Optimal Allocation of Distributed Generations and Capacitor Banks in Distribution Systems Using Arithmetic Optimization Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The placement and capacity of each DG and CB have been successfully determined by minimizing total power losses and voltage deviation with AOA.
- DGs and CBs are placed in the distribution networks both separately and together under different scenarios.
- The optimal power factor, which is an important parameter of DG and is not examined adequately in the literature, has been determined with AOA in addition to the optimal location and capacity.
- The proposed algorithm has been implemented in the IEEE 33-bus and IEEE 69-bus systems in various scenarios and the obtained results are compared with the results of other well-known optimization methods.
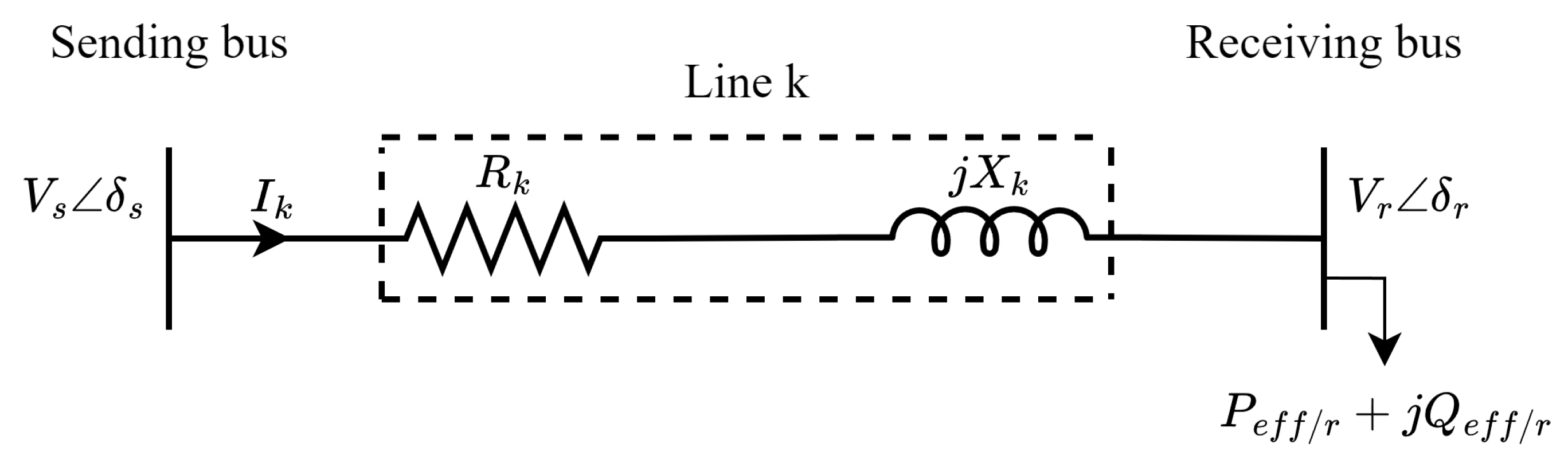
2. Problem Formulation
2.1. Objective Functions
2.1.1. Reduction in Real Power Losses
2.1.2. Minimization of Total Voltage Deviation
2.2. Constraints
2.2.1. Equality Constraints
2.2.2. Inequality Constraints
- (1)
- Active power limits of each DG
- (2)
- Reactive power limits of each CB
- (3)
- Voltage limits
- (4)
- Power factor limits
- (5)
- Total active power injection
- (6)
- Total reactive power injection
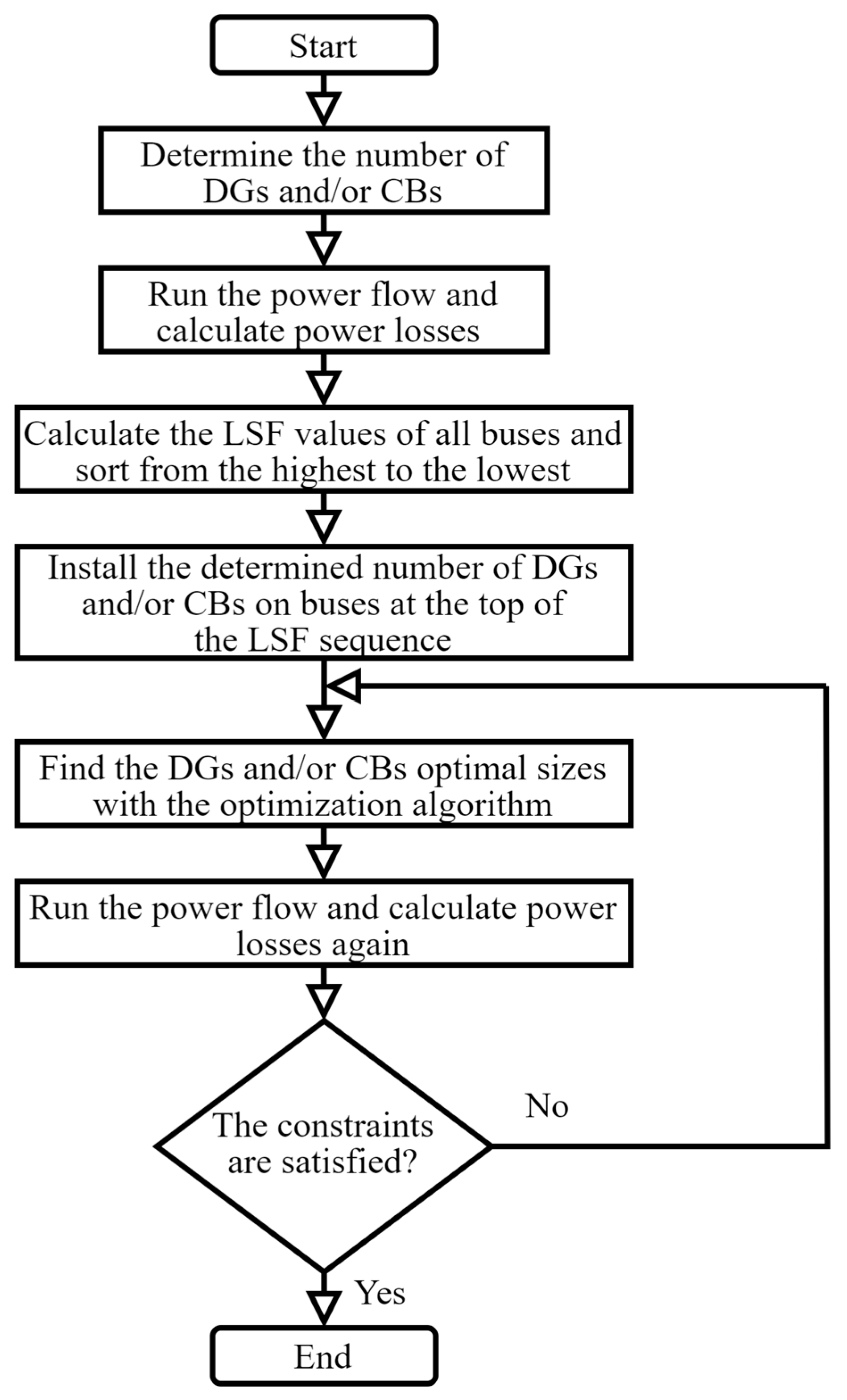
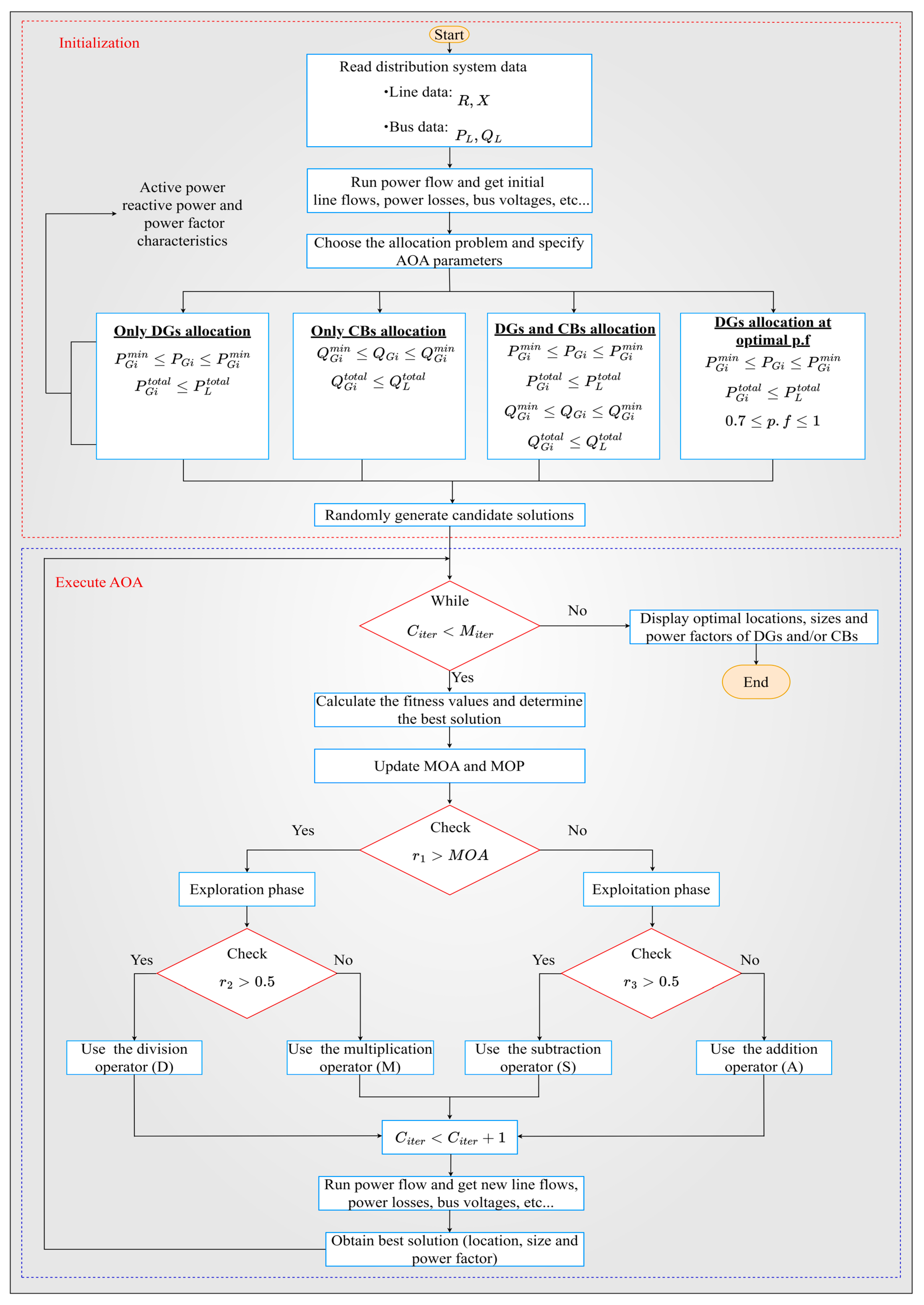
2.3. Optimal Location
Loss Sensitivity Factor
2.4. Optimal Capacity and Power Factor
3. Experimental Results
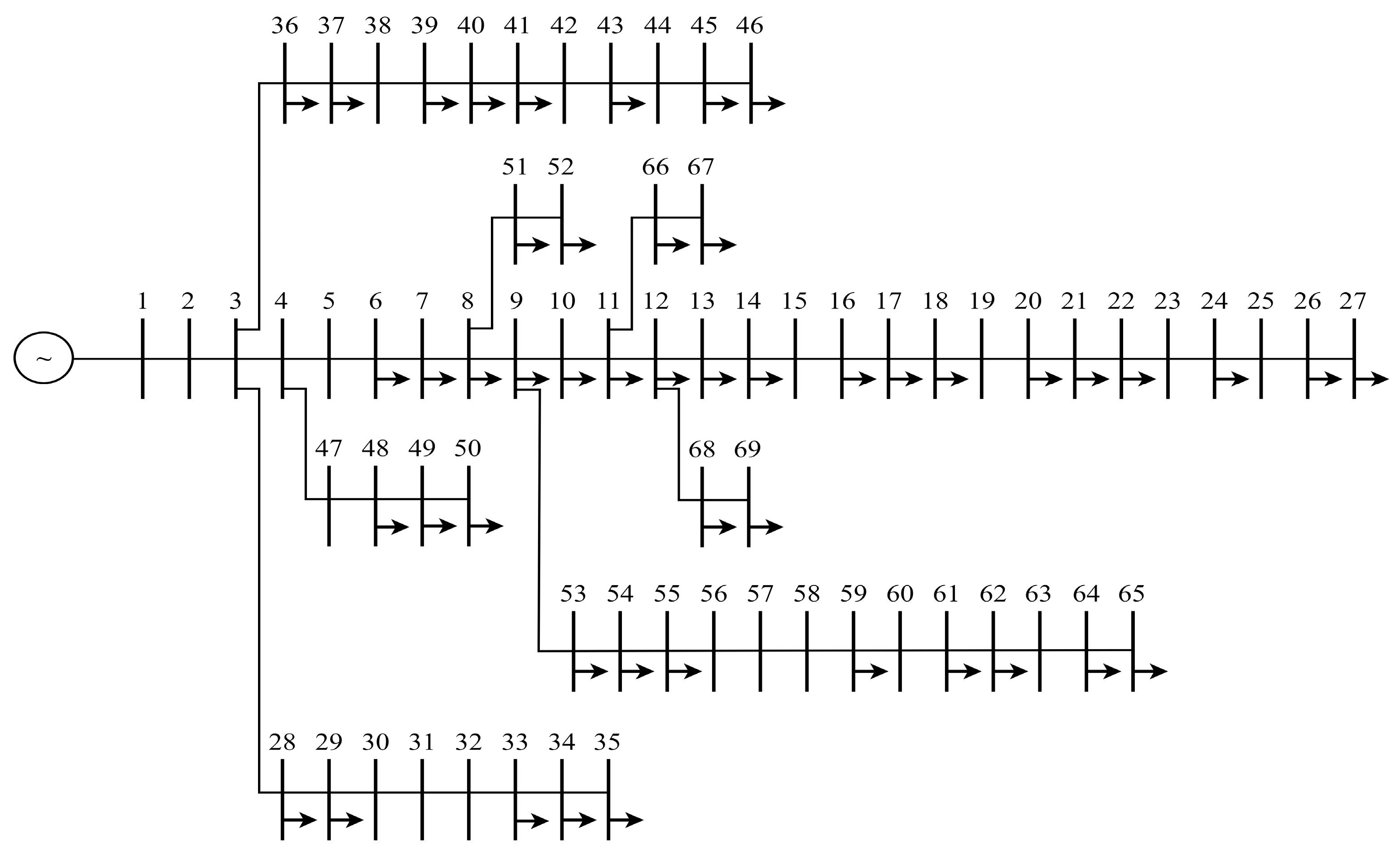
3.1. Results of IEEE 33-Bus System
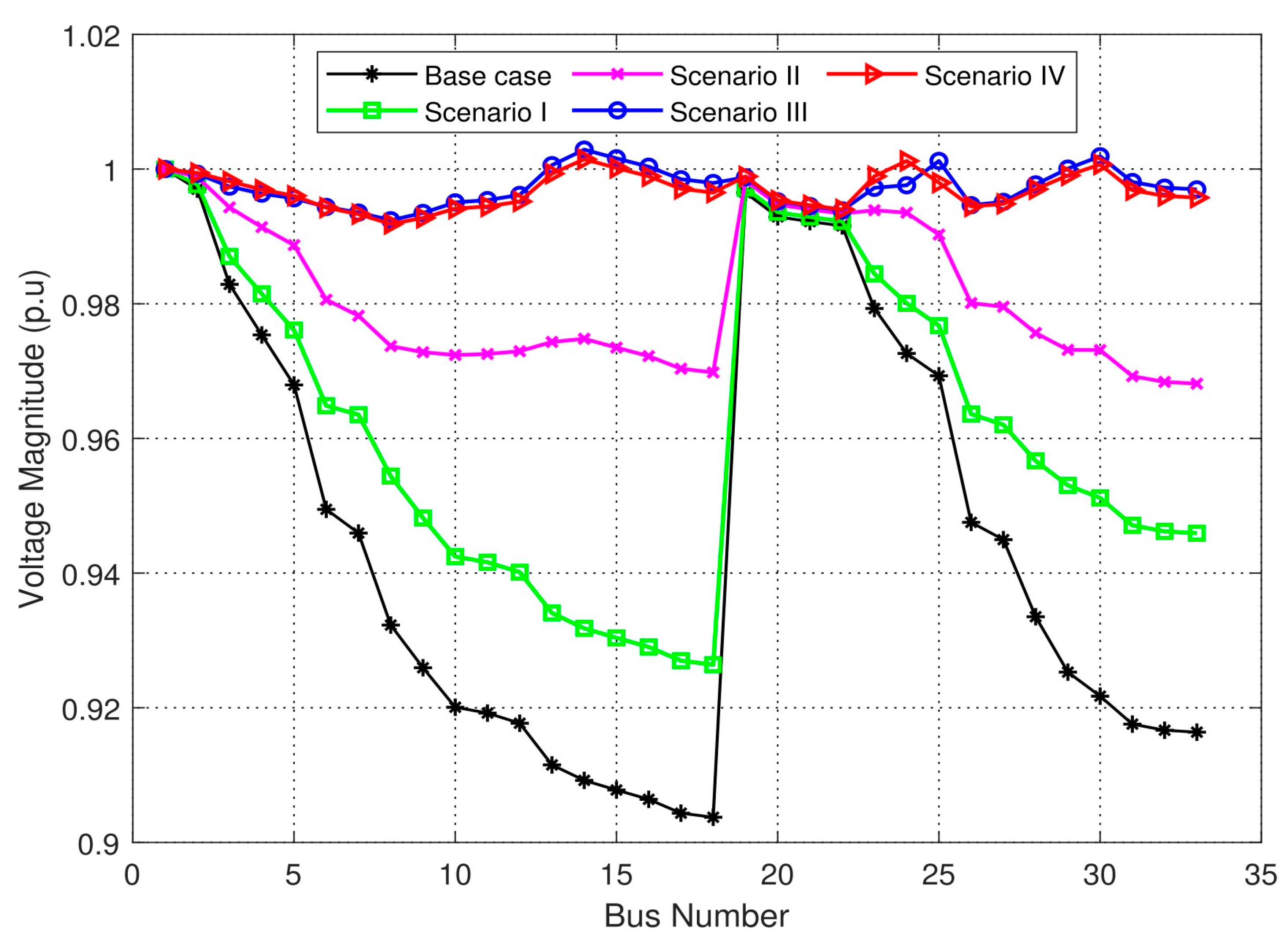
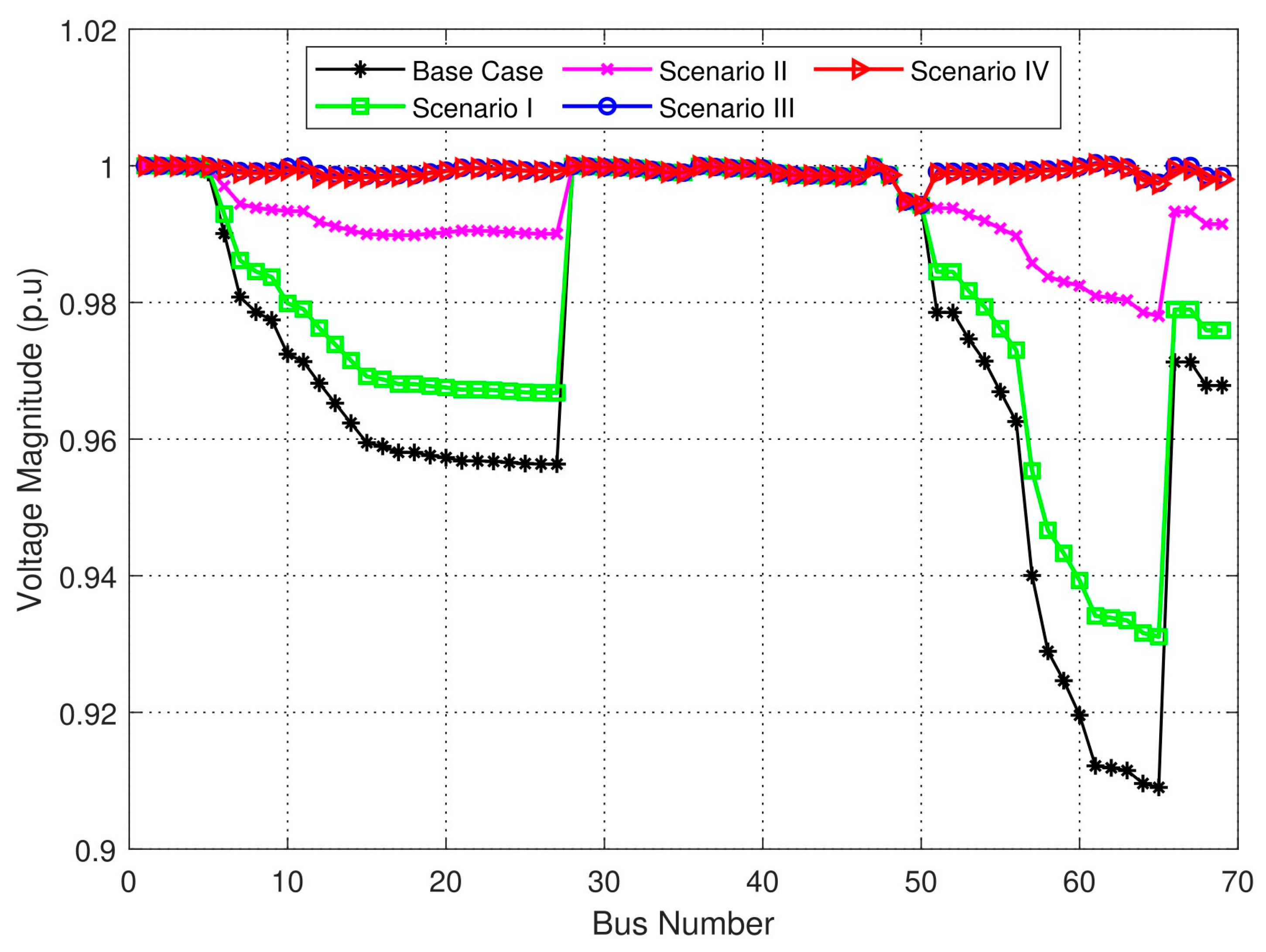
- Scenario I: Installation of only DGs
- Scenario II: Installation of only CBs
- Scenario III: Installation of DGs and CBs simultaneously
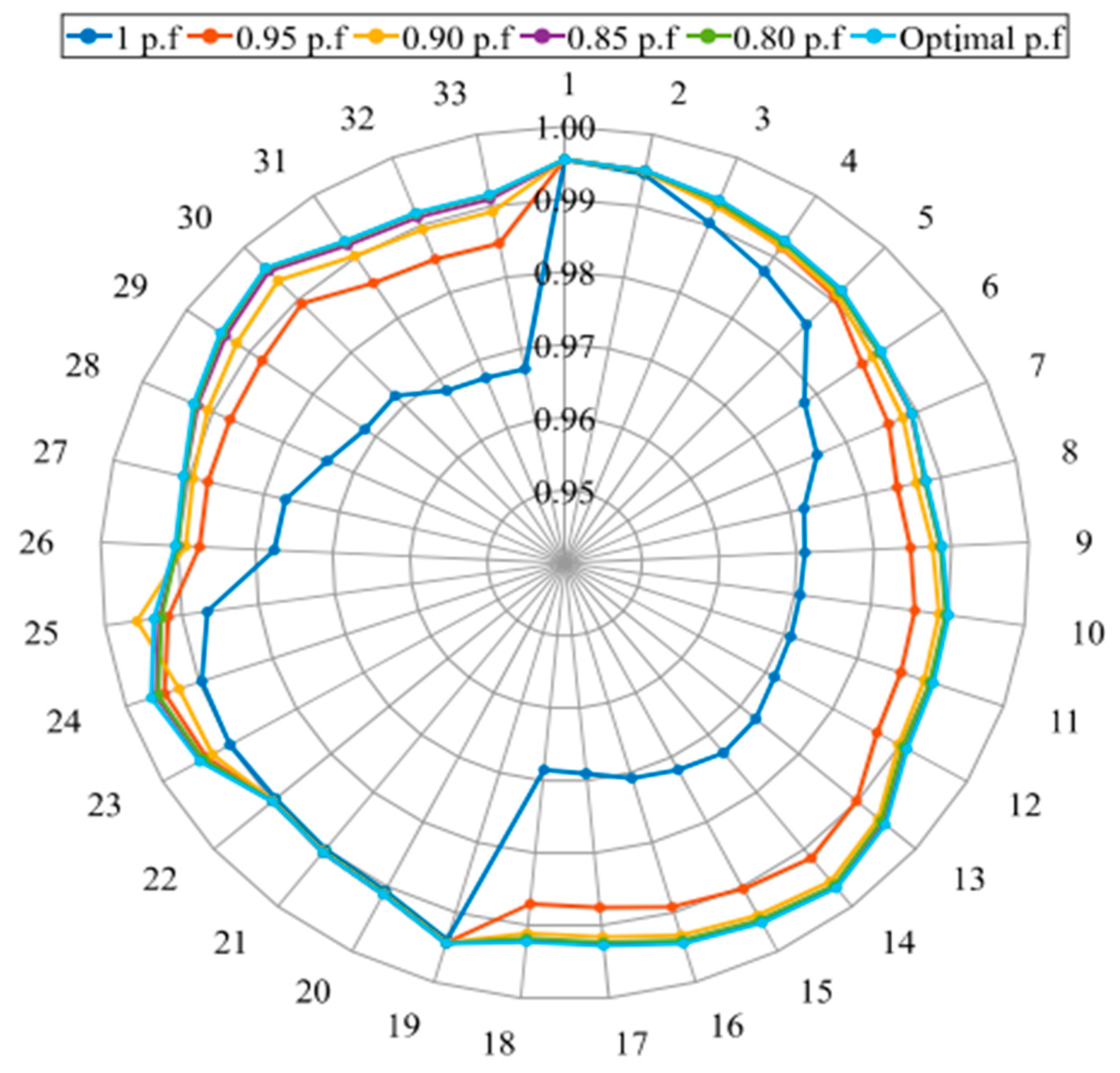
- Scenario IV: Installation of DGs at the optimal power factor
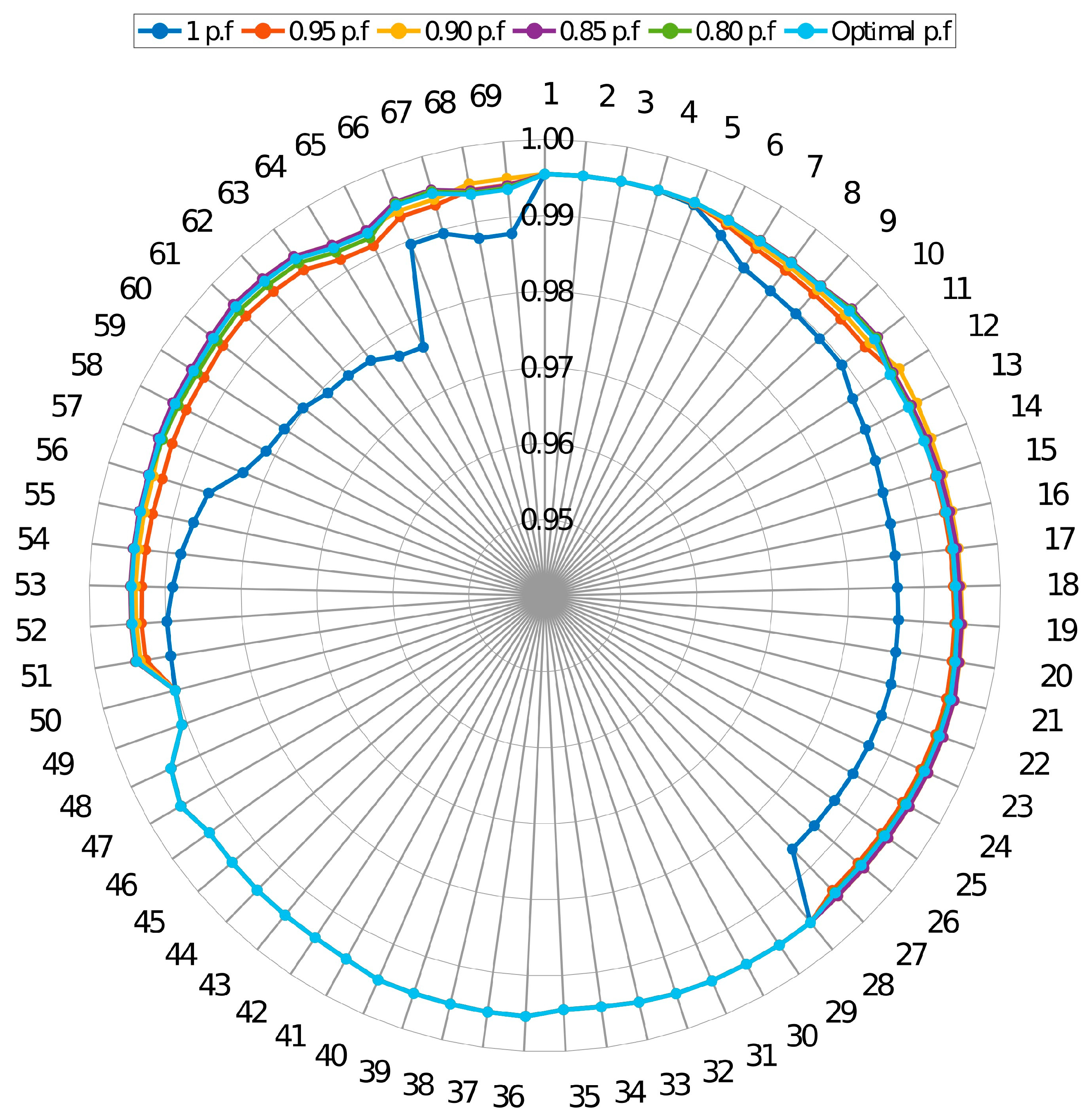
3.1.1. Voltage Profile
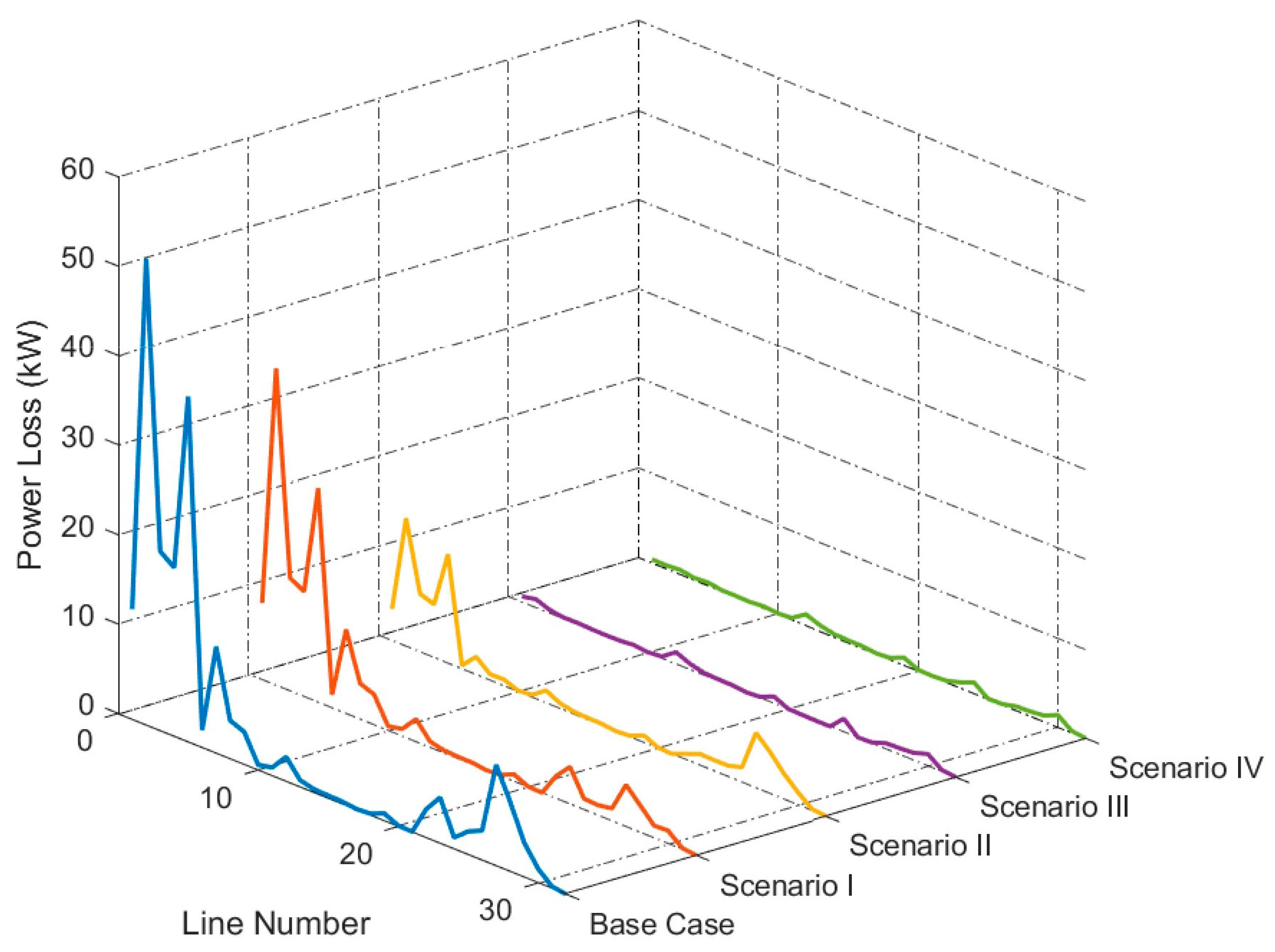
3.1.2. Power Losses
3.2. Results of IEEE 69-Bus System
- Scenario I: Installation of only DGs
- Scenario II: Installation of only CBs
- Scenario III: Installation of DGs and CBs simultaneously
- Scenario IV: Installation of DGs at the optimal power factor
3.2.1. Voltage Profile
