Handwritten Signature Generation Using Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models with Auxiliary Classification Processes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
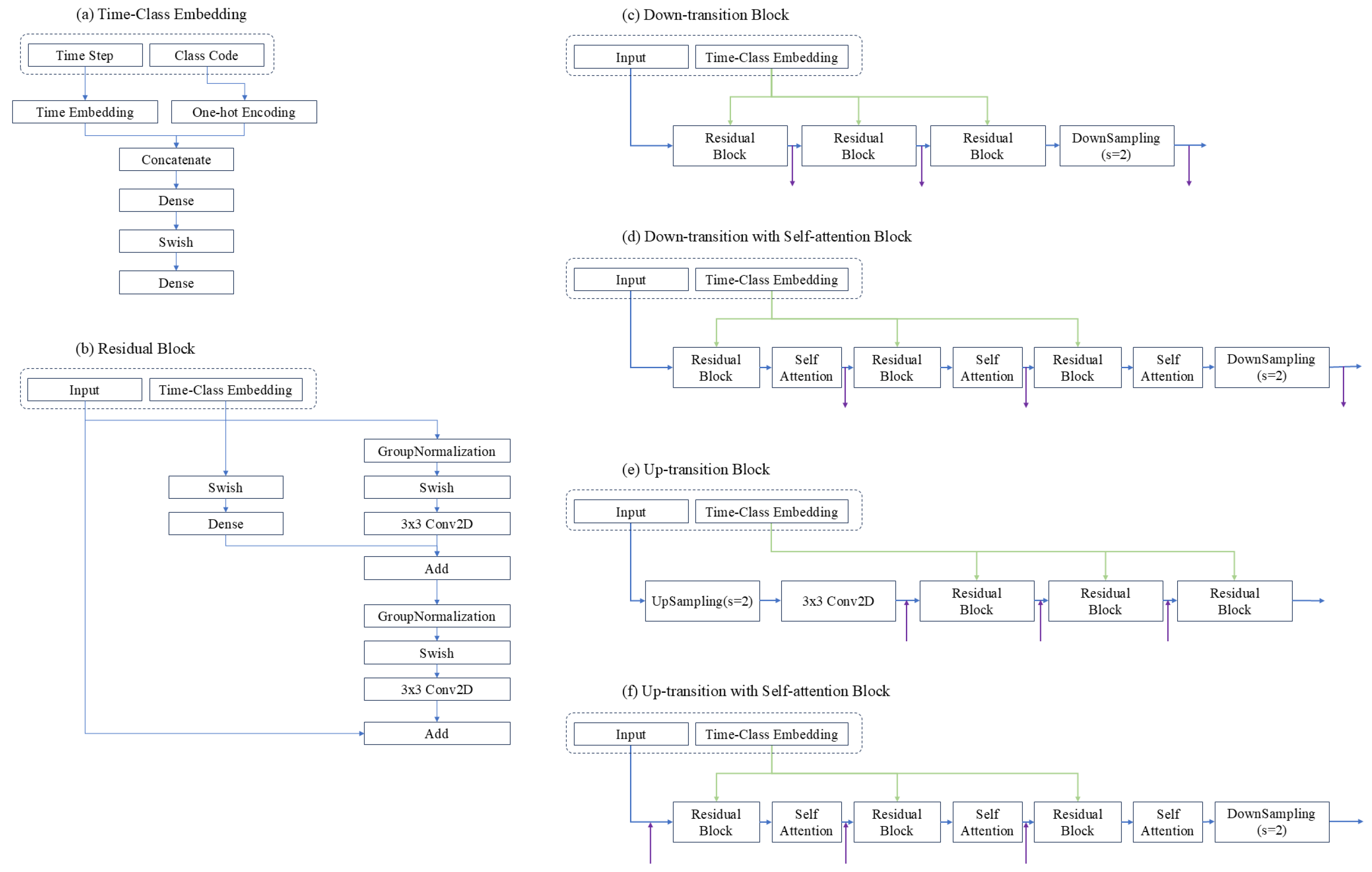
2.1. Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model
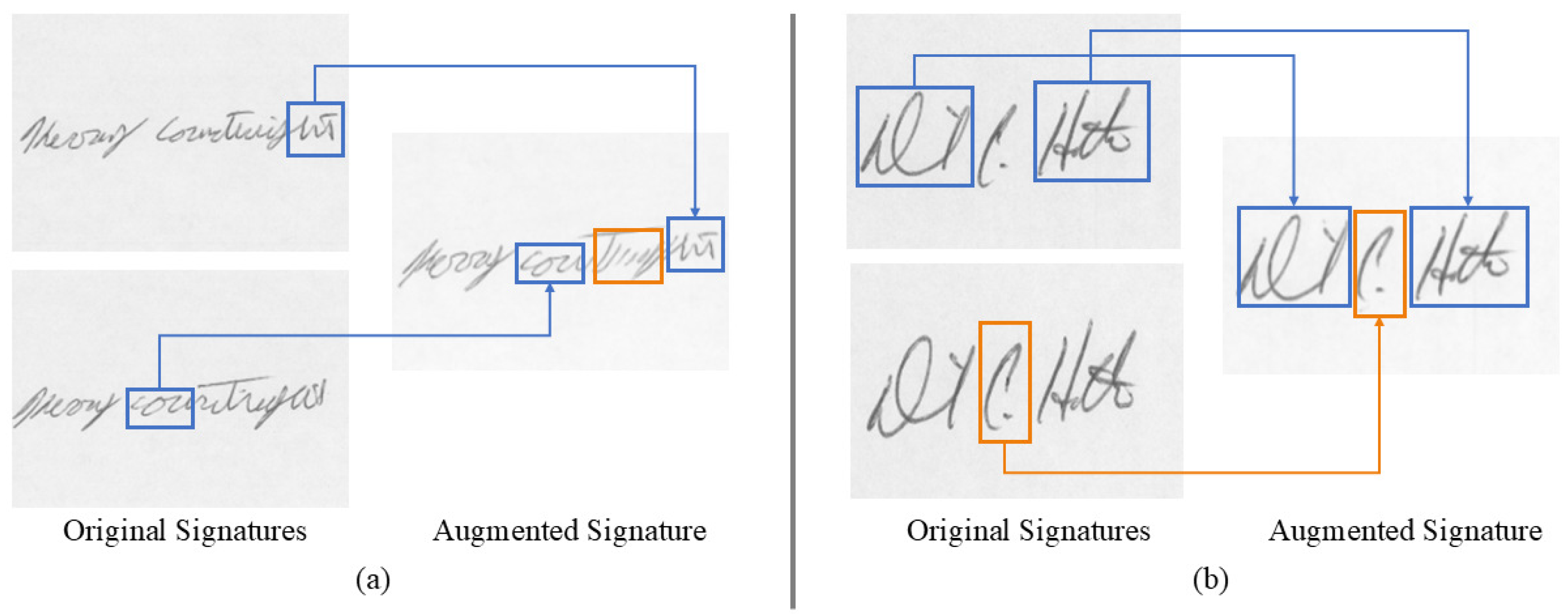
2.2. Proposed Signature Image Generation Model
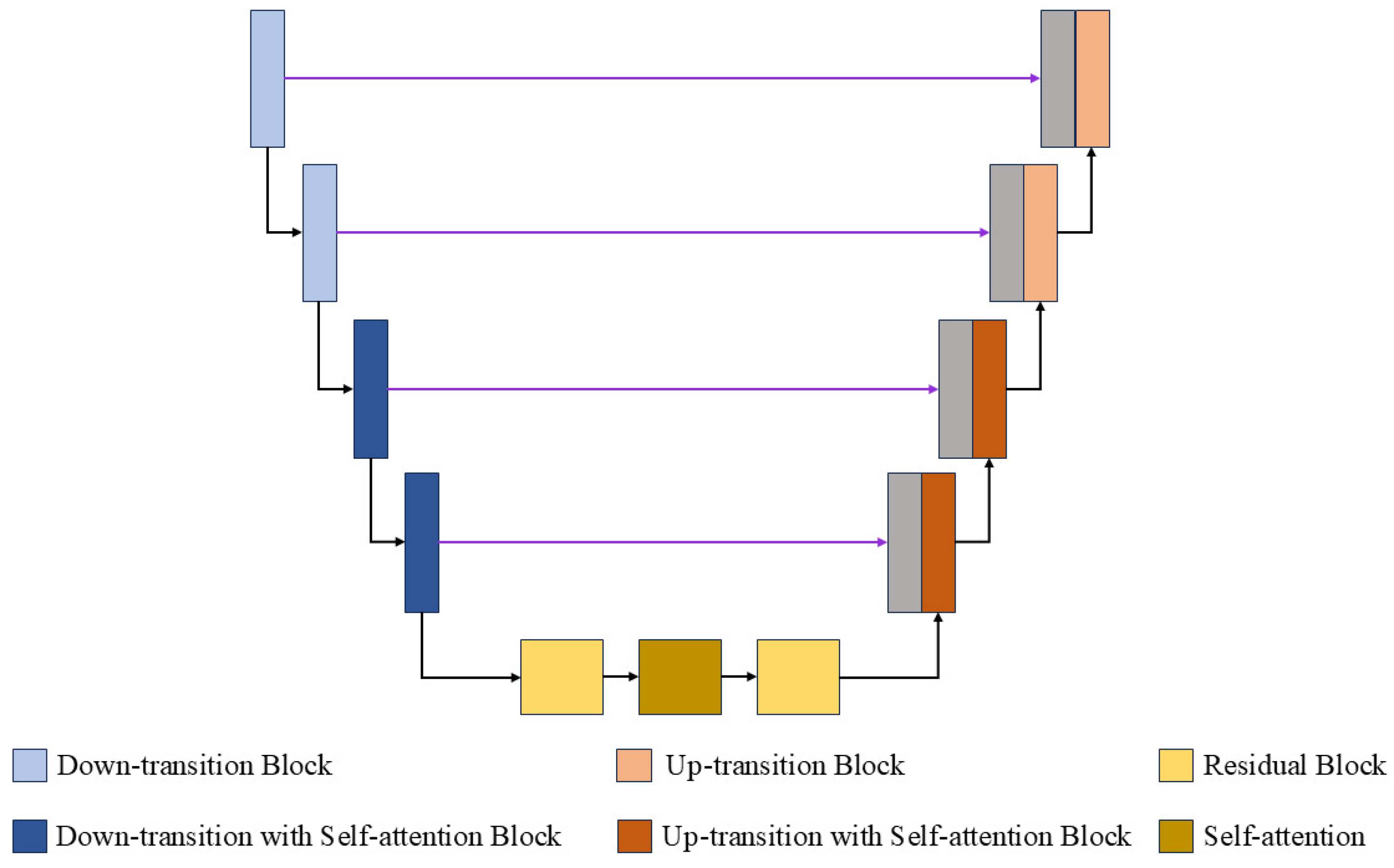
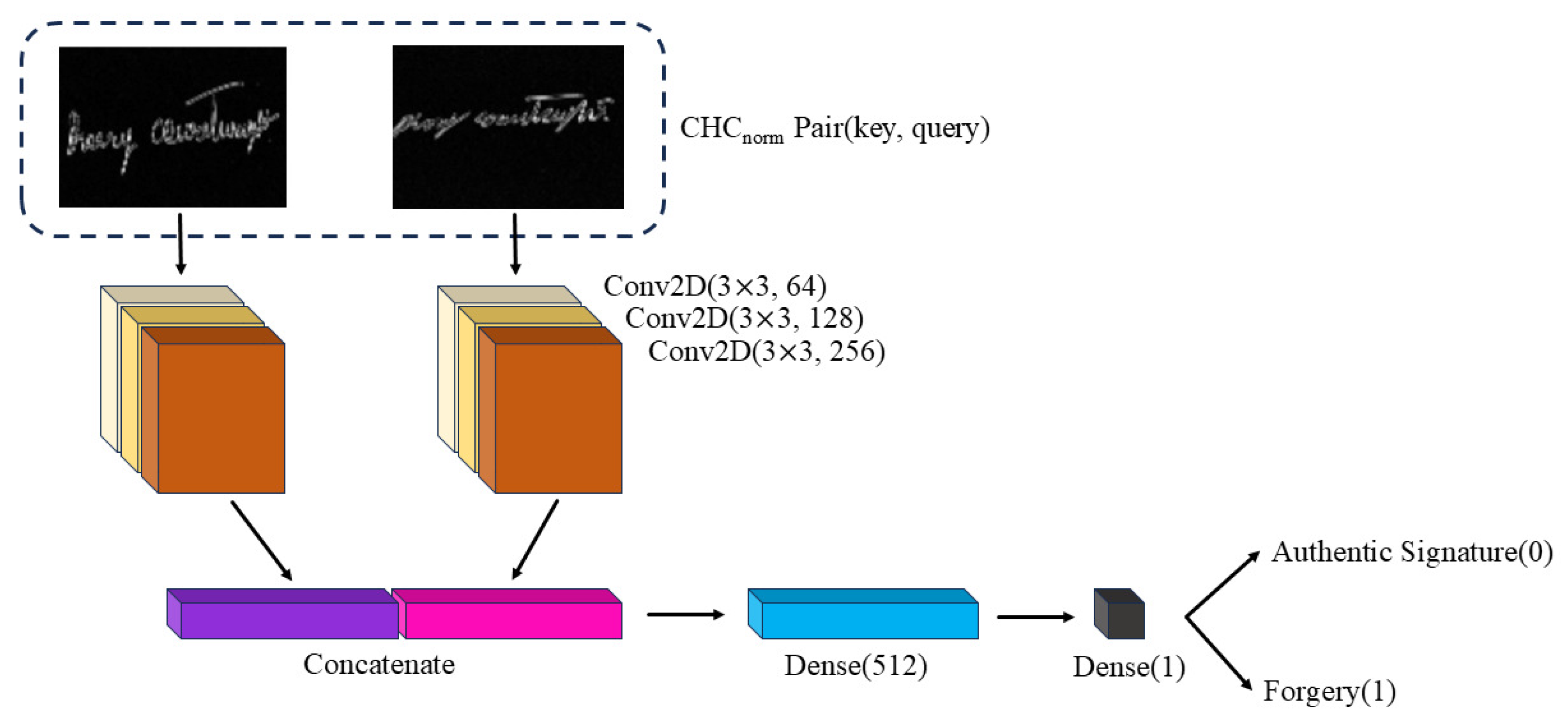
2.3. Classifier for Distinguishing Forged Signatures
3. Results
3.1. Dataset
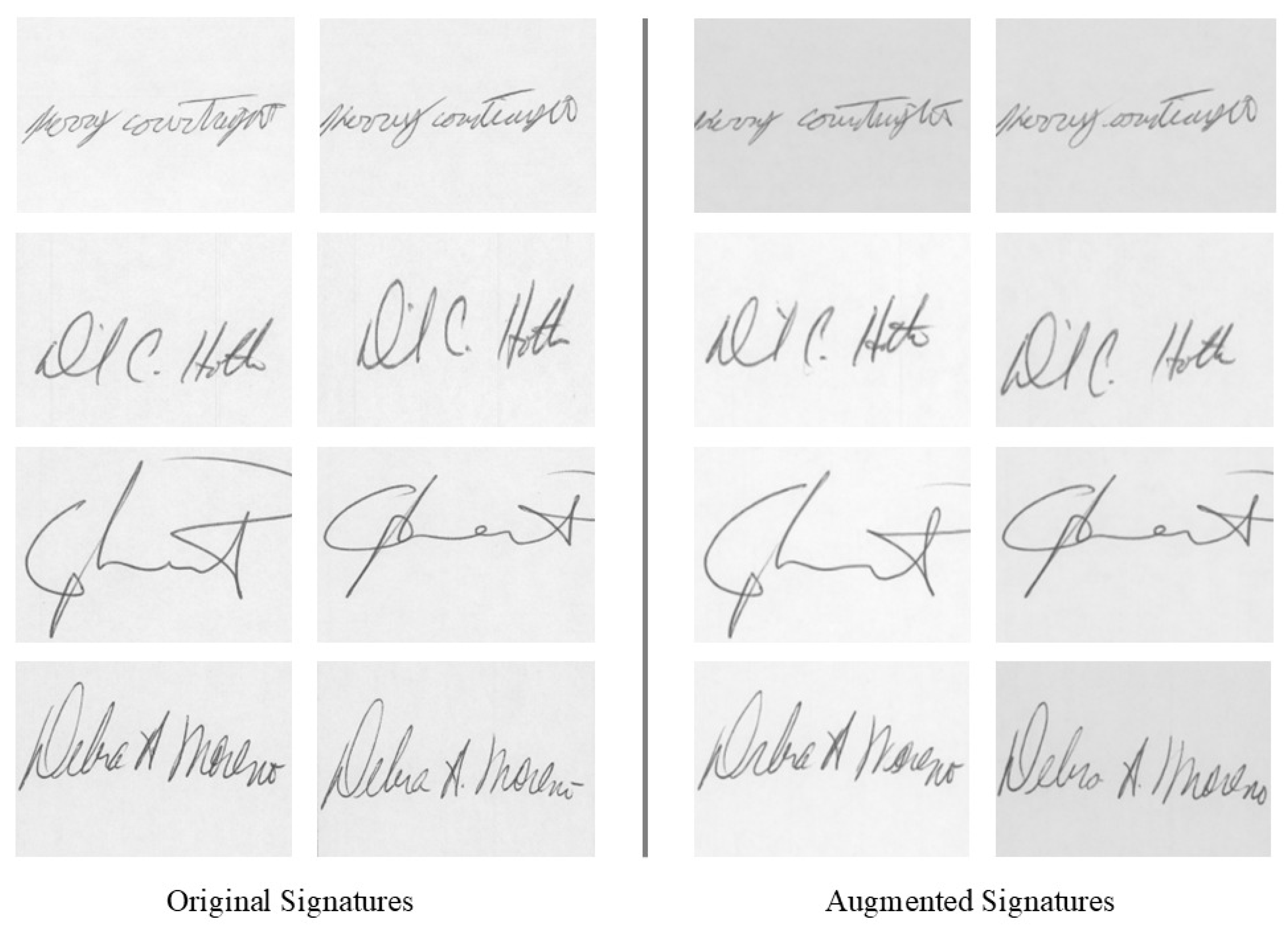
3.2. Implementation Details
3.3. Data Generation Results
3.4. Evaluation Metrics
3.5. Signature Verification Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Julian, F.; Javier, O.G.; Daniel, R.; Joaquin, G.R. HMM-based on-line signature verification: Feature extraction and signature modeling. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2007, 28, 2325–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narwade, P.N.; Sawant, R.R.; Bonde, S.V. Offline signature verification using shape correspondence. Int. J. Biom. 2018, 10, 272–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okawa, M. Synergy of foreground-background images for feature extraction: Offline signature verification using Fisher vector with fused KAZE features. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 79, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, M.; Khan, M.A.; Faisal, M.; Yasmin, M.; Fernandes, S.L. A framework for offline signature verification system: Best features selection approach. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2020, 139, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R. A Recurrent Neural Network based deep learning model for offline signature verification and recognition system. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 168, 114249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Singh, S.K.; Singh, K.P. A Handwritten signature verification using shallow convolutional neural network. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 19993–20018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Li, H.; Hu, P. Inverse Discriminative Networks for Handwritten Signature Verification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 5764–5772. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, C.; Singh, P.; Rana, P. Offline signature verification system with Gaussian mixture models (GMM). Int. J. Comput. Technol. 2013, 10, 1700–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Huang, L.; Yin, F.; Chen, Y. Offline signature verification using a region based deep metric learning network. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 118, 108009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorugunti, C.S.; Pulabaigari, V.; Gorthi, R.K.S.S.; Mukherjee, P. OSVFuseNet: Online Signature Verification by feature fusion and depth-wise separable convolution based deep learning. Neurocomputing 2020, 409, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anmol, C.; Vansh, J.; Rajas, B. SigScatNet: A Siamese + Scattering based Deep Learning Approach for Signature Forgery Detection and Similarity Assessment. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Modeling, Simulation & Intelligent Computing, Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 7–9 December 2023; pp. 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaouhar, F.; Feriel, S.; Mohamed, M.; Ridha, G.; Emil, P.; Baha, E.L. Handwritten Signature Recognition using Parallel CNNs and Transfer Learning for Forensics. In Proceedings of the 2024 10th International Conference on Control, Decision and Information Technologies (CoDIT), Vallette, Malta, 1–4 July 2024; pp. 1697–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudharshan, D.P.; Vismaya, R.N. Handwritten signature verification system using deep learning. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Data Science and Information System (ICDSIS), Hassan, India, 29–30 July 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, L.; Ping, W.; Ping, H. AVN: An Adversarial Variation Network Model for Handwritten Signature Verification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2022, 24, 594–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.; Edbert, E.; Elwirehardja, G.N.; Pardamean, B. Offline signature verification using a region based deep metric learning network. ICIC Express Lett. 2023, 17, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, Y.; Ankit; Kulkarni, S.; Jain, P. Handwritten signature verification using transfer learning and data augmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Cyber-Physical Systems, Jaipur, India, 16–18 April 2021; pp. 233–245. [Google Scholar]
- Najda, D.; Saeed, K. Impact of augmentation methods in online signature verification. Innov. Syst. Softw. Eng. 2024, 20, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, T.M.; Oliveira, L.S.; Britto, A.S.; Sabourin, R. Intrapersonal parameter optimization for offline handwritten signature augmentation. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2020, 16, 1335–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galbally, J.; Fierrez, J.; Martinez, M.; Ortega, J. Synthetic generation of handwritten signatures based on spectral analysis. In Proceedings of the Optics and Photonics in Global Homeland Security V and Biometric Technology for Human Identification VI, Orlando, FL, USA, 5 May 2009; pp. 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, N.; Nemmour, H.; Chibani, Y. A new synthetic feature generation scheme based on artificial immune systems for robust offline signature verification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 213, 119306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkata, M.M.; Vempati, K. Generation of Synthesis Handwritten Signatures Using Image Processing Techniques for Biometrics. J. Eng. Sci. 2019, 10, 946–953. [Google Scholar]
- Hameed, M.M.; Ahmad, R.; Kiah, L.M.; Murtaza, G.; Mazhar, N. OffSig-Sin GAN: A Deep Learning-Based Image Augmentation Model for Offline Signature Verification. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2023, 76, 1267–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.; Jain, A.; Abbeel, P. Denoising diffusion probabilistic models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 6840–6851. [Google Scholar]
- CEDAR Signature Database. Available online: http://www.cedar.buffalo.edu/NIJ/data/signatures.rar (accessed on 5 November 2024).
