Abstract
The compute-in-memory (CIM) which embeds computation inside memory is an attractive scheme to circumvent von Neumann bottlenecks. This study proposes a logic-compatible embedded DRAM architecture that supports data storage as well as versatile digital computations. The proposed configurable memory unit operates in three modes: (1) memory mode in which it works as a normal dynamic memory, (2) logic–arithmetic mode where it performs bit-wise Boolean logic and full adder operations on two words stored within the memory array, and (3) convolution mode in which it executes digitally XNOR-and-accumulate (XAC) operation for binarized neural networks. A 1.0-V 4096-word × 8-bit computational DRAM implemented in a 45-nanometer CMOS technology performs memory, logic and arithmetic operations at 241, 229, and 224 MHz while consuming the energy of 7.92, 8.09, and 8.19 pJ/cycle. Compared with conventional digital computing, it saves energy and latency of the arithmetic operation by at least 47% and 46%, respectively. For VDD = 1.0 V, the proposed CIM unit performs two 128-input XAC operations at 292 MHz with an energy consumption of 20.8 pJ/cycle, achieving 24.6 TOPS/W. This marks at least 11.9× better energy efficiency and 38.8× better delay, thereby achieving at least 461× better energy-delay product than traditional 8-bit wide computing hardware.
1. Introduction
Massive and frequent data move between memory banks and processing elements incurs substantial latency and energy cost in the traditional von Neumann machine. Compute-in-memory (CIM), which performs computations inside the memory units, is an attractive approach to solve such memory wall issues and thereby sustain the throughput and energy requirements of data-driven computing applications such as voice/image recognition, autonomous driving, artificial intelligence (AI), and similar big data technologies [1,2]. It is desirable for the CIM design to be compatible with logic CMOS process, to achieve short latency as well as high energy efficiency, and to offer dense bit cell footprint and robust computation against process variations.
In recent years, various memory hierarchies such as SRAM, 1T/1C DRAM, and emerging memories have been explored in order to implement CIM schemes. The SRAM-based CIM designs [3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31] are compatible with the logic CMOS process and feature short latency. But the bit area is large (e.g., 6T, 7T, 8T, 8T/1C, 9T, 9T/1C, 10T, 12T, or 16T bit cells), thus the limited memory capacity in the CIM macros restricts the complexity of energy-efficient computing systems. Furthermore, SRAM arrays suffer from substantial leakage power dissipation, often dominating the total power budget of the entire computing systems. The embedded 1T/1C DRAM-based CIM design [32] might be an alternative to SRAM-based architecture with its higher integration density. However, the 1T/1C DRAM structure requires additional process steps for storage capacitors and cannot perform dot product computations directly on the memory bitlines because of its destructive readout. The CIM implementations based on nonvolatile memories such as RRAM [33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40], PCRAM [41], STT-MRAM [42], or memristor [43] have also fostered computing in memory, but such emerging technologies are still immature. Poor reliability and the low endurance of RRAM devices [44], the long write time and high write energy of PCRAMs [45], the low on–off ratio of STT-MRAM cells [46], the bad scalability and limited yield of memristive devices [47], etc., make them less attractive for accurate and efficient CIM units.
In particular, the embedded gain cell DRAM (GCDRAM) is one of the prospective candidates to realize the CIM scheme, owing to its compatibility with standard logic CMOS process and compact bit cell area. Despite the relatively short retention time of the embedded gain cell itself, the prior GCDRAMs [48,49,50,51,52,53] achieved better area efficiency and much smaller standby power dissipation compared with 6T or read-decoupled (RD) 8T SRAMs. In addition, recent GCDRAM-based CIM works [54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61] have demonstrated the multiply-and-average (MAV) or multiply-and-accumulate (MAC) computations within the gain cell array. They improved substantially both power consumption and throughput in processing the deep neural networks (DNNs). In this work, we propose another GCDRAM-based CIM unit, called the digital computing gain cell DRAM (DC-GCDRAM). The proposed DC-GCDRAM array supports three modes of operation: memory mode, logic–arithmetic mode, and convolution mode. In the memory mode, the DC-GCDRAM works as a usual DRAM compatible with standard CMOS technology. In the logic–arithmetic mode, the proposed architecture performs bit-wise Boolean logic as well as arithmetic computations on operands stored within the memory array. In the convolution mode, the proposed DC-GCDRAM executes the binary XNOR-and-accumulate (XAC) operation on weights stored within the cell array and external input activations. This full-digital CIM unit maintains high circuit reliability. It effectively eliminates the analog design issues such as data conversion overheads and computing accuracy loss caused by process variations. All of the results were obtained using 45-nanometer generic CMOS technology.
2. Logic-Compatible 3T Memory Cell
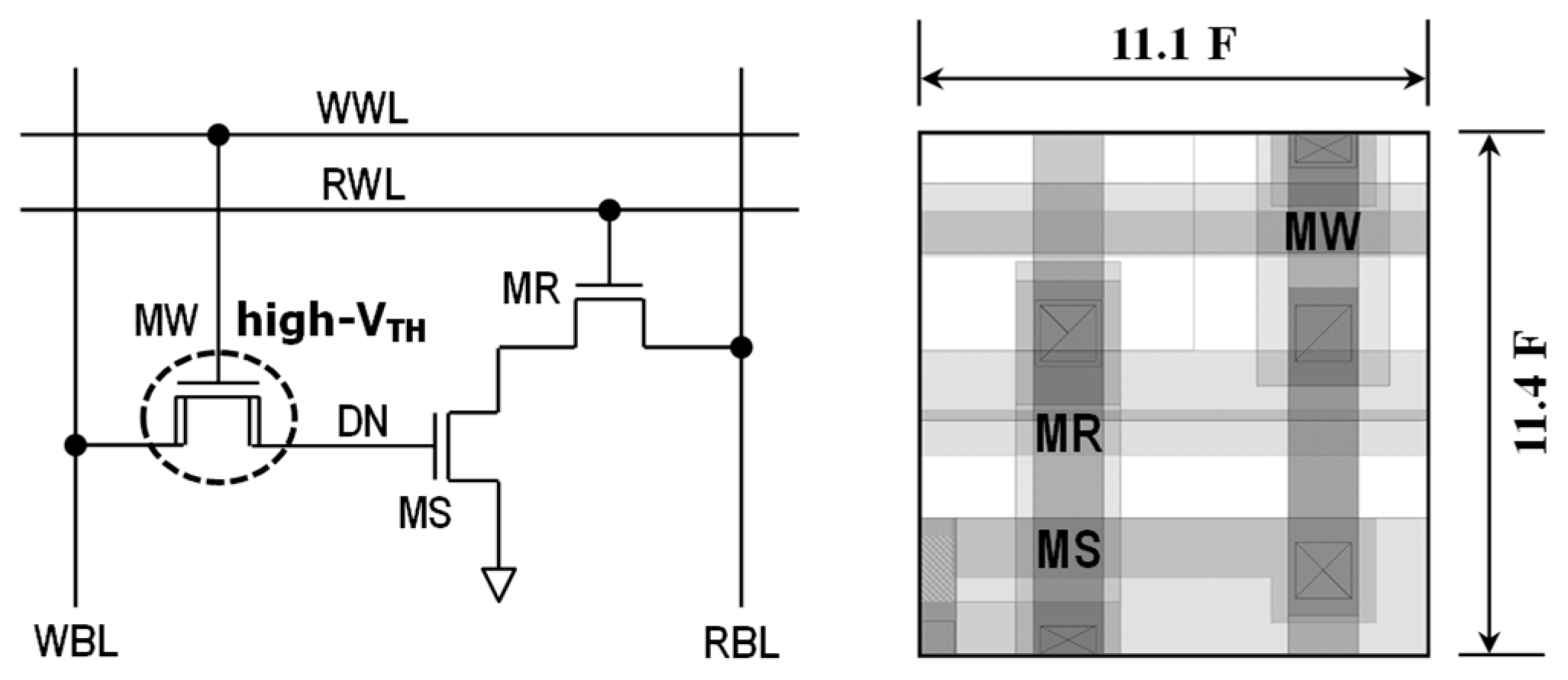
In Figure 1, we show the hybrid 3T gain cell schematic and its layout. Here, MW denotes the high threshold-voltage (VTH) write-transistor, MR is the standard VTH read-transistor, and MS is the standard VTH storage-transistor. In addition, DN means data node, RBL is read-bitline, RWL is read-wordline, WWL is write-wordline, WBL is write-bitline, and so on. The bit cell area is 0.5 × 0.515 µm2, which is 59.2% and 49.9% smaller than those of RD-8T and 6T SRAM in the same 45 nm generic process.
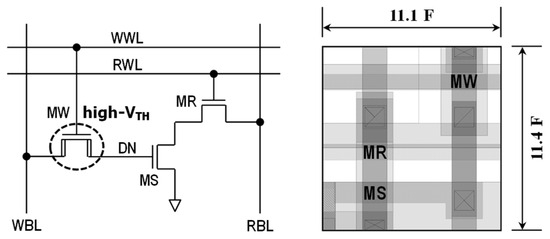
Figure 1.
Schematic and layout of hybrid 3T gain cell. (DN: data node, RBL: read-bitline, RWL: read-wordline, WWL: write-wordline, WBL: write-bitline).
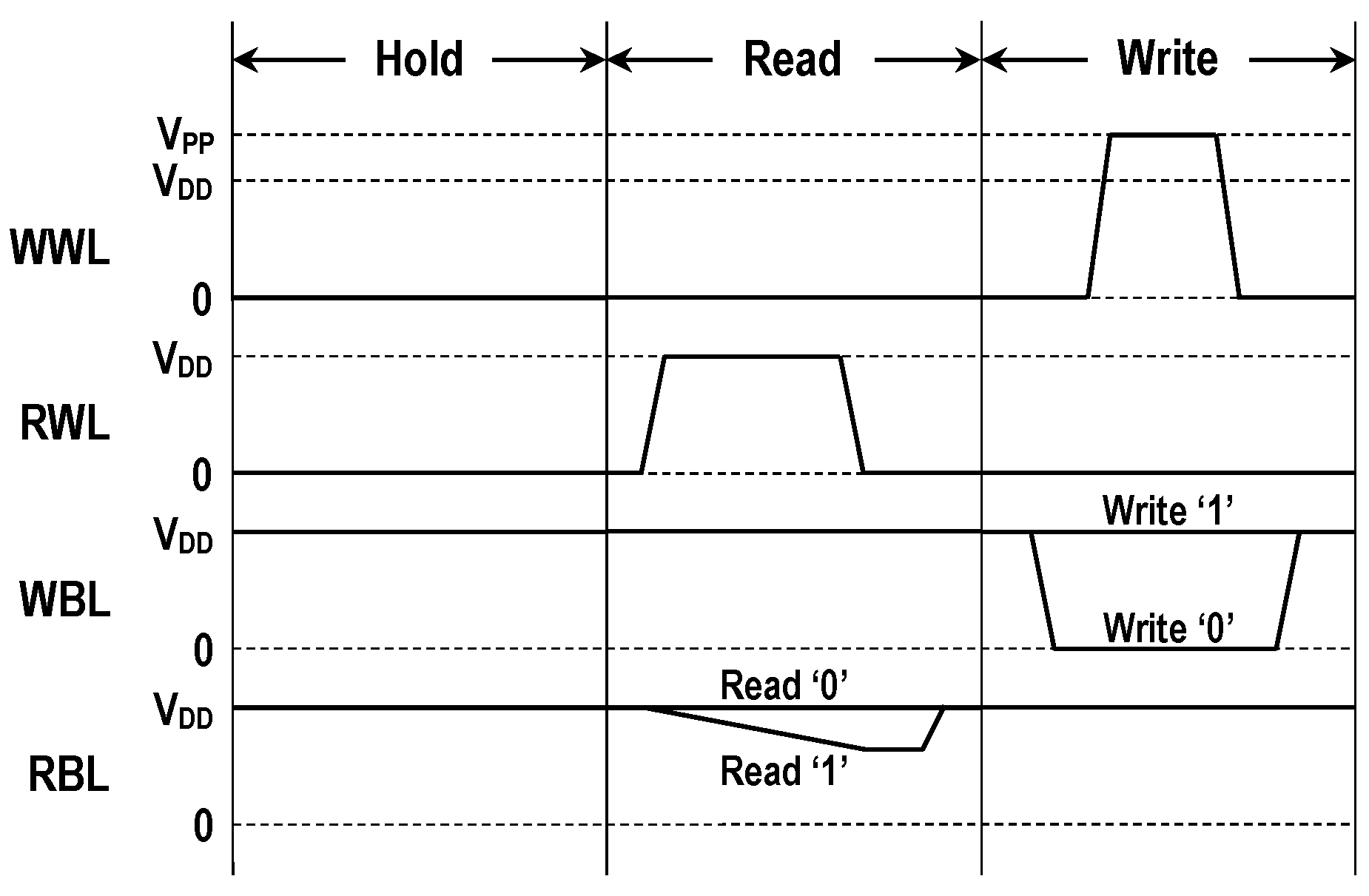
The voltage waveforms depicted in Figure 2 explain the operating principle of the 3T cell. During the standby, RWL and WWL are grounded while both WBL and RBL are precharged to VDD. This hold condition turns MW and MR off, thus storage in the DN is preserved. To read the stored information, RWL is raised to high while WWL is grounded. If DN is low, MS is in the off state; hence, RBL is kept at VDD. If DN is high, MS is turned on; thus, a read current from RBL flows to the ground. This lowers the RBL level. Two different RBL levels are detected by a voltage sense amplifier (SA). To write a datum on the cell, WBL is driven to either low or high while RWL is grounded. WWL is then boosted to VPP which is higher than the supply voltage. This allows a new datum from the write-bitline to be fully written to DN through the high VTH write-transistor.
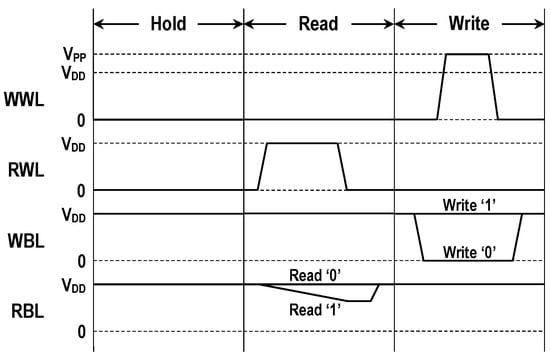
Figure 2.
Signal voltages for bit cell operation.