3.2.2. Power Losses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McMeekin, A.; Geels, F.W.; Hodson, M. Mapping the winds of whole system reconfiguration: Analysing low-carbon transformations across production, distribution and consumption in the UK electricity system (1990–2016). Res. Policy 2019, 48, 1216–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayalew, M.; Khan, B.; Giday, I.; Mahela, O.P.; Khosravy, M.; Gupta, N.; Senjyu, T. Integration of renewable based distributed generation for distribution network expansion planning. Energies 2022, 15, 1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanelytė, D.; Radziukynas, V. Analysis of voltage and reactive power algorithms in low voltage networks. Energies 2022, 15, 1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.P.; Nguyen, T.A.; Phan, T.V.H.; Vo, D.N. A comprehensive analysis for multi-objective distributed generations and capacitor banks placement in radial distribution networks using hybrid neural network algorithm. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2021, 231, 107387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ufa, R.A.; Malkova, Y.Y.; Rudnik, V.E.; Andreev, M.V.; Borisov, V.A. A review on distributed generation impacts on electric power system. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 20347–20361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.D.L.; Yahyaoui, I.; Fiorotti, R.; de Menezes, L.S.; Fardin, J.F.; Rocha, H.R.O.; Tadeo, F. Optimal allocation of distributed generation and capacitor banks using probabilistic generation models with correlations. Appl. Energy 2022, 307, 118097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, K.; Islam, R.; Rahman, M.; Azizivahed, A.; Fekih, A. State-of-the-art technologies for volt-var control to support the penetration of renewable energy into the smart distribution grids. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 8630–8651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, V.; Dubey, H.M.; Pandit, M. Assessment of optimal size and location of DG/CB in distribution systems using coulomb–franklin’s algorithm. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. B 2022, 103, 1885–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetouh, T.; Elsayed, A.M. Optimal control and operation of fully automated distribution networks using improved tunicate swarm intelligent algorithm. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 129689–129708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huy, P.D.; Ramachandaramurthy, V.K.; Yong, J.Y.; Tan, K.M.; Ekanayake, J.B. Optimal placement, sizing and power factor of distributed generation: A comprehensive study spanning from the planning stage to the operation stage. Energy 2020, 195, 117011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayal, P.; Chanda, S.; Chanda, C.K. An analytical approach for allocation and sizing of distributed generations in radial distribution network. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2017, 27, e2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, A.M.; Kowsalya, M.; Kothari, D. A novel integration technique for optimal network reconfiguration and distributed generation placement in power distribution networks. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2014, 63, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaballi, S.; Kale, V.S. Pareto optimality and game theory approach for optimal deployment of dg in radial distribution system to improve techno-economic benefits. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 92, 106234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.D.; Nguyen, T.T.; Dinh, B.H. Find optimal capacity and location of distributed generation units in radial distribution networks by using enhanced coyote optimization algorithm. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 4343–4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Bhattacharya, A. Quasi-oppositional swine influenza model based optimization with quarantine for optimal allocation of dg in radial distribution network. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2016, 74, 348–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, S.; Amin, A.; Selim, A.; Ahmed, M.H. Optimal placement of dg and capacitor in radial distribution systems considering load variation. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Computer, Control, Electrical, and Electronics Engineering (ICCCEEE), Khartoum, Sudan, 21–23 September 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balu, K.; Mukherjee, V. Optimal siting and sizing of distributed generation in radial distribution system using a novel student psychology-based optimization algorithm. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 15639–15667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuaib, Y.M.; Kalavathi, M.S.; Rajan, C.C.A. Optimal capacitor placement in radial distribution system using gravitational search algorithm. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2015, 64, 384–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowsalya, M.; Mohamed Imran, A. Optimal distributed generation and capacitor placement in power distribution networks for power loss minimization. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Advances in Electrical Engineering (ICAEE), Vellore, India, 9–11 January 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Fergany, A.A.; Abdelaziz, A.Y. Capacitor allocations in radial distribution networks using cuckoo search algorithm. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2014, 8, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saonerkar, A.; Bagde, B. Optimized dg placement in radial distribution system with reconfiguration and capacitor placement using genetic algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Advanced in Communications, Control and Computing Technologies, Ramanathapuram, India, 8–10 May 2014; pp. 1077–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou El-Ela, A.A.; El-Sehiemy, R.A.; Abbas, A.S. Optimal placement and sizing of distributed generation and capacitor banks in distribution systems using water cycle algorithm. IEEE Syst. J. 2018, 12, 3629–3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, M.S.; Injeti, S.K. Simultaneous optimal placement of DGs and fixed capacitor banks in radial distribution systems using BSA optimization. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2014, 108, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Phisuthsaingam, P.; Larbwisuthisaroj, S.; Chaitusaney, S. An analysis of potentials and economic benefits of distributed generations as reactive power providers in Thailand. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Electrical Engineering/Electronics, Computer, Telecommunications and Information Technology (ECTI-CON), Prachuap Khiri Khan, Thailand, 24–27 May 2022; p. 21797863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abualigah, L.; Diabat, A.; Mirjalili, S.; Abd Elaziz, M.; Gandomi, A.H. The arithmetic optimization algorithm. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2021, 376, 113609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirishti, S.; Gupta, A.R. DG allocation using arithmetic optimization algorithm in radial and mesh distribution system. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Power, Control and Computing Technologies (ICPC2T), Raipur, India, 1–3 March 2022; p. 21764243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Mawgoud, H.; Fathy, A.; Kamel, S. An effective hybrid approach based on arithmetic optimization algorithm and sine cosine algorithm for integrating battery energy storage system into distribution networks. J. Energy Storage 2022, 49, 104154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golla, N.K.; Sudabattula, S.K.; Suresh, V. Optimal placement of charging station and distributed generator along with scheduling in distribution system using arithmetic optimization algorithm. Int. J. Renew. Energy Res. IJRER 2022, 12, 970–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, B.; Younesi, S.; Ceylan, O.; Ozdemir, A. The arithmetic optimization algorithm for optimal energy resource planning. In Proceedings of the 56th International Universities Power Engineering Conference (UPEC), Middlesbrough, UK, 31 August–3 September 2021; p. 21159677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinakara Prasad Reddy, P.; Veera Reedy, V.C.; Gowri Manohar, T. Optimal renewable resources placement in distribution networks by combined power loss index and whale optimization algorithms. J. Electr. Syst. Inf. Technol. 