Abstract
Geological anomalies within the working face likely induce geological disasters, such as water, gas, and coal mine roof fall, directly impacting the rational planning and safe mining of underground resources. Constrained by the conditions of underground closed spaces, effective reconstruction under incomplete and highly sparse projection is the central challenge when evaluating geo-environmental conditions. This work proposes a new hybrid intelligent optimization model (MPGA-SIRT) that integrates a multiple-population genetic algorithm (MPGA) with the simultaneous iterative reconstruction technique (SIRT) to finely reconstruct the geo-environmental conditions within a working face based on electromagnetic wave tomography theory. MPGA-SIRT can provide a more precise initial inversion model for the conventional linear reconstruction technique of SIRT, incorporating a local search property by leveraging the robust global search capacity of MPGA. The advantages of MPGA-SIRT have been demonstrated through numerical modeling, theoretical testing, and engineering practices on the 8208 working face in the Datong mining area, Shanxi Province. In comparison to individual SIRT inversion models, MPGA-SIRT reconstruction yields more accurate and stable performance, as demonstrated by the evolution curve of the objective function and the corresponding convergence tomography results. Consequently, the geomagnetic wave absorption coefficient within the area of reconstruction can be precisely ascertained through the use of our proposed technique. This innovation represents a groundbreaking strategy for assessing geological anomaly zones within a working face. The introduced method stands as a valuable theoretical instrument for confronting the complexities associated with geo-environmental reconstruction in underground engineering.
1. Introduction
Being one of the primary fossil energy sources, coal has long held significant strategic value globally [1]. China has abundant coal resources with a large distribution range; however, the occurrence conditions of coal resources are complex and vary greatly. There are many folds and faults within coal seams, and the geological structures are complex and changeable. The thickness of coal seams varies from very thin coal seams to thick and extra-thick coal seams, from near horizontal coal seams, and gently inclined coal seams to sharply inclined coal seams. Statistics indicate that 33.09% of China’s medium and large coal mines face complex and extremely complex coal seam conditions, with only 23.09% categorized as simple mines. Within this, complex and extremely complex mines constitute 25.04% of large- and medium-sized coal mines, while simple ones make up 39.49%. Geological anomalies, including fractures, pores, folds, and faults within the working face, significantly impact underground mining [2].
With increasing mining depth, geo-environmental conditions become increasingly complex. From the perspective of safety, geological structures easily evolve into water channels, and mine water can inrush into the working space when the stress structure is destroyed, posing a serious threat to life and property [3]. At the same time, abnormal geo-environmental sites are also some of the main gas enrichment areas, and gas accidents often occur when gas-rich faults are exposed by mistake [4]. The development of geological structures and drastic changes in coal thickness not only cause technical problems for resource recovery but also mean that coal resources cannot be maximized. At the same time, it is increasingly difficult to accurately formulate technical measures and programs for possible safety problems. Therefore, meticulous descriptions of the geological environment within a coal seam can effectively reduce waste in coal mining [5,6,7], which is also a key issue that needs to be solved when constructing intelligent mines [8,9].
2. Geo-Environmental Condition Evaluation Methods
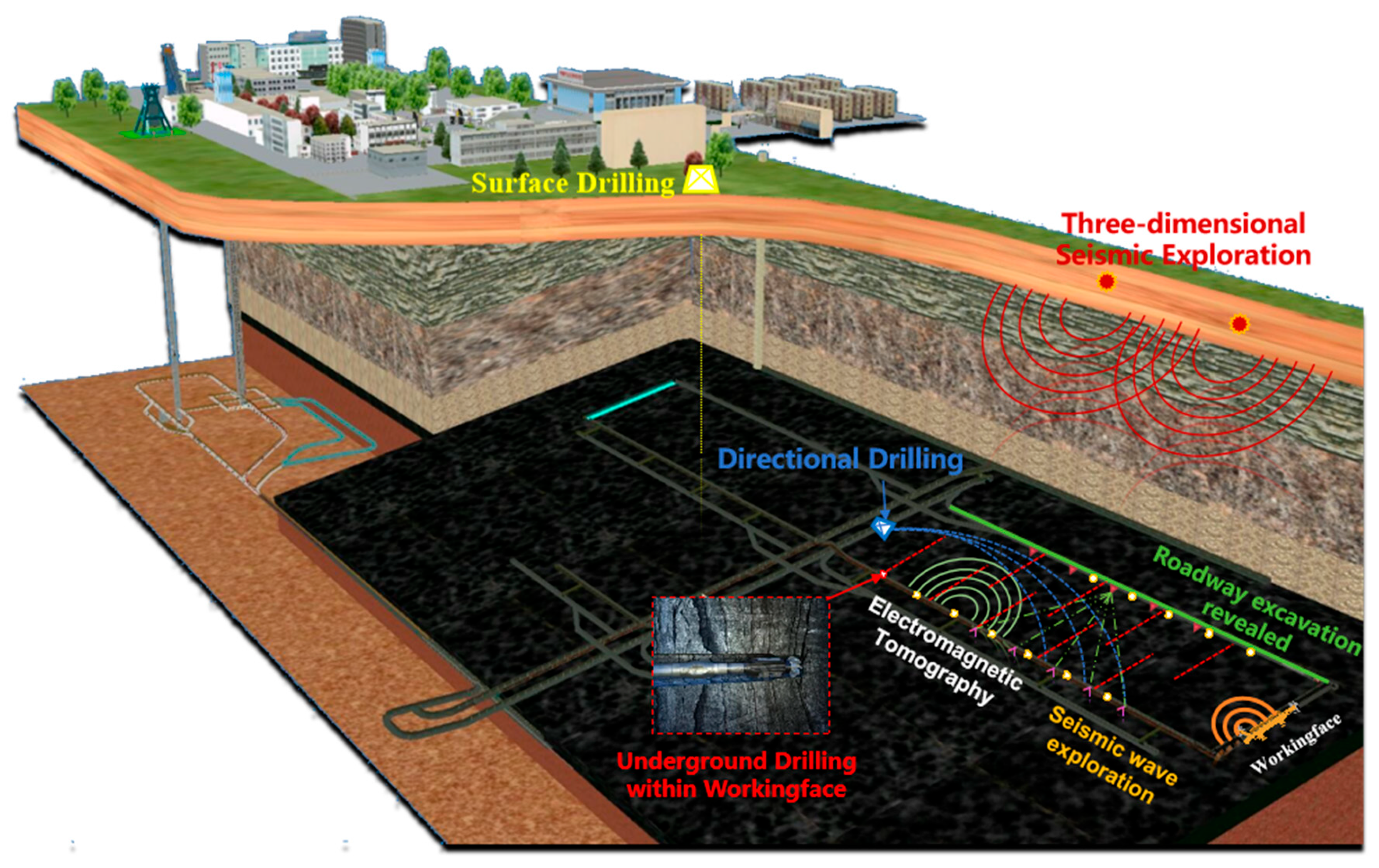
To minimize resource waste and safeguard the environment, precise mining of the underground resource is crucial, which requires fine reconstruction of the occurrence state of underground resources. At present, exploration technologies mainly based on geological analysis, drilling, geophysical exploration, geochemical exploration, and remote sensing provide foundational data for safe, efficient, and intelligent mining of coal mines in China, as shown in Figure 1.
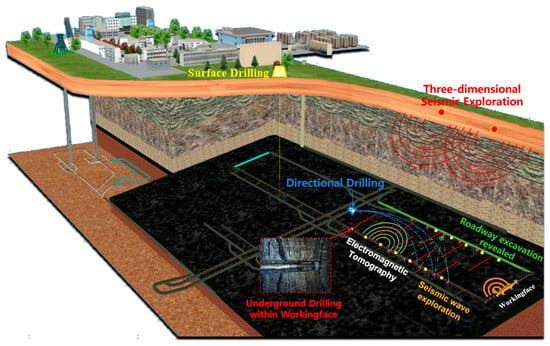
Figure 1.
The exploratory technology used to assess geo-environmental conditions within a working face.
Conventionally, the resolution of geological analysis has been largely contingent upon the thoroughness and precision of geological data [10]. The results obtained when drilling have the characteristics of being direct and true; however, such results come at the cost of higher time and economic cost, which is accompanied by the potential risk of blind zone detection [11]. In contrast, as one of the methods used in geophysical exploration, electromagnetic tomography (EMT) is widely applied due to its economic advantages and rapidness; it is also a non-destructive technique when implemented [12]. Due to the significant differences in the absorption abilities of various media to electromagnetic waves, abnormal areas within a working face can be imaged. However, unlike in the medical industry, where electromagnetic waves can cover the human body with a 360-degree field of view, coal mine working faces are often narrow and rectangular, with roofs and floors covered by rock layers, making it difficult to arrange the transmitting source and the receiving device [13]. As a result, the obtained projection data are insufficient and incomplete in terms of precisely reconstructing geological environments within the detection areas of working faces, which is considered to be the burning issue in intelligent mines that are under development [14].
As an indispensable technology in the coal mine industry, electromagnetic tomography (EMT) was developed from the theoretical basis of tomography known as the Radon transform, which was put forward by Radon in 1917 [15]. Limited by the shape of coal mine working faces and observation systems, the target matrix equation to be inversed by EMT does not always contain the full rank of the column, resulting in infinite solutions [16]. The most classical solutions to the matrix equation are the algebra reconstruction algorithm (ART) proposed by R. Gordon [17] and the simultaneous iterative reconstruction technique (SIRT) algorithm proposed by P. Gilbert [18] and their optimization algorithms. Subsequently, many scholars stated that the regularization method could be used in the tomographic inversion of a working surface [19]. However, the majority of these widely used tomographic inversion methods start with a single initial model and repeatedly approach the improved adjacent solution set until the final solution is obtained and the permitted requirements are satisfied [20]. As a result, the initial model choice has a significant impact on the inversion results. If the initial model is poorly chosen, the objective function is vulnerable to local optimal solutions, which could have a negative impact on the stability and accuracy of the reconstruction of the geological environment in working faces. Currently, utilizing EMT technology to provide a more accurate, stable, and reliable initial model for the traditional tomographic inversion algorithm has become the core in the related field [21,22], which is also the focus of this research.
Since 1949, intelligent algorithms that emulate the principles of survival and evolutionary dynamics in nature have been gradually developed, such as the Monte-Carlo method [23], BP neural network [24], single genetic algorithm (SGA) [25], and particle swarm optimization algorithm [26]. Because these heuristic evolutionary algorithms have strong global search capabilities and evolutionary search mechanisms, they are less dependent on the initial model and offer fresh perspectives on the solutions to challenging multi-dimensional issues [27].
Therefore, this research aims to leverage the global search capabilities inherent to intelligent optimization algorithms to furnish the initial model for electromagnetic wave computed tomographic inversion of a working face. This will be coupled with the traditional linear iterative algorithm, which is known for its robust local search ability, to create a hybrid intelligent optimization reconstruction algorithm tailored for incomplete projection conditions. The proposed hybrid algorithm in this research has the potential to enhance the accuracy of predicting unknown geological environments within a working face, offering essential data support for the intelligent and precise mining of coal mines. Additionally, it introduces new methods for the precise exploration of enclosed underground spaces.
3. Theoretical Analysis and Model Construction
3.1. Mathematical Model of Electromagnetic Wave CT Reconstruction
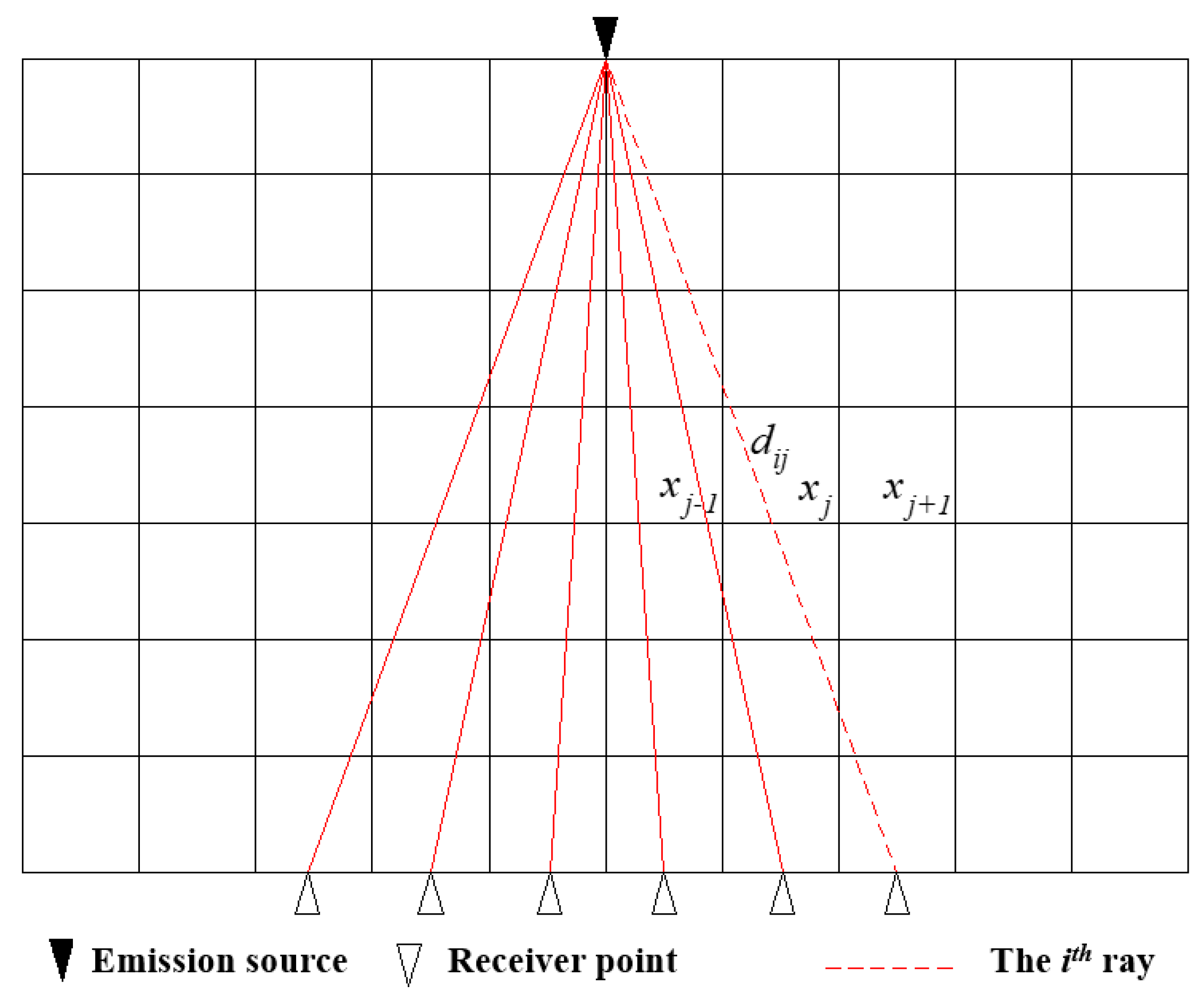
In the tomographic inversion and reconstruction calculation processes of coal mine working faces using electromagnetic tomography technology, the target detection area is discretized and divided into hypothetical B grids, as shown in Figure 2. Each grid is called a pixel, and xj represents the true absorption coefficient of the jth grid, j = 1, 2, 3… B.
