Determination of Nonylphenol in a Highly Sensitive Chemiluminescent Immunoenzyme Assay of Natural Waters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Components
2.2. Methods
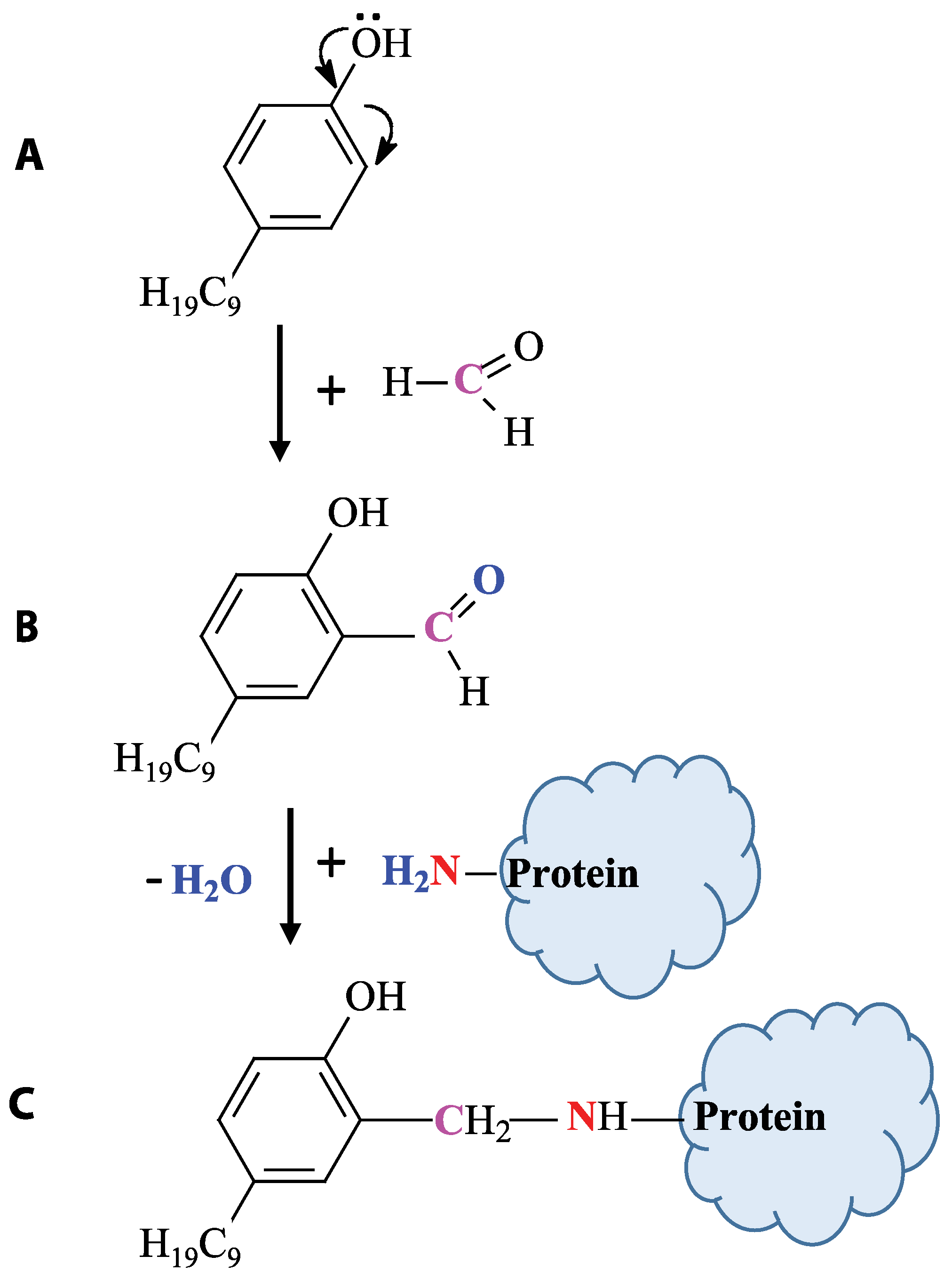
2.2.1. Synthesis of the Conjugate of Hapten and Carrier Protein Conjugate
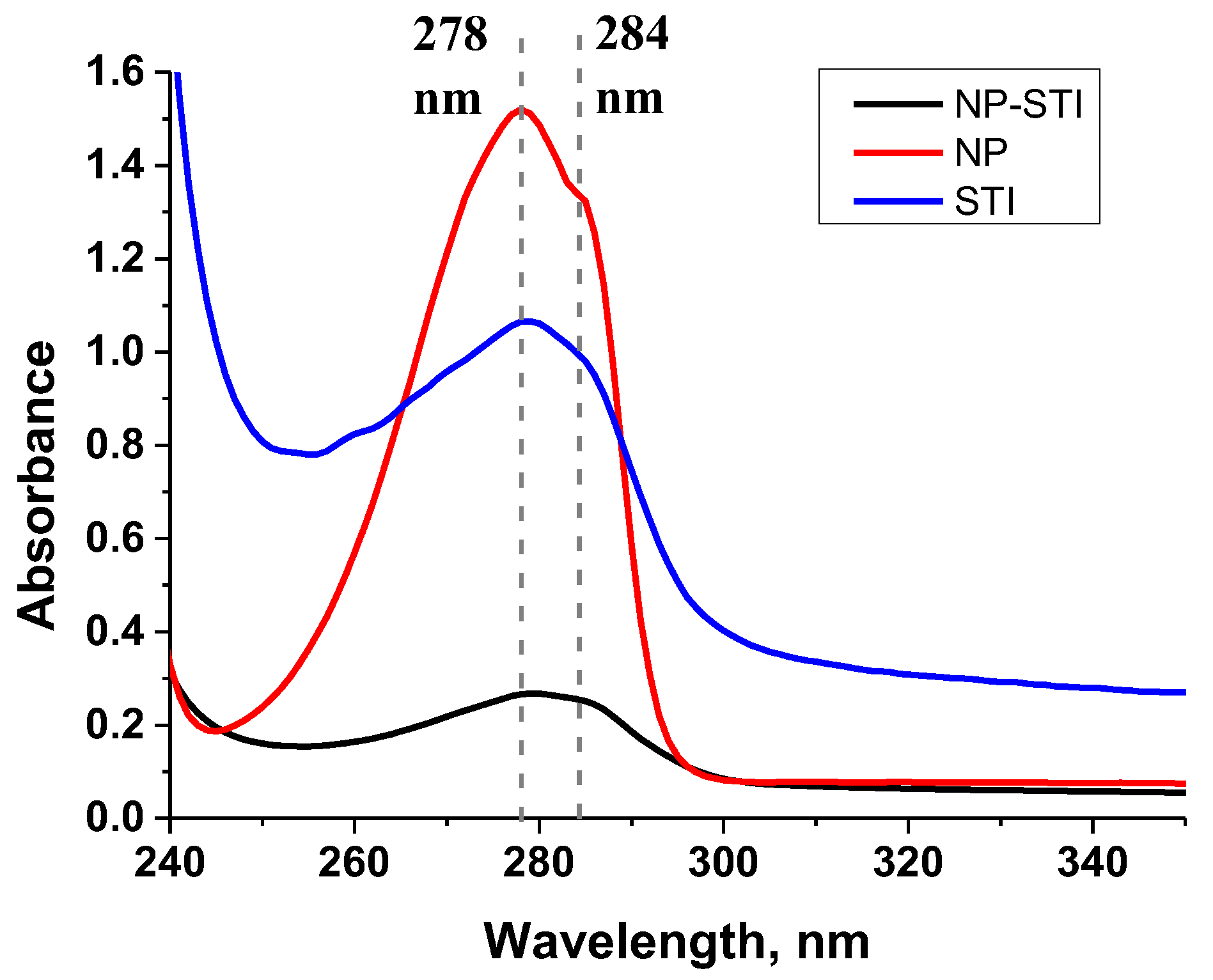
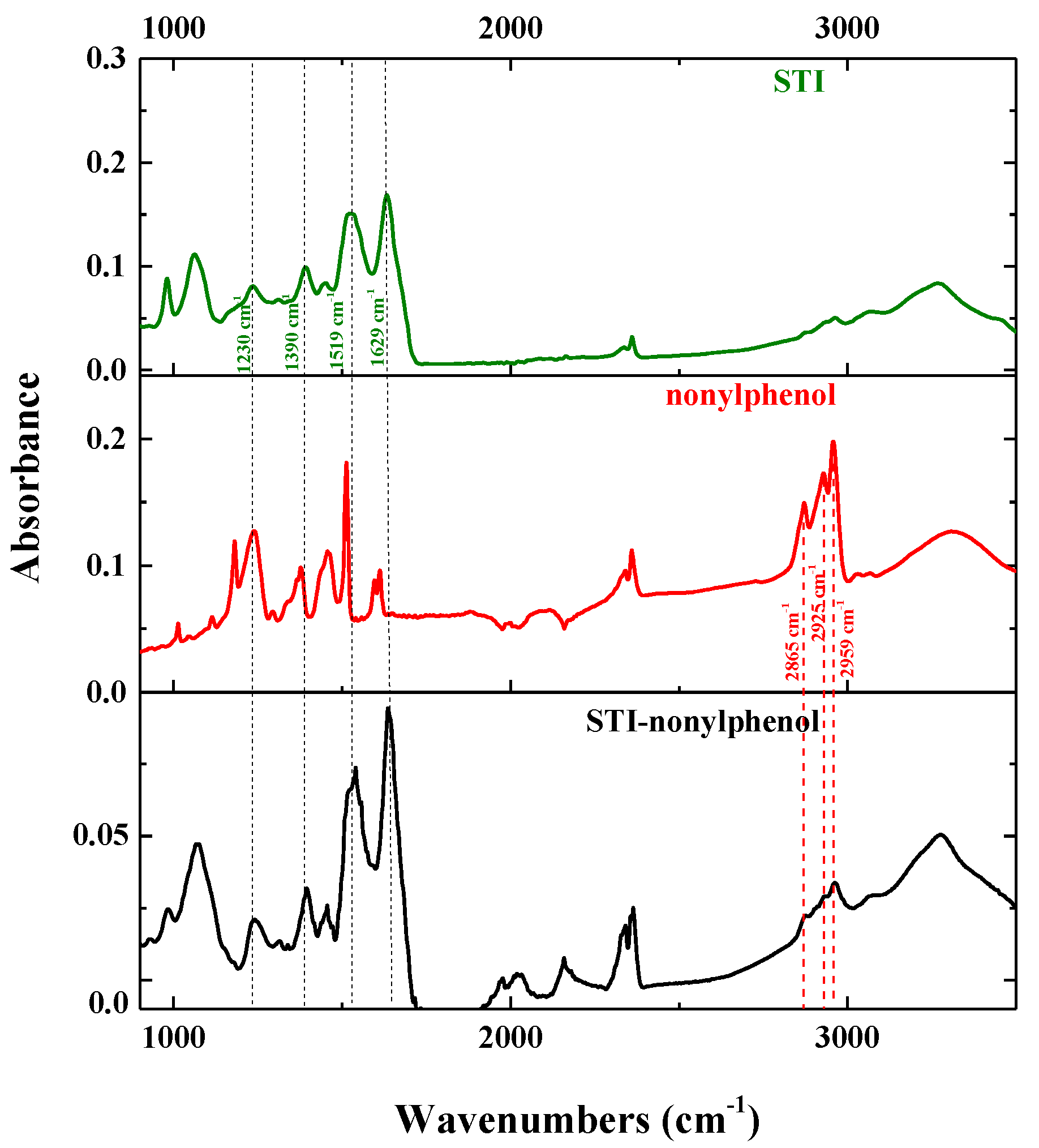
2.2.2. Characteristics of the NP–STI Conjugate
2.2.3. Collection and Storage of Water Samples
2.2.4. Colorimetric EIA
2.2.5. Chemiluminescent EIA
2.2.6. EIA Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Hapten–Protein Conjugate
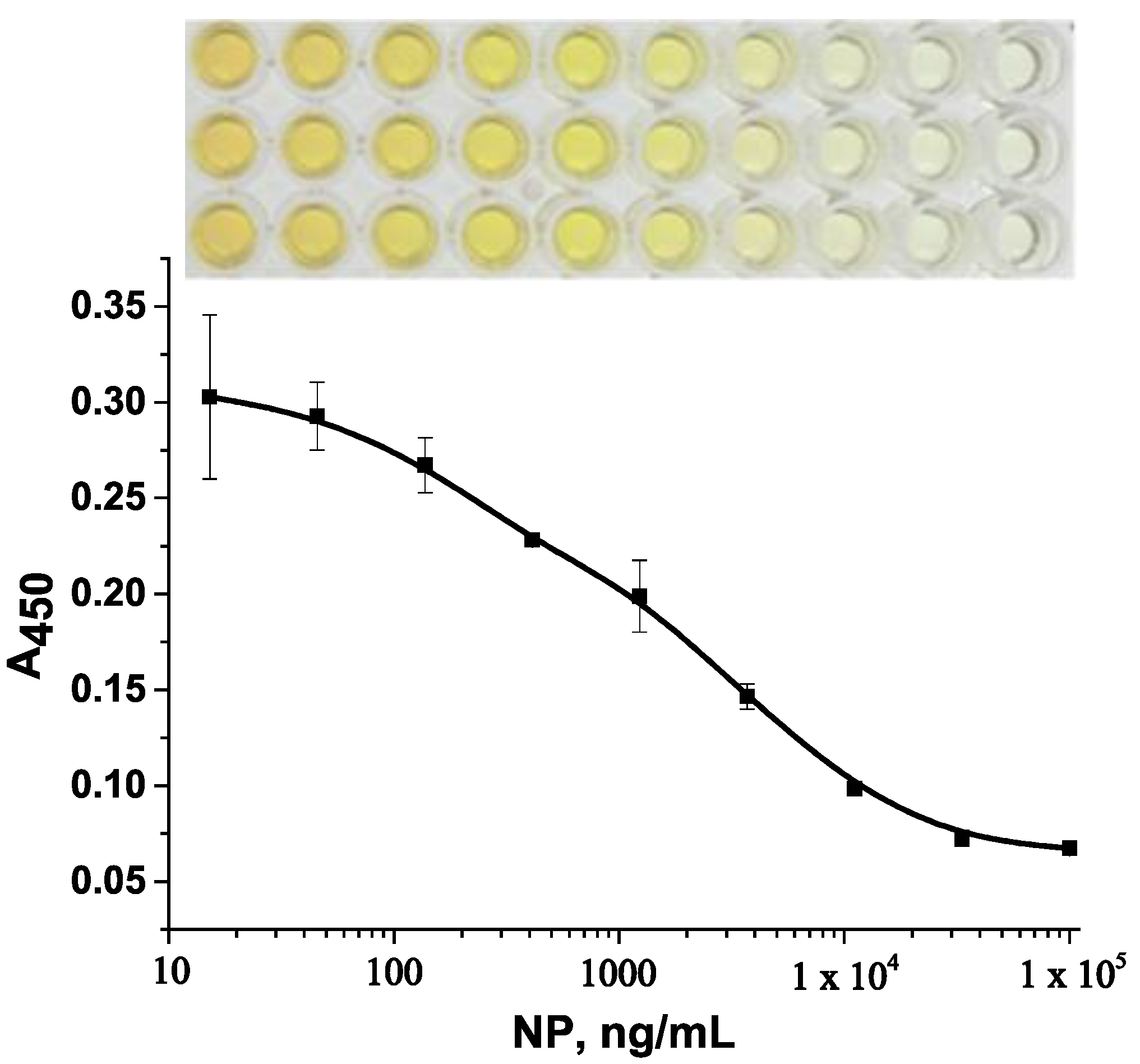
3.2. Competitive EIA with Colorimetric Detection
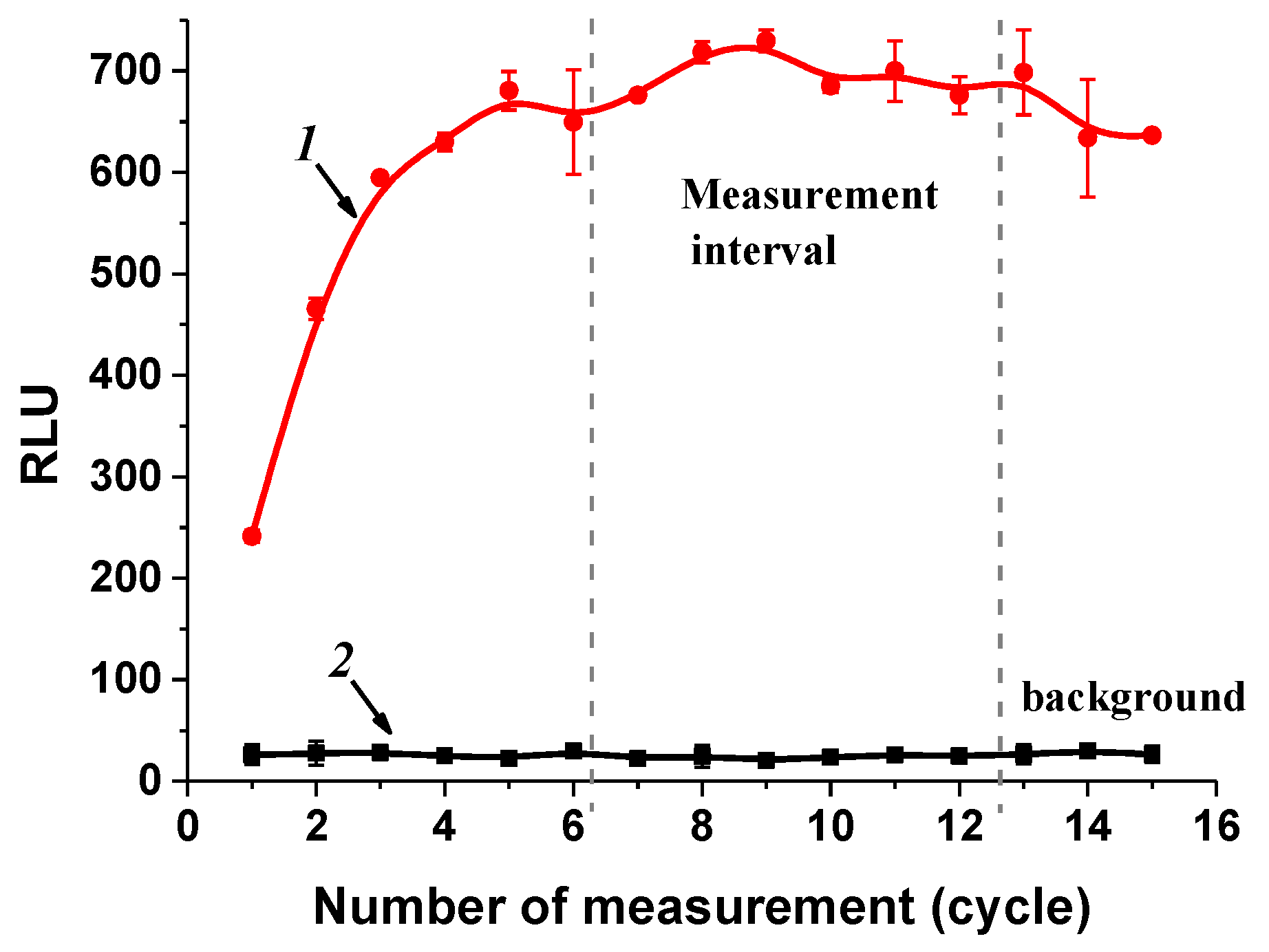
3.3. Chemiluminescent EIA
3.4. Optimizing Parameters of Chemiluminescent EIA Test System
3.4.1. The Choice of STI–NP Concentrations and Antiserum Dilution
3.4.2. Optimization of Competitive Stage Duration
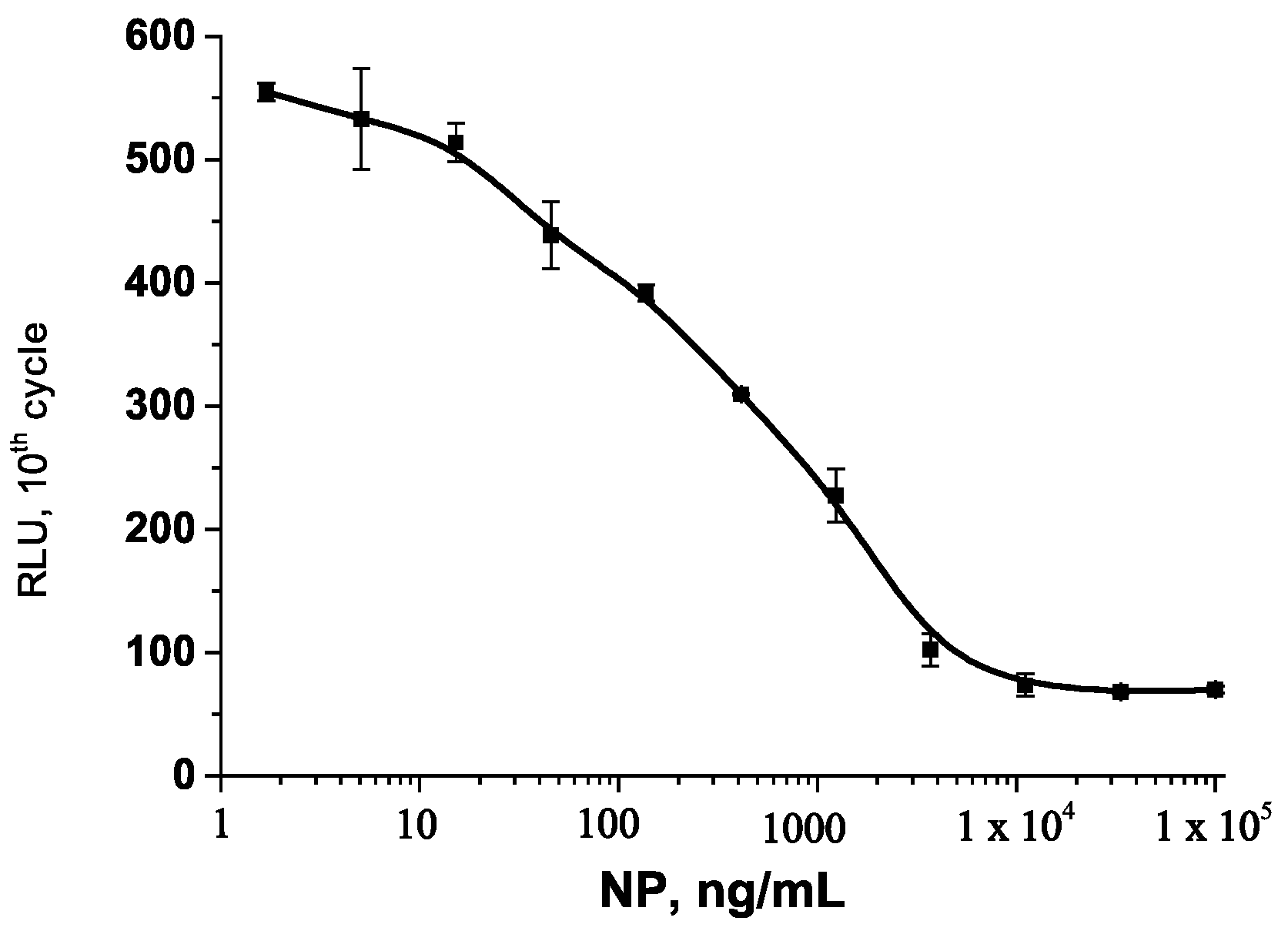
3.5. Chemiluminescent EIA of NP in Natural Waters
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Babuji, P.; Thirumalaisamy, S.; Duraisamy, K.; Periyasamy, G. Human Health Risks due to Exposure to Water Pollution: A Review. Water 2023, 15, 2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Sabarathinam, C.; Elumalai, V. Groundwater pollution and its remediation for sustainable water management. Chemosphere 2023, 329, 138621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revel, M.; Châtel, A.; Mouneyrac, C. Micro (nano) plastics: A threat to human health? Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2018, 1, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fred-Ahmadu, O.H.; Bhagwat, G.; Oluyoye, I.; Benson, N.U.; Ayejuyo, O.O.; Palanisami, T. Interaction of chemical contaminants with microplastics: Principles and perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 135978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, G.; Laneri, S.; Di Lorenzo, R.; Neri, I.; Dini, I.; Ciampaglia, R.; Grumetto, L. Monitoring of Pollutants Content in Bottled and Tap Drinking Water in Italy. Molecules 2022, 27, 3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, I.C.; Chao, H.