Analysis of Nutritional Composition of the Pearl Oyster Pinctada radiata as a New Mediterranean “Bioresource” for Human Consumption
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sampling Positions
2.2. Physicochemical Seawater Characterization
2.3. Biochemical Composition Analysis
- AI: atherogenicity index (Ulbricht and Southgate 1991) [22]:
- 2.
- TI: thrombogenicity index (Ulbricht and Southgate 1991) [22]:
- 3.
- HH: hypocholesterolemic/hypercholesterolemic ratios [23]:
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Seawater Parameters of the Sampling Sites
3.2. Pearl Oyster Proximate Composition and Calorific Value
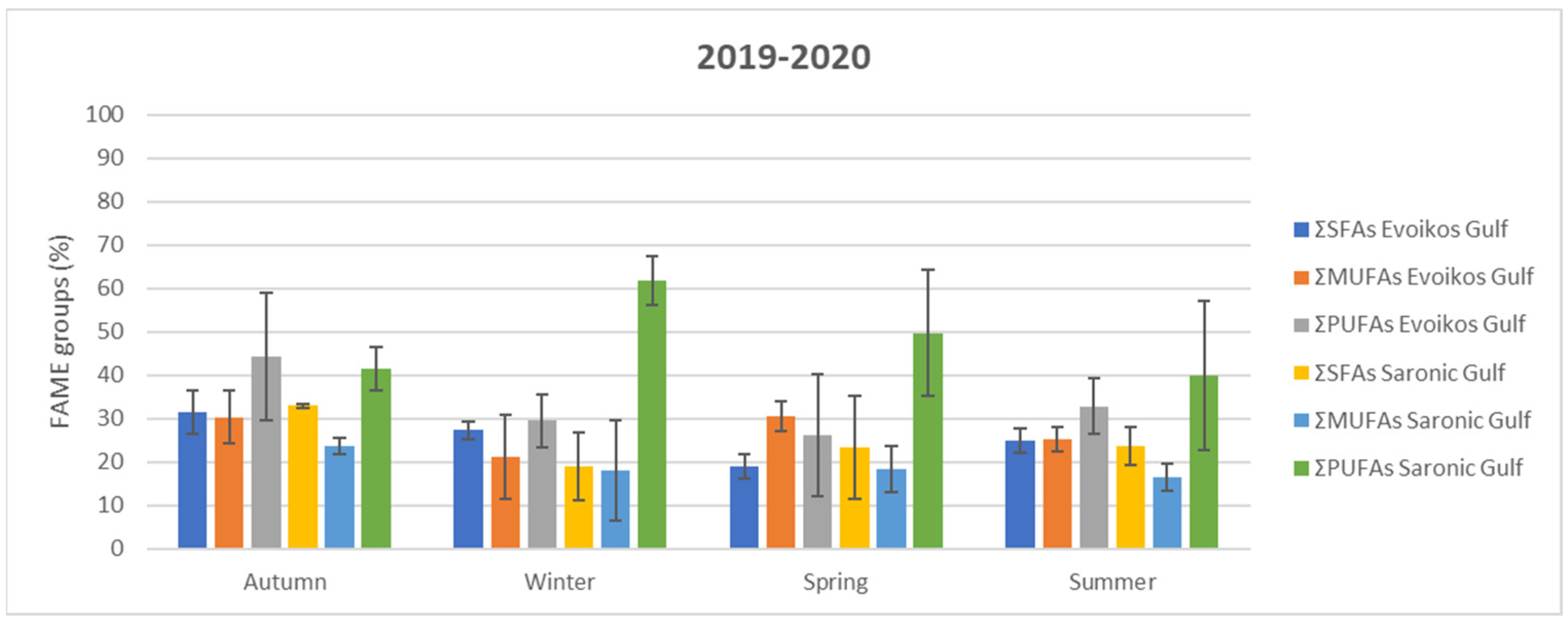
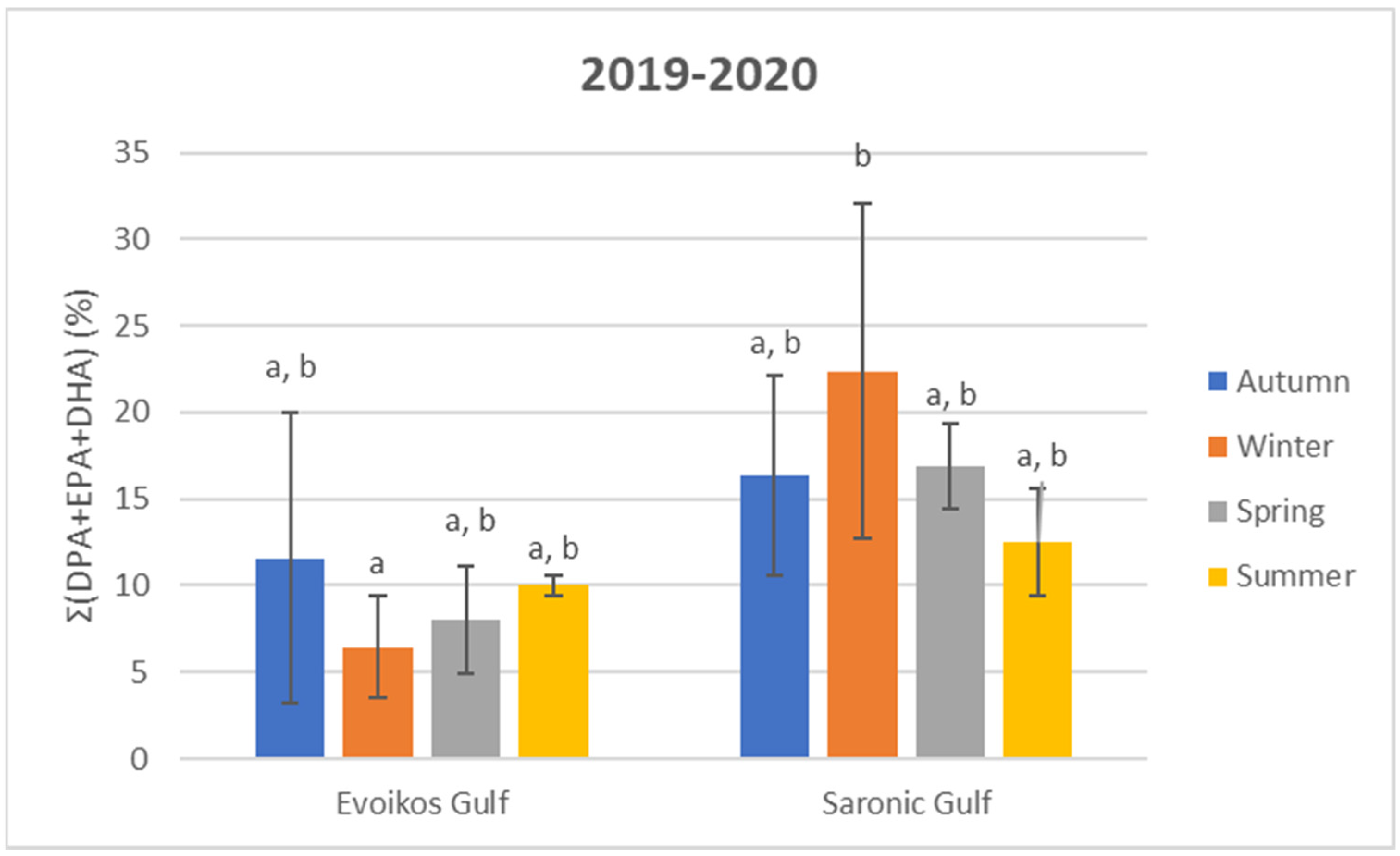
3.3. Total Fatty Acid (TFA) Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Theodorou, J.A.; Makri, M.; Douvi, X.; Ramfos, A.; Spinos, E. Seasonal variation in the biochemical composition, condition index, and meat yield of the non-indigenous pearl oyster Pinctada imbricata radiata (Leach, 1814) from the West of the Aegean Sea, Greece. Aquac. Fish 2023, 8, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.K.; Kang, J.Y.; Kim, K.D.; Kim, I.S.; Jeong, B.Y. Lipid Components of the Cultured Pearl Oyster (Pinctada fucata martensii) in Korea. Fish Aquat. Sci. 2005, 8, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Anacleto, P.; Maulvault, A.L.; Bandarra, N.M.; Repolho, T.; Nunes, M.L.; Rosa, R.; Marques, A. Effect of warming on protein, glycogen and fatty acid content of native and invasive clams. Food Res. Int. 2014, 64, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biandolino, F.; Parlapiano, I.; Grattagliano, A.; Fanelli, G.; Prato, E. Comparative Characteristics of Percentage Edibility, Condition Index, Biochemical Constituents and Lipids Nutritional