Mars In Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU) with Focus on Atmospheric Processing for Near-Term Application—A Historical Review and Appraisal
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Place the relatively mature MOXIE technology advance and solid oxide electrolysis in general in perspective to the historical evolution of low TRL Mars ISRU technology.
- Provide a summary of advances in Mars ISRU technology since the 1990s.
- Develop a perspective of how the MOXIE Project relates to other advances in Mars ISRU technology.
- Review the accomplishments of MOXIE and follow-on work, and identify technical issues left incomplete for Mars ISRU.
- Suggest further work needed to fill the gaps left by MOXIE, as well as additional opportunities in solid-oxide electrochemical cell (SOEC) technology.
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
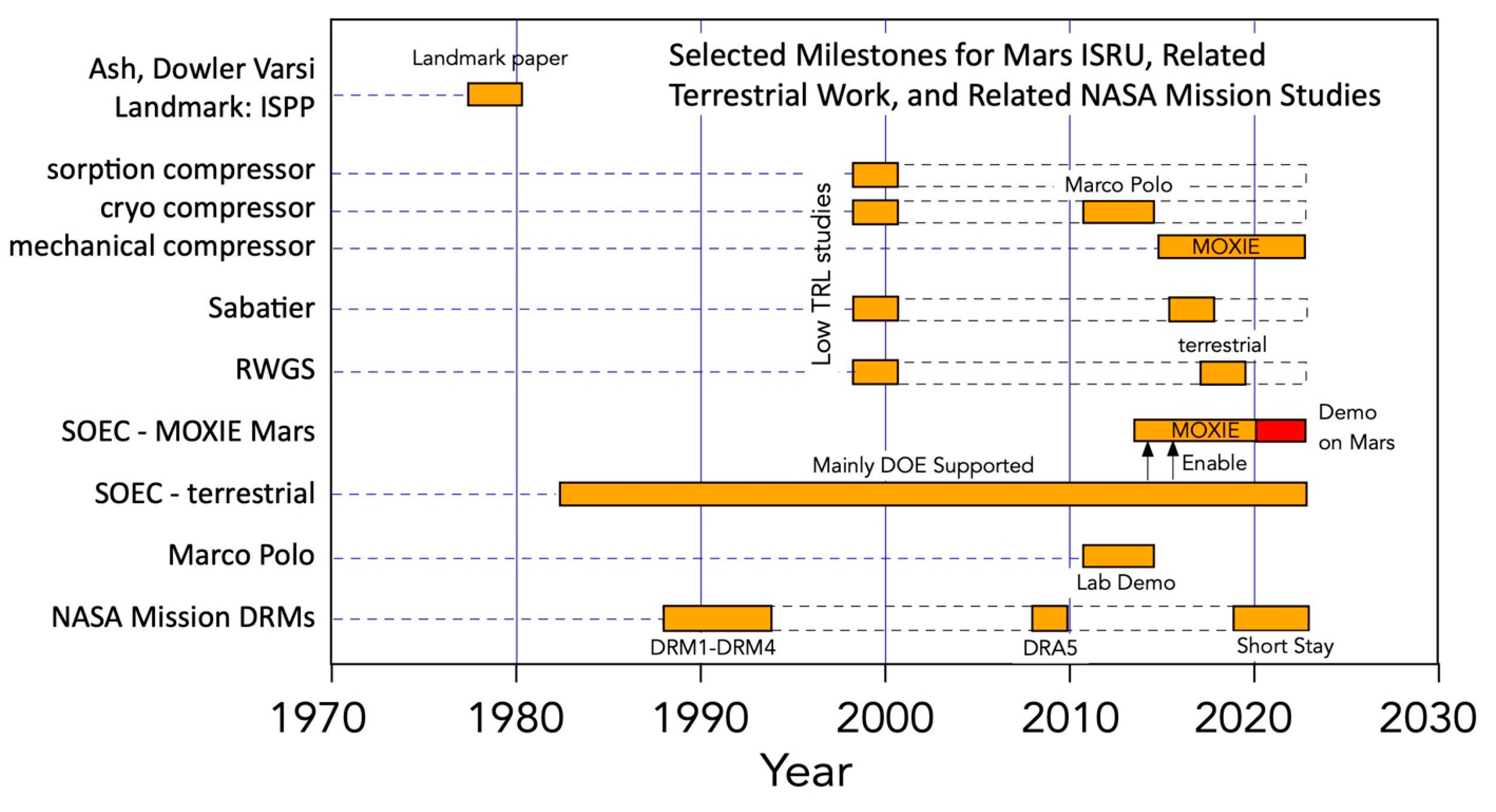
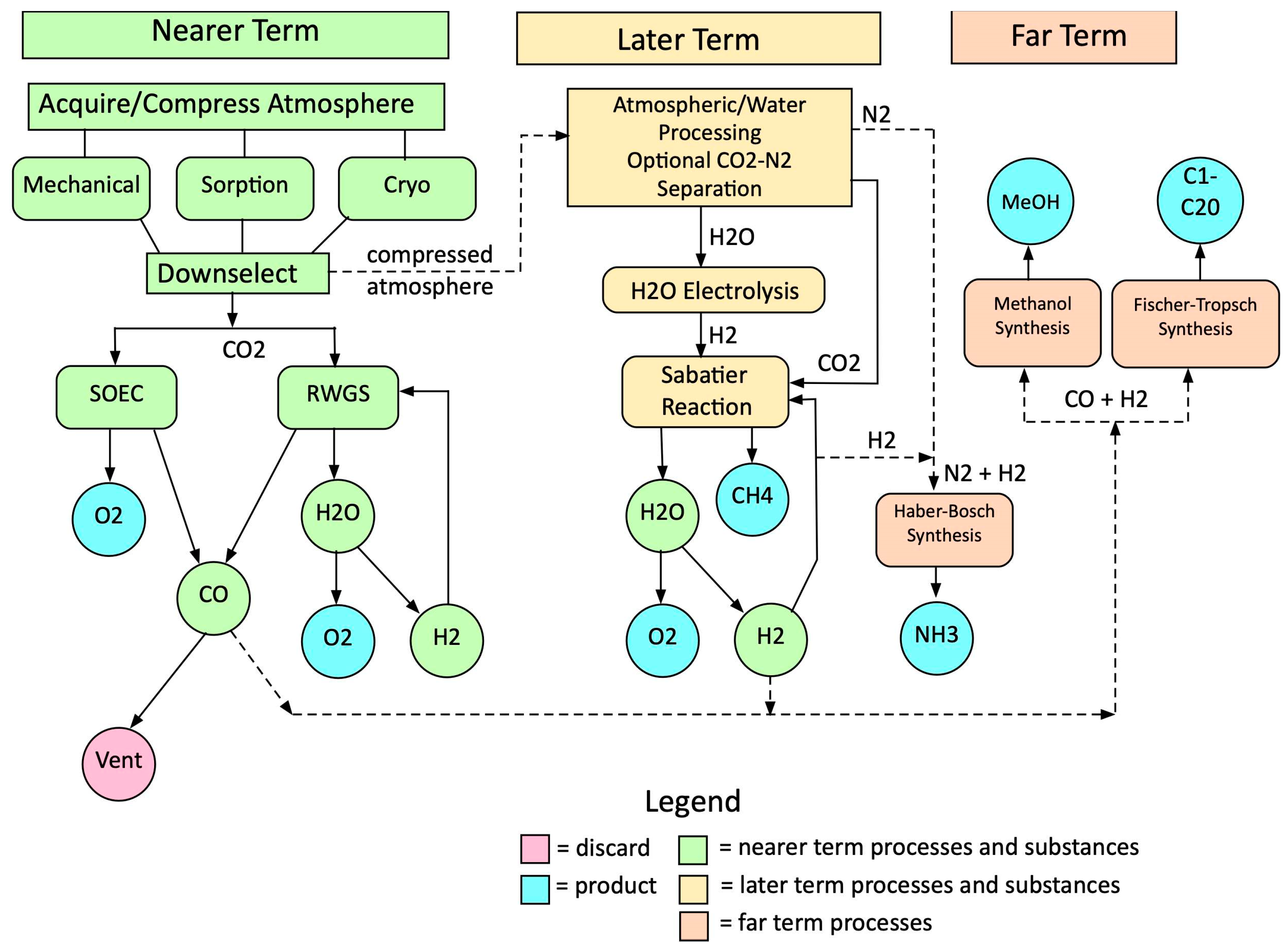
3.1. Overview of Mars ISRU Technologies
3.2. Advances in Mars ISRU Technology 1996–2014
- A small grant to test a cell for SOEC of CO2 [17]. This device utilized Pt electrodes and produced oxygen at TRL 2. Funds were not available to continue the work.
