High-Quality Cutting of Soda–Lime Glass with Bessel Beam Picosecond Laser: Optimization of Processing Point Spacing, Incident Power, and Burst Mode
Abstract
:1. Introduction
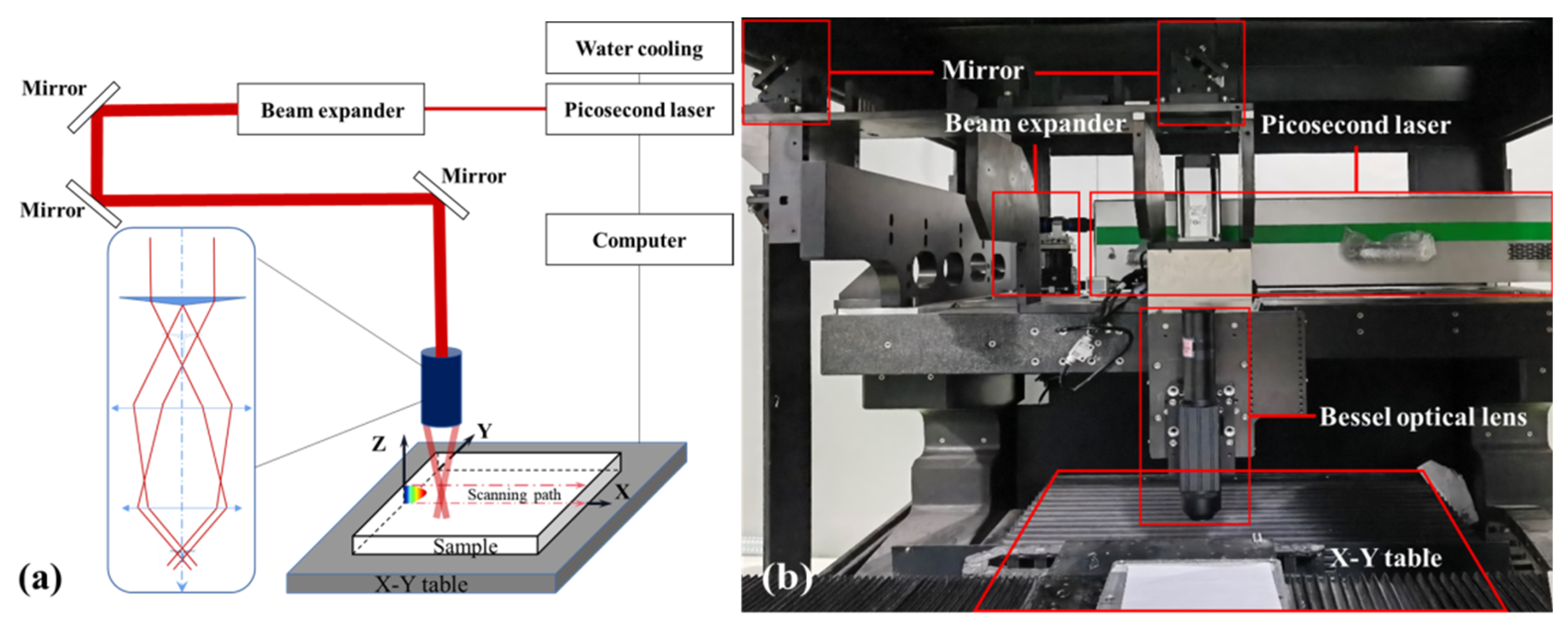
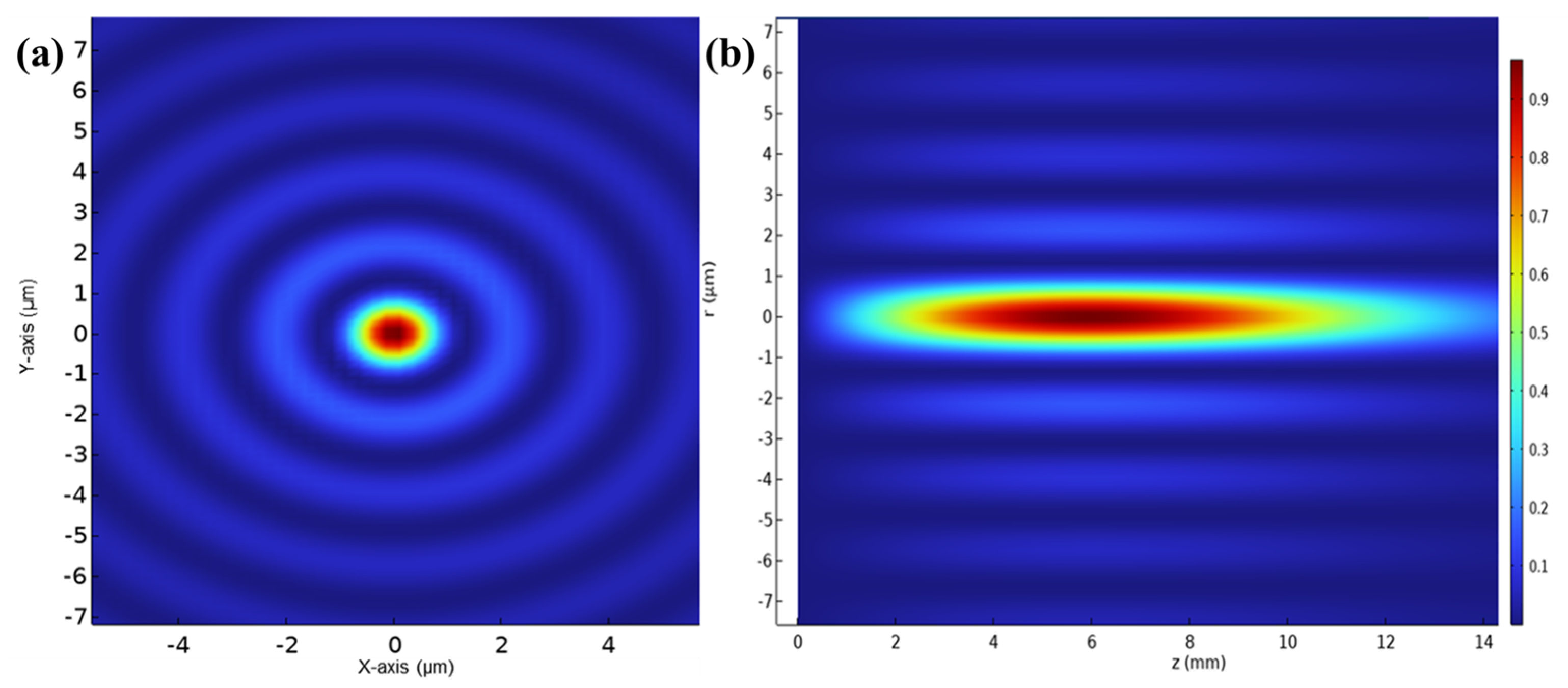
2. Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
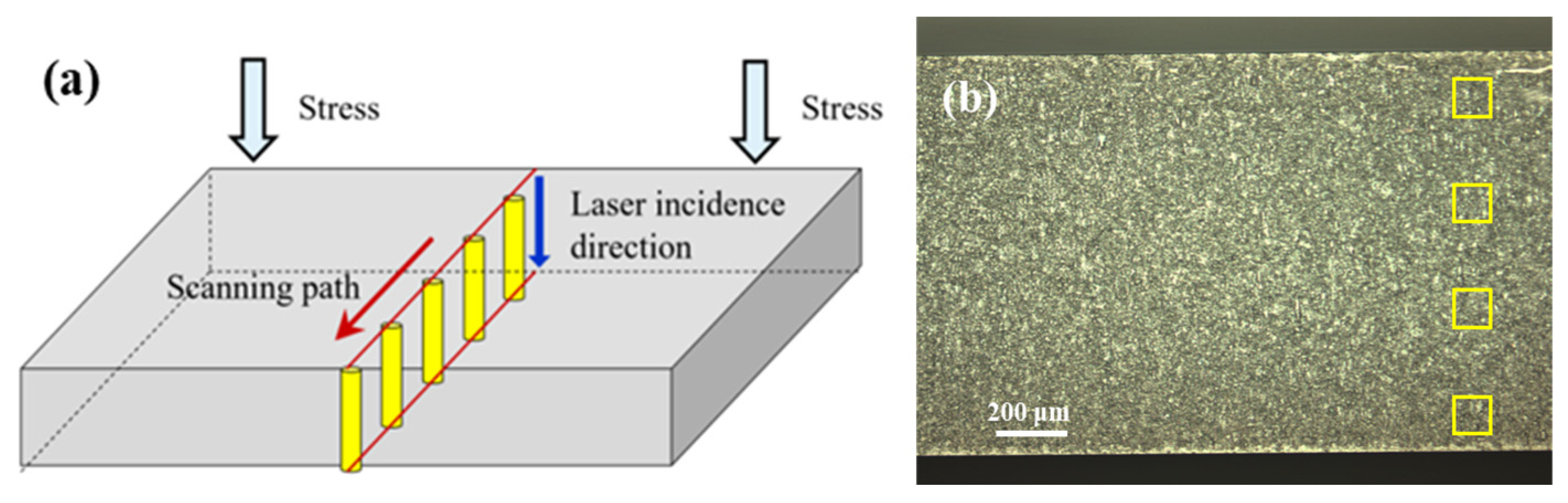
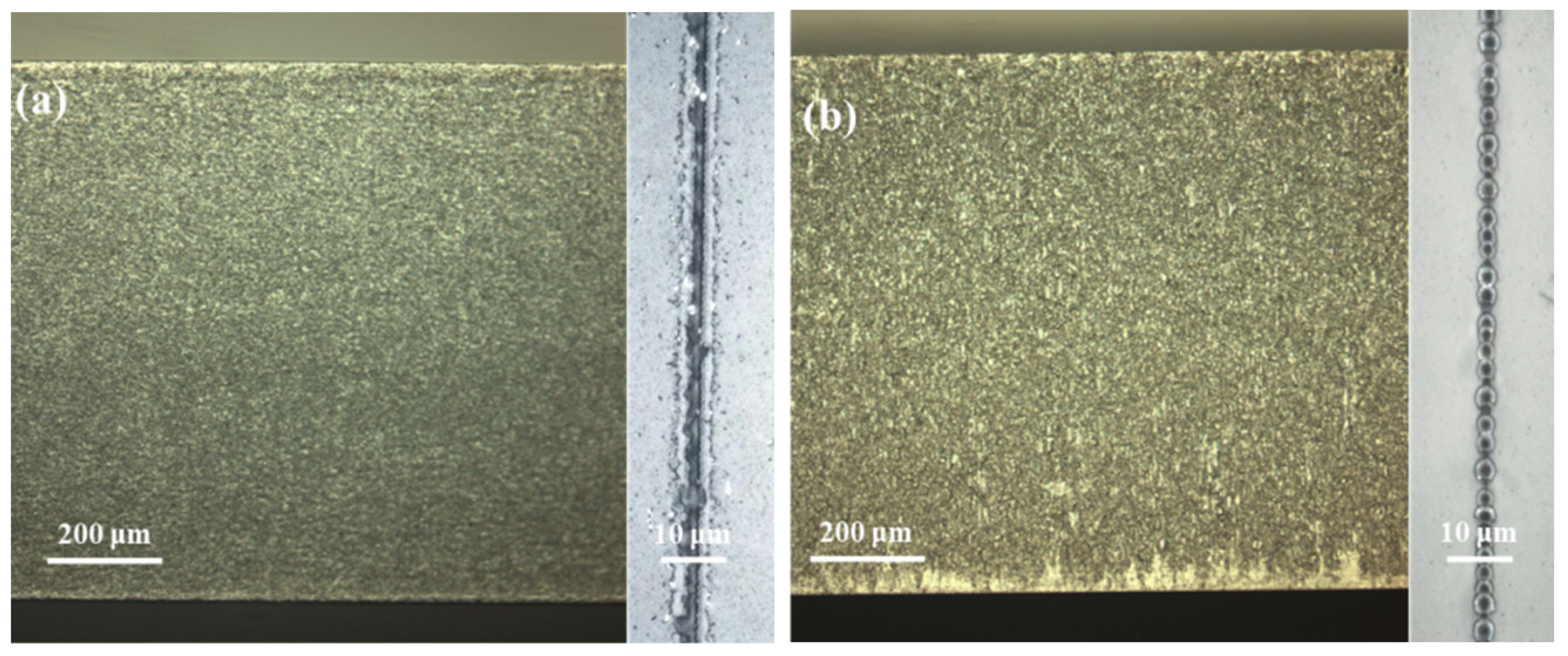
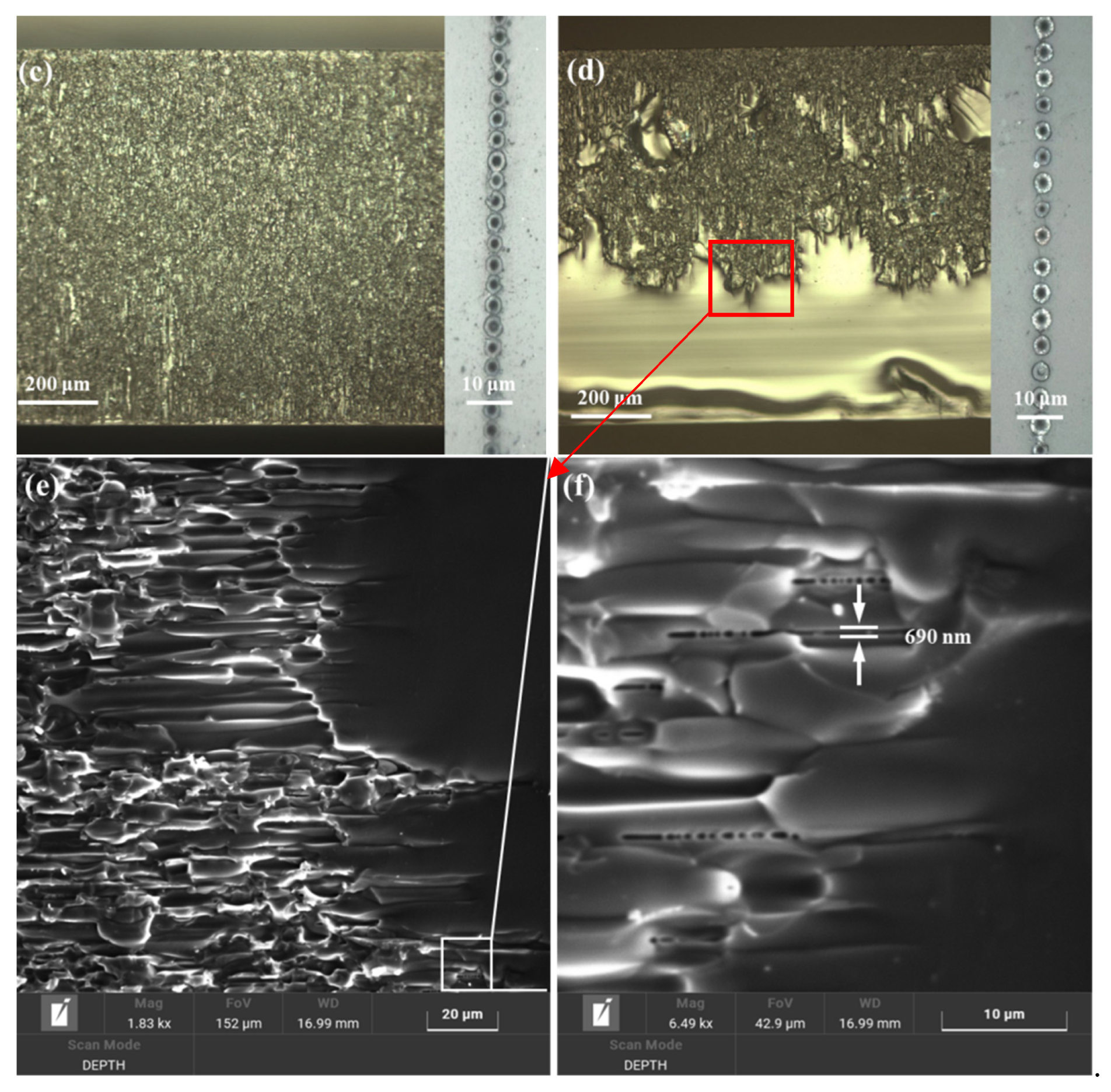
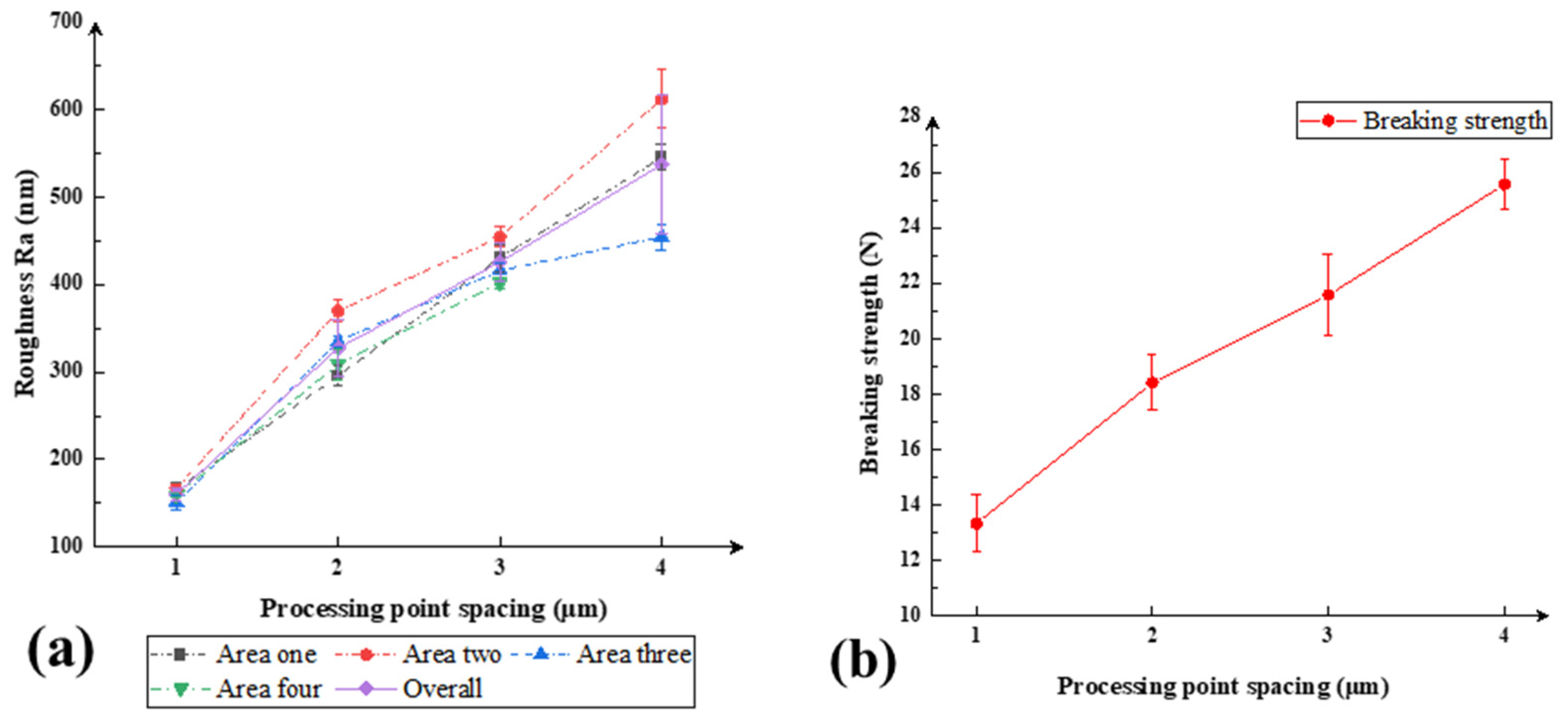
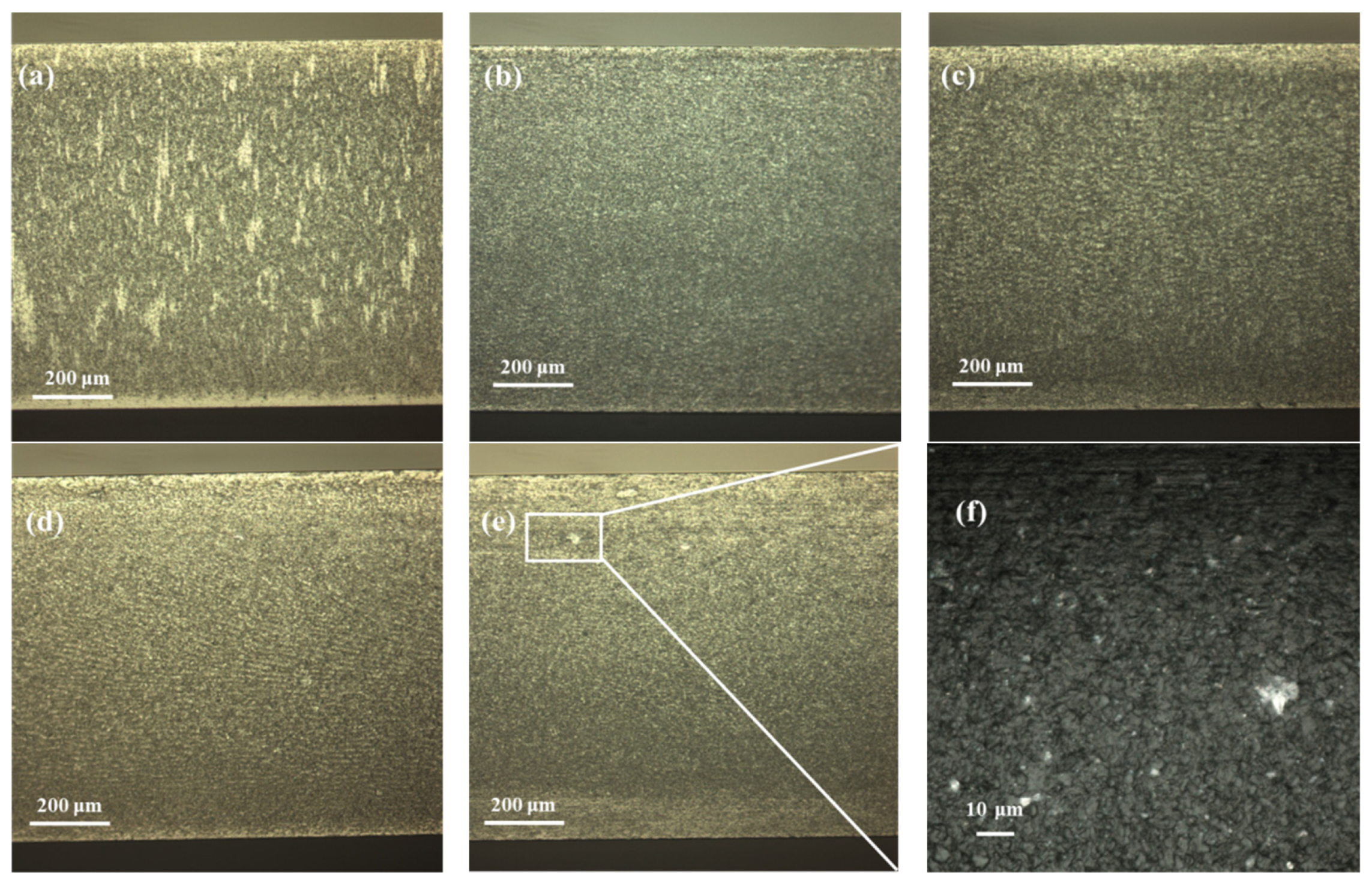
3.1. Influence of Processing Point Spacing on Cutting Quality
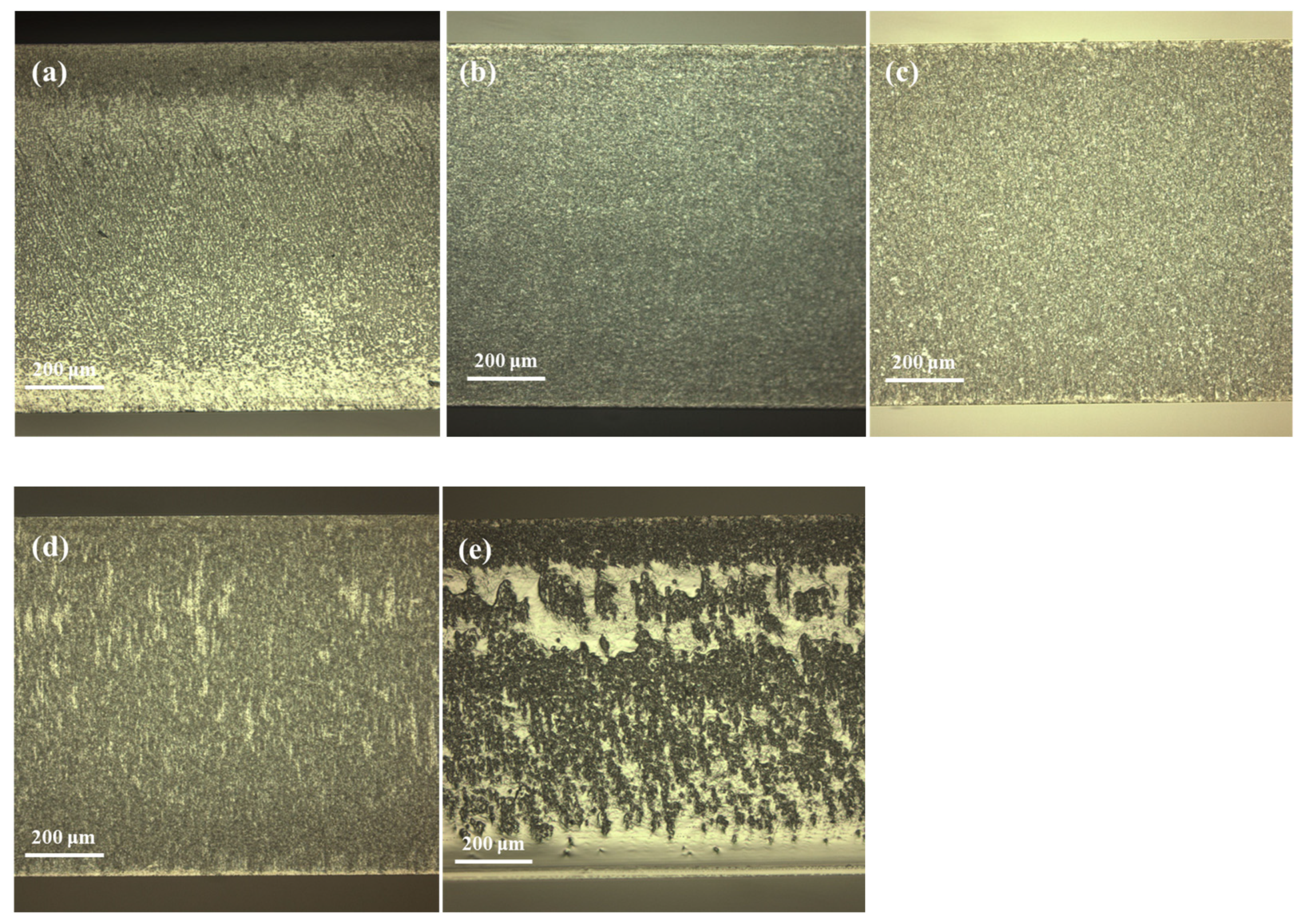
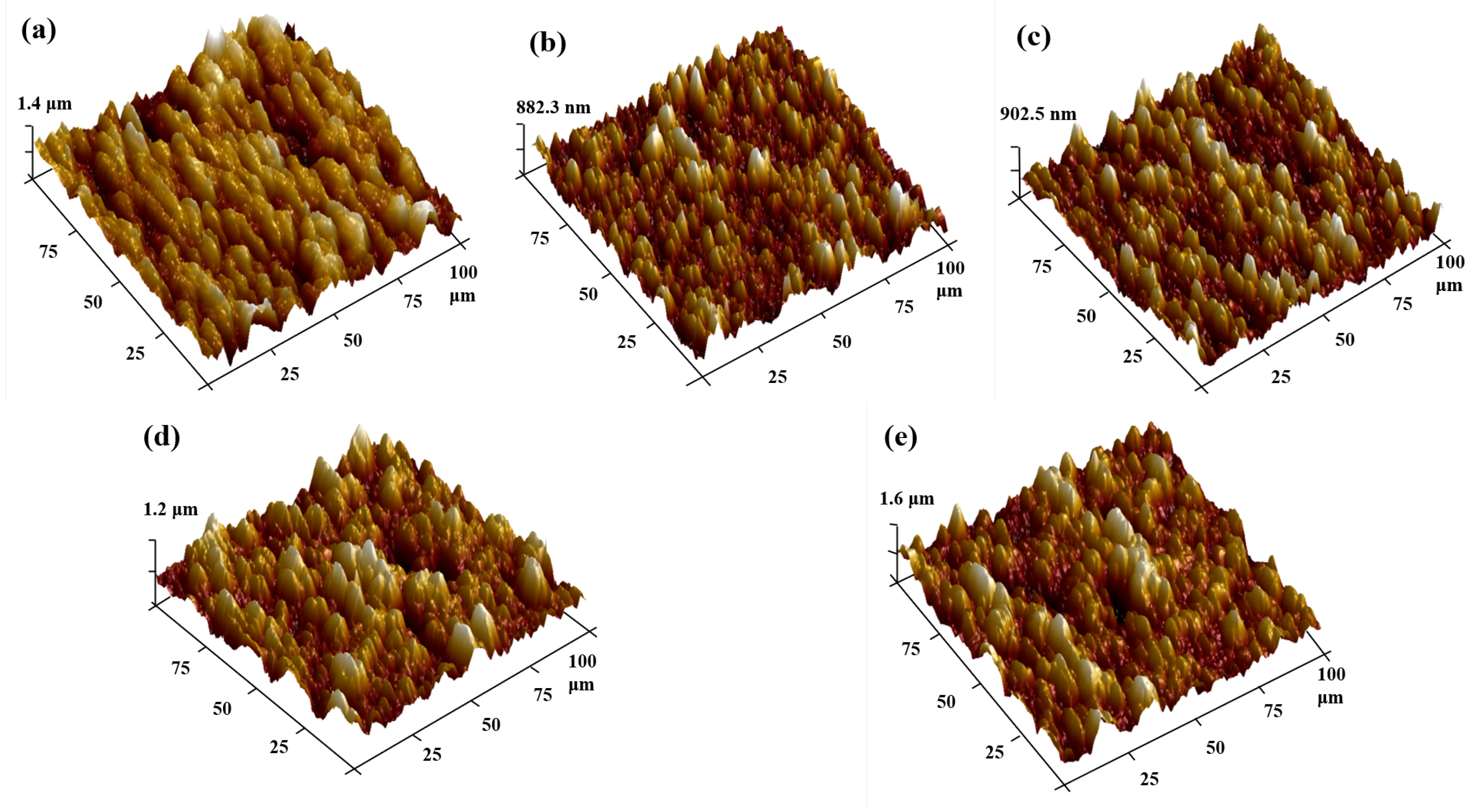
3.2. Influence of Incident Laser Power on Cutting Results
3.3. Influence of the Number of Burst Modes Processed on Cutting Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kartopu, G.; Oklobia, O.; Tansel, T.; Jones, S.; Irvine, S. A facile photolithography process enabling pinhole-free thin film photovoltaic modules on soda-lime glass. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2023, 251, 112112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuehnapfel, S.; Severin, S.; Kersten, N.; Harten, P.; Stegemann, B.; Gall, S. Multi crystalline silicon thin films grown directly on low cost soda-lime glass substrates. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2019, 203, 110168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, S.; Chaudhari, A.; Zhao, Z.; Efstathiadis, H. Textured (111) crystalline silicon thin film growth on flexible glass by e-beam evaporation. Mater. Lett. 2015, 158, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, L.; Norarat, R.; Napari, M.; Kivistö, H.; Chienthavorn, O.; Whitlow, H. Lithographic fabrication of soda-lime glass based microfluidics. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2013, 306, 296–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Chen, M.; Lin, Y.; Li, Z.; Jia, X.; Li, B. A novel adversarial domain adaptation transfer learning method for tool wear state prediction. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 254, 109537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Chen, Y. Sawing stress of sic single crystal with void defect in diamond wire saw slicing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 103, 1019–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Su, H.; Dai, J.; Yu, T.; Zheng, Y. Numerical investigation on the influence of cutting-edge radius and grinding wheel speed on chip formation in sic grinding. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 21451–21460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fang, F.; An, H.; Wu, S.; Qi, H.; Cai, Y.; Guo, G. Laser machining fundamentals: Micro, nano, atomic and close-to-atomic scales. Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. 2023, 5, 012005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, B.; Hojati, F.; Daneshi, A.; Azarhoushang, B. Simulation of laser ablation mechanism of silicon nitride by ultrashort pulse laser. Procedia CIRP 2019, 82, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorhouse, C. Advantages of picosecond laser machining for cutting-edge technologies. Phys. Procedia 2013, 41, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuenschwander, B.; Kramer, T.; Lauer, B.; Jaeggi, B. Burst mode with ps-and fs-pulses: Influence on the removal rate, surface quality, and heat accumulation. In Proceedings of the Laser Applications in Microelectronic and Optoelectronic Manufacturing (LAMOM) XX, San Francisco, CA, USA, 9–12 February 2015; pp. 79–92. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, J.; Ren, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Xu, K.; Wang, Z.; Wang, C. A numerical study of picosecond laser micro-grooving of single crystalline germanium: Mechanism discussion and process simulation. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 69, 351–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinuevo, J.; Rodríguez-Vidal, E.; Quintana, I.; Morales, M.; Molpeceres, C. Experimental investigation into ultrafast laser ablation of polypropylene by burst and single pulse modes. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 152, 108098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Li, K.; Li, Z.; Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Cui, S. Multi-scan picosecond laser welding of non-optical contact soda lime glass. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 161, 109164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Yu, H.; He, C.; Zhao, S.; Ning, C.; Jiang, L.; Lin, X. Laser slicing of 4h-sic wafers based on picosecond laser-induced micro-explosion via multiphoton processes. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 154, 108323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Mei, W.; Wang, Y. Simulation of femtosecond laser ablation sapphire based on free electron density. Opt. Laser Technol. 2019, 113, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Cheng, L.; Tu, X.; He, K.; Ye, Y.; Tao, Y.; Ren, X. Precise preparation of quartz pendulous reed by using picosecond laser modification assisted wet etching. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 163, 109341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriakose, A.; Chiappini, A.; Sotillo, B.; Britel, A.; Aprà, P.; Picollo, F.; Jedrkiewicz, O. Fabrication of conductive micro electrodes in diamond bulk using pulsed bessel beams. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2023, 136, 110034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudutis, J.; Pipiras, J.; Stonys, R.; Daknys, E.; Kilikevičius, A.; Kasparaitis, A.; Račiukaitis, G.; Gečys, P. In-depth comparison of conventional glass cutting technologies with laser-based methods by volumetric scribing using bessel beam and rear-side machining. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 32133–32151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, R.; Jacquot, M.; Giust, R.; Safioui, J.; Rapp, L.; Furfaro, L.; Lacourt, P.-A.; Dudley, J.M.; Courvoisier, F. Single-shot ultrafast laser processing of high-aspect-ratio nanochannels using elliptical bessel beams. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 4307–4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Hoyo, J.; Meyer, R.; Furfaro, L.; Courvoisier, F. Nanoscale confinement of energy deposition in glass by double ultrafast bessel pulses. Nanophotonics 2020, 10, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, K.; Shen, H.; Yao, Z. Experimental study on direct fabrication of micro channel on fused silica by picosecond laser. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 55, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, J.; Niane, S.; Bonamis, G.; Balage, P.; Audouard, E.; Hönninger, C.; Mottay, E.; Manek-Hönninger, I. Percussion drilling in glasses and process dynamics with femtosecond laser ghz-bursts. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 12533–12544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudutis, J.; Stonys, R.; Račiukaitis, G.; Gečys, P. Bessel beam asymmetry control for glass dicing applications. Procedia CIRP 2018, 74, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, K.; Wang, W.; Mei, X.; Cui, J.; Li, M.; Li, X. An analytical model to predict the sizes of modified layer in glass with femtosecond bessel beam. Optik 2019, 185, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Xia, X.; Gai, B.; Liu, D.; Cai, X.; Lou, M.; Li, X.; Guo, J. Laser-induced multiphoton and collisional ionizations in sodium-argon mixture. J. Lumin. 2020, 225, 117370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Yan, T.; Ma, R. Ionization behavior and dynamics of picosecond laser filamentation in sapphire. Opto-Electron. Adv. 2019, 2, 190003. [Google Scholar]
- Jedrkiewicz, O.; Minardi, S.; Couairon, A.; Jukna, V.; Selva, M.; Di Trapani, P. Plasma absorption evidence via chirped pulse spectral transmission measurements. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 231101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergner, K.; Seyfarth, B.; Lammers, K.; Ullsperger, T.; Döring, S.; Heinrich, M.; Kumkar, M.; Flamm, D.; Tünnermann, A.; Nolte, S. Spatio-temporal analysis of glass volume processing using ultrashort laser pulses. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 4618–4632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Eppelt, U.; Hartmann, C.; Schulz, W.; Zhu, J.; Lin, Z. Damage morphology and mechanism in ablation cutting of thin glass sheets with picosecond pulsed lasers. Opt. Laser Technol. 2016, 80, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Wang, R.; Tao, H. Ultrafast laser micromachining the ultra-low expansion glass-ceramic: Optimization of processing parameters and physical mechanism. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2021, 41, 5990–5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Q.; Chen, J.; Huang, G.; Cui, C.; Mu, D. Dependence of monocrystalline sapphire dicing on crystal orientation using picosecond laser bessel beams. Micromachines 2023, 14, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchene, A.; Mollon, G.; Ollivier, M.; Sedao, X.; Pascale-Hamri, A.; Dumazer, G.; Serris, E. Roughness and wettability control of soda-lime silica glass surfaces by femtosecond laser texturing and curing environments. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 630, 157490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Allegre, O.; Guo, W.; Gao, W.; Jia, N.; Li, L. Stealth dicing of sapphire sheets with low surface roughness, zero kerf width, debris/crack-free and zero taper using a femtosecond bessel beam. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 135, 106713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishchik, K.; Chassagne, B.; Javaux-Léger, C.; Hönninger, C.; Mottay, E.; Kling, R.; Lopez, J. Dash line glass-and sapphire-cutting with high power usp laser. In Proceedings of the Frontiers in Ultrafast Optics: Biomedical, Scientific, and Industrial Applications XVI, San Francisco, CA, USA, 14–16 February 2016; pp. 91–106. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, K.; Wang, W.; Mei, X.; Liu, B. High quality full ablation cutting and stealth dicing of silica glass using picosecond laser bessel beam with burst mode. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 9805–9816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudutis, J.; Zubauskas, L.; Daknys, E.; Markauskas, E.; Gvozdaitė, R.; Račiukaitis, G.; Gečys, P. Quality and flexural strength of laser-cut glass: Classical top-down ablation versus water-assisted and bottom-up machining. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 4564–4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.; Kim, D. Strength of ultra-thin glass cut by internal scribing using a femtosecond bessel beam. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 129, 106307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Mechanical Properties | Standard Values |
|---|---|
| Density | 2.2 g/cm3 |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.14~0.17 |
| Thermal conductivity (20 °C) | 1.4 W/m °C |
| Mohs hardness | 7 |
| Refractive index | 1.45845 |
| Coefficient of thermal expansion | 5.4 × 10−7 |
| Young’s modulus | 72,000 MPa |
| Specific heat capacity (20~350 °C) | 670 J/Kg °C |
| Parameters Related to Processing Systems | Standard Values |
|---|---|
| Laser operating frequency | 50 kHz~1000 kHz |
| Pulse width | 15 ps |
| Maximum output power | 30 W |
| Wavelength | 1064 nm |
| Positioning accuracy of the platform | ±5 μm |
| Repetition accuracy | ±2 μm |
| Scaling factor of telescope system | 8 |
| Refractive index of the axial cones | 1.45 |
