Applications of Nanomaterials in RFID Wireless Sensor Components
Abstract
:1. Introduction
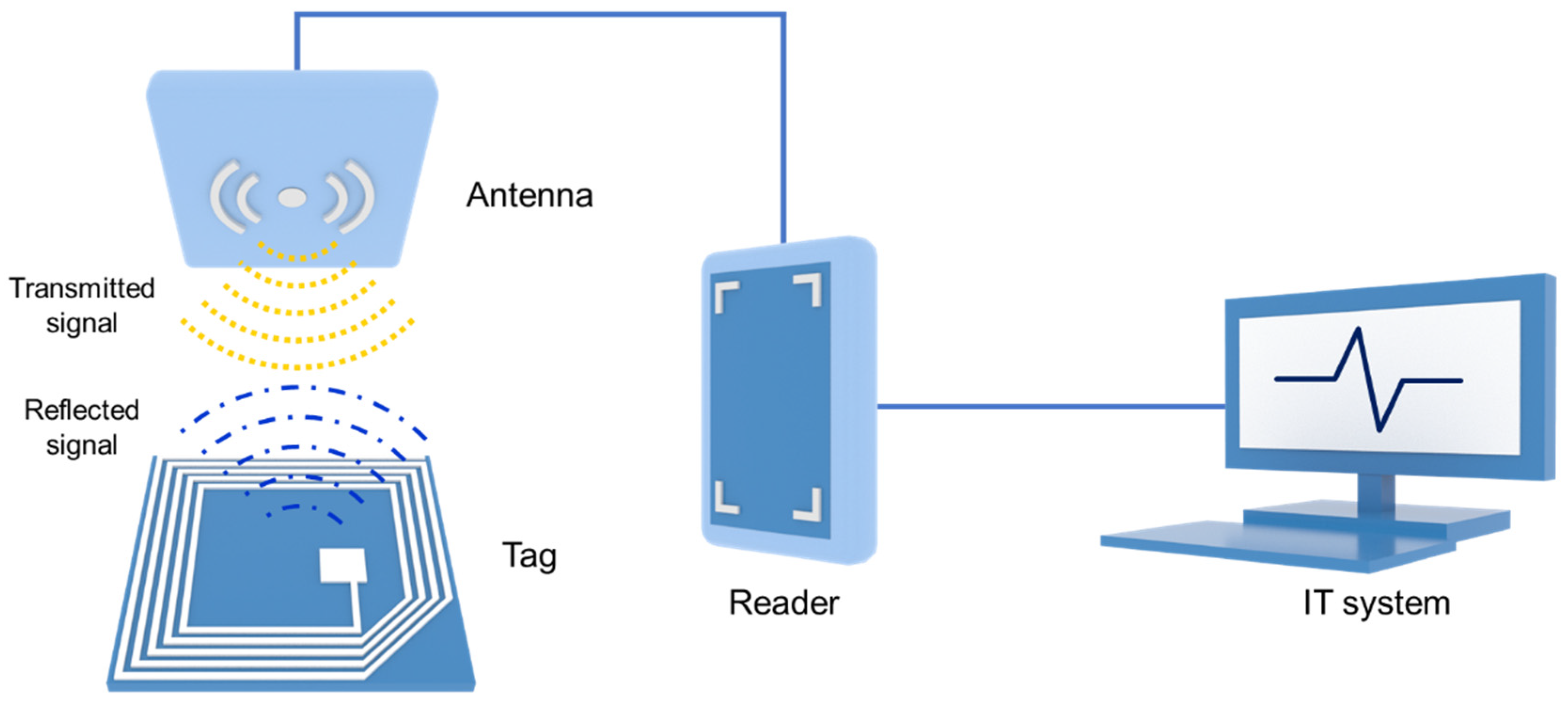
2. RFID System
3. RFID Sensor Technology
4. Nanomaterials for RFID-Based Sensing System
4.1. Polymer
4.2. Metal Nanoparticles
4.3. Carbon Nanostructures
4.4. Others
5. Applications
5.1. Gas Sensing
5.2. Environmental Monitoring
5.3. Healthcare
5.4. Food Fresh Management
5.5. Agriculture
5.6. Others
6. Summary and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nadeem, I.; Alibakhshikenari, M.; Babaeian, F.; Althuwayb, A.A.; Virdee, B.S.; Azpilicueta, L.; Khan, S.; Huynen, I.; Falcone, F.; Denidni, T.A. A comprehensive survey on ‘circular polarized antennas’ for existing and emerging wireless communication technologies. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2022, 55, 033002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanh, Q.V.; Hoai, N.V.; Manh, L.D.; Le, A.N.; Jeon, G. Wireless communication technologies for IoT in 5G: Vision, applications, and challenges. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2022, 2022, 3229294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyato, D.; Kim, D.I.; Maso, M.; Han, Z. Wireless powered communication networks: Research directions and technological approaches. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2017, 24, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Yan, F.; Liu, X. Study of wireless communication technologies on internet of things for precision agriculture. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2019, 108, 1785–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattanik, S.K.; Samal, S.R.; Bandopadhaya, S.; Swain, K.; Choudhury, S.; Das, J.K.; Mihovska, A.; Poulkov, V. Future wireless communication technology towards 6G IoT: An application-based analysis of IoT in real-time location monitoring of employees inside underground mines by using BLE. Sensors 2022, 22, 3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landaluce, H.; Arjona, L.; Perallos, A.; Falcone, F.; Angulo, I.; Muralter, F. A review of IoT sensing applications and challenges using RFID and wireless sensor networks. Sensors 2020, 20, 2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Shen, W.; Wang, X. Applications of wireless sensor networks in marine environment monitoring: A survey. Sensors 2014, 14, 16932–16954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buratti, C.; Conti, A.; Dardari, D.; Verdone, R. An overview on wireless sensor networks technology and evolution. Sensors 2009, 9, 6869–6896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corke, P.; Wark, T.; Jurdak, R.; Hu, W.; Valencia, P.; Darren, M. Environmental wireless sensor networks. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 1903–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeramani, S.; Mahammad, S.N. An approach to place sink node in a wireless sensor network (WSN). Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2019, 111, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainetti, L.; Palano, L.; Patraono, M.; Stefanizzi, M.L.; Vergallo, R. Integration of RFID and WSN technologies in a Smart Parking System. In Proceedings of the 2014 22nd International Conference on Software, Telecommunications and Computer Networks (SoftCOM), Split, Croatia, 17–19 September 2014; pp. 104–110. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, R.Y.; Dai, Q.Y.; Qu, T.; Hu, G.J.; Huang, G.Q. RFID-enabled real-time manufacturing execution system for mass-customization production. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2013, 29, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irani, Z.; Gunasekaran, A.; Dwivedi, Y.K. Radio frequency identification (RFID): Research trends and framework. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2010, 48, 2485–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, N.; Meng, Z.; Li, Z. Radio frequency identification and sensing techniques and their applications—A review of the state-of-the-art. Sensors 2019, 19, 4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Yu, S.; Wu, K.; Ni, Q.; Janecek, C.; Nordstad, J. Radio frequency identification: Technologies, applications, and research issues. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2007, 7, 457–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, E.; Adán, A.; Cerrada, C. Evolution of RFID applications in construction: A literature review. Sensors 2015, 15, 15988–16008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.C.; Chen, C.; Huang, P.B. Supply chain management with lean production and RFID application: A case study. Expert Syst. Appl. 2013, 40, 3389–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domdouzis, K.; Kumar, B.; Anumba, C. Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) applications: A brief introduction. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2007, 21, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.C.; Cheng, C.H.; Huang, P.B.; Wang, K.J.; Huang, C.J.; Ting, T.C. Warehouse management with lean and RFID application: A case study. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 69, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Garcia, L.; Lunadei, L. The role of RFID in agriculture: Applications, limitations and challenges. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2011, 79, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Yin, Y.; Vasilakos, A.V.; Lu, S. Managing RFID data: Challenges, opportunities and solutions. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2014, 16, 1294–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadi, S. Applications and opportunities for radio frequency identification (RFID) technology in intelligent transportation systems: A case study. Int. J. Inf. Eng. Electron. Bus. 2013, 3, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakita, Y.; Nakamura, O.; Uo, Y.; Murai, J. Use of RFID at large-scale events. IATSS Res. 2005, 29, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Sunny, A.L.; Zhang, G.; Tian, G. Feature extraction for robust crack monitoring using passive wireless RFID antenna sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 6273–6280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Pu, L.; Wang, G.; Zhan, Y. RF Energy Harvesting Wireless Communications: RF Environment, Device Hardware and Practical Issues. Sensors 2019, 19, 3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, D.S.; Ram, G.; Kumar, G.A. Time-modulated multi-tone antenna array for wireless information and power transfer. Int. J. Commun. 2022, 36, e5419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Ren, P.; Song, R.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Q.; Dong, J.; O’Connor, B.T.; Zhu, Y. Nanomaterial-enabled flexible and stretchable sensing systems: Processing, integration, and applications. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1902343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhan, X.; Song, X.; Si, S.; Chen, R.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; He, J.; Xiao, X. A review of recent applications of ion beam techniques on nanomaterial surface modification: Design of nanostructures and energy harvesting. Small 2019, 31, 1901820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moinudeen, G.K.; Ahmad, F.; Kumar, D.; Al-Douri, Y.; Ahamd, S. IoT applications in future foreseen guided by engineered nanomaterials and printed intelligence technologies a technology review. IEEE Internet Things J. 2017, 6, 106–148. [Google Scholar]
- Choy, K.L.; Ho, G.T.S.; Lee, C.K.H. A RFID-based storage assignment system for enhancing the efficiency of order picking. J. Intell. Manuf. 2014, 28, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, V.; Frechet, J.M.M.; Chang, P.C.; Huang, D.C.; Lee, J.B.; Molesa, S.E.; Redinger, D.R.; Volkman, S.K. Progress toward development of all-printed RFID tags: Materials, processes, and devices. Proc. IEEE 2005, 93, 1330–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saarinen, K.; Björninen, T.; Ukkonen, L.; Frisk, L. Reliability analysis of RFID tags in changing humid environment. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 4, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potyrailo, R.A.; Nagraj, N.; Tang, Z.; Mondello, F.J.; Surman, C.; Morris, W. Battery-free radio frequency identification (RFID) sensors for food quality and safety. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 8535–8543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potyrailo, R.A.; Morris, W.G.; Sivavec, T.; Tomlinson, H.W.; Klensmeden, S.; Lindh, K. RFID sensors based on ubiquitous passive 13.56-MHz RFID tags and complex impedance detection. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2008, 9, 1318–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, K.M.; Andandarajah, P.; Colline, D. Current progress towards the integration of thermocouple and chipless RFID technologies and the sensing of a dynamic stimulus. Micromachines 2020, 11, 1019. [Google Scholar]
- Baumbauer, C.L.; Anderson, M.G.; Ting, J.; Sreekumar, A.; Rabaey, J.M.; Arias, A.C.; Thielens, A. Printed, flexible, compact UHF-RFID sensor tags enabled by hybrid electronics. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Cheng, X.; Guo, Z.; Sun, Q.; Wang, J.; Wang, C. Design, fabrication and applications of flexible RFID antennas based on printed electronic materials and technologies. J. Mater. Chem. C 2023, 11, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhan, C.; Li, H.; Yu, H.; Zhang, J.; Qiu, H.; Liang, J.; Wu, J.; Su, M.; Shi, Y.; et al. Wearable near-field communication sensors for healthcare: Materials, fabrication and application. Micromachines 2022, 13, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Romaguera, V.; Wünscher, S.; Turki, B.M.; Abbel, R.; Barbosa, S.; Tate, D.J.; Oyeka, D.; Batchelor, J.C.; Parker, E.A.; Schubert, U.S.; et al. Inkjet printed paper based frequency selective surfaces and skin mounted RFID tags: The interrelation between silver nanoparticle ink, paper substrate and low temperature sintering technique. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 2132–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarycheva, A.; Polemi, A.; Liu, Y.; Dandekar, K.; Anasori, B.; Gogotsi, Y. 2D titanium carbide (MXene) for wireless communication. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaau0920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, B.; Reynolds, F.; Want, R. RFID technology and applications. IEEE Pervasive Comput. 2006, 5, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzalli, M.S.; Mahdi, M.A.; Ismail, A.; Shafie, S.M.; Adam, H. Design and development of wireless communication transceiver to support RFID reader at UHF band. J. Electromagn. Waves Appl. 2010, 24, 14–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baballe, M.A.; Nababa, F.A. A Comparative Study on Radio Frequency Identification System and Its Various Applications. Int. J. Adv. Appl. Sci. 2021, 10, 392–398. [Google Scholar]