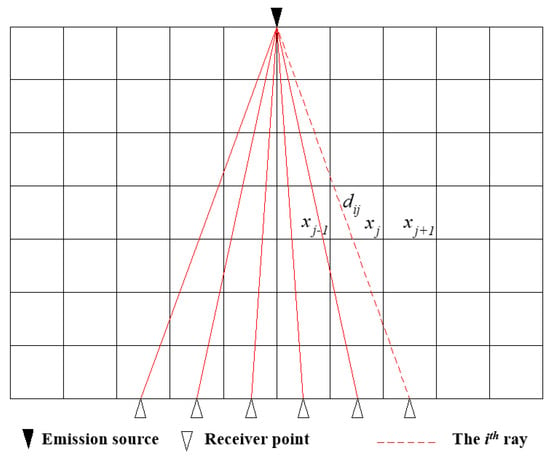
Figure 2.
The schematic diagram of mesh discretization for electromagnetic wave tomography.
Assuming that the ith ray passes through the detection area from the transmitting end to the receiving end, the intercept of the ray in the jth grid is dij. If the number of rays is set to A, the attenuation yi of the electromagnetic wave on the ith ray path can be expressed as follows:
The electromagnetic waves in the detection process were generated at multiple emission points. Further, each emission point corresponds to multiple receiving points to collect data concerning the generated electromagnetic waves. Therefore, Equation (1) can be further extended to the following:
that is
In the above formula, refers to the A × B coefficient matrix and represents the intercept of each ray passing through each grid, where the number of rays is A and the number of grids is B.
is the (A × 1) constant matrix, and the constant is related to the measured field strength under each observation method. The attenuation amount yi can be calculated from the field-measured data as follows:
In the above formula, H0 is the original field strength emitted at the signal source, Hi represents electromagnetic wave field strength data for the ith ray, and ri represents the length of the ith ray.
is the (B × 1) geomagnetic wave absorption unknown coefficient matrix, representing the electromagnetic wave absorption coefficient of each pixel, which is the target value to be reconstructed by inversion. Specifically, the absorption coefficient of each pixel needs to be obtained, and the image generated by numerical fitting will directly show the geological environment in the working face.
Due to the limitation of the underground enclosed space conditions, the number of rays A that can be collected around the working face is far less than the number of grids B. Therefore, the solution of the matrix Equation (2) under incomplete and highly sparse projection conditions is the core of this work.
3.2. Reconstruction Model of Hybrid Intelligent Optimization Algorithm
3.2.1. Reconstruction Objectives of Geo-Environmental Conditions
With the rapid development of artificial intelligence and interdisciplinary collaboration, some advanced intelligent algorithms have been successfully applied in various industries [28,29,30,31,32]. Since 1985, these algorithms have been applied to geophysical inversion, especially in seismic inversion [33]. Subsequently, they were used in magnetotelluric inversion. However, there are not many studies and applications involving the use of intelligent algorithms in the electromagnetic wave tomographic inversion of working faces. The introduction of electromagnetic wave CT technology into the reconstruction and prediction of geological environments in working faces will overcome the conventional inversion algorithm’s strong dependence on the single initial model and its theoretical local optimal solution problem.
Intelligent algorithms are garnering increasing interest due to their capability for random nonlinear optimization [34], which reduces the dependence of their results on the initial model. This research converts the matrix problem in Formulas (1)–(4) into a functional extremum problem in order to incorporate intelligent algorithms into the electromagnetic wave CT reconstruction of the working face. The approximate solution of the matrix equation is then obtained when the objective function reaches the extreme value in the intelligent algorithm, which is then used as the initial solution of the conventional linear reconstruction model.
The objective function is often defined as the gap between the observed data and the theoretical data. In the calculation of electromagnetic wave tomographic inversion, the measured field strength was first obtained from the receiving equipment, and then the measured loss of electromagnetic wave field strength during propagation could be derived according to Equation (4). In addition, the absorption coefficient value of the medium in the detection range within a certain range is randomly assigned, and then the theoretical loss value of the field strength of electromagnetic waves in the propagation process is calculated according to Equation (1). Finally, the theoretical values of the absorption coefficients of each grid are repeatedly updated by the intelligent algorithm until the difference between the measured and theoretical values of field strength loss reaches a minimum, i.e., when the stopping condition is satisfied, the value of absorption coefficient of each grid at the current moment can be output. The specific objective function is defined as shown in Equation (5) below:
where is the vector of absorption coefficients to be inverted.
Therefore, the geological anomaly stratigraphic inversion model can be defined as follows: find such that
where is the value of the absorption coefficient obtained for each grid corresponding to the inversion when the objective function is minimized. lb and ub are the upper and lower limits of the variation of the variables, respectively.
3.2.2. Options of the Hybrid Intelligent Algorithms
To solve the extreme value of the objective function, the Monte-Carlo method converges toward the local optimal solution when the number of samples is relatively small and lacks practicality, especially when the dimensionality of the solution parameters is large [35]. Neural network algorithms are also found to be limited in their ability to solve multi-covariate optimization problems. With efficient, parallel, and global search capabilities, the SGA intelligent algorithm is able to adjust the evolutionary direction autonomously through the previously accumulated evolutionary knowledge in the search process until the permissive conditions are satisfied [36] and the optimal solution of the objective function can thus be found. The genetic algorithm is a practical, efficient, and robust optimization technology [37]. Due to the open nature of its algorithm, it has good improvement potential and has thus developed very rapidly into a widely used intelligent search algorithm for optimization. Currently, it is a research hotspot at home and abroad [38].
As a global optimization stochastic search algorithm, the SGA intelligent algorithm’s search performance is mainly determined by the crossover operator and variational operator with a probabilistic nature. During the evolution of an SGA search, the performance of the core genetic operation depends mainly on the crossover probability Pc and the variation probability Pm. Since the final search result of SGA is sensitive to Pc and Pm, different values will bring different evolutionary results [25].
The choice of genetic parameters is particularly important because an SGA often uses a single fixed genetic parameter. Experts across various sectors have introduced distinct methodologies for determining genetic parameters when employing genetic algorithms to address a range of problems. So far, there is still no uniform rule for parameter selection; therefore, a large number of tests are often required to select the optimal result when faced with a new problem, which is time-consuming and cannot obtain globally optimal results. Therefore, immature convergence (also called “premature”) in a genetic algorithm has become a nonnegligible problem [39].
In order to solve the aforementioned problem relating to the SGA, this research introduces a multiple-population genetic algorithm (MPGA) to improve the SGA using a multiple-population coevolution strategy. In SGA evolutionary search, crossover and variation operators are the core means of new individual generation, playing an important role in influencing the SGA’s global and local search performance. Usually, larger crossover probability Pc and smaller variation probability Pm tend to be used in SGA applications. However, it is still confronted with a wide range of selections in terms of genetic parameters, and different values yield different evolutionary results. The MPGA improves SGA by enabling multiple-population collaborative evolutionary searches with different genetic parameters. It ameliorates the population’s performance in terms of both global searches and local searches.
During the evolution of the MPGA, each population is relatively independent of each other and transmits information mainly through the migration operator. The migration operator exchanges high-quality information between multiple populations with the rule that the highest-quality individual in the current population (i.e., the individual with the highest fitness value) replaces the worst-quality individual in the target population (i.e., the individual with the lowest fitness value).
Traditional linear reconstruction algorithms for the electromagnetic wave CT reconstruction of working faces include back projection (BP), the conjugate gradient method (CG), and the least square method (LSQR) for solving the inverse matrix, algebraic iteration (ART), instantaneous iteration method (SIRT), etc. [40]. Because of SIRT’s fitness for sparse, irregular, and low signal-to-noise ratio measured data, as well as its robust operational performance, it is widely used to solve matrix equations with pathological characteristics obtained under incomplete projection conditions in underground engineering [41].
Therefore, this research firstly applied the MPGA to solve the global optimization problem of the target function when it reached the minimal value in electromagnetic wave CT reconstruction of the working face, and then used the obtained optimal solution as the initial model for further iterations of the traditional linear reconstruction algorithm, SIRT, to form a hybrid intelligent algorithm model: MPGA-SIRT. Finally, the EM wave absorption coefficient distribution in the working face exploration area was obtained. Due to the fact that the results are closer to reality, this hybrid intelligent algorithm can provide a basis for the accurate prediction of the geological environments of coal mine working faces.
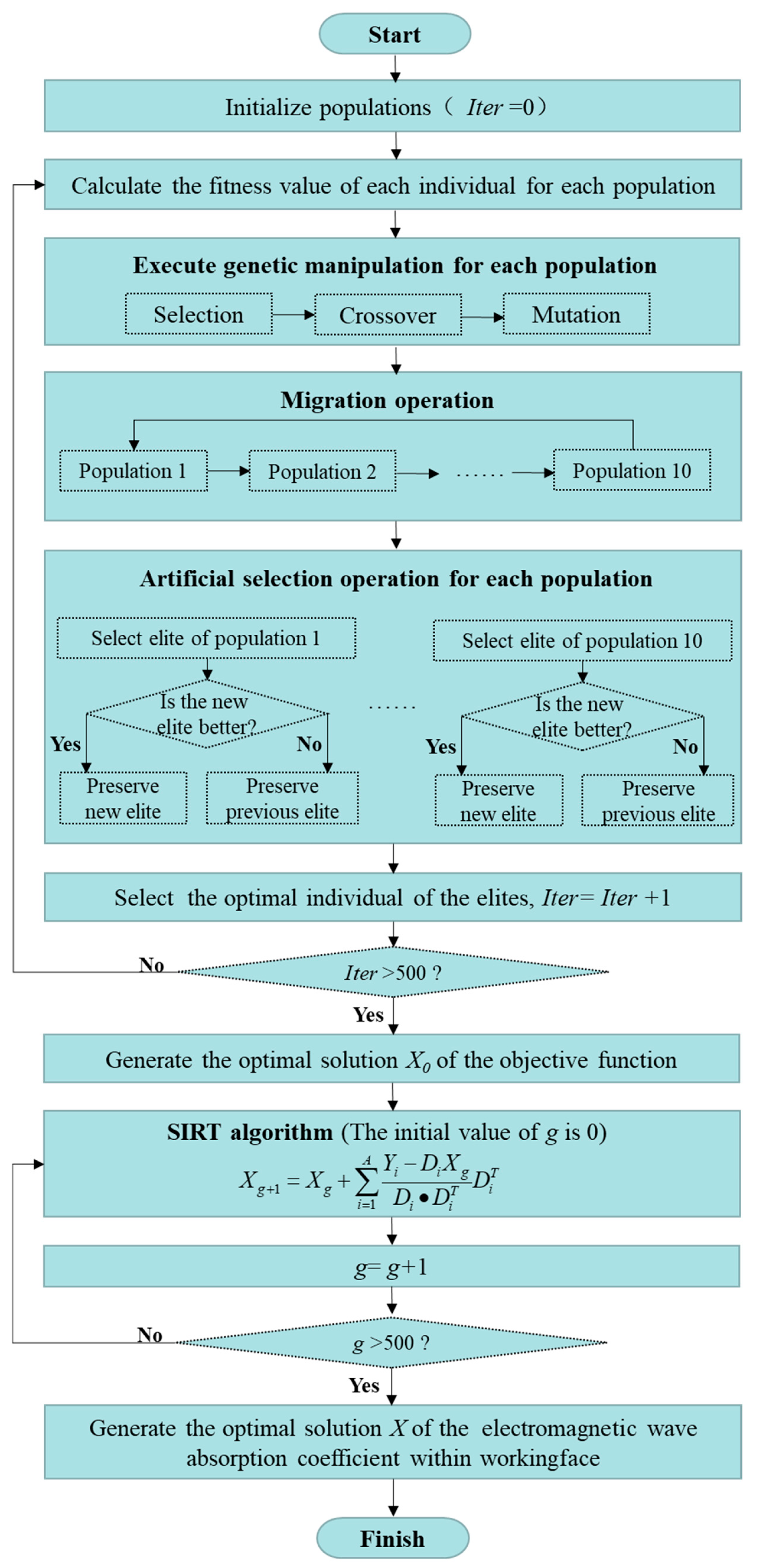
3.2.3. The Program of MPGA-SIRT Hybrid Intelligent Algorithm
In this study, the hybrid intelligence algorithm of MPGA-SIRT has been adopted to reconstruct the geological environment within a working face, which can fully combine the advantages of the global search provided by an intelligent algorithm and the local search provided by a traditional linear algorithm. The flow chart of the proposed MPGA-SIRT program is shown in Figure 3.
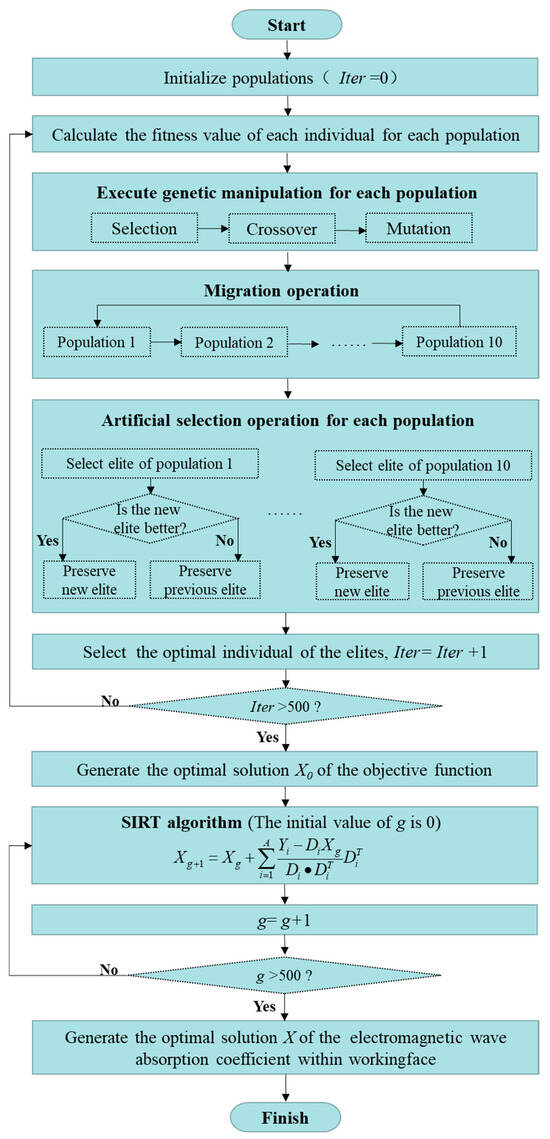
Figure 3.
