A Graph Neural Network Approach with Improved Levenberg–Marquardt for Electrical Impedance Tomography
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Solving the problem of inadequate previous knowledge in EIT experiments is commonly dependent on simulation data, which are obtained from the ACT3 and the KIT4 system. With these systems, we carry out finite element calculations to generate prior data for solving the EIT forward problem. Acquiring a training set by training on public datasets will enhance the understanding and adaptability of the training model to various EIT problems.
- We presents an enhanced LM graph neural network algorithm for EIT imaging. The proposed algorithm utilizes the ILM algorithm to update the parameters of the ill-conditioned non-linear inverse problem in the EIT process. The presented algorithm effectively addresses the limitations of the inverse problem, successfully suppressing or removing artifacts, ultimately enhancing its overall effectiveness.
- The proposed algorithm’s accuracy is assessed through experiments, and the feasibility of the algorithm is validated using the ACT3 and KIT4 datasets. Experimental findings indicate that the physical models of ACT3 and KIT4 display superior performance.
2. Related Work
3. Background
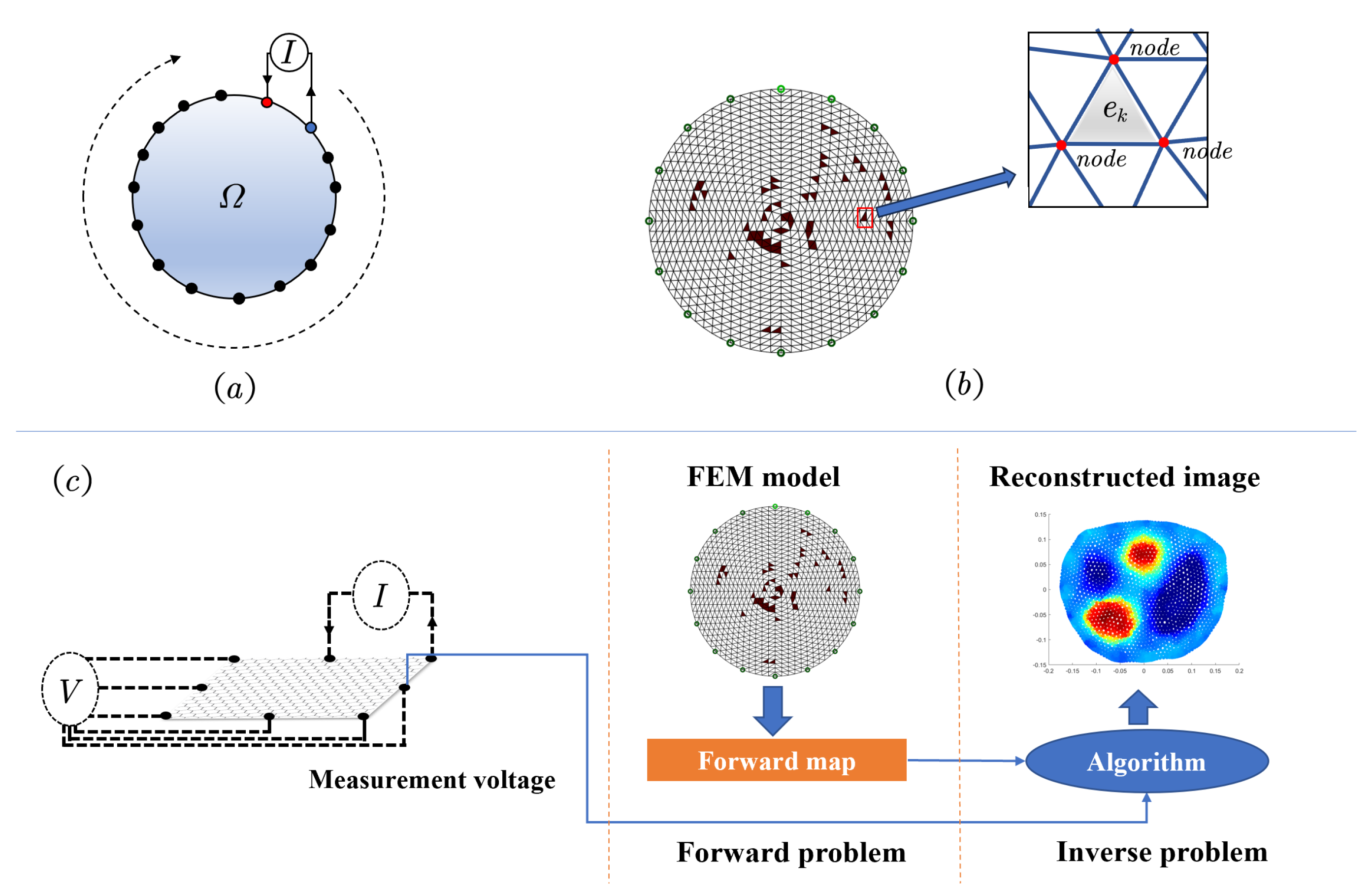
3.1. EIT Forward Model
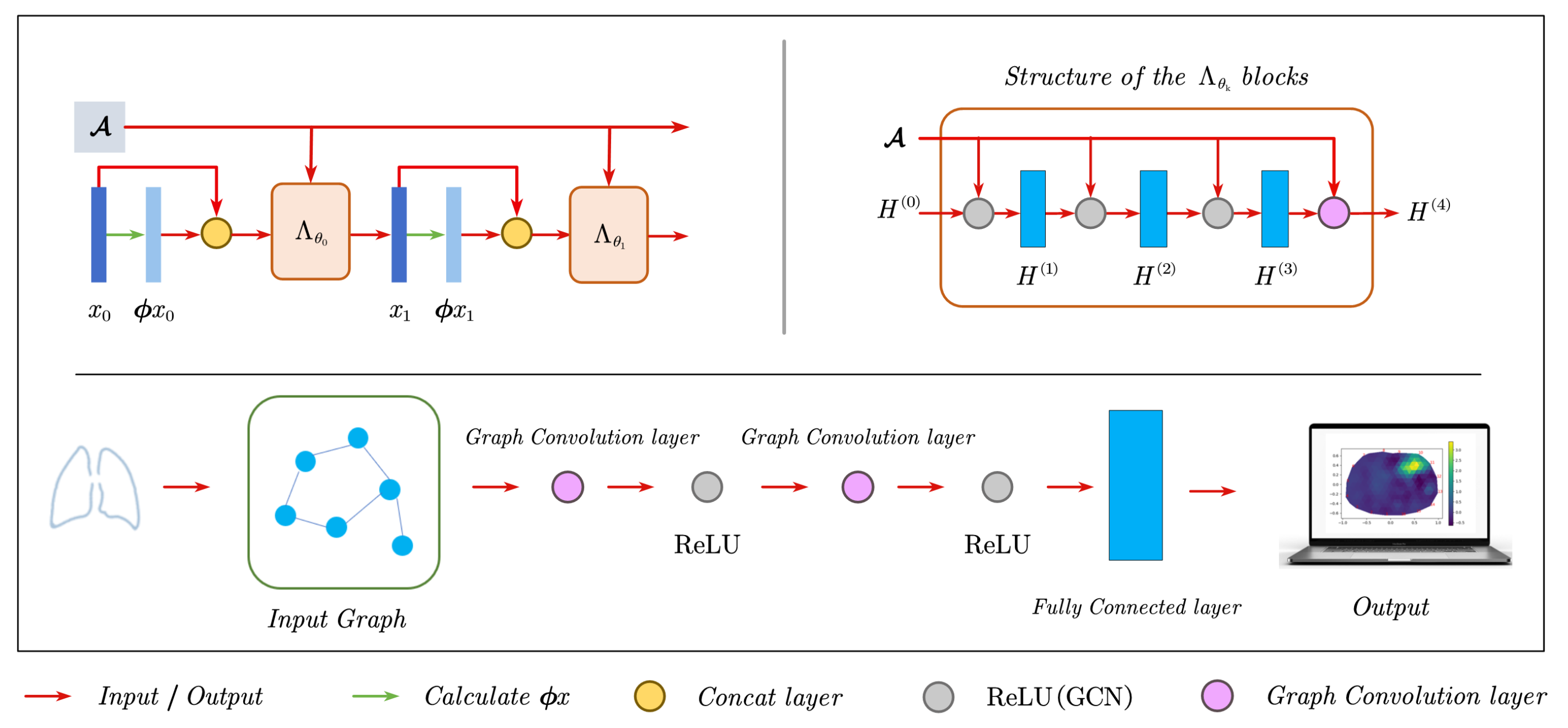
3.2. Graph Convolutional Neural Networks
4. Method
4.1. EIT Inverse Model
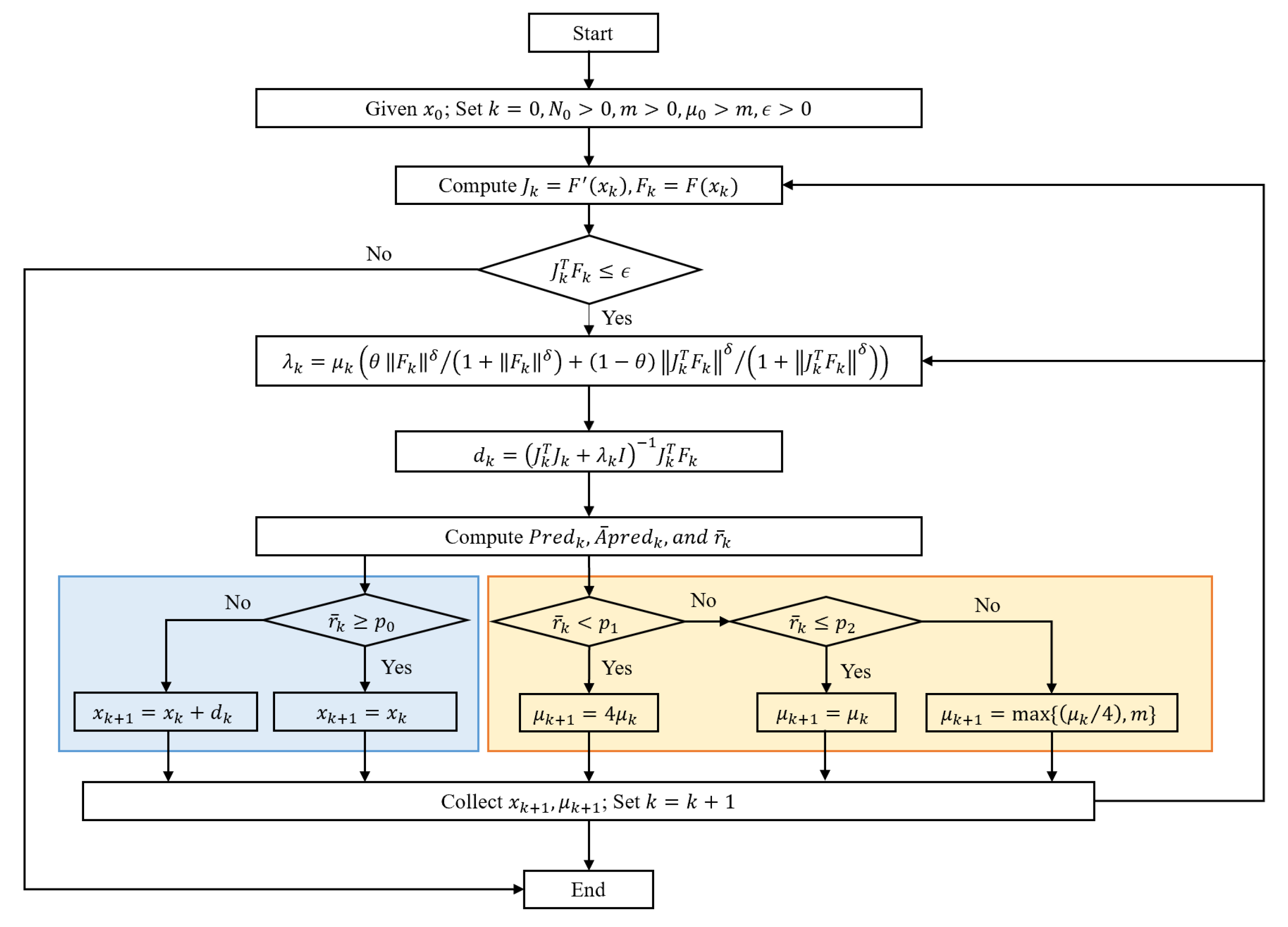
4.1.1. Improved Levenberg–Marquardt Method
4.1.2. Regularized Gauss–Newton
4.2. Metrics
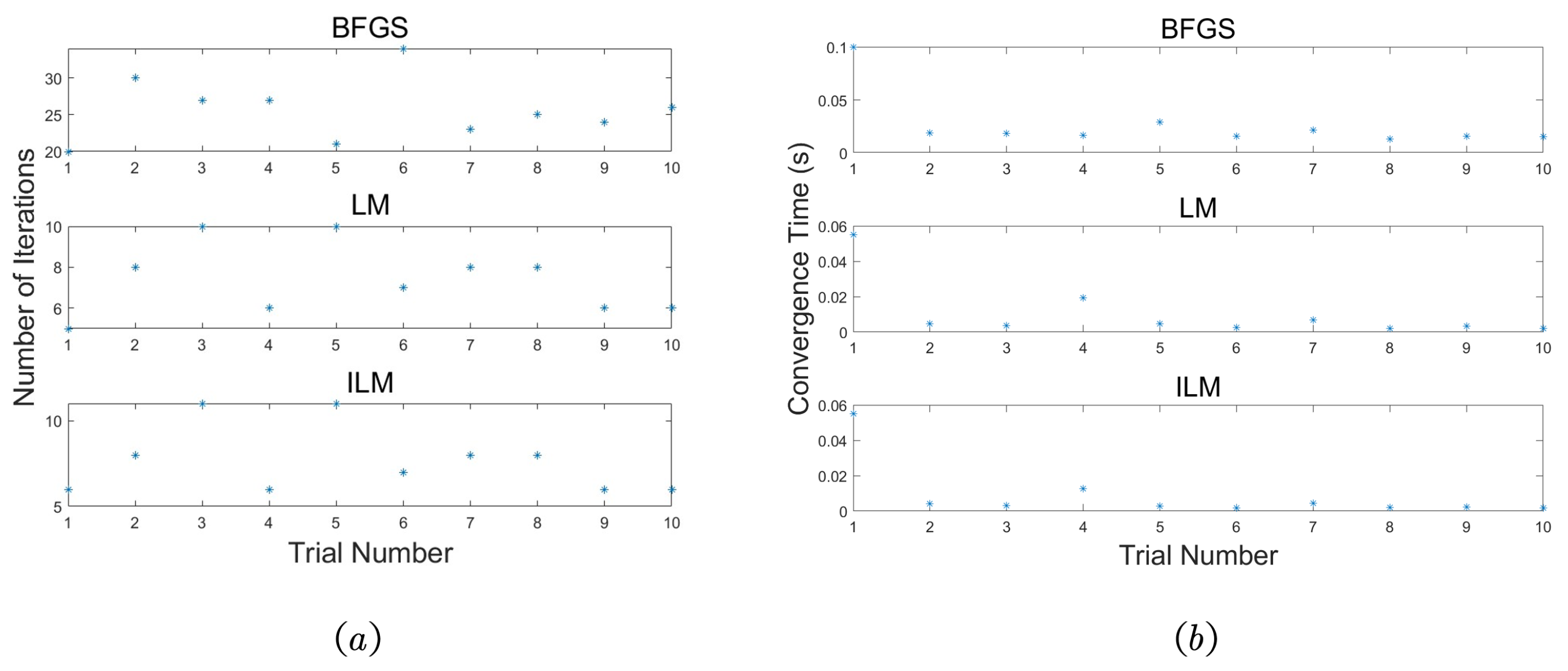
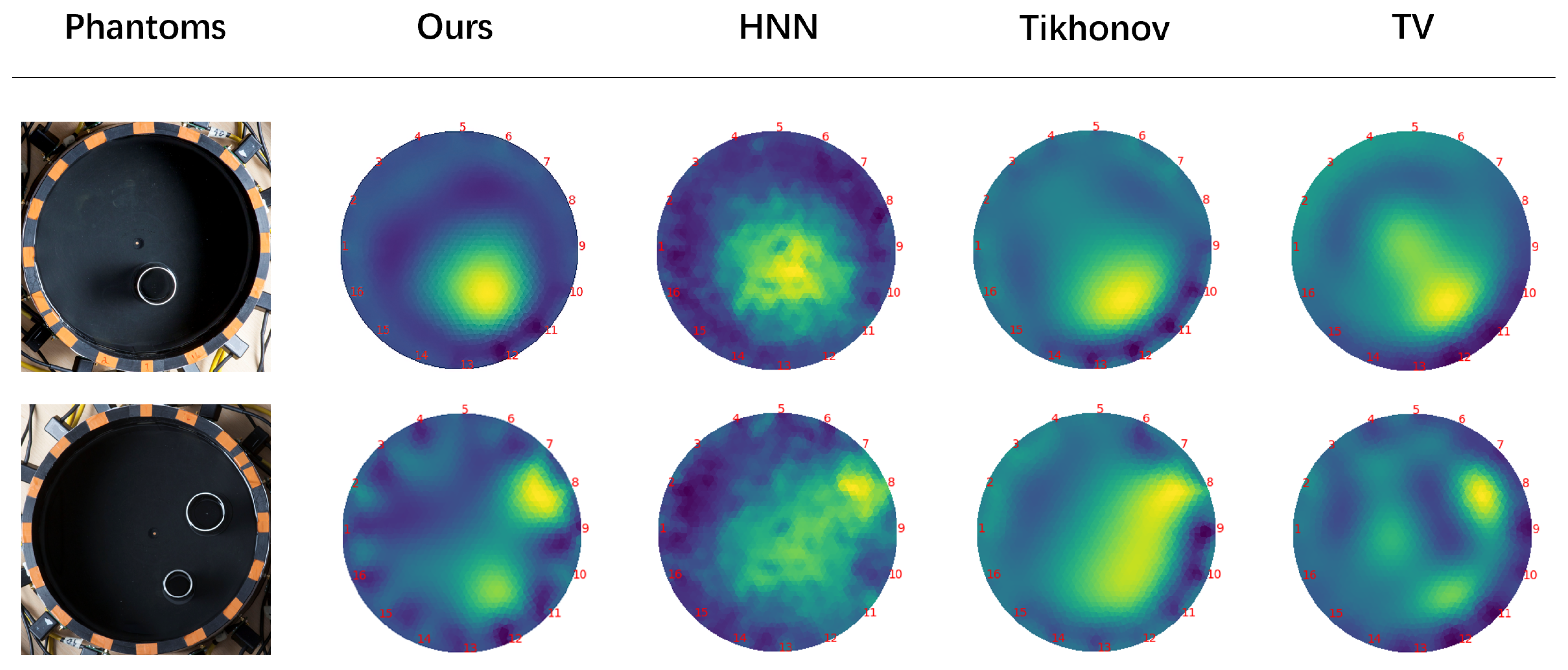
5. Experiment and Analysis