Quality Indices of Wild and Farmed Scallops (Flexopecten glaber). Water 2020, 12, 1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prato, E.; Fanelli, G.; Parlapiano, I.; Biandolino, F. Bioactive fatty acids in seafood from Ionian Sea and relation to dietary recommendations. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 71, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.-N.; Zhang, D.-l.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, S.; Liu, B.-S.; Huang, G.-J.; Yu, D.-H. A baseline study on lipid and fatty acid composition in the pearl oyster, Pinctada fucata. Aquac. Int. 2016, 24, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsangaris, C.; Simboura, N.; Strogyloudi, E.; Zeri, C.; Kaberi, H.; Pavlidou, A.; Chatzianestis, I.; Bordbar, L.; Catsiki, A.V.; Tzempelikou, E.; et al. Pollution Pressures and Impacts in the North Evoikos Gulf (Aegean Sea). In The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Mente, E.; Pantazis, P.; Neofitou, C.; Aifanti, S.; Santos, M.B.; Oxouzi, E.; Bagiatis, V.; Papapanagiotou, E.; Kourkouta, V.; Soutsas, K. Socioeconomic interactions of fisheries and aquaculture in Greece: A case study of south Evoikos gulf. Aquacult. Econ. Manag. 2007, 11, 313–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenetos, A.; Ovalis, P.; Giakoumi, S.; Kontadakis, C.; Lefkaditou, E.; Mpazios, G.; Simboura, N.; Tsiamis, K. Saronikos Gulf: A hotspot area for alien species in the Mediterranean Sea. Bioinvasions Rec. 2020, 9, 873–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serbetis, C.D. L’acclimatation de la Meleagrina Pinctada margaritifera (Lam.) en Grèce. Rapp. Procès-Verbaux Réunions Comm. Int. Pour L’ Explor. Sci. Mer Méditerranée 1963, 17, 271–272. [Google Scholar]