2018, 5, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Delgado, G.; Contreras, J.; Arroyo, J.M. Distribution system expansion planning considering non-utility-owned DG and an independent distribution system operator. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2019, 34, 2588–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, K.; Sydulu, M. Particle swarm optimization based capacitor placement on radial distribution systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE Power Engineering Society General Meeting, Tampa, FL, USA, 24–28 June 2007; p. 10301029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, M.E.; Wu, F.F. Network reconfiguration in distribution systems for loss reduction and load balancing. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 1989, 4, 1401–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Fergany, A. Optimal allocation of multi-type distributed generators using backtracking search optimization algorithm. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2015, 64, 1197–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, D.Q.; Mithulananthan, N. Multiple distributed generator placement in primary distribution networks for loss reduction. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 1700–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, K.; Yorino, N.; Ahmed, A. Optimal distributed generation allocation in distribution systems for loss minimization. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2016, 31, 960–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, M.E.; Wu, F.F. Optimal sizing of capacitors placed on a radial distribution system. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 1989, 4, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, A.A.; Mohamed, A.-A.A.; Hemeida, A.M.; Ibrahim, A.A. Comparison of different optimization techniques for optimal allocation of multiple distribution generation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Innovative Trends in Computer Engineering (ITCE), Aswan, Egypt, 19–21 February 2018; pp. 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambaiah, K.S.; Jayabarathi, T. Optimal allocation of renewable distributed generation and capacitor banks in distribution systems using salp swarm algorithm. Int. J. Renew. Energy Res. IJRER 2019, 9, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Scenarios # | Installation Mode | Network |
