Corn Cropping Systems in Agricultural Soils from the Bajio Region of Guanajuato: Soil Quality Indexes (SQIs)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Preparation and Maintenance of Samples
2.4. Physicochemical Characterization
2.5. Biological Characterization
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. SQI Development
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical and Biological Characterisation of Soils
3.2. Soil Enzyme Profile
3.3. PCA
3.4. Establishment of the SQI
3.5. Considerations and Perspectives
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muñoz-Rojas, M.; Erickson, T.E.; Dixon, K.W.; Merritt, D.J. Soil Quality Indicators to Assess Functionality of Restored Soils in Degraded Semiarid Ecosystems. Restor. Ecol. 2016, 24, S43–S52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales [SEMARNAT]. NOM-021-RECNAT-2002; Diario Oficial de la Federación; Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales: Mexico City, Mexico, 2002. Available online: https://biblioteca.semarnat.gob.mx/janium/Documentos/Ciga/libros2009/DO2280n.pdf (accessed on 19 March 2024).
- Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales [SEMARNAT]. Estrategia Nacional de Manejo Sustentable de Tierras; Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales: Mexico City, Mexico, 2011.
- Etchevers, J.; Hidalgo, C.; Paz Pellat, F. Soil Degradation and the Need for Public Policies. Elem. Para Políticas Públicas 2022, 3, 267–273. [Google Scholar]
- García-Lara, S.; Serna-Saldivar, S.O. Corn History and Culture. In Corn; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 1–18. ISBN 978-0-12-811971-6. [Google Scholar]
- Rangel-Peraza, J.G.; Padilla-Gasca, E.; López-Corrales, R.; Medina, J.R.; Bustos-Terrones, Y.; Amabilis-Sosa, L.E.; Rodríguez-Mata, A.E.; Osuna-Enciso, T. Robust Soil Quality Index for Tropical Soils Influenced by Agricultural Activities. J. Agric. Chem. Environ. 2017, 06, 199–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, A.; Ascanio, M.; Morales, M.; Borjórquez, I.; García, N.; García, D. El Suelo: Fundamentos Sobre su Formación, los Cambios Globales y su Manejo; Universidad Autónoma de Nayarit: Tepic, Mexico, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Juhos, K.; Czigány, S.; Madarász, B.; Ladányi, M. Interpretation of Soil Quality Indicators for Land Suitability Assessment—A Multivariate Approach for Central European Arable Soils. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 99, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuñez-Peñaloza, J.L.; Pérez-Nieto, J.; Prado-Hernández, J.V. Análisis de indicadores e índices de calidad de suelos en México. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Agríc. 2023, 14, e3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Fattah, M.K.; Mohamed, E.S.; Wagdi, E.M.; Shahin, S.A.; Aldosari, A.A.; Lasaponara, R.; Alnaimy, M.A. Quantitative Evaluation of Soil Quality Using Principal Component Analysis: The Case Study of El-Fayoum Depression Egypt. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Bhattacharyya, R.; Das, T.K.; Sharma, A.R.; Dwivedi, B.S.; Meena, M.C.; Dey, A.; Biswas, S.; Aditya, K.; Aggarwal, P.; et al. Soil Quality Indices in a Conservation Agriculture Based Rice-Mustard Cropping System in North-Western Indo-Gangetic Plains. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 208, 104914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto Nacional para el Federalismo y el Desarrollo Municipal [INAFED]. Sistema Nacional de Información Municipal 2022. Available online: http://www.snim.rami.gob.mx/ (accessed on 19 March 2024).
- Deckers, J.A.; Driessen, P.M.; Nachtergaele, F.O.; Spaargaren, O.C. World Reference Base for Soil Resources. In Encyclopedia of Soil Science; Marcel Dekker: New City, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 1446–1451. [Google Scholar]
- Vasu, D.; Singh, S.K.; Ray, S.K.; Duraisami, V.P.; Tiwary, P.; Chandran, P.; Nimkar, A.M.; Anantwar, S.G. Soil Quality Index (SQI) as a Tool to Evaluate Crop Productivity in Semi-Arid Deccan Plateau, India. Geoderma 2016, 282, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales [SEMARNAT]. NOM-004-SEMARNAT-2002; Diario Oficial de la Federación; Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales: Mexico City, Mexico, 2003. Available online: https://www.dof.gob.mx/nota_detalle.php?codigo=691939&fecha=15/08/2003#gsc.tab=0 (accessed on 19 March 2024).