- Antit, M.; Gofas, S.; Salas, C.; Azzouna, A. One hundred years after Pinctada: An update on alien Mollusca in Tunisia. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2011, 12, 53–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodorou, J.A.; Viaene, J.; Sorgeloos, P.; Tzovenis, I. Production and Marketing Trends of the Cultured Mediterranean Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis Lamarck 1819, in Greece. J. Shellfish Res. 2011, 30, 859–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodola, A.; Nicolini, L.; Savini, D.; Deidun, A.; Occhipinti-Ambrogi, A. Range expansion and biometric features of Pinctada imbricata radiata (Bivalvia: Pteriidae) around Linosa Island, Central Mediterranean Sea (Italy). Ital. J. Zool. 2013, 80, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigitkurt, S.; Lök, A.; Kirtik, A.; Acarli, S.; Kurtay, E.; Küçükdermenci, A.; Durmaz, Y. Spat efficiency in the pearl oyster (Leach, 1814) in the surface and bottom water at Karantina Island. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. St. 2020, 49, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutopoulos, D.K.; Ramfos, A.; Theodorou, J.A.; Katselis, G. Biological aspects, population and fishery dynamics of the non-indigenous pearl oyster Pinctada imbricata radiata (Leach, 1814) in the Eastern Mediterranean. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 45, 101821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukova, N.V. Fatty Acids of Marine Mollusks: Impact of Diet, Bacterial Symbiosis and Biosynthetic Potential. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- D5176-08; Standard Test Method for the Total Chemically Bound Nitrogen in Water by Pyrolysis and Chemiluminescence Detection. ASTM International, Designation: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2008.