Flow chart of the proposed MPGA-SIRT program.
- (1)
- Initialize populations
There were a total of 10 populations in the calculation process during each iteration. Each population contained 20 individuals, and each individual represented a feasible solution for the electromagnetic wave absorption coefficient required for optimization. Binary encoding was applied in this program with an encoded bit number of 20, and the initialized populations were generated. The initial iterative algebra Iter is set to 1.
The fitness value of each individual for each population was calculated, and then the genetic operations were performed according to the fitness value to generate a better solution of the absorption coefficient distribution. The selection probability is the ratio between the number of parent individuals selected for genetic manipulation and the total number of individuals, which is randomly selected between 0.9 and 0.95. Different populations perform different crossover and mutation probabilities; the crossover probability is randomly selected between 0.7 and 0.9, and the mutation probability is randomly selected between 0.001 and 0.05 [42,43].
- (2)
- Immigration operation
For each population that had undergone genetic operations, migration operations were performed to enable the exchange of high-quality information between multiple populations. Specifically, the individual with the worst quality (i.e., the lowest fitness value) in the target population was replaced with the one with the highest quality (i.e., the highest fitness value) in the source population. Through the coevolutionary search by multiple populations with different genetic parameters, the performance of the global search for the objective function’s optimal solution could be improved.
- (3)
- Manual selection operation
After evolution, the optimal individual in each population was selected, and then the optimal individuals of all populations (i.e., elite individuals) were chosen and stored separately in the Iter generation after comparison. Iter = Iter + 1. To ensure that elite individuals produced by different populations during evolution were not destroyed or omitted, they did not undergo genetic operations.
If Iter > 500, the process of genetic evolution would stop, and the result of electromagnetic wave absorption coefficient distribution was acquired. Otherwise, go to (2).
- (4)
- SIRT algorithm
The result obtained by the global search of MPGA was used as the initial model for the local inversion of the SIRT, and the repeated iteration was conducted according to the following formula:
where Di was the ith row vector of D, was the transpose of Di, g was the current iteration steps of SIRT, and the initial value of g was 1. Xg represents the electromagnetic wave absorption coefficient distribution results after the iteration steps of g. The distribution result with a global optimum was finally obtained when the current iteration steps g reached the maximum 500 iterations.
4. Numerical Experiment and Analysis
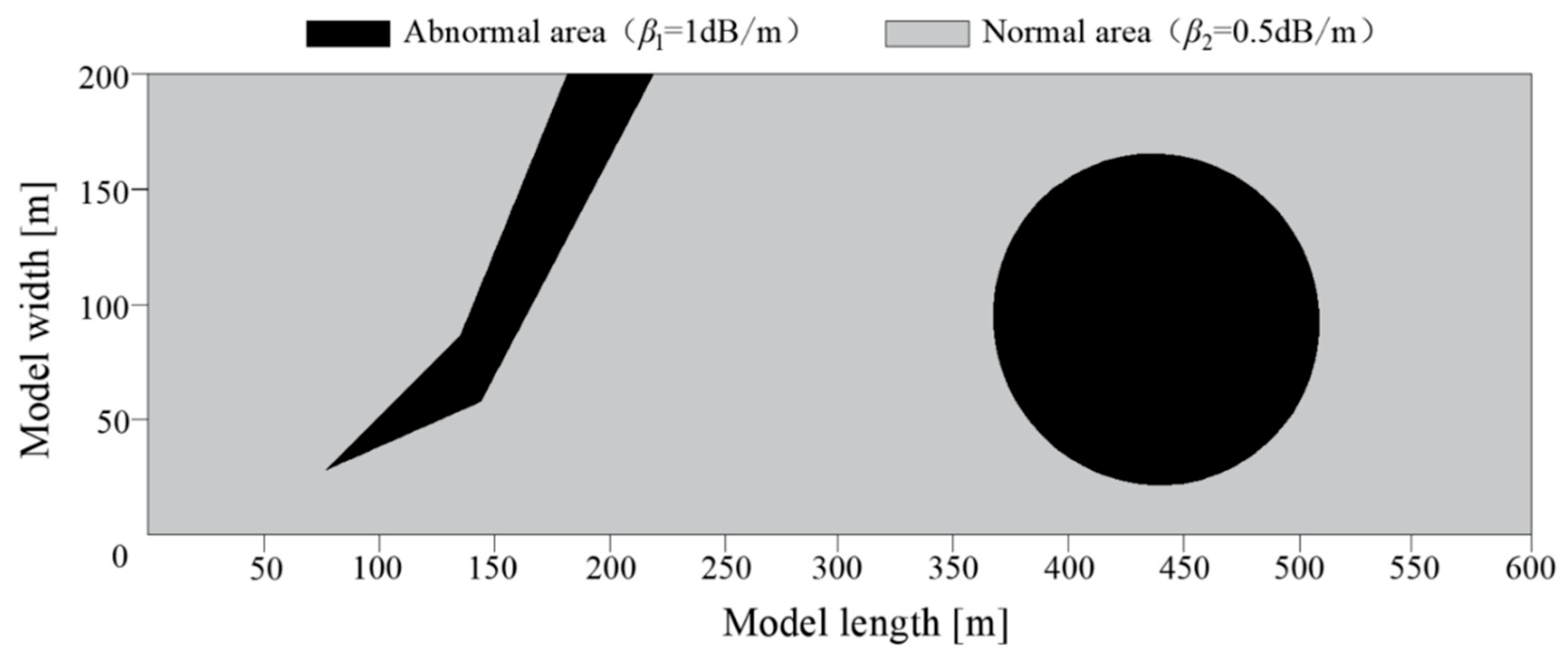
The MPGA-SIRT algorithm was implemented on a PC (3.3 GHz CPU, 8.0 G memory) to demonstrate its effectiveness, and all algorithms were implemented in the MATLAB 2017b programming environment (MathWorks Inc., Natick, MA, USA, 2017). A 600 m long and 200 m wide model was established according to the shape characteristics of the coal mine working face, as shown in Figure 4. Considering that the differences in the absorption capacities of electromagnetic waves between the coal seam and the geological anomaly medium provide the basis for the inversion calculation of geological anomalies at the working face, the electromagnetic wave absorption coefficient of the abnormal area was set to β1 = 1 dB/m, and that of the rest of the normal area was set to β2 = 0.5 dB/m according to the previous project detection experience, which could verify the feasibility of the prediction method proposed in this research.