-R.; Mansor, W.-N.-W.; Peng, C.-W.; Hsu, Y.-C.; Yu, T.-Y.; Chang, W.-H.; Fu, L.-M. Levels of Phthalates, Bisphenol-A, Nonylphenol, and Microplastics in Fish in the Estuaries of Northern Taiwan and the Impact on Human Health. Toxics 2021, 9, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa, J.P.; Santos, P.S.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. (Nano) plastics in the environment–sources, fates and effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Parra-Guerra, A.C.; Acevedo-Barrios, R. Studies of Endocrine Disruptors: Nonylphenol and Isomers in Biological Models. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2023, 42, 1439–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Anquandah, G.A.; Yngard, R.A.; Kim, H.; Fekete, J.; Bouzek, K.; Ray, A.K.; Golovko, D. Nonylphenol, octylphenol, and bisphenol-A in the aquatic environment: A review on occurrence, fate, and treatment. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2009, 44, 423–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, F.; Liang, C.; He, L.; Jiao, W.; Wu, W. Adsorption of EDCs on Reclaimed Water-Irrigated Soils: A Comparative Analysis of a Branched Nonylphenol, Nonylphenol and Bisphenol A. Water 2021, 13, 2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Sun, S.; Xue, H.; Kang, C.; Yu, S. Polypropylene microplastics aging under natural conditions in winter and summer and its effects on the sorption and desorption of nonylphenol. Environ. Res. 2023, 225, 115615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, M.; Maadurshni, G.B.; Manivannan, J. Exposure to low dose of Bisphenol A (BPA) intensifies kidney oxidative stress, inflammatory factors expression and modulates Angiotensin II signaling under hypertensive milieu. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2023, 38, e23533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, S.; D’Souza, L.C.; Shetty, N.G.; Raghu, S.V.; Sharma, A. Hsp27, a potential EcR target, protects nonylphenol-induced cellular and organismal toxicity in Drosophila melanogaster. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 293, 118484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaniyan, L.W.B.; Okoh, O.O.; Mkwetshana, N.T.; Okoh, A.I. Environmental Water Pollution, Endocrine Interference and Ecotoxicity of 4-tert-Octylphenol: A Review. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology Volume 248; de Voogt, P., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 81–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penserini, L.; Cantoni, B.; Gabrielli, M.; Sezenna, E.; Saponaro, S.; Antonelli, M. An integrated human health risk assessment framework for alkylphenols due to drinking water and crops’ food consumption. Chemosphere 2023, 325, 138259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascale, R.; Acquavia, M.A.; Onzo, A.; Cataldi, T.R.I.; Calvano, C.D.; Bianco, G. Analysis of surfactants by mass spectrometry: Coming to grips with their diversity. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2023, 42, 1557–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, H. Monoplex and multiplex immunoassays: Approval, advancements, and alternatives. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2022, 31, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, E.; Iha, K.; Yoshimura, T.; Nakaishi, K.; Watabe, S. Chapter Four—Early diagnosis with ultrasensitive ELISA. In Advances in Clinical Chemistry; Makowski, G.S., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 101, pp. 121–133. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Li, G.; Xu, X.; Zhu, L.; Huang, R.; Chen, X. Application of nano-ELISA in food analysis: Recent advances and challenges. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 113, 140–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mart’ianov, A.A.; Zherdev, A.V.; Eremin, S.A.; Dzantiev, B.B. Preparation of antibodies and development of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for nonylphenol. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2004, 84, 965–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wu, J.; Wu, J.; He, X. Adsorption of nonylphenol on coastal saline soil: Will microplastics play a great role? Chemosphere 2023, 311, 137032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, S.; Li, L.; Quan, X.; Zhao, H. Electrochemically enhanced adsorption of nonylphenol on carbon nanotubes: Kinetics and isotherms study. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 415, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Song, J.; Wu, D.; Tang, T.; Sun, Y. One-step synthesis of hydrophobic mesoporous silica and its application in nonylphenol adsorption. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2015, 86, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronberg, B.; Stenius, P.; Thorssell, Y. Adsorption of nonylphenol—Poly(propylene oxide)—Poly(ethylene oxide) nonionic surfactants on polystyrene latex. Colloids Surf. 1984, 12, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, H.; Shelver, W.L.; Wang, Z.; Li, Q.X.; Li, J.; Xu, T. Development of a monoclonal antibody-based, congener-specific and solvent-tolerable direct enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether in environmental samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 401, 2249–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlina, A.N.; Zherdev, A.V.; Xu, C.; Eremin, S.A.; Dzantiev, B.B. Development of lateral flow immunoassay for rapid control and quantification of the presence of the colorant Sudan I in spices and seafood. Food Control 2017, 73, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlina, A.N.; Ragozina, M.Y.; Gusev, D.I.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B. Development of Chemiluminescent ELISA for Detection of Diisobutyl Phthalate in Water, Lettuce and Aquatic Organisms. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tré-Hardy, M.; Wilmet, A.; Beukinga, I.; Dogné, J.-M.; Douxfils, J.; Blairon, L. Validation of a chemiluminescent assay for specific SARS-CoV-2 antibody. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. (CCLM) 2020, 58, 1357–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiebert, J.; Zubach, V.; Charlton Carmen, L.; Fenton, J.; Tipples Graham, A.; Fonseca, K.; Severini, A. Evaluation of Diagnostic Accuracy of Eight Commercial Assays for the Detection of Measles Virus-Specific IgM Antibodies. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e03161-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Shah, S.H.; Salman, M.; Abdullah, M.; Hayat, F.; Akbar, S. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay versus Chemiluminescent Immunoassay: A General Overview. Glob. J. Med. Pharm. Biomed. Update 2023, 18, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabello, M.C.; Bartoloni, F.H.; Bastos, E.L.; Baader, W.J. The Molecular Basis of Organic Chemiluminescence. Biosensors 2023, 13, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Han, T.; Deng, A.; Li, L.; Zhu, J.-J. Resonance energy transfer in electrochemiluminescent and photoelectrochemical bioanalysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 123, 115745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepa, S.; Venkatesan, R.; Jayalakshmi, S.; Priya, M.; Kim, S.-C. Recent advances in catalyst-enhanced luminol chemiluminescence system and its environmental and chemical applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giussani, A.; Farahani, P.; Martínez-Muñoz, D.; Lundberg, M.; Lindh, R.; Roca-Sanjuán, D. Molecular Basis of the Chemiluminescence Mechanism of Luminol. Chem.—A Eur. J. 2019, 25, 5202–5213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquette, C.A.; Blum, L.J. Applications of the luminol chemiluminescent reaction in analytical chemistry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 385, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, K.; Kanungo, L. Chemiluminescence and fluorescence biosensors for food application: A review. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2023, 5, 100137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, T.; Matsuhashi, C. Soft Crystal Chemiluminescence Systems Using Organic Peroxides. In Soft Crystals: Flexible Response Systems with High Structural Order; Springer Nature Singapore: Singapore, 2023; pp. 155–177. [Google Scholar]
