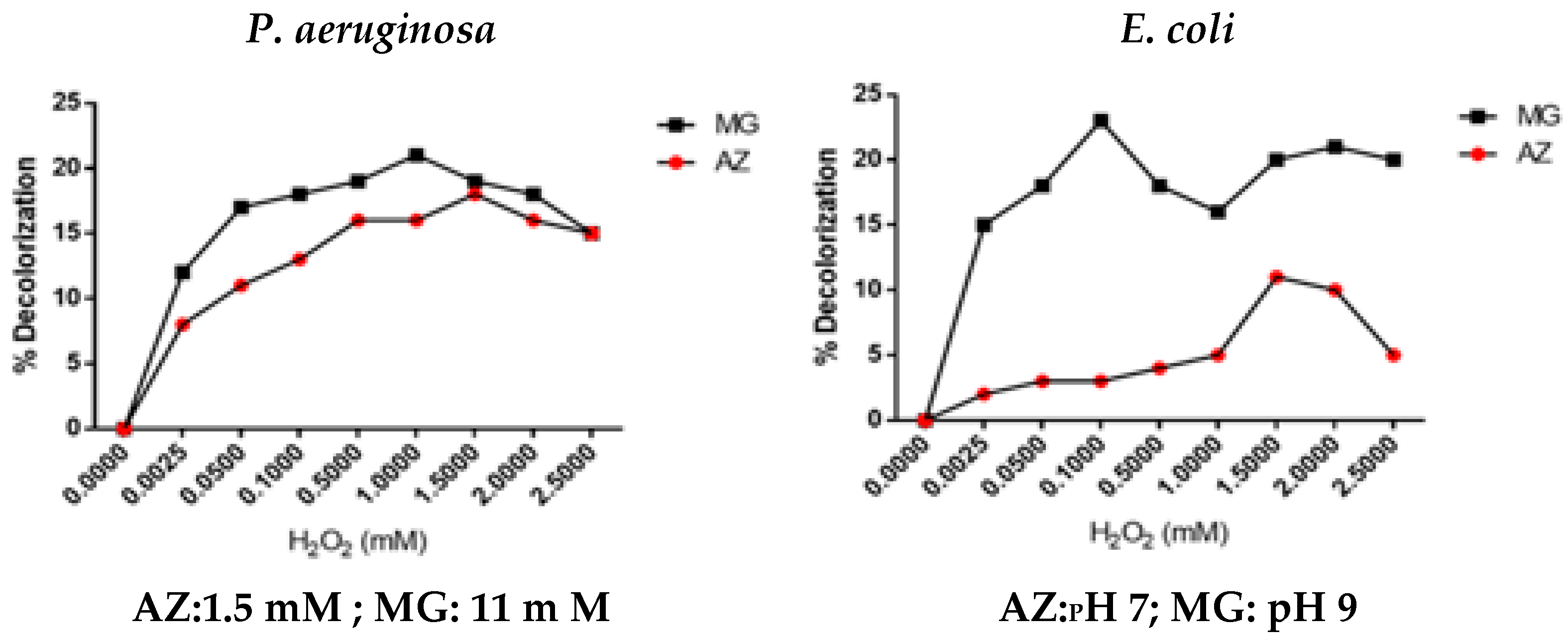
3.2.5. Effect of Substrate (H2O2) Concentration
3.2.6. Effect of Incubating Time
3.2.7. Effect of Inhibitors
3.3. Bacterial Toxicity Test
3.4. Determination of Decolorization Kinetics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tehrani-Bagha, A.R.; Holmberg, K. Solubilization of hydrophobic dyes in surfactant solutions. Mater 2013, 6, 580–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, L.; Papinutti, L.; Forchiassin, F. Evaluation of Argentinean white rot fungi for their ability to produce lignin-modifying enzymes and decolorize industrial dyes. Bioresour. Technol. 2004, 94, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandounas, L.; Wierckx, N.J.; de Winde, J.H.; Ruijssenaars, H.J. Isolation and characterization of novel bacterial strains exhibiting ligninolytic potential. BMC Biotechnol. 2011, 11, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassaan, M.A.; El Nemr, A. Health and environmental impacts of dyes: Mini review. Am. J. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2017, 1, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnif, I.; Fendri, R.; Ghribi, D. Malachite green bioremoval by a newly isolated strain Citrobacter sedlakii RI11; enhancement of the treatment by biosurfactant addition. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 72, 1283–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lellis, B.; Fávaro-Polonio, C.Z.; Pamphile, J.A.; Polonio, J.C. Effects of textile dyes on health and the environment and bioremediation potential of living organisms. BIORI 2019, 3, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, J.; Munoz-Dorado, J.; De la Rubia, T.D.L.R.; Martinez, J. Biodegradation and biological treatments of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin: An overview. Int. Microbiol. 2002, 5, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Cheng, J. Hydrolysis of lignocellulosic materials for ethanol production: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 83, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falade, A.O.; Eyisi, O.A.; Mabinya, L.V.; Nwodo, U.U.; Okoh, A.I. Peroxidase production and ligninolytic potentials of freshwater bacteria Raoultella ornithinolytica and Ensifer adhaerens. Biotechnol. Rep. 2017, 16, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.B.; Wang, B.Q.; Wu, A.G.; Cheng, G.J.; Li, Z.; Dong, S.J. A method to construct a third-generation horseradish peroxidase biosensor; self-assembling gold nanoparticles to three-dimensional sol-gel network. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 2217–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, E.; Hernandez-Ruiz, J.; Arnao, M.B.; Milrand, S.R.; Tigier, H.A.; Acosta, M.A. Peroxidase isoenzyme secreted by turnip (Brassica napus) hairy-root culture inactivation by hydrogen peroxide and application in diagnostic kits. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2002, 35, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyani, D.C.; Phugare, S.S.; Shedbalkar, U.U.; Adhar, J.P. Purification and characterization of a bacterial peroxidase from the isolated strain Pseudomonas sp. SUK1 and its application for textile dye decolourization. Ann. Microbiol. 2011, 61, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draelos, Z.D. A split-face evaluation of a novel pigment-lightening agent compared with no treatment and hydroquinone. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2015, 72, 105–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taboada-Puig, R.; Lu-Chau, T.A.; Eibes, G.; Feijoo, G.; Moreira, M.T.; Lema, J.M. Continuous removal of endocrine disruptors by versatile peroxidase using a two-stage system. Biotechnolo. Prog. 2015, 31, 908–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timothy, C.C.; Lars, B.; Vera, M. Something old, something new: Challenges and developments in Aspergillus niger biotechnology. Essays Biochem. 2012, 65, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schallmey, M.; Singh, A.; Ward, O.P. Developments in the use of Bacillus species for industrial production. Can. J. Microbiol. 2004, 50, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevinc, N.; Demirkan, E. Production of protease by Bacillus sp. N-40 isolated from soil and its enzymatic properties. J. Biol. Environ. Sci. 2011, 5, 95–103. [Google Scholar]
- Barros, F.F.C.; Simiqueli, A.P.R.; de Andrade, C.J.; Pastore, G.M. Production of enzymes from agro industrial wastes by biosurfactant-producing strains of Bacillus subtilis. Biotechnol. Res. Int. 2013, 103960, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, G.; Prakash, A.; Pavani, J.V.P.; Bera, S.; Deviram, G.V.N.S.; Kumar, A.; Panchpuri, M.; Prasuna, R.G. Production, optimization and partial purification of protease from Bacillus subtilis. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2015, 9, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, M.M.C.N.; Da Silva, R.; Carmona, E.C.; Gomes, E. Pectinolytic enzyme production by Bacillus species and their potential application on juice extraction. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2001, 17, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, P.V.S.; Ramos, K.O.; Padilha, I.Q.M.; Araújo, D.A.M.; Santos, S.F.M.; Silva, F.L.H. Optimization of cellulase production by Bacillus sp. isolated from sugarcane cultivated soil. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2014, 38, 227–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilha, I.Q.M.; Carvalho, L.C.T.; Dias, P.V.S.; Grisi, T.C.S.L.; Honorato, D.A.; Silva, F.L.S.; Santos, F.M.; Araújo, D.A.M. Production and characterization of thermophilic carboxymethyl cellulase synthesized by Bacillus sp. growing on sugarcane bagasse in submerged fermentation. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 32, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janusz, G.; Pawlik, A.; Sulej, J.; Świderska-Burek, U.; Jarosz-Wilkołazka, A.; Paszczyński, A. Lignin degradation: Microorganisms, enzymes involved, genomes analysis and evolution. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 941–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.W. 2009. Structure and action mechanism of ligninolytic enzymes. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2009, 157, 174–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhary, P.A.N.K.A.J.; Saxena, G.A.U.R.A.V.; Bharagava, R.N. Role of Laccase Enzyme in Bioremediation of Industrial Wastes and Its Biotechnological Application. Bioremediation of Industrial Pollutants; Write and Print Publication: Delhi, India, 2016; pp. 307–331. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, S.R. Production and purification of lignin peroxidase from Bacillus megaterium and its application in bioremediation. CIB Technol. J. Microbiol. 2014, 3, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube, S.L.; Osunsanmi, F.O.; Ngcobo, B.P.; Mkhwanazi, L.B.; Jobe, Z.Z.; Aruleba, R.T.; Mosa, R.A.; Opoku, A.R. Isolation and Characterization of Potential Lignin Peroxidase-Producing Bacteria from Compost Samples at Richards Bay (South Africa). Pol. J. Microbiol. 2023, 72, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmedi, A.; Abouseoud, M.; Couvert, A.; Amrane, A. Enzymatic degradation of Congo Red by turnip (Brassica rapa) peroxidase. Z. Naturforsch C 2012, 67, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, S.A.; Prasada Rao, U.J. Purification and characterization of peroxidase from sprouted green gram (Vigna radiata) roots and removal of phenol and p-chlorophenol by immobilized peroxidase. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 3249–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daâssi, D.; Zouari-Mechichi, H.; Frikha, F.; Martinez, M.J.; Nasri, M.; Mechichi, T. Decolorization of the Azo Dye Acid Orange 51 by Laccase Produced in Solid Culture of a Newly Isolated Trametestrogii Strain. 3 Biotech 2013, 3, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalnunhlimi, S.; Krishnaswamy, V. Decolorization of azo dyes (Direct Blue 151 and Direct Red 31) by moderately alkaliphilic bacterial consortium. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2016, 47, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, D.C.; Biswas, S.K.; Saha, A.K.; Sikdar, B.; Rahman, M.; Roy, A.R.; Prodhan, Z.H.; Tang, S.S. Biodegradation of crystal violet dye by bacteria isolated from textile industry effluents. PeerJ 2018, 6, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, H.; Dutta, A. The microbial aspect of climate change. Energ. Ecol. Environ. 2016, 1, 209–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, P.K. Enzymes: Principles and biotechnology applications. Essays Biochem. 2015, 59, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.S.; Mostafa, M.K.; Mohamed, S.A.; Sobhy, N.A.; Nasr, M. Bioremediation of red azo dye from aqueous solution by Aspergillus niger strain isolated from textile wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falade, A.; Jaouani, A.; Mabinya, L.; Okoh, A.; Nwodo, U. Exoproduction and molecular characterization of peroxidase from Ensiferadhaerens. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, R.; Kelkar, A.; Baraniya, D.; Molaei, A.; Moulick, A.; Meena, R.S.; Formanek, P. Enzymatic degradation of lignin in soil: A review. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorjup, B.; Lampič, N.; Penca, R.; Perdih, A.; Perdih, M. Solvent effects on ligninases. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 1999, 25, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Huang, X.; Song, S.; Wang, D.; Lu, X.; Qu, Y.; Gao, P. Kinetics of the H2O2-dependent ligninase-catalyzed oxidation of veratryl alcohol in the presence of cationic surfactant studied by spectrophotometric technique. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2003, 59, 2547–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Cassia Pereira, J.; Giese, E.C.; de Souza Moretti, M.M.; dos Santos Gomes, A.C.; Perrone, O.M.; Boscolo, M.; da Silva, R.; Gomes, E.; Martins, D.A.B. Effect of metal ions, chemical agents and organic compounds on lignocellulolytic enzymes activities. In Enzyme Inhibitors and Activators; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017; pp. 139–164. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, G.; Tian, F.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, M.; Liu, W.; Liu, C.; Xue, S.; Kong, W.; Sun, Y.; Wang, S. Aerobic decolorization and detoxificationof acid scarlet GR by a newly isolated salt-tolerant yeast strain Galactomyces geotrichum GG. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2019, 145, 104818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Chang, C.F.; Liu, S.M. Partial degradation mechanisms of malachite green and methyl violet B by Shewanella decolorationis NTOU1 under anaerobic conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gokulakrishnan, S.; Parakh, P.; Prakash, H. Degradation of Malachite green by Potassium persulphate, its enhancement by 1, 8-dimethyl-1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 13-hexaazacyclotetradecane nickel (II) perchlorate complex, and removal of antibacterial activity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 213, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Zheng, J.; Lu, Y.; Jia, R. Degradation and detoxification of the triphenylmethane dye malachite green catalyzed by crude manganese peroxidase from Irpexlacteus F17. ESPR 2016, 23, 9585–9597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
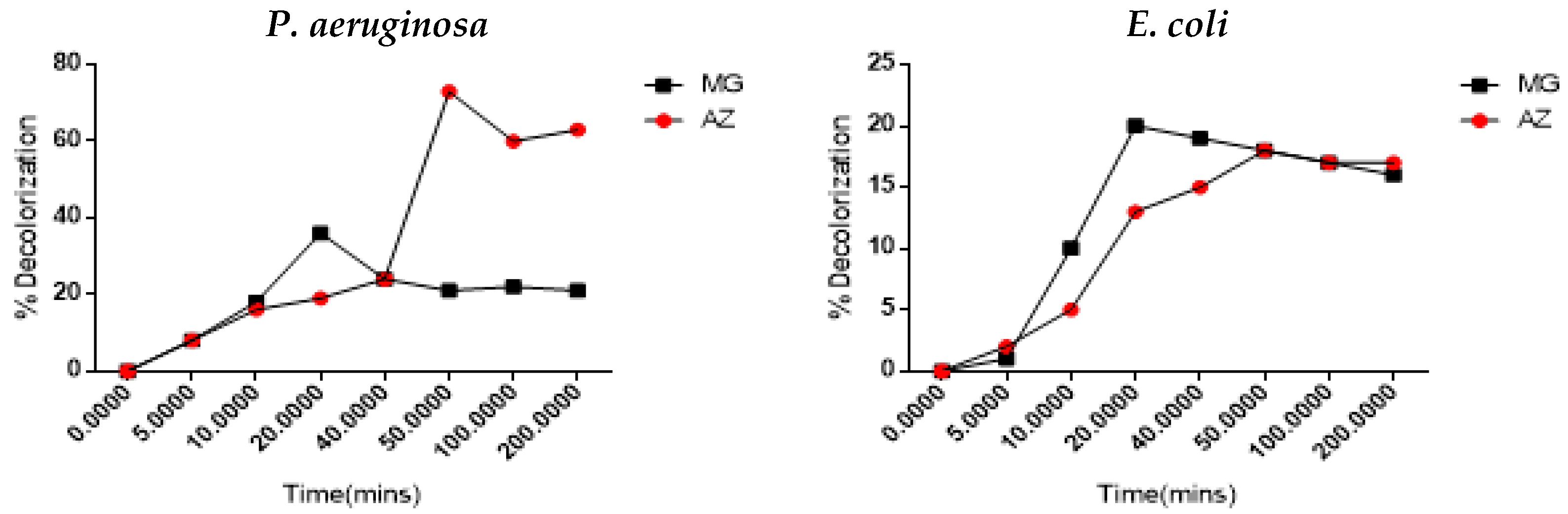
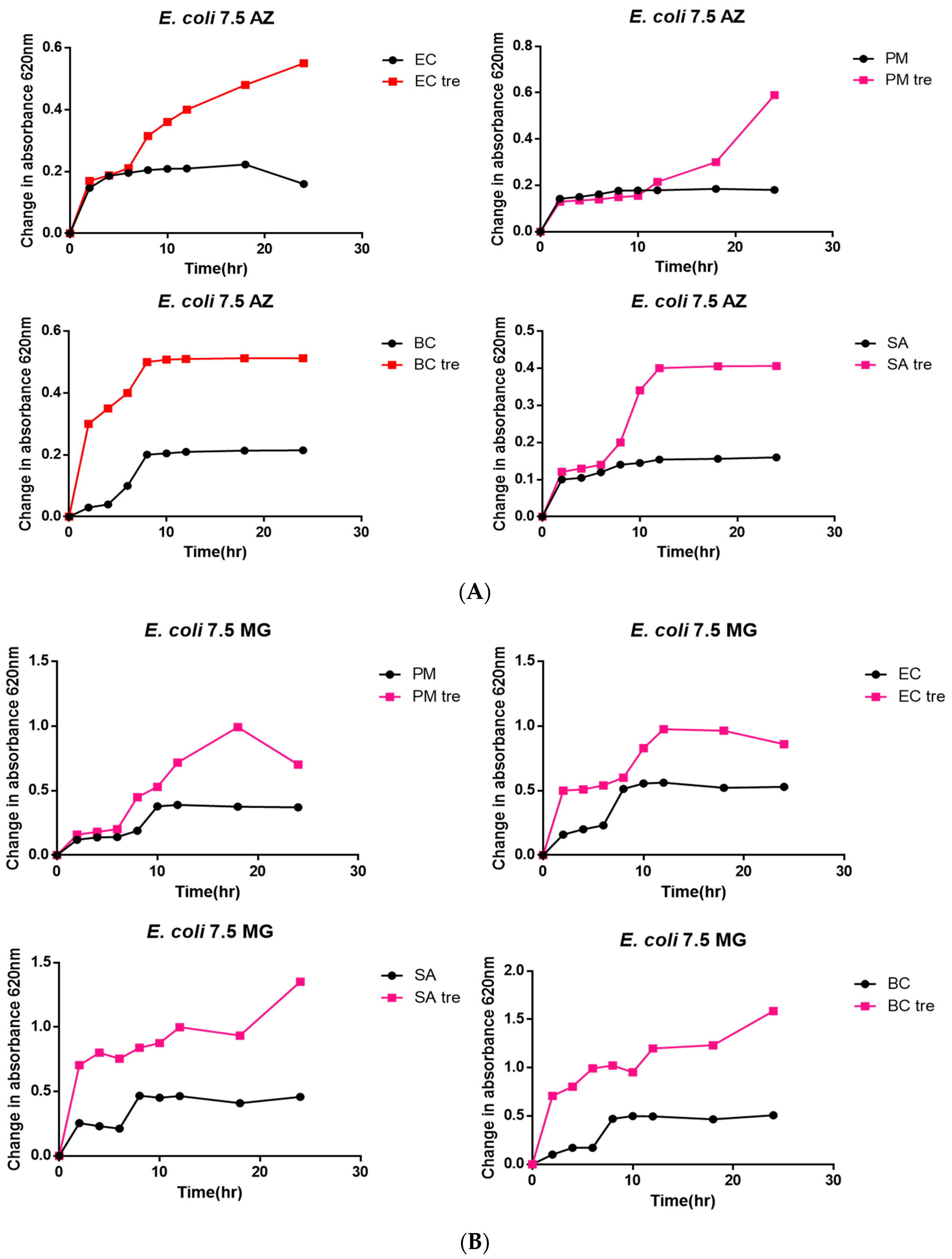

| Dyes | Crude Enzyme from Escherichia coli | Crude Enzyme from Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Commercial Lignin Peroxidase |
|---|---|---|---|
| AZ | 63 ± 1.34 a | 56 ± 2.11 b | 72 ± 1.45 c |
| RBBR | 11 ± 1.12 a | 6 ± 1.78 b | 0 ± 0.13 c |
| CR | 8 ± 0.45 a | 3 ± 1.88 b | 0 ± 1.77 c |
| MG | 53 ± 1.44 a | 52 ± 2.06 a | 80 ± 1.33 c |
| Enzyme Concentrations (mg/mL) | AZ (% Dye Decolorization) E. coli | MG (% Dye Decolorization) E. coli | AZ (% Dye Decolorization) P. aeruginosa | MG (% Dye Decolorization) P. aeruginosa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.5 ± 1.22 a | 9 ± 1.11 f | 2 ± 2.66 i | 6 ± 1.56 a |
| 5 | 20 ± 0.39 b | 11 ± 2.23 f | 9.3 ± 3.56 f | 24 ± 2.12 j |
| 10 | 32 ± 2.14 c | 35 ± 3.12 c | 31 ± 1.44 c | 43 ± 2.88 k |
| 20 | 68 ± 1.88 d | 55 ± 1.78 g | 52 ± 2.11 h | 55 ± 1.66 g |
| 40 | 60 ± 2.03 e | 55 ± 1.48 g | 51 ± 3.99 h | 55 ± 2.33 g |
| 50 | 62 ± 3.11 e | 52 ± 2.74 h | 50 ± 3.22 h | 53 ± 2.71 h |
| 100 | 62 ± 2.99 e | 50 ± 1.32 h | 50 ± 0.47 h | 54 ± 2.31 g |