|---|---|---|
| Scenario I | Installation of only DGs | IEEE 33-bus network |
| Scenario II | Installation of only CBs | IEEE 33-bus network |
| Scenario III | Installation of DGs and CBs simultaneously | IEEE 33-bus network |
| Scenario IV | Installation of DGs at the optimal p.f | IEEE 33-bus network |
| Scenario I | Installation of only DGs | IEEE 69-bus network |
| Scenario II | Installation of only CBs | IEEE 69-bus network |
| Scenario III | Installation of DGs and CBs simultaneously | IEEE 69-bus network |
| Scenario IV | Installation of DGs at the optimal p.f | IEEE 69-bus network |
| Method | Optimal Location (Bus No.) | Optimal DG Size (MW) | Power Loss (kW) | Loss Reduction (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AM [11] | 13 29 31 | 1.121 1.027 0.126 | 89.5 | 57.28 |
| FWA [12] | 14 18 32 | 0.5897 0.1895 1.0146 | 88.68 | 56.24 |
| MTLBO [13] | 23 32 15 | 1.066 0.847 0.885 | 80.22 | 62 |
| JAYA [13] | 29 25 12 | 0.921 0.795 1.110 | 76.66 | 63.6 |
| GWO [13] | 12 25 30 | 0.955 0.889 1.037 | 74.10 | 64.88 |
| COA [14] | 14 25 30 | 0.7096 0.5954 0.9972 | 76 | 63.98 |
| ECOA [14] | 14 25 30 | 0.7376 0.6518 1.0705 | 74.6 | 64.64 |
| SIMBO-Q [15] | 14 24 29 | 0.7638 1.0415 1.1352 | 73.4 | 65.20 |
| QOSIMBO-Q [15] | 14 24 30 | 0.7708 1.0965 1.0655 | 72.8 | 65.48 |
| AA [16] | 13 24 30 | 0.79 1.07 1.012 | 72.89 | 65.45 |
| HHO [17] | 13 24 30 | 0.8173 1.0829 1.0465 | 72.80 | 65.4956 |
| SPBO [17] | 14 24 30 | 0.7723 1.1059 1.0685 | 72.79 | 65.5003 |
| AOA | 14 24 30 | 0.7764 1.0990 1.0702 | 72.79 | 65.50 |
| Method | Bus No. | CB Size (kVAR) | Power Loss (kW) | Loss Reduction (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9 | 450 | |||
| IP [18] | 29 | 800 | 171.78 | 18.58 |
| 30 | 900 | |||
| 10 | 450 | |||
| SA [18] | 30 | 350 | 151.75 | 28.07 |
| 14 | 900 | |||
| 18 | 349.6 | |||
| BFOA [19] | 30 | 820.6 | 144.04 | 31.72 |
| 33 | 277.3 | |||
| 8 | 556 | |||
| AOA | 24 | 513 | 139.41 | 33.92 |
| 30 | 965 |
| Method | Bus No. | DG Size (kW) | Bus No. | CB Size (kVAR) | Power Loss (kW) | Loss Reduction (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16 | 0.25 | 18 | 300 | |||
| GA [21] | 22 | 0.25 | 29 | 300 | 71.25 | 64.661 |
| 30 | 0.50 | 30 | 600 | |||
| 17 | 0.5424 | 18 | 163.2 | |||
| BFOA [19] | 18 | 0.1604 | 30 | 541.0 | 41.41 | 80.37 |
| 33 | 0.8955 | 33 | 338.4 | |||
| 25 | 0.973 | 23 | 465 | |||
| WCA [22] | 29 | 1.04 | 30 | 565 | 24.688 | 87.82 |
| 11 | 0.563 | 14 | 535 | |||
