Experimental Study of Bedform Development Characteristics and Their Effects on Sediment Transport
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Setup and Methods
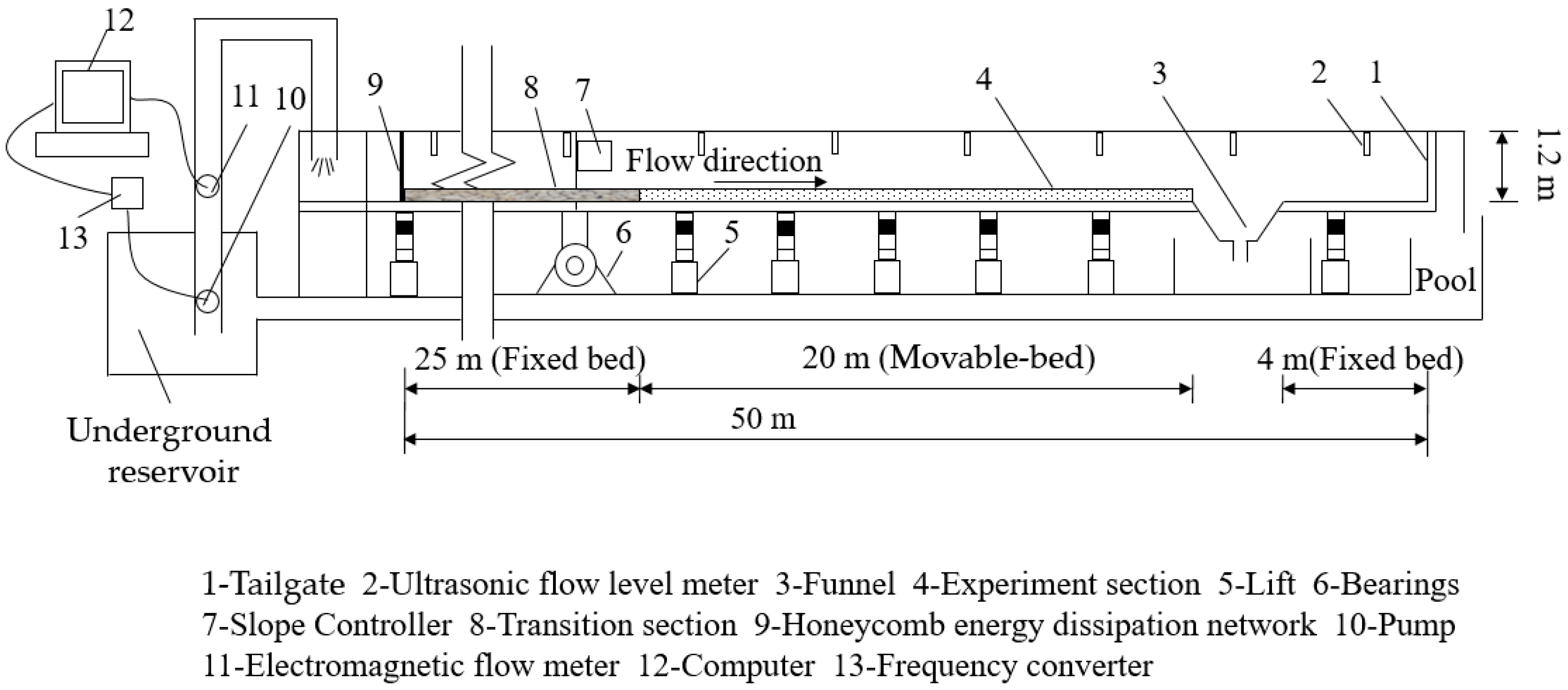
2.1. Experimental Setup
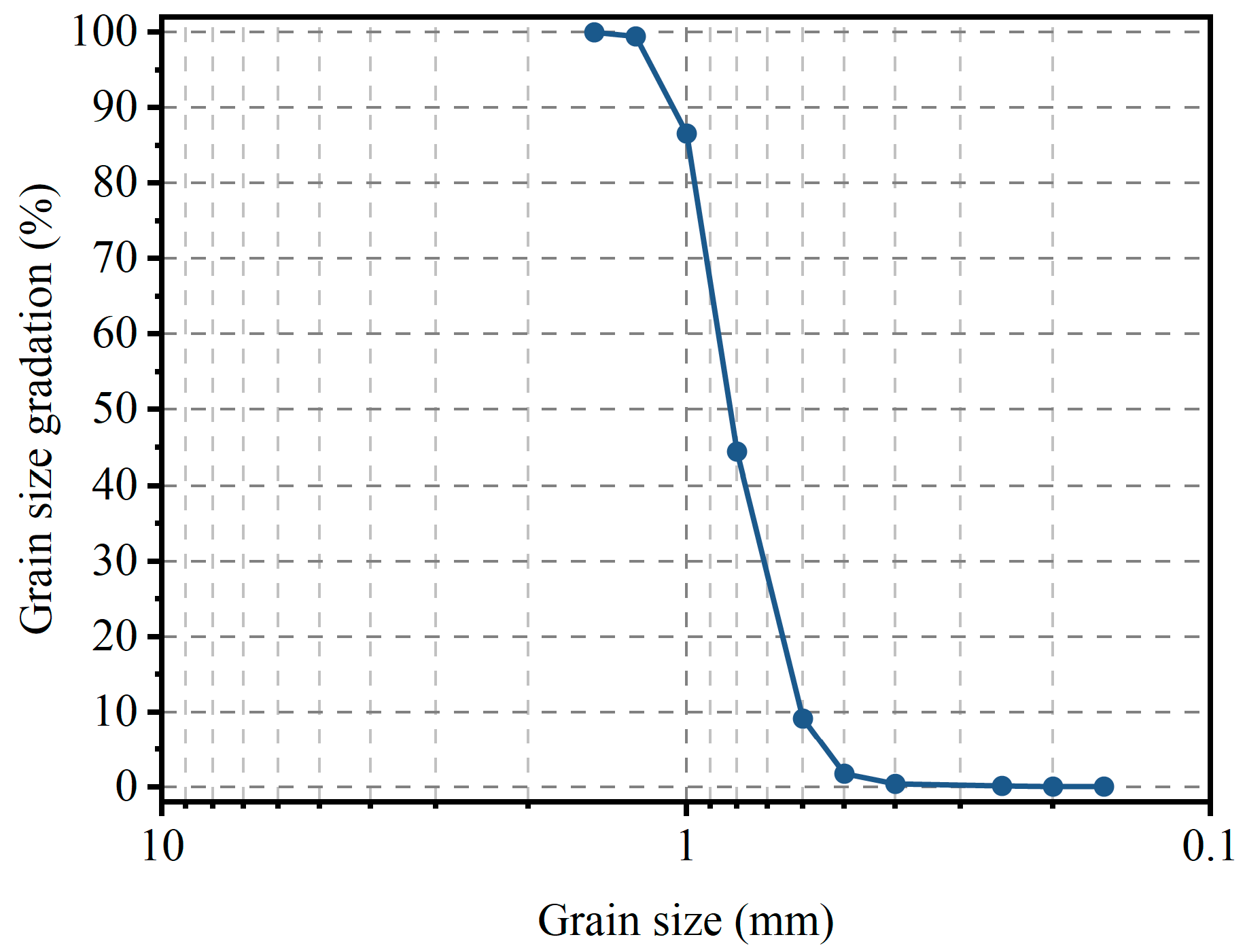
2.2. Experimental Design and Methods
2.3. Measurement Parameters
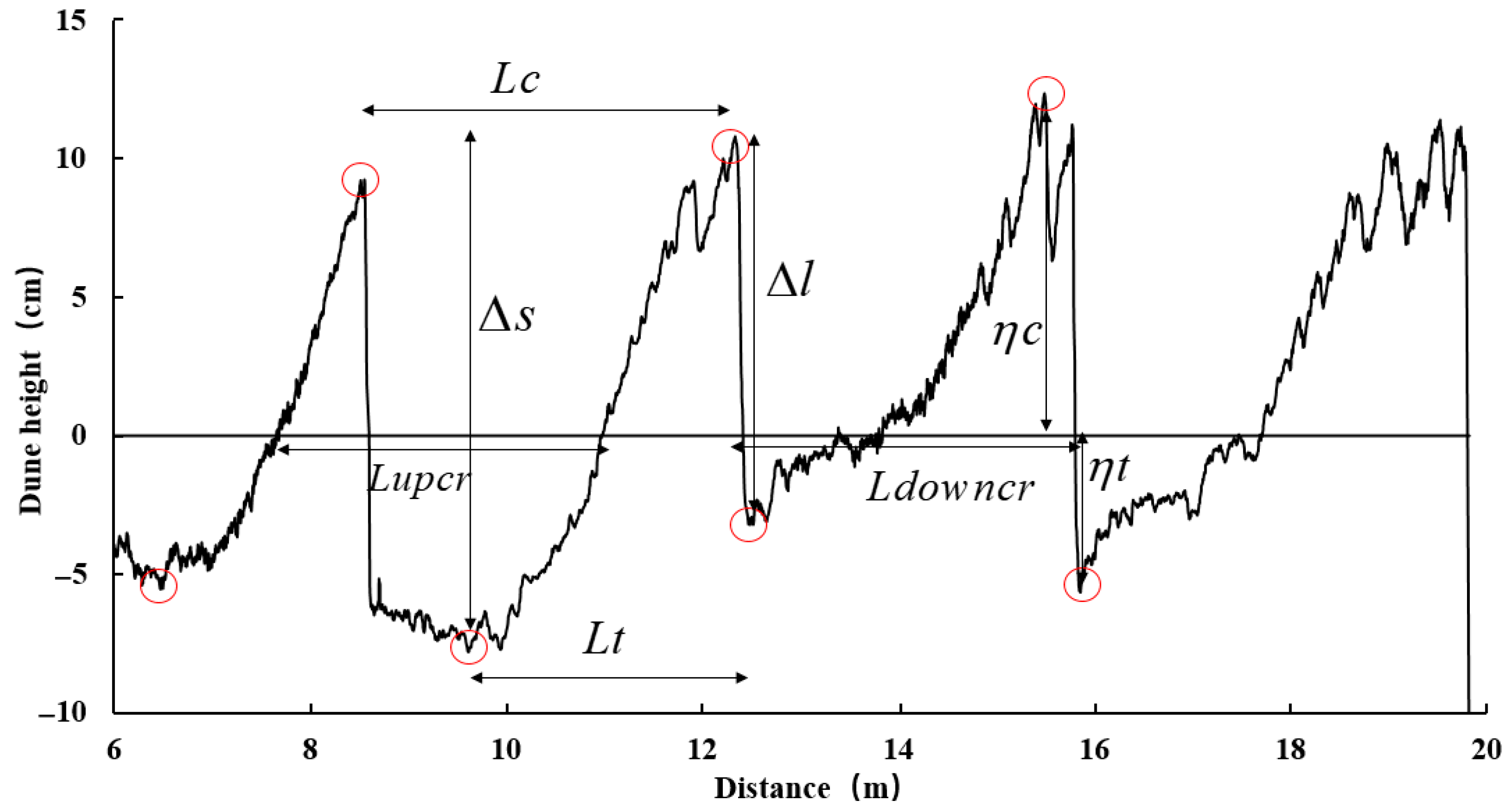
2.3.1. Bedform Parameters
2.3.2. Bedload Transport Intensity and Flow Intensity
2.3.3. Bed Resistance
3. Results
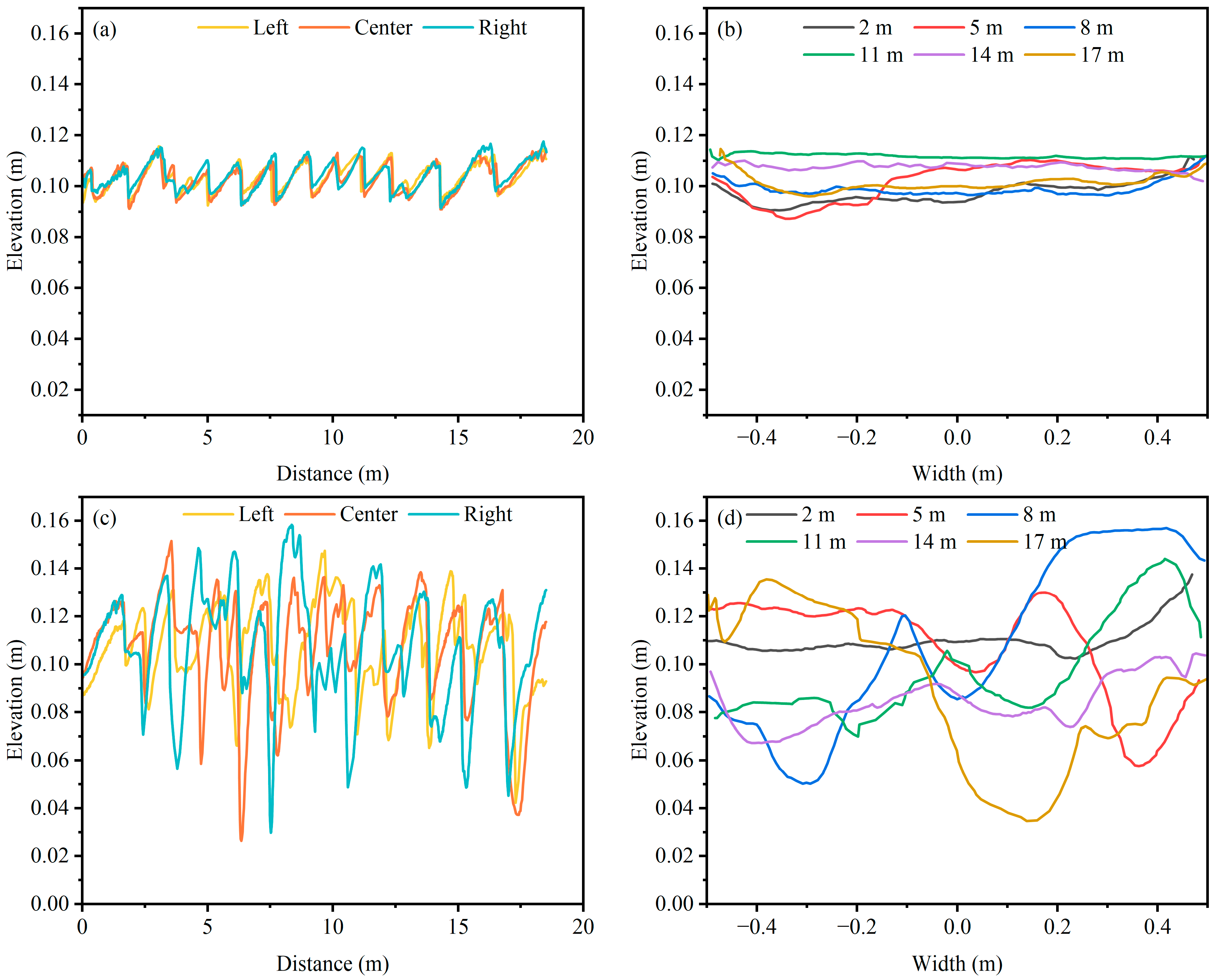
3.1. Statistical Patterns of Bedform Features
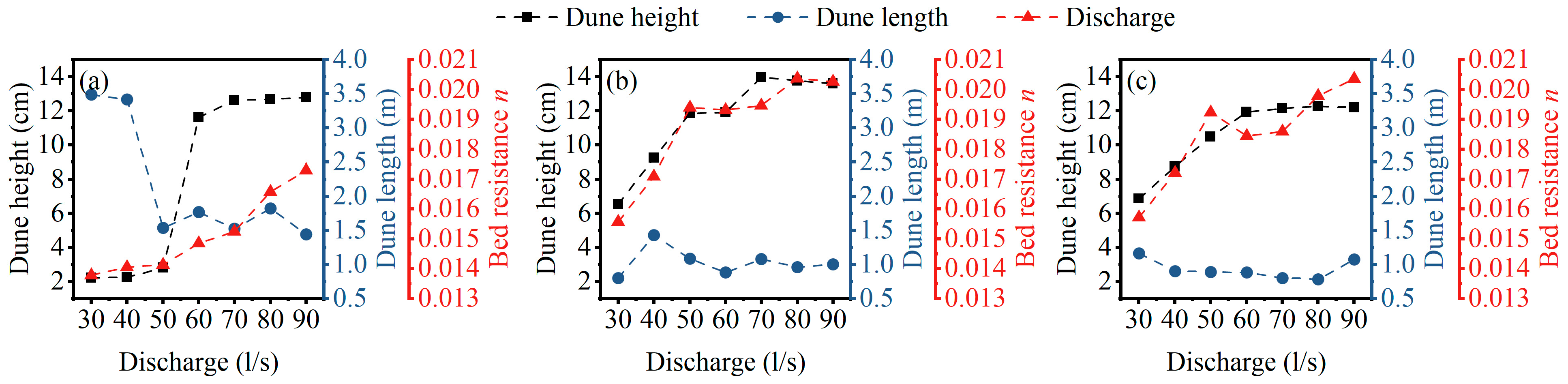
3.1.1. Dune Length Variation Characteristics
3.1.2. Dune Height Variation Characteristics
3.1.3. Crest Height and Trough Depth Variation Characteristics
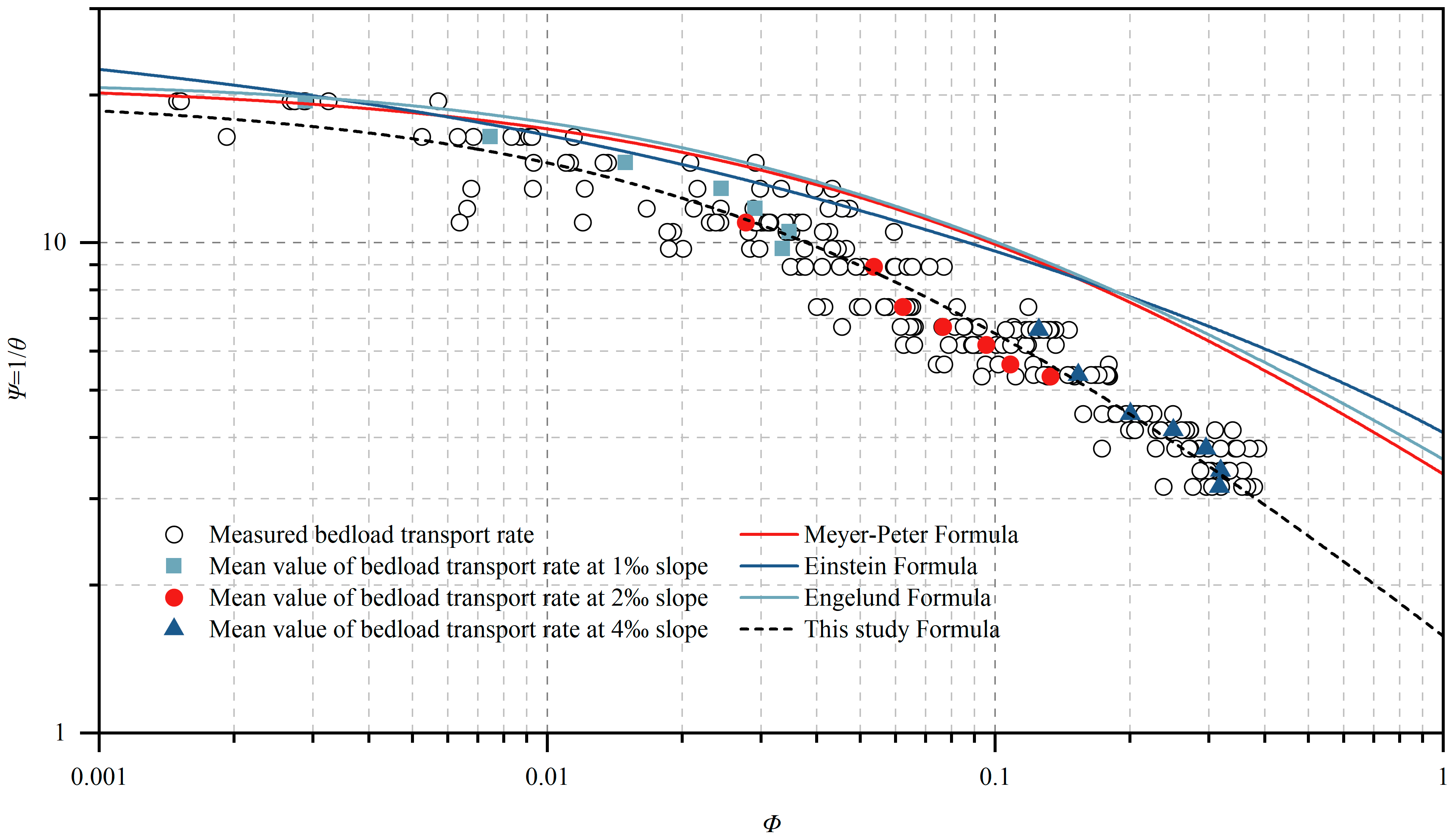
3.2. Bedload Transport Rate on Dune Bedforms
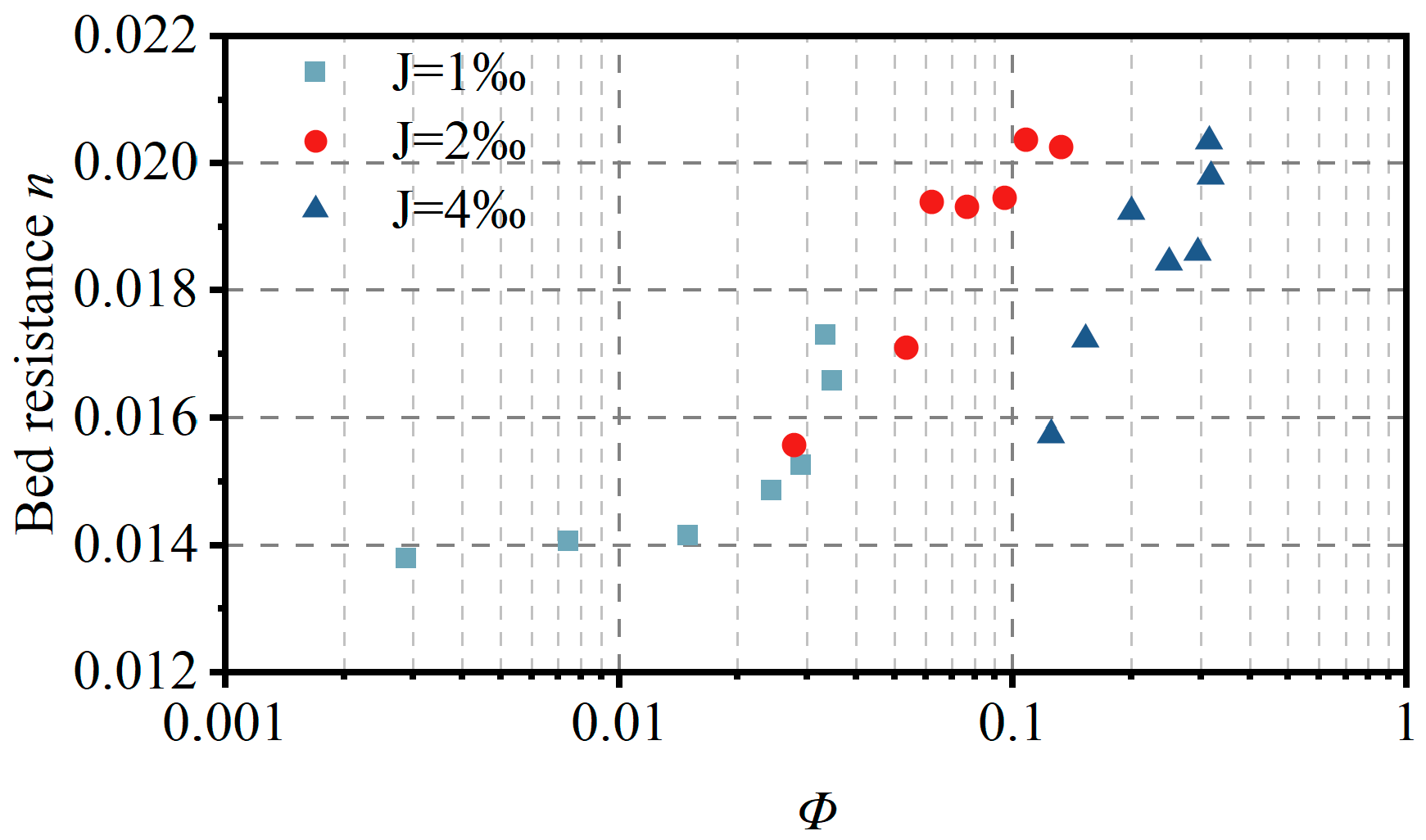
3.3. Bed Resistance
4. Discussion
4.1. Quantification of Bedforms
4.2. Bedload Transport Rate Related to Bedforms
4.3. Bed Resistance Associated with Bedforms
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ashley, G.M. Classification of large-scale subaqueous bedforms; a new look at an old problem. J. Sediment. Res. 1990, 60, 160–172. [Google Scholar]