3. Proposed DC-GCDRAM Architecture
3.1. Overview
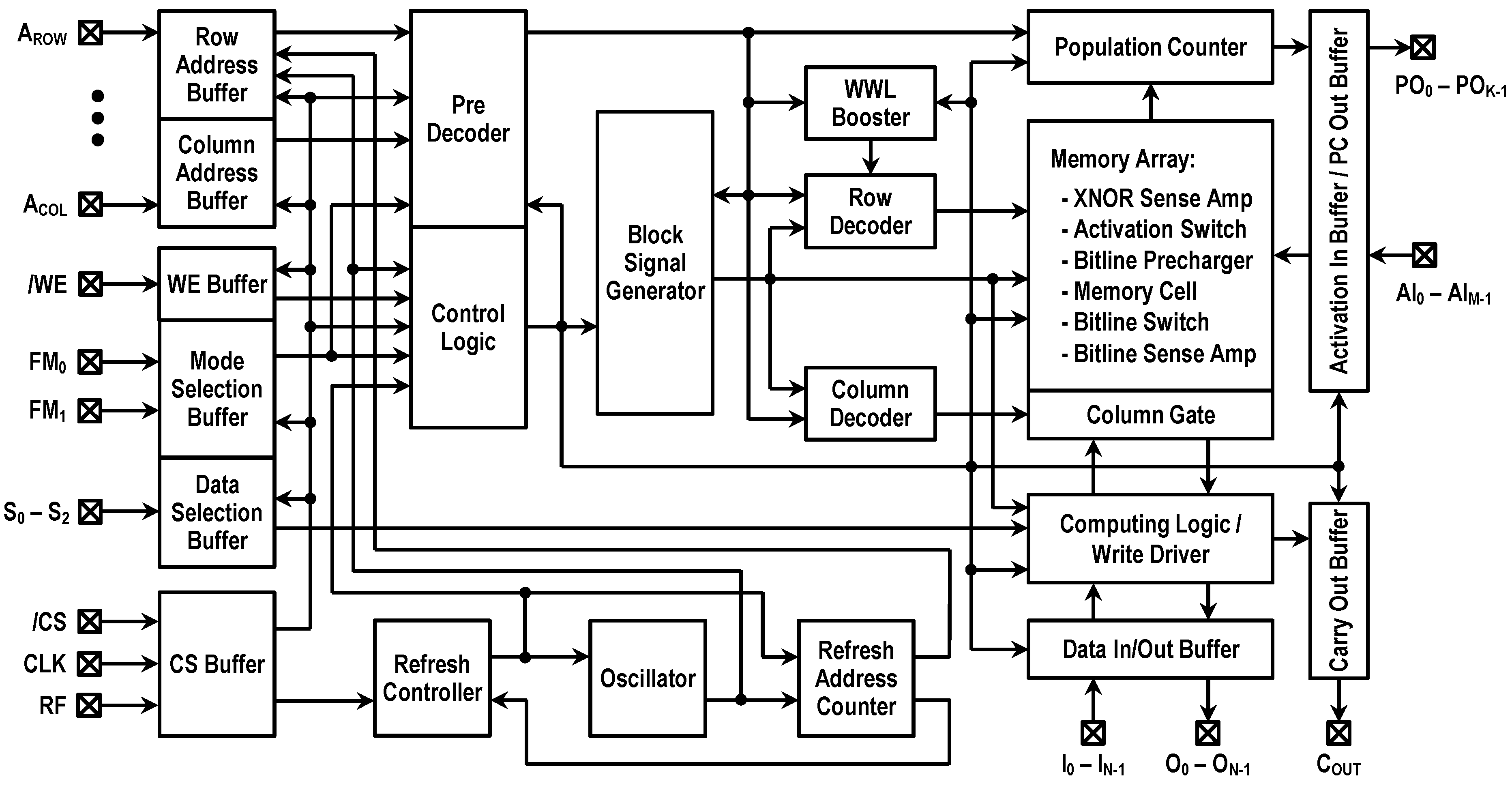
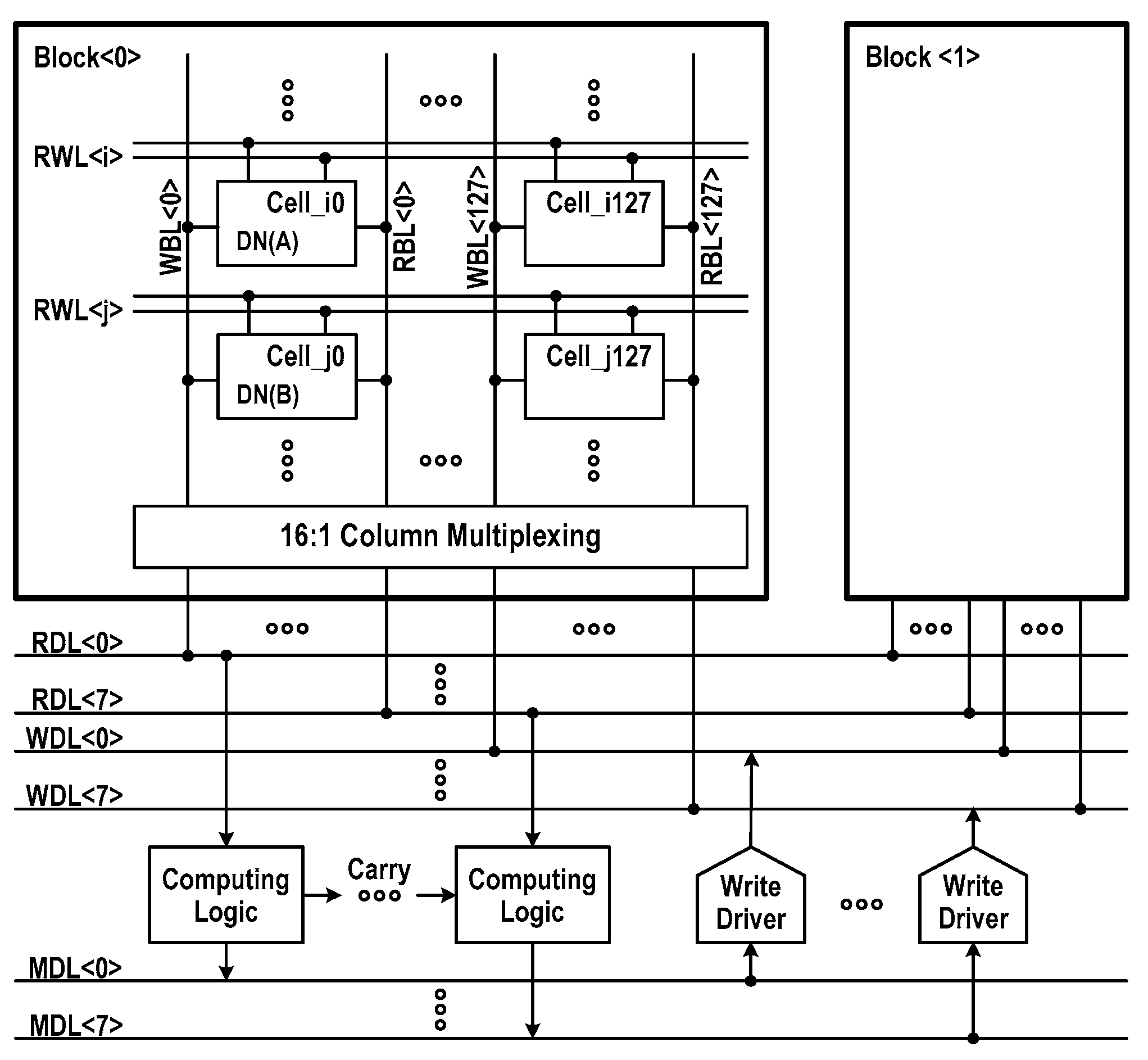
Figure 3 represents the overall structure of the reconfigurable DC-GCDRAM. The bit storage element of this CIM macro is the 3T gain cell described in Section 2. Basically, the memory array comprises a pair of 16 kbit storage blocks. Each block consists of 128 columns and 128 rows. The memory I/O is 8 bits wide. This CIM macro contains two WWL boosters, dedicated to 16 kbit block each, supplying the VPP voltage. The entire CIM macro is operating at single power supply.
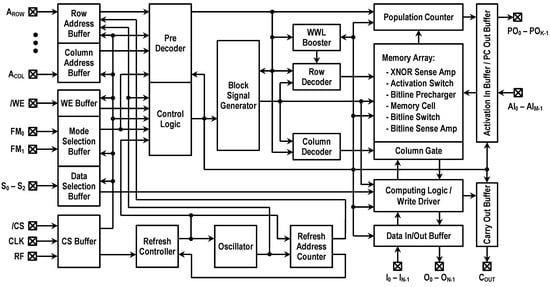
Figure 3.
Block diagram of the reconfigurable DC-GCDRAM macro.
The proposed DC-GCDRAM allows functional mode switching among memory, logic–arithmetic, and convolution operations. The operational modes are selected with the external signals named FM0 and FM1. If both FM1 and FM0 are low or high, the CIM macro operates in the memory mode where it performs read/write/refresh as regular DRAM. If FM1 is low and FM0 is high, the macro operates in the logic–arithmetic mode. In this mode, the macro turns on two rows at once and uses binary logic SAs within the computing logic to generate bit-wise Boolean logic primitives and addition results. If FM0 is low and FM1 is high, the macro enters the convolution mode. In this functional mode, the macro allows the XNOR and population count operation for binarized neural networks (BNNs). For each cycle, the CIM macro utilizes XNOR sense amplifiers (XNOR-SAs) within each memory block to compute bit-wise XNORs between activation inputs and row-wise stored weights, and then generates the accumulation results at each population counter output. The details of these three modes of operation are described in the following subsections.
3.2. Memory Mode
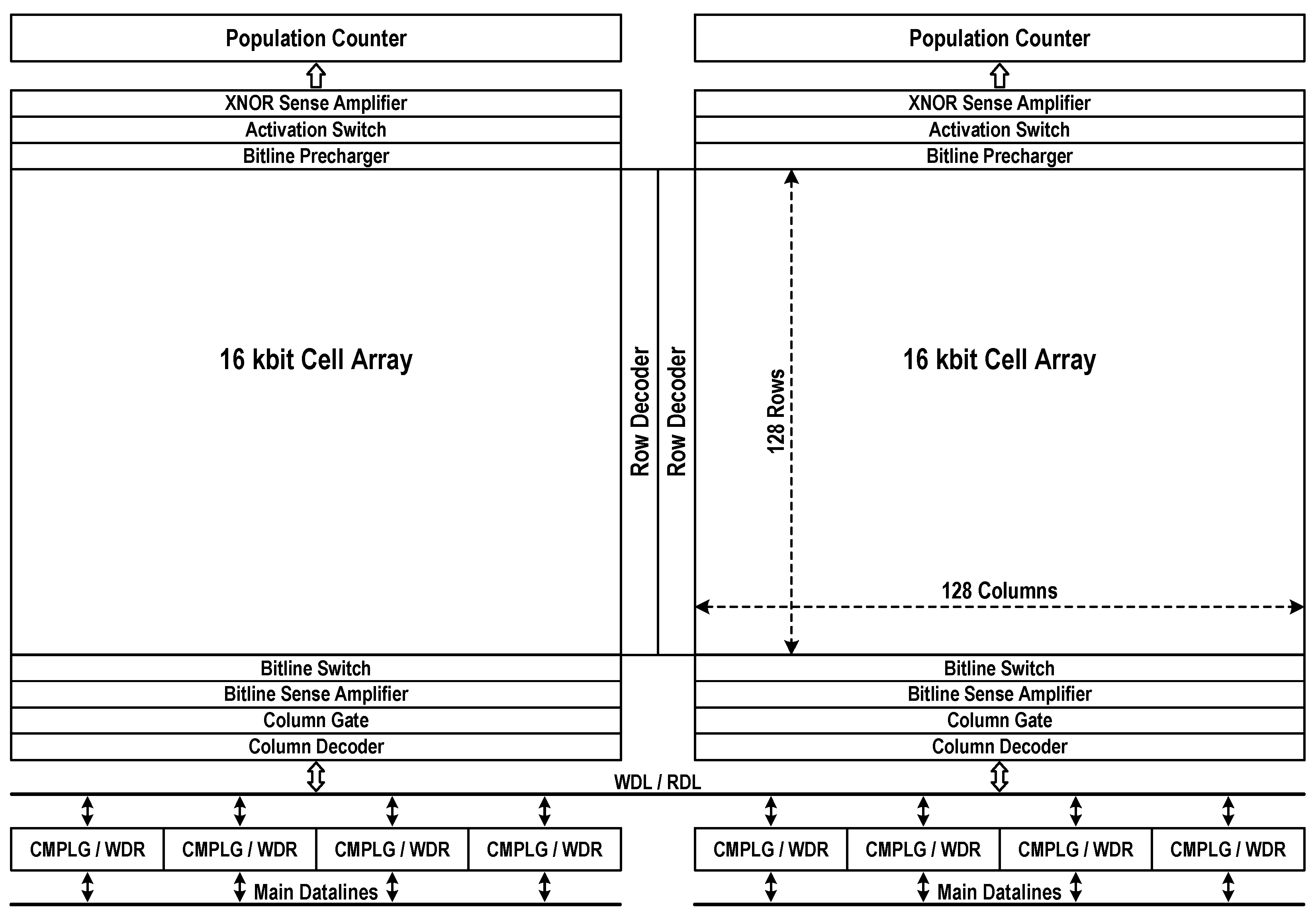
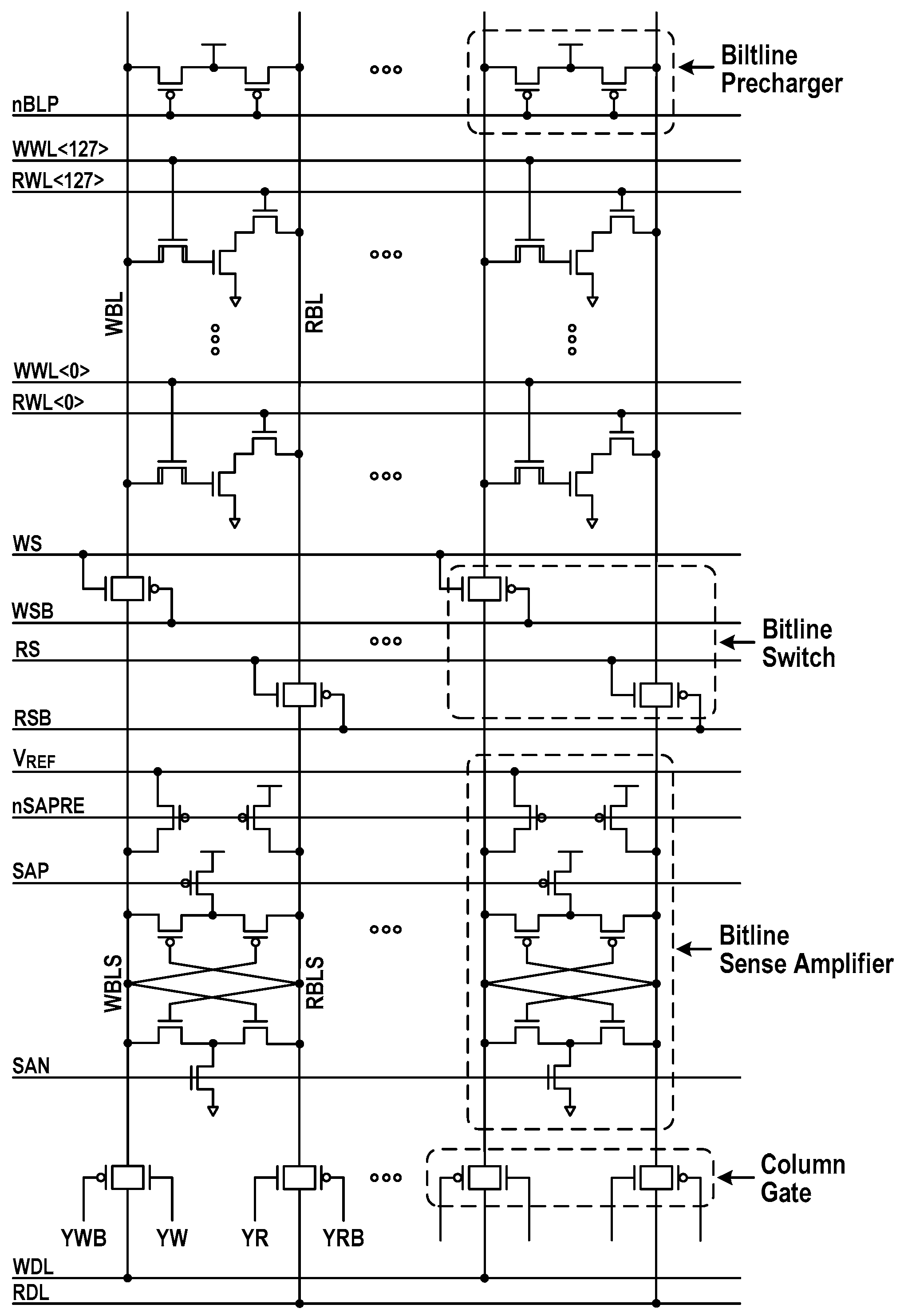
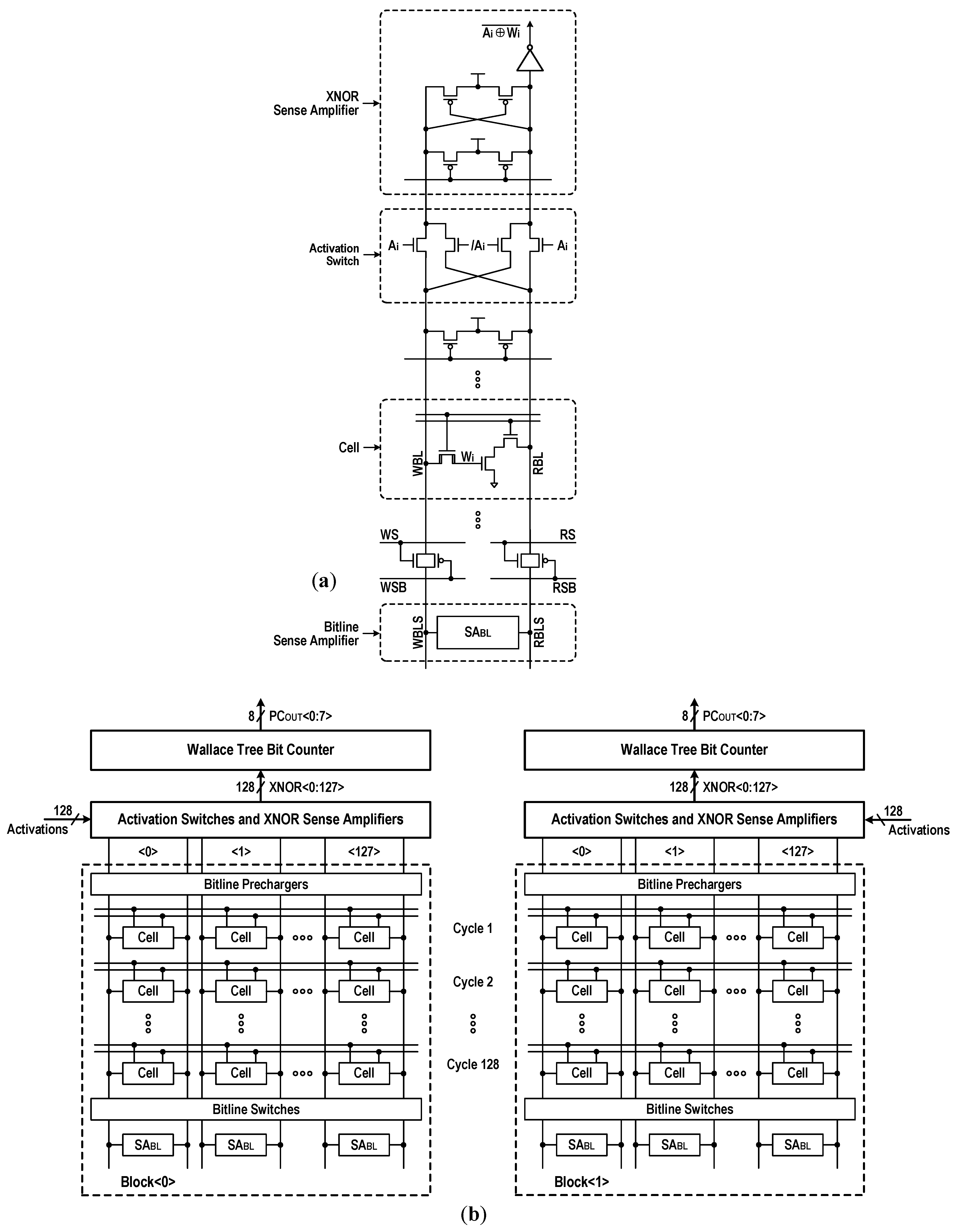
Figure 4 details the physical and logical organization of compute-in-memory. The whole memory array comprises bilaterally symmetric two 16 kbit storage blocks with row decoders in the middle. The fundamental organization is 4k-word × 8-bit. Inside each 16 kbit storage block, the bitline (BL) switches, BL sense amplifiers (BL-SAs), column decoders, and column gates are placed on the bottom of array, while the XNOR-SAs, activation switches and BL prechargers are placed on the other side of array. The population counters are placed over the storage blocks, while the computing logics (CMPLGs) and write drivers (WDRs) are placed under the two adjacent blocks. The read-datalines (RDLs) and write-datalines (WDLs), which are shared by two storage blocks, are used to transfer single-ended 8-bit signals between selected columns and CMPLGs or WDRs.