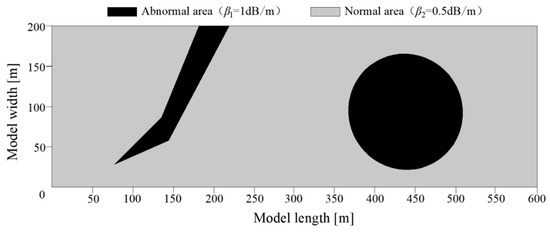
Figure 4.
Distribution diagram of the model construction.
The observation system had a 30 m separation between transmitting stations and a 10 m separation between comparable receiving locations. A total of 420 transmission rays were captured in total. Prior to the tomographic inversion calculation, the detection area was first discretized into grids, and the size of each grid was 10 × 10 m. The detection area was planned to be divided into A = 1200 grids, and the absorption coefficient value represented by these 1200 grids was the target requiring solution via inversion.
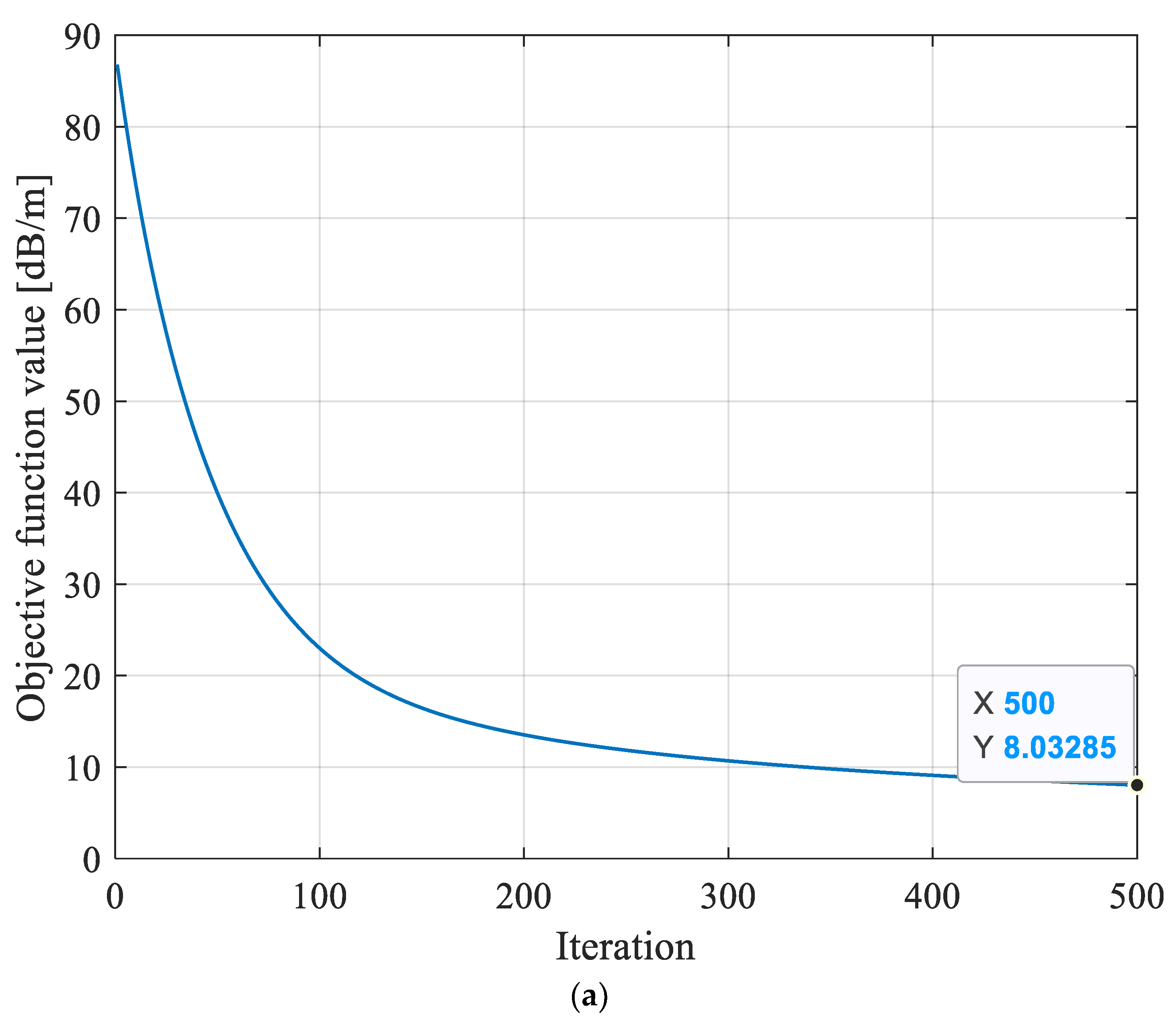
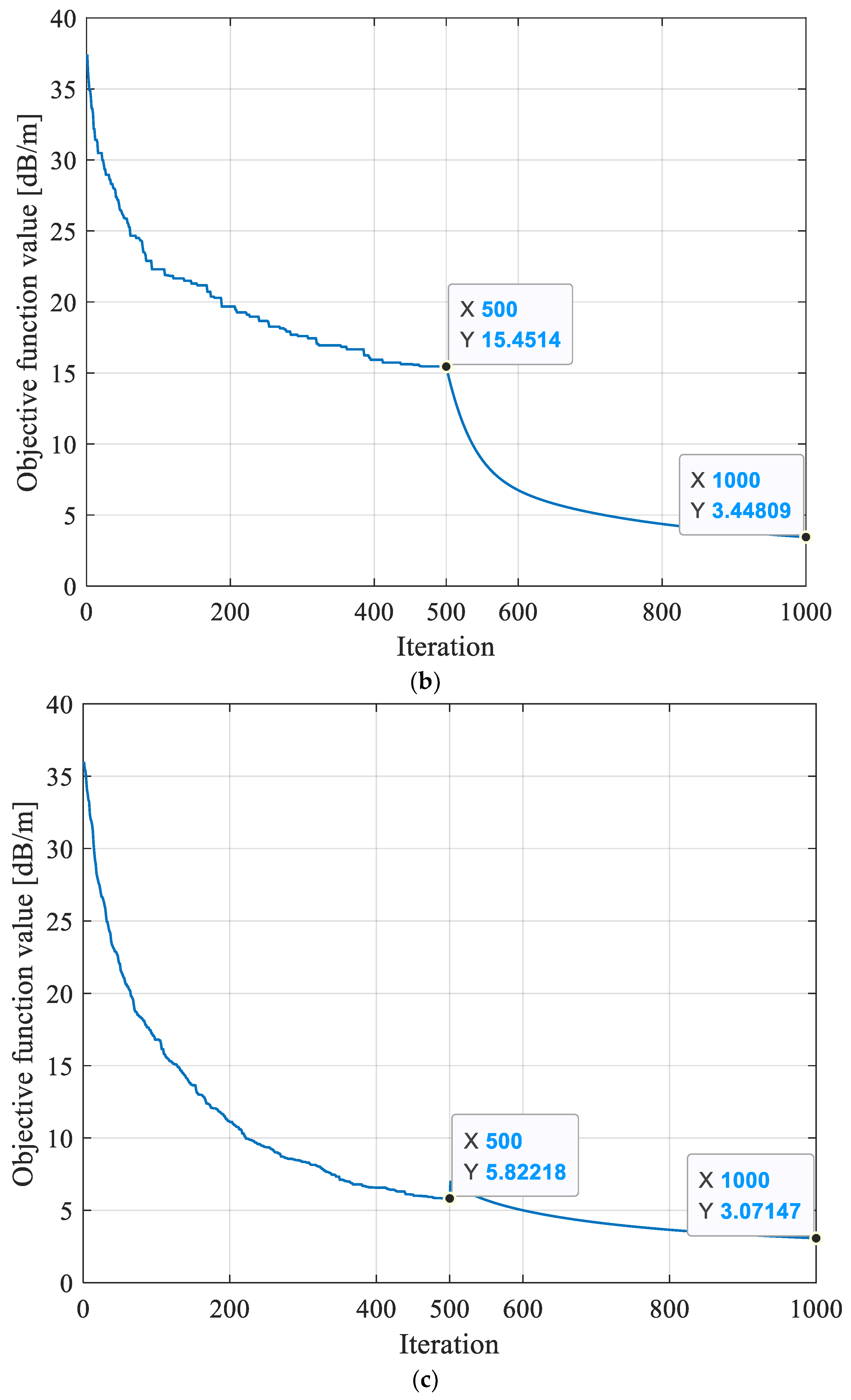
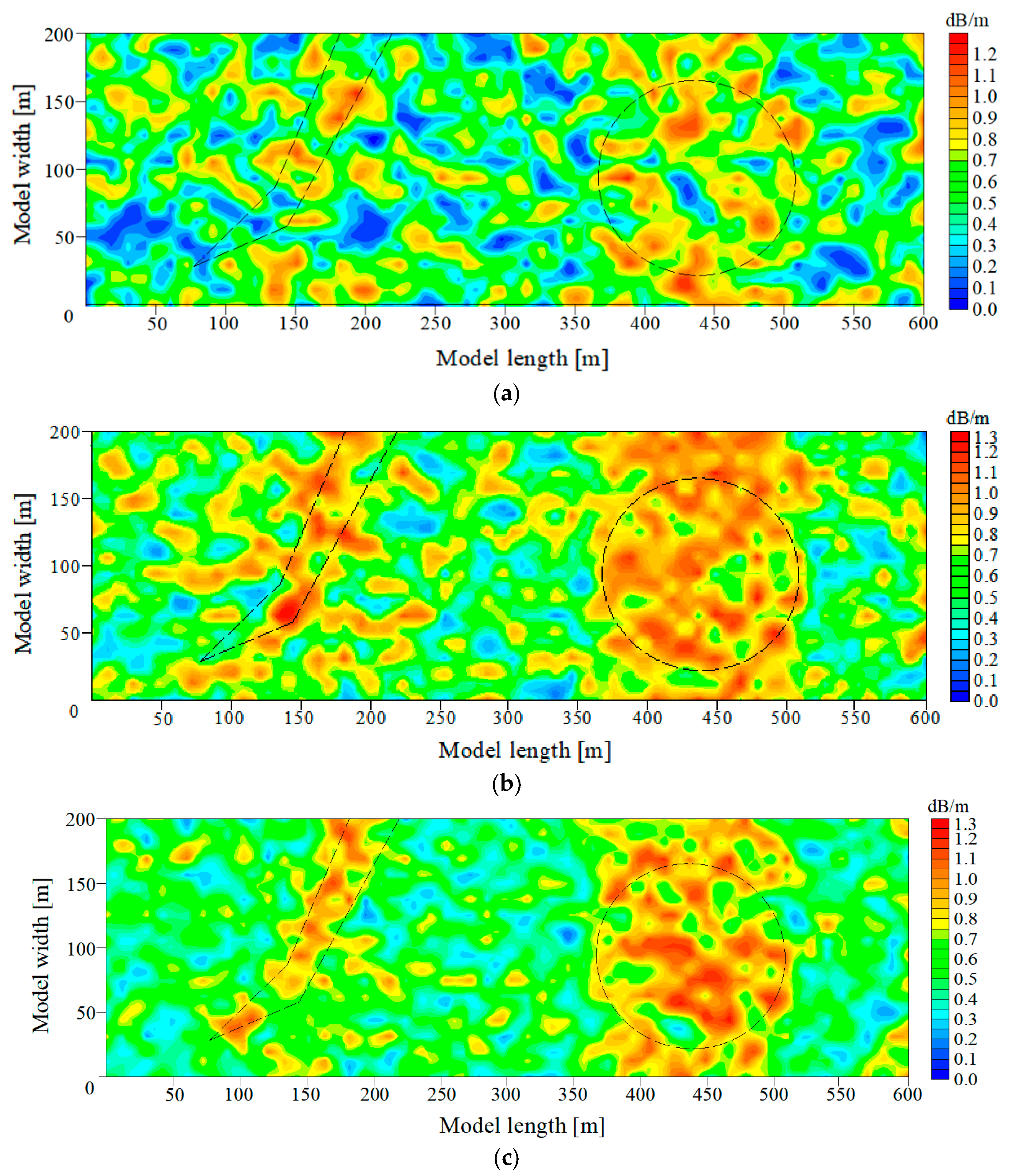
In order to assess the efficacy of the hybrid intelligent optimization algorithm of MPGA-SIRT proposed in this paper, this research reversed the geological anomaly of the working face shown in Figure 5 using three different reconstruction models, including the SIRT conventional linear reconstruction algorithm, SGA-SIRT, and the MPGA-SIRT hybrid intelligent algorithm. After 500 generations of iterations, the final convergence for the objective function f was 8.033 dB/m based on the SIRT, 15.451 dB/m based on SGA, and 5.882 dB/m based on MPGA, as shown in Figure 6a. Therefore, the MPGA had stronger global search performance compared to SGA. Subsequently, the absorption coefficient matrix X0 corresponding to the convergence based on SGA and MPGA intelligent algorithms was used as the initial model of the SIRT, respectively, and iterative inversion was continued. The convergence results of the final objective function f were 3.448 dB/m and 3.071 dB/m, respectively, as shown in Figure 5b,c. The optimal solution X of the objective function obtained at the time of convergence based on the three different reconstruction algorithms of SIRT, SGA-SIRT, and MPGA-SIRT was imaged using tomography, as shown in Figure 5. As a result, the MPGA-SIRT hybrid intelligent reconstruction’s distribution of geological anomalies is most compatible with the model’s setting region. Therefore, the introduction of intelligent algorithms could effectively improve the search performance of the SIRT for the objective function. Stronger global and local search capabilities of the MPGA-SIRT hybrid intelligent algorithm can increase the inversion and prediction accuracy of the geological anomaly layer within a working face.
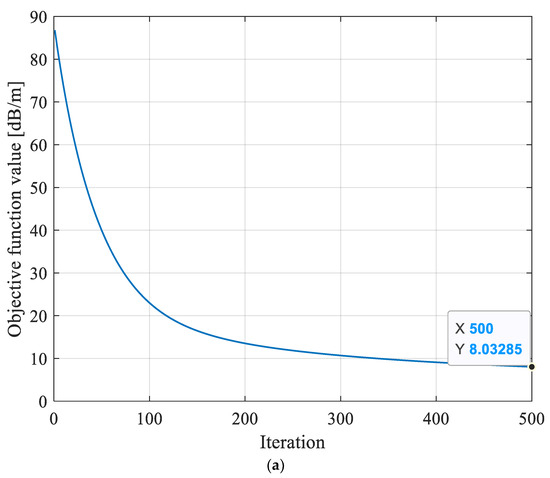
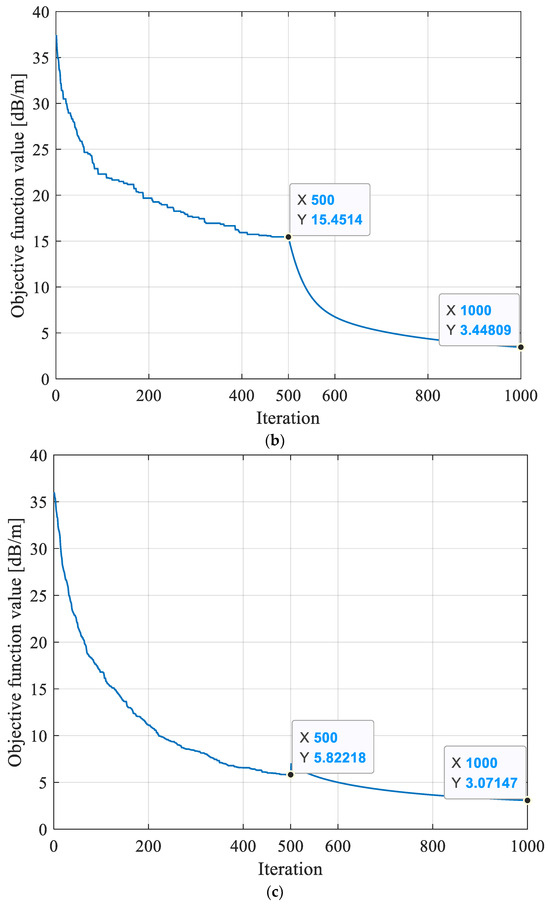
Figure 5.
Evolution curves of objective function f obtained based on different reconstruction models. (a) Evolution curve of objective function inversion based on the SIRT algorithm. (b) Evolution curve of objective function inversion based on the SGA-SIRT hybrid intelligent optimization algorithm. (c) Evolution curve of objective function inversion based on the MPGA-SIRT hybrid intelligent optimization algorithm.
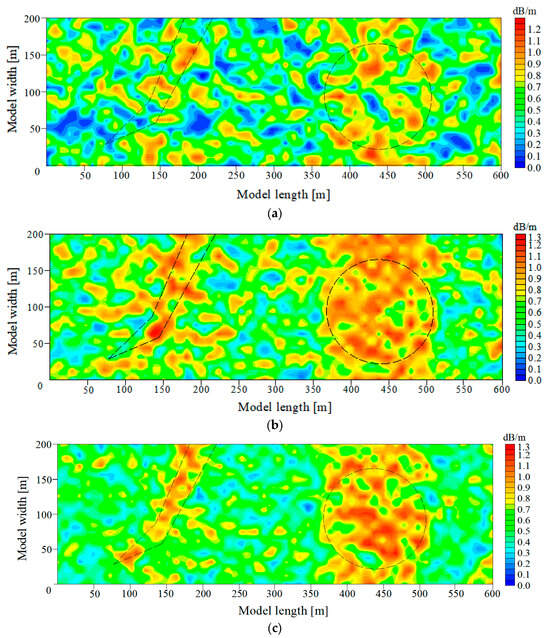
Figure 6.
Tomography inversion results obtained using different reconstruction models. (a) Tomography inversion result obtained via the SIRT algorithm. (b) Tomography inversion result obtained via the SGA-SIRT algorithm. (c) Tomography inversion result obtained via the MPGA-SIRT algorithm.
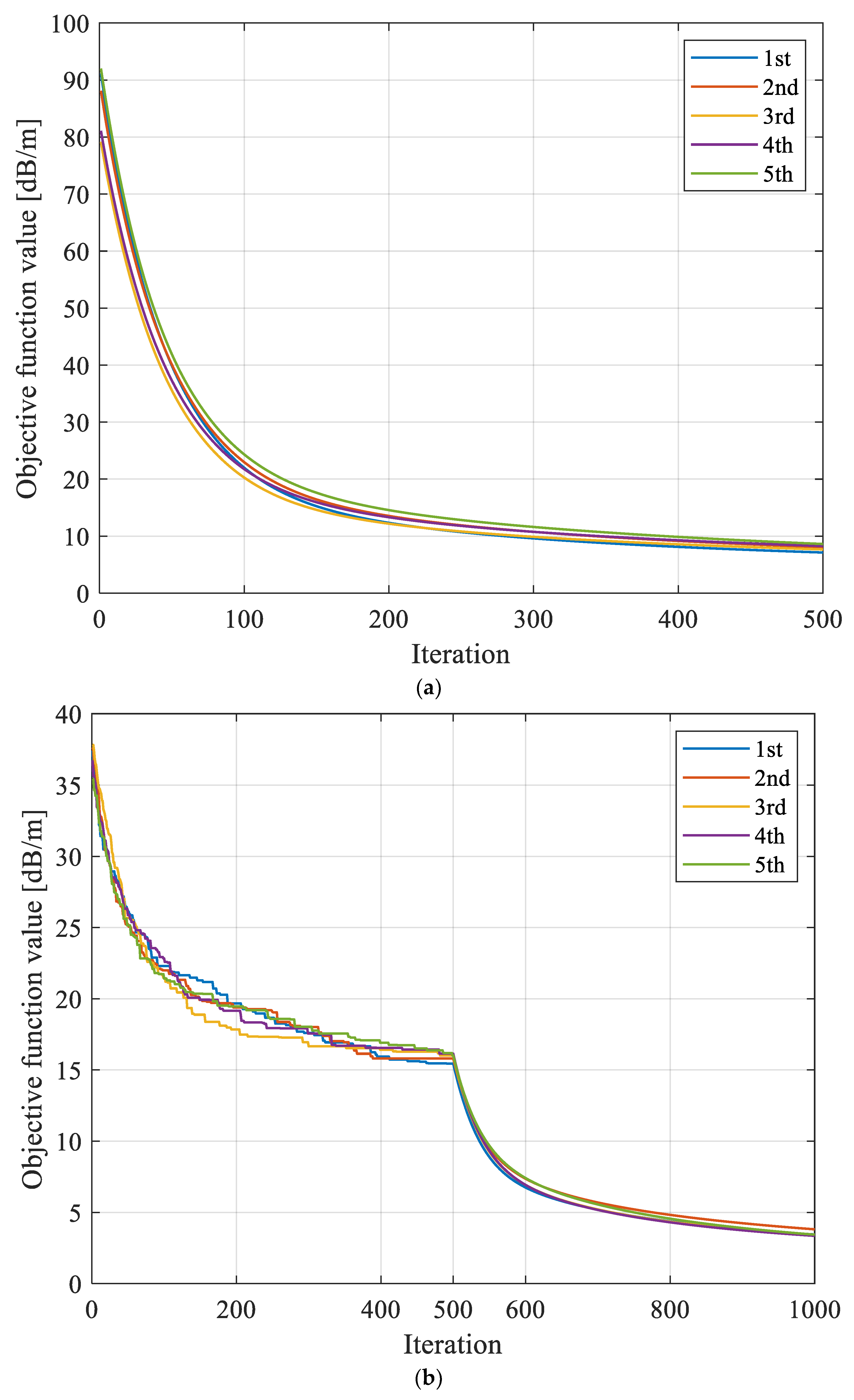
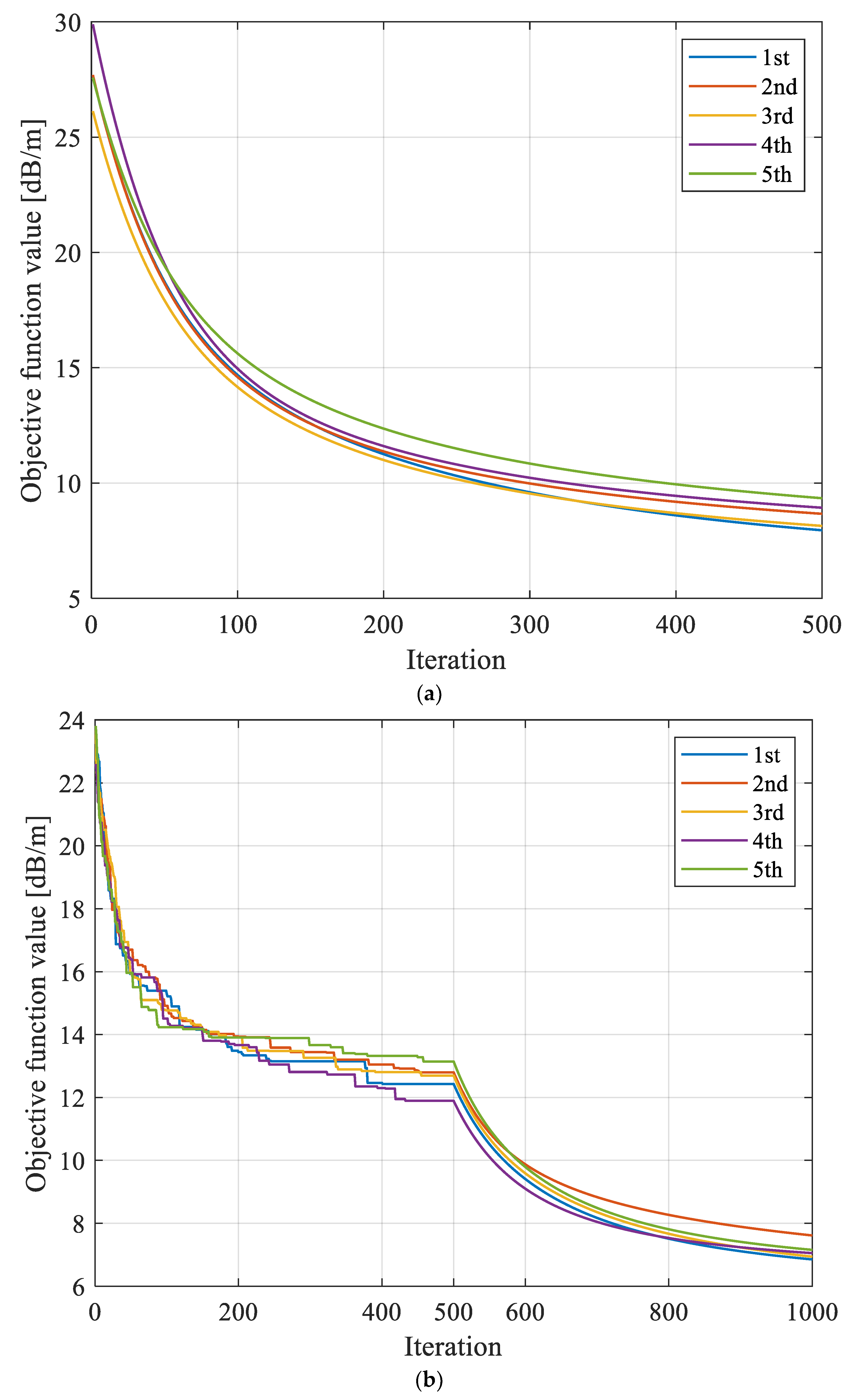
In addition to accuracy, stability is also an important indicator of a model’s performance. Therefore, in order to verify the stability of the proposed hybrid intelligent algorithm, five repetitive reconstruction operations were performed on the anomalous area of the working face. The evolution curves of the objective function based on different reconstruction models are shown in Figure 7, and the convergence results are shown in Figure 8.