- Kostaschuk, R. A field study of turbulence and sediment dynamics over subaqueous dunes with flow separation. Sedimentology 2000, 47, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julien, P.; Klaassen, G.; Ten Brinke, W.; Wilbers, A. Case study: Bed resistance of Rhine River during 1998 flood. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2002, 128, 1042–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilbers, A. The Development and Hydraulic Roughness of Subaqueous Dunes; Utrecht University: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Mark, C.; Blom, A.; Hulscher, S. Quantification of variability in bedform geometry. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2008, 113, F03020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqshband, S.; Hurther, D.; Giri, S.; Bradley, R.; Kostaschuk, R.; Venditti, J.; Hoitink, A. The influence of slipface angle on fluvial dune growth. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2021, 126, e2020JF005959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, P.; Lau, Y.L. Computation of bed load using bathymetric data. J. Hydraul. Div. 1980, 106, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venditti, J.G.; Bennett, S.J. Spectral analysis of turbulent flow and suspended sediment transport over fixed dunes. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2000, 105, 22035–22047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, S.; Nikora, V. Fluvial dunes: Initiation, characterization, flow structure. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2011, 36, 39–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unsworth, C.; Parsons, D.; Hardy, R.; Reesink, A.; Best, J.; Ashworth, P.; Keevil, G. The impact of nonequilibrium flow on the structure of turbulence over river dunes. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 6566–6584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, J. The fluid dynamics of river dunes: A review and some future research directions. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2005, 110, F04S02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shugar, D.H.; Kostaschuk, R.; Best, J.L.; Parsons, D.R.; Lane, S.N.; Orfeo, O.; Hardy, R.J. On the relationship between flow and suspended sediment transport over the crest of a sand dune, Río Paraná, Argentina. Sedimentology 2010, 57, 252–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, T.A.; Lindenbergh, R.C.; Egberts, P.J. Separating bathymetric data representing multiscale rhythmic bed forms: A geostatistical and spectral method compared. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2008, 113, F04017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, R.R.; Abad, J.D.; Parsons, D.R.; Best, J.L. Discrimination of bed form scales using robust spline filters and wavelet transforms: Methods and application to synthetic signals and bed forms of the Río Paraná, Argentina. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2013, 118, 1400–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisneros, J.; Best, J.; van Dijk, T.; Almeida, R.P.d.; Amsler, M.; Boldt, J.; Freitas, B.; Galeazzi, C.; Huizinga, R.; Ianniruberto, M. Dunes in the world’s big rivers are characterized by low-angle lee-side slopes and a complex shape. Nat. Geosci. 2020, 13, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Flemming, B.W.; Wang, Y.; Gao, S. An automated procedure to calculate the morphological parameters of superimposed rhythmic bedforms. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2020, 45, 3496–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheiber, L.; Lojek, O.; Götschenberg, A.; Visscher, J.; Schlurmann, T. Robust methods for the decomposition and interpretation of compound dunes applied to a complex hydromorphological setting. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2021, 46, 478–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zomer, J.; Naqshband, S.; Hoitink, A. Short communication: A tool for determining multiscale bedform characteristics from bed elevation data. Earth Surf. Dyn. 2022, 10, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wren, D.G.; Kuhnle, R.A.; Langendoen, E.J. Sediment transport and bed-form characteristics for a range of step-down flows. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2020, 146, 04019060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijn, L. Equivalent Roughness of Alluvial Bed. J. Hydraul. Div. ASCE 1982, 108, 1215–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, A.; Winter, C. Predicting bed form roughness: The influence of lee side angle. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2016, 36, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schippa, L.; Cilli, S.; Ciavola, P.; Billi, P. Dune Contribution to Flow Resistance in Alluvial Rivers. Water 2019, 11, 2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aberle, J.; Nikora, V.; Henning, M.; Ettmer, B.; Hentschel, B. Statistical characterization of bed roughness due to bed forms: A field study in the Elbe River at Aken, Germany. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Musa, M.; Guala, M. Scale-dependent bedform migration and deformation in the physical and spectral domains. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2021, 126, e2020JF005811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vittori, G.; Blondeaux, P. Predicting offshore tidal bedforms using stability methods. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2022, 235, 104234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer-Peter, E.; Müller, R. Formulas for bed-load transport. In Proceedings of the 2nd Meeting of the International Association for Hydraulic Structures Research, Delft, The Netherlands, 7 June 1948; pp. 39–64. [Google Scholar]
- Einstein, H.A. The Bed-Load Function for Sediment Transportation in Open Channel Flows; US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1950.
- Bagnold, R.A. An Approach to the Sediment Transport Problem from General Physics; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1966.