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van, D.M.L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, P.; Uszkoreit, J.; Vaswani, A. Self-attention with relative position representations. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.02155. [Google Scholar]
- Leedham, G.; Chen, Y.A.N.; Takru, K.; Tan, J.H.N.; Mian, L. Comparison of Some Thresholding Algorithms for Text/Background Segmentation in Difficult Document Images. In Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition, Edinburgh, UK, 3 August 2003; pp. 859–864. [Google Scholar]
- Sevilla, L.; Sun, D.; Jampani, V.; Black, M.J. Optical flow with semantic segmentation and localized layers. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 3889–3898. [Google Scholar]
- Shensa, M.J. The discrete wavelet transform: Wedding the a trous and Mallat algorithms. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1992, 40, 2464–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, W.; Zhao, H. Nonlinear systems modelling based on self-organizing fuzzy neural network with hierarchical pruning scheme. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 95, 106516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Hyperparameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input Image Size (H, W) | (128, 256) |
| Optimizer | Adam |
| Optimizer Learning Rate | 2 × 10−4 |
| Number of Time Steps (T) | 1000 |
| Beta Schedule | Linear |
| Beta Start | 1 × 10−4 |
| Beta End | 0.02 |
| Noise Schedule Type | Linear |
| Model | Cases | Max | Min | Avg. | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Org-Forg | Train Set | 0.9976 | 0.9749 | 0.9915 | 0.1658 |
| Org-Forg | Highest Class (46) | 0.9976 | 0.9900 | 0.9955 | 0.1427 |
| Aux | All Classes | 0.9999 | 0.8486 | 0.9806 | 0.1819 |
| Aux | Highest Class (41) | 0.9999 | 0.9899 | 0.9965 | 0.1219 |
| Non-Aux | All Classes | 0.9967 | 0.8459 | 0.9722 | 0.2059 |
| Non-Aux | Highest Class (46) | 0.9967 | 0.9839 | 0.9921 | 0.1563 |
| Model | Cases | Max | Min | Avg. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | Signatures included in Class 46 of forgery | 0.9976 | 0.9900 | 0.9955 |
| Aux | Including the auxiliary classification | 0.9980 | 0.9676 | 0.9870 |
| Non-Aux | Not including the auxiliary classification | 0.9967 | 0.9839 | 0.9921 |
| Train Set | Precision | Recall | Acc. (%) | ERR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original train data | 0.9615 | 0.9220 | 94.26 | 0.0570 |
| Included generated signatures | 0.9554 | 0.9414 | 94.87 | 0.0518 |
| Included generated signatures (not using the classifier) | 0.9308 | 0.9118 | 92.20 | 0.0749 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, D.-J.; Chang, W.-D.; Cha, E.-Y. Handwritten Signature Generation Using Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models with Auxiliary Classification Processes. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 10233. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142210233
Hong D-J, Chang W-D, Cha E-Y. Handwritten Signature Generation Using Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models with Auxiliary Classification Processes. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(22):10233. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142210233
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, Dong-Jin, Won-Du Chang, and Eui-Young Cha. 2024. "Handwritten Signature Generation Using Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models with Auxiliary Classification Processes" Applied Sciences 14, no. 22: 10233. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142210233
APA StyleHong, D.-J., Chang, W.-D., & Cha, E.-Y. (2024). Handwritten Signature Generation Using Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models with Auxiliary Classification Processes. Applied Sciences, 14(22), 10233. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142210233