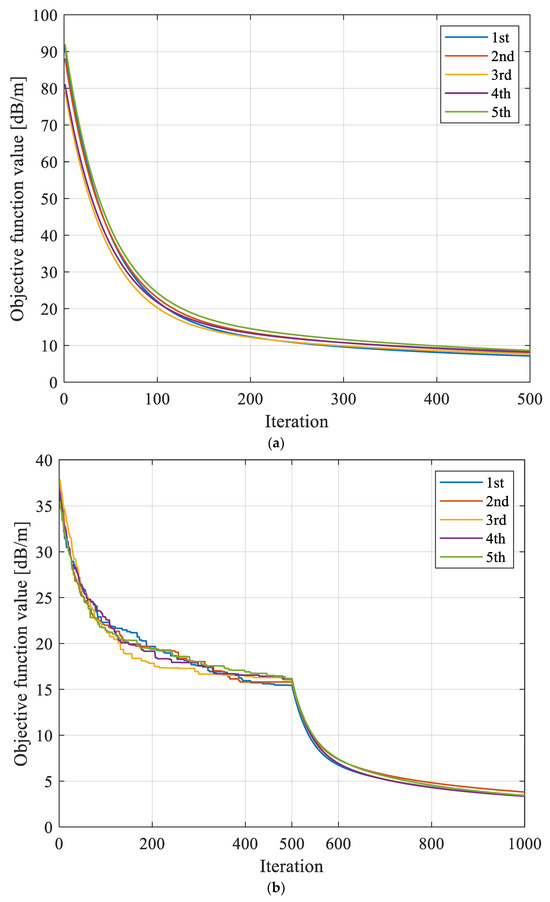
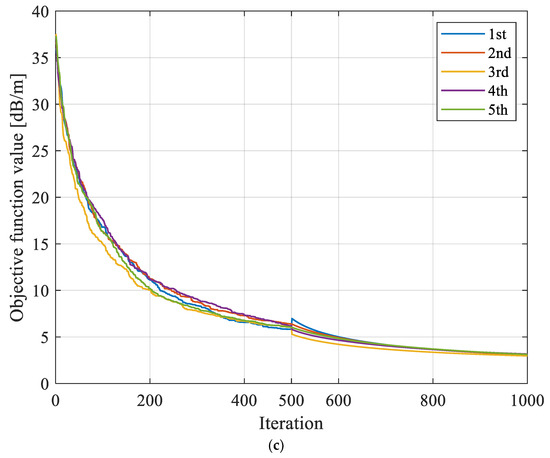
Figure 7.
Evolution curves of objective function f obtained based on different reconstruction models with repeated tests. (a) Evolution curves of objective function based on SIRT with repeated tests. (b) Evolution curves of objective function based on SGA-SIRT with repeated tests. (c) Evolution curves of objective function based on MPGA-SIRT with repeated tests.
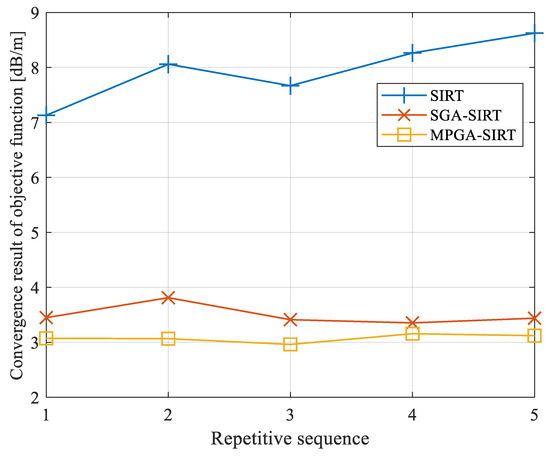
Figure 8.
Convergence results of objective function f obtained based on different reconstruction models with repeated tests.
The standard deviation S, as a measure of statistical data dispersion, can well evaluate the stability of each reconstructed model, which is defined as follows.
In the above equation, F represents the convergence results of repeated inversions based on different reconstruction models. is the average value of F. n is the number of repeated inversion operations of each reconstruction model, and n = 5.
As shown in Table 1, after 500 generations of iterations, the mean values of the convergence outcomes of the objective functions achieved by the SGA and MPGA with numerous repeated evolutionary searches were 15.885 dB/m and 6.037 dB/m, respectively. The standard deviations were 0.272 dB/m and 0.114 dB/m. In conclusion, the MPGA has stronger stability compared with the SGA, also proving the accuracy of the global search performance of the MPGA.

Table 1.
Convergence results with repetitive sequence obtained via the SGA and MPGA [dB/m].
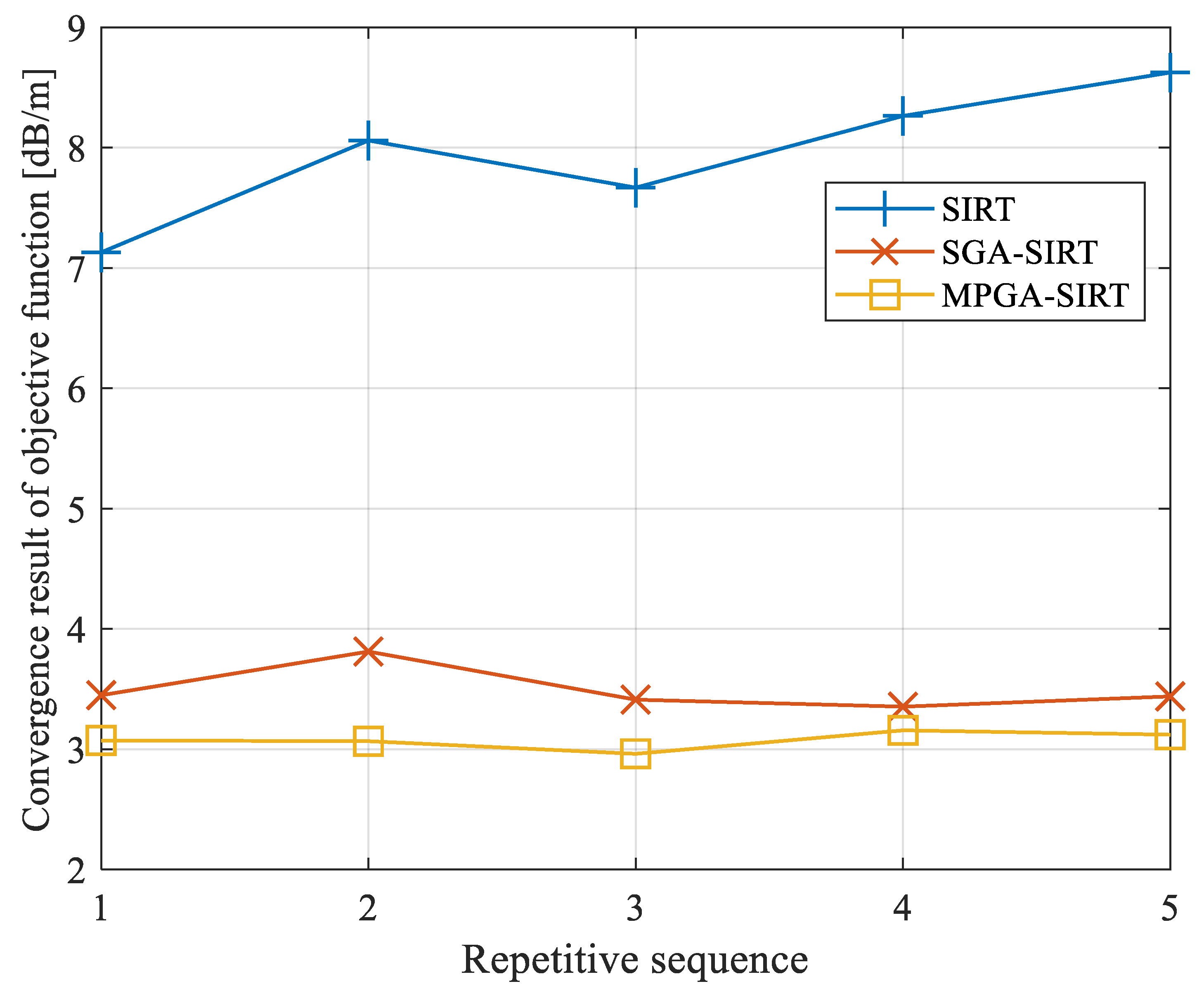
As shown in Table 2, after five iterations, the mean values of the final convergence results obtained via the SIRT, SGA-SIRT, and MPGA-SIRT were 7.948 dB/m, 3.492 dB/m, and 3.075 dB/m, with standard deviations of 0.574 dB/m, 0.182 dB/m, and 0.071 dB/m, respectively. Therefore, MPGA-SIRT offers better performance in terms of both accuracy and stability.

Table 2.
Convergence results with repetitive sequence for different inversion models [dB/m].
5. Experimental Section
5.1. Survey Area
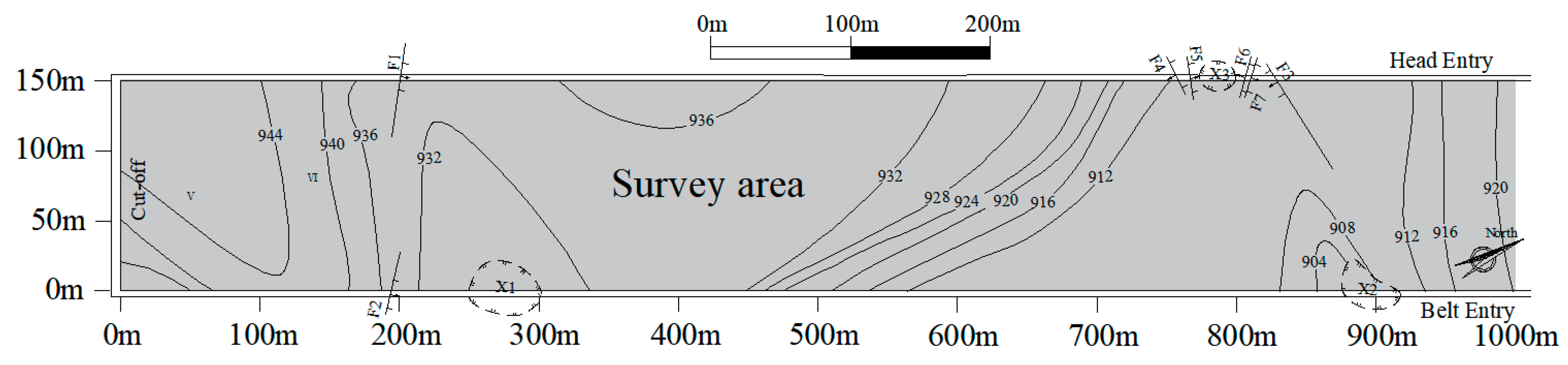
To verify the effectiveness and feasibility of the proposed hybrid intelligent algorithm, this research reconstructs and predicts the geological anomaly area within the 8208 working face of Datong mine, Shanxi. The strike length of the 8208 working face is 1000 m, and the inclined width is 150 m. The coal thickness is unstable, varying from 4.29 m to 9.44 m, containing 1–4 layers of gangue. The coal seam dip angle varies from 2° to 10°. With seven faults and three trap columns in the two lanes in the working face, the internal coal seam occurrence state is relatively complex, as shown in Figure 9. In the observation arrangement used for electromagnetic wave CT detection, the transmitting point spacing was 50 m, the receiving point spacing was 10 m, and a total of 418 electromagnetic wave transmission rays were collected.