- Engelund, F.; Fredsøe, J. A sediment transport model for straight alluvial channels. Hydrol. Res. 1976, 7, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackers, P.; White, W. Bed material transport: A theory for total load and its verification. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on River Sedimentation, Beijing, China, 24–29 March 1980. Paper B. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, M. Sedimentation Engineering: Processes, Measurements, Modeling, and Practice; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Poorhosein, M.; Afzalimehr, H.; Sui, J.; Singh, V.P.; Azareh, S. Empirical bed load transport equations. Int. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2014, 3, 93–101. [Google Scholar]
- Guala, M.; Heisel, M.; Singh, A.; Musa, M.; Buscombe, D.; Grams, P. A mixed length scale model for migrating fluvial bedforms. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e10.1029/2019GL086625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancey, C. Bedload transport: A walk between randomness and determinism. Part 1. The state of the art. J. Hydraul. Res. 2020, 58, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancey, C. Bedload transport: A walk between randomness and determinism. Part 2. Challenges and prospects. J. Hydraul. Res. 2020, 58, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridge, J.S. The interaction between channel geometry, water flow, sediment transport and deposition in braided rivers. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1993, 75, 13–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebbeydokhti, B.N.; Hekmatzadeh, A.; Rakhshandehroo, G.R. Experimental modeling of dune bed form in a sand-bed channel. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. B Eng. 2006, 30, 503–516. [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre, A.; Ernstsen, V.B.; Winter, C. Estimation of roughness lengths and flow separation over compound bedforms in a natural-tidal inlet. Cont. Shelf Res. 2013, 61, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zomer, J.Y.; Vermeulen, B.; Hoitink, A.J. Coexistence of two dune scales in a lowland river. Earth Surf. Dyn. Discuss. 2023, 2023, 1283–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuhong, Z.; Wenxin, H. Application of artificial neural network to predict the friction factor of open channel flow. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2009, 14, 2373–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brakenhoff, L.; Schrijvershof, R.; van der Werf, J.; Grasmeijer, B.; Ruessink, G.; van der Vegt, M. From ripples to large-scale sand transport: The effects of bedform-related roughness on hydrodynamics and sediment transport patterns in delft3d. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Nelson, P.A. Patterns of alluviation in mixed bedrock-alluvial channels: 2. Controls on the formation of alluvial patches. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2024, 129, e2023JF007293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, A.A.; Patel, M. Machine learning approaches for adequate prediction of flow resistance in alluvial channels with bedforms. Water Sci. Technol. 2024, 89, 290–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Nelson, P.A. Patterns of alluviation in mixed bedrock-alluvial channels: 1. Numerical model. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2024, 129, e2023JF007292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.W. Roughness in the earth sciences. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2014, 136, 202–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, R.W.; Venditti, J.G. Mechanisms of dune growth and decay in rivers. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL094572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Boys, M. The Rhone and streams with movable beds. Ann. Des Pontes Chaussees 1879, 18, 141–195. [Google Scholar]