- Bekiari, V.; Avramidis, P. Data quality in water analysis: Validation of combustion-infrared and combustion-chemiluminescence methods for the simultaneous determination of Total Organic Carbon (TOC) and Total Nitrogen (TN). Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2014, 94, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffrey, S.W.; Humphrey, G.F. New spectrophotometric equations for determining chlorophylls a, b, c1 and c2 in higher plants, algae and natural phytoplankton. Biochem. Physiol. Pflanz. 1975, 167, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurens, L.M.L.; Quinn, M.; Van Wychen, S.; Templeton, D.W.; Wolfrum, E.J. Accurate and reliable quantification of total microalgal fuel potential as fatty acid methyl esters by in situ transesterification. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbricht, T.L.V.; Southgate, D.A.T. Coronary heart disease: Seven dietary factors. Lancet 1991, 338, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Silva, J.; Bessa, R.J.B.; Santos-Silva, F. Effect of genotype, feeding system and slaughter weight on the quality of light lambs: II. Fatty acid composition of meat. Livest. Prod. Sci. 2002, 77, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Malva, A.; Santillo, A.; Francavilla, M.; Caroprese, M.; Marino, R.; Sevi, A.; Albenzio, M. Mussel Culture Farming Systems in the Northern Gargano Coast (Adriatic Sea): Changes in the Nutritional Profile of the Mytilus galloprovincialis. Foods 2024, 13, 2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Cássia Divino Lima, R.; Ferreira, J.P.R.; do Espírito Santo, C.M.; da Silva, F.C.; de Miranda Gomes, C.H.A.; de Oliveira Ramos, C.; de Melo, C.M.R. Spat of pacific oysters (Crassostrea gigas) grown in subtropical environments. J. Appl. Aquacult. 