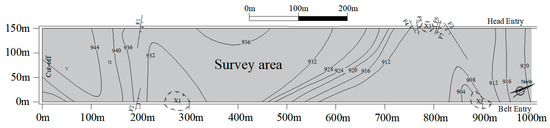
Figure 9.
The distribution diagram of the 8208 working face survey area.
5.2. Evolution Curve Feature Results Based on Different Algorithms
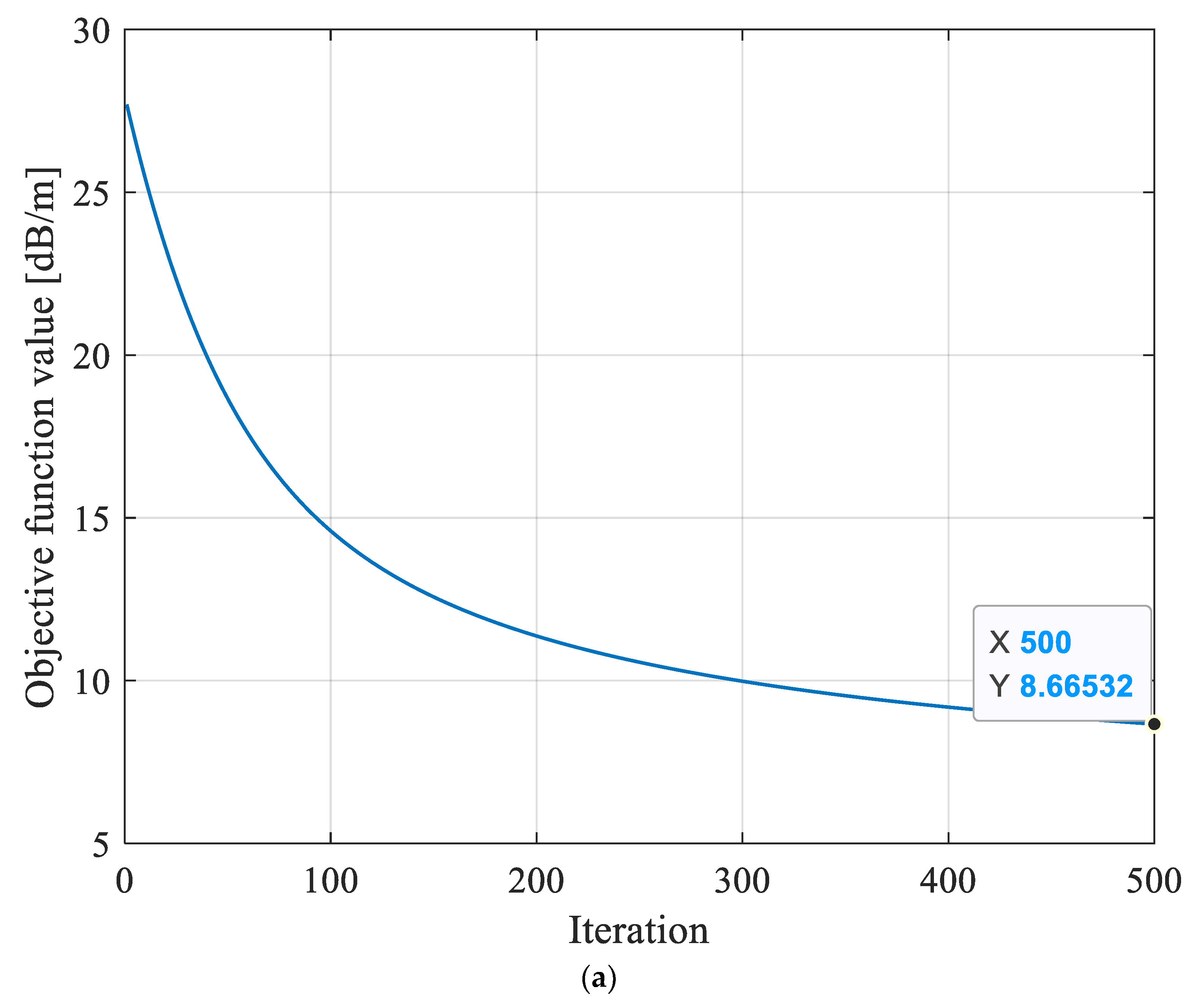
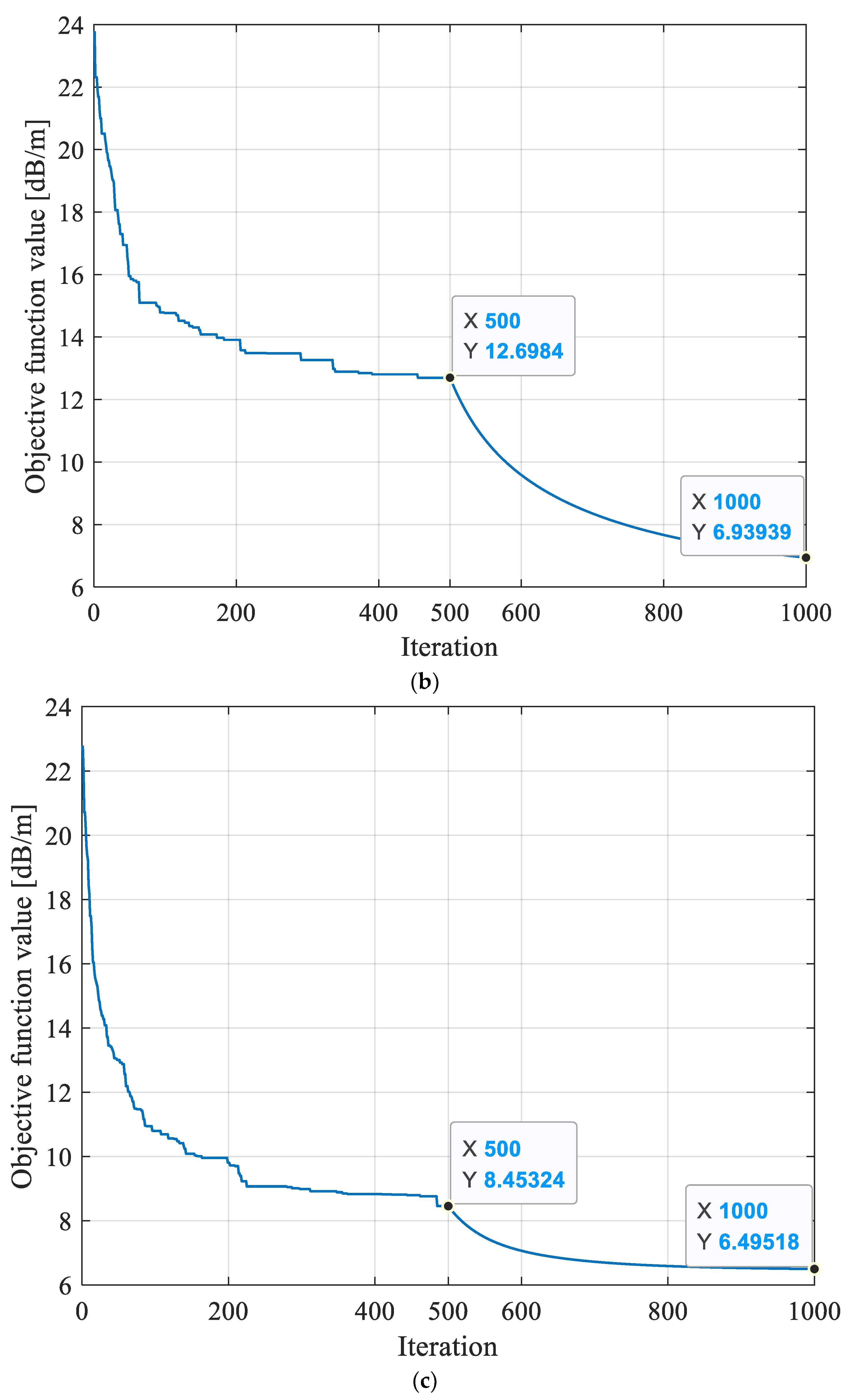
Prior to the inversion reconstruction of the 8208 working face, the detecting region in the working face was grid discretized. The discrete grid was divided into 1470 grids with a size of 10.3 m × 10.3 m to ensure that the electromagnetic wave transmission beams were distributed evenly inside it. The final convergence result of the objective function f based on MPGA-SIRT was 6.495 dB/m, as shown in Figure 10, which was the closest to the global optimal solution among the three reconstruction models and thus showed stronger search performance.
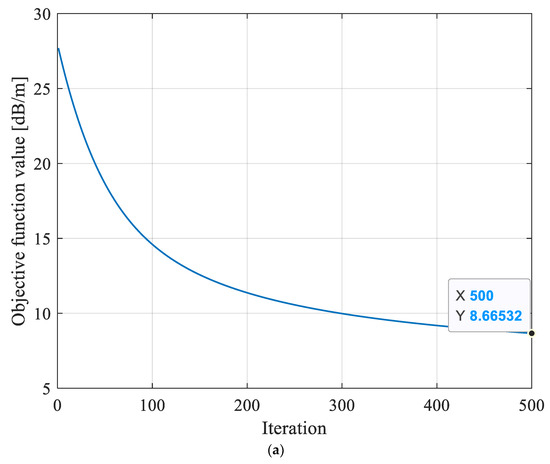
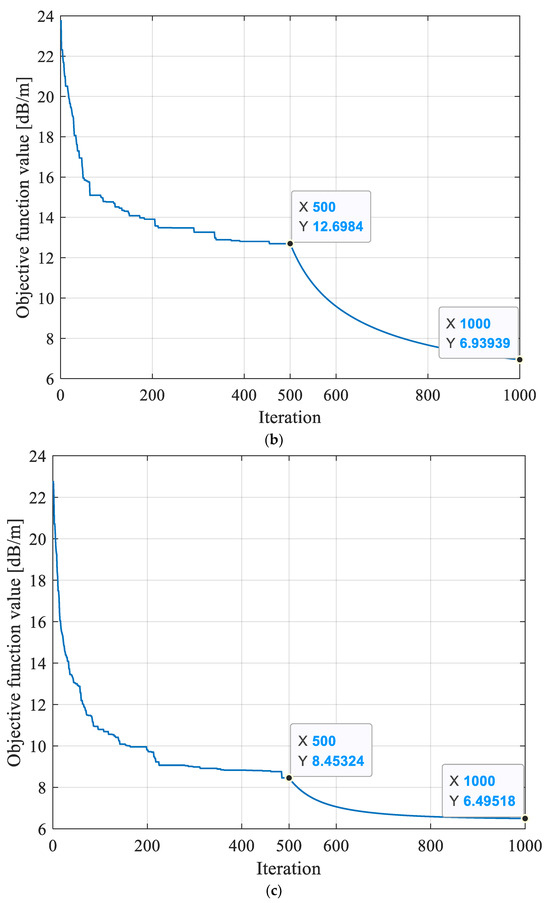
Figure 10.
Evolution curves of objective function obtained based on different reconstruction models for 8208 working face. (a) Evolution curve of objective function inversion based on SIRT algorithm. (b) Evolution curve of objective function inversion based on SGA-SIRT hybrid intelligent optimization algorithm. (c) Evolution curve of objective function inversion based on MPGA-SIRT hybrid intelligent optimization algorithm.
5.3. Tomography Results Corresponding to Different Algorithms
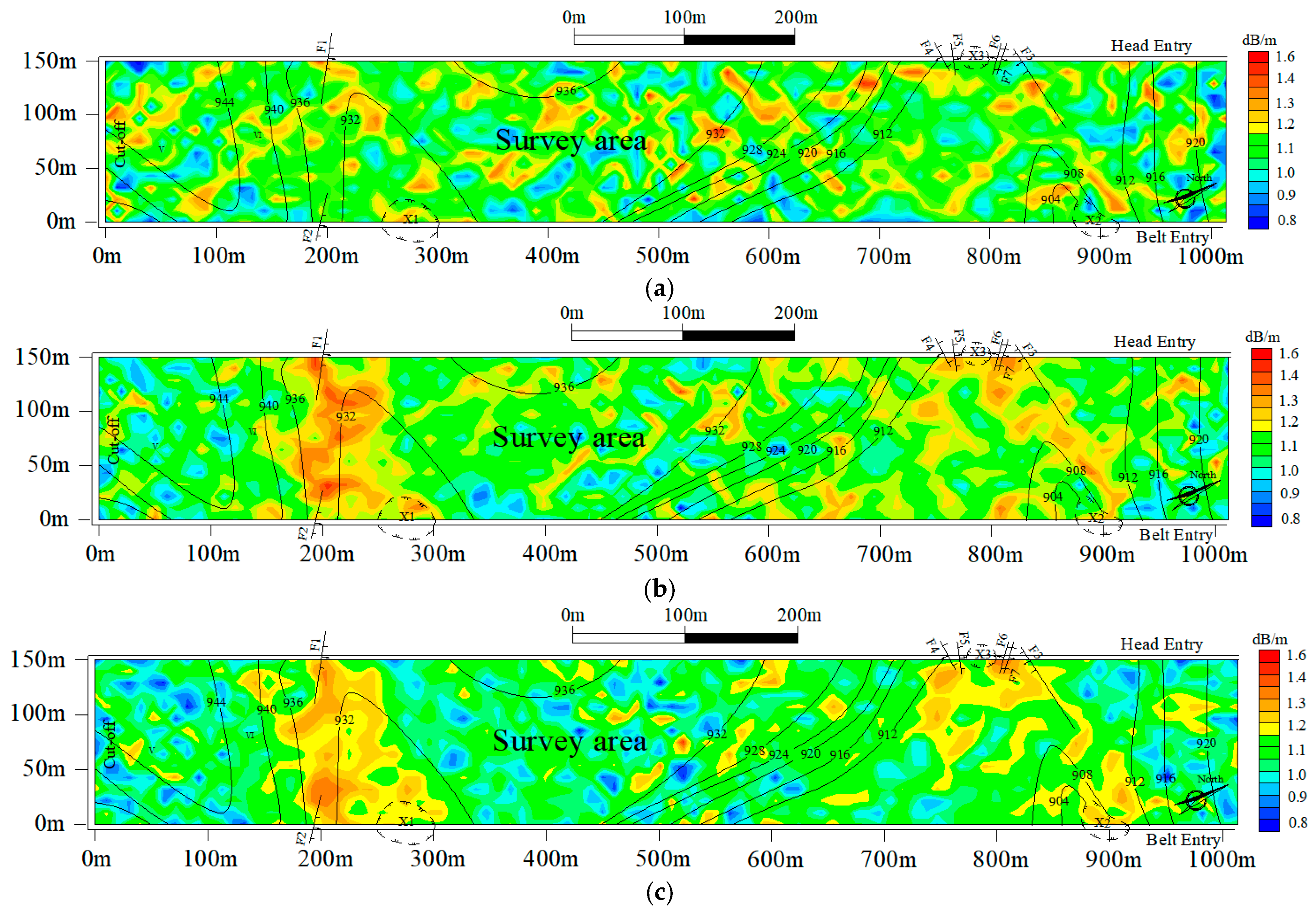
When the objective function f based on the three different reconfiguration models reached convergence, the results of the electromagnetic wave absorption coefficient distribution of the 8208 working surface were obtained, as shown in Figure 11. Compared with the SIRT, the distribution of the geological anomalies reconstructed using SGA-SIRT was relatively ameliorated, while the geological anomaly tomography results based on MPGA-SIRT were the closest to reality and more accurate in terms of determining the distribution of geological anomalies. As shown in Figure 11c, it could be predicted that the 8208 working face contained two geological anomalies, which were around 170–310 m and 720–940 m, respectively. They had great possibility in terms of penetrating the whole working face, significantly impacting the recovery of the working face. It is recommended that the two anomalous areas be avoided in the recovery plan. When the recovery reaches the region of these two anomalous areas, drilling should be improved, and certain safety precautions should be intensified to prevent interfering with the effective and safe mining of the working face.