- An experimental study of a Sabatier reactor that achieved very high conversion [18]. This work was complete at TRL 4. Oddly, two NASA studies about 18 years later did not refer to this work.
- Joint JPL-Lockheed-Martin Astronautics (LMA) development of a sorption compressor [19]. A large sorption compressor was built and tested but the results did demonstrate that this approach had great merit in terms of power efficiency.
- Several JPL chemical engineers demonstrated methane reforming with excellent conversion at TRL 3 [20]. The Sabatier process produces excess methane.
- CO2 compression by freezing at TRL 3 [23]. Compression by freezing remains a possibility for the future.
3.3. Advances in Terrestrial Energy Technology by DOE and the International Community Relevant to Mars ISRU
3.4. The MOXIE Project (2014–2023)
- Demonstrated production of oxygen on Mars up to ~12 g/h;
- Produced oxygen purity of ~100% with anode pressure > cathode pressure;
- Produced oxygen at low Mars temperature in early hours after midnight and warm Mars temperature in early afternoon in all seasons;
- Demonstrated low rate of degradation through more than 20 thermal cycles;
- Demonstrated a mechanical compressor to acquire Mars atmospheric gas.
- Demonstrated sealed stacks of cells that could electrolyze essentially pure CO2 without oxidation of the electrodes or reduction of product CO—a new first;
- Demonstrated that the Flight Model MOXIE on Mars was essentially identical in performance to the Engineering Model MOXIE in Lab. This was a major observation that showed that operation on Mars could be replicated in the lab on Earth;
- Explored the relationship between stack voltage and current (oxygen production rate was explored extensively);
- The intrinsic area-specific cell resistance (iASR) was evaluated over a wide range of operating settings and iASR was found to be small enough to allow efficient full-scale operation with such stacks;
- By comparing iASR from Mars run to Mars run, it was demonstrated that degradation due to thermal cycling was well within acceptable limits;
- Carried out extensive testing and analysis of filters for Martian dust and determined that dust removal in a full-scale Mars ISRU could be achieved with a reasonably sized filter system.
3.5. Advances in SOEC beyond MOXIE (2017–2023)
- Scaled up the active area of cells from 22.7 cm2 to 100 cm2;
- Assembled a 65-cell stack (MOXIE stacks were limited to 10 cells);
- Demonstrated use of the stack for electrolysis of CO2, CO2 + H2O, or H2O.
3.6. Issues Remaining after MOXIE
- (1)
- Lack of measurement of degradation due to long-term steady state operation. It is expected that a full-scale Mars ISRU would operate for about 10,000 h in a steady state without interruption, except for rare shutdowns. MOXIE did not generate data on the degradation of the stack or the compressor for such long-term operation. MOXIE did acquire considerable data on stack degradation of efficiency due to thermal cycling aftershort duration runs, but the connection between degradation from long-term operation and thermal cycling remains unclear. OxEon Energy LLC recently carried out some studies of degradation due to steady operation, but a significant gap remains regarding degradation from 10,000 h of operation. The compressor for MOXIE was not designed for long life and no data are available on long duration testing.
- (2)
- Uncertain quality control from stack to stack. MOXIE produced eleven approximately equivalent stacks. Stacks were characterized by (1) the absolute stack intrinsic area-specific resistance (iASR), (2) the variation in individual cell voltages after manufacture, and (3) leakage between the anode and cathode. The stack with the lowest iASR and lowest range of cell voltages was chosen as the stack that was sent to Mars. The eleven stacks varied widely in the magnitude of the three basic attributes. After MOXIE, OxEon Energy LLC made a point of assembling a large stack of 65 cells, but it is not clear what the variation was from cell-to-cell voltages within that large stack, or how reproducible such stacks can be manufactured.
