DCSPose: A Dual-Channel Siamese Framework for Unseen Textureless Object Pose Estimation
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Pose Estimation
2.2. Template-Based Method
2.3. Contrastive Learning and Siamese Network
3. Materials and Methods
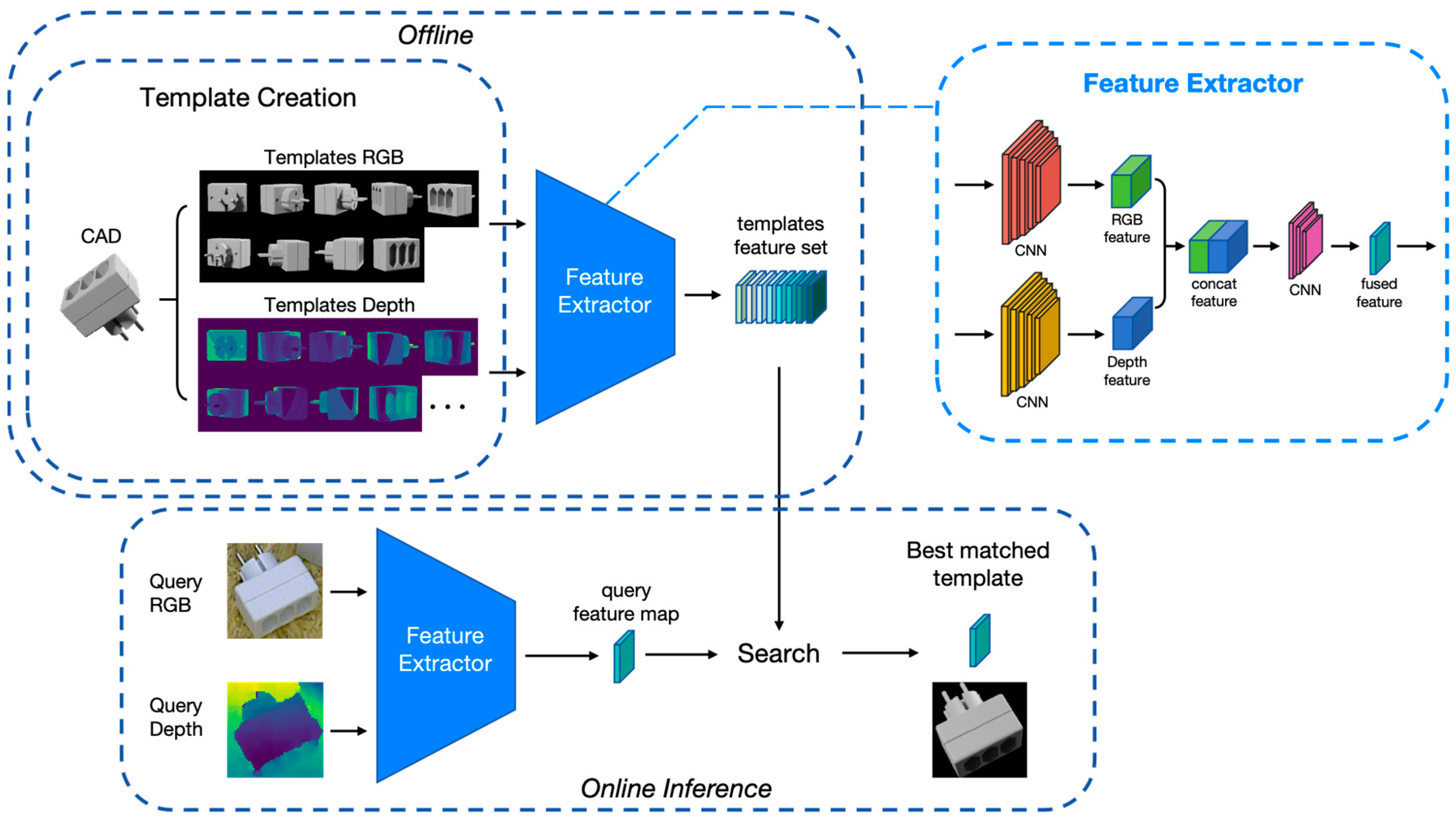
3.1. Framework
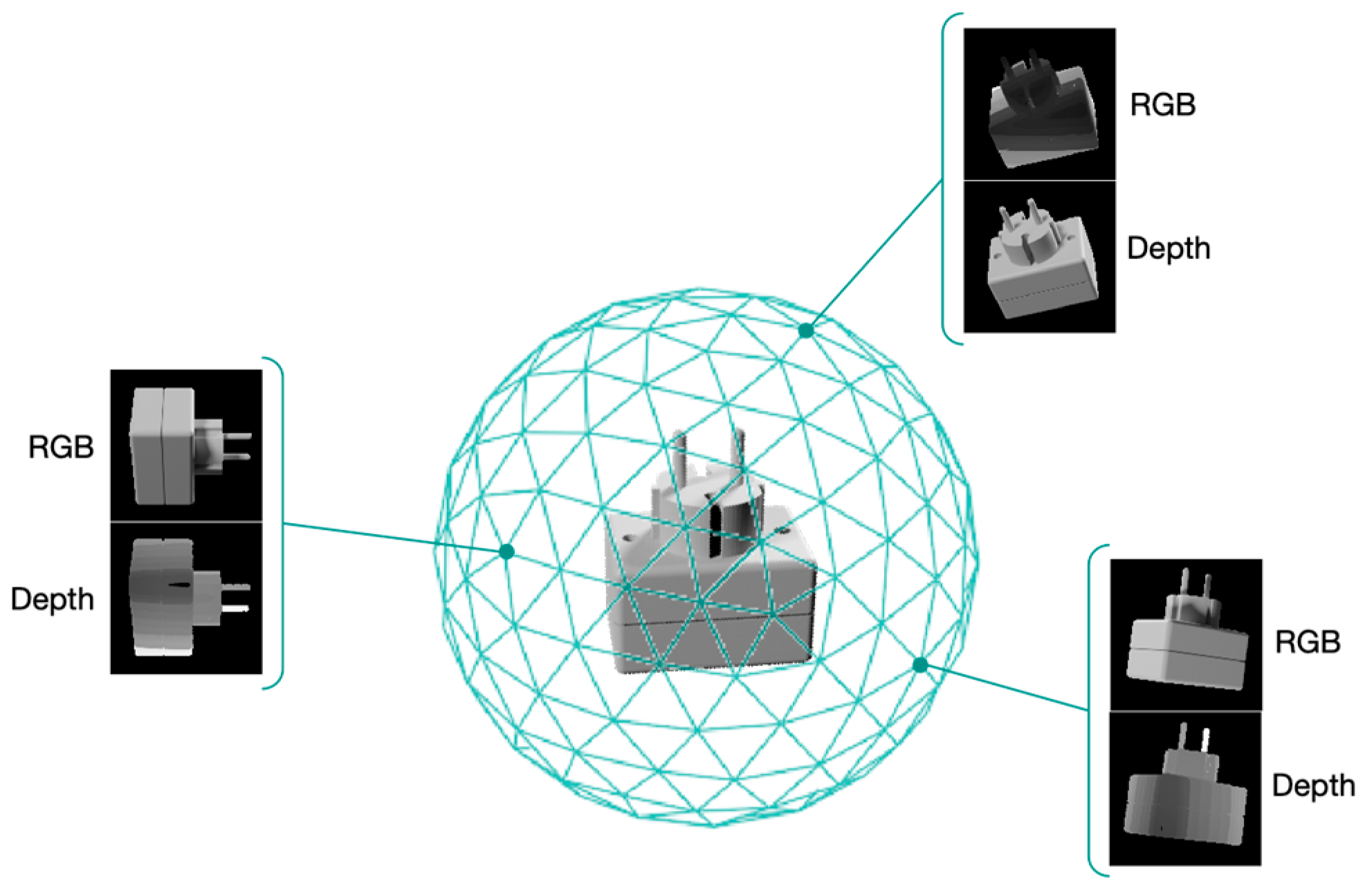
3.2. Template Creation
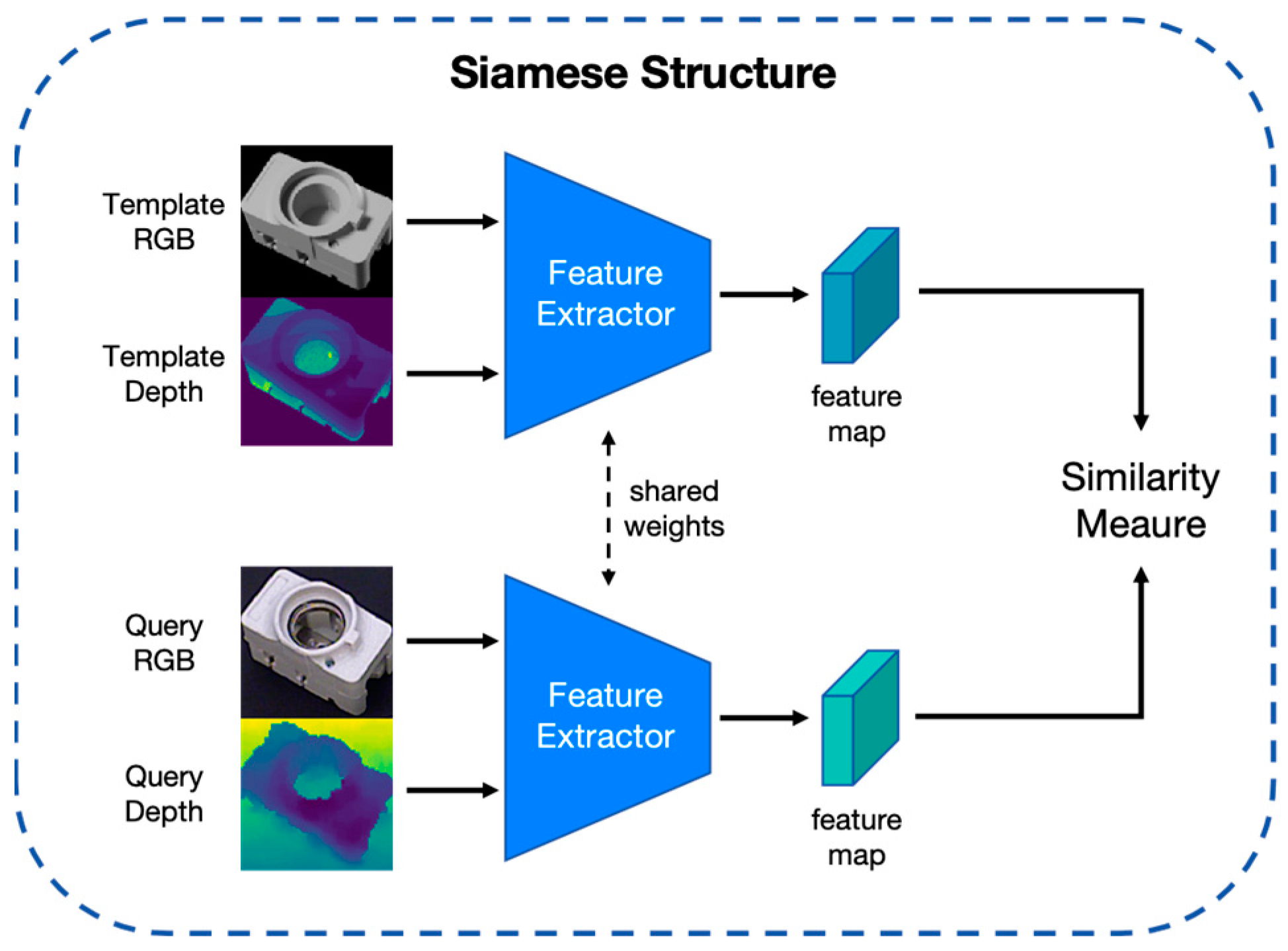
3.3. Feature Extractor
3.4. Training Phase
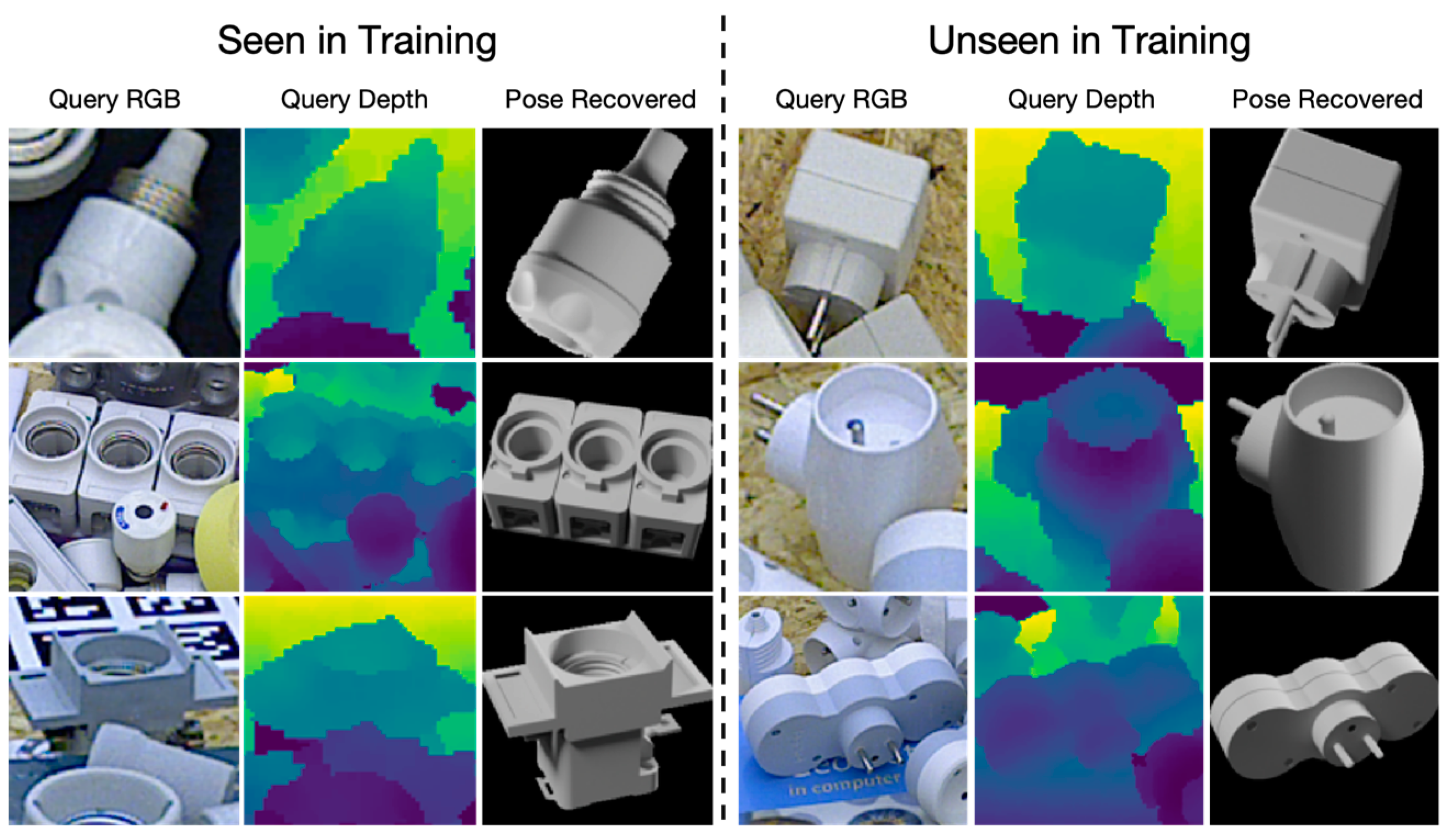
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.2. Comparison
4.3. Experiment of Depth Mask
4.4. Experiment of Feature Extractor
4.5. Performance Analysis
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A


References
- Hodan, T.; Michel, F.; Brachmann, E.; Kehl, W.; Buch, A.G.; Kraft, D.; Drost, B.; Vidal, J.; Ihrke, S.; Zabulis, X.; et al. BOP: Benchmark for 6D Object Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 19–35. [Google Scholar]
- Sundermeyer, M.; Hodaň, T.; Labbe, Y.; Wang, G.; Brachmann, E.; Drost, B.; Rother, C.; Matas, J. Bop challenge 2022 on detection, segmentation and pose estimation of specific rigid objects. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 2784–2793. [Google Scholar]
- Du, G.; Wang, K.; Lian, S.; Zhao, K. Vision-based robotic grasping from object localization, object pose estimation to grasp estimation for parallel grippers: A review. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2021, 54, 1677–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, Y. Autonomous driving with deep learning: A survey of state-of-art technologies. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.06091. [Google Scholar]
- Marchand, E.; Uchiyama, H.; Spindler, F. Pose estimation for augmented reality: A hands-on survey. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2015, 22, 2633–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Feng, W.; Zhao, X.; Lv, Y. 6D Pose Estimation of Objects: Recent Technologies and Challenges. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, S.; Arafat, M.Y.; Xu, S.; Maiti, A.; Wei, Y. A Comprehensive Review on 3D Object Detection and 6D Pose Estimation With Deep Learning. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 143746–143770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugo, G.; Hajari, N.; Cheng, I. Semi-supervised learning approach for localization and pose estimation of texture-less objects in cluttered scenes. Array 2022, 16, 100247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nguyen, N.; Hu, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Salzmann, M.; Lepetit, V. Templates for 3D Object Pose Estimation Revisited: Generalization to New Objects and Robustness to Occlusions. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 6761–6770. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, D.W.; Cao, Q.; Zhuang, Z.L.; Huang, H.Z.; Gao, R.Z.; Qin, W. An Improved Method for Model-Based Training, Detection and Pose Estimation of Texture-Less 3D Objects in Occlusion Scenes. In Proceedings of the 11th CIRP Conference on Industrial Product-Service Systems, Zhuhai, China, 29–31 May 2019; pp. 541–546. [Google Scholar]
- Sundermeyer, M.; Durner, M.; Puang, E.Y.; Marton, Z.-C.; Vaskevicius, N.; Arras, K.O.; Triebel, R. Multi-path learning for object pose estimation across domains. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, Washington, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 13916–13925. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, M.; Yao, W.; Chen, C. A review of 6d object pose estimation. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 10th Joint International Information Technology and Artificial Intelligence Conference (ITAIC), Chongqing, China, 17–19 June 2022; pp. 1647–1655. [Google Scholar]
- Marullo, G.; Tanzi, L.; Piazzolla, P.; Vezzetti, E. 6D object position estimation from 2D images: A literature review. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 24605–24643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chen, L.; Wu, S. A Novel Metric-Learning-Based Method for Multi-Instance Textureless Objects’ 6D Pose Estimation. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Jiang, X.; Miao, S.; Zhou, W.; Liu, Y. Texture-Less Shiny Objects Grasping in a Single RGB Image Using Synthetic Training Data. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Chen, F.; Liang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wang, C.; Wu, X. A Manufacturing-Oriented Intelligent Vision System Based on Deep Neural Network for Object Recognition and 6D Pose Estimation. Front. Neurorobot. 2021, 14, 616775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, C.; Zhao, H.; Li, S.; Ding, H. Pose prediction of textureless objects for robot bin picking with deep learning approach. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2023, 237, 449–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.W.; Li, C.L.; Chen, J.L.; Lee, J.J. Robot grasping in dense clutter via view-based experience transfer. Int. J. Intell. Robot. Appl. 2022, 6, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Gong, Y.; Poslad, S. Regression-Based Camera Pose Estimation through Multi-Level Local Features and Global Features. Sensors 2023, 23, 4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Ji, Y.-M.; Liu, S.-D. Dynamic Vehicle Pose Estimation with Heuristic L-Shape Fitting and Grid-Based Particle Filter. Electronics 2023, 12, 1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Zheng, H.; Li, C.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, T. AGCNNs: Attention-guided convolutional neural networks for infrared head pose estimation in assisted driving system. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2022, 123, 104146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Jung, C.; Lee, K.; Seo, S. A study on recognizing multi-real world object and estimating 3D position in augmented reality. J. Supercomput. 2022, 78, 7509–7528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhao, W.; Peng, J.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Q.; Wang, J. Augmented reality museum display system based on object 6D pose estimation. J. Northwest Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2021, 51, 816–823. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Manhardt, F.; Tombari, F.; Ji, X.Y.; Ieee Comp, S.O.C. GDR-Net: Geometry-Guided Direct Regression Network for Monocular 6D Object Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 16606–16616. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Vutukur, S.R.; Yu, H.; Shugurov, I.; Busam, B.; Yang, S.; Ilic, S. Nerf-pose: A first-reconstruct-then-regress approach for weakly-supervised 6d object pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 2123–2133. [Google Scholar]
- Sundermeyer, M.; Marton, Z.-C.; Durner, M.; Brucker, M.; Triebel, R. Implicit 3d orientation learning for 6d object detection from rgb images. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 699–715. [Google Scholar]
- Konishi, Y.; Hattori, K.; Hashimoto, M. Real-time 6D object pose estimation on CPU. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Macau, China, 3–8 November 2019; pp. 3451–3458. [Google Scholar]
- Sundermeyer, M.; Marton, Z.-C.; Durner, M.; Triebel, R. Augmented Autoencoders: Implicit 3D Orientation Learning for 6D Object Detection. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2020, 128, 714–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labbé, Y.; Manuelli, L.; Mousavian, A.; Tyree, S.; Birchfield, S.; Tremblay, J.; Carpentier, J.; Aubry, M.; Fox, D.; Sivic, J. MegaPose: 6D Pose Estimation of Novel Objects via Render & Compare. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2212.06870. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, R. Unseen Object Pose Estimation via Registration. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Real-Time Computing and Robotics (RCAR), Xining, China, 15–19 June 2021; pp. 974–979. [Google Scholar]
- Pateraki, M.; Sapoutzoglou, P.; Lourakis, M. Crane Spreader Pose Estimation from a Single View. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Manolis-Lourakis/publication/367051971_Crane_Spreader_Pose_Estimation_from_a_Single_View/links/63f3218151d7af05403c16ad/Crane-Spreader-Pose-Estimation-from-a-Single-View.pdf (accessed on 3 January 2024).