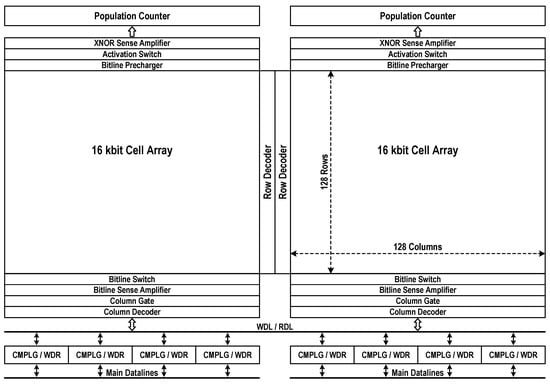
Figure 4.
Compute-in-memory organization. (RDL: read-dataline; WDL: write-dataline; CMPLG: computing logic; WDR: write-driver).
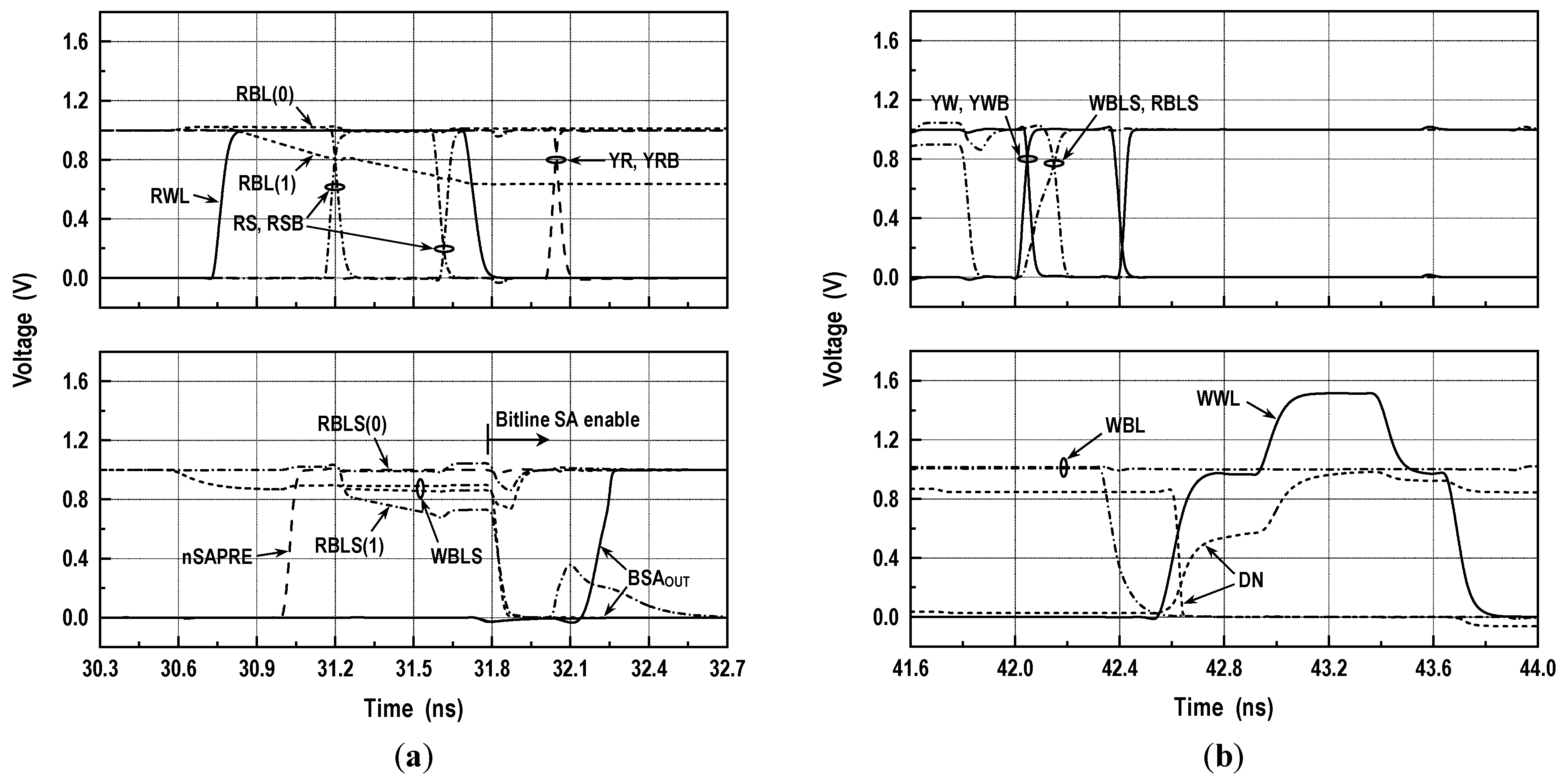
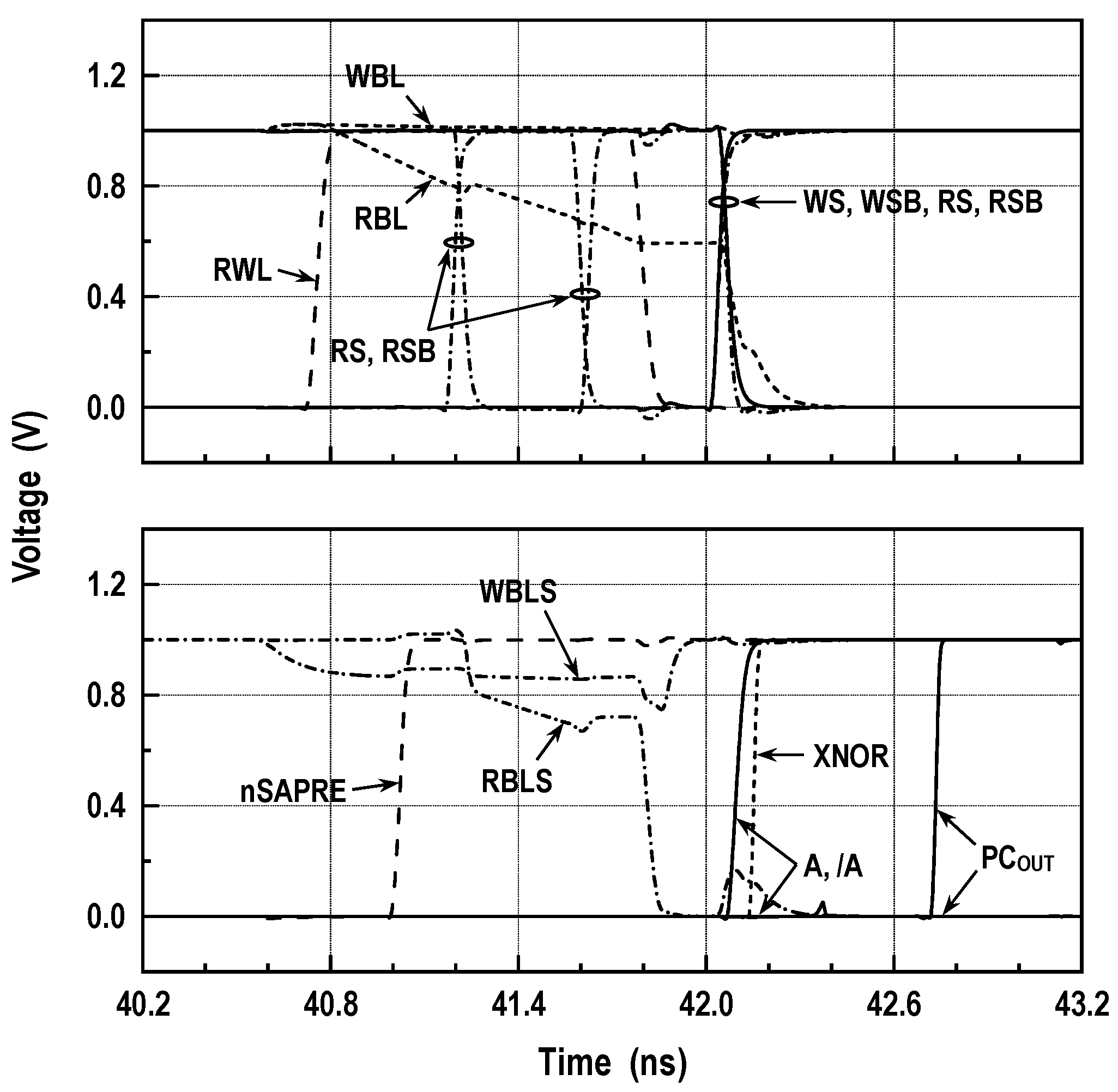
Figure 5 depicts the simplified circuitry of a 16 kbit storage array. During the hold, the BL switches are in an off state, and both WBL and RBL are precharged to VDD. Every memory access turns on a row and activates the corresponding BL-SA. The latch-type BL-SA in this design makes use of a reference signal (VREF) that is positioned in-between data ‘0’ and data ‘1’ signals. In Figure 6a, we show the simulated waveforms for read operation. After turning off the BL prechargers, the read access begins by activating RWL, causing the RBL level to remain stationary or to discharge. Meanwhile, WBLS and RBLS are initially precharged to VREF and VDD, respectively, and then floated by raising nSAPRE to VDD. Triggering RS and RSB forwards the RBL signal to RBLS. Before sensing the data, the read BL switches are turned off. Then, the BL-SAs are activated by firing SAP and SAN. Afterward, triggering YR and YRB transfers a full-swing RBLS signal to RDL. The latency from RWL to block SA output (BSAOUT) measures 1.5 ns at the 1.0 V supply. Simulated waveforms in Figure 6b illustrate the write operation. After BL-SAs determine the status of accessed cells, an internal write-back operation follows. To store external data on the cells, the new data for selected columns are driven into WBLSs when YW and YWB are triggered. The BL-SAs toggle if the new contents are different from the accessed ones. Next, WBLs are connected to WBLSs by switching WS and WSB. Then, WWL is fired, allowing the external data to be fully written to the selected cells.
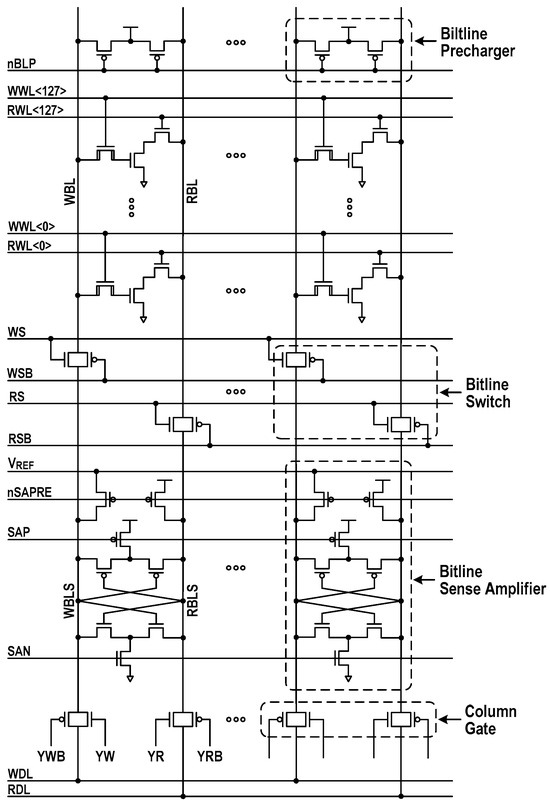
Figure 5.
Simplified configuration of a 16 kbit memory array.
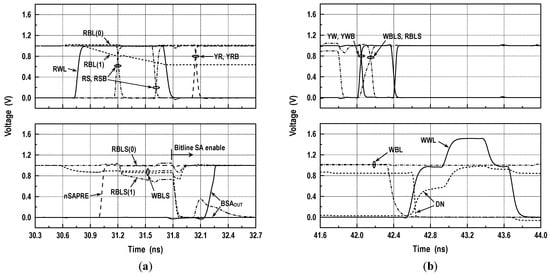
Figure 6.
Simulations for memory operation (VDD = 1.0 V, room temperature): (a) read-waveforms and (b) write-waveforms. Here, the signal names are denoted in the circuit schematic shown in Figure 5, BSAOUT denotes the block SA output within the computing logic, and DN represents the data node of the memory cell. In addition, RBL(1) and RBL(0) denote the read-bitline signals corresponding to data ‘1’ and ‘0’, and RBLS(1) and RBLS(0) represent the RBLS signals corresponding to data ‘1’ and ‘0’, respectively.
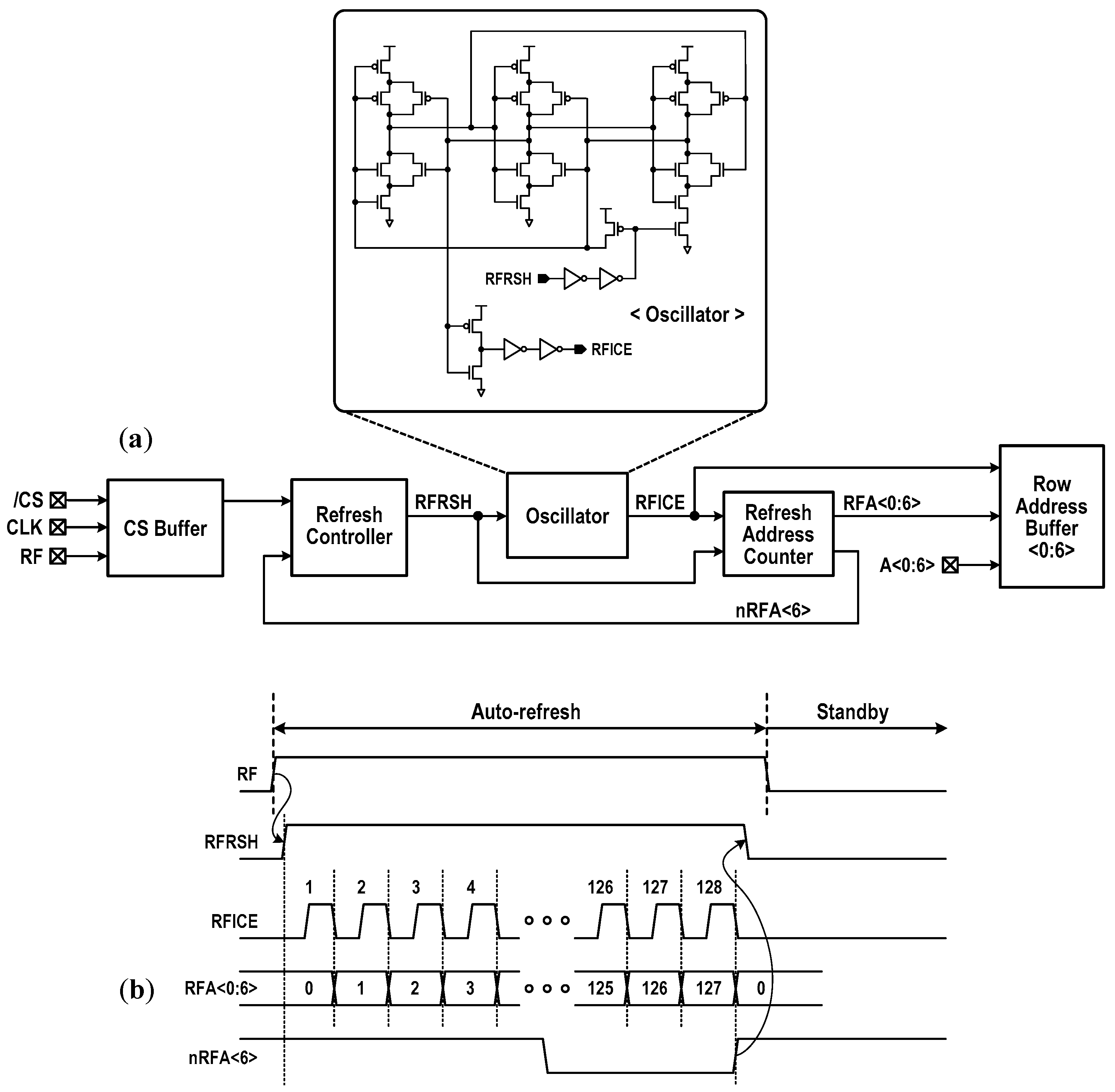
In Figure 7, we show the data refresh scheme used in this design. Basic refresh circuitry consists of a refresh controller and a 7-bit address counter with an oscillator. The row address buffers switched by internal refresh signals provide either the refresh address (RFA<0>~RFA<6>) or the normal row address (A<0>~A<6>) to the storage array. If an external signal RF is low, the CIM macro is available for memory or two other mode operations. To enter into the auto-refresh, RF is set to high for 0.96 μs or over. This blocks the incoming functional command and initiates a series of refresh cycles for all memory rows, corresponding to simple read and write-back with column gate off. The rise in RF activates a refresh demanding signal RFRSH, then the 7-bit counter begins to increase the address of row to be refreshed one by one. A refresh cycle activates two rows (one from each 16 kbit storage block in Figure 4) at the same time, thus 256 bits are restored for each cycle. Right after the last row refresh, RFRSH is finally reset to low. In this design, a refresh time of 100 μs or longer achieves a refresh overhead less than 1%.
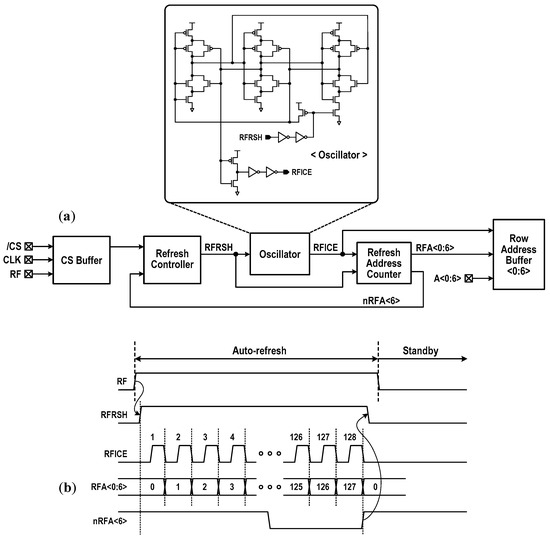
Figure 7.