- (3)
- Role of individual cells in creating the properties of stacks. While measurements on individual cells were made on the eleven MOXIE stacks as manufactured, only very limited measurements were made on stacks after cycling, and we lack data on how the cells contribute to the observed changes in stacks due to cycling (or long-term operation). Of particular interest is how the worst cell (with highest resistance) affects susceptibility to carbon formation. Within a stack, it is possible that non-uniformity in manifolding might contribute significantly to stack variability.
- (4)
- Low cathode pressure operation. The side reaction that limits how high a voltage can be applied to cells for oxygen production involves reduction of CO to carbon. The voltage limit is determined by the Nernst voltage for carbon formation, which increases at lower cathode pressures. It is therefore desirable to operate at lower cathode pressures, permitting higher cell voltage, and therefore higher current density. MOXIE was able to lower the cathode pressure to about 0.22 bar, but we have no data below that pressure. Lower cathode pressure also reduces the power required for compression of Mars gas. This parameter will be important in larger scale system designs.
- (5)
- Acquisition and compression of Mars atmosphere gas. Any Mars ISRU system requires acquisition and compression of Mars atmosphere gas. The simplest, most appealing approach is to use a mechanical compressor which runs continuously. While a prototype mechanical compressor was used successfully on MOXIE, it is not clear what the characteristics of a next generation compressor would be (mass, efficiency, lifetime). Two batch-type systems for acquisition and compression of Mars atmosphere gas based on sorption and cryogenic freezing were studied briefly. In the sorption process, a sorbent at low temperature is open to the atmosphere where it absorbs CO2. Then it is closed off and heated to release CO2 at comparatively very high pressure. In the cryogenic method, CO2 is frozen out using a cryocooler while exposed to the atmosphere and then warmed after closing off, to release CO2 at comparatively very high pressure [19,23,25,26,27,48,49]. These cannot yet be ruled out, pending further development.
- (6)
- How will NASA deal with the legacy of MOXIE? The field of SOEC technology for terrestrial applications is worldwide and funded at much higher levels than NASA could consider. MOXIE demonstrated that this technology is also applicable to Mars ISRU technology. Post-MOXIE activities by OxEon Energy LLC showed that this technology might be applied to lunar ISRU as well via electrolysis of water. MOXIE left behind it a well-equipped state of the art laboratory for testing SOEC devices and systems. It seems likely that NASA could leverage the field of SOEC technology with a relatively small investment, by continuing to adapt advances in terrestrial SOEC technology to space applications. While MOXIE was a small-scale demonstration, Hinterman (2022) developed a detailed model of a full-scale version of MOXIE, including a very detailed analysis of requirements and expected performance of all subsystems. He optimized the design based on mass, power, risk, and ancillary factors [50]. Rapp and Hinterman (2023) tested how Hinterman’s design would perform with several alternative control schemes against 10,000 h of Mars atmospheric data at half-hourly intervals [51]. They evaluated power requirements and determined the most efficient control scheme based on power and avoidance of carbon formation. These results provided further evidence that an extension of MOXIE technology would prove effective on Mars.
3.7. Advances in Other Mars ISRU Technology (2014–2023)
- Did not include dust filtering;
- Utilized the Sabatier process for CH4 and O2 production with water and CO2 as feedstocks;
- Assumed that water-laden soil was available as a source of water.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rapp, D. Human Missions to Mars, 3rd ed.; Springer-Praxis Books; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Portree, D.S.F. Humans to Mars: Fifty Years of Mission Planning, 1950–2000; Monographs in Aerospace History, Series, Number 21; NASA History Division, Office of Policy and Plans; NASA Headquarters: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Platoff, A. Eyes on the Red Planet: Human Mars Mission Planning, 1952–1970, NASA Report, NASA/CR-2001-208928, July 2001. Available online: https://escholarship.org/content/qt0dx7866r/qt0dx7866r_noSplash_0311d690a533bc3c9c94d74fb41c8f3a.pdf?t=nwvlqw (accessed on 29 November 2023).
- Ash, R.L.; Dowler, W.L.; Varsi, G. Feasibility of Rocket Propellant Production on Mars. Acta Astronaut. 1978, 5, 705–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, B.G. (Ed.) Human Exploration of Mars Design Reference Architecture 5.0. NASA Report. 2009. Available online: https://ntrs.nasa.gov/api/citations/20090012109/downloads/20090012109.pdf (accessed on 29 November 2023).
