Artificial Intelligence-Powered Recommender Systems for Promoting Healthy Habits and Active Aging: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Selection Criteria
- Works not clearly focused on the fields of physical activity, exercise, active aging, health, mental health, dietary habits, and sleep habits;
- Work focused on specific diseases;
- Systematic review articles;
- Doctoral thesis;
- Articles focused on the technical characteristics of different types of recommendation algorithms without direct application to the proposed field.
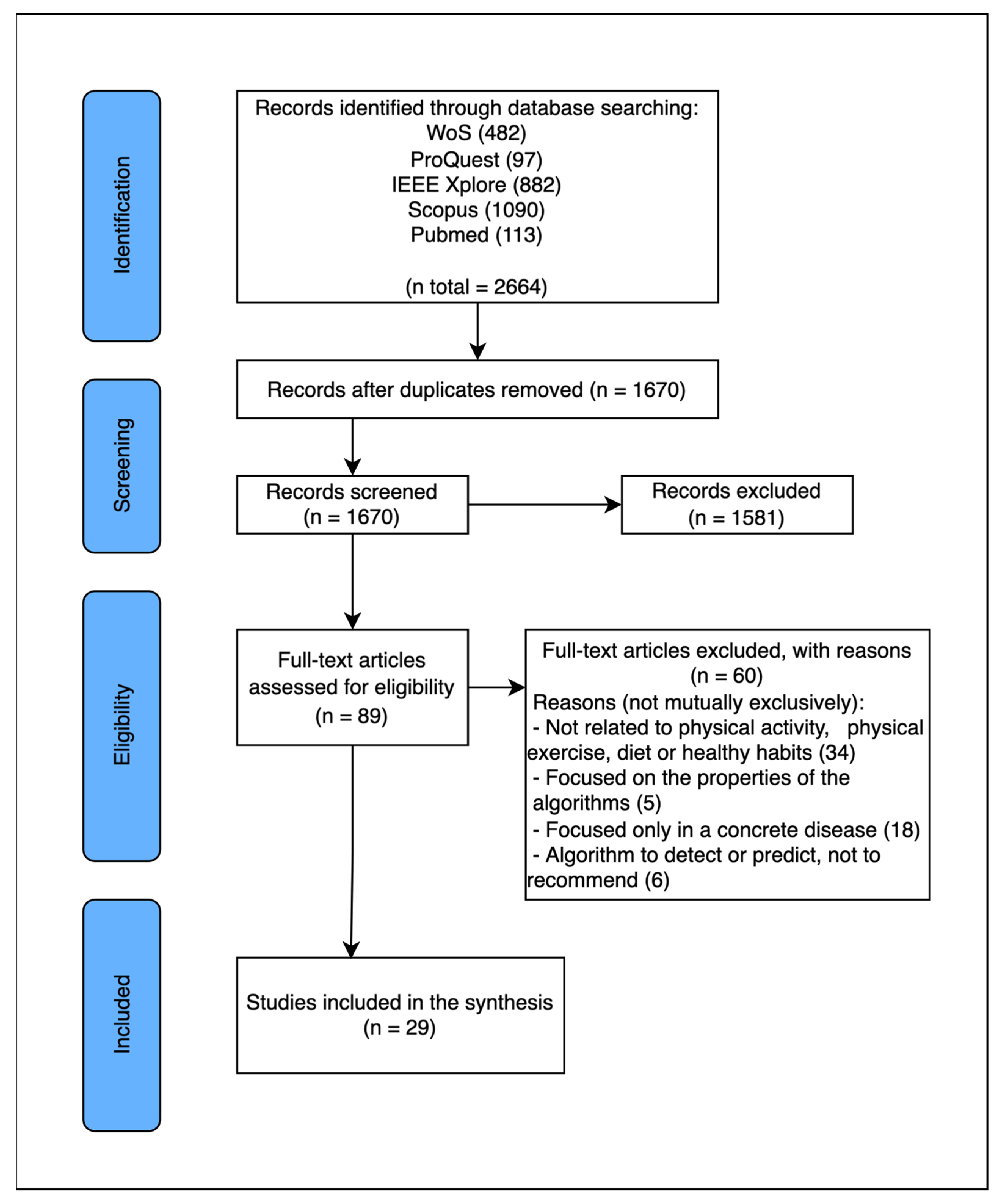
2.3. Selection Process
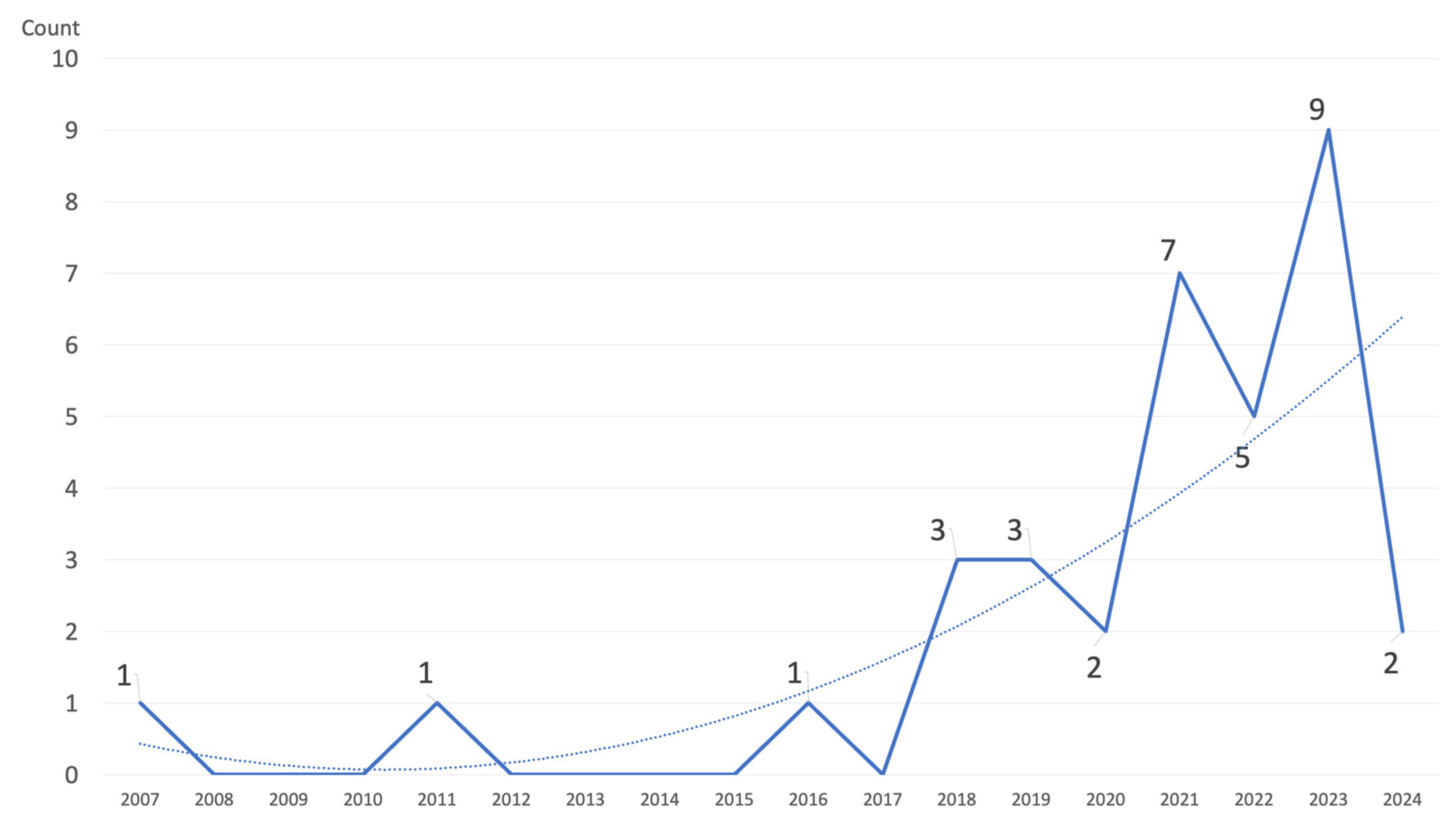
3. Results
- Diet.
- Physical Activity.
- Physical Activity, Social Activities and Diet.
- Physical Activity and Diet.
