Fast Fake: Easy-to-Train Face Swap Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
3. Methodology
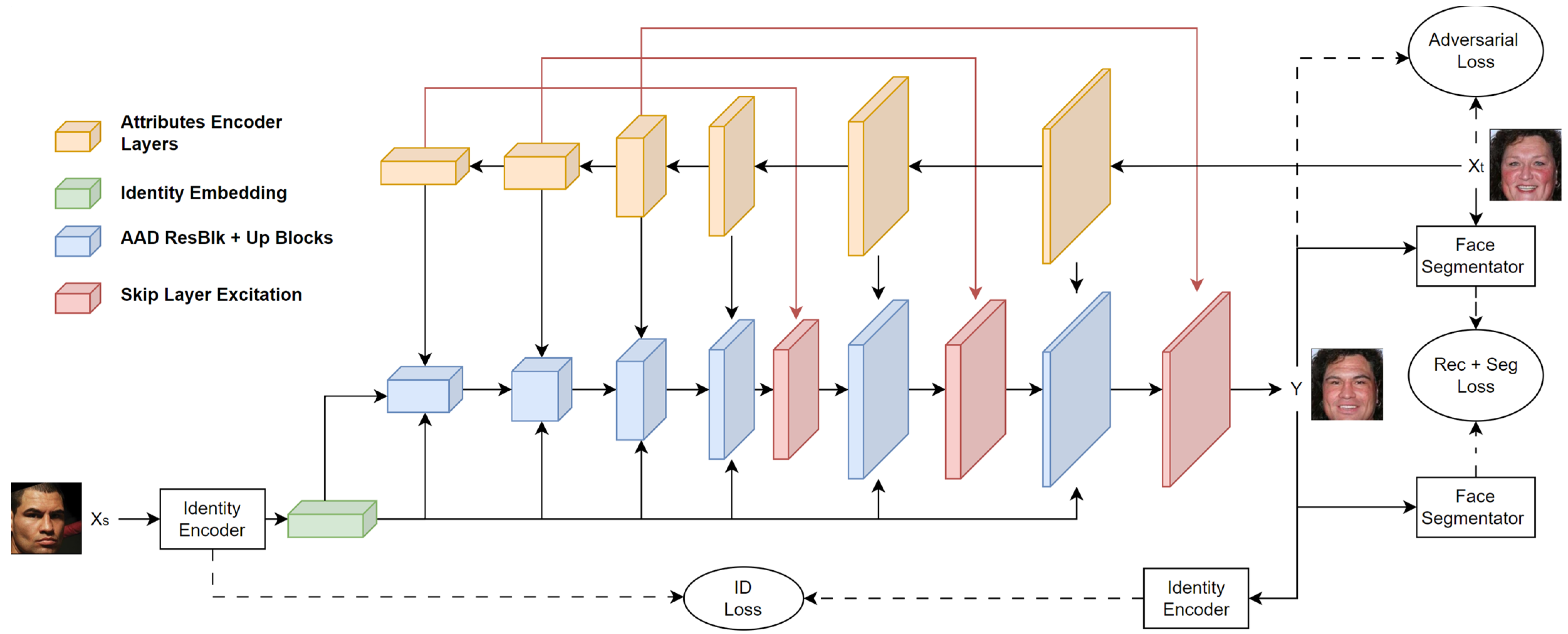
3.1. Architecture
3.2. Loss Functions
4. Experiments
4.1. Implementation Details
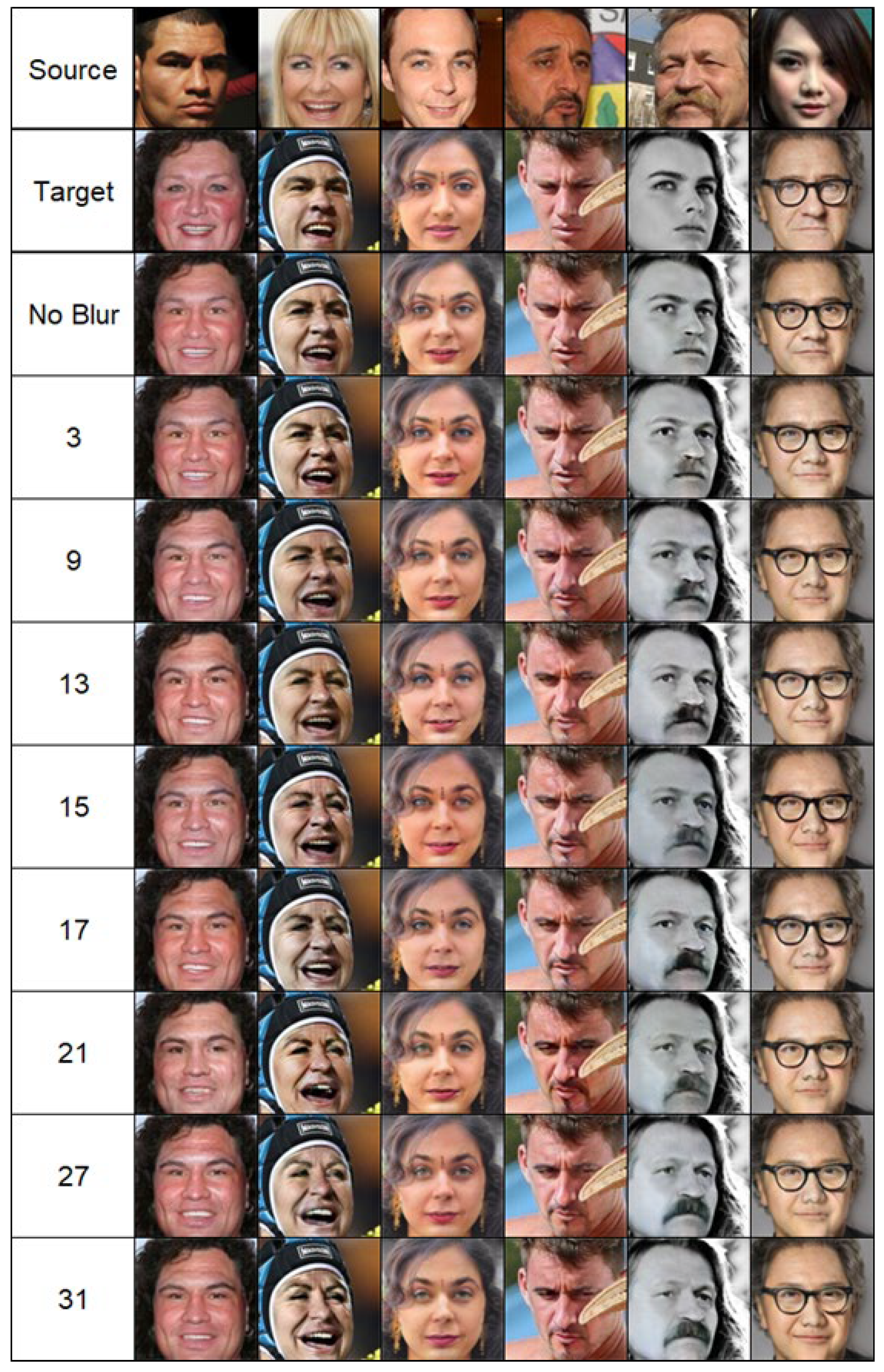
4.2. Results
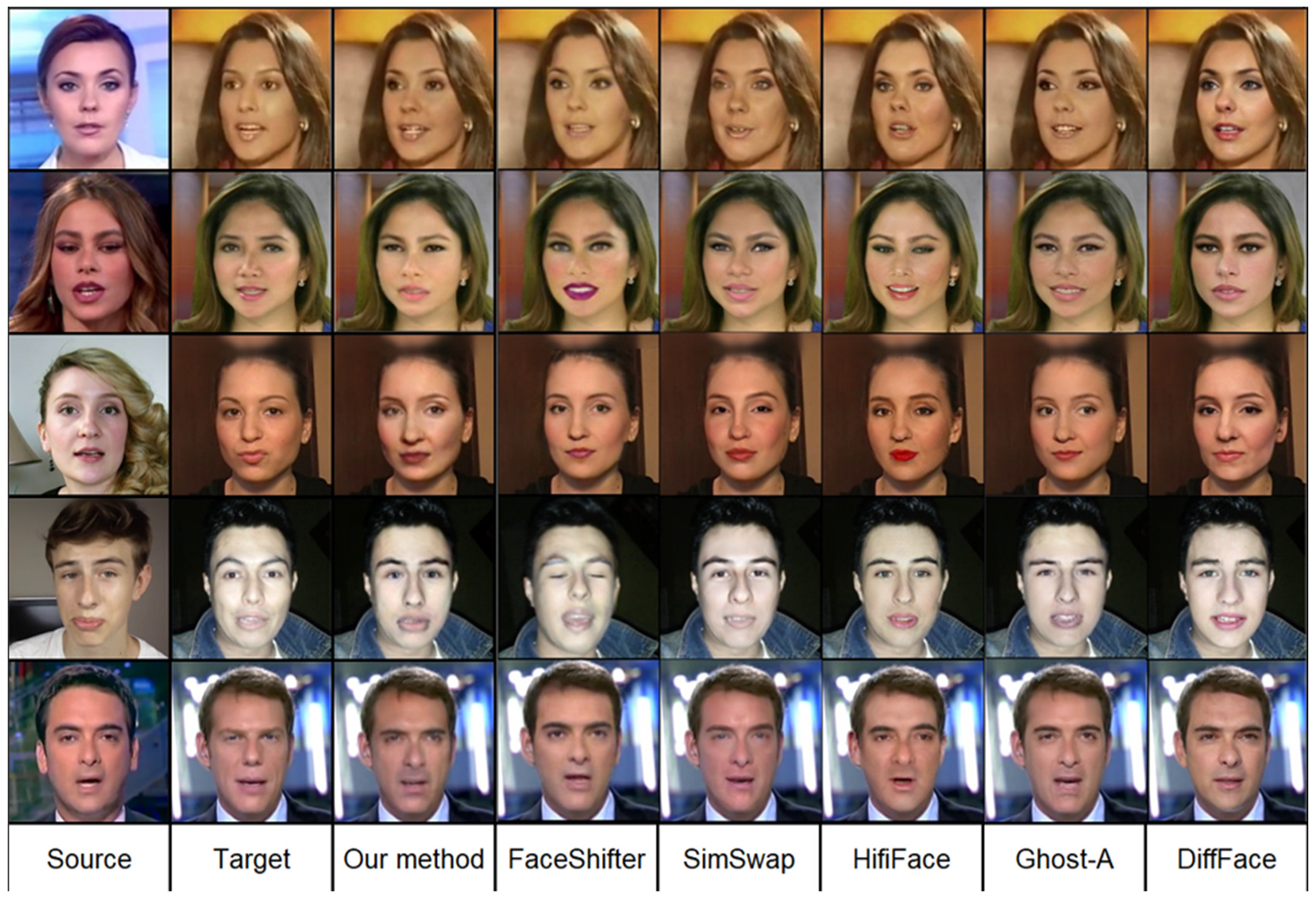
4.3. Comparison with Other Methods
4.4. Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mirsky, Y.; Lee, W. The Creation and Detection of Deepfakes: A Survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2022, 54, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swathi, P.; Saritha, S.K. DeepFake Creation and Detection: A Survey. In Proceedings of the 2021 Third International Conference on Inventive Research in Computing Applications (ICIRCA), Coimbatore, India, 2–4 September 2021; pp. 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, B.U.; Sharmin, A. Deep Insights of Deepfake Technology: A Review. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2105.00192. [Google Scholar]
- Walczyna, T.; Piotrowski, Z. Quick Overview of Face Swap Deep Fakes. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczyna, T.; Piotrowski, Z. Overview of Voice Conversion Methods Based on Deep Learning. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, H.F.; Rustam, F.; Flores, E.S.; Luís Vidal Mazón, J.; de la Torre Diez, I.; Ashraf, I. A Review of Image Processing Techniques for Deepfakes. Sensors 2022, 22, 4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usukhbayar, B. Deepfake Videos: The Future of Entertainment 2020. Master’s Thesis, American University in Bulgaria, Sofia, Bulgaria, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-C.; Rahmanti, A.R.; Huang, C.-W.; Li, Y.-C.J. How Can Research on Artificial Empathy Be Enhanced by Applying Deepfakes? J. Med. Internet Res. 2022, 24, e29506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medical Deepfakes Are the Real Deal. Available online: https://www.mddionline.com/artificial-intelligence/medical-deepfakes-are-the-real-deal (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- Artificial Intelligence: Deepfakes in the Entertainment Industry. Available online: https://www.wipo.int/wipo_magazine/en/2022/02/article_0003.html (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- Caporusso, N. Deepfakes for the Good: A Beneficial Application of Contentious Artificial Intelligence Technology. In Proceedings of the AHFE 2020 Virtual Conferences on Software and Systems Engineering, and Artificial Intelligence and Social Computing, San Diego, CA, USA, 16–20 July 2020; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biddle, S.U.S. Special Forces Want to Use Deepfakes for Psy-Ops. Available online: https://theintercept.com/2023/03/06/pentagon-socom-deepfake-propaganda/ (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- Nasu, H. Deepfake Technology in the Age of Information Warfare. Available online: https://lieber.westpoint.edu/deepfake-technology-age-information-warfare/ (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- Bistron, M.; Piotrowski, Z. Artificial Intelligence Applications in Military Systems and Their Influence on Sense of Security of Citizens. Electronics 2021, 10, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althnian, A.; AlSaeed, D.; Al-Baity, H.; Samha, A.; Dris, A.B.; Alzakari, N.; Abou Elwafa, A.; Kurdi, H. Impact of Dataset Size on Classification Performance: An Empirical Evaluation in the Medical Domain. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigato, L.; Iocchi, L. A Close Look at Deep Learning with Small Data. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.12843. [Google Scholar]
- Olivier, N.; Baert, K.; Danieau, F.; Multon, F.; Avril, Q. FaceTuneGAN: Face Autoencoder for Convolutional Expression Transfer Using Neural Generative Adversarial Networks. Comput. Graph. 2023, 110, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durall, R.; Chatzimichailidis, A.; Labus, P.; Keuper, J. Combating Mode Collapse in GAN training: An Empirical Analysis using Hessian Eigenvalues. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2012.09673. [Google Scholar]
- Thanh-Tung, H.; Tran, T. On Catastrophic Forgetting and Mode Collapse in Generative Adversarial Networks. arXiv 2020, arXiv:1807.04015. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Zhu, Y.; Song, K.; Elgammal, A. Towards Faster and Stabilized GAN Training for High-fidelity Few-shot Image Synthesis. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.04775. [Google Scholar]
- Zendran, M.; Rusiecki, A. Swapping Face Images with Generative Neural Networks for Deepfake Technology—Experimental Study. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021, 192, 834–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perov, I.; Gao, D.; Chervoniy, N.; Liu, K.; Marangonda, S.; Umé, C.; Dpfks, M.; Facenheim, C.S.; RP, L.; Jiang, J.; et al. DeepFaceLab: Integrated, flexible and extensible face-swapping framework. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2005.05535. [Google Scholar]
- Deepfakes. Deepfakes_Faceswap, v2.10.0; GitHub: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2020; Available online: https://github.com/deepfakes/faceswap (accessed on 3 May 2023).
- Chen, R.; Chen, X.; Ni, B.; Ge, Y. SimSwap: An Efficient Framework for High Fidelity Face Swapping. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Seattle, WA, USA, 12–16 October 2020; pp. 2003–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Bao, J.; Yang, H.; Chen, D.; Wen, F. FaceShifter: Towards High Fidelity and Occlusion Aware Face Swapping. arXiv 2020, arXiv:1912.13457. [Google Scholar]
- Groshev, A.; Maltseva, A.; Chesakov, D.; Kuznetsov, A.; Dimitrov, D. GHOST—A New Face Swap Approach for Image and Video Domains. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 83452–83462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhariwal, P.; Nichol, A. Diffusion Models Beat GANs on Image Synthesis. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.05233. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.; Kim, Y.; Cho, S.; Seo, J.; Nam, J.; Lee, K.; Kim, S.; Lee, K. DiffFace: Diffusion-based Face Swapping with Facial Guidance. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2212.13344. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhu, J.; Chu, W.; Tai, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Wu, Y.; Huang, F.; Ji, R. HifiFace: 3D Shape and Semantic Prior Guided High Fidelity Face Swapping. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.09965. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Guo, J.; Yang, J.; Xue, N.; Kotsia, I.; Zafeiriou, S. ArcFace: Additive Angular Margin Loss for Deep Face Recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 44, 5962–5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Wang, J.; Peng, C.; Gao, C.; Yu, G.; Sang, N. BiSeNet: Bilateral Segmentation Network for Real-time Semantic Segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1808.00897. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, N.; Gu, Y.; Liu, X.; Huo, Y.; Qiu, J.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, L.; et al. Pre-Trained Models: Past, Present and Future. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.07139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Wang, N.; Chen, T.; Li, M. Empirical Evaluation of Rectified Activations in Convolutional Network. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1505.00853. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1512.03385. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Albanie, S.; Sun, G.; Wu, E. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1709.01507. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Liu, Z.; Lin, J.; Zhu, J.-Y.; Han, S. Differentiable Augmentation for Data-Efficient GAN Training. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.10738. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A.; Shechtman, E.; Wang, O. The Unreasonable Effectiveness of Deep Features as a Perceptual Metric. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.03924. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, A.; Tapia, S.L.; Molina, R.; Katsaggelos, A.K. Generative Adversarial Networks and Perceptual Losses for Video Super-Resolution. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 3312–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Diakopoulos, N.; Johnson, D. Anticipating and Addressing the Ethical Implications of Deepfakes in the Context of Elections. New Media Soc. 2019, 23, 2072–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Ruiter, A. The Distinct Wrong of Deepfakes. Philos. Technol. 2021, 34, 1311–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasavva, V.; Noorbhai, A. The Real Threat of Deepfake Pornography: A Review of Canadian Policy. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2021, 24, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wan, Y. Norms or fun? The influence of ethical concerns and perceived enjoyment on the regulation of deepfake information. Internet Res. 2023, 33, 1750–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bistroń, M.; Piotrowski, Z. Efficient Video Watermarking Algorithm Based on Convolutional Neural Networks with Entropy-Based Information Mapper. Entropy 2023, 25, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczyński, M.; Piotrowski, Z.; Pietrow, D. High-Quality Video Watermarking Based on Deep Neural Networks for Video with HEVC Compression. Sensors 2022, 22, 7552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczyński, M.; Piotrowski, Z. High-Quality Video Watermarking Based on Deep Neural Networks and Adjustable Subsquares Properties Algorithm. Sensors 2022, 22, 5376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Walczyna, T.; Piotrowski, Z. Fast Fake: Easy-to-Train Face Swap Model. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2149. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14052149
Walczyna T, Piotrowski Z. Fast Fake: Easy-to-Train Face Swap Model. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(5):2149. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14052149
Chicago/Turabian StyleWalczyna, Tomasz, and Zbigniew Piotrowski. 2024. "Fast Fake: Easy-to-Train Face Swap Model" Applied Sciences 14, no. 5: 2149. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14052149
APA StyleWalczyna, T., & Piotrowski, Z. (2024). Fast Fake: Easy-to-Train Face Swap Model. Applied Sciences, 14(5), 2149. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14052149