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adler, A.; Boyle, A. Electrical impedance tomography: Tissue Properties to image measures. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 64, 2494–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benning, M.; Burger, M. Modern regularization methods for inverse problems. Acta Numer. 2018, 27, 1–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, J.; Öktem, O. Solving ill-posed inverse problems using iterative deep neural networks. Inverse Probl. 2017, 33, 124007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harikumar, R.; Prabu, R.; Raghavan, S. Electrical impedance tomography (EIT) and its medical applications: A review. Int. J. Soft Comput. Eng 2013, 3, 193–198. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.D.; Soleimani, M. Capacitively Coupled Electrical Impedance Tomography for Brain Imaging. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 38, 2104–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bader, O.; Hafsa, M.; Amara, N.E.B.; Kanoun, O. Two-dimensional forward modeling for human thorax imaging based on electrical impedance tomography. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Workshop on Impedance Spectroscopy (IWIS), Chemnitz, Germany, 29 September–1 October 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 114–117. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Dong, X. Advancements in electrical impedance tomography and its clinical applications. High Volt. Eng. 2014, 40, 3738–3745. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Q.; Zhang, Y.; He, Q.; Xu, C.; Pan, X. Image reconstruction method for electrical impedance tomography based on RBF and attention mechanism. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2023, 110, 108826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrabuska, R.; Prauzek, M.; Venclikova, M.; Konecny, J. Image reconstruction for electrical impedance tomography: Experimental comparison of radial basis neural network and Gauss–Newton method. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2018, 51, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vauhkonen, M.; Vadász, D.; Karjalainen, P.A.; Somersalo, E.; Kaipio, J.P. Tikhonov regularization and prior information in electrical impedance tomography. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1998, 17, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsic, A.; Graham, B.M.; Adler, A.; Lionheart, W.R. In vivo impedance imaging with total variation regularization. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2009, 29, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, V.; Recht, B.; Parrilo, P.A.; Willsky, A.S. The convex geometry of linear inverse problems. Found. Comput. Math. 2012, 12, 805–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Pei, Y.; Dong, F. An adaptive Tikhonov regularization parameter choice method for electrical resistance tomography. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2016, 50, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Sun, J. A new approach to solve inverse problems: Combination of model-based solving and example-based learning. Sci. Sin. (Math.) 2017, 47, 1345–1354. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Ma, G.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, B.; Soleimani, M. Application of deep neural network to the reconstruction of two-phase material imaging by capacitively coupled electrical resistance tomography. Electronics 2021, 10, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Bin, G.; Wu, S. Comparative study on reconstruction methods of electrical impedance tomography. China Med. Devices 2022, 37, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, T.D.C.; Sato, A.K.; Moura, F.S.D.; de Camargo, E.D.L.B.; Tsuzuki, M.D.S.G. A Review of Electrical Impedance Tomography in Lung Applications: Theory and Algorithms for Absolute Images. Annu. Rev. Control 2019, 