- Physical Activity and Sleep Quality.
- Physical Activity, Physical Exercise, and Diet.
- Physical Exercise.
- Physical Exercise and Diet.
- Physical Exercise and Mental Health.
- Sport.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lippke, S.; Schalk, T.M.; Kühnen, U.; Shang, B. Pace of Life and Perceived Stress in International Students. PsyCh J. 2021, 10, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Hua, Q.; Chang, Y.-S.; Wang, B.; Zhang, L.; Kong, X. A Survey of Collaborative Filtering-Based Recommender Systems: From Traditional Methods to Hybrid Methods Based on Social Networks. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 64301–64320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M. A Survey of Collaborative Filtering Techniques. Adv. Artif. Intell. 2009, 2009, 421425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Guo, Q.; Yang, J.; Fang, H.; Guo, G.; Zhang, J.; Burke, R. Research Commentary on Recommendations with Side Information: A Survey and Research Directions. Electron. Commer. Res. Appl. 2019, 37, 100879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afoudi, Y.; Lazaar, M.; Al Achhab, M. Collaborative Filtering Recommender System; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 332–345. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez Bocanegra, C.L.; Sevillano Ramos, J.L.; Rizo, C.; Civit, A.; Fernandez-Luque, L. HealthRecSys: A Semantic Content-Based Recommender System to Complement Health Videos. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2017, 17, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adomavicius, G.; Tuzhilin, A. Toward the next Generation of Recommender Systems: A Survey of the State-of-the-Art and Possible Extensions. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2005, 17, 734–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lika, B.; Kolomvatsos, K.; Hadjiefthymiades, S. Facing the Cold Start Problem in Recommender Systems. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 2065–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasebi, F.; Meghdadi, M.; Ahmadian, S.; Valiallahi, K. A Hybrid Recommendation System Based on Profile Expansion Technique to Alleviate Cold Start Problem. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 2339–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adomavicius, G.; Tuzhilin, A. Context-Aware Recommender Systems. In Recommender Systems Handbook; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 217–253. [Google Scholar]
- Verbert, K.; Manouselis, N.; Ochoa, X.; Wolpers, M.; Drachsler, H.; Bosnic, I.; Duval, E. Context-Aware Recommender Systems for Learning: A Survey and Future Challenges. IEEE Trans. Learn. Technol. 2012, 5, 318–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokrzadeh, Z.; Feizi-Derakhshi, M.-R.; Balafar, M.-A.; Mohasefi, J.B. Knowledge Graph-Based Recommendation System Enhanced by Neural Collaborative Filtering and Knowledge Graph Embedding. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2024, 15, 102263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahesh, B. Machine Learning Algorithms—A Review. Int. J. Sci. Res. IJSR 2020, 9, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, B.; Karypis, G.; Konstan, J.; Riedl, J. Item-Based Collaborative Filtering Recommendation Algorithms. In Proceedings of the Web Conference, Hong Kong, China, 1–5 May 2001; pp. 285–295. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Shen, F.; Liu, W.; He, X.; Luan, H.; Chua, T.-S. Discrete Collaborative Filtering. In Proceedings of the SIGIR ‘16: Proceedings of the 39th International ACM SIGIR conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Pisa, Italy, 17–21 July 2016; pp. 325–334. [Google Scholar]
- Stevens, G.; Mascarenhas, M.; Mathers, C. Global Health Risks: Progress and Challenges. Bull. World Health Organ. 2009, 87, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yürüten, O. Recommender Systems for Healthy Behavior Change; EPFL: Lausanne, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo, J.I.; Maqueda, E.; Risco-Martín, J.L.; Cuesta-Infante, A.; Colmenar, J.M.; Nobel, J. glUCModel: A Monitoring and Modeling System for Chronic Diseases Applied to Diabetes. J. Biomed. Inform. 2014, 48, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabbi, M.; Aung, M.H.; Zhang, M.; Choudhury, T. MyBehavior: Automatic Personalized Health Feedback from User Behaviors and Preferences Using Smartphones. In Proceedings of the 2015 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing, Osaka, Japan, 7–11 September 2015; pp. 707–718. [Google Scholar]
- Radha, M.; Willemsen, M.C.; Boerhof, M.; IJsselsteijn, W.A. Lifestyle Recommendations for Hypertension through Rasch-Based Feasibility Modeling. In Proceedings of the UMAP ‘16: Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on User Modeling Adaptation and Personalization, Halifax, NS, Canada, 13–17 July 2016; pp. 239–247. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Díaz, R.; García-Rodríguez, A. Bibliotecas, Juegos y Gamificación: Una Tendencia de Presente Con Mucho Futuro. Anu. ThinkEPI 2018, 12, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. Int. J. Surg. 2010, 8, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JabRef—Free Reference Manager—Stay on Top of Your Literature. Available online: https://www.jabref.org/ (accessed on 3 July 2024).