- Bouyoucos, G.J. Hydrometer Method Improved for Making Particle Size Analyses of Soils 1. Agron. J. 1962, 54, 464–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA). Soil Survey Manual; United Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1951.
- Thomas, G.W. Soil pH and Soil Acidity. In Chemical Methods; Sparks, D.L., Page, A.L., Helmke, P.A., Loeppert, R.H., Soltanpour, P.N., Tabatabai, M.A., Johnston, C.T., Summer, M.E., Eds.; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 2018; pp. 475–490. [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickx, J.M.H.; Das, B.; Corwin, D.L.; Wraith, J.M.; Kachanoski, R.G. Relationship Between Soil Water Solute Concentration and Apparent Soil Electrical Conductivity. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 4; Dane, J.H., Topp, G.C., Eds.; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 2002; pp. 1275–1282. [Google Scholar]
- Nannipieri, P. Soil Is Still an Unknown Biological System. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkley, A.; Black, I.A. An Examination of Different Methods for Determining Soil Organic Matter and a Proposed Modification of the Chromic Acid Titration Method. Soil Sci. 1934, 37, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, E.; Sönmez, M. The Role of Organic/Bio–Fertilizer Amendment on Aggregate Stability and Organic Carbon Content in Different Aggregate Scales. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 168, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremner, J.M. Nitrogen-Total. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Chemical Methods; Sparks, D.L., Page, A.L., Helmke, P.A., Loeppert, R.H., Soltanpour, P.N., Tabatabai, M.A., Johnston, C.T., Summer, M.E., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Madison, WI, USA, 2018; pp. 1085–1121. [Google Scholar]
- Bettinelli, M.; Baroni, U. A Microwave Oven Digestion Method for the Determination of Metals in Sewage Sludges by ICP-AES and GFAAS. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 1991, 43, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottenie, A. Soil and Plant Testing as a Basis of Fertilizer Recommendations. FAO Soils Bull. 1980, 382, 64–65. [Google Scholar]
- Alef, K.; Nannipieri, P. Methods in Applied Soil Microbiology and Biochemistry; Elsevier: London, UK, 1995; ISBN 978-0-12-513840-6. [Google Scholar]
- Joergensen, R.G.; Brookes, P.C. Ninhydrin-Reactive Nitrogen Measurements of Microbial Biomass in 0.5 m K2SO4 Soil Extracts. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1990, 22, 1023–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparling, G.P. Ratio of Microbial Biomass Carbon to Soil Organic Carbon as a Sensitive Indicator of Changes in Soil Organic Matter. Aust. J. Soil Res. 1992, 30, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, V.S.; Stott, D.E.; Diack, M. Assay for Fluorescein Diacetate Hydrolytic Activity: Optimization for Soil Samples. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T.H.; Domsch, K.M. Ratios of Microbial Biomass Carbon to Total Organic-C in Arable Soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1989, 21, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, D.; Molina, M.J.; Sánchez, J.; Moscatelli, M.C.; Marinari, S. API ZYM Assay to Evaluate Enzyme Fingerprinting and Microbial Functional Diversity in Relation to Soil Processes. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2016, 52, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.; Gismondi, R.; Alsaffar, A.; Tiquia-Arashiro, S.M. Applicability of API ZYM to Capture Seasonal and Spatial Variabilities in Lake and River Sediments. Environ. Technol. 2019, 40, 3227–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team R: Language and Environment for Statistical Computing 2021. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/mirrors.html (accessed on 19 March 2024).