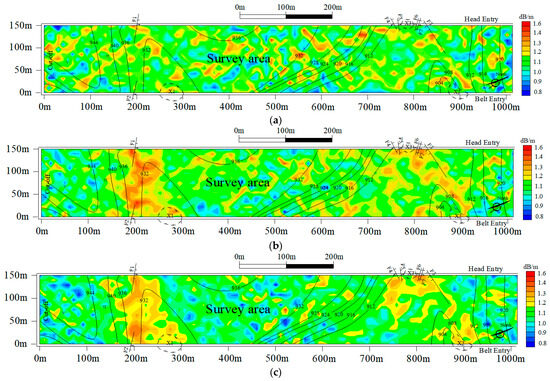
Figure 11.
Tomography inversion results of the 8208 working face obtained using different reconstruction models. (a) Tomography inversion result obtained using the SIRT algorithm. (b) Tomography inversion result obtained using the SGA-SIRT algorithm. (c) Tomography inversion result obtained using the MPGA-SIRT algorithm.
5.4. Stability Analysis of Different Reconstruction Models
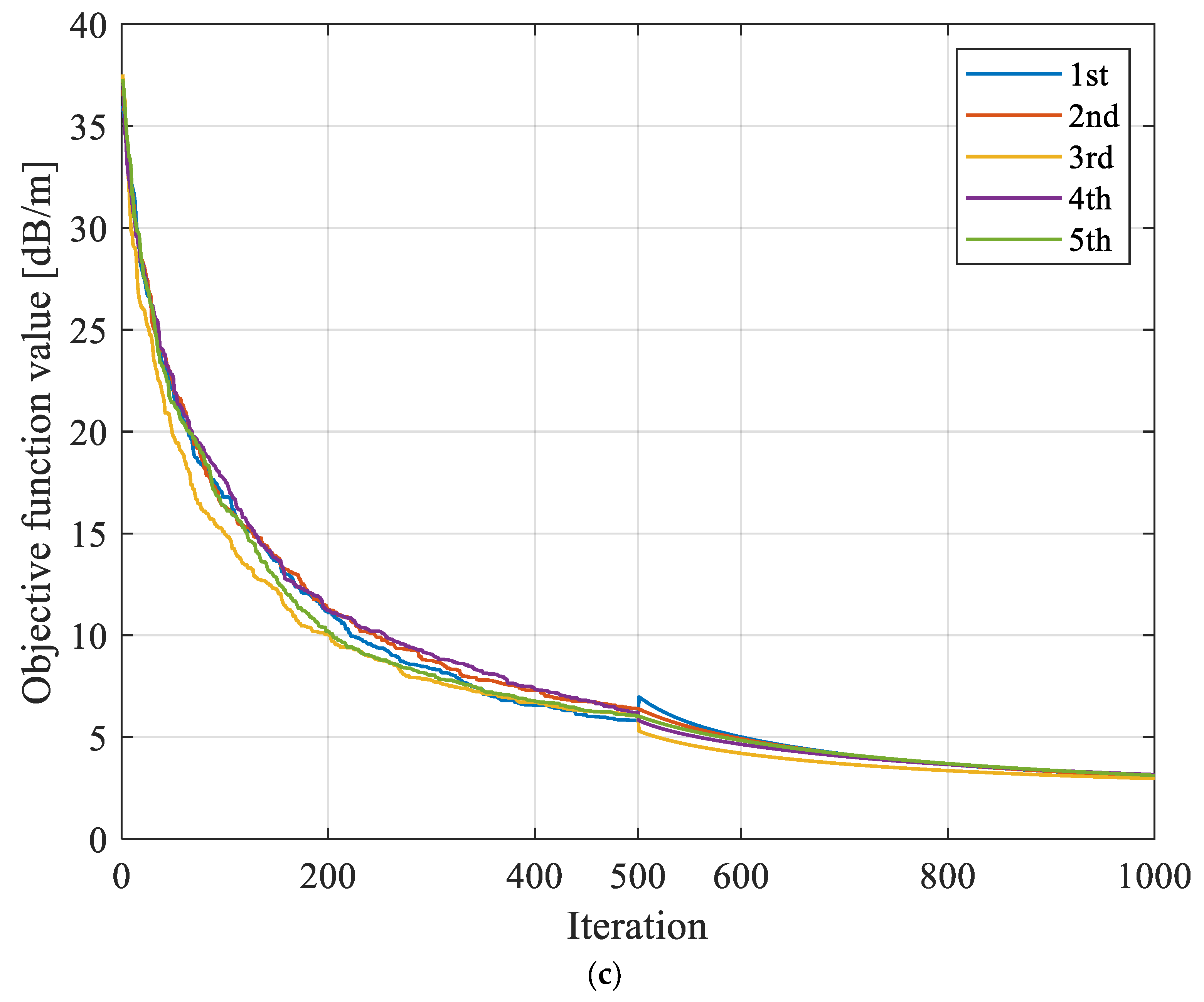
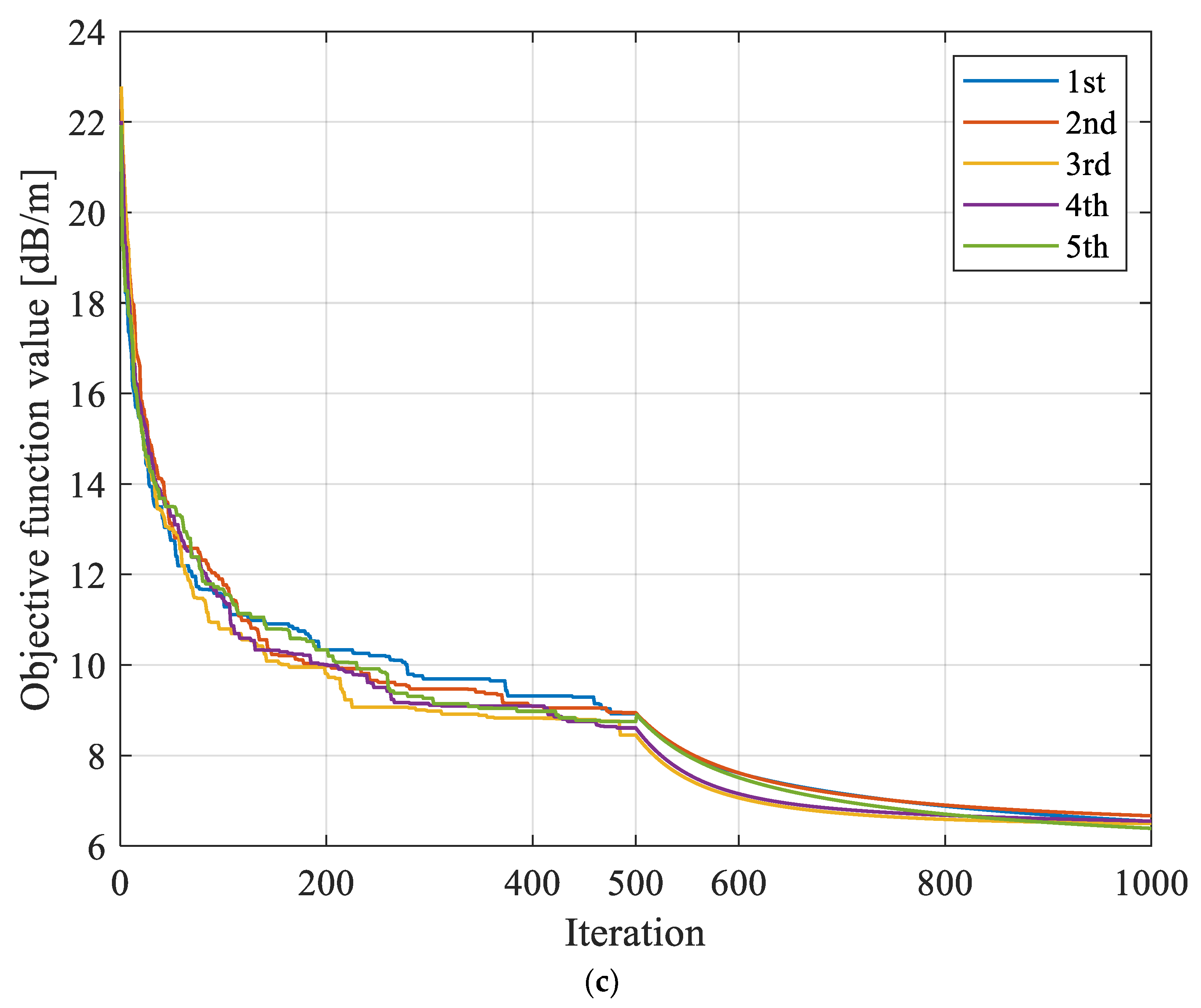
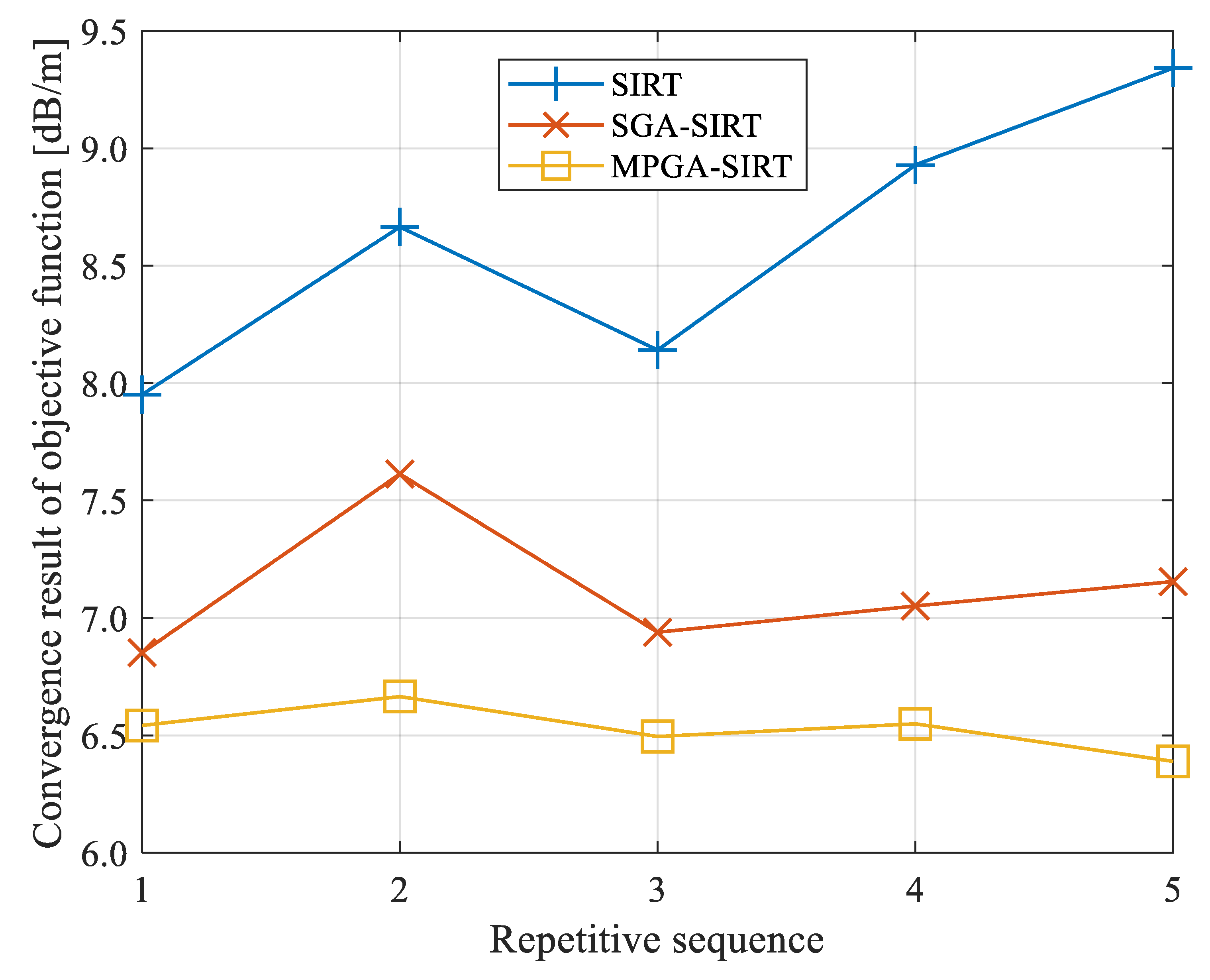
The SIRT had large variations in convergence in repeated inversion calculations, with a maximum variation value of 1.391 dB/m, while the variation amplitudes based on SGA-SIRT and MPGA-SIRT were 0.762 dB/m and 0.277 dB/m, respectively, as shown in Figure 12 and Figure 13.