| % Inhibition of E. coli (AZ) | % Inhibition of E. coli (MG) | % Inhibition of P. aeruginosa (AZ) | % Inhibition of P. aeruginosa (MG) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mM NaN3 | 83 ± 1.34 a | 68 ± 2.76 b | 71 ± 3.86 b | 63 ± 2.76 c |
| 1 mM EDTA | 67 ± 3.21 b | 68 ± 3.36 b | 75 ± 2.73 d | 79 ± 3.22 a |
| 1 mM FeCl3 | 60 ± 4.23 c | 67 ± 3.29 b | 55 ± 2.06 e | 58 ± 4.22 e |
| Enzyme Kinetics | E. coli (LiP Extract) | P. aeruginosa (LiP Extract) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AZ | MG | AZ | MG | |
| Vmax (µmol m−3 s−1) | 1.4 ± 1.23 × 104 | 3.0 ± 2.23 × 103 | 1.5± 0.33 × 104 | 1.0 ± 2.11 × 104 |
| Km (µmol/L) | 6.7 ± 0.82 × 104 | 8 ± 1.42 × 103 | 7 ± 2.11 × 104 | 3.5 ± 0.32 × 104 |
| kcat (s−1) | 6.6 ± 1.93 × 102 | 1.4 ± 0.27 × 102 | 7.9 ± 0.77 × 102 | 5.3 ± 0.11 × 102 |
| Catalytic efficiency = kcat/ Km(µmol−1 s−1) | 9.9 ± 1.44 × 101 | 1.8 ± 0.22 × 101 | 1.1± 0.09 × 101 | 1.5 ± 0.07 × 101 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dube, S.L.; Osunsanmi, F.O.; Ikhane, A.O.; Mosa, R.A.; Opoku, A.R. Biodegradation and Detoxification of Some Dyes by Crude Lignin Peroxidase Complex Produced by Escherichia coli Accession No: LR0250096.1 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa Accession No: CP031449.2. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 8012. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14178012
Dube SL, Osunsanmi FO, Ikhane AO, Mosa RA, Opoku AR. Biodegradation and Detoxification of Some Dyes by Crude Lignin Peroxidase Complex Produced by Escherichia coli Accession No: LR0250096.1 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa Accession No: CP031449.2. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(17):8012. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14178012
Chicago/Turabian StyleDube, Sindiswa Lungile, Foluso Oluwagbemiga Osunsanmi, Albert Olufemi Ikhane, Rebamang Anthony Mosa, and Andrew Rowland Opoku. 2024. "Biodegradation and Detoxification of Some Dyes by Crude Lignin Peroxidase Complex Produced by Escherichia coli Accession No: LR0250096.1 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa Accession No: CP031449.2" Applied Sciences 14, no. 17: 8012. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14178012
APA StyleDube, S. L., Osunsanmi, F. O., Ikhane, A. O., Mosa, R. A., & Opoku, A. R. (2024). Biodegradation and Detoxification of Some Dyes by Crude Lignin Peroxidase Complex Produced by Escherichia coli Accession No: LR0250096.1 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa Accession No: CP031449.2. Applied Sciences, 14(17), 8012. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14178012