| 14 | 0.794 | 14 | 384 | |||
| AOA | 25 | 0.881 | 25 | 436 | 12.6571 | 94.00 |
| 30 | 1.100 | 30 | 1009 |
| Method | Bus No. | DG Size (MW) | OPF | Power Loss (kW) | Loss Reduction (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13 | 0.698 | 0.86 | |||
| BSOA [34] | 29 | 0.402 | 0.71 | 29.65 | 85.94 |
| 31 | 0.658 | 0.70 | |||
| 6 | 0.9004 | 0.82 | |||
| IA [35] | 14 | 0.6298 | 0.82 | 22.29 | 89.45 |
| 30 | 0.9004 | 0.82 | |||
| 13 | 0.798 | 0.9 | |||
| EA [36] | 24 | 1.099 | 0.9 | 11.80 | 94.41 |
| 30 | 1.050 | 0.71 | |||
| 14 | 0.7776 | 0.9081 | |||
| AOA | 24 | 1.0535 | 0.9018 | 11.7752 | 94.42 |
| 30 | 1.0504 | 0.7136 |
| Scenarios | Active Power Loss (kW) | Loss Reduction (%) | Reactive Power Loss (kVAR) | Loss Reduction (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base Case | 210.98 | 143.14 | ||
| Scenario I | 72.79 | 65.50 | 50.73 | 64.56 |
| Scenario II | 139.41 | 33.92 | 95.01 | 33.62 |
| Scenario III | 12.6571 | 94.00 | 10.37 | 92.75 |
| Scenario IV | 11.7752 | 94.42 | 9.83 | 93.13 |
| Method | Optimal Location (Bus No.) | Optimal DG Size (MW) | Power Loss (kW) | Loss Reduction (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FWA [12] | 65 61 27 | 0.4085 1.1986 0.2258 | 77.85 | 65.39 |
| MTLBO [13] | 20 62 57 | 0.446 1.836 0.477 | 77.36 | 65.61 |
| JAYA [13] | 61 50 12 | 2.000 0.100 1.016 | 75.83 | 66.29 |
| GWO [13] | 61 50 12 | 2.000 0.586 0.792 | 73.43 | 67.36 |
| SIMBO-Q [15] | 61 9 17 | 1.500 0.6189 0.5297 | 71.3 | 68.3 |
| QOSIMBO-Q [15] | 9 18 61 | 0.8336 0.4511 1.500 | 71.0 | 68.43 |
| AA [16] | 11 17 61 | 0.499 0.377 1.668 | 69.55 | 69.09 |
| HHO [17] | 12 61 62 | 0.7341 1.1912 0.7623 | 74.14 | 67.046 |
| SPBO [17] | 11 18 61 | 0.5599 0.3692 1.1731 | 69.45 | 69.1306 |
| WOA [38] | 49 18 61 | 0.84046 0.53352 1.8084 | 70.19 | 68.40 |
| DA [38] | 66 14 61 | 0.23147 0.52993 1.7632 | 71.10 | 68.40 |
| MFO [38] | 11 61 21 | 0.54917 1.7458 0.35254 | 69.46 | 69.13 |
| AOA | 11 61 21 | 0.5716 1.7199 0.341 | 69.43 | 69.14 |
| Method | Bus No. | CB Size (kVAR) | Power Loss (kW) | Loss Reduction (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9 | 600 | |||
| CSA [20] | 21 | 250 | 147.95 | 34.21 |
| 62 | 1200 | |||
| 58 | 900 | |||
| SA [18] | 11 | 450 | 155.45 | 30.91 |
| 59 | 600 | |||
| 26 | 150 | |||
| GSA [18] | 13 | 150 | 145.9 | 35.16 |
| 15 | 1050 | |||
| 11 | 368 | |||
| AA [16] | 21 | 231 | 145.21 | 35.46 |
| 61 | 1196 | |||
| 11 | 410 | |||
| AOA | 21 | 233 | 145.096 | 35.51 |
| 61 | 1234 |
| Method | Bus No. | DG Size (kW) | Bus No. | CB Size (kVAR) | Power Loss (kW) | Loss Reduction (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17 | 0.5408 | 2 | 1187.9 | |||