Refresh scheme: (a) circuit configuration for auto-refresh and (b) internal timing.
3.3. Logic–Arithmetic Mode
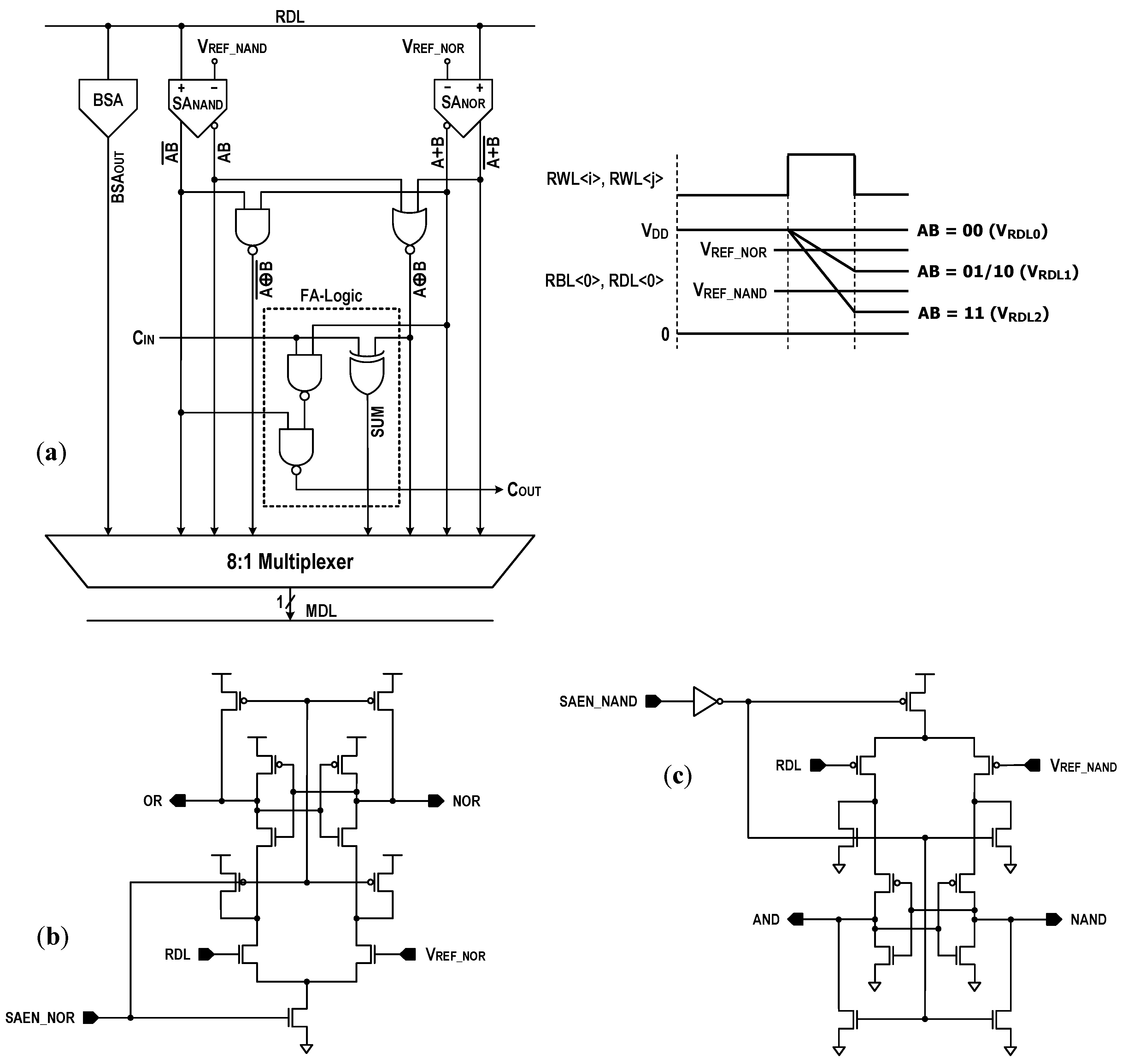
The configurable DC-GCDRAM can perform a certain logical and arithmetical operations between the row-wise stored DRAM words. In Figure 8, we show their computation schemes. During this operation mode, the CIM macro employs two row address decoders to activate two RWLs simultaneously and utilizes a NOR sense amplifier (NOR-SA) and a NAND sense amplifier (NAND-SA) within the computing logic to produce bit-wise Boolean logic primitives and addition results. The 8-bit-wide computation is realized by 16:1 column multiplexing.
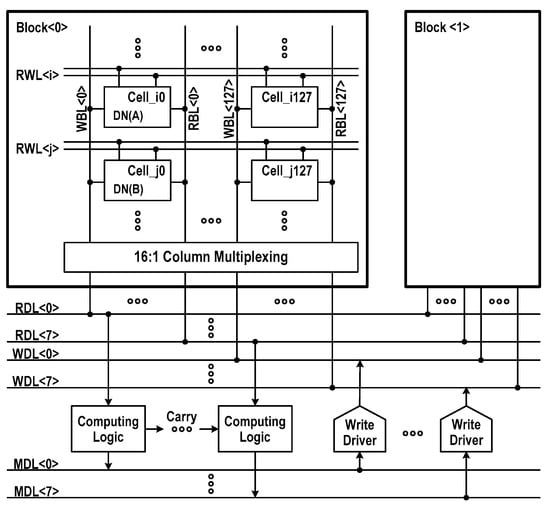
Figure 8.
Schematic of logic and arithmetic operations. (MDL: main dataline).
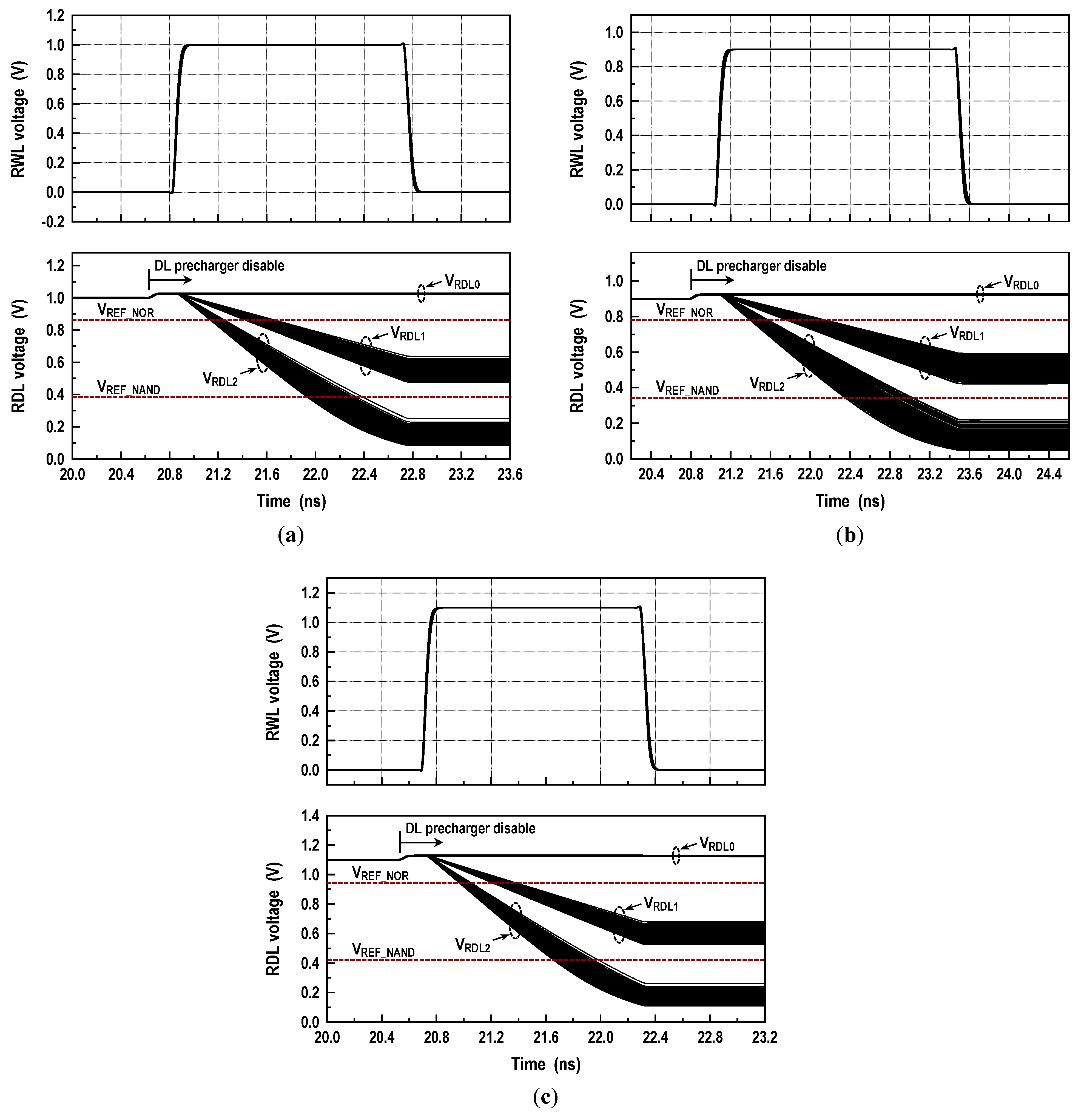
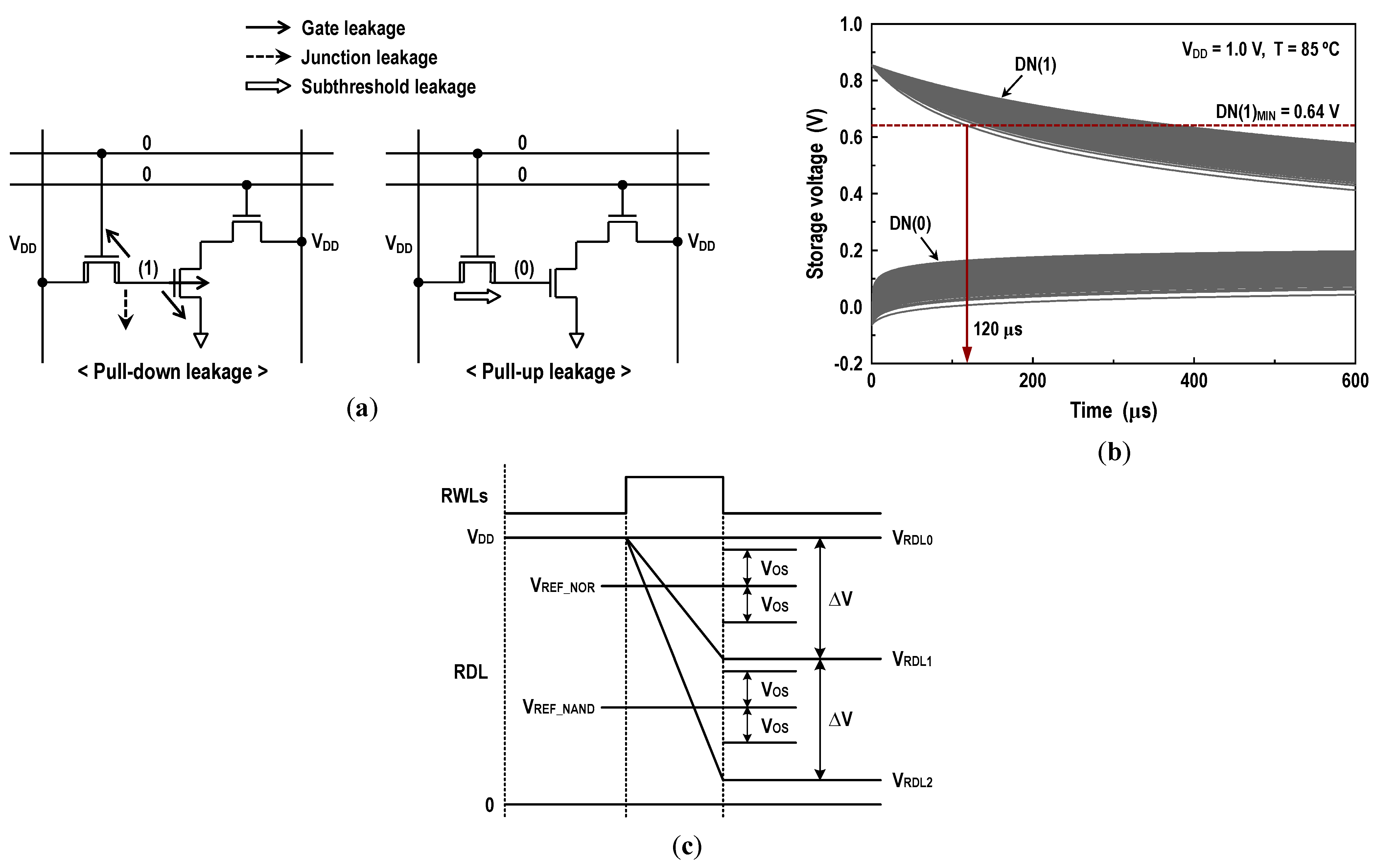
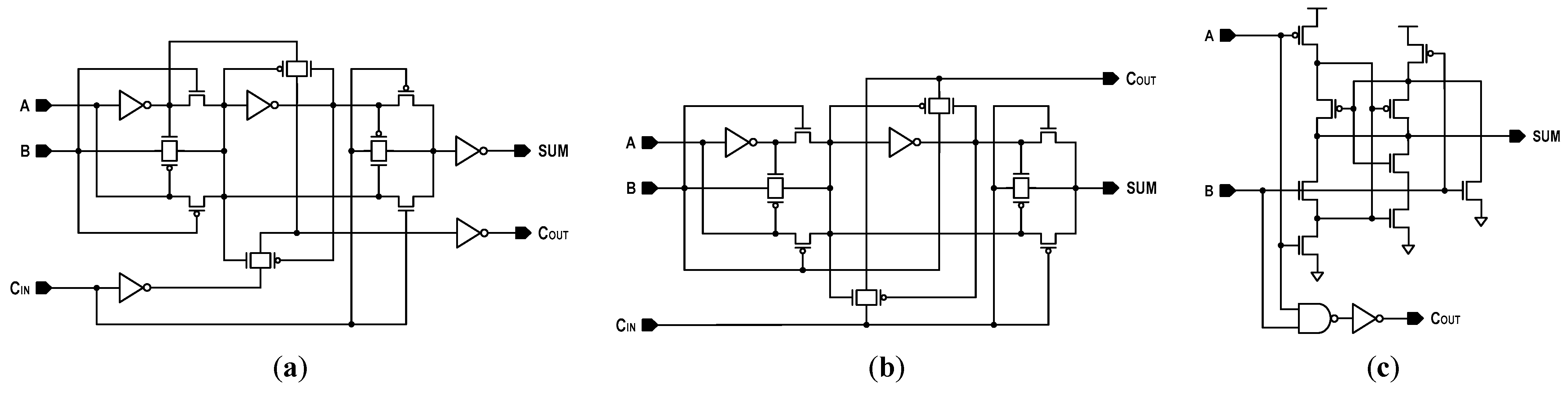
The logic–arithmetic operation begins by turning on the RBL switches and the read column gates after the BL and dataline (DL) prechargers are disabled. Then, two RWLs (RWL<i> and RWL<j>), which correspond to the memory cells storing operands ‘A’ and ‘B’, are activated. Depending on the status of the operands, the RDL will discharge, as shown in Figure 9, at three different levels. If AB = 00, the RDL does not discharge. Hence, the corresponding RDL voltage (VRDL0) is VDD. If AB = 10 or 01, one bit discharges the RDL. The resulting RDL voltage is VRDL1. If AB = 11, the RDL discharges more quickly, resulting in a lower RDL voltage (VRDL2). Comparing the RDL level against a NOR reference voltage (VREF_NOR) with the NOR-SA (SANOR) generates the NOR/OR results. Simultaneously, comparing the RDL level against a NAND reference voltage (VREF_NAND) with the NAND-SA (SANAND) produces the NAND/AND results. Moreover, the XOR operation is implemented by wiring the NOR and AND results to a NOR circuit. Similarly, the XNOR result is obtained by wiring the NAND and OR results to a NAND circuit. In addition, these Boolean logic primitives permit a full adder (FA) to be realized. A traditional FA produces SUM and carry-out (COUT) by adding three input operands A and B and carry-in (CIN). The Boolean equations for the SUM and carry-out can be expressed as follows:
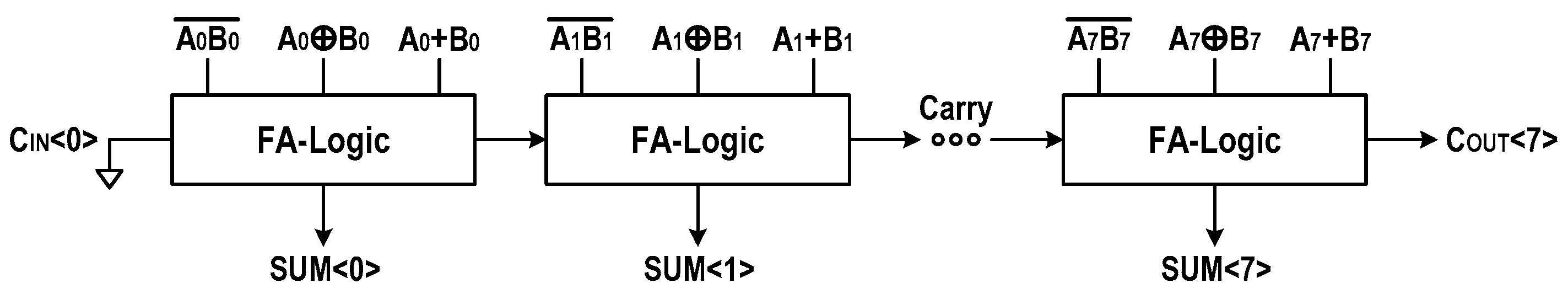
These indicate that a primitive can implement the FA’s sum using a XOR gate, and that two primitives, and , can implement COUT using two additional NAND gates. In Figure 9a, we have shown a circuitry implementing the bit-wise FA operation by the name of FA-logic. By cascading FA-logics, we realized an eight-bit ripple-carry adder (RCA), as shown in Figure 10. This 8-bit RCA operation is fully performed in one operating cycle.