- Chien, N.; Wan, Z. Mechanics of Sediment Transport; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Chien, N. A Comparison of the Bed Load Formulas. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1980, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Nordin, C.F. Statistical Properties of Dune Profiles; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1971.
- Wang, W.; Shen, H. Statistical properties of alluvial bed forms. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Stochastic Hydraulics, Tokyo, Japan, 5–7 August 1980; pp. 371–389. [Google Scholar]
- Annambhotla, V.S.; Sayre, W.W.; Livesey, R.H. Statistical properties of Missouri River bed forms. J. Waterw. Harb. Coast. Eng. Div. 1972, 98, 489–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclair, S.F.; Bridge, J.S.; Wang, F. Preservation of cross-strata due to migration of subaqueous dunes over aggrading and non-aggrading beds: Comparison of experimental data with theory. Geosci. Can. 1997, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Prent, M.T.; Hickin, E.J. Annual regime of bedforms, roughness and flow resistance, Lillooet River, British Columbia, BC. Geomorphology 2001, 41, 369–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternberg, R.W. Predicting Initial Motion and Bedload Transport of Sediment Particles in the Shallow Marine Environment; University of Washington Press: Seattle, WA, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.S. On Bagnold’s sediment transport equation in tidal marine environments and the practical definition of bedload. Sedimentology 1986, 33, 465–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Berg, J.H. Bedform migration and bed-load transport in some rivers and tidal environments. Sedimentology 1987, 34, 681–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqshband, S.; Hoitink, A.; McElroy, B.; Hurther, D.; Hulscher, S.J. A sharp view on river dune transition to upper stage plane bed. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 11437–11444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leary, K.C.; Buscombe, D. Estimating sand bed load in rivers by tracking dunes: A comparison of methods based on bed elevation time series. Earth Surf. Dyn. 2020, 8, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokin, L.; Warmink, J.; Bomers, A.; Hulscher, S. River dune dynamics during low flows. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2021GL097127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, A.; Cisneros, J. The influence of dune lee side shape on time-averaged velocities and turbulence. Earth Surf. Dyn. 2023, 11, 575–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; White, W.R. Alluvial resistance in transition regime. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1993, 119, 725–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostaschuk, R. Sediment Transport Mechanics and Subaqueous Dune Morphology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Naqshband, S.; Ribberink, J.S.; Hulscher, S.J. Using both free surface effect and sediment transport mode parameters in defining the morphology of river dunes and their evolution to upper stage plane beds. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2014, 140, 06014010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latella, M.; Notti, D.; Baldo, M.; Giordan, D.; Camporeale, C. Short-term biogeomorphology of a gravel-bed river: Integrating remote sensing with hydraulic modelling and field analysis. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2024, 49, 1156–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, M.; Tabatabai, M.R.M.; Najafabadi, S.H.G. Numerical simulation of flow structures over dunes to develop an empirical relationship for separation zone dimensions. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2023, 89, 102275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassi, A.; Mir, A.A.; Kumar, B.; Patel, M. A comprehensive study of various regressions and deep learning approaches for the prediction of friction factor in mobile bed channels. J. Hydroinform. 2023, 25, 2500–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| J | No. | Q | h | u | Fr | Re | u* | gb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| l/s | cm | m/s | ×104 | cm/s | kg/m/min | |||
| 1‰ | 1 | 30 | 7.86 | 0.382 | 0.435 | 2.59 | 2.581 | 0.042 |
| 2 | 40 | 9.56 | 0.418 | 0.432 | 3.36 | 2.806 | 0.108 | |
| 3 | 50 | 11.08 | 0.451 | 0.433 | 4.09 | 2.983 | 0.216 | |
| 4 | 60 | 12.88 | 0.466 | 0.415 | 4.77 | 3.170 | 0.354 | |
| 5 | 70 | 14.50 | 0.483 | 0.405 | 5.43 | 3.321 | 0.421 | |
| 6 | 80 | 16.74 | 0.478 | 0.373 | 5.99 | 3.508 | 0.503 | |
| 7 | 90 | 18.64 | 0.483 | 0.357 | 6.56 | 3.650 | 0.485 | |
| 2‰ | 8 | 30 | 6.82 | 0.440 | 0.538 | 2.64 | 3.431 | 0.401 |
| 9 | 40 | 8.68 | 0.461 | 0.499 | 3.41 | 3.809 | 0.775 | |
| 10 | 50 | 10.86 | 0.460 | 0.446 | 4.11 | 4.184 | 0.898 | |
| 11 | 60 | 12.19 | 0.492 | 0.450 | 4.82 | 4.385 | 1.105 | |
| 12 | 70 | 13.55 | 0.517 | 0.448 | 5.51 | 4.573 | 1.380 | |
| 13 | 80 | 15.25 | 0.525 | 0.429 | 6.13 | 4.788 | 1.561 | |
| 14 | 90 | 16.43 | 0.548 | 0.431 | 6.77 | 4.926 | 1.920 | |
| 4‰ | 15 | 30 | 5.52 | 0.543 | 0.739 | 2.70 | 4.417 | 1.807 |
| 16 | 40 | 7.00 | 0.571 | 0.690 | 3.51 | 4.909 | 2.214 | |
| 17 | 50 | 8.65 | 0.578 | 0.627 | 4.26 | 5.379 | 2.896 | |
| 18 | 60 | 9.46 | 0.634 | 0.658 | 5.05 | 5.587 | 3.609 | |
| 19 | 70 | 10.50 | 0.667 | 0.657 | 5.79 | 5.835 | 4.262 | |
| 20 | 80 | 11.92 | 0.671 | 0.621 | 6.46 | 6.146 | 4.598 | |
| 21 | 90 | 13.11 | 0.686 | 0.605 | 7.13 | 6.384 | 4.572 |
| Statistic | 2D Bedforms | 3D Bedforms | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Distribution Form | Distribution Parameters | Distribution Form | Distribution Parameters | |||
| Log Mean (μ) | Log Standard Deviation (σ) | Log Mean (μ) | Log Standard Deviation (σ) | |||
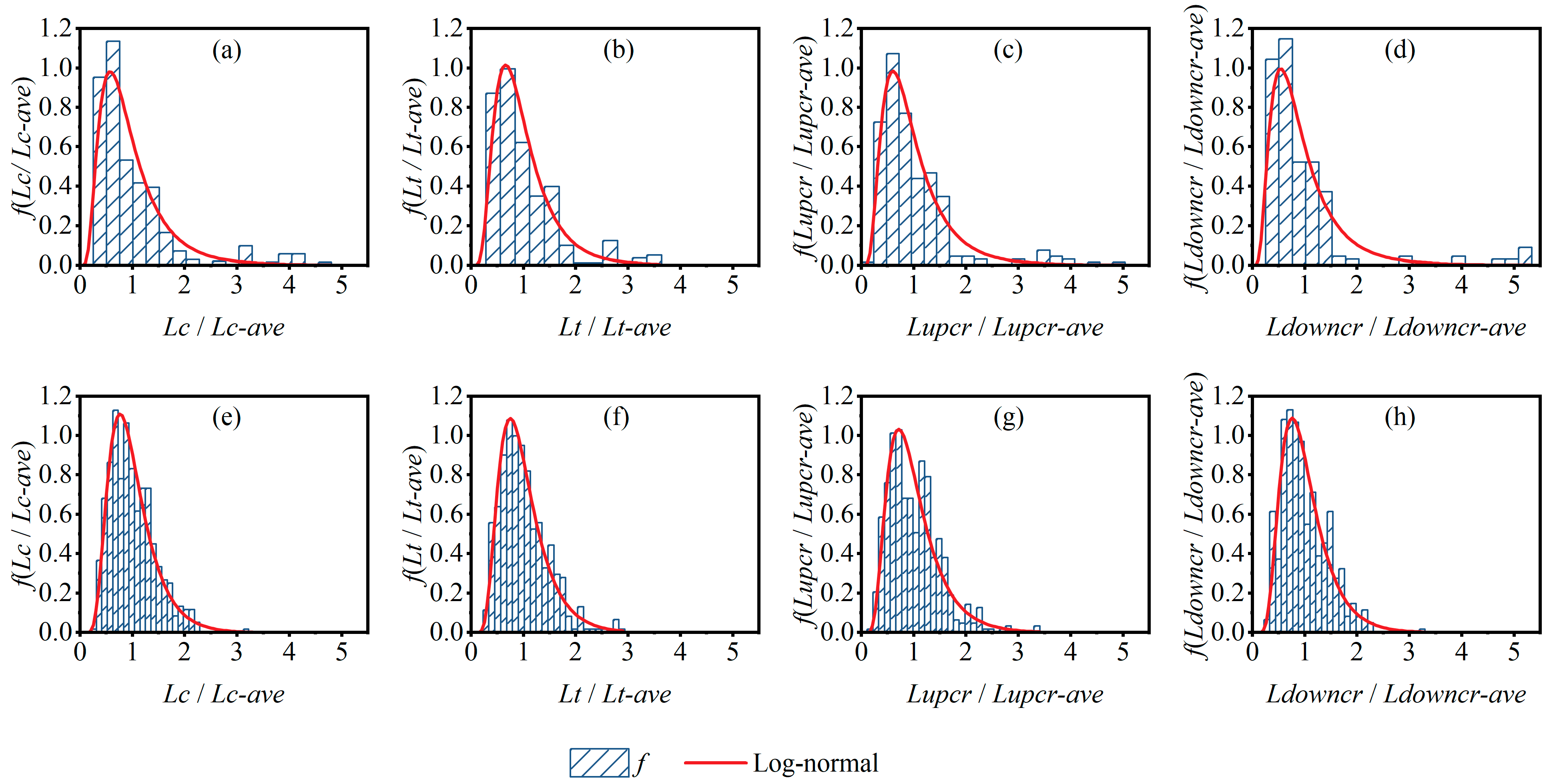
| Lc | Lognormal | −0.205 | 0.595 | Lognormal | −0.091 | 0.432 |
| Lt | Lognormal | −0.150 | 0.524 | Lognormal | −0.097 | 0.446 |
| Lupcr | Lognormal | −0.190 | 0.580 | Lognormal | −0.115 | 0.488 |
| Ldowncr | Lognormal | −0.247 | 0.622 | Lognormal | −0.096 | 0.445 |
| Statistic | 2D Bedforms | 3D bedforms | ||||
| Distribution Form | Distribution Parameters | Distribution Form | Distribution Parameters | |||
| Shape Parameter (α) | Scale Parameter (β) | Log Mean (μ) | Log Standard Deviation (σ) | |||
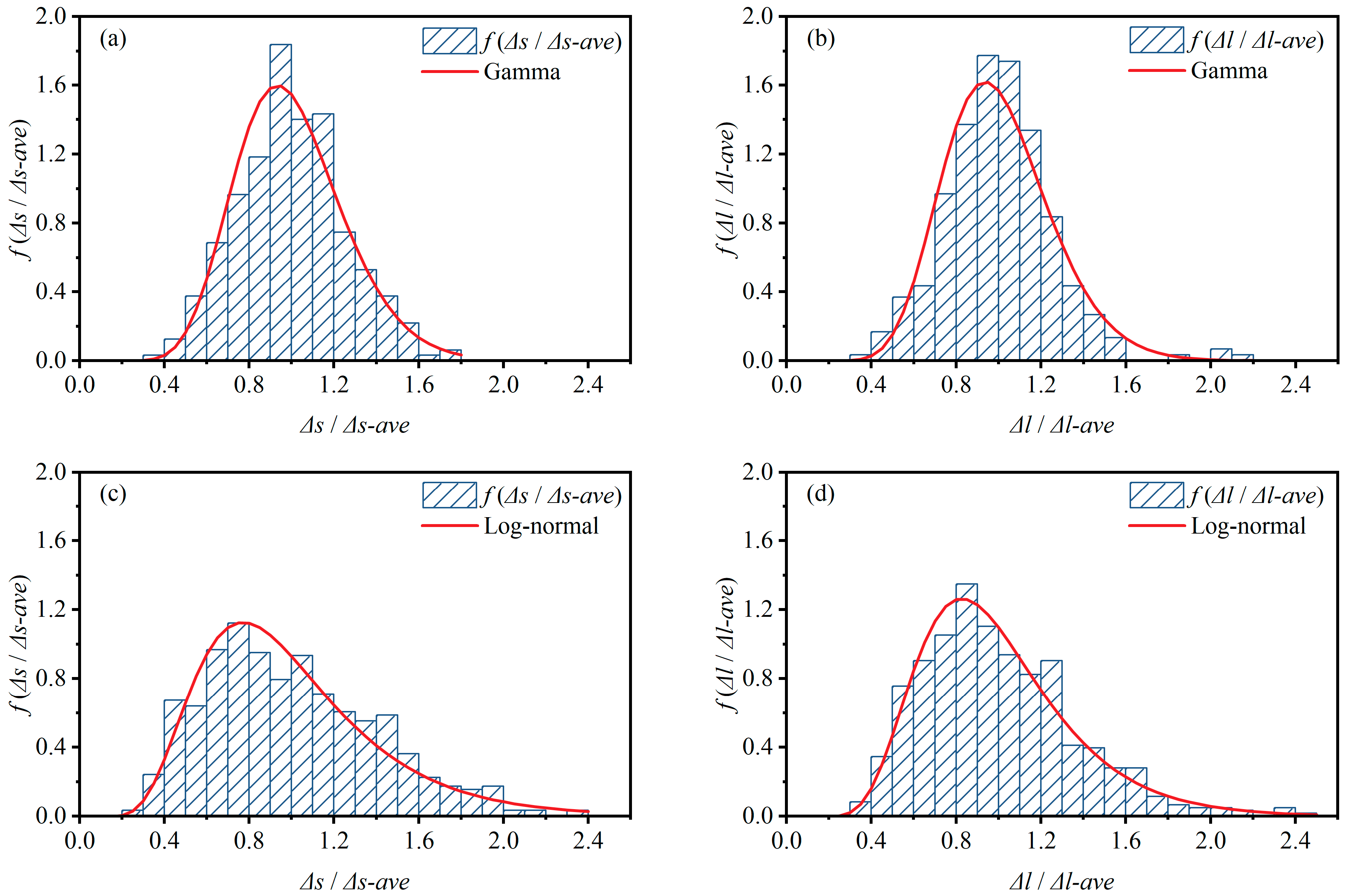
| Δs | Gamma | 15.185 | 0.066 | Lognormal | −0.084 | 0.420 |
| Δl | Gamma | 15.610 | 0.064 | Lognormal | −0.063 | 0.358 |
| Statistic | 2D Bedforms | 3D Bedforms | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Distribution Form | Distribution Parameters | Distribution Form | Distribution Parameters | |||
| Mean (μ) | Standard Deviation (σ) | Shape Parameter (α) | Scale Parameter (β) | |||
| ηc | Normal | 1.0 | 0.334 | Gamma | 4.906 | 0.204 |
| ηt | Normal | 1.0 | 0.416 | Gamma | 3.083 | 0.324 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geng, X.; Cao, W.; Liu, C.; Zhang, G. Experimental Study of Bedform Development Characteristics and Their Effects on Sediment Transport. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 9823. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14219823
Geng X, Cao W, Liu C, Zhang G. Experimental Study of Bedform Development Characteristics and Their Effects on Sediment Transport. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(21):9823. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14219823
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeng, Xu, Wenhong Cao, Chunjing Liu, and Guangming Zhang. 2024. "Experimental Study of Bedform Development Characteristics and Their Effects on Sediment Transport" Applied Sciences 14, no. 21: 9823. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14219823
APA StyleGeng, X., Cao, W., Liu, C., & Zhang, G. (2024). Experimental Study of Bedform Development Characteristics and Their Effects on Sediment Transport. Applied Sciences, 14(21), 9823. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14219823