- Sanders, G.; Kleinhenz, J. In Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU) Strategy—Scope, Plans, and Priorities. In Proceedings of the NASA Advisory Council (NAC) Technology Innovation, and Engineering Committee, Washington DC, USA, 15 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hecht, M.H.; Hoffman, J.; Rapp, D. Mars Oxygen ISRU Experiment (MOXIE). Space Sci. Rev. 2021, 217, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rucker, M.A.; Craig, D.A.; Burke, L.M.; Chai, P.R.; Chappell, M.B.; Drake, B.G.; Troutman, P.A. NASA’s Strategic Analysis Cycle 2021 (SAC21) Human Mars Architecture. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Conference Proceedings, Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 5–12 March 2022. Also see Rapp (2023) loc cit. [Google Scholar]
- Rapp, D. Use of Extraterrestrial Resources for Human Space Missions to Moon or Mars, 2nd ed.; Springer-Praxis Books; Also see Rapp (2023) loc cit; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- NASA. Reference Surface Activities for Crewed Mars Mission Systems and Utilization; Document No: HEOMD-415, 1/24/2022; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Starr, S.O.; Muscatello, A.C. Mars in situ resource utilization: A review. Planet Space Sci. 2020, 182, 104824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezdek, M.J.; Chirik, P.J. A fresh approach to ammonia synthesis. Nature 2019, 568, 464–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, P.; Carpenter, J.; Woods, J.; Goberman, D.; Gavin, L.; Garr, J.; Ulrich, B. Poisoning Evaluation of On-Orbit Sabatier Assembly. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Environmental Systems, Changchun, China, 21–23 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Vogt, C.; Monai, M.; Kramer, G.J.; Weckhuysen, B.M. The renaissance of the Sabatier reaction and its applications on Earth and in space. Nat. Catal. 2019, 2, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubrin, R.M.; Muscatello, A.C.; Berggren, M. Integrated Mars In Situ Propellant Production System. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2013, 26, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Interbartolo, M.A.; Sanders, G.B.; Oryshchyn, L.; Lee, K.; Vaccaro, H.; Santiago-Maldonado, E.; Muscatello, A.C. Prototype Development of an Integrated Mars Atmosphere and Soil-Processing System. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2013, 26, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Crow, S.C. The MOXCE Project: New Cells for Producing Oxygen on Mars. In Proceedings of the 33rd Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit, Seattle, WA, USA, 6–9 July 1997; AIAA 97-2766. Available online: https://arc.aiaa.org/doi/abs/10.2514/6.1997-2766 (accessed on 29 November 2023).
- Clark, D.L. In-Situ Propellant Production on Mars: A Sabatier/Electrolysis Demonstration Plant. In Proceedings of the 33rd Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit, Seattle, WA, USA, 6–9 July 1997. AIAA 97-2764. [Google Scholar]
- Rapp, D.; Karlmann, P.; Clark, D.L.; Carr, C.M. Adsorption Pump for Acquisition and Compression of Atmospheric CO2 on Mars. In Proceedings of the 33rd Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit, Seattle, WA, USA, 6–9 July 1997. AIAA 97-2763. [Google Scholar]
- Rapp, D.; Voecks, G.; Sharma, P.; Rohatgi, N. Methane Reforming for Mars Applications. Internal JPL Report, JPL Report D-15560, 30 March 1998. In Proceedings of the Intersociety Energy Conversion Engineering Conference, Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 2–6 August 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Zubrin, R.; Frankie, B.; Kito, T. Mars In-Situ Resource Utilization Based on the Reverse Water Gas Shift. In Proceedings of the 33rd AIAA/ASME Joint Propulsion Conference, Seattle, WA, USA, 6–9 July 1997. AIAA-97-2767. [Google Scholar]
- Whitlow, J.E.; Parrish, C.F. Operation, Modeling and Analysis of the Reverse Water Gas Shift Process. In Space Technology and Applications Int. Forum-STAIF 2003: Conf. on Thermophysics in Microgravity; Commercial/Civil Next Generation Space Transportation; Human Space Exploration. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings; American Institute of Physics: College Park, MD, USA, 2003; Volume 654, pp. 1116–1123. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, D.L.; Payne, K. CO2 Collection and Purification System for Mars; AIAA 2001-4660; AIAA: Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Adan-Plaza, S.; Carpenter, K.; Elias, L. Extraction of Atmospheric Water on Mars. HEDS-UP Mars Exploration Forum, January 1998. Available online: https://marspapers.org/paper/MAR98062.pdf (accessed on 29 November 2023).