- Johnson, R.; Wichern, D. Applied Multivariate Statistical Analysis, 6th ed.; Pearson Education Limited: Edinburgh, UK, 2014; ISBN 978-1-292-02494-3. [Google Scholar]
- Mahajan, G.; Das, B.; Morajkar, S.; Desai, A.; Murgaokar, D.; Kulkarni, R.; Sale, R.; Patel, K. Soil Quality Assessment of Coastal Salt-Affected Acid Soils of India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 26221–26238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villazón Gómez, J.; Martín-Gutiérrez, G.; Cobo-Vidal, Y. Análisis Multivariado de Las Propiedades Químicas de los Suelos Pardos Erosionados. Cent. Agric. 2017, 44, 56–62. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Z.; Caspari, T.; Gonzalez, M.R.; Batjes, N.H.; Mäder, P.; Bünemann, E.K.; de Goede, R.; Brussaard, L.; Xu, M.; Ferreira, C.S.S.; et al. Effects of Agricultural Management Practices on Soil Quality: A Review of Long-Term Experiments for Europe and China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 265, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Zhou, D. Selecting the Minimum Data Set and Quantitative Soil Quality Indexing of Alkaline Soils Under Different Land Uses in Northeastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, A.C.R.; Brussaard, L.; Totola, M.R.; Hoogmoed, W.B.; de Goede, R.G.M. A Functional Evaluation of Three Indicator Sets for Assessing Soil Quality. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2013, 64, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-Méndez, J.; Prieto-García, F.; Acevedo-Sandoval, O.A.; Méndez-Marzo, M.A. Indicadores e Indices de Calidad de Los Suelos (ICS) Cebaderos del Sur Del Estado de Hidalgo, México. Agron. Mesoam. 2013, 24, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Lee, S.H.; Ji, H.C.; Kabir, A.H.; Jones, C.S.; Lee, K.W. Importance of Mineral Nutrition for Mitigating Aluminum Toxicity in Plants on Acidic Soils: Current Status and Opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Li, D.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, W.; Xiao, K.; Wang, K. Nitrogen Addition Aggravates Microbial Carbon Limitation: Evidence from Ecoenzymatic Stoichiometry. Geoderma 2018, 329, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, N.; Bahuguna, V.; Kumar, V. A Review on Microalgae Application in Bioenergy Generation & Integrated Wastewater Management. SSRN Electron. J. 2018. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3298651 (accessed on 19 March 2024).
- Costa, O.Y.A.; Raaijmakers, J.M.; Kuramae, E.E. Microbial Extracellular Polymeric Substances: Ecological Function and Impact on Soil Aggregation. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 337094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leogrande, R.; Vitti, C. Use of Organic Amendments to Reclaim Saline and Sodic Soils: A Review. Arid Land Res. Manag. 2019, 33, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, S.; Ma, R.; Chen, M.; Wei, W.; Ding, X. Carbon Sequestration Under Different Organic Amendments in Saline-Alkaline Soils. CATENA 2021, 196, 104882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanor, G.A.; López Pérez, M.E.; Martínez Yáñez, R.; Ramírez Santoyo, L.F.; Gutiérrez Vargas, S.; León Galván, M.F. Mejoramiento de Las Propiedades Físicas y Químicas de Un Suelo Agrícola Mezclado Con Lombricompostas de Dos Efluentes de Biodigestor. Ing. Investig. Tecnol. 2018, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, V.N.L.; Greene, R.S.B.; Dalal, R.C.; Murphy, B.W. Soil Carbon Dynamics in Saline and Sodic Soils: A Review. Soil Use Manag. 2010, 26, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zungu, N.S.; Egbewale, S.O.; Olaniran, A.O.; Pérez-fernández, M.; Magadlela, A. Soil Nutrition, Microbial Composition and Associated Soil Enzyme Activities in KwaZulu-Natal Grasslands and Savannah Ecosystems Soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 155, 103663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Razavi, B.S.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, S.; Wu, J.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Ge, T. Labile Carbon Matters More than Temperature for Enzyme Activity in Paddy Soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 135, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacprzak, M.; Kupich, I.; Jasinska, A.; Fijalkowski, K. Bio-Based Waste’ Substrates for Degraded Soil Improvement—Advantages and Challenges in European Context. Energies 2022, 15, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzi, M.; Shahbazi, K.; Kharazