Asynchronous and Slow-Wave Oscillatory States in Connectome-Based Models of Mouse, Monkey and Human Cerebral Cortex
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
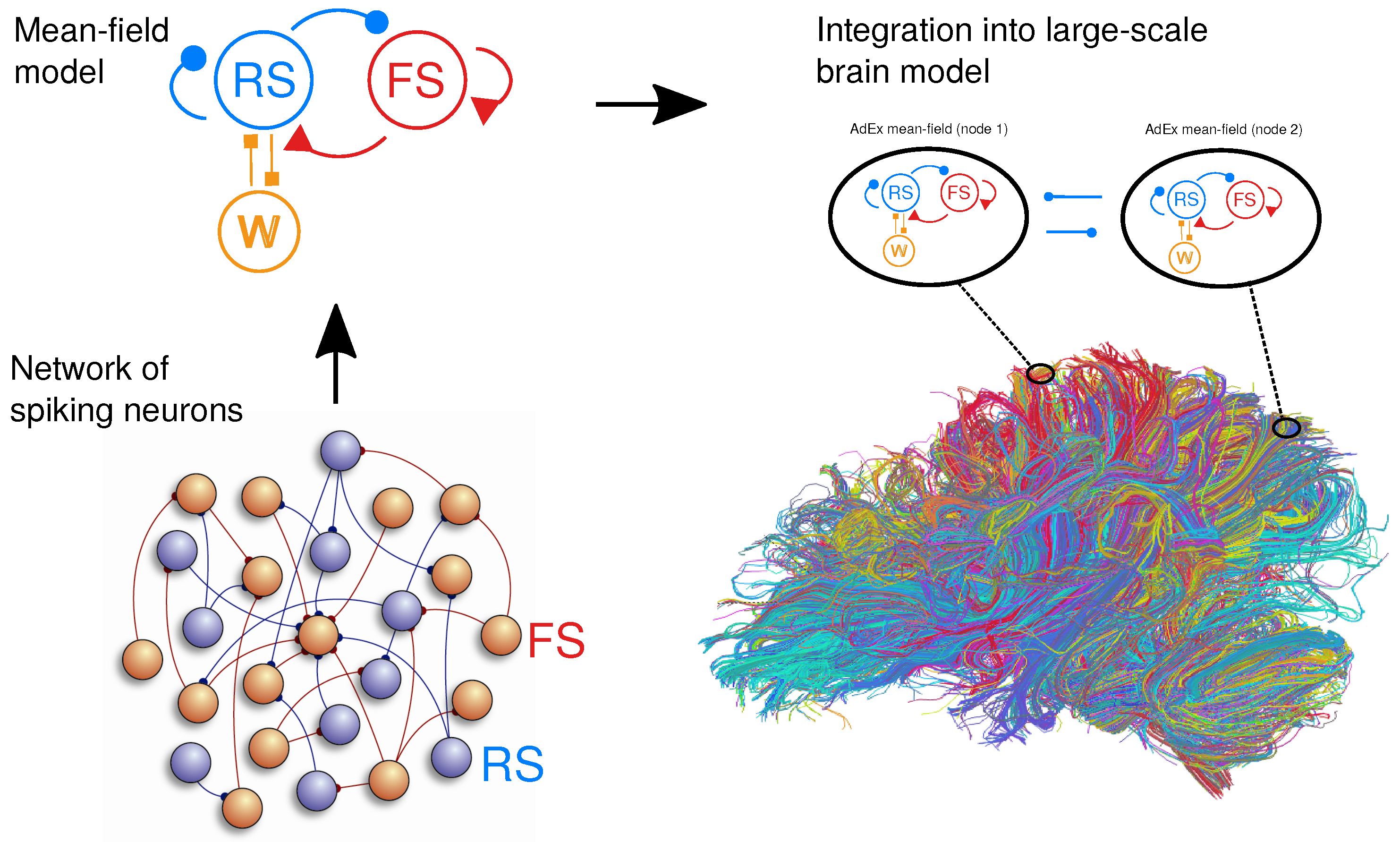
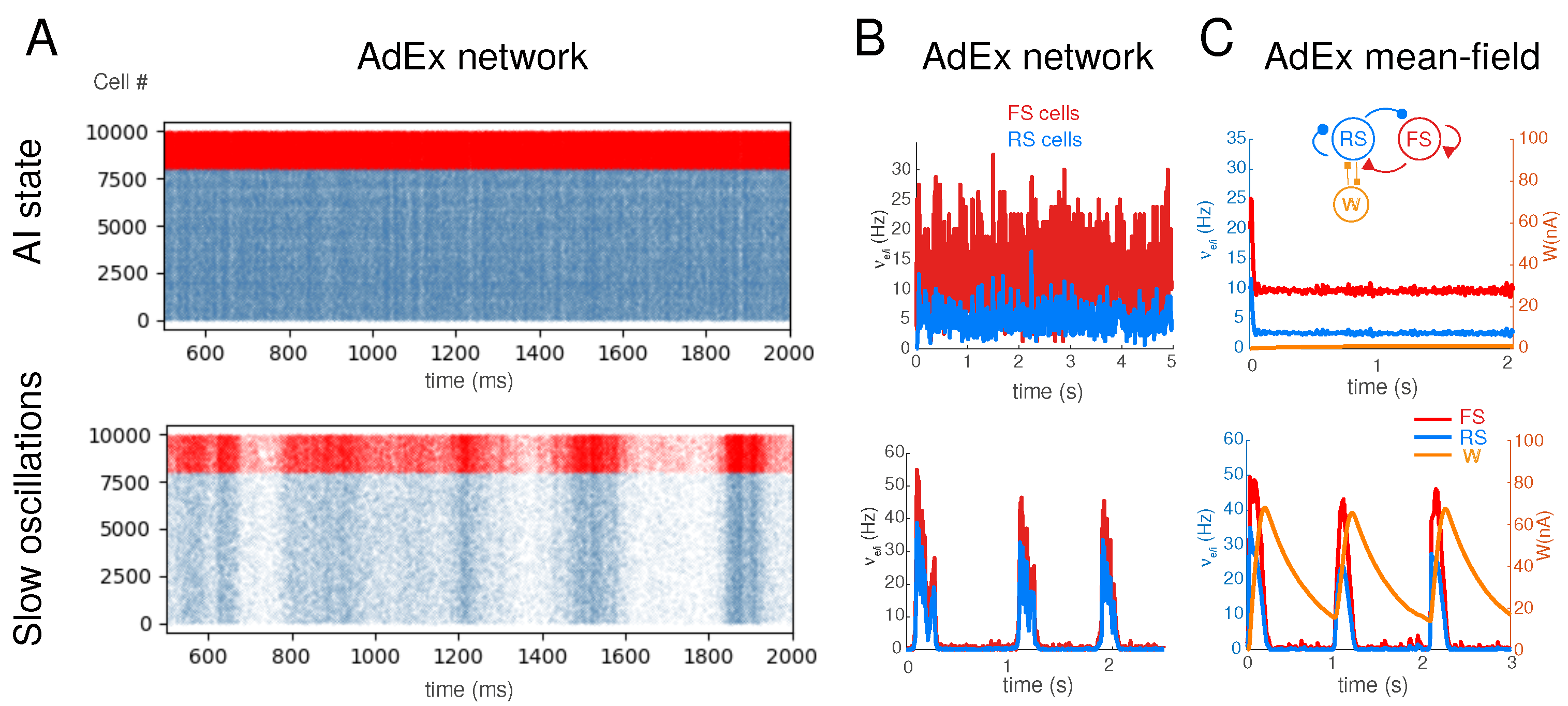
2.1. Spiking Network Model
2.2. Mean-Field Models
2.3. Networks of Mean-Field Models
2.4. Connectomes for the Three Species
2.5. Integration in The Virtual Brain
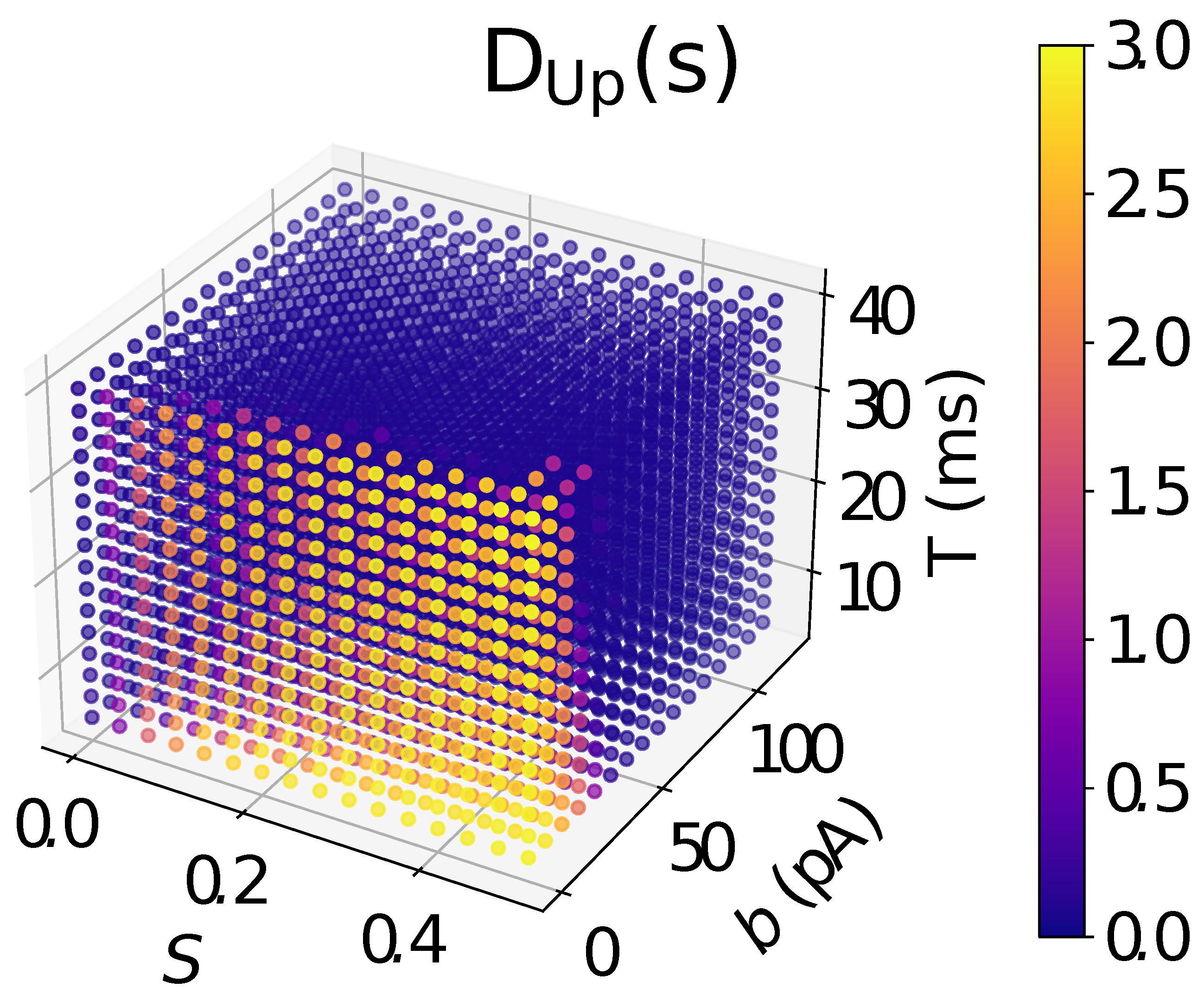
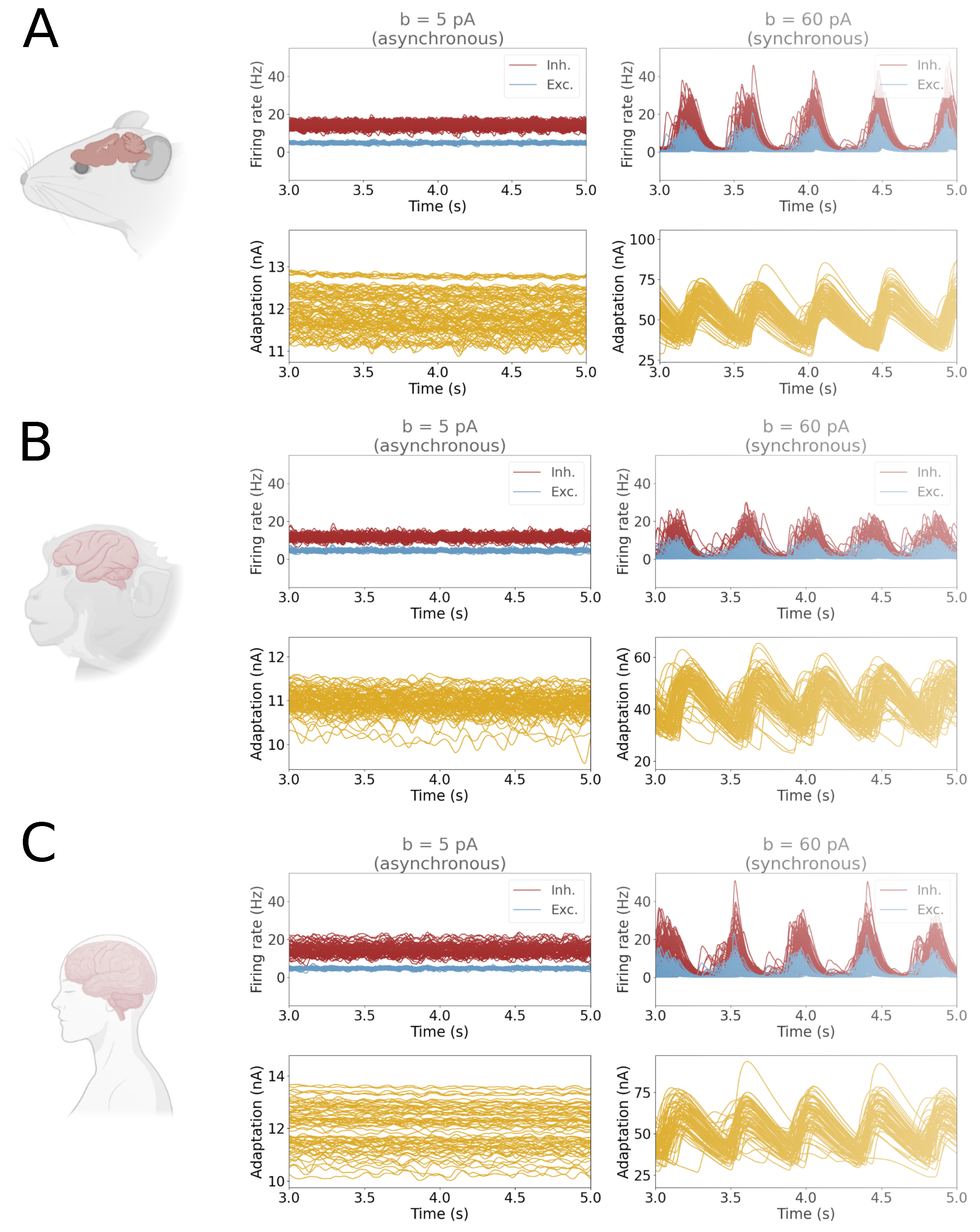
2.6. Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Steriade, M. Neuronal Substrates of Sleep and Epilepsy; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Niedermeyer, E.; Lopes da Silva, F.H. Electroencephalography: Basic Principles, Clinical Applications, and Related Fields; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Compte, A.; Sanchez-Vives, M.V.; McCormick, D.A.; Wang, X.J. Cellular and network mechanisms of slow oscillatory activity (<1 Hz) in a cortical network model. J. Neurophysiol. 2003, 89, 2707–2725. [Google Scholar]
- Van Vreeswijk, C.; Sompolinsky, H. Chaos in neuronal networks with balanced excitatory and inhibitory activity. Science 1996, 274, 1724–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunel, N. Dynamics of sparsely connected networks of excitatory and inhibitory spiking neurons. J. Comput. Neurosci. 2000, 8, 183–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerlaut, Y.; Chemla, S.; Chavane, F.; Destexhe, A. Modeling mesoscopic cortical dynamics using a mean-field model of conductance-based networks of adaptive exponential integrate-and-fire neurons. J. Comput. Neurosci. 2018, 44, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazhenov, M.; Timofeev, I.; Steriade, M.; Sejnowski, T.J. Model of thalamocortical slow-wave sleep oscillations and transitions to activated states. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 8691–8704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- di Volo, M.; Romagnoni, A.; Capone, C.; Destexhe, A. Biologically realistic mean-field models of conductance-based networks of spiking neurons with adaptation. Neural Comput. 2019, 31, 653–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Vives, M.V.; McCormick, D.A. Cellular and network mechanisms of rhythmic recurrent activity in neocortex. Nat. Neurosci. 2000, 3, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.W.; Harris, J.A.; Ng, L.; Winslow, B.; Cain, N.; Mihalas, S.; Wang, Q.; Lau, C.; Kuan, L.; Henry, A.M.; et al. A mesoscale connectome of the mouse brain. Nature 2014, 508, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kötter, R. Online retrieval, processing, and visualization of primate connectivity data from the CoCoMac database. Neuroinformatics 2004, 2, 127144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Essen, D.C.; Ugurbil, K.; Auerbach, E.; Barch, D.; Behrens, T.E.; Bucholz, R.; Chang, A.; Chen, L.; Corbetta, M.; Curtiss, S.W.; et al. The Human Connectome Project: A data acquisition perspective. Neuroimage 2012, 62, 2222–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, J.S.; Kusch, L.; Yalçinkaya, B.H.; Depannemaecker, D.; Nghiem, T.A.E.; Jirsa, V.; Destexhe, A. Brain-scale emergence of slow-wave synchrony and highly responsive asynchronous states based on biologically realistic population models simulated in The Virtual Brain. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, J.S.; Kusch, L.; Llorens, D.A.; Yalçinkaya, B.H.; Depannemaecker, D.; Ancourt, K.; Nghiem, T.A.E.; Jirsa, V.; Destexhe, A. A comprehensive neural simulation of slow-wave sleep and highly responsive wakefulness dynamics. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1058957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cakan, C.; Dimulescu, C.; Khakimova, L.; Obst, D.; el, A.; Obermayer, K. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Adaptation-Induced Slow Oscillations in a Whole-Brain Model of Slow-Wave Sleep. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 800101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destexhe, A. Self-sustained asynchronous irregular states and up–down states in thalamic, cortical and thalamocortical networks of nonlinear integrate-and-fire neurons. J. Comput. Neurosci. 2009, 27, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brette, R.; Gerstner, W. Adaptive exponential integrate-and-fire model as an effective description of neuronal activity. J. Neurophysiol. 2005, 94, 3637–3642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Boustani, S.; Destexhe, A. A master equation formalism for macroscopic modeling of asynchronous irregular activity states. Neural Comput. 2009, 21, 46–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, H.R.; Cowan, J.D. Excitatory and inhibitory interactions in localized populations of model neurons. Biophys. J. 1972, 12, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormick, D.A. Neurotransmitter actions in the thalamus and cerebral cortex and their role in neuromodulation of thalamocortical activity. Prog. Neurobiol. 1992, 39, 337–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melozzi, F.; Woodman, M.M.; Jirsa, V.K.; Bernard, C. The Virtual Mouse Brain: A computational neuroinformatics platform to study whole mouse brain dynamics. eNeuro 2017, 4, 0111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, K.; Bezgin, G.; Schirner, M.; Ritter, P.; Everling, S.; McIntosh, A.R. A macaque connectome for large-scale network simulations in TheVirtualBrain. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirner, M.; Rothmeier, S.; Jirsa, V.K.; McIntosh, A.R.; Ritter, P. An automated pipeline for constructing personalized virtual brains from multimodal neuroimaging data. NeuroImage 2015, 117, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jirsa, V.K.; Proix, T.; Perdikis, D.; Woodman, M.M.; Wang, H.; Gonzalez-Martinez, J.; Bernard, C.; Bénar, C.; Guye, M.; Chauvel, P.; et al. The virtual epileptic patient: Individualized whole-brain models of epilepsy spread. Neuroimage 2017, 145, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva Pereira, S.; Hindriks, R.; Mühlberg, S.; Maris, E.; van Ede, F.; Griffa, A.; Hagmann, P.; Deco, G. Effect of Field Spread on Resting-State Magneto Encephalography Functional Network Analysis: A Computational Modeling Study. Brain Connect. 2017, 7, 541–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, P.; Schirner, M.; McIntosh, A.R.; Jirsa, V.K. The virtual brain integrates computational modelling and multimodal neuroimaging. Brain Connect. 2013, 3, 121–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aquilué-Llorens, D.; Goldman, J.; Destexhe, A. High-density exploration of activity states in a multi-area brain model. NeuroInformatics, 2023, in press. [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, N.; Peyrache, A.; Telenczuk, B.; Le Van Quyen, M.; Halgren, E.; Cash, S.S.; Hatsopoulos, N.G.; Destexhe, A. Dynamic balance of excitation and inhibition in human and monkey neocortex. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyrache, A.; Dehghani, N.; Eskandar, E.N.; Madsen, J.R.; Anderson, W.S.; Donoghue, J.A.; Hochberg, L.R.; Halgren, E.; Cash, S.S.; Destexhe, A. Spatiotemporal dynamics of neocortical excitation and inhibition during human sleep. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1731–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, S.P.; Cui, N.; McKillop, L.E.; Gemignani, J.; Bannerman, D.M.; Oliver, P.L.; Peirson, S.N.; Vyazovskiy, V.V. Stereotypic wheel running decreases cortical activity in mice. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destexhe, A.; Contreras, D.; Steriade, M. Spatiotemporal analysis of local field potentials and unit discharges in cat cerebral cortex during natural wake and sleep states. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 4595–4608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destexhe, A.; Sacha, M.; Kusch, L.; Goldman, J. Python code to simulate mouse, monkey and human brains. Zenodo 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzi, R.M.; Geminiani, A.; Zerlaut, Y.; Destexhe, A.; Gandini Wheeler-Kingshott, C.A.; Palesi, F.; Casellato, C.; D’Angelo, E. A multi-layer mean-field model for the cerebellar cortex: Design, validation, and prediction. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2023, 19, e1011434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overwiening, J.; Tesler, F.; Guarino, D.; Destexhe, A. A multi-scale study of thalamic state-dependent responsiveness. bioRxiv 2023, 567941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter Name | Symbol | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cellular Properties | |||
| Leak conductance | 10 | nS | |
| Leak reversal potential | −65 | mV | |
| Membrane capacitance | 200 | pF | |
| Resting voltage | −65 | mV | |
| Action Potential threshold | −50 | mV | |
| Refractory period | 5 | ms | |
| Adaptation time constant | 500 | ms | |
| Excitatory Neuron | |||
| Spike sharpness | 2 | mV | |
| Adaptation current increment | varies | pA | |