2023, 36, 342–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokoglu, N.; Gokoglu, M.; Yerlikaya, P. Seasonal variations in proximate and elemental composition of pearl oyster (Pinctada radiata, Leach, 1814). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2006, 86, 2161–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehteshami, F.; Christianus, A.; Rameshi, H.; Harmin, S.A.; Saad, C.R. Proximate and fatty acid composition of the gonads of wild versus hatchery-conditioned Pinctada margaritifera broodstock. Aquac. Nutr. 2011, 17, e675–e682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, H. Nutritional Indices for Assessing Fatty Acids: A Mini-Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolaosho, T.L.; Elegbede, I.O.; Akinota, S.L.; Jimoh, A.A.-A. Biometric and gonadosomatic indices and chemical constituents of edible tissues and exoskeletons of Callinectes amnicola and their potential for reuse in the circular economy paradigm. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodorou, J.A.; Minasidis, V.; Ziou, A.; Douligeri, A.S.; Gkikas, M.; Koutante, E.; Katselis, G.; Anagnopoulos, N.; Bourdaniotis, N.; Moutopoulos, D.K. New Product Value Chain for The Pearl Oyster Pinctada imbricata radiata: A preliminary survey. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutopoulos, D.K.; Minasidis, V.; Ziou, A.; Douligeri, A.S.; Katselis, G.; Theodorou, J.A. Investigating the Acceptance of a New Bivalve Product in the Greek Shellfish Market: The Non-Indigenous Pearl Oyster Pinctada imbricata radiata. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


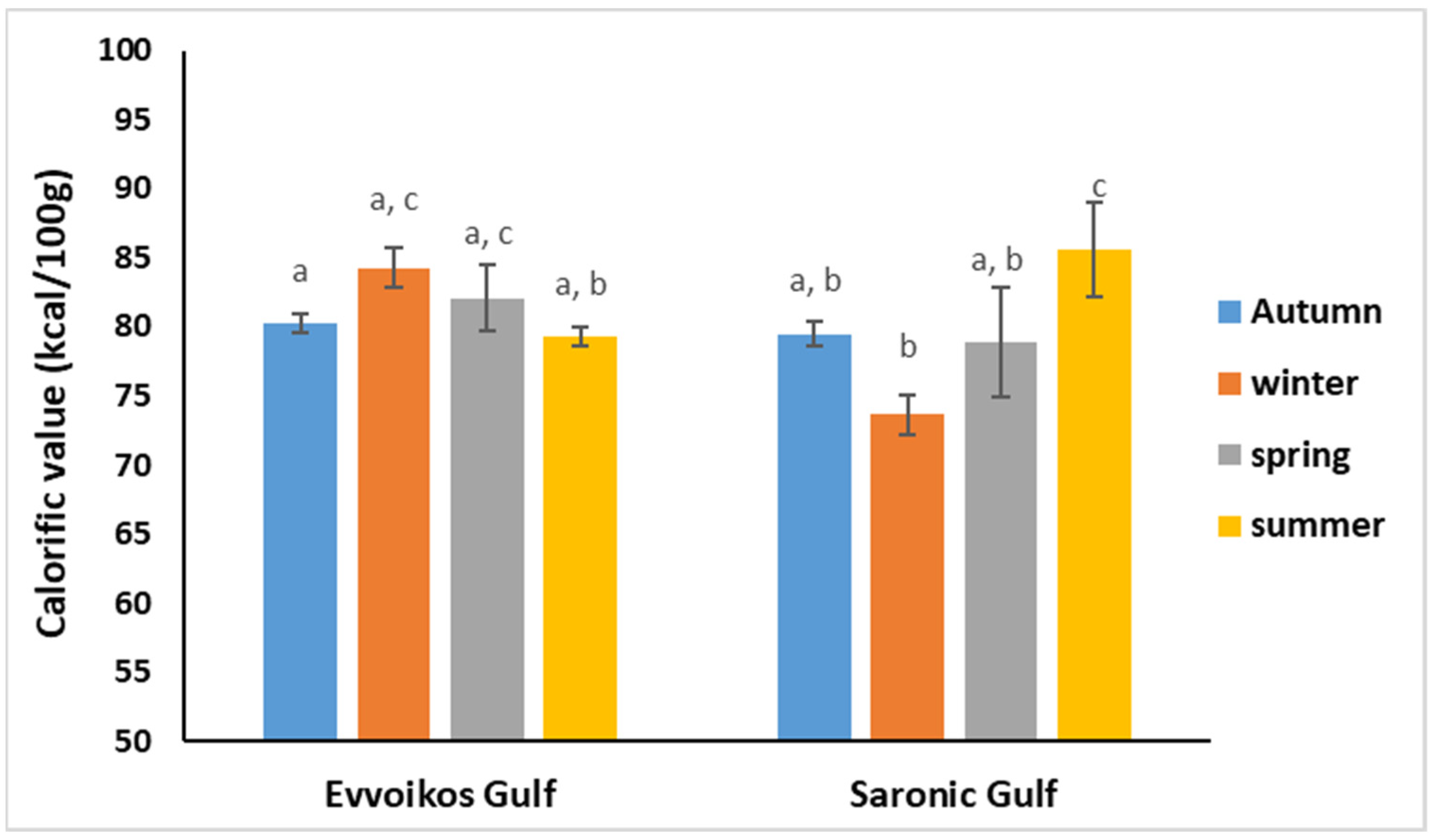
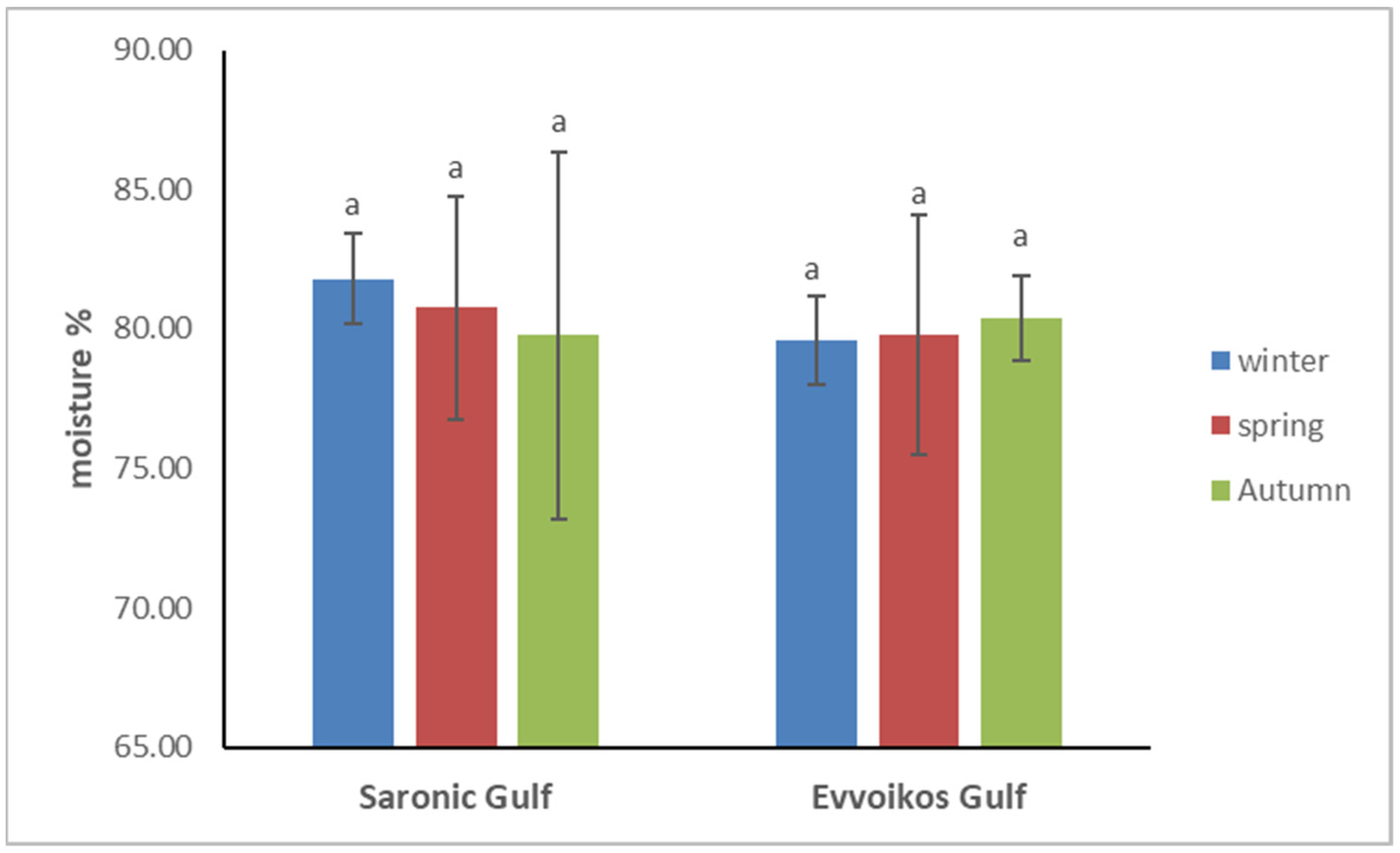
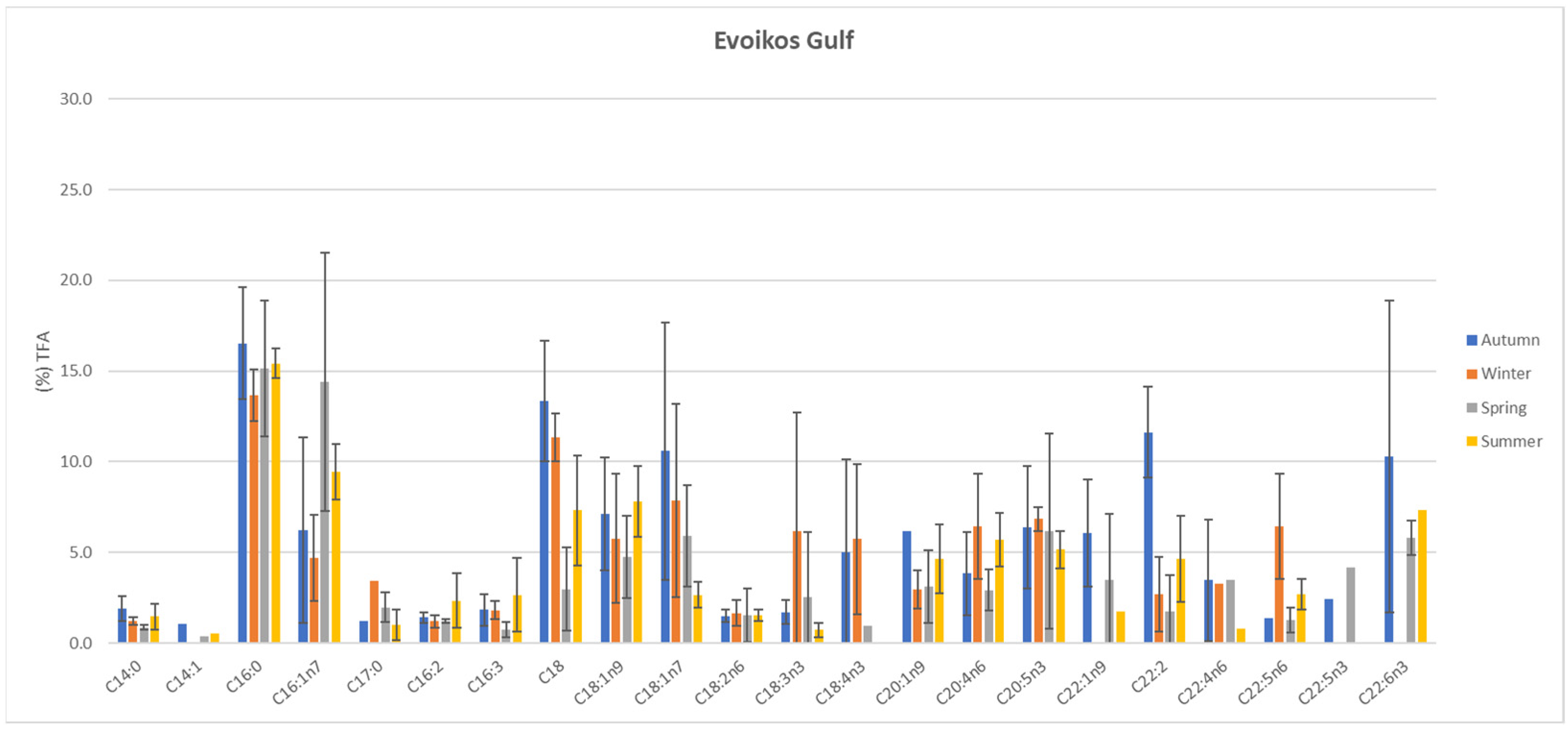

| Sampling Season | Evoikos Gulf | Saronikos Gulf | |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | Autumn | 8.1 ± 0.02 | 8.2 ± 0.02 |
| Winter | 8.2 ± 0.02 | 8.2 ± 0.02 | |
| Spring | 8.0 ± 0.02 | 8.5 ± 0.02 | |
| Summer | 8.4 ± 0.02 | 8.4 ± 0.02 | |
| Salinity (ppt) | Autumn | 40 ± 3 | 39 ± 3 |
| Winter | 40 ± 3 | 39 ± 3 | |
| Spring | 37 ± 3 | 39 ± 3 | |
| Summer | 36 ± 3 | 37 ± 3 | |
| TOC (mg C/L) | Autumn | 6.93 ± 0.5 c | 3.69 ± 0.3 d |
| Winter | 7.13 ± 0.5 c | 3.96 ± 0.3 d | |
| Spring | 19.4 ± 1.5 a | 12.6 ± 1.0 b | |
| Summer | 19.2 ± 1.5 a | 12.8 ± 1.0 b | |
| TN (mg N/L) | Autumn | 0.16 ± 0.01 e | 0.06 ± 0.01 g |
| Winter | 0.21 ± 0.02 c,d | 0.08 ± 0.01 f,g | |
| Spring | 0.39 ± 0.03 b | 0.18 ± 0.01 d | |
| Summer | 0.50 ± 0.03 a | 0.25 ± 0.02 c | |
| NO3-N (mg N/L) | Autumn | 0.12 ± 0.01 e | 0.02 ± 0.01 g |
| Winter | 0.18 ± 0.01 c | 0.04 ± 0.01 f | |
| Spring | 0.36 ± 0.03 b | 0.16 ± 0.01 d | |
| Summer | 0.41 ± 0.03 a | 0.18 ± 0.02 c | |
| NO2-N (mg N/L) | Autumn | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Winter | <0.01 | <0.01 | |
| Spring | <0.01 | <0.01 | |
| Summer | <0.01 | <0.01 | |