- Brooks, K.P.; Rassat, S.D.; TeGrotenhuis, W.E. Development of a Microchannel ISPP System PNNL Report, PNNL-15456, September 2005. Available online: https://www.osti.gov/biblio/859429 (accessed on 29 November 2023).
- Holladay, J.D.; Brooks, K.P.; Wegeng, R.; Hua, J.; Sanders, J.; Baird, S. Microreactor development for Martian in situ propellant production. Catal. Today 2007, 120, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrell, R.C. Microchannel ISPP as an Enabling Technology for Mars Architecture Concepts; AIAA 2007-6055; AIAA: Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hauch, A.; Kungas, R.; Blennow, P. Recent advances in solid oxide cell technology for electrolysis. Science 2020, 370, eaba6118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebbesen, S.D.; Mogensen, M. Electrolysis of carbon dioxide in Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cells. J. Power Sources 2009, 193, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, J.E.; Stoots, C.M.; Herring, J.S. Hydrogen production performance of a 10-cell planar solid-oxide electrolysis stack. J. Fuel Cell Sci. Technol. 2006, 3, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herring, J.S.; O’Brien, J.; Stoots, C.M. Progress in high-temperature electrolysis for hydrogen production using planar SOFC technology. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2007, 32, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoots, C.; O’Brien, J.; Hartvigsen, J. Results of recent high temperature co-electrolysis studies at the Idaho National Laboratory. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 4208–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Yang, K.R.; You, Z. Catalytic manganese oxide nanostructures for the reverse water gas shift reaction. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 16677–16688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Song, C. Recent Advances in Supported Metal Catalysts and Oxide Catalysts for the Reverse Water- Gas Shift Reaction China Postdoctoral Science Foundation. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindenthal, L.; Popovich, J.; Rameshan, R. Novel perovskite catalysts for CO utilization—Exsolution enhanced reverse water-gas shift activity. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2021, 292, 120183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mine, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Ting, K.W. Reverse water-gas shift reaction over Pt/MoO/TiO: Reverse Mars-van Krevelen mechanism via redox of supported MoOx. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2021, 11, 4172–4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubrin, R.M.; Bergren, M.H. Demonstration of a Piloted Mars Mission Scale RWGS System. In Proceedings of the Space Resource Roundtable, Colorado School of Mines, Golden, CO, USA, 12 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- McClean, J.B.; Hoffman, J.A.; Hecht, M.H. Pre-landing plans for Mars Oxygen In-Situ Resource Utilization Experiment (MOXIE) science operations. Acta Astronaut. 2022, 192, 301–313, Lunar and Planetary Science XLVIII (2017). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, J.A.; Hinterman, E.R.; Hecht, M.H.; Rapp, D.; Hartvigsen, J.J. Hartvigsen 18 Months of MOXIE (Mars oxygen ISRU experiment) operations on the surface of Mars—Preparing for human Mars exploration. Acta Astronautica. 2022, 210, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, J.A.; Hecht, M.H.; Rapp, D. Mars Oxygen ISRU Experiment (MOXIE)—Preparing for human Mars exploration. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabp8636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClean, J.B.; Merrison, J.B.; Iversen, J.J. Testing the Mars 2020 Oxygen In-Situ Resource Utilization Experiment (MOXIE) Hepa Filter and Scroll Pump In Simulated Mars Conditions. In Proceedings of the Lunar and Planetary Science XLVIII, The Woodlands, TX, USA, 20–24 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hollist, M.; Larsen, D.; Gomez, A. Scale Up and Coupling of the MOXIE Solid Oxide Electrolyzer for Mission-Scale Lunar and Martian Applications. In Proceedings of the 52nd International Conference on Environmental Systems ICES-2023-297, Calgary, AB, Canada, 16–20 July 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hollist, M.; Elwell, J.; Hartvigsen, J. Mission-Scale MOXIE Development Driven Prospects for ISRU and Atmosphere Revitalization. In Proceedings of the 52nd International Conference on Environmental Systems ICES-2023-297, Calgary, AB, Canada, 16–20 July 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hafen, T.; Rane, T.; Larsen, D. Redox Tolerant Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cathode for CO2 and Steam. ECS Trans. 