- Santos-Gago, J.M.; Ramos-Merino, M.; Vallarades-Rodriguez, S.; Álvarez-Sabucedo, L.M.; Fernández-Iglesias, M.J.; García-Soidán, J.L. Innovative Use of Wrist-Worn Wearable Devices in the Sports Domain: A Systematic Review. Electronics 2019, 8, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, C.A.S.; Cardoso, T.R.; Duarte, R.P. Meal Suggestions for Caregivers and Indecisive Individuals Without a Set Food Plan. In International Conference on Smart Objects and Technologies for Social Good; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 556, pp. 172–183. [Google Scholar]
- Ramaraj, K.; Narayan, V.; Dhivyaprabha, T.T.; Subashini, P. A Healthy Nutrition Suggestion Model for Indian Women Sports Players & Active Youth Using Long Short-Term Memory. Internet Technol. Lett. 2023, 7, e452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orte, S.; Migliorelli, C.; Sistach-Bosch, L.; Gómez-Martínez, M.; Boqué, N. A Tailored and Engaging mHealth Gamified Framework for Nutritional Behaviour Change. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdollahi Oskouei, S.; Hashemzadeh, M. FoodRecNet: A Comprehensively Personalized Food Recommender System Using Deep Neural Networks. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 2023, 65, 3753–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.C.; Gorgulho, B.; Marchioni, D.M.; Alvim, S.M.; Giatti, L.; de Araujo, T.A.; Alonso, A.C.; Santos, I.d.S.; Lotufo, P.A.; Benseñor, I.M. Recommender System Based on Collaborative Filtering for Personalized Dietary Advice: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of the ELSA-Brasil Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, R.Y.; Alzahrani, A.A.; Martinez, L. A Food Recommender System Considering Nutritional Information and User Preferences. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 96695–96711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouh, R.M.; Lee, H.-H.; Lee, W.-J.; Lee, J.-D. A Smart Recommender Based on Hybrid Learning Methods for Personal Well-Being Services. Sensors 2019, 19, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vairavasundaram, S.; Varadarajan, V.; Srinivasan, D.; Balaganesh, V.; Damerla, S.B.; Swaminathan, B.; Ravi, L. Dynamic Physical Activity Recommendation Delivered through a Mobile Fitness App: A Deep Learning Approach. Axioms 2022, 11, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A.; Pahari, N.; Prinz, A.; Riegler, M. Machine Learning and Ontology in eCoaching for Personalized Activity Level Monitoring and Recommendation Generation. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A.; Prinz, A.; Gerdes, M.; Martinez, S.; Pahari, N.; Meena, Y.K. ProHealth eCoach: User-Centered Design and Development of an eCoach App to Promote Healthy Lifestyle with Personalized Activity Recommendations. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2022, 22, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Arya, A.; Orji, R.; Chan, G. Physical Activity Recommendation for Exergame Player Modeling Using Machine Learning Approach. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 8th International Conference on Serious Games and Applications for Health (SeGAH), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 12–14 August 2020; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Das, S.; Codella, J.; Hao, T.; Lin, K.; Maduri, C.; Chen, C.-H. An Adaptive, Data-Driven Personalized Advisor for Increasing Physical Activity. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2018, 23, 999–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.; Afzal, M.; Hussain, M.; Ali, M.; Siddiqi, M.H.; Lee, S.; Kang, B.H. Multimodal Hybrid Reasoning Methodology for Personalized Wellbeing Services. Comput. Biol. Med. 2016, 69, 10–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Song, Y.; Chen, W.; Du, H.; Su, X.; Wang, H. Research and Implementation of Personalized Recommendation Algorithm for Senior Diet Exercise Based on Collaborative Filtering. In Proceedings of the ISAIMS ‘23: Proceedings of the 2023 4th International Symposium on Artificial Intelligence for Medicine Science, Chengdu, China, 20–22 October 2023; pp. 796–804. [Google Scholar]