- Habeeb, A.F.S.A. Determination of free amino groups in proteins by trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid. Anal. Biochem. 1966, 14, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakharov, I.Y.; Berlina, A.N.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B. Advantages of Soybean Peroxidase over Horseradish Peroxidase as the Enzyme Label in Chemiluminescent Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay of Sulfamethoxypyridazine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 3284–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.; Yu, S. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic analysis of protein secondary structures. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2007, 39, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonenfant, D.; Niquette, P.; Mimeault, M.; Furtos-Matei, A.; Hausler, R. UV-VIS and FTIR spectroscopic analyses of inclusion complexes of nonylphenol and nonylphenol ethoxylate with β-cyclodextrin. Water Res. 2009, 43, 3575–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zvereva, E.A.; Byzova, N.A.; Sveshnikov, P.G.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B. Cut-off on demand: Adjustment of the threshold level of an immunochromatographic assay for chloramphenicol. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 6378–6384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mart’ianov, A.A.; Dzantiev, B.B.; Zherdev, A.V.; Eremin, S.A.; Cespedes, R.; Petrovic, M.; Barcelo, D. Immunoenzyme assay of nonylphenol: Study of selectivity and detection of alkylphenolic non-ionic surfactants in water samples. Talanta 2005, 65, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, C.; Romay, C. Effect of antioxidants on chemiluminescence produced by reactive oxygen species. J. Biolumin. Chemilumin. 1992, 7, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ring Biotechnology Co., Ltd. Nonylphenol Ethoxylates, NPE ELISA Kit. Available online: https://foodtestkit.com/products/nonylphenol-ethoxylates-npe-elisa-kit/ (accessed on 18 February 2024).