- Kabachinski, J. An Introduction to RFID. Biomed. Instrum. Technol. 2005, 39, 131–134. [Google Scholar]
- Herrojo, C.; Paredes, F.; Mata-Contreras, J.; Martin, F. Chipless-RFID: A review and recent developments. Sensors 2019, 19, 3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preradovic, S.; Chander, N.; Balbin, I. RFID transponders. IEEE Microw. Mag. 2008, 9, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, G.R.T.; Gardiner, G.; Prabhakar, G.P.; Razak, A.A. A comparison of barcoding and RFID technologies in practice. J. Inf. Technol. 2007, 2, 119–132. [Google Scholar]
- Alamin, M.; Tian, G.Y.; Andrews, A.; Jackson, P. Corrosion detection using low-frequency RFID technology. Insight 2012, 54, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, A.; Qing, X.M.; Chen, Z.N. High frequency RFID smart table antenna. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2007, 49, 2074–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, B.; Kashif, M.; Amin, Y.; Tenhunen, H. Low-profile magnetically coupled dual resonance patch antenna for UHF RFID applications. Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2021, 133, 153672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Smith, J.R.; Philipose, M.; Roy, S.; Sundara-Rajan, K.; Mamishev, A.V. Energy Scavenging for Inductively Coupled Passive RFID Systems. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2007, 56, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, A.; Bolic, M.; Yagoub, M. Magnetic-field coupling characteristics of ferrite-coil antennas for low-frequency RFID applications. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2010, 7, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, P.; Bolic, M.; Yagoub, M.; Stewart, R. RFID technology for tracking and tracing explosives and detonators in mining services applications. J. Appl. Geophys. 2012, 76, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Li, Z. RFID tag as a sensor-a review on the innovative designs and applications. Meas. Sci. Rev. 2016, 6, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Roh, S.; Lin, W.; Jung, Y.; Cho, Y. Investigation of the signal reach performance of the ultra-high-frequency identification tag for underground utility management. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, G.; Tian, G.; Liu, H. Underground passive LF RFID localization method based on magnetic field model of reader coil antenna. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 73, 8000410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching, S.; Tai, A. HF RFID versus UHF RFID-technology for library service transformation at city university of hong kong. J. Acad. Librariansh. 2009, 35, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barge, P.; Merlino, G.; Tortia, C. Radio frequency identification technologies for livestock management and meat supply chain traceability. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 93, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad, E.; Palacio, F.; Nuin, M.; Zarate, G.; Juarros, A.; Gomez, J.; Marco, S. RFID smart tag for traceability and cold chain monitoring of foods: Demonstration in an intercontinental fresh fish logistic chain. J. Food Eng. 2009, 93, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Sandhu, M.; Mohan, N.; Sandhu, P.S. RFID technology principles, advantages, limitations & its applications. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2011, 3, 1793–8163. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, G.; Aflaki, P.; Lang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Tao, T.; Py, C.; Lu, P.; Martin, C. Printed UHF RFID reader antennas for potential retail applications. IEEE J. Radio Freq. Identif. 2018, 2, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanaro, T.; Sergi, I.; Motroni, A.; Buffi, A.; Nepa, P.; Pirozzi, M.; Catarinucci, L.; Colella, R.; Chietera, F.P.; Patrono, L. An IoT-aware smart system exploiting the electromagnetic behavior of UHF-RFID tags to improve worker safety in outdoor environments. Electronics 2022, 11, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tentzeris, M. Applications of fast-moving RFID tags in high-speed railway systems. Int. J. Eng. Bus. Manag. 2011, 3, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, J.; Oh, J.; Shin, D.H.; Kim, S.G.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, W.; Jang, J. Wireless, room temperature volatile organic compound sensor based on Polypyrrole nanoparticle immobilized ultrahigh frequency radio frequency identification tag. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 33139–33147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Oh, J.; Jun, J.; Jang, J. Wireless hydrogen smart sensor based on Pt/Graphene-immobilized radio-frequency identification tag. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 7783–7790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babar, A.A.; Bjornien, T.; Bhagavati, V.A.; Sydanheimo, L.; Kalio, P.; Ukkonen, L. Small and flexible metal mountable passive UHF RFID tag on high-dielectric polymer-ceramic composite substrate. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2012, 11, 1319–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.K.; Hsu, J.; Hung, Y. Analysis and design of an UHF RFID metal tag using magnetic composite material as substrate. Prog. Electromagn. Res. B 2010, 24, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björninen, T.; Babar, A.A.; Elsherbeni, A.; Ukkonen, L. Compact metal mountable UHF RFID tag on a barium titanate based substrate. Prog. Electromagn. Res. C 2012, 26, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, P.A.; Fernandes, D.F.; Silva, A.F.; Marque, D.G.; de Almeida, A.T.; Majidi, C.; Tavakoli, M. Bi-phasic Ag–In–Ga-embedded elastomer inks for digitally printed, ultra-stretchable, multi-layer electronics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 14552–14561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedjini, S.; Kakrmakar, N.; Perret, E.; Vena, A.; Koswatta, R.; E-Azim, R. Hold the Chips: Chipless Technology, an Alternative Technique for RFID. IEEE Microw. Mag. 2013, 14, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, F.; Genovesi, S.; Borgese, M.; Michel, A.; Dicandia, F.A.; Manara, G. A review of RFID sensors, the new frontier of internet of things. Sensors 2021, 21, 3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulloni, V.; Donelli, M. Chipless RFID sensors for the internet of things: Challenges and opportunities. Sensors 2020, 20, 2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vena, A.; Perret, E.; Tedjini, S. Chipless RFID tag using hybrid coding Technique. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2011, 59, 3356–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subrahmannian, A.; Behera, S.K. Chipless RFID: A unique technology for mankind. IEEE J. Radio Freq. Identif. 2022, 6, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.F.; Cheung, S.W.; Yuk, T.I.; Liu, L. Design of chipless UWB RFID system using a CPW multi-resonator. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2013, 55, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbati, M.; Perret, E.; Siragusa, R.; Halopè, C. Toward chipless RFID reading systems independent of tag orientation. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2017, 27, 1158–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovesi, S.; Costa, F.; Monorchio, A.; Manara, G. Chipless RFID tag exploiting multifrequency delta-phase quantization encoding. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. 2016, 15, 738–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Saha, J.K.; Karmakar, N.C. Smart Sensing: Chipless RFID Solutions for the Internet of Everything. IEEE Microw. Mag. 2015, 16, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaeian, F.; Karmakar, N.C. Development of Cross-Polar Orientation-Insensitive Chipless RFID Tags. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2020, 68, 5159–5170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiddes, K.L.; Yan, N. RFID tags for wireless electrochemical detection of volatile chemicals. Sens. Actuators B 2013, 186, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, F.; Li, S.; Sun, W.; Han, G. Reversible conductivity modulation of PEDOT:PSS based on pH. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2017, 186, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spielberg, D.H.; Arndt, R.A.; Damask, A.C.; Lefkowitz, I. Dielectric and neutron inelastic scattering measurements on phenanthrene. J. Chem. Phys. 1971, 54, 2597–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, M.; Kumar, A. Carbon nanotube (CNT) gas sensors for emissions from fossil fuel burning. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 203, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.; Zuo, P.; Wen, K.; Wu, X. Novel soil environment monitoring system based on RFID sensor and LoRa. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 169, 105169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Chu, C.; Li, Z. The adoption and implementation of RFID technologies in healthcare: A literature review. J. Med. Syst. 2011, 36, 3507–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Reinitz, H.W.; Simunovic, J.; Sandeep, K.P.; Franzon, P.D. Overview of RFID technology and its applications in the food industry. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, R101–R106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asad, M.; Sheikhi, M.H. Highly sensitive wireless H2S gas sensors at room temperature based on CuO-SWCNT hybrid nanomaterials. Sens. Actuators B 2016, 231, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clément, P.; Ramos, A.; Lazaro, A.; Molina-luna, L.; Bittencourt, C.; Gribau, D.; Llobet, E. Oxygen plasma treated carbon nanotubes for the wireless monitoring of nitrogen dioxide levels. Sens. Actuators B 2015, 208, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potyrailo, R.A.; Surman, C.; Morris, W.G.; Go, S.; Lee, Y.; Cella, J.; Chichak, K.S. Selective quantitation of vapors and their mixtures using individual passive multivariable RFID sensors. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on RFID (IEEE RFID 2010), Orlando, FL, USA, 14–16 April 2010; pp. 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Le, N.N.; Fribourg-blanc, E.; Phan, H.C.T.; Dang, D.M.T.; Dang, C.M. A RFID-based wireless NH3 gas detector using spin coated carbon nanotubes as sensitive layer. Int. J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 15, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, A.; Sunny, A.I.; Li, L.; Wang, T. Machine learning-based structural health monitoring using RFID for harsh environmental conditions. Electronics 2022, 11, 1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaid, J.; Abdulhadi, A.E.; Denidni, T.A. Miniaturized multi-port microstrip patch antenna using metamaterial for passive UHF RFID-tag sensor applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, G.; Kang, W.; Wang, C.; Li, W.; Li, M.; Xie, L.; Chen, L. Separating strain sensor based on dual-resonant circular patch antenna with chipless RFID tag. Smart Mater. Struct. 