2023, 111, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pike, J.; Larsen, D.; Hafen, T. Reversible SOFC/SOEC System Development and Demonstration. ECS Trans. 2023, 111, 1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myung, J.; Neagu, D.; Miller, D.N. Switching on electrocatalytic activity in solid oxide cells. Nature 2016, 537, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neagu, D.; Irvine, J.T.S.; Wang, J. Roadmap on exsolution for energy applications. Phys. Energy 2023, 5, 031501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscatello, A.C.; Devor, R.; Captain, J. Atmospheric Processing Module for Mars Propellant Production. Earth Space 2014, 2014, 444–454. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, J.; Iannetti, A. Experimental Design and Preliminary Analysis of a Mars CO2 Rapid Cycle Adsorption Pump. In Proceedings of the Space Resource Roundtable, Colorado School of Mines, Golden, CO, USA, 11 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hinterman, E. Multi-Objective System Optimization of a Mars Atmospheric ISRU Plant. Ph.D. Dissertation, MIT, Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Cambridge, MA, USA, June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Rapp, D.; Hinterman, E. Adapting a Mars ISRU System to the Changing Mars Environment. Space Sci. Technol. 2023, 3, 0041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscatello, A.C. Atmospheric Capture on Mars (and Processing). In Proceedings of the Technology and Future of ISRU Seminar, Orlando, FL, USA, 27 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.A. Water Electrolysis for In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU). In Proceedings of the 2016 Annual Technical Symposium, Houston, TX, USA, 6 May 2016. JSC Report CN-35703. [Google Scholar]
- Meier, A.J.; Shah, M.; Hintze, P.; Petersen, E.; Muscatello, A. Mars Atmospheric Conversion to Methane and Water: An Engineering Model of the Sabatier Reactor with Characterization of Ru/Al2O3 for Long Duration Use on Mars. In Proceedings of the 47th International Conference on Environmental Systems ICES-2017-161, Charleston, SC, USA, 16–20 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hintze, P.E.; Meyer, A.J.; Malay, G.S. Sabatier System Design Study for a Mars ISRU Propellant Production Plant. In Proceedings of the 48th International Conference on Environmental Systems ICES-2018-155 8-12, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 8 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Franco, C.; Devor, R.W.; Snyder, S.J. Study of Sabatier Catalyst Performance for a Mars ISRU Propellant Production Plant. In Proceedings of the 49th International Conference on Environmental Systems, Boston, MA, USA, 7–11 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, J.; Iannetti, A.; Hasseeb, H. Hasseeb Experimental Configuration and Preliminary Results of Testing a Rapid Cycle Adsorption Pump for Martian CO2 Acquisition. In Proceedings of the 49th International Conference on Environmental Systems ICES-2019-40, Boston, MA, USA, 7–11 July 2019; Available online: https://ttu-ir.tdl.org/items/63158992-564a-4514-b9cc-92842ea16ecd (accessed on 29 November 2023).
- Ermanoski, I. Breathing Mars Air: Stationary and Portable O2 Generation. NASA Phase I Selection. 2022. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/directorates/spacetech/niac/2022/Breathing_Mars_Air/#:~:text=Ivan%20Ermanoski,-Arizona%20State%20University&text=We%20propose%20to%20evaluate%2C%20computationally,other%20breakthrough%20performance%20improve%2Dments (accessed on 29 November 2023).
- Guerra, V.; Silva, T.; Pinhão, N.; Guaitella, O.; Guerra-Garcia, C.; Peeters, F.J.J.; Tsampas, M.N.; van de Sanden, M.C.M. Plasmas for in situ resource utilization on Mars: Fuels, life support, and agriculture. J. Appl. Phys. 2022, 132, 070902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscatello; Anthony, C.; Santano-Maldonado, E. Mars in Situ Resource Utilization Technology Evaluation. In Proceedings of the 50th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting, Nashville, TN, USA, 9–12 January 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Muscatello, A.; Devor, R.; Captain, J. Mars Atmosphere and Regolith Collector/Processor for Lander Ops (MARCO POLO) Atmospheric Processing Module. (MARCO POLO APM). 2014. Available online: https://techport.nasa.gov/view/16846 (accessed on 29 November 2023).