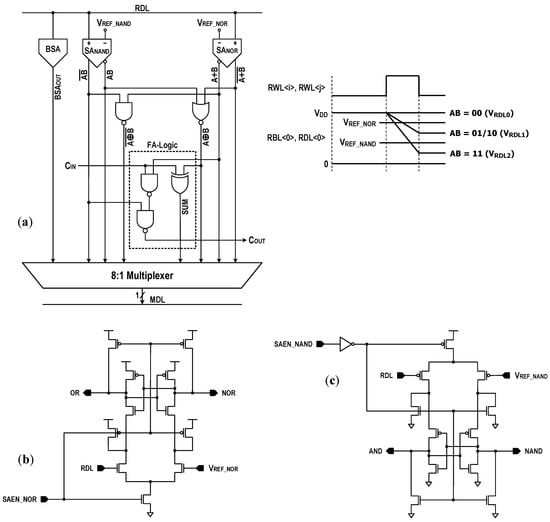
Figure 9.
Computing logic: (a) circuit schematic (BSA: block sense amplifier), (b) NOR-SA, and (c) NAND-SA. The BSA consists of gated skewed inverters for single-ended RDL sensing. It is activated only during the read operation of the memory mode.
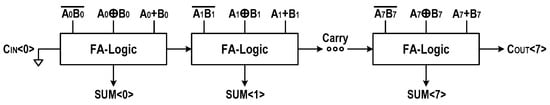
Figure 10.
Implementation of 8-bit ripple-carry adder.
One thing to be designed with care might be the voltage reference scheme. In order to produce the correct logic functions, the reference voltages should satisfy the following conditions:
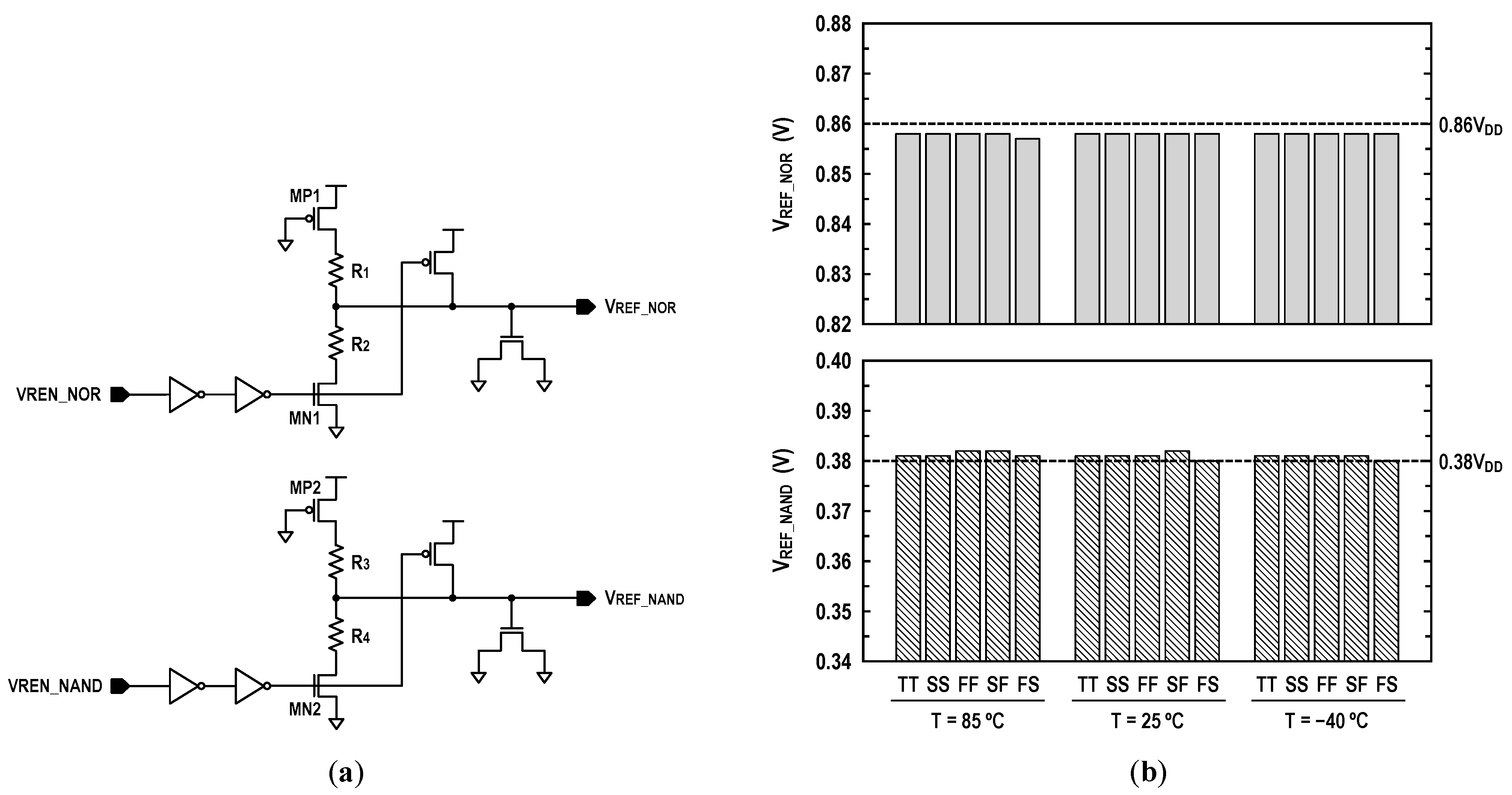
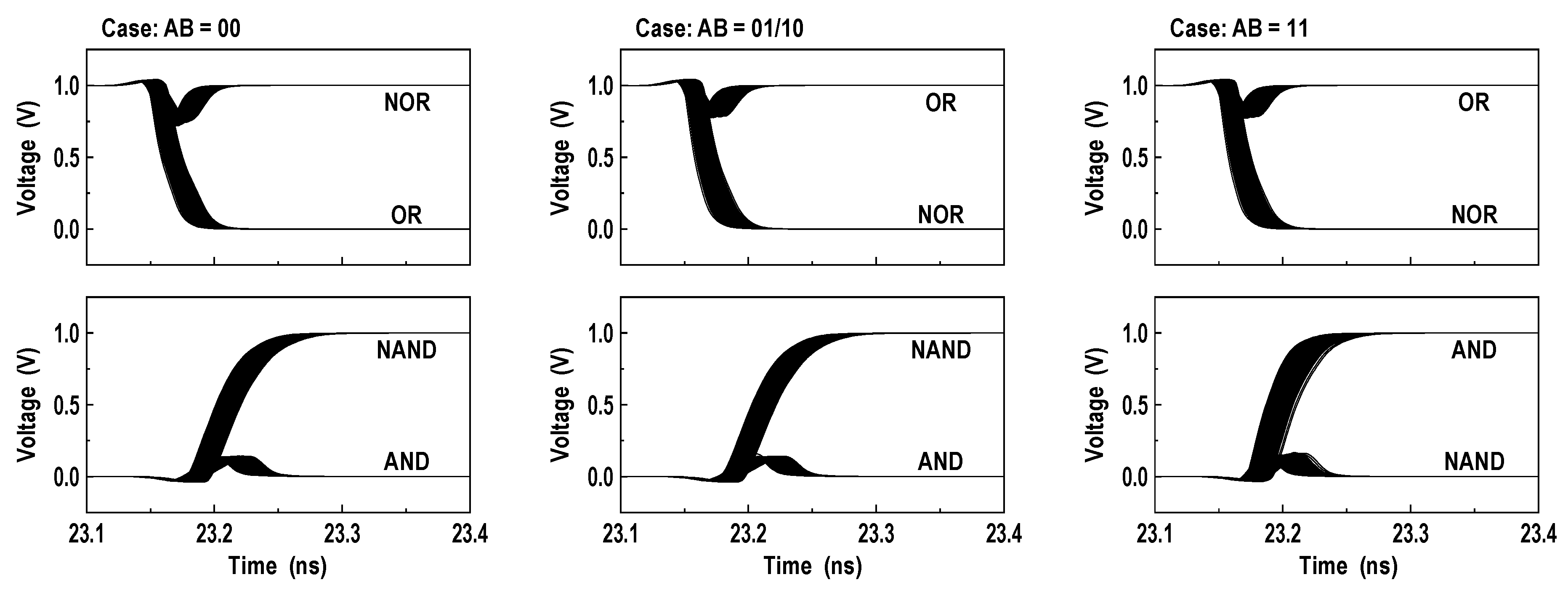
where VOS is an offset voltage of the latch-isolation NOR/NAND-SAs in Figure 9b,c. In this design, we set the target levels of VREF_NOR and VREF_NAND to 0.86VDD and 0.38VDD as shown in Figure 11. In Figure 12a, we show the reference circuits for the NOR/OR and NAND/AND operations. They form a ratioed circuit with two resistors. When the control signals (VREN_NOR, VREN_NAND) transit from low to high, the VREF voltage levels are simply determined by the ratio of two poly-silicon resistors: and where the equivalent resistances of transistors MP1, MN1, MP2, and MN2 are negligible. To obtain robust reference levels, the resistors were sized carefully across all specified temperature and process variations. Figure 12b shows the simulated characteristics of the VREF_NOR and VREF_NAND generators for temperature variations (−40 °C, 25 °C and 85 °C) as well as all possible process corners including skewed FS and SF. At the 1.0 V supply, the relative errors between the reference targets (0.86VDD and 0.38VDD) and generated voltages are less than 0.35% for VREF_NOR and 0.53% for VREF_NAND. In Figure 13, the 2500-point Monte Carlo simulations for the NOR/OR and NAND/AND outputs are shown for the three possible cases (AB = 00, 01/10, and 11). The functional results are all correct with the proposed reference scheme.
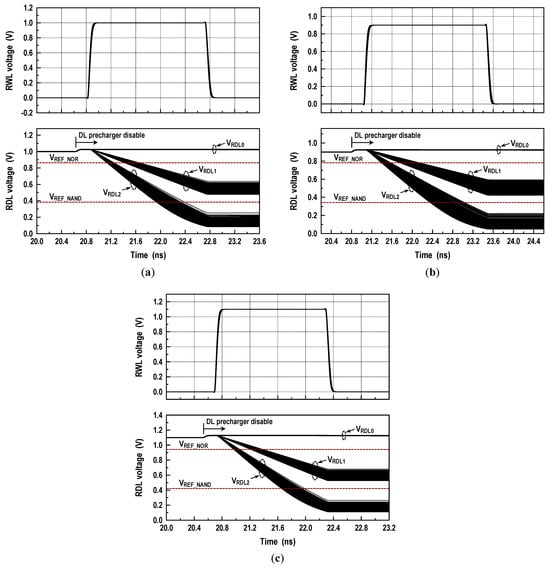
Figure 11.
Monte Carlo simulations for RDL voltage (25 °C, 2500 iterations): (a) VDD = 1.0 V; (b) VDD = 0.9 V; (c) VDD = 1.1 V.
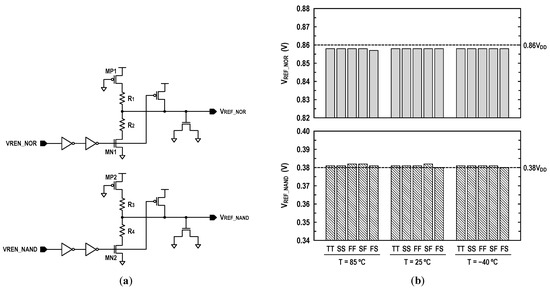
Figure 12.
Reference scheme: (a) circuit schematic and (b) reference voltages at VDD = 1.0 V across process and temperature variation. FS: fast N/slow P; SF: slow N/fast P; FF: fast N/fast P; SS: slow N/slow P; TT: typical N/typical P.
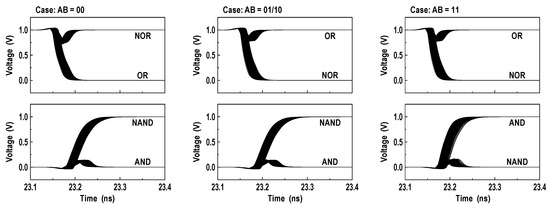
Figure 13.
Monte Carlo simulations for NOR/OR and NAND/AND outputs. VDD = 1.0 V; T = 25 °C; 2500 iterations.
The other thing to be considered with care when designing the DRAM-based CIM unit would be the data retention of the dynamic memory. In the DC-GCDRAM, the data stored on the gain cells are destroyed by the cell leakages. This storage degradation not only affects the retention time of the GCDRAM but may also induce a computational error in the logical operation. To prevent this leakage-induced computing error [55,56], we set a constraint on retention time, as shown in Figure 14. During standby, storage in the DN is left floating, and thus the gain cell leakages cause the stored information to change with time. Note that the retention time of all-NMOS cells with unbalanced leakages is predominantly determined by the bit cells with data ‘1’ [49,52]. Meanwhile, in the logic operation, the unit cell current ICELL drawn by a single bit with data ‘1’ for a time interval of τ develops an RDL voltage difference, i.e., , where CRBL and CRDL are the RBL and RDL capacitance. If two bits discharge the RDL, the corresponding voltage drop will be . Here, we define a minimum high-level storage DN(1)MIN to ensure that the RDL voltage drop by two bits is larger than . This specific DN level might guarantee the correct NOR/OR and NAND/AND operations during the logic–arithmetic mode. From extensive simulations, DN(1)MIN in this work has been observed to be 0.64 V at 1.0 V and 85 °C with VOS of 80 mV. The corresponding retention time at this condition was found to be 120 μs.
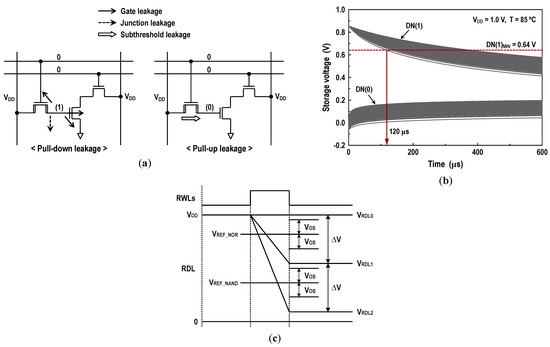
Figure 14.
Retention time constraint: (a) leakage currents during data hold; (b) storage voltage variations after data write (1.0 V, 85 °C, 5000 samples); and (c) RDL voltages for three possible cases—AB = 00 (VRDL0), AB = 01/10 (VRDL1), and AB = 11 (VRDL2).
3.4. Convolution Mode
The convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and deep learning are currently widely used for modern AI tasks such as traffic prediction, speech recognition, or image classification. But they consume extensive computing and memory resources. To reduce their arithmetic complexity and memory access, in recent algorithms called binarized neural networks [62], network weights and input activations are restricted to single bits (+1 or −1), such that the MAC operation, the most dominant operation in DNNs, is replaced by a simple bit-wise XNOR followed by population count (XNOR-and-accumulate) operation. The binarized neural networks (BNNs) are one of good candidates for deep learning implementation on DNN hardware, owing to their extreme energy efficiency.
In Figure 15, we show how the configurable DC-GCDRAM perform the XAC operation for BNNs. The memory array composed of 3T cells stores network weights (Wi) in a binary format. Activation switches [34] in Figure 15a, controlled by the input activations (marked with Ai and /Ai in a complementary style), connect a pair of bitlines to a bit-wise XNOR-SA. Thus, an XNOR result between Wi and Ai can be calculated during a read access. Figure 15b represents a simplified configuration to illustrate how the DC-GCDRAM executes the XAC operation. For each operating cycle, two rows (one from each 16-kbit array) are activated by enabling their RWLs. After the BL-SAs (SABL) are fired, the XNOR-SAs compute the bit-wise XNORs between activations and weights, and then the results are forwarded to the bit counters to carry out the population count operation. Each counter takes 128 bit inputs and generates an 8-bit count as output. Although this digital architecture has a limited throughput compared to the analog XAC implementations which activate all their rows at once [18,19], this approach does not need analog-to-digital converters incurring huge area/power overhead and provides extremely accurate computation results even with process–voltage–temperature (PVT) variation.
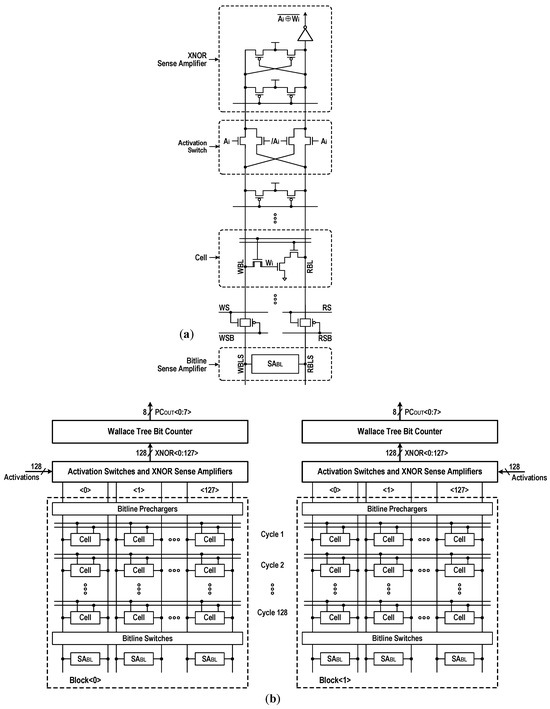
Figure 15.
XAC operation for BNNs: (a) bit-wise XNOR sensing scheme; (b) simplified configuration.