- Hemaraju, S.; Kaloor, P.M.; Arasu, K. Yourcare: A Diet and Fitness Recommendation System Using Machine Learning Algorithms; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2023; Volume 2655. [Google Scholar]
- Annapoorna, E.; Sai, P.N.; Goud, K.R.S.; Koushik, K.; Saini, M. Automated Diet and Exercise Suggestion Based on Obesity Classification; EDP Sciences: Les Ulis, France, 2023; Volume 430, p. 01049. [Google Scholar]
- Palomares, I.; Alcaraz-Herrera, H.; Shen, K.-Y. F-EvoRecSys: An Extended Framework for Personalized Well-Being Recommendations Guided by Fuzzy Inference and Evolutionary Computing. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, 24, 2783–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojarad, R.; Attal, F.; Chibani, A.; Amirat, Y. Context-Aware Adaptive Recommendation System for Personal Well-Being Services. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 32nd International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence (ICTAI), Baltimore, MD, USA, 9–11 November 2020; pp. 192–199. [Google Scholar]
- Erdeniz, S.; Menychtas, A.; Maglogiannis, I.; Felfernig, A.; Tran, T. Recommender Systems for IoT Enabled Quantified-Self Applications. Evol. Syst. 2019, 11, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla Vecchia, A.; Oliboni, B.; Quintarelli, E. ICARE: The Principles of Explainable AI in a Context-Aware Recommendation APP. In EDBT/ICDT Workshops; CEUR-WS: Aachen, Germany, 2024; Available online: https://ceur-ws.org/Vol-3651/HeDAI-2.pdf (accessed on 4 November 2024).
- Anusari, T.G.M.; Amarasinghe, B.Y.; Munasinghe, G.K.; Epitawala, E.K.N.; Pemadasa, M.N.; Weerasinghe, L. SriHealth: A Single Platform for Meal Plans, Workouts, Yoga Schedules Based on SriLankan Lifestyle. In Proceedings of the 2021 3rd International Conference on Advancements in Computing (ICAC), Colombo, Sri Lanka, 9–11 December 2021; pp. 216–221. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.-K.; Chen, F.-H.; Lin, S.-F. An Ai-Based Exercise Prescription Recommendation System. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basnayake, C.; Peiris, C.; Wickramarathna, H.; Jayathunga, P. Recommender System Based on Food and Exercise Ontologies to Find the Suitable Fitness Exercise Plan with the Aid of Python. In Proceedings of the 2021 5th SLAAI International Conference on Artificial Intelligence (SLAAI-ICAI), Colombo, Sri Lanka, 6–7 December 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, T.T.; Choi, J.W.; Dang, C.V.; SuPark, G.; Baek, J.Y.; Kim, J.W. Recommender System with Artificial Intelligence for Fitness Assistance System. In Proceedings of the 2018 15th International Conference on Ubiquitous Robots (UR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 26–30 June 2018; pp. 489–492. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, A.; Martinez-Martin, E.; Cazorla, M.; Julian, V. PHAROS–PHysical Assistant RObot System. Sensors 2018, 18, 2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadhasivam, S.; Sarvesvaran, M.; Prasanth, P.; Latha, L. Diet and Workout Recommendation Using ML. In Proceedings of the 2023 2nd International Conference on Advancements in Electrical, Electronics, Communication, Computing and Automation (ICAECA), Coimbatore, India, 16–17 June 2023; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Gaikwad, S.; Awatade, P.; Sirdeshmukh, Y.; Prasad, C. Diet Plan and Home Exercise Recommendation System Using Smart Watch. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence for Innovations in Healthcare Industries (ICAIIHI), Raipur, India, 29–30 December 2023; Volume 1, pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Balpande, M.; Sharma, J.; Nair, A.; Khandelwal, M.; Dhanray, S. AI Based Gym Trainer and Diet Recommendation System. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 4th Annual Flagship India Council International Subsections Conference (INDISCON), Mysore, India, 5–7 August 2023; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Jamil, F.; Qayyum, F.; Alhelaly, S.; Javed, F.; Muthanna, A. Intelligent Microservice Based on Blockchain for Healthcare Applications. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2021, 69, 2513–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, F.; Kahng, H.K.; Kim, S.; Kim, D.-H. Towards Secure Fitness Framework Based on IoT-Enabled Blockchain Network Integrated with Machine Learning Algorithms. Sensors 2021, 21, 1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donciu, M.; Ionita, M.; Dascalu, M.; Trausan-Matu, S. The Runner--Recommender System of Workout and Nutrition for Runners. In Proceedings of the 2011 13th International Symposium on Symbolic and Numeric Algorithms for Scientific Computing, Timisoara, Romania, 26–29 September 2011; pp. 230–238. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Byung, H.-Y.; Choe, H.; Park, B.-Y.; Park, R.-W.; Park, P.; Hwang, H.-J.; Lee, B.-M.; Lee, Y.-H.; Kang, U.-G. Lifestyle Recommendation System Using Framingham Heart Study Based Clinical Decision Support System (CDSS). In World Congress on Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering 2006: August 27–September 1, 2006 COEX Seoul, Korea “Imaging the Future Medicine”; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 14, pp. 4016–4019. [Google Scholar]
- Mahyari, A.; Pirolli, P. Physical Exercise Recommendation and Success Prediction Using Interconnected Recurrent Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Digital Health (ICDH), Chicago, IL, USA, 5–10 September 2021; pp. 148–153. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Sun, F. Sports Training Analysis Method Based on Collaborative Filtering. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on High Performance Big Data and Intelligent Systems (HPBD&IS), Macau, China, 5–7 December 2021; pp. 83–87. [Google Scholar]
- The Definitions of the TRL Levels to Be Used Are in General Annexes/Annex G; European Commission: Luxembourg, 2014; Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/research/participants/data/ref/h2020/other/wp/2018-2020/annexes/h2020-wp1820-annex-g-trl_en.pdf (accessed on 4 November 2024).
- Koivisto, J.; Hamari, J. Gamification of Physical Activity: A Systematic Literature Review of Comparison Studies; CEUR-WS: Aachen, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Shi, H.; Shen, M.; Ni, Y.; Zhang, X.; Pang, Y.; Yu, T.; Lian, X.; Yu, T.; Yang, X. The Effects of mHealth-Based Gamification Interventions on Participation in Physical Activity: Systematic Review. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2022, 10, e27794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zichermann, G.; Cunningham, C. Gamification by Design: Implementing Game Mechanics in Web and Mobile Apps; O’Reilly Media, Inc.: Sebastopol, CA, USA, 2011; ISBN 1-4493-1539-9. [Google Scholar]
- Williamson, C.; Baker, G.; Tomasone, J.R.; Bauman, A.; Mutrie, N.; Niven, A.; Richards, J.; Oyeyemi, A.; Baxter, B.; Rigby, B. The Physical Activity Messaging Framework (PAMF) and Checklist (PAMC): International Consensus Statement and User Guide. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2021, 18, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Barreiro, J.; Alvarez-Sabucedo, L.; Garcia-Soidan, J.L.; Santos-Gago, J.M. Towards a Blockchain Hybrid Platform for Gamification of Healthy Habits: Implementation and Usability Validation. Appl. Syst. Innov. 2024, 7, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Barreiro, J.; Garcia-Soidan, J.L.; Alvarez-Sabucedo, L.; Santos-Gago, J.M. Practical Approach to Designing and Implementing a Recommendation System for Healthy Challenges. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Research Question | Statement |
|---|---|
| RQ1 | To what extent have personalized healthy activity recommendation systems been developed? |