- Werkheiser, N.; Sanders, G.B. In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU) Overview. In Proceedings of the NASA Advisory Council (NAC) Technology Innovation, and Engineering Committee, 15 May 2023; NASA Headquarters: Washington, DC, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Sanders, G.B.; Kleinhenz, J.E. Update on NASA ISRU Plans, Priorities, and Activities. Luxembourg Space Resources Week. 2023. Available online: https://ntrs.nasa.gov/api/citations/20230004027/downloads/Update%20on%20NASA%20ISRU%20Plans%20Priorities%20and%20Activities_Sanders_V1.pdf (accessed on 29 November 2023).
- Kleinhenz, J.; Paz, A.; Mueller, R. Benefits of Mars ISRU Regolith Water Processing: A case study for the NASA Evolvable Mars Campaign. In Proceedings of the Space Resource Roundtable, Colorado School of Mines, Golden, CO, USA, 7 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, S.; Andrews, A.; Watts, K. “Mining” Water Ice on Mars: An Assessment of ISRU Options in Support of Future Human Missions. 2016. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/wp-content/uploads/2015/06/mars_ice_drilling_assessment_v6_for_public_release.pdf (accessed on 29 November 2023).
- Susante, P.J.; Jeffrey, S.T.; Eisele, T.C. Water Extraction from Rock Gypsum on Mars. Proceedings Earth and Space Science 2021, 15 April 2021. Available online: https://ascelibrary.org/doi/10.1061/9780784483374.061 (accessed on 29 November 2023).
- Putzig, T.; Morgan, G.A.; Bain, Z.M. SWIM Subsurface Water Ice Mapping in the Northern Hemisphere of Mars. In Proceedings of the Space Resource Roundtable, Colorado School of Mines, Golden, CO, USA, 11 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Barmatz, M.; Voecks, G.; Steinfeld, D. Efficient microwave approaches for extracting water from hydrated minerals. In Proceedings of the Space Resource Roundtable, Colorado School of Mines, Golden, CO, USA, 7 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
| Component | % |
|---|---|
| CO2 | 95 |
| Ar | 1.6 |
| N2 | 2.7 |
| O2 | 0.013 |
| H2O | ~30 ppm |
| Process | Description | Conditions | Common Materials |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reactions | |||
| RWGS | CO + H2O | 700–900 °C 1 bar | * Fe2O3@ Al2O3 |
| Sabatier | CH4 + H2O | 200–500 °C 10–30 bar | * Ni@Al2O3 |
| Fischer–Tropsch | CnH2n+2 + nH2O CnH2n + nH2O | 300–350 °C 20–40 bar | * Fe3O4@ Al2O3 |
| Methanol | CH3OH CH3OH + H2O | 200–300 °C 16–150 bar | * CuO@Al2O3 |
| Haber–Bosch | 2NH3 | 400–650 °C 200–400 bar | * Fe3O4@ Al2O3 |
| Other | |||
| SOEC | CO + 0.5O2 0.5O2 + H2 Gas phase | 800–1000 °C | Zr2O Perovskite |
| Electrolysis | O2 + H2 Aqueous phase | 25 °C/1 bar | Polymers |
| Cryogenic separation | CO2 (s) | −78 °C–1 bar | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rapp, D.; Inglezakis, V.J. Mars In Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU) with Focus on Atmospheric Processing for Near-Term Application—A Historical Review and Appraisal. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14020653
Rapp D, Inglezakis VJ. Mars In Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU) with Focus on Atmospheric Processing for Near-Term Application—A Historical Review and Appraisal. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(2):653. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14020653
Chicago/Turabian StyleRapp, Donald, and Vassilis J. Inglezakis. 2024. "Mars In Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU) with Focus on Atmospheric Processing for Near-Term Application—A Historical Review and Appraisal" Applied Sciences 14, no. 2: 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14020653
APA StyleRapp, D., & Inglezakis, V. J. (2024). Mars In Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU) with Focus on Atmospheric Processing for Near-Term Application—A Historical Review and Appraisal. Applied Sciences, 14(2), 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14020653