2021, 30, 015007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarsri, N.; Myllymäki, S.; Sonkki, M.; Srifi, M.N. Matching approach for UHF RFID tag antenna immersed in dielectric materials. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2020, 84, 106611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.Y.; Hong, J.Y.; Jang, J. Micropatterning of graphene sheets by inkjet printing and its wideband dipole-antenna application. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 2113–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Tan, Q.; Kou, H.; Wu, D.; Zhang, W.; Xiong, J. Highly sensitive NH3 wireless sensor based on Ag-RGO composite operated at room-temperature. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchi, G.; Mulloni, V.; Acerbi, F.; Donelli, M.; Lorenzelli, L. Tailoring the performance of a Nafion 117 humidity chipless RFID sensor: The choice of the substrate. Sensors 2023, 23, 1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belsey, K.E.; Parry, A.V.S.; Rumen, C.V.; Ziai, M.A.; Yeates, S.G.; Batchelor, J.C.; Holder, S.J. Switchable disposable passive RFID vapour sensors from inkjet printed electronic components integrated with PDMS as a stimulus responsive material. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi, F.; Guilaume, C.; Gontard, N.; Soril, B. Wheat gluten, a bio-polymer to monitor carbon dioxide in food packaging: Electric and dielectric characterization. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 250, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, A.S.G.; Narakathu, B.B.; Atashbar, M.Z.; Rebros, M.; Rerosova, E.; Joyce, M.K. Fully printed flexible humidity sensor. Procedia Eng. 2011, 25, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerchouche, K.; Herth, E.; Calvet, L.E.; Roland, N.; Loyez, C. Conductive polymer based antenna for wireless green sensors applications. Microelectron. Eng. 2017, 182, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuppuswami, S.; Mondal, S.; Kumar, D.; Chahal, P. RFID coupled passive digital ammonia sensor for quality control of packaged food. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2020, 20, 4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Chen, P.; Cheng, W.; Yan, K.; Pan, L.; Shi, Y.; Yu, G. Highly sensitive, printable nanostructured conductive polymer wireless sensor for food spoilage detection. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 4570–4575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, M.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, Q.; Liu, R.; Xu, Y.; Wang, K.; Shi, X.; Ye, S. Patterned Ag/PI RFID tag integrated with humidity sensing by in situ metallization. Langmuir 2022, 38, 11478–11485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larpant, N.; Pham, A.D.; Shafaat, A.; Gonzalez-martinez, J.F.; Sotres, J.; Sjöholm, J.; Laiwattanapaisal, W.; Faridbod, F.; Genjali, M.R.; Arnebard, T.; et al. Sensing by wireless reading Ag/AgCl redox conversion on RFID tag: Universal, battery-less biosensor design. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karuppuswami, S.; Matta, L.L.; Alocilja, E.C.; Chahal, P. A wireless RFID compatible sensor tag using gold nanoparticle markers for Pathogen detection in the liquid food supply chain. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2018, 2, 350704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xia, F.; Xu, W.; Wang, G.; Hong, S.; Cheng, F.; Wu, B.; Zheng, N. Antioxidant high-conductivity copper pastes based on core–shell copper nanoparticles for flexible printed electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2215127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Ye, S.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tang, R.; Souxa, M.M.D.; Liu, X.; Zhao, X. Reactive inkjet printing of graphene based flexible circuits and radio frequency antennas. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 13182–13192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Occhiuzzi, C.; Rida, A.; Marrocco, G.; Tentzeris, M. RFID passive gas sensor integrating carbon nanotubes. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory 2011, 59, 2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, A.; Akram, S.; Ali, M.R.; Muhammad, T.; Zainab, S.; Jehangir, S. Radio frequency identification temperature/CO2 sensor using carbon nanotubes. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Hou, B.; Wang, S.; Shang, Y.; Chen, B.; Ju, Y. A highly sensitive paper-based chipless RFID humidity sensor based on graphene oxide. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2023, 358, 114457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, Y.; Liu, L.; Ji, D.; Li, S.; Liu, Q. Passive and wireless near field communication tag sensors for biochemical sensing with smartphone. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 246, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, D.; Che, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, S. Design and application of special sensors and internet of things (IoT)-based wireless system for agricultural information monitor. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1646, 012130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanguy, N.R.; Wiltshire, B.; Arjmand, M.; Zarifi, M.H.; Yan, N. Highly sensitive and contactless ammonia detection based on nanocomposites of phosphate-functionalized reduced graphene oxide/polyaniline immobilized on microstrip resonators. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 9746–9754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Wu, B.; Zhang, X.; Huang, B. Demonstration of wireless gas sensor using reduced graphene oxide loaded patch antenna. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Computational Electromagnetics (ICCEM), Chengdu, China, 26–28 March 2018; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, F.; Wu, H.; Tao, B.; Zang, Y. A passive-chipless LC carbon dioxide sensor with non-contact ZnO/CuO/RGO nanocomposites at room temperature. Vacuum 2023, 215, 112261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.G.; Jun, J.; Lee, J.S.; Jang, J. A highly sensitive wireless nitrogen dioxide gas sensor based on an organic conductive nanocomposite paste. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 8451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, F.; Tian, P.; Tao, B.; Zang, Y. Passive RFID microstrip antenna sensor for temperature monitoring. Vacuum 2022, 201, 111108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, W.; Manjakkal, L.; Navaraj, W.T.; Lorenzelli, L.; Vinciguerra, V.; Dahiya, R. Stretchable wireless system for sweat pH monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 107, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, S.; Matsuhisa, N.; Beker, L.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Yan, X.; Yun, Y.; Bernett, W.; Poon, A.S.Y.; et al. A wireless body area sensor network based on stretchable passive tags. Nat. Electron. 2019, 2, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, F.; Han, Y.; Tian, P.; Tao, B.; Zang, Y.; Chu, P.K. Integrated sensor for humidity, temperature, light, and carbon dioxide based on passive RFID. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 390, 133913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivaldi, F.; Melai, B.; Bonini, A.; Poma, N.; Salvo, P.; Kirchhain, A.; Tintori, S.; Bigongiari, A.; Bertuccelli, F.; Isola, G.; et al. A temperature-sensitive RFID tag for the identification of cold chain failures. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 313, 112182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Gao, Y.; Huang, Q.; Guo, X.; Yang, A.; Zhang, Y.; Zhuang, Q.; Chen, D.; Chen, L.; Ju, X.; et al. Inkjet-printed xerogel scaffolds enabled room-temperature fabrication of high-quality metal electrodes for flexible electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2203730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sun, R.; Pan, J.; Shi, Z.; Lv, J.; An, Z.; He, Y.; Chen, Q.; Han, R.P.S.; Zhang, F.; et al. All-MXene-printed RF resonators as wireless plant wearable sensors for in situ ethylene detection. Small 2023, 19, 2207889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, S.; Kim, H.; Quan, Y.; Kim, H.; Lyu, J.; Lee, G.; Ahn, S. Stretchable chipless RFID multi-strain sensors using direct printing of aerosolised nanocomposite. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 313, 112224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Wei, L.; Uw, X.; Jaing, C.; Yao, Y.; Peng, B.; Chen, H.; Huangfu, J.; Ying, Y.; Zhang, C.J.; et al. Room-temperature high-precision printing of flexible wireless electronics based on MXene inks. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dautta, M.; Alshetaiwi, M.; Escobar, A.; Torres, F.; Bernardo, N.; Tseng, P. Multi-functional hydrogel-interlayer RF/NFC resonators as a versatile platform for passive and wireless biosensing. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2020, 6, 1901311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelli, I.; Fort, A.; Mugnaini, M.; Panzardi, E.; Pozzebon, A.; Tani, M.; Vignoli, V. Battery-less LF RFID sensor tag for soil moisture measurements. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 70, 9504113. [Google Scholar]
- Yakimets, I.; MacKerron, D.; Giesen, P.; Kilmartin, K.J.; Goorhuis, M.; Meinders, E.; MacDonald, W.A. Polymer substrates for flexible electronics: Achievements and challenges. Adv. Mater. Res. 2010, 93–94, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaid, J.; Farahani, M.; Denidni, T.A. Magneto-dielectric substrate-based microstrip antenna for RFID applications. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2017, 11, 1389–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.; Jang, J. Conducting-polymer nanomaterials for high-performance sensor applications: Issues and challenges. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 1567–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, R.W. Nanoelectrochemistry: Metal nanoparticles, nanoelectrodes, and nanopores. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2688–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczech, J.B.; Megaridis, C.M.; Zhang, J.; Gamota, D.R. Ink jet processing of metallic nanoparticle suspensions for electronic circuitry fabrication. Nanoscale Microscale Thermophys. Eng. 2004, 8, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, L.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K.; Ramadoss, A. A review on inkjet printing of nanoparticle inks for flexible electronics. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 8771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, N.C.; Al-Shamery, K. Inkjet printing metals on flexible materials for plastic and paper electronics. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, N.; Akindoyo, J.O.; Mariatti, M. Recent development in silver-based ink for flexible electronics. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Dev. 2022, 7, 100395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, A.; Aaen, P.H.; Lewandowski, A.; Shkunov, M.; Rigas, G.; Blanchard, P.T.; Wallis, T.M.; Devanbhaktuni, V.K. Robust microwave characterization of inkjet-printed coplanar waveguides on flexible substrates. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2017, 66, 3271–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titirici, M.M.; White, R.J.; Brun, N.; Budarin, V.L.; Su, D.S.; Del Monte, F.; Clark, J.H.; MacLachlan, M.J. Sustainable carbon materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamanna, L.; Rizzi, F.; Bhethanabotla, V.R.; Vittorio, M.D. GHz AlN-based multiple mode SAW temperature sensor fabricated on PEN substrate. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 315, 112268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, D.L.T.; Li, R.C.M. Surface-acoustic-wave resonators. Proc. IEEE 1976, 64, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengue, P.; Paulmier, B.; Hage-Ali, S.; Noirel, C.; Poncot, M.; Floer, C.; M’Jahed, H.; Shvetsov, A.; Zhgoon, S.; Nicolay, P.; et al. Temperature and strain SAW/BAW sensors on metallic substrates with RFID capability. Smart Mater. Struct. 2023, 32, 095017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazoe, N.; Miura, N. Environmental gas sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1994, 20, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kim, H.; Hanche, G.P. Environmental monitoring systems: A review. IEEE Sens. J. 1994, 13, 1329–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.; Lee, G.B. Humidity sensors: A review. Sens. Lett. 2005, 3, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Ma, C.; Wu, H.; Luo, X.; Peng, Y.; Luo, Z.; Li, L.; Tan, Y.; Omisore, O.M.; Zhu, Z.; et al. Printable, highly sensitive flexible temperature sensors for human body temperature monitoring: A review. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbon, A.; Levner, E.; Cheng, T.C.E. Perishable inventory management with dynamic pricing using time–temperature indicators linked to automatic detecting devices. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2014, 147, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemdar, H.; Ersoy, C. Wireless sensor networks for healthcare: A survey. Comput. Netw. 2010, 54, 2688–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Qiang, T.; Ma, Y.; Liang, J.; Jiang, Y. RFID-based microwave biosensor for non-contact detection of glucsose solution. Biosensors 2021, 11, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bibi, F.; Guilaume, C.; Gonard, N.; Sorli, B. A review: RFID technology having sensing aptitudes for food industry and their contribution to tracking and monitoring of food products. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 62, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.; Feng, J.; Gameiro, M.G.; Tain, Y.; Laing, J.; Wang, Y.; Ding, J.; He, Q. RFID-based sensing in smart packaging for food applications: A review. Future Foods 2022, 6, 100198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machiels, J.; Appeltans, R.; Bauer, D.K.; Segers, E.; Henckens, Z.; Rompaey, W.V.; Adons, D.; Peeters, R.; Geiβler, M.; Kuehnoel, K.; et al. Screen printed antennas on fiber-based substrates for sustainable HF RFID assisted E-fulfilment smart packaging. Materials 2021, 14, 5500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejias-Morillo, C.R.; Gbaguidi, A.; Kim, D.W.; Namilae, S.; Rojas-Nastrucci, E. UHF RFID-based additively manufactured passive wireless sensor for detecting micrometeoroid and orbital debris impacts. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Wireless for Space and Extreme Environments (WiSEE), Ottawa, ON, Canada, 16–18 October 2019; pp. 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Teckin, M.; Paker, S.; Bahadir, S.K. UHF-RFID enabled wearable flexible printed sensor with antenna performance. Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2022, 157, 154410. [Google Scholar]












| Classification | Materials | Component | Property | Analytes | Sensing Range | Sensitivity | LOD | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polymer | PET | Substrate | Flexible | - | - | - | - | Gas sensing | [96] |
| Nafion 117 | Sensing material | Humidity-sensitive | Humidity | 3–33% | 0.012–0.05% | - | Humidity sensing | [97] | |
| PDMS | Substrate | Stimuli-responsive | - | - | - | - | - | [98] | |
| Wheat gluten | Sensing material | CO2-sensitive | CO2 | 0~40% | - | 40% CO2 | Food | [99] | |
| pHEMA | Sensing material | Humidity-sensitive | Humidity | 30–80%RH | 172% (ΔC/C0) | - | Agriculture | [100] | |
| Conducting polymer | Carboxyl group-functionalized PPy nanoparticles | Sensing material | NH3-sensitive | NH3 | 0.1–25 ppm | >3% | 0.1 ppm | Gas sensing | [64] |
| PEDOT:PSS | Sensing material | - | - | - | - | - | Printing technology | [101] | |
| PANI | Sensing material | NH3-sensitive | NH3 | 0–18 ppm | - | 3 ppm | Food | [102] | |
| PTS-PANI | Sensing material | NH3-sensitive | NH3 | 5–200 ppm | 225%(R/R0) | 5 ppm | Food | [103] | |
| Metal nanoparticle | Patterned Ag | Antenna, sensing material | Humidity-sensitive | Humidity | - | - | - | Humidity sensing | [104] |
| AgNP/HRP-assisted AuNP | Antenna, sensing material | H2O2- and glucose-sensitive | H2O2, glucose | 10−6—10−3 M, 1–20 mM | 71% (Δf) | 10−6 M, 1 mM | Healthcare | [105] | |
| Dextrin-capped AuNP | Antenna, sensing material | Biosensitive | E. coli | - | - | -- | Food | [106] | |
| Core-shell CuNP | Antenna | High-performance and anti-oxidant | - | - | - | - | Printing technology | [107] | |
| Carbon-based | rGO conductive pattern | Antenna, | Mechanical durability; high electrical conductivity | - | - | - | - | Printing technology | [108] |
| SWCNT film (buckypaper) | Antenna, sensing material | Gas-sensitive; isotropic conductivity; good mechanical strength; flexibility | NH3 | - | - | - | Gas sensing | [109] | |
| MWCNT | Antenna, sensing material | Gas- and temperature-sensitive; lightweight | CO2, temperature | - | - | - | Temperature sensing, Gas sensing | [110] | |
| GO film | Antenna | Humidity-sensitive | Humidity | 30–99%RH | 6.25 MHz/%RH | 30%RH | Humidity sensing | [111] | |
| Graphene | Sensing material | Biochemical-sensitive | Ethanol, KCl, Staphylococcus aures | 1–5 ppm, 0.008–1 M, 0–1.0 × 106 CFU/mL | - | 1 ppm, 0.0009 M, 105 CFU/mL | Healthcare | [112] | |
| Graphene oxide | Sensing material | Humidity-sensitive | Humidity | - | - | - | Agriculture | [113] | |
| Composite | Pt-decorated rGO | Sensing material | H2 gas-sensitive | H2 | 1–100 ppm- | - | 1 ppm | Gas sensing | [65] |
| Ag-rGO | Sensing material | NH3 gas-sensitive | NH3 | 5–100 ppm | 1.25% | 5 ppm | Gas sensing | [96] | |
| PANI-incorporated P-GO | Sensing material | NH3 gas-sensitive | NH3 | 2–200 ppm | 15.9 | 1 ppm | Gas sensing | [114] | |
| rGO/Ag-ink | Antenna, sensing material | NH3 gas-sensitive | NH3 | 0–200 ppm | - | - | Gas sensing | [115] | |
| ZnO/CuO/rGO | Sensing material | CO2 gas-sensitive | CO2 | 500–1600 ppm | 0.009 ppm/dB | 500 ppm | Gas sensing | [116] | |
| Fe2O3 hollow nanoparticle/PANI:PSS | Sensing material | NO2 gas-sensitive | NO2 | 1–100 ppm | - | 0.5 ppm | Gas sensing | [117] | |
| ZnO/MoS2/rGO | Antenna, sensing material | Temperature sensitive | Temperature | 0–200 °C | 1.46 °C/dB | - | Temperature sensing | [118] | |
| Graphite-polyurethane | Sensing material | pH-sensitive; stretchable | pH | 0–14 pH | 11.13 ± 5.8 mV/pH | - | Bio sensing | [119] | |
| Ag ink/CNT | Sensing material | Strain-sensitive | Strain | 0–50% | - | - | Healthcare | [120] | |
| SnO2/MoS2/RGO, ZnO/MoS2/RGO, TiO2/Co3O4/RGO, In2O3/CuO/RGO | Sensing material | Humidity-sensitive; temperature-sensitive; light-sensitive; gas-sensitive | Humidity, temperature, light, CO2 | 10–50% RH, 5–25 °C, 700–1900 lux, 800–1600 ppm | 2 MHz/%RH, 0.63 dB/°C, 0.02 dB/Lux, 0.012 dB/ppm | - | Agriculture | [121] | |
| Others | Aluminum nitride thin film | Sensing material | Temperature-sensitive | Temperature | 20–120 °C | 64 ppm/°C | - | Temperature sensing | [120 |
| Cu-doped ionic liquid | Sensing material | Temperature-sensitive | Temperature | 8 °C (threshold) | - | - | Temperature sensing | [122] | |
| Xerogel-based Cu electrode | Antenna | High pattern resolution; mechanical stability | - | - | - | - | Printing technology | [123] | |
| MXene/PdNPs | Antenna, sensing material | Decent printing resolution; conductivity; mechanical robustness; gas-sensitive | Ethylene | 0.5–20 ppm | - | 0.084 ppm | Gas sensing | [124] | |
| Aerosolized Ag/MWCNT nanocomposite | Antenna | Mechanical durability; strain-sensitive | Strain | 0–75° | - | >20% | Strain sensor | [125] | |
| MXene ink | Antenna, sensing material | Large single-layer ratio; narrow flake size distribution; metallic conductivity | Temperature, humidity | 20–55 °C, 20–80%RH | - | - | Temperature sensing, humidity sensing | [126] | |
| PAM hydrogel | Sensing material | Wide range of elastic moduli; bio-analytes-sensitive | Pressure, sweat, temperature | 0–120 kPa, 0–70 mg/dL, 3–6 pH, 25–45 °C | - | - | Healthcare | [127] | |
| TiO2 | Sensing material | Humidity-sensitive | Humidity | 0–100%RH | - | - | Agriculture | [128] |
| Substrate | Dielectric Constant | RH Low [%] | RH High [%] | Frequency Shift [MHz/%] | Δ|S21|min [dB/%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DiClad | 2.33 | 15 | 70 | 3.909 | 0.012 |
| RO4003C | 3.88 | 15 | 75 | 2.683 | 0.018 |
| FR4 | 4.6 | 10 | 65 | 3.454 | 0.017 |
| RO3010 | 11.2 | 10 | 90 | 1.562 | 0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roh, S.; Nguyen, T.D.; Lee, J.S. Applications of Nanomaterials in RFID Wireless Sensor Components. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14031216
Roh S, Nguyen TD, Lee JS. Applications of Nanomaterials in RFID Wireless Sensor Components. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(3):1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14031216
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoh, Sojeong, Trong Danh Nguyen, and Jun Seop Lee. 2024. "Applications of Nanomaterials in RFID Wireless Sensor Components" Applied Sciences 14, no. 3: 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14031216
APA StyleRoh, S., Nguyen, T. D., & Lee, J. S. (2024). Applications of Nanomaterials in RFID Wireless Sensor Components. Applied Sciences, 14(3), 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14031216