48, 442–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, A.; Arnold, J.H.; Bayford, R.; Borsic, A.; Brown, B.; Dixon, P.; Faes, T.J.; Frerichs, I.; Gagnon, H.; Gärber, Y.; et al. GREIT: A unified approach to 2D linear EIT reconstruction of lung images. Physiol. Meas. 2009, 30, S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Jiang, J. Construct Deep Neural Networks based on Direct Sampling Methods for Solving Electrical Impedance Tomography. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 2021, 43, B678–B711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Jia, J.; Zhang, Y.D.; Yang, Y. Image reconstruction in electrical impedance tomography based on structure-aware sparse Bayesian learning. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 2090–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzberg, W.; Rowe, D.B.; Hauptmann, A.; Hamilton, S.J. Graph convolutional networks for model-based learning in nonlinear inverse problems. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2021, 7, 1341–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.K.; Kim, K.C.; Jargal, A.; Lee, K.; Harrach, B. A Learning-Based Method for Solving Ill-Posed Nonlinear Inverse Problems: A Simulation Study of Lung EIT. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 2019, 12, 1275–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauhiainen, J.; Kuusela, P.; Seppanen, A.; Valkonen, T. Relaxed Gauss–Newton methods with applications to electrical impedance tomography. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 2020, 13, 1415–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, Y. Multimodal Image Reconstruction of Electrical Impedance Tomography Using Kernel Method. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayford, R.H. Bioimpedance tomography (electrical impedance tomography). Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 8, 63–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fessler, J.A. Model-based image reconstruction for MRI. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2010, 27, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Zhong, H.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, L.; Wang, H. Calderón’s Method-Guided Deep Neural Network for Electrical Impedance Tomography. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Ying, L. Solving electrical impedance tomography with deep learning. J. Comput. Phys. 2020, 404, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wei, Z. A review of algorithms and hardware implementations in electrical impedance tomography. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2020, 169, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, J.; Isaacson, D.; Mueller, J. Electrical Impedance Tomography. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2002, 21, 553–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gernandt, H.; Rohleder, J. A Calderón type inverse problem for tree graphs. Linear Algebra Its Appl. 2022, 646, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.; Khan, T.R.; Maass, P. A reconstruction algorithm for electrical impedance tomography based on sparsity regularization. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2012, 89, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, A.; Lionheart, W.R.B. Uses and abuses of EIDORS: An extensible software base for EIT. Physiol. Meas. 2006, 27, S25–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kipf, T.N.; Welling, M. Semi-Supervised Classification with Graph Convolutional Networks. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1609.02907. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Cui, G.; Hu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, C.; Sun, M. Graph neural networks: A review of methods and applications. AI Open 2020, 1, 57–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Pan, S.; Chen, F.; Long, G.; Zhang, C.; Yu, P.S. A Comprehensive Survey on Graph Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 32, 4–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, A.; Iliadis, M.; Molina, R.; Katsaggelos, A.K. Using deep neural networks for inverse problems in imaging: Beyond analytical methods. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2018, 35, 20–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulakala, R.; Markert, B.; Stoffel, M. Graph Neural Network enhanced Finite Element modelling. PAMM 2023, 22, e202200306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifnaraghi, N.; De Gelidi, S.; Nordebo, S.; Kallio, M.; Frerichs, I.; Tizzard, A.; Suo-Palosaari, M.; Sophocleous, L.; van Kaam, A.H.; Sorantin, E.; et al. Model selection based algorithm in neonatal chest EIT. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 68, 2752–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proença, M.; Braun, F.; Solà, J.; Thiran, J.P.; Lemay, M. Noninvasive pulmonary artery pressure monitoring by EIT: A model-based feasibility study. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2017, 55, 949–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J. Accelerating the modified Levenberg-Marquardt method for nonlinear equations. Math. Comput. 2014, 83, 1173–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilamowski, B.M.; Yu, H. Improved Computation for Levenberg–Marquardt Training. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2010, 21, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.L.; Liao, L.Z.; Wah Tam, H. Convergence analysis of the Levenberg–Marquardt method. Optim. Methods Softw. 2007, 22, 659–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Huang, J.; Pan, J. An adaptive multi-step Levenberg–Marquardt method. J. Sci. Comput. 