- Yoon, Y.; DeSouza, G.N.; Kak, A.C. Real-time tracking and pose estimation for industrial objects using geometric features. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (Cat. No. 03CH37422), Taipei, Taiwan, 14–19 September 2003; pp. 3473–3478. [Google Scholar]
- Chicco, D. Siamese neural networks: An overview. In Artificial Neural Networks; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 73–94. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Q.; Feng, W.; Zhou, C.; Huang, R.; Wan, L.; Wang, S. Learning dynamic siamese network for visual object tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1763–1771. [Google Scholar]
- Melekhov, I.; Kannala, J.; Rahtu, E. Siamese network features for image matching. In Proceedings of the 2016 23rd international conference on pattern recognition (ICPR), Cancun, Mexico, 4–8 December 2016; pp. 378–383. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.; Wang, K.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, M.; You, Y. Crafting better contrastive views for siamese representation learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 16031–16040. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; He, K. Exploring simple siamese representation learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 15750–15758. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Chen, C.P.; Zhang, T. A survey on siamese network: Methodologies, applications, and opportunities. IEEE Trans. Artif. Intell. 2022, 3, 994–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denninger, M.; Sundermeyer, M.; Winkelbauer, D.; Zidan, Y.; Olefir, D.; Elbadrawy, M.; Lodhi, A.; Katam, H. BlenderProc. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.01911. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- van den Oord, A.; Li, Y.; Vinyals, O. Representation Learning with Contrastive Predictive Coding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.03748. [Google Scholar]
- Hodan, T.; Haluza, P.; Obdržálek, Š.; Matas, J.; Lourakis, M.; Zabulis, X. T-LESS: An RGB-D dataset for 6D pose estimation of texture-less objects. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Santa Rosa, CA, USA, 24–31 March 2017; pp. 880–888. [Google Scholar]
- Kehl, W.; Manhardt, F.; Tombari, F.; Ilic, S.; Navab, N. SSD-6D: Making RGB-Based 3D Detection and 6D Pose Estimation Great Again. In Proceedings of the 16th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1530–1538. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Fan, H.; Girshick, R.; He, K. Improved Baselines with Momentum Contrastive Learning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.04297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

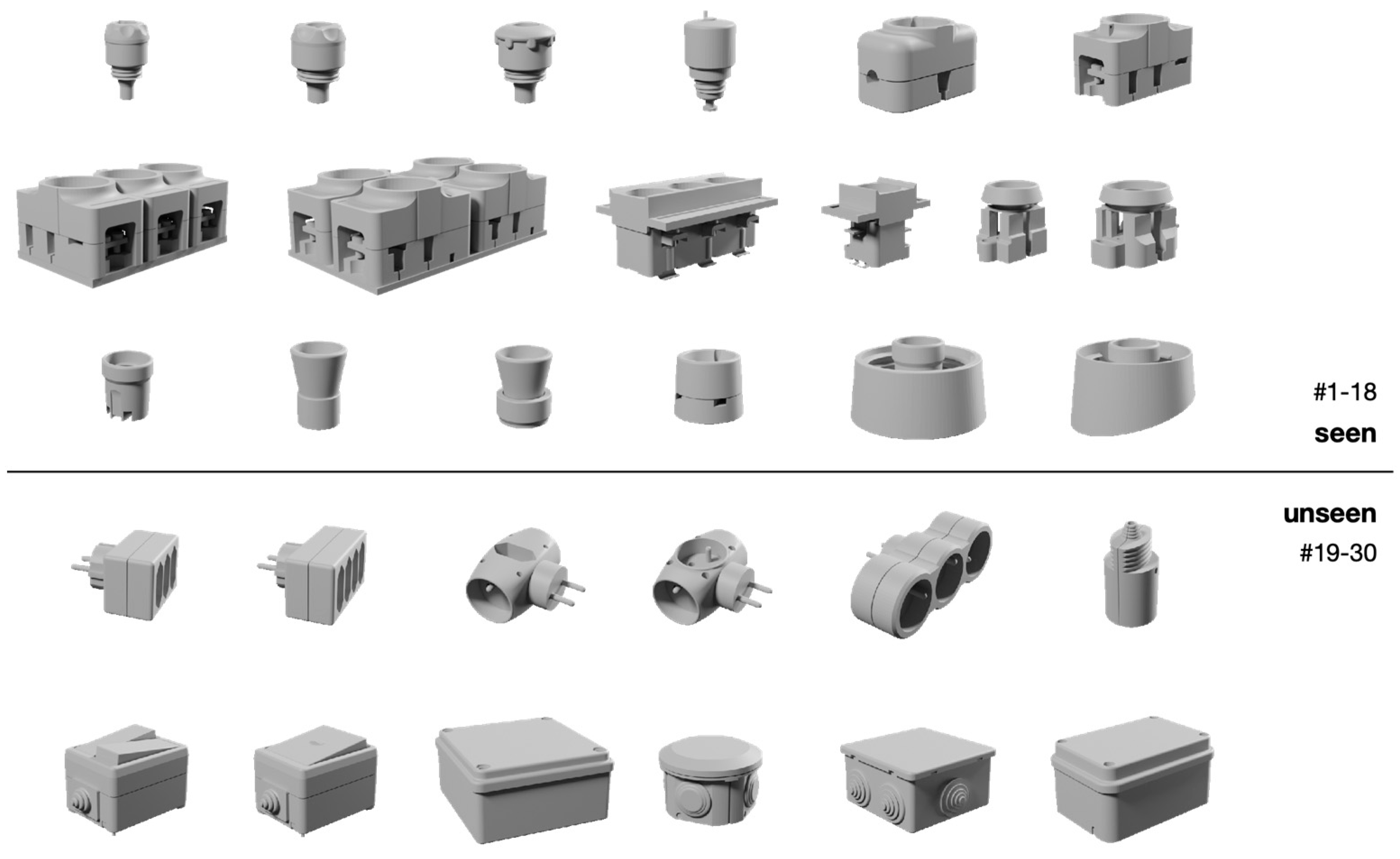
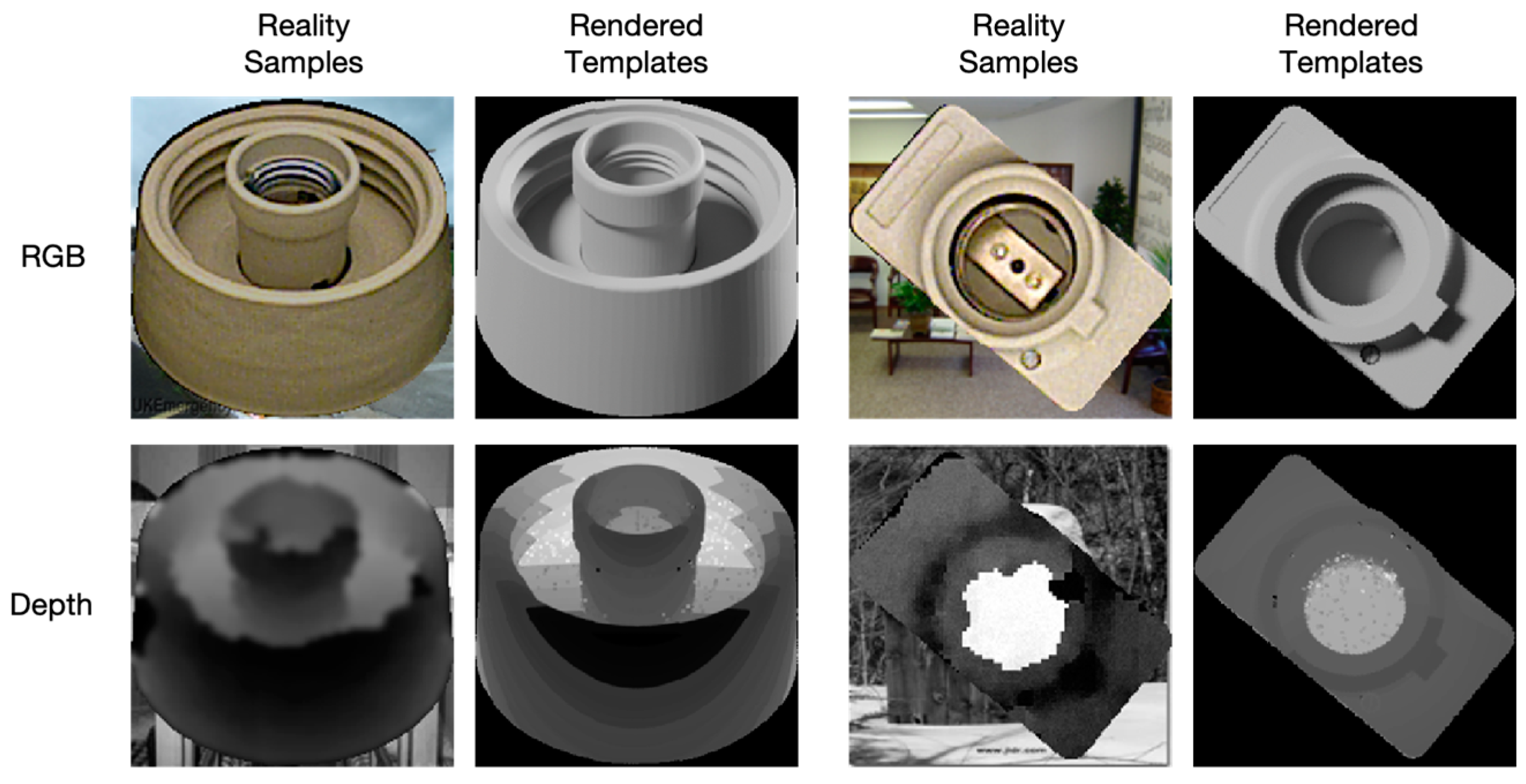
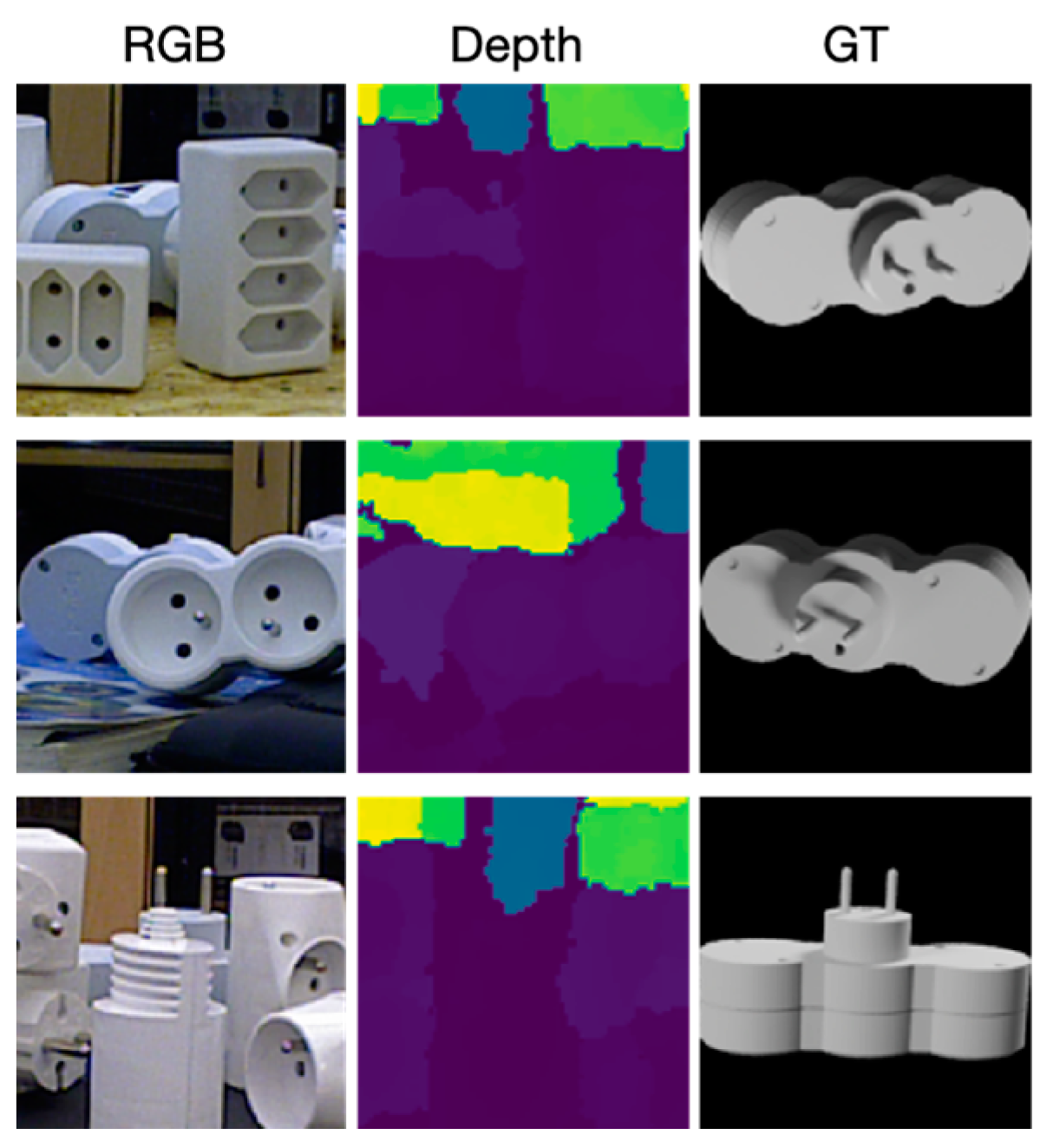
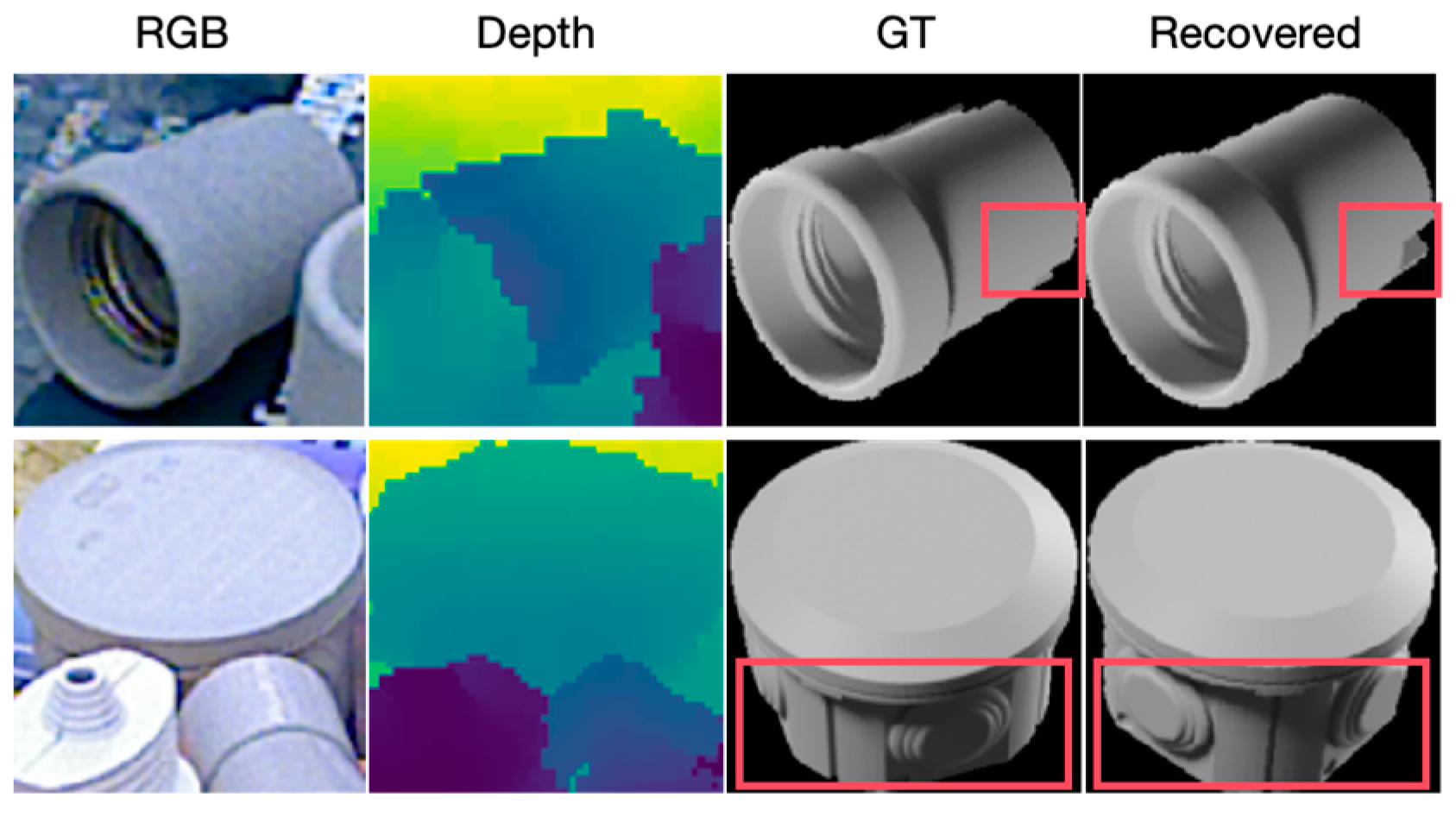
| Hardware | CPU | Intel(R) Xeon(R) Platinum 8336C CPU @ 2.30 GHz |
| GPU | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4090 | |
| Training | Batch size | 12 |
| Optimizer | Adam | |
| Learning rate | 2.0 | |
| Weight decay | 5 | |
| Milestones | 20, 30, 35 | |
| Decay rate | 0.2 |
| Method | Number Templates | Mean VSD Recall | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seen Obj. 1–18 | Unseen Obj. 19–30 | Total | ||
| MPL [11] | 92 K | 35.25 | 33.17 | 34.42 |
| Implicit [26] | 92 K | 35.60 | 42.45 | 38.34 |
| TPO [9] | 21 K | 59.14 | 56.91 | 58.25 |
| DCSPose (ours) | 21 K | 65.86 | 62.53 | 64.20 |
| Experiments | Mean VSD Recall | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Seen Obj. 1–18 | Unseen Obj. 19–30 | Total | |
| DCSPose-basic-1CH | 63.05 | 61.62 | 62.34 |
| DCSPose-basic | 65.86 | 62.53 | 64.20 |
| DCSPose-masked-1CH | 65.54 | 63.89 | 67.22 |
| DCSPose-masked | 69.74 | 68.48 | 69.11 |
| Obj. | #1 | #2 | #3 | #4 | #5 | #6 | #7 | #8 | #9 | #10 | #11 | #12 | #13 | #14 | #15 | #16 | #17 | #18 |
| VSD | 0.65 | 0.70 | 0.85 | 0.65 | 0.68 | 0.77 | 0.43 | 0.27 | 0.52 | 0.64 | 0.72 | 0.68 | 0.61 | 0.71 | 0.74 | 0.87 | 0.83 | 0.76 |
| Obj. | #19 | #20 | #21 | #22 | #23 | #24 | #25 | #26 | #27 | #28 | #29 | #30 | ||||||
| VSD | 0.70 | 0.58 | 0.50 | 0.70 | 0.48 | 0.60 | 0.62 | 0.73 | 0.44 | 0.69 | 0.65 | 0.84 |
| Number of Templates | Offline | Online | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Templates Rendering | Features Extraction | Run-Time Inference | |
| 21,672 | 5.6 min | 1.77 min | 28 fps |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yue, Z.; Han, Z.; Yang, X.; Liu, L. DCSPose: A Dual-Channel Siamese Framework for Unseen Textureless Object Pose Estimation. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 730. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14020730
Yue Z, Han Z, Yang X, Liu L. DCSPose: A Dual-Channel Siamese Framework for Unseen Textureless Object Pose Estimation. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(2):730. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14020730
Chicago/Turabian StyleYue, Zhen, Zhenqi Han, Xiulong Yang, and Lizhuang Liu. 2024. "DCSPose: A Dual-Channel Siamese Framework for Unseen Textureless Object Pose Estimation" Applied Sciences 14, no. 2: 730. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14020730
APA StyleYue, Z., Han, Z., Yang, X., & Liu, L. (2024). DCSPose: A Dual-Channel Siamese Framework for Unseen Textureless Object Pose Estimation. Applied Sciences, 14(2), 730. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14020730