| RQ2 | What types of algorithms do they use? Do they use ML? Other AI techniques? |
| RQ3 | Is gamification used to encourage healthy practices? |
| RQ4 | What user data are used to make the recommendation? |
| Author/Year | Domain | Item Recommended | Recommendation Model | Data from User | Support Database | TRL | Gamification (Reward) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Nouh et al., 2019) [31] | Diet | Food | CF and CBF. Technique used: K-NN | Sociodemographic, health status, and personal information | NEM | 4 | NEM |
| (Toledo et al., 2019) [30] | Daily meals | NEM. Technique used: AHPSort | Sociodemographic, heart rate, burned calories, and daily PA level | NEM (conventional) | 5 | NEM | |
| (Silva et al., 2022) [29] | Diet plans | CF. Techniques used: NEM | Sociodemographic and eating habits | NEM (conventional) | 5 | NEM | |
| (Hamdollahi and Hashemzadeh, 2023) [28] | Meals | NEM. Techniques used: FCNN and CNN | User preferences, health conditions, sociodemographic information, food ingredients, type of cooking, food category, food tags, diet, and allergies | NEM (conventional) | 4 | NEM | |
| (Orte et al., 2023) [27] | Key food groups | KBF. Technique used: RBR | Modified food-frequency questionnaire | Conventional | 5 | Yes (Missions) | |
| (Ramaraj et al., 2023) [26] | Meals | NEM. Techniques used: LSTM and GRU | Sociodemographic | NEM (conventional) | 4 | NEM | |
| (Cunha et al., 2024) [25] | Meals | Data driven. Techniques used: MLPN | User preferences and daily goals | NEM (conventional) | 4 | NEM | |
| (Ali et al., 2016) [37] | PA | Walking, running, climbing, bicycling, hiking… | NEM. Techniques used: RBR, CBR, and PBR | BMI | Distributed (Microsoft Azure) | 4 | NEM |
| (Li et al., 2018) [36] | Daily steps | NEM. Technique used: Multi-level clustering | Sociodemographic and PA level | NEM (conventional) | 4 | NEM | |
| (Zhao et al., 2020) [35] | Walking, running, climbing, bicycling, hiking… | CF. Techniques used: SVM and K-MC | Sociodemographic, daily steps, active calories, walking/running distances, calendar events, location, player type, and exercise type | NEM (conventional) | 4 | Yes (Exergames) | |
| (Chatterjee, Pahari et al., 2022) [33] | NEM | Hybrid (data driven and rule based). Techniques used: SVC, GNB, DTC, RFC, K-NN, and DC | NEM | NEM | 4 | NEM | |
| (Chatterjee, Prinz et al., 2022) [34] | Daily and weekly steps | Hybrid (data driven and rule based) Techniques used: NEM | Sociodemographic, activity levels, and health status | NEM | 4 | Yes (motivational messages and rewards) | |
| (Vairavasundaram et al., 2022) [32] | Hour and daily steps | NEM. Techniques used: RFC, SVR, RNN, and LSTM | Sociodemographic, activity levels, and step count | NEM (conventional) | 5 | NEM | |
| (Wang et al., 2023) [38] | PA, social activities, and diet | Meals, social activities and PA | CF. Techniques used: NEM | User preferences | Conventional | 4 | NEM |
| (Mojarad et al., 2020) [42] | PA and diet | Healthy lifestyle (stretching, stop eating, listening to music…) | KBF. Technique used: PASP | NEM | NEM (conventional) | 5 | NEM |
| (Palomares et al., 2022) [41] | Meals and PA (swimming, dancing, bicycling…) | NEM. Techniques used: GA and RBF using a fuzzy inference engine | User preferences, physical condition, and goals | NEM (conventional) | 5 | NEM | |
| (Annapoorna et al., 2023) [40] | Walking, jogging, strength training, HIIT, and personalized menus | NEM. Technique used: DTC | Diet and exercise preferences | NEM (conventional) | 4 | NEM | |
| (Hemaraju et al., 2023) [39] | Foods depending on goals and preferences and hiking, running, bicycling... | NEM. Techniques used: K-MC, LR, DTC, RFC, and XGBC | Sociodemographic and diseases | NEM (conventional) | 3 | NEM | |
| (Erdeniz et al., 2019) [43] | PA and sleep quality | Steps and sleep time. | CF and CBF. Technique used: K-NN | Sociodemographic, physical condition, medical history, chronic diseases, and cardiovascular diseases | NEM | 4 | NEM |