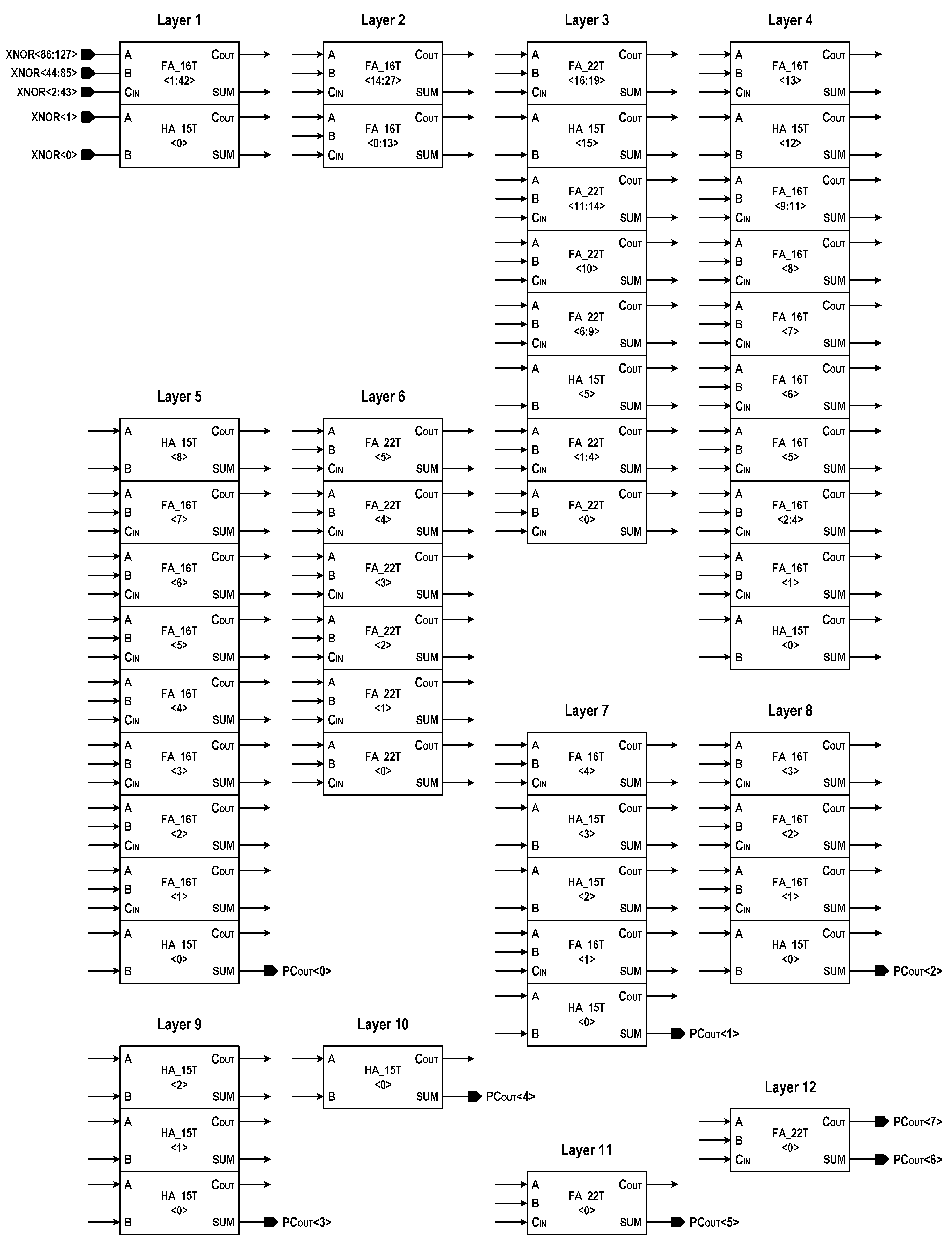
Figure 16 shows the digital bit counter implemented in this design, which adds all of the bit-wise XNOR results to generate a population count. The counter circuit uses a Wallace-tree structure to compress the 128-bit digital input (XNOR<0:127>) to an 8-bit digital output (PCOUT<0:7>), which ranges from 0 to 128. The 12-layer tree structure achieves maximum possible reduction using 120 FAs and 15 half-adders (HAs), in which the schematics of adders are shown in Figure 17. Here, two kinds of FAs (22T FA with driving inverter and 16T FA without driving inverter) are interleaved to trade off the circuit delay against the circuit area. At 1.0 V and 25 °C, the total power dissipation and critical-path delay of the bit counter in performing a 128-bit population count have been observed to be 0.84 mW and 0.58 ns, respectively.
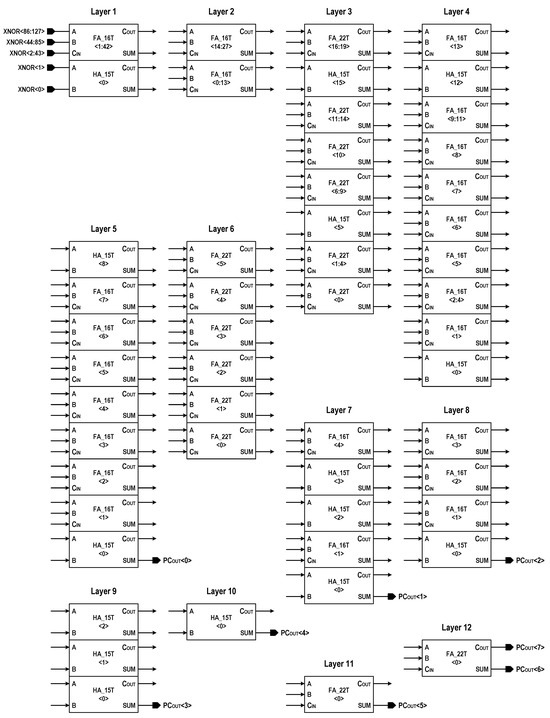
Figure 16.
Wallace tree population counter. The internal wire connections in tree structure are not shown.
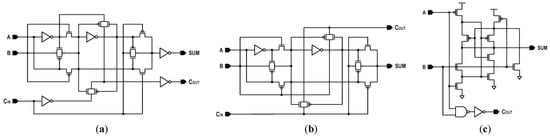
Figure 17.
CMOS adder circuits: (a) 22T full adder (FA_22T); (b) 16T full adder (FA_16T); (c) 15T half-adder (HA_15T).
To verify the operation of convolution mode within the DC-GCDRAM array, circuit-level simulations have been performed for all XAC combinations. The simulated waveforms shown in Figure 18 plot the results for the case when both 128 network weights and 128 input activations are all logic-high. The convolution operation, similar to the read operation of memory mode, begins by pulling RWL up to a high level after the BL and XNOR-SA prechargers are disabled. At the same moment, WBLS and RBLS are initially precharged to VREF and VDD, respectively, and then floated by raising nSAPRE to high. Triggering RS and RSB forwards the RBL signal, which depends on the status of weight, to RBLS. Then, the RBL switches are disabled, and the BL-SAs are fired. After RWL is returned back to a low level, both WBL and RBL switches are turned on to reflect the value of weight onto WBL and RBL in a complementary format. Afterward, the activations in a complementary format, which come from the activation input buffers, are developed at the gates of the activation switches. This allows the XNOR-SAs to compute the bit-wise XNORs between weights and activations and to send the results to the Wallace tree bit counter. The latency from RWL to the bit counter output (PCOUT) measures 1.98 ns at 1.0 V supply.
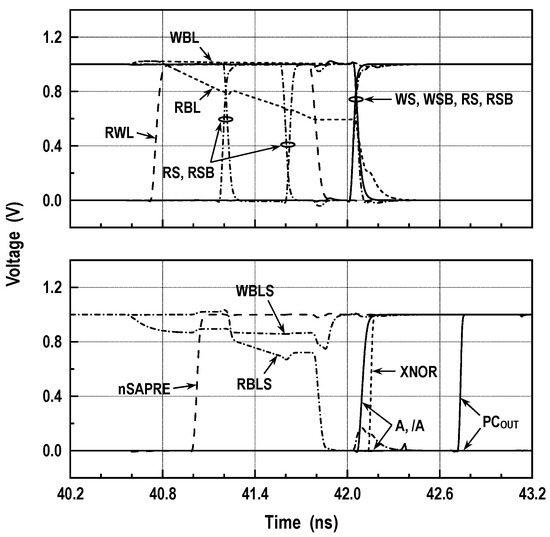
Figure 18.
Simulated waveforms for XAC operation; VDD = 1.0 V and T = 25 °C.
4. Evaluation Results and Discussion
The proposed DC-GCDRAM shown in Figure 3 has been evaluated under different operating modes by extensive simulations using 45 nm CMOS technology. Basically, the designed computational DRAM consists of two 16-kbit memory arrays and the peripheral circuitries like address buffers, predecoders, block signal generators, control buffers, control logic, refresh controller, oscillator, refresh address counter, and I/O buffers. The CIM macro contains two WWL boosters, 256 row decoders, 32 column decoders, 8 computing logics, 8 write drivers, and 2 population counters. In the memory mode, the data-in or data-out is 8 bits wide. In the logic–arithmetic mode, the macro outputs 8-bit wide logic computation results or produces 8-bit wide addition results with a single-bit carry-out. In the convolution mode, the CIM macro takes two 128-bit activations and generates two 8-bit counts as output. The operation cycle of each functional mode is self-timed from the positive clock (CLK) edge.
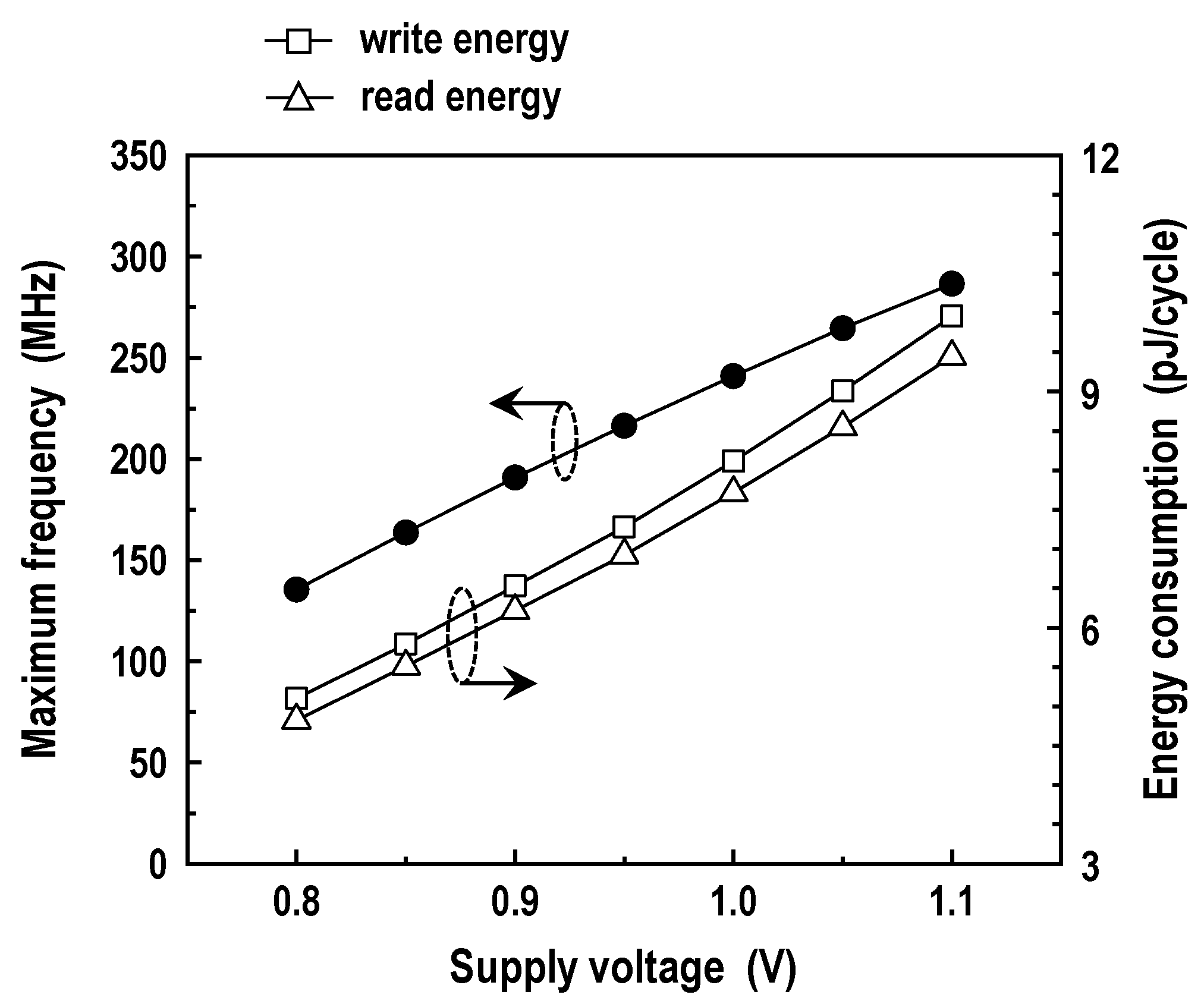
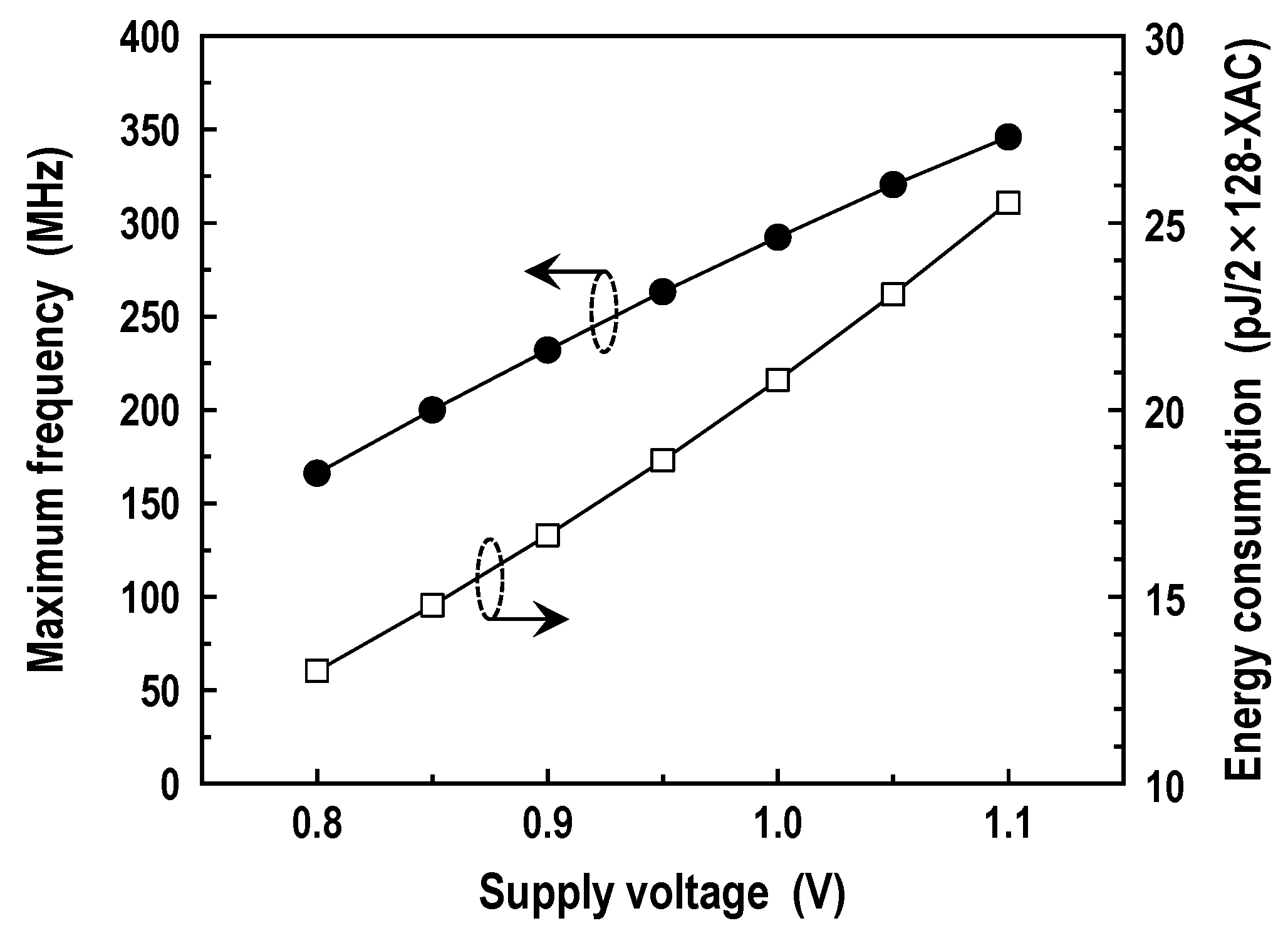
In Figure 19, we have shown the maximum frequency and energy dissipation of the memory operation from 1.1 down to 0.8 V. The energy consumption here represents a whole energy wasted in bitlines, datalines, main datalines, wordlines, decoders, BL-SAs, BSAs, write drivers, WWL booster, predecoders, control logic, I/O buffers, and other peripheral circuits. The simulations are consistent with the predictions; reducing the supply voltage brings about longer delays and lower energy consumption. For the supply voltage of 1.0 V, the DC-GCDRAM functions at 241 MHz with write and read energy figures of 8.12 and 7.72 pJ/cycle, respectively. The write energy is 5.2% higher than the read energy because of the WWL boost.
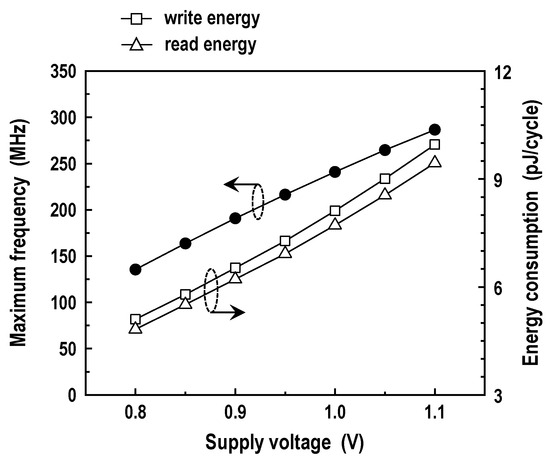
Figure 19.