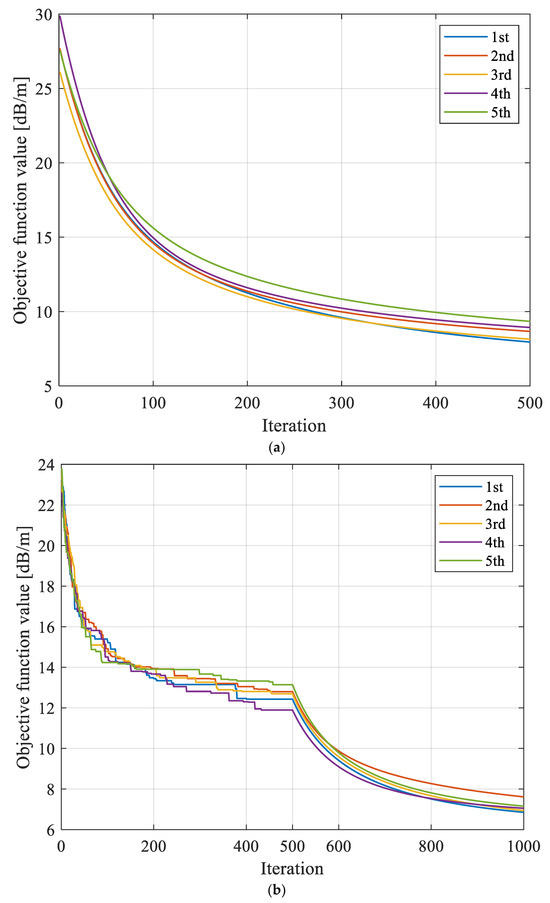
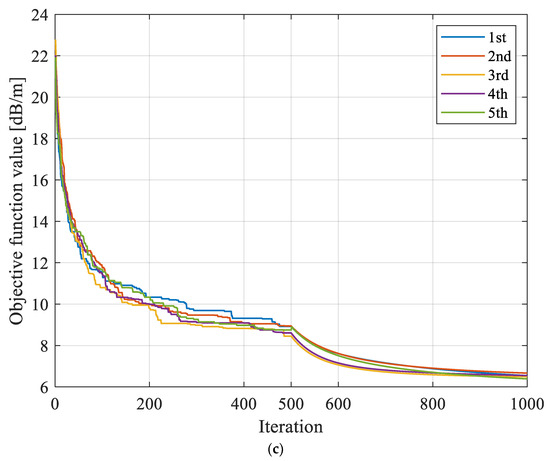
Figure 12.
Evolution curves of objective function f obtained based on different reconstruction models with repeated tests for 8208 working face. (a) Evolution curves of objective function based on SIRT with repeated tests. (b) Evolution curves of objective function based on SGA-SIRT with repeated tests. (c) Evolution curves of objective function based on MPGA-SIRT with repeated tests.
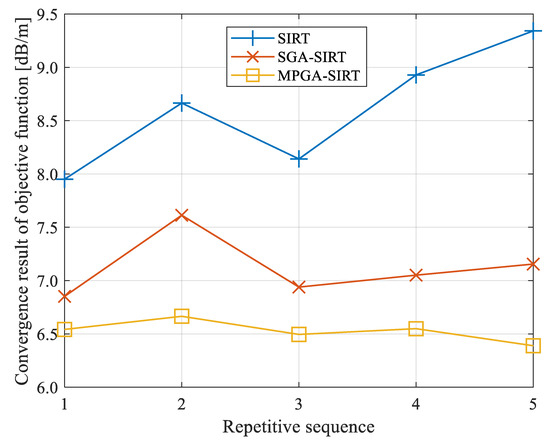
Figure 13.
Convergence results of objective function f obtained based on different reconstruction models with repeated tests for 8208 working face.
The mean values of the objective function’s convergence results based on the SIRT, SGA-SIRT, and MPGA-SIRT were 8.606 dB/m, 7.122 dB/m, and 6.528 dB/m, with standard deviations of 0.569 dB/m, 0.297 dB/m and 0.099 dB/m, respectively, as shown in Table 3. The engineering practices of the 8208 working face verified that MPGA-SIRT showed stronger accuracy and stability with the combination of the intelligent algorithm’s global search characteristics and the traditional linear algorithm’s local search characteristics.

Table 3.
Convergence results with repetitive sequence for different inversion models [dB/m].
6. Conclusions
In this study, a novel MPGA-SIRT hybrid intelligent reconstruction algorithm is introduced to evaluate the geo-environmental conditions within a working face. The efficacy of the proposed method was substantiated through both numerical simulations and field measurement tests. This work contributes to a deeper understanding of the effective reconstruction mechanisms involved in geo-environmental conditions within an underground closed space. In summary, the following conclusions can be drawn based on the results of this study:
(1) Given the limitations of projection data, anticipating the anomalous areas within the working face becomes challenging. In this scenario, the coupled algorithm of MPGA and SIRT can be employed to reconstruct the geo-environmental conditions within a working face, even with insufficient projection data.
(2) The MPGA outperforms the SGA in terms of accuracy and stability through the coevolution of multiple populations, providing a more rational initial model for the SIRT algorithm and mitigating its dependence on the initial model flaw.
(3) The MPGA-SIRT hybrid intelligent algorithm, combining the robust global evolutionary ability of the MPGA intelligent algorithm with the local search characteristics of the SIRT linear reconstruction algorithm, proves effective in enhancing the accuracy of reconstructing geo-environmental conditions within a working face.
In conclusion, the algorithm presented in this paper, with its distinctive combination of a multiple-population genetic algorithm (MPGA) and simultaneous iterative reconstruction technique (SIRT), effectively resolves issues faced by traditional linear reconstruction techniques. The MPGA-SIRT model overcomes the constraints of underground confined spaces, providing a more precise initial inversion model for geological environments within working faces based on electromagnetic wave tomography theory. Simultaneously, this algorithm ingeniously utilizes the global search capability of the MPGA and the local search properties of the SIRT, significantly enhancing the accuracy and stability of the inversion process. Validated through numerical modeling, theoretical testing, and practical applications in actual mining areas, this algorithm exhibits superior performance in terms of objective function convergence and tomography results compared to conventional methods. Therefore, it offers a novel and accurate means for assessing mine geology while providing scientific and reliable data support for engineering planning, design, construction, and other phases. This contributes to ensuring environmentally friendly and efficient mining practices, mitigating potential geological risks and enhancing the safety and stability of engineering operations.
In light of the successful applications of the MPGA-SIRT model in reconstructing geo-environmental conditions within a working face, the refinement of the MPGA-SIRT algorithm could involve integrating advanced machine learning techniques to further enhance its ability to handle complex and dynamic geo-environmental data. This could lead to more precise and real-time monitoring of underground conditions, thereby improving the safety and efficiency of mining operations. Moreover, the model could be expanded to include a broader range of geophysical parameters, such as seismic wave velocities or electrical resistivity, to provide a more comprehensive assessment of the subsurface environment. By pursuing these avenues, our research can continue to contribute to the advancement of underground resource extraction and the mitigation of geological hazards, ultimately leading to more sustainable and safe mining practices.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.G., X.M. and W.J.; Software, C.G., T.T., Z.Z. and D.Z.; Formal analysis, C.G., L.M. and D.Z.; Investigation, L.M. and Z.Z.; Resources, X.M.; Data curation, T.T.; Writing—original draft, T.T., L.M. and W.J.; Writing—review & editing, C.G. and W.J.; Funding acquisition, C.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the [National Natural Science Foundation of China] grant number [52404146], and the [Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province] grant number [BK20221130].
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Ma Liuzhu and Zhang Zhicong were employed by the company China Coal Technology and Engineering Group Corp. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Al Mubarak, F.; Rezaee, R.; Wood, D.A. Economic, Societal, and Environmental Impacts of Available Energy Sources: A Review. Eng 2024, 5, 1232–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenli, Y.; Sharifzadeh, M.; Yang, Z.; Xu, G.; Fang, Z. Assessment of fracture characteristics controlling fluid flow in discrete fracture networks (DFN). J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 178, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L. Geological anomaly, including fractures, pores, folds, and faults within the working face, significantly impact underground mining. J. China Coal Soc. 2021, 46, 716–725. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Wu, M.M.; Wang, R.; Xu, H.; Song, X. Height of the mining-induced fractured zone above a coal face. Eng. Geol. 2017, 216, 140–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Tian, C.; Jin, G.; Han, K. Principal component analysis and Fisher discriminant analysis of environmental and ecological quality, and the impacts of coal mining in an environmentally sensitive area. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olena, H.; Grygorii, G. Coal mining and water resources: Impacts, challenges, and strategies for sustainable environmental management. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2024, 1348, 012017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.W.; Rong, T.L.; Wang, L.J.; Mou, R.Y.; Ren, W.G. A new anisotropic coal permeability model under the influence of stress, gas sorption and temperature: Development and verification. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2020, 132, 104407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, N.; Li, M.; Zhang, W. A model for evaluating the production system of an intelligent mine based on unascertained measurement theory. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2020, 38, 1865–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Kang, L.; Chen, X.; He, M.; Zhu, C.; Li, D. A Review of Intelligent Unmanned Mining Current Situation and Development Trend. Energies 2022, 15, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackin, J. Rational and Empirical Methods of Investigation in Geology. In Fluvial Geomorphology—Geomorphology: Critical Concepts in Geography; Routledge: London, UK, 2013; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, S.; Pan, Z.; Tang, S.; Chen, S. Current status and geological conditions for the applicability of CBM drilling technologies in China: A review. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2019, 202, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhdanov, M.S. Geophysical Electromagnetic Theory and Methods; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, K.; Qiu, C.-H.; Primrose, K. Super-sensing technology: Industrial applications and future challenges of electrical tomography. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2016, 374, 20150328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Zhu, M.; Wang, Y.; Yue, H.; Cui, W. Cascade construction of geological model of longwall panel for intelligent precision coal mining and its key technology. J. China Coal Soc. 2019, 44, 2285–2295. [Google Scholar]
- Radon, J. Berichte über die Verhandlungen der Königlich-Sächsischen Gesellschaft der Wissenschaften zu Leipzig. Math.-Phys. Kl. 1917, 69, 262–277. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Yang, Z.; Wu, X.; Tan, T.; Zhao, K. Application of an adaptive multi-population parallel genetic algorithm with constraints in electromagnetic tomography with incomplete projections. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, R.; Bender, R.; Herman, G.T. Algebraic reconstruction techniques (ART) for three-dimensional electron microscopy and X-ray photography. J. Theor. Biol. 1970, 29, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, P. Iterative methods for the three-dimensional reconstruction of an object from projections. J. Theor. Biol. 1972, 36, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Lin, Z.; Liu, Z.; Mukerji, T. A Comparative Experiment on Heterogeneous Distributions of Stress Field for Underground Panels With Different Geological Setting in North China. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5900318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, L.; Li, B.; Ming, D.; Wang, W. Multislice spiral CT image analysis and meta-analysis of inspiratory muscle training on respiratory muscle function. J. Healthc. Eng. 2021, 2021, 1738205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.J.; Tweeton, D.R. MIGRATOM: Geophysical Tomography Using Wavefront Migration and Fuzzy Constraints; United States Bureau of Mines: Washington, DC, USA, 1994.
- MacLennan, K.; Karaoulis, M.; Revil, A. Complex conductivity tomography using low-frequency crosswell electromagnetic data. Geophysics 2014, 79, E23–E38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metropolis, N.; Ulam, S. The monte carlo method. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1949, 44, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buscema, M. Back propagation neural networks. Subst. Use Misuse 1998, 33, 233–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitley, D.; Starkweather, T. Genitor II: A distributed genetic algorithm. J. Exp. Theor. Artif. Intell. 1990, 2, 189–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venter, G.; Sobieszczanski-Sobieski, J. Particle swarm optimization. AIAA J. 2003, 41, 1583–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, J.; Hui, G. Human Evolutionary Optimization Algorithm. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 241, 122638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancilla, J.C.; Pradana-Lopez, S.; Perez-Calabuig, A.M.; Lopez-Ortega, S.; Rodrigo, C.; Torrecilla, J.S. Distinct thermal patterns to detect and quantify trace levels of wheat flour mixed into ground chickpeas. Food Chem. 2022, 384, 132468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wu, H.; Wang, W. A hybrid ant colony optimization with fireworks algorithm to solve capacitated vehicle routing problem. Appl. Intell. 2022, 53, 7326–7342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Yao, C.; Song, E.; Yang, Q.; Yang, X. Optimal control of transient processes in marine hybrid propulsion systems: Modeling, optimization and performance enhancement. Appl. Energy 2022, 321, 119404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Zhang, H.; Mao, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, H.; Wang, Y. Review on the COVID-19 pandemic prevention and control system based on AI. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 114, 105184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Fu, Q.; Li, C.; Liu, F.; Wang, H.; Han, L.; Quevedo, R.P.; Chen, T.; Lei, N. Modeling landslide susceptibility using data mining techniques of kernel logistic regression, fuzzy unordered rule induction algorithm, SysFor and random forest. Nat. Hazards 2022, 114, 3327–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, Q. Intelligent inversion method for pre-stack seismic big data based on MapReduce. Comput. Geosci. 2018, 110, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brezočnik, L.; Fister, I.; Podgorelec, V. Swarm intelligence algorithms for feature selection: A review. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, S.H.; Beck, J.L. Bayesian model updating using hybrid Monte Carlo simulation with application to structural dynamic models with many uncertain parameters. J. Eng. Mech. 2009, 135, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Chen, C.X.; Meng, F.; Zhang, H.N.; Xia, K.Z.; Chen, X.B. Assessing the Stability of Rock Slopes with Respect to Block-Flexure Toppling Failure Using a Force-Transfer Model and Genetic Algorithm. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2020, 53, 3433–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.-L.; Lü, Q.; Sun, H.-Y.; Shang, Y.-Q. Estimating the rainfall threshold of a deep-seated landslide by integrating models for predicting the groundwater level and stability analysis of the slope. Eng. Geol. 2019, 253, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabaei, A.; Hamian, M.; Parsaei, M.R.; Safdari, R.; Samad-Soltani, T.; Zarrabi, H.; Ghassemi, A. Topologies and performance of intelligent algorithms: A comprehensive review. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2018, 49, 79–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.-C.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, W.Y.; Chen, L.-Y.; Panigrahi, B. Cyclic electric load forecasting by seasonal SVR with chaotic genetic algorithm. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2013, 44, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papas, C.H. Theory of Electromagnetic Wave Propagation; Courier Corporation: Chelmsford, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira, F.L.; Chew, W.C. Finite-difference computation of transient electromagnetic waves for cylindrical geometries in complex media. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 1530–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Quan, Y.; Gu, M. Estimation of directional design wind speeds via multiple population genetic algorithm. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2021, 210, 104534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Yang, H.; Lin, L.; Koo, P. Wind turbine layout optimization using multi-population genetic algorithm and a case study in Hong Kong offshore. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2015, 139, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).