- Sharma, M.; Chadha, P.; Madhu Sharma, C. Toxicity of non-ionic surfactant 4-nonylphenol an endocrine disruptor: A review. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2018, 6, 190–197. [Google Scholar]
- Babay, P.A.; Itria, R.F.; Romero Ale, E.E.; Becquart, E.T.; Gautier, E.A. Ubiquity of Endocrine Disruptors Nonylphenol and Its Mono-and Di-E thoxylates in Freshwater, Sediments, and Biosolids Associated with High and Low Density Populations of Buenos Aires, Argentina. CLEAN–Soil Air Water 2014, 42, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Peterson, J.R.; Gooding, J.J.; Lee, N.A. Development of a Competitive ELISA for the Detection of 4-tert-Octylphenol in Seafood. Food Anal. Methods 2015, 8, 1923–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, L.; Song, S.; Guo, S.; Kuang, H.; Xu, C. Development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for octylphenol. Food Agric. Immunol. 2014, 25, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlina, A.N.; Ragozina, M.Y.; Komova, N.S.; Serebrennikova, K.V.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B. Comparison of Au, Au–Pt, and Au–Ag nanoparticles as markers for immunochromatographic determination of nonylphenol. Chim. Techno Acta 2023, 10, 202310103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlina, A.N.; Komova, N.S.; Serebrennikova, K.V.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B. Comparison of different formats for immunochromatographic detection of surfactant nonylphenol. Eng. Proc. 2023, 48, 9. [Google Scholar]
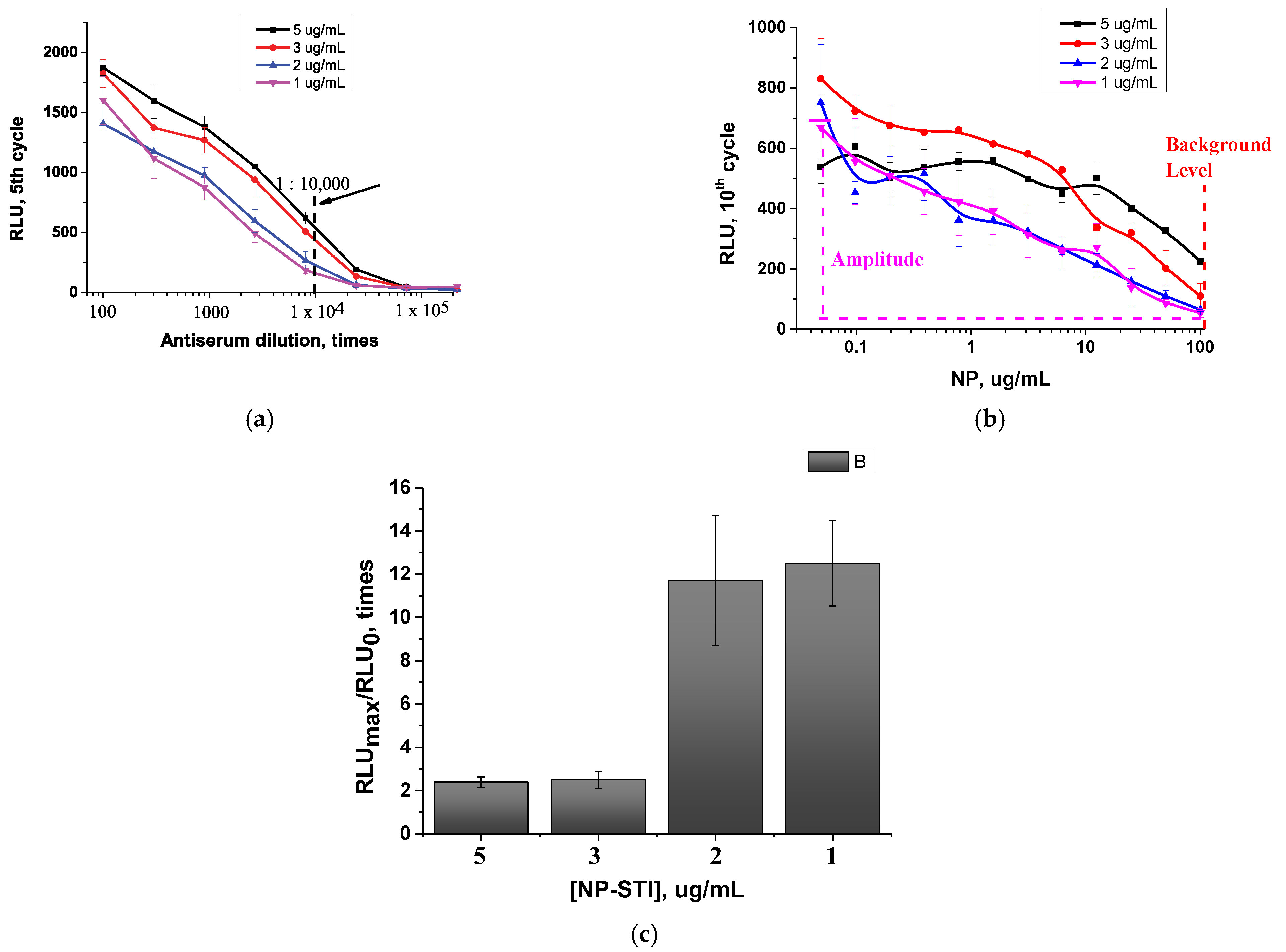
| Concentration of NP–STI | IC10, ng/mL | IC20, ng/mL | IC50, ng/mL | IC80, ng/mL | Responses max/min | Error *, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 µg/mL | 77 | 175 | 1900 | 21,900 | 0.33/0.18 | 6.2 |
| 3 µg/mL | 490 | 350 | 1230 | 19,400 | 0.31/0.18 | 1.9 |
| 2 µg/mL | 115 | 614 | 1820 | 11,100 | 0.29/0.12 | 2.8 |
| 1 µg/mL | 55 | 190 | 1590 | 13,300 | 0.3/0.05 | 5.6 |
| 0.5 µg/mL | 23 | 83 | 768 | 7120 | 0.22/0.06 | 2.9 |
| 0.1 µg/mL | 18 | 50 | 290 | 1740 | 0.11/0.06 | 4.3 |
| 0.01 µg/mL | 92 | 93 | 94 | 95 | 0.08/0.06 | 4.8 |
| Duration of Competition | IC10, ng/mL | IC20, ng/mL | IC50, ng/mL | IC80, ng/mL | Responses max/min | Error *, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60 min | 29 | 76 | 400 | 2100 | 685/24 | 6.5 |
| 45 min | 9 | 25 | 138 | 758 | 606/21 | 8.2 |
| 30 min | 8 | 20 | 87 | 380 | 442/24 | 13.9 |
| 15 min | 13 | 24 | 63 | 170 | 134/24 | 17.3 |
| No. | Medium | IC10, ng/mL | IC20, ng/mL | IC80, ng/mL | IC50, ng/mL | Responses max/min | Error *, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Distilled water | 15.0 | 60.97 | 5300 | 669.80 | 765/70 | 5.3 |
| 2 | PBS 1 mM | 8.9 | 32.27 | 2633.1 | 291.51 | 574/153 | 6.8 |
| 3 | PBS 10 mM | 28.4 | 85.67 | 3731.93 | 565.44 | 608/140 | 9.2 |
| 4 | PBS 50 mM | 22.0 | 51.8 | 970.13 | 224.10 | 550/101 | 8.4 |
| 5 | PBST | 4.06 | 17.80 | 2778.7 | 222.34 | 580/92 | 4.2 |
| 6 | 50 mM PBS + 0.1% gelatin | 24.1 | 73.11 | 3251.55 | 487.56 | 640/95 | 6.0 |
| Added, NP | Detected, NP, Chemiluminescence | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probe 1 (River) | Probe 2 (Waterfall) | Probe 3 (Pond) | ||||
| ng/mL | ng/mL | % | ng/mL | % | ng/mL | % |
| 45 | 55 ± 8.4 | 122 ± 15.2 | 53 ± 2.3 | 117.7 ± 4.3 | 50 ± 5.3 | 111.1 ± 10.5 |
| 135 | 140 ± 13.7 | 103.7 ± 9.8 | 130 ± 7.5 | 96.3 ± 5.8 | 148 ± 10.4 | 109.6 ± 7.0 |
| 400 | 431 ± 49.1 | 107.8 ± 11.4 | 411 ± 42.3 | 102.8 ± 10.3 | 395 ± 15.0 | 98.8 ± 3.8 |
| 1200 | 1023 ± 53.2 | 85.3 ± 5.2 | 954 ± 127.8 | 79.5 ± 13.4 | 992 ± 69.3 | 82.7 ± 7.0 |
| Detected, NP, Colorimetry | ||||||
| 200 | 235 ± 3.2 | 117.5 ± 1.4 | 184 ± 8.1 | 92 ± 4.4 | 234 ± 7.9 | 117.0 ± 3.4 |
| 600 | 589 ± 6.4 | 98.2 ± 1.1 | 532 ± 16.5 | 88.7 ± 3.1 | 519.6 ± 16.6 | 86.6 ± 3.2 |
| 800 | 830 ± 12.2 | 103.8 ± 14.7 | 792 ± 13.6 | 99 ± 1.8 | 762.4 ± 11.4 | 95.3 ± 1.5 |
| 1000 | 1206 ± 10.4 | 120.6 ± 0.9 | 998 ± 19.2 | 99.8 ± 2.0 | 832 ± 16.2 | 83.2 ± 2.0 |
| No. | Technique | Detection | Sample | Antibody | IC10 or IC50 | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ELISA | Colorimetry | Prawn and clam samples (seafood) | polyclonal | 10 μg/L 20 μg/L | [48] |
| 2 | ELISA | Colorimetry | Lake water | Monoclonal, polyclonal | 76 ng/mL—OP 24 ng/mL—NP | [49] |
| 3 | LFIA | Colorimetry | - | polyclonal | 1 μg/mL | [50] |
| 4 | LFIA | Colorimetry | Spring water | polyclonal | 1.1 and 0.4 μg/mL | [51] |
| 5 | EIA | Chemiluminescent | Spring water | polyclonal | 7 ng/mL | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Berlina, A.N.; Komova, N.S.; Serebrennikova, K.V.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B. Determination of Nonylphenol in a Highly Sensitive Chemiluminescent Immunoenzyme Assay of Natural Waters. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1685. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14051685
Berlina AN, Komova NS, Serebrennikova KV, Zherdev AV, Dzantiev BB. Determination of Nonylphenol in a Highly Sensitive Chemiluminescent Immunoenzyme Assay of Natural Waters. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(5):1685. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14051685
Chicago/Turabian StyleBerlina, Anna N., Nadezhda S. Komova, Kseniya V. Serebrennikova, Anatoly V. Zherdev, and Boris B. Dzantiev. 2024. "Determination of Nonylphenol in a Highly Sensitive Chemiluminescent Immunoenzyme Assay of Natural Waters" Applied Sciences 14, no. 5: 1685. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14051685
APA StyleBerlina, A. N., Komova, N. S., Serebrennikova, K. V., Zherdev, A. V., & Dzantiev, B. B. (2024). Determination of Nonylphenol in a Highly Sensitive Chemiluminescent Immunoenzyme Assay of Natural Waters. Applied Sciences, 14(5), 1685. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14051685