| Incident Laser Power (W) | Average Roughness of Cross-Section (nm) | Maximum Difference in the Regions (nm) |
|---|---|---|
| 8.4 | 185.92 | 7.33 |
| 11.5 | 159.58 | 15.67 |
| 14.2 | 204.83 | 13.33 |
| 16.83 | 236.58 | 68 |
| 19.01 | 315.5 | 98.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Yang, J.; Chen, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhong, J.; Pan, X. High-Quality Cutting of Soda–Lime Glass with Bessel Beam Picosecond Laser: Optimization of Processing Point Spacing, Incident Power, and Burst Mode. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1885. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14051885
Liu J, Yang J, Chen H, Li J, Zhang D, Zhong J, Pan X. High-Quality Cutting of Soda–Lime Glass with Bessel Beam Picosecond Laser: Optimization of Processing Point Spacing, Incident Power, and Burst Mode. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(5):1885. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14051885
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jiaxuan, Jianjun Yang, Hui Chen, Jinxuan Li, Decheng Zhang, Jian Zhong, and Xinjian Pan. 2024. "High-Quality Cutting of Soda–Lime Glass with Bessel Beam Picosecond Laser: Optimization of Processing Point Spacing, Incident Power, and Burst Mode" Applied Sciences 14, no. 5: 1885. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14051885
APA StyleLiu, J., Yang, J., Chen, H., Li, J., Zhang, D., Zhong, J., & Pan, X. (2024). High-Quality Cutting of Soda–Lime Glass with Bessel Beam Picosecond Laser: Optimization of Processing Point Spacing, Incident Power, and Burst Mode. Applied Sciences, 14(5), 1885. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14051885