| Adaptation conductance | 4 | nS | |
| Inhibitory Neuron | |||
| Spike sharpness | 0.5 | mV | |
| Adaptation current increment | 0 | pA | |
| Adaptation conductance | 0 | ns | |
| Synaptic Properties | |||
| Excitatory Neuron | |||
| Reversal potential | 0 | mV | |
| Quantal conductance | 1 | nS | |
| Decay time of synaptic conductance | 5 | ms | |
| Inhibitory Neuron | |||
| Reversal potential | −80 | mV | |
| Quantal conductance | 5 | nS | |
| Decay time of synaptic conductance | 5 | ms | |
| Network Properties | |||
| Total network size | N | 10,000 | |
| Connectivity probability | p | 0.05 | |
| Fraction of inhibitory cells | 0.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sacha, M.; Goldman, J.S.; Kusch, L.; Destexhe, A. Asynchronous and Slow-Wave Oscillatory States in Connectome-Based Models of Mouse, Monkey and Human Cerebral Cortex. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14031063
Sacha M, Goldman JS, Kusch L, Destexhe A. Asynchronous and Slow-Wave Oscillatory States in Connectome-Based Models of Mouse, Monkey and Human Cerebral Cortex. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(3):1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14031063
Chicago/Turabian StyleSacha, Maria, Jennifer S. Goldman, Lionel Kusch, and Alain Destexhe. 2024. "Asynchronous and Slow-Wave Oscillatory States in Connectome-Based Models of Mouse, Monkey and Human Cerebral Cortex" Applied Sciences 14, no. 3: 1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14031063
APA StyleSacha, M., Goldman, J. S., Kusch, L., & Destexhe, A. (2024). Asynchronous and Slow-Wave Oscillatory States in Connectome-Based Models of Mouse, Monkey and Human Cerebral Cortex. Applied Sciences, 14(3), 1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14031063