Maximum frequency and energy dissipation in the memory mode (T = 25 °C).
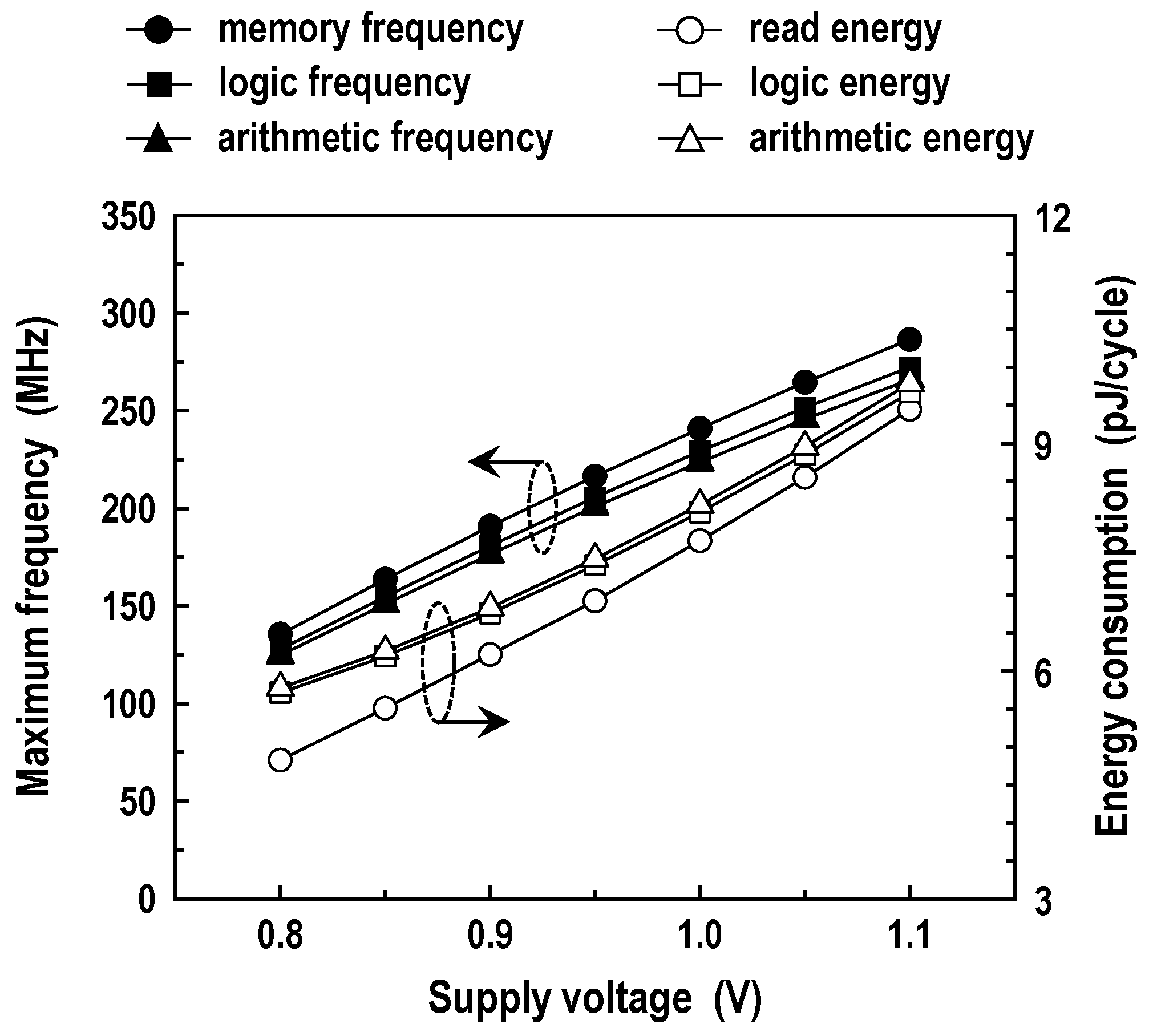
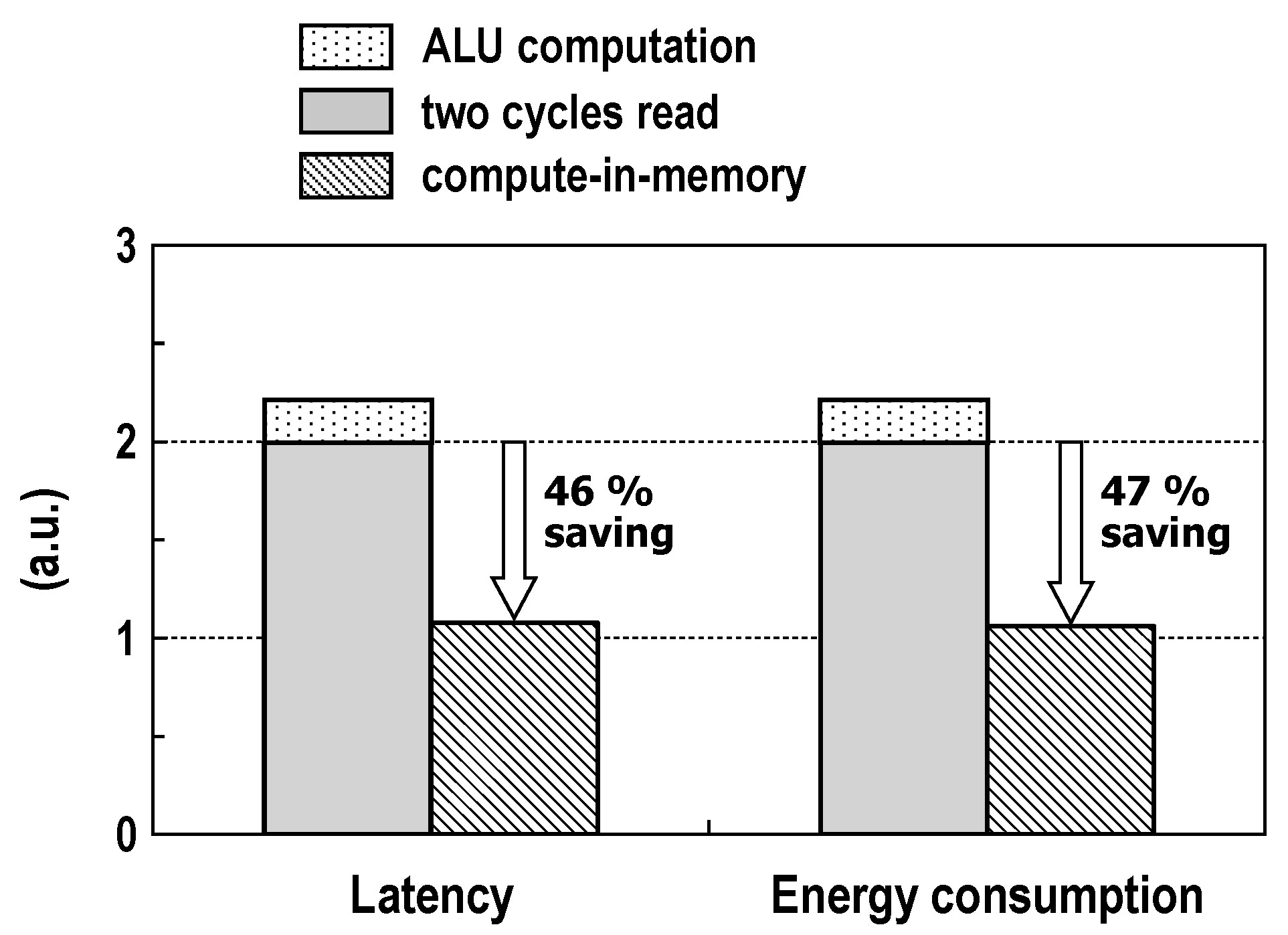
The operation of the logic–arithmetic mode is alike to the read operation in the memory mode, but the difference is that two RWLs are activated at the same time and two binary logic SAs are used in the logic–arithmetic mode. In Figure 20, we show the simulated frequency and energy consumption across the supply voltage for the logic (NOR/OR, NAND/AND, XNOR/XOR) and arithmetic (SUM, carry-out) operations between two words in two rows at room temperature. As VDD decreases, the energy dissipation and the frequency of both operations are reduced. The logic operation, in general, consumes higher energy than that dissipated by the memory read operation due to activations of two rows and two SAs. The latency of logic operation is about 5% longer than that of the memory read operation. Compared with the logic operation, the arithmetic operation has a slightly longer delay and slightly worse energy consumption because of a few additional logic gates. At VDD = 1.0 V, the maximum frequencies for the logic and arithmetic operation are 229 and 224 MHz, and the energy consumptions measure 8.09 and 8.19 pJ/cycle, respectively. Using the simulation results in this study, we compared CIM with conventional digital computing, which reads two words for two memory cycles and calculates them within ALUs, in Figure 21. For the arithmetic (FA) operation at 1.0 V supply, it is estimated that the proposed CIM architecture saves energy and latency by at least 47% and 46% compared with the conventional digital hardware.
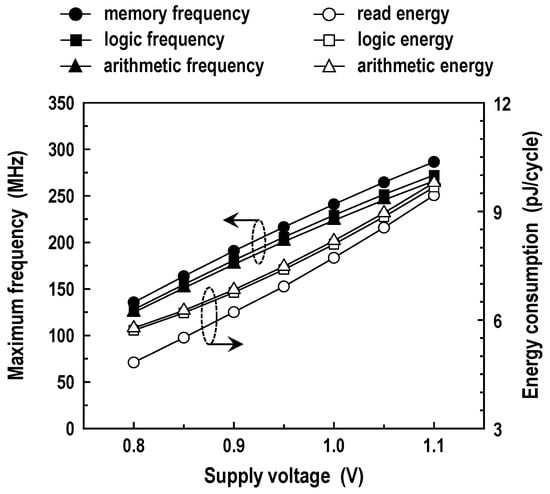
Figure 20.
Maximum frequency and energy dissipation in the logic–arithmetic mode (T = 25 °C).
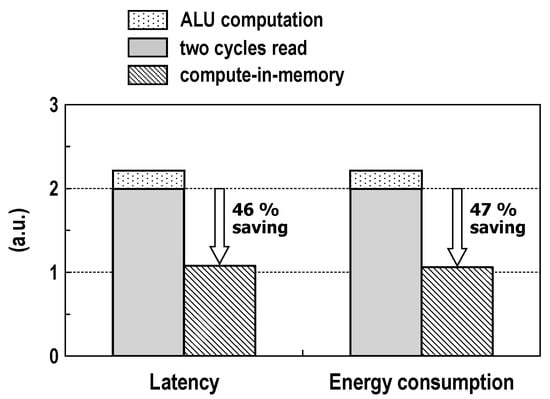
Figure 21.
Comparison between CIM and conventional digital computing for a two-word RCA operation (VDD = 1.0 V and T = 25 °C).
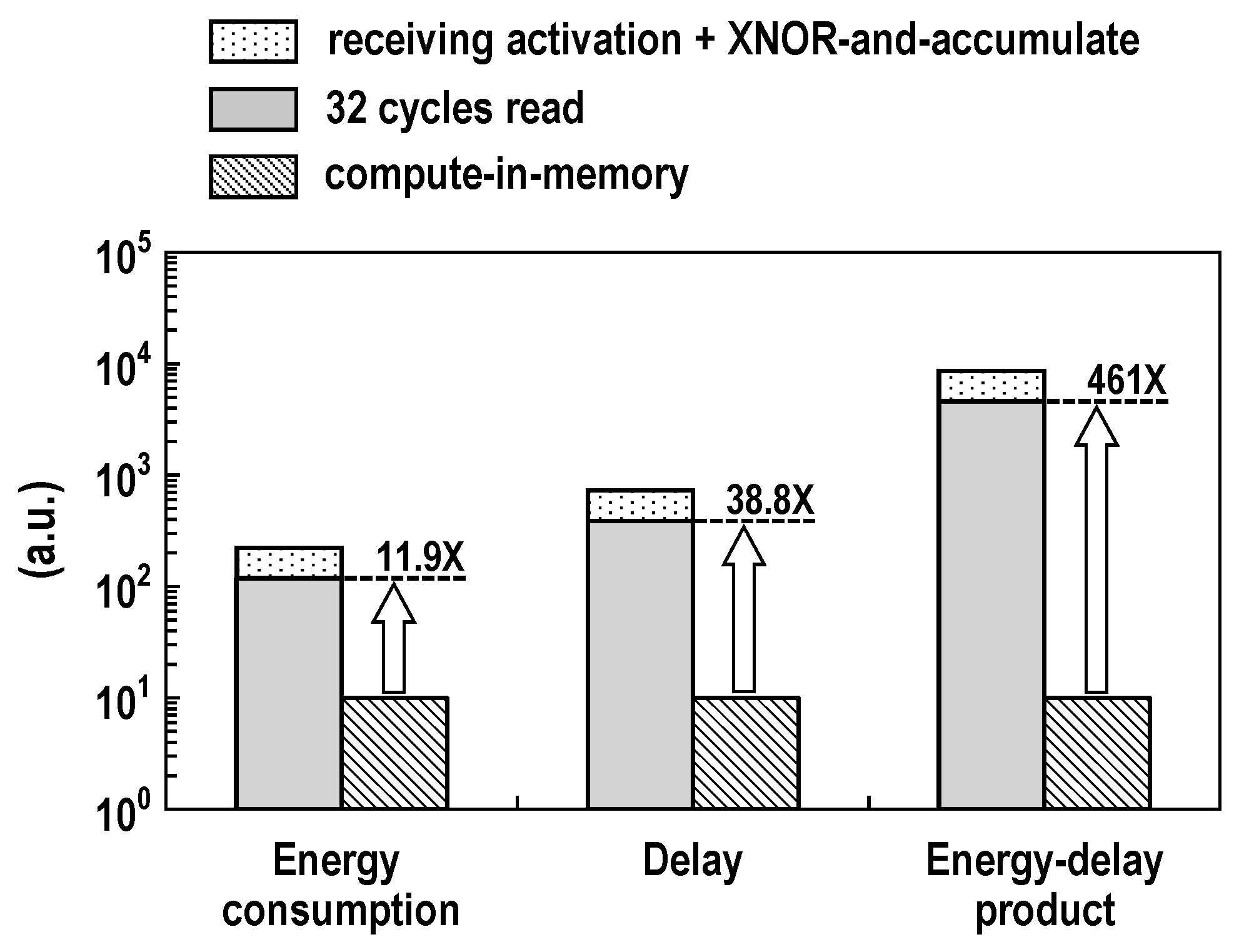
We also evaluated the energy wasted by the binary XAC operation under a range of conditions. In the convolution mode, the total power or energy consumption of the DC-GCDRAM much depends on the bit-wise XNOR results. This is because the outputs of the XNOR-SAs are initially all tied to the ground. The CIM macro computes two independent 128-input XACs in one cycle. Thus, the weights and activations which correspond to two XAC values being 128 each is the worst case for power consumption. Under this worst case, we evaluated the energy dissipation and frequency across the operating voltage as shown in Figure 22. The energy consumption and maximum frequency increase with the supply voltage. At 1.0 V and room temperature, the CIM macro takes 3.42 ns and consumes 20.8 pJ for two 128-input XAC operations, reaching an efficiency of 24.6 TOPS/W. Using the evaluation results in Figure 19 and Figure 22, we compared the proposed CIM architecture with conventional digital computing in Figure 23. For two 128-input XAC operations at 1.0 V supply, it was estimated that the proposed CIM macro obtains at least 11.9× higher energy efficiency, improves the delay by at least 38.8×, and thereby achieves at least 461× better energy-delay product compared with the conventional 8-bit wide digital hardware, which reads 256 weights byte-by-byte; receives 256 activations, also byte-by-byte; and eventually accumulates two XAC values over 32 cycles.
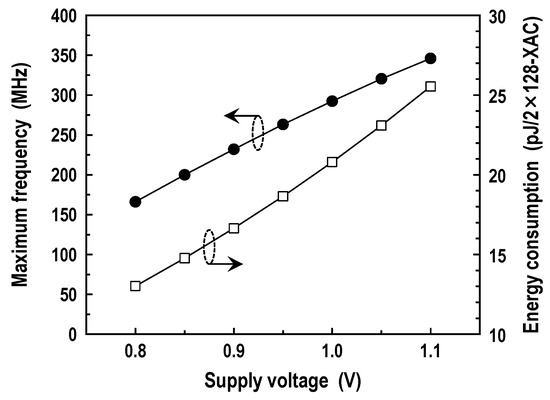
Figure 22.
Maximum frequency and energy consumption in the convolution mode (T = 25 °C).
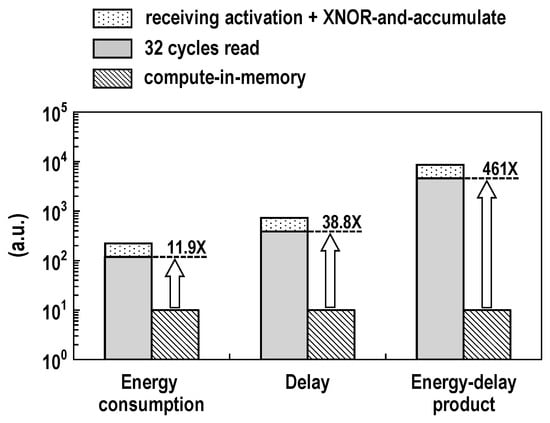
Figure 23.
Comparison between CIM and conventional digital computing for two 128-input XAC operations (VDD = 1.0 V and T = 25 °C).