| WCA [22] | 61 | 2.0 | 62 | 1237.3 | 33.339 | 85.18 |
| 69 | 1.1592 | 69 | 269.7 | |||
| 19 | 0.294 | 7 | 450 | |||
| BSA [23] | 22 | 0.219 | 2 | 300 | 7.6047 | 96.61 |
| 61 | 1.768 | 3 | 150 | |||
| 19 | 0.358 | 11 | 600 | |||
| SSA [39] | 10 | 0.518 | 48 | 600 | 4.837 | 97.85 |
| 60 | 1.6735 | 60 | 1200 | |||
| 61 | 1.6511 | 61 | 1282 | |||
| AOA | 11 | 0.521 | 11 | 414 | 4.6243 | 97.94 |
| 21 | 0.334 | 21 | 234 |
| Method | Bus No. | DG Size (MW) | OPF | Power Loss (kW) | Loss Reduction (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 61 | 1.8076 | 0.85 | |||
| WOA [38] | 4 | 1.9887 | 0.85 | 7.89 | 96.49 |
| 17 | 0.53472 | 0.85 | |||
| 11 | 0.49634 | 0.85 | |||
| DA [38] | 61 | 1.7481 | 0.85 | 5.01 | 97.77 |
| 17 | 0.39501 | 0.85 | |||
| 11 | 0.51573 | 0.85 | |||
| MFO [38] | 61 | 1.7456 | 0.85 | 5.0 | 97.77 |
| 18 | 0.38617 | 0.85 | |||
| 17 | 0.510 | 0.82 | |||
| IA [35] | 5 | 0.6798 | 0.82 | 4.95 | 97.74 |
| 61 | 1.6999 | 0.82 | |||
| 11 | 0.548 | 0.82 | |||
| EA [36] | 18 | 0.380 | 0.83 | 4.48 | 98.00 |
| 61 | 1.733 | 0.82 | |||
| 11 | 0.453 | 0.7071 | |||
| AOA | 21 | 0.349 | 0.8342 | 4.44 | 98.03 |
| 61 | 1.7064 | 0.8290 |
| Scenarios | Active Power Loss (kW) | Loss Reduction (%) | Reactive Power Loss (kVAR) | Loss Reduction (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base Case | 224.95 | 102.13 | ||
| Scenario I | 69.43 | 69.14 | 34.95 | 65.78 |
| Scenario II | 145.096 | 35.51 | 67.64 | 33.77 |
| Scenario III | 4.6243 | 97.94 | 6.89 | 93.25 |
| Scenario IV | 4.44 | 98.03 | 6.82 | 93.32 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pamuk, N.; Uzun, U.E. Optimal Allocation of Distributed Generations and Capacitor Banks in Distribution Systems Using Arithmetic Optimization Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14020831
Pamuk N, Uzun UE. Optimal Allocation of Distributed Generations and Capacitor Banks in Distribution Systems Using Arithmetic Optimization Algorithm. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(2):831. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14020831
Chicago/Turabian StylePamuk, Nihat, and Umut Emre Uzun. 2024. "Optimal Allocation of Distributed Generations and Capacitor Banks in Distribution Systems Using Arithmetic Optimization Algorithm" Applied Sciences 14, no. 2: 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14020831
APA StylePamuk, N., & Uzun, U. E. (2024). Optimal Allocation of Distributed Generations and Capacitor Banks in Distribution Systems Using Arithmetic Optimization Algorithm. Applied Sciences, 14(2), 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14020831