| PO4-P (mg P/L) | Autumn | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Winter | <0.01 | <0.01 | |
| Spring | <0.01 | <0.01 | |
| Summer | <0.01 | <0.01 | |
| Chlorophyll-a (µg/L) | Autumn | 0.3 ± 0.05 b,c | 0.1 ± 0.05 c,d |
| Winter | 0.4 ± 0.05 a,b | 0.2 ± 0.05 c | |
| Spring | 0.5 ± 0.05 a | 0.3 ± 0.05 b,c | |
| Summer | 0.5 ± 0.05 a | 0.5 ± 0.05 a |
| Location | Season | ΣSFAs | ΣMUFAs | ΣPUFAs | ΣPUFAs/ΣSFAs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Evoikos Gulf | Autumn | 31.55 a ± 5.096 | 30.33 a ± 6.125 | 44.34 a ± 14.56 | 1.380 a ± 0.235 |
| Winter | 27.33 a,b ± 2.028 | 21.25 a ± 9.639 | 29.56 b ± 6.128 | 1.083 a ± 0.226 | |
| Spring | 19.04 b ± 2.937 | 30.60 a ± 3.506 | 26.11 b ± 14.03 | 1.321 a ± 0.561 | |
| Summer | 24.86 a,b ± 2.868 | 25.26 a ± 2.673 | 32.80 a,b ± 6.416 | 1.328 a ± 0.304 | |
| Saronic Gulf | Autumn | 32.94 a ± 0.543 | 23.78 a ± 1.813 | 41.46 b ± 4.931 | 1.260 b ± 0.170 |
| Winter | 19.08 b ± 7.777 | 18.10 a ± 11.58 | 61.84 a ± 5.533 | 3.665 a ± 1.561 | |
| Spring | 23.47 a ± 11.93 | 18.35 a ± 5.340 | 49.77 b ± 14.38 | 3.049 a ± 2.846 | |
| Summer | 23.79 a ± 4.377 | 16.50 a ± 3.023 | 39.88 b ± 17.19 | 1.747 a,b ± 0.974 |
| Location | Season | AI | TI | HH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Evoikos Gulf | Autumn | 0.297 a,b ± 0.068 | 0.359 a ± 0.089 | 1.615 a± 0.476 |
| Winter | 0.365 a ± 0.023 | 0.333 a± 0.054 | 1.651 a ± 0.199 | |
| Spring | 0.315 a ± 0.073 | 0.278 a ± 0.094 | 1.650 a ± 1.065 | |
| Summer | 0.370 a ± 0.048 | 0.374 a ± 0.076 | 1.661 a ± 0.337 | |
| Saronic Gulf | Autumn | 0.306 a,b ± 0.005 | 0.446 a ± 0.108 | 2.019 a ± 0.639 |