In Table 1, the performance of this design has been summarized in comparison with prior GCDRAM-based CIM units. Compared to the previous analog CIM macros [54,55,56,57] which support only the MAC or MAV operation with a certain amount of computation errors, the digital CIM architectures (this work and [61]) are configurable between different operating modes and supports data storage as well as versatile CIM operations without accuracy degradation even under PVT variation. This design supports the logic, arithmetic, and XAC computations, while the work in [61] offers the MAC computation based on an embedded DRAM look-up table.

Table 1.
Performance comparison with prior GCDRAM-based CIM units.
5. Conclusions
The embedded GCDRAM is one of the prospective candidates for the realization of the CIM scheme because of its compatibility with the logic CMOS process and compact bit area. In this study, we proposed a computational GCDRAM architecture called DC-GCDRAM, which supports a range of Boolean logic and FA operations for off-load computations and computes XAC operations for binarized neural networks while operating as a normal DRAM for general-purpose workloads. To validate the effectiveness of the proposed DC-GCDRAM, a 4096-word × 8-bit CIM macro using logic-compatible 3T dynamic cell, which can be configurable to memory and a range of computing operations, has been implemented with a 45-nanometer generic CMOS technology. For VDD = 1.0 V, the proposed architecture performs memory, logic, and FA operations at 241, 229, and 224 MHz with energy figures of 7.92, 8.09, and 8.19 pJ/cycle. Compared with conventional digital computing, the DC-GCDRAM saves energy and latency of the FA operation by at least 47% and 46%, respectively. At the same supply voltage, the proposed CIM design takes 3.42 ns and consumes 20.8 pJ for two 128-input XAC operations, reaching 24.6 TOPS/W. The results indicate that the proposed architecture achieves an at least 11.9× higher energy efficiency as well as an at least 461× better energy-delay product compared to the traditional 8-bit-wide computing hardware.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.C.; methodology, Y.C.; investigation, T.K. and Y.C.; validation, T.K.; writing—original draft, T.K.; writing—review and editing, Y.C.; supervision, Y.C.; project administration, Y.C.; funding acquisition, Y.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (RS-2023-00242945) and the BK21 FOUR Program funded by the Ministry of Education of Korea (4199990113966).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in the article.
Acknowledgments
The EDA tool was supported by the IC Design Education Center in Korea.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Verma, N.; Jia, H.; Valavi, H.; Tang, Y.; Ozatay, M.; Chen, L.-Y.; Zhang, B.; Deaville, P. In-memory computing advances and prospects. IEEE Solid-State Circuits Mag. 2019, 11, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, B.; Zheng, Q.; Li, Z.; Li, S.; Chen, Y. Processing-in-memory technology for machine learning: From basic to ASIC. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst.-II Express Briefs 2022, 69, 2598–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeloka, S.; Akesh, N.B.; Sylvester, D.; Blaauw, D. A 28 nm configurable memory (TCAM/BCAM/SRAM) using push-rule 6T bit cell enabling logic-in-memory. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2016, 51, 1009–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Jeloka, S.; Saligane, M.; Kim, Y.; Kawaminami, M.; Harada, A.; Miyoshi, S.; Yasuda, M.; Blaauw, D.; Sylvester, D. A 4 + 2T SRAM for searching and in-memory computing with 0.3-V VDDmin. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2018, 53, 1006–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Eckert, C.; Subramaniyan, A.; Das, R.; Blaauw, D.; Sylvester, D. A 28-nm compute SRAM with bit-serial logic/arithmetic operations for programmable in-memory vector computing. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2020, 55, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chih, Y.-D.; Lee, P.-H.; Fujiwara, H.; Shih, Y.-C.; Lee, C.-F.; Naous, R.; Chen, Y.-L.; Lo, C.-P.; Lu, C.-H.; Mori, H.; et al. An 89TOPS/W and 16.3TOPS/mm2 all-digital SRAM-based full-precision compute-in memory macro in 22nm for machine-learning edge applications. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–22 February 2021; pp. 252–253. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.-H.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.; Heo, J.; Kim, J.-Y. Z-PIM: A sparsity-aware processing-in-memory architecture with fully variable weight bit-precision for energy-efficient deep neural networks. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2021, 56, 1093–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Zhan, H.; Peng, C.; Wu, X.; Yao, Y.; Niu, J.; Chen, J. Two-direction in-memory computing based on 10T SRAM with horizontal and vertical decoupled read ports. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2021, 56, 2832–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-C.; Tolentino, L.K.S.; Huang, C.-Y.; Yeh, C.-H. A 40-nm CMOS multifunctional computing-in-memory (CIM) using single-ended disturb-free 7T 1-Kb SRAM. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2021, 29, 2172–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Mu, J.; Yu, C.; Kim, T.T.-H.; Kim, B. A 1-16b reconfigurable 80Kb 7T SRAM-based digital near-memory computing macro for processing neural networks. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst.-I Regul. Pap. 2023, 70, 1580–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Tong, Z.; Wang, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, P.; Xu, T.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Wu, X.; et al. In situ storing 8T SRAM-CIM macro for full-array Boolean logic and copy operations. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2023, 58, 1472–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Verma, N. In-memory computation of a machine-learning classifier in a standard 6T SRAM array. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2017, 52, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Gonugondla, S.K.; Patil, A.; Shanbhag, N.R. A multi-functional in-memory inference processor using a standard 6T SRAM array. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2018, 53, 642–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.; Chandrakasan, A.P. CONV-SRAM: An energy-efficient SRAM with in-memory dot-product computation for low-power convolutional neural networks. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2019, 54, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Kong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, B.; Yin, S.; Shi, L. Sandwich-RAM: An energy-efficient in-memory BWN architecture with pulse-width modulation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 17–21 February 2019; pp. 394–395. [Google Scholar]
- Si, X.; Khwa, W.-S.; Chen, J.-J.; Li, J.-F.; Sun, X.; Liu, R.; Yu, S.; Yamauchi, H.; Li, Q.; Chang, M.F. A dual-split 6T SRAM-based computing-in-memory unit-macro with fully parallel product-sum operation for binarized DNN edge processors. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst.-I Regul. Pap. 2019, 66, 4172–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, X.; Chen, J.-J.; Tu, Y.-N.; Huang, W.-H.; Wang, J.-H.; Chiu, Y.-C.; Wei, W.C.; Wu, S.Y.; Sun, X.; Liu, R.; et al. A twin-8T SRAM computation-in-memory unit-macro for multibit CNN-based AI edge processors. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2020, 55, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Jiang, Z.; Seo, J.-S.; Seok, M. XNOR-SRAM: In-memory computing SRAM macro for binary/ternary deep neural networks. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2020, 55, 1733–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Yin, S.; Seo, J.-S.; Seok, M. C3SRAM: An in-memory-computing SRAM macro based on robust capacitive coupling computing mechanism. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2020, 55, 1888–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinangil, M.E.; Erbagci, B.; Naous, R.; Akarvardar, K.; Sun, D.; Khwa, W.-S.; Liao, H.J.; Wang, Y.; Chang, J. A 7-nm compute-in-memory SRAM macro supporting multi-bit input, weight and output and achieving 351 TOPS/W and 372.4 GOPS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2021, 56, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, Z.; Jin, Q.; He, Y.; Wang, J.; Lin, S.; Li, D.; Wang, Y.; Yang, K. CAP-RAM: A charge-domain in-memory computing 6T-SRAM for accurate and precision-programmable CNN inference. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2021, 56, 1924–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Lin, L.; Alioto, M. ±CIM SRAM for signed in-memory broad-purpose computing from DSP to neural processing. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2021, 56, 2981–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.-W.; Si, X.; Chou, Y.-C.; Chang, T.-W.; Huang, W.-H.; Tu, Y.-N.; Liu, R.; Lu, P.J.; Liu, T.W.; Wang, J.H.; et al. Two-way transpose multibit 6T SRAM computing-in-memory macro for inference-training AI edge chips. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2022, 57, 609–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, W.; Kim, S.; Park, S.; Jeon, D. An in-memory computing SRAM macro for memory-augmented neural network. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst.-II Express Briefs 2022, 69, 1687–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Song, J.; Tang, X.; Luo, H.; Pan, N.; Cui, X.; Wang, R.; Wang, Y. A 65 nm 73 kb SRAM-based computing-in-memory macro with dynamic-sparsity controlling. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst.-II Express Briefs 2022, 69, 2977–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Yoo, T.; Chai, K.T.C.; Kim, T.T.-H.; Kim, B. A 65-nm 8T SRAM compute-in-memory macro with column ADCs for processing neural networks. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2022, 57, 3466–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, R.; Dorrance, R.; Dasalukunte, D.; Lake, D.; Carlton, B. A charge domain SRAM compute-in-memory macro with C-2C ladder-based 8-bit MAC unit in 22-nm FinFET process for edge inference. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2023, 58, 1037–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, S.; Lee, K.; Park, J. A 2941-TOPS/W charge-domain 10T SRAM compute-in-memory for ternary neural network. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst.-I Regul. Pap. 2023, 70, 2085–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Cui, X.; Qiao, X.; Song, J.; Luo, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y. A 28nm 32Kb SRAM computing-in-memory macro with hierarchical capacity attenuator and input sparsity-optimized ADC for 4b Mac operation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst.-II Express Briefs 2023, 70, 1816–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehgal, R.; Thareja, T.; Xie, S.; Ni, C.; Kulkarni, J.P. A bit-serial, compute-in-SRAM design featuring hybrid-integrating ADCs and input dependent binary scaled precharge eliminating DACs for energy-efficient DNN inference. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2023, 58, 2109–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.-C.; Su, J.-W.; Hong, L.-Y.; Ren, J.-S.; Chien, C.-H.; Chen, H.-Y.; Ke, C.E.; Hsiao, H.M.; Li, S.H.; Sheu, S.S. A floating-point 6T SRAM in-memory-compute macro using hybrid-domain structure for advanced AI edge chips. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2024, 59, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Ni, C.; Sayal, A.; Jain, P.; Hamzaoglu, F.; Kulkarni, J.P. eDRAM-CIM: Reconfigurable charge domain compute-in-memory design with embedded dynamic random access memory array realizing adaptive data converters. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2024, 59, 1950–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-H.; Li, K.-X.; Lin, W.-Y.; Hsu, K.-H.; Li, P.-Y.; Yang, C.-H.; Xue, C.X.; Yang, E.Y.; Chen, Y.K.; Chang, Y.S.; et al. A 65nm 1Mb nonvolatile computing-in-memory ReRAM macro with sub-16ns multiply-and-accumulate for binary DNN AI edge processors. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 11–15 February 2018; pp. 494–495. [Google Scholar]
- Bocquet, M.; Hirztlin, T.; Klein, J.-O.; Nowak, E.; Vianello, E.; Portal, J.-M.; Querlioz, D. In-memory and error-immune differential RRAM implementation of binarized deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, 1–5 December 2018; pp. 20.6.1–20.6.4. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, C.-X.; Chen, W.-H.; Liu, J.-S.; Li, J.-F.; Lin, W.-Y.; Lin, W.-E.; Wang, J.H.; Wei, W.C.; Huang, T.Y.; Chang, T.W.; et al. Embedded 1-Mb ReRAM-based computing-in-memory macro with multibit input and weight for CNN-based AI edge processors. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2020, 55, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, Y.; Nowak, E.; Li, J. Liquid silicon: A nonvolatile fully programmable processing-in-memory processor with monolithically integrated ReRAM. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2020, 55, 908–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.-X.; Hung, J.-M.; Kao, H.-Y.; Huang, Y.-H.; Huang, S.-P.; Chang, F.-C.; Chen, P.; Liu, T.W.; Jhang, C.J.; Su, C.I.; et al. A 22nm 4Mb 8b-precision ReRAM computing-in-memory macro with 11.91 to 195.7TOPS/W for tiny AI edge devices. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–22 February 2021; pp. 246–247. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, J.-H.; Chang, M.; Khwa, W.-S.; Chih, Y.-D.; Chang, M.-F.; Raychowdhury, A. A 40-nm 118.44-TOPS/W voltage-sensing compute-in-memory RRAM macro with write verification and multi-bit encoding. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2022, 57, 845–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Sun, X.; Huang, S.; Jiang, H.; Yu, S. A 40-nm MLC-RRAM compute-in-memory macro with sparsity control, on-chip write-verify, and temperature-independent ADC references. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2022, 57, 2868–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Z.; An, J.; Li, W.; Gao, H.; Li, Z.; Yue, J.; Hu, H.; Xu, X.; et al. A 28-nm RRAM computing-in-memory macro using weighted hybrid 2T1R cell array and reference subtracting sense amplifier for AI edge inference. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2023, 58, 2839–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaddam-Aljameh, R.; Stanisavljevic, M.; Mas, J.F.; Karunaratne, G.; Brändli, M.; Liu, F.; Singh, A.; Müller, S.M.; Egger, U.; Petropoulos, A.; et al. HERMES-core—A 1.59-TOPS/mm2 PCM on 14-nm CMOS in-memory compute core using 300-ps/LSB linearized CCO-based ADCs. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2022, 57, 1027–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, D.-Q.; Chiu, Y.-C.; Khwa, W.-S.; Li, C.-Y.; Hsieh, F.-L.; Chien, Y.-A.; Lo, C.C.; Liu, R.S.; Hsieh, C.C.; Tang, K.T.; et al. An 8b-precision 8-Mb STT-MRAM near-memory-compute macro using weight-feature and input-sparsity aware schemes for energy-efficient edge AI devices. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2024, 59, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Q.; Man, S.; Sun, J.; Du, S.; Zhang, J. Programmable in-memory computing circuit for solving combinatorial matrix operation in one step. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst.-I Regul. Pap. 2023, 70, 2916–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nail, C.; Molas, G.; Blaise, P.; Piccolboni, G.; Sklenard, B.; Cagli, C.; Bernard, M.; Roule, A.; Azzaz, M.; Vianello, E.; et al. Understanding RRAM endurance, retention and window margin trade-off using experimental results and simulations. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, 3–7 December 2016; pp. 4.5.1–4.5.4. [Google Scholar]
- Mittal, S.; Vetter, J.S.; Li, D. A survey of architectural approaches for managing embedded DRAM and non-volatile on-chip caches. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2015, 26, 1524–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, C.-M.; Chen, W.-H.; Xue, C.-X.; Lin, W.-Y.; Lin, W.-E.; Li, J.-Y.; Lin, H.T.; Chang, M.F. Nonvolatile circuits-devices interaction for memory, logic and artificial intelligence. In Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on VLSI Technology, Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 171–172. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Li, S.; Ang, K.-W.; Zhang, Y.-W. Recent advances in in-memory computing: Exploring memristor and memtransistor arrays with 2D materials. Nano-Micro Lett. 2024, 16, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, K.C.; Jain, P.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, C.H. A 3T gain cell embedded DRAM utilizing preferential boosting for high density and low power on-die caches. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2011, 46, 1495–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, K.C.; Jain, P.; Kim, T.-H.; Kim, C.H. A 667 MHz logic-compatible embedded DRAM featuring an asymmetric 2T gain cell for high speed on-die caches. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2012, 47, 547–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, K.C.; Zhang, W.; Jain, P.; Kim, C.H. A 2T1C embedded DRAM macro with no boosted supplies featuring a 7T SRAM based repair and a cell storage monitor. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2012, 47, 2517–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chun, K.C.; Kim, C.H. A write-back-free 2T1D embedded DRAM with local voltage sensing and a dual-row-access low power mode. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst.-I Regul. Pap. 2013, 60, 2030–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Das, H.; Chung, Y. A logic-compatible embedded DRAM utilizing common-body toggled capacitive cross-talk. J. Semicond. Technol. Sci. 2016, 16, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manisankar, S.; Chung, Y. P-channel logic 2 T eDRAM macro with high retention bit architecture. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2018, 46, 1416–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, X.; Gu, J. A 65nm 3T dynamic analog RAM-based computing-in-memory macro and CNN accelerator with retention enhancement, adaptive analog sparsity and 44TOPS/W system energy efficiency. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–22 February 2021; pp. 240–241. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Yoo, T.; Kim, H.; Kim, T.T.-H.; Chuan, K.C.T.; Kim, B. A logic-compatible eDRAM compute-in-memory with embedded ADCs for processing neural networks. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst.-I Regul. Pap. 2021, 68, 667–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.; Kim, S.; Han, D.; Um, S.; Yoo, H.-J. A 36.2 dB high SNR and PVT/leakage-robust eDRAM computing-in-memory macro with segmented BL and reference cell array. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst.-II Express Briefs 2022, 69, 2433–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Ni, C.; Jain, P.; Hamzaoglu, F.; Kulkarni, J.P. Gain-cell CIM: Leakage and bitline swing aware 2T1C gain-cell eDRAM compute in memory design with bitline precharge DACs and compact Schmitt trigger ADCs. In Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on VLSI Technology and Circuits, Honolulu, HI, USA, 13–17 June 2022; pp. 112–113. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Li, Z.; Um, S.; Jo, W.; Ha, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Han, D.; Yoo, H.J. DynaPlasia: An eDRAM in-memory computing-based reconfigurable spatial accelerator with triple-mode cell. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2024, 59, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Um, S.; Jo, W.; Lee, J.; Ha, S.; Li, Z.; Yoo, H.J. Scaling-CIM: eDRAM in-memory-computing accelerator with dynamic-scaling ADC and adaptive analog operation. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2024, 59, 2694–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Yang, Y.; Xue, C.; He, Y.; Cui, X.; Jia, S.; Wang, Y. An eDRAM-based computing-in-memory macro with full-valid-storage and channel-wise-parallelism for depthwise neural network. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst.-II Express Briefs 2024, 71, 2539–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Fan, S.; Li, X.; Lei, L.; Jia, W.; Tang, C.; Li, Y.; Huang, Z.; Du, Z.; Yue, J.; et al. A 28nm 2.4Mb/mm2 6.9-16.3TOPS/mm2 eDRAM-LUT-based digital-computing-in-memory macro with in-memory encoding and refreshing. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 18–22 February 2024; pp. 578–579. [Google Scholar]
- Simons, T.; Lee, D.-J. A review of binarized neural networks. Electronics 2019, 8, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).