2019, 78, 531–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Li, S.; Fairbank, M.; Wunsch, D.C.; Alonso, E. Training recurrent neural networks with the Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm for optimal control of a grid-connected converter. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2014, 26, 1900–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.; Ma, C. The Modulus-Based Levenberg-Marquardt Method for Solving Linear Complementarity Problem. Numer. Math. Theory Methods Appl. 2019, 12, 154–168. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Yang, H. A Discretizing Levenberg-Marquardt Scheme for Solving Nonlinear Ill-Posed Integral Equations. J. Comput. Math. 2022, 40, 686–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J. The modified levenberg-marquardt method for nonlinear equations with cubic convergence. Math. Comput. 2012, 81, 447–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.y. A modified Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm for singular system of nonlinear equations. J. Comput. Math. 2003, 21, 625–636. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, S.J.; Mueller, J.; Santos, T. Robust computation in 2D absolute EIT (a-EIT) using D-bar methods with the ‘exp’approximation. Physiol. Meas. 2018, 39, 064005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haji, S.H.; Abdulazeez, A.M. Comparison of optimization techniques based on gradient descent algorithm: A review. PalArch’s J. Archaeol. Egypt/Egyptol. 2021, 18, 2715–2743. [Google Scholar]
- Bollapragada, R.; Nocedal, J.; Mudigere, D.; Shi, H.J.; Tang, P.T.P. A progressive batching L-BFGS method for machine learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; pp. 620–629. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, L.; Zhang, F.; Fan, H.; Zhang, C. Brief review of image denoising techniques. Vis. Comput. Ind. Biomed. Art 2019, 2, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
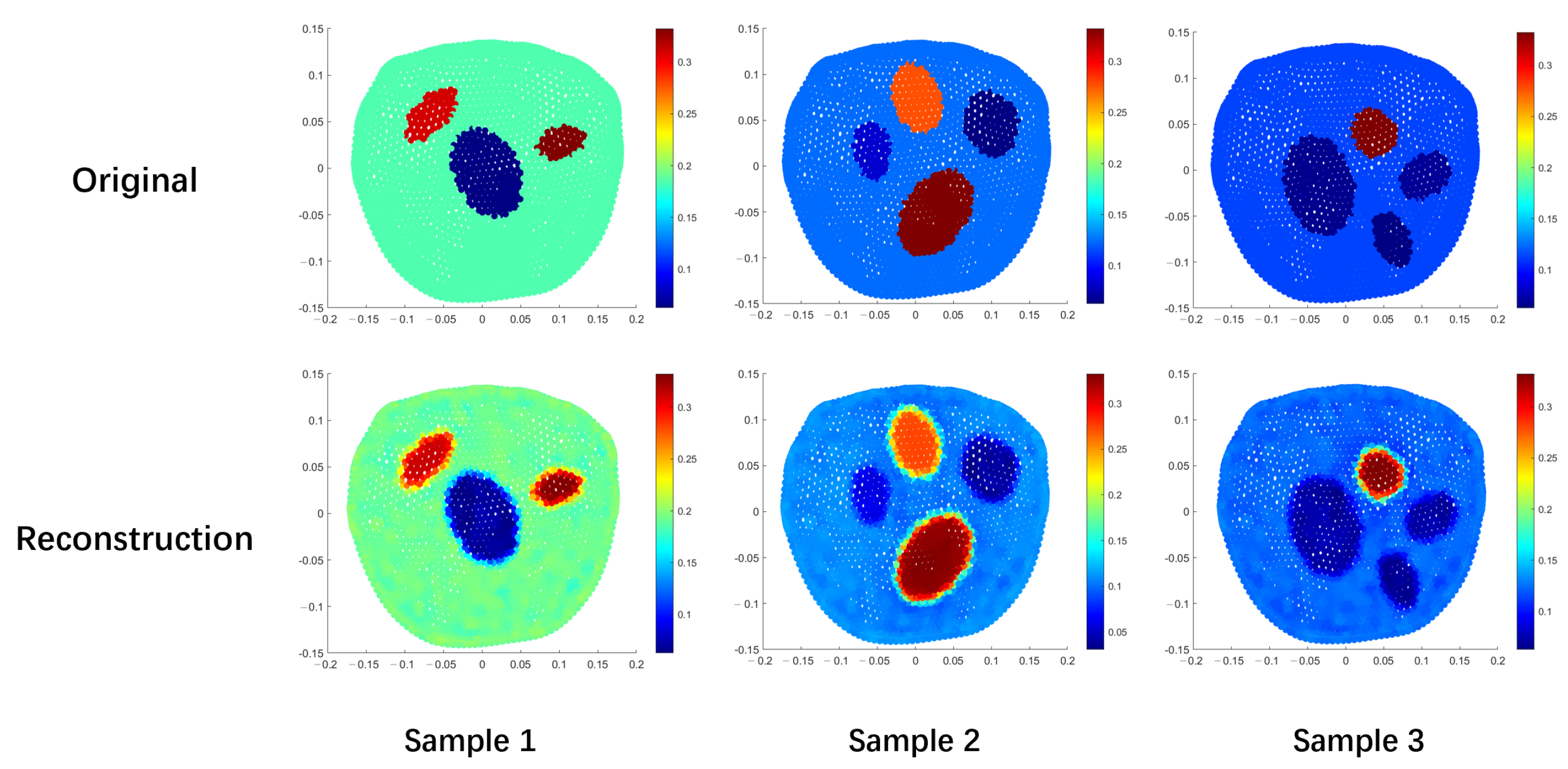
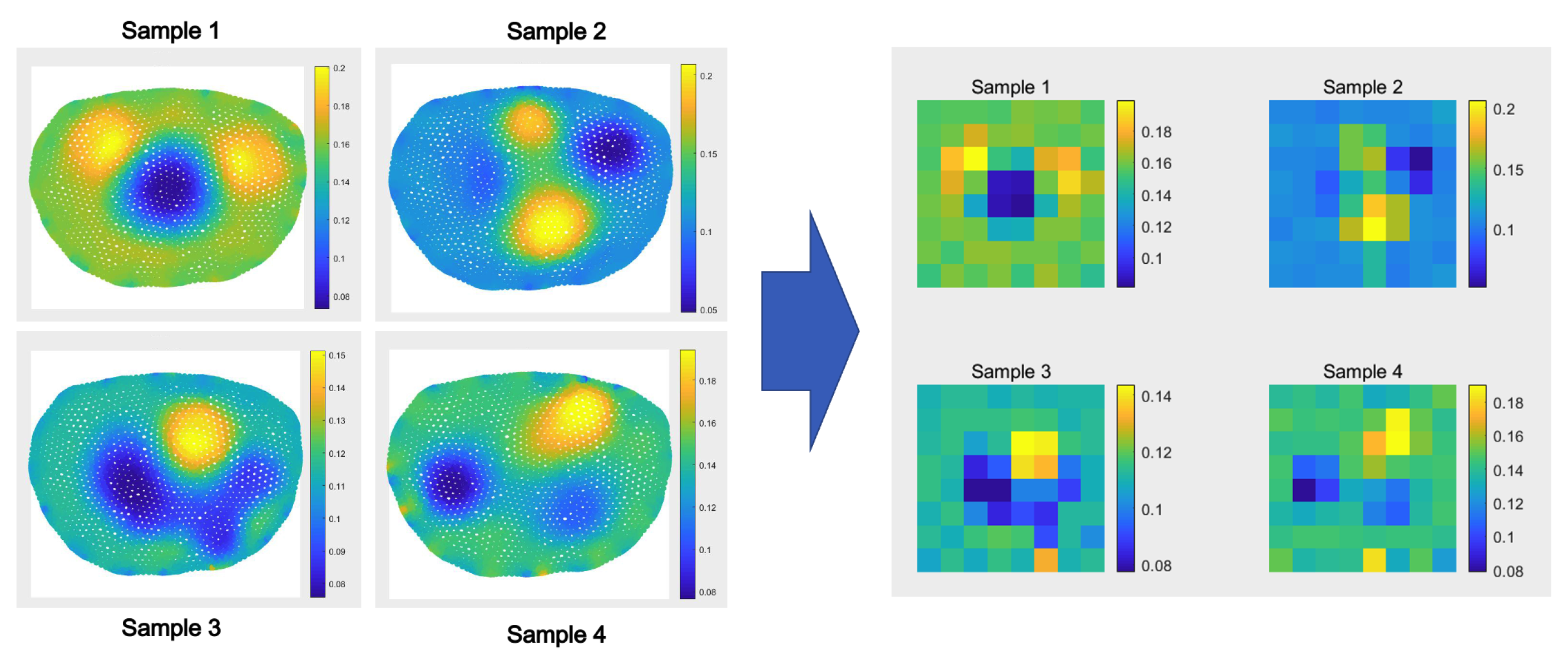
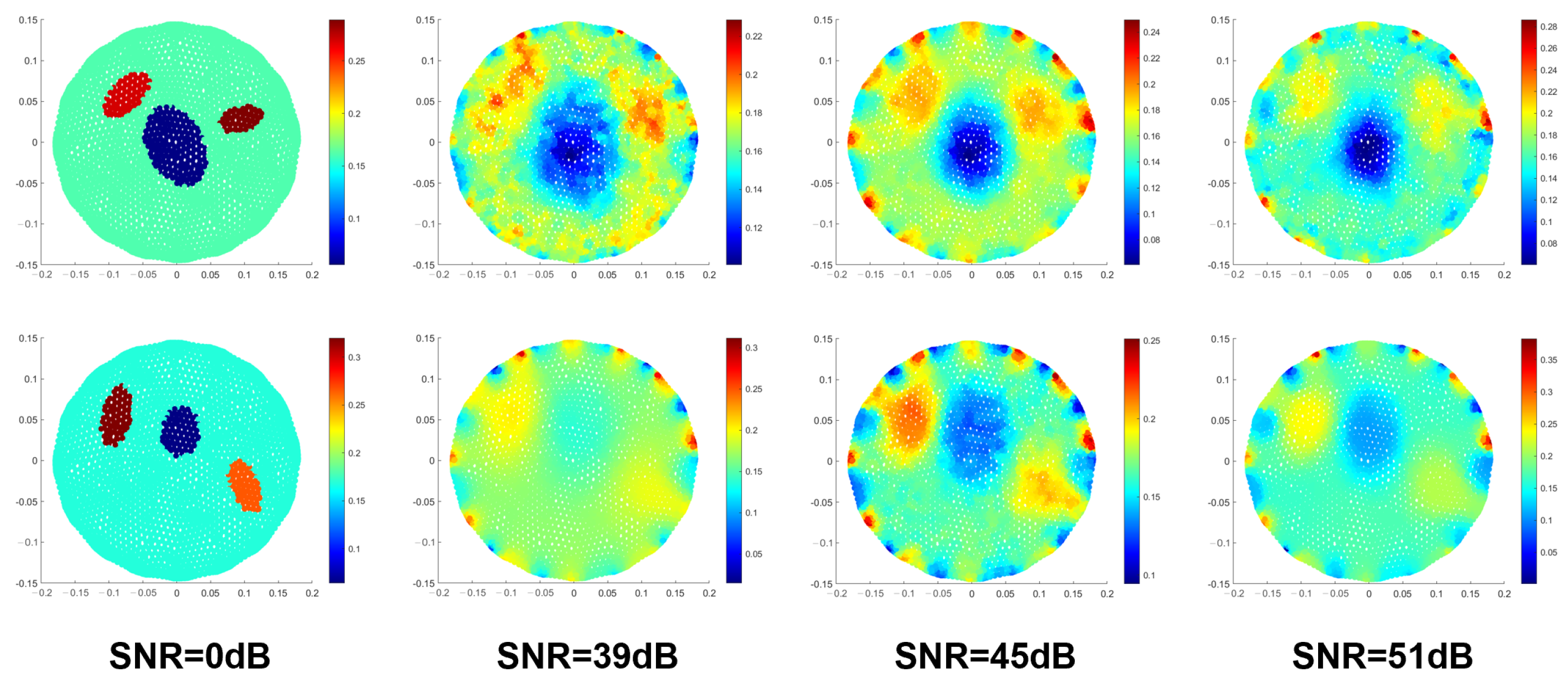
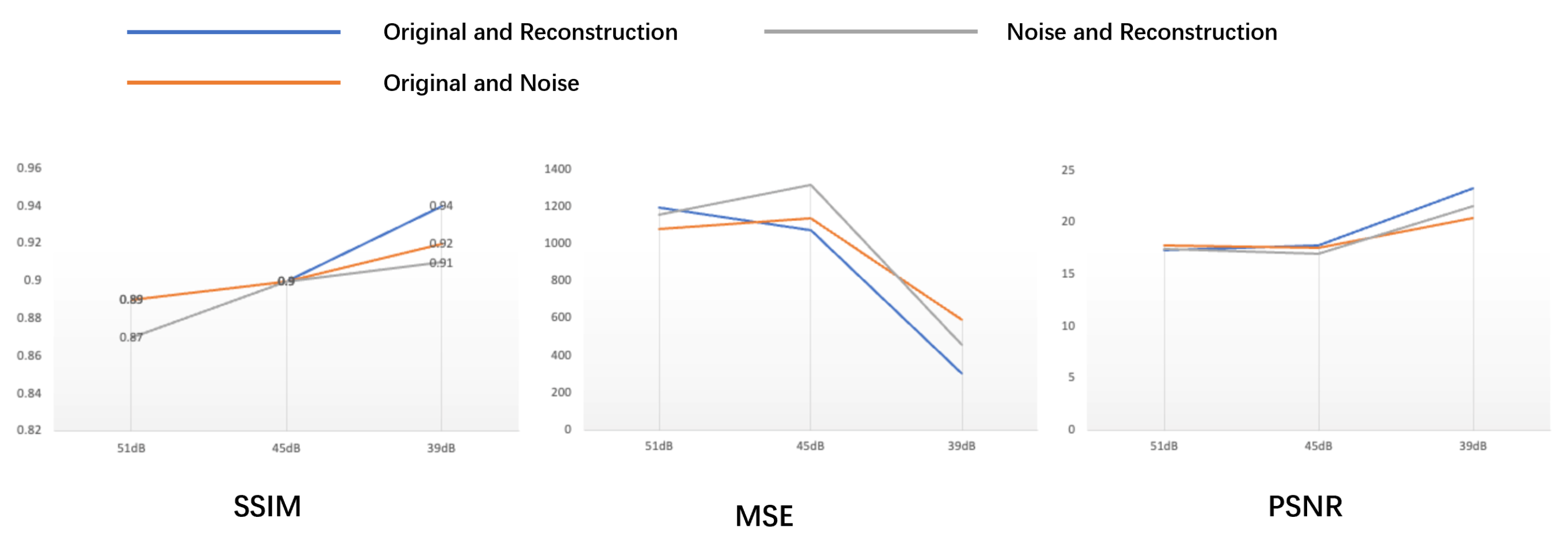
| Sample 1 | Sample 2 | Sample 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MSE | 155.01 | 438.20 | 361.47 |
| PSNR | 26.23 | 21.71 | 22.55 |
| SSIM | 0.97 | 0.93 | 0.94 |
| MSE | PSNR | SSIM | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ours | 1314.36 | 34.7755 | 0.8658 |
| HNN | 938.56 | 33.9552 | 0.8398 |
| Tikhonov | 1073.80 | 34.2260 | 0.8509 |
| TV | 1138.56 | 34.0933 | 0.8465 |
| Ours | 1179.74 | 33.9058 | 0.8594 |
| HNN | 589.62 | 33.8748 | 0.84590 |
| Tikhonov | 1081.04 | 34.0121 | 0.8444 |
| TV | 1156.31 | 33.8860 | 0.8557 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, R.; Xu, C.; Zhu, Z.; Mo, W. A Graph Neural Network Approach with Improved Levenberg–Marquardt for Electrical Impedance Tomography. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14020595
Zhao R, Xu C, Zhu Z, Mo W. A Graph Neural Network Approach with Improved Levenberg–Marquardt for Electrical Impedance Tomography. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(2):595. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14020595
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Ruwen, Chuanpei Xu, Zhibin Zhu, and Wei Mo. 2024. "A Graph Neural Network Approach with Improved Levenberg–Marquardt for Electrical Impedance Tomography" Applied Sciences 14, no. 2: 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14020595
APA StyleZhao, R., Xu, C., Zhu, Z., & Mo, W. (2024). A Graph Neural Network Approach with Improved Levenberg–Marquardt for Electrical Impedance Tomography. Applied Sciences, 14(2), 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14020595