| Winter | 0.108 b ± 0.008 | 0.174 a ± 0.075 | 5.127 b ± 1.047 | |
| Spring | 0.223 a,b ± 0.120 | 0.263 a ± 0.131 | 3.623 a,b ± 1.454 | |
| Summer | 0.278 a,b ± 0.083 | 0.317 a ± 0.085 | 2.240 a ± 0.369 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Theodorou, J.A.; Bekiari, V.; Douvi, X.; Ramfos, A.; Tzovenis, I. Analysis of Nutritional Composition of the Pearl Oyster Pinctada radiata as a New Mediterranean “Bioresource” for Human Consumption. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 9757. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14219757
Theodorou JA, Bekiari V, Douvi X, Ramfos A, Tzovenis I. Analysis of Nutritional Composition of the Pearl Oyster Pinctada radiata as a New Mediterranean “Bioresource” for Human Consumption. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(21):9757. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14219757
Chicago/Turabian StyleTheodorou, John A., Vlasoula Bekiari, Xanthi Douvi, Alexis Ramfos, and Ioannis Tzovenis. 2024. "Analysis of Nutritional Composition of the Pearl Oyster Pinctada radiata as a New Mediterranean “Bioresource” for Human Consumption" Applied Sciences 14, no. 21: 9757. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14219757
APA StyleTheodorou, J. A., Bekiari, V., Douvi, X., Ramfos, A., & Tzovenis, I. (2024). Analysis of Nutritional Composition of the Pearl Oyster Pinctada radiata as a New Mediterranean “Bioresource” for Human Consumption. Applied Sciences, 14(21), 9757. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14219757