| (Dalla Vecchia et al., 2024) [44] | Sleep time and intensity of PA | ALBA | PA levels and sleep quality | NEM (conventional) | 4 | NEM | |
| (Anusari et al., 2021) [45] | PA, PE, and diet | NEM | Knowledge-based filtering. Used techniques: NB, RFC, DTC, and SVM | Sociodemographic, user preferences, health conditions, PA levels, bedtime, and medical records | NEM (conventional) | 4 | NEM |
| (Costa et al., 2018) [49] | PE | Workout routines | NEM. Techniques used: RNN, C2R and GRUNN | Health status, user preferences and daily activity in the workouts | NEM (conventional) | 5 | NEM |
| (Tran et al., 2018) [48] | Workout routines | NEM. Techniques used: ANN and LR | User preferences and user daily activity in the workouts | NEM (conventional) | 4 | NEM | |
| (Basnayake et al., 2021) [47] | Play some sport, bicycling, running, walking, and the intensity of the activity | Expert system using Ontology | Sociodemographic, exercise preferences, diet details, and medical records | NEM (conventional) | 5 | NEM | |
| (Chen et al., 2021) [46] | Running, hiking and indoor exercise | A four-layer neural network | Sociodemographic and rest heart rate | Conventional | 4 | NEM | |
| (Lee et al., 2007) [56] | PE and diet | Healthier diet and PE | NEM | General index based on diet and medical records | NEM (conventional) | 4 | Yes (Personalized feedback) |
| (Donciu et al., 2011) [55] | Daily diet and workout | NEM | Personal information, hobbies, nutrition preferences, sports preferences, and declared purpose | NEM (conventional) | 4 | NEM | |
| (Jamil, Qayyum et al., 2021) [53] | Diet plans and workout routines | NEM. Techniques used: NEM | Sociodemographic and PA levels using IoT | Distributed (blockchain) | 4 | NEM | |
| (Jamil, Kahng et al., 2021) [54] | Diet plans and workout routines | KBF. Techniques used: DTC, LR, SVM, and K-NN | NEM | Distributed (blockchain) | 3 | NEM | |
| (Balpande et al., 2023) [52] | Workout routines and food suggestions | NEM | Sociodemographic and BMI | NEM (conventional) | 5 | NEM | |
| (Gaikwad et al., 2023) [51] | Diet plans and home exercise routines | NEM | Sociodemographic, nutritional deficiencies, and chronic diseases | NEM (conventional) | 4 | NEM | |
| (Sadhasivam et al., 2023) [50] | Diet plans and workout routines | NEM. Techniques used: K-MC and RFC | Sociodemographic and BMI | NEM (conventional) | 4 | NEM | |
| (Mahyari and Pirolli, 2021) [57] | PE and mental health | Workout exercises and meditation | Association rules and RNN | NEM | NEM | 3 | NEM |
| (Li and Sun, 2021) [58] | Sport | Sports training items | CF. Techniques used: NEM | NEM | NEM (conventional) | 4 | NEM |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lopez-Barreiro, J.; Garcia-Soidan, J.L.; Alvarez-Sabucedo, L.; Santos-Gago, J.M. Artificial Intelligence-Powered Recommender Systems for Promoting Healthy Habits and Active Aging: A Systematic Review. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 10220. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142210220
Lopez-Barreiro J, Garcia-Soidan JL, Alvarez-Sabucedo L, Santos-Gago JM. Artificial Intelligence-Powered Recommender Systems for Promoting Healthy Habits and Active Aging: A Systematic Review. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(22):10220. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142210220
Chicago/Turabian StyleLopez-Barreiro, Juan, Jose Luis Garcia-Soidan, Luis Alvarez-Sabucedo, and Juan M. Santos-Gago. 2024. "Artificial Intelligence-Powered Recommender Systems for Promoting Healthy Habits and Active Aging: A Systematic Review" Applied Sciences 14, no. 22: 10220. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142210220
APA StyleLopez-Barreiro, J., Garcia-Soidan, J. L., Alvarez-Sabucedo, L., & Santos-Gago, J. M. (2024). Artificial Intelligence-Powered Recommender Systems for Promoting Healthy Habits and Active Aging: A Systematic Review. Applied Sciences, 14(22), 10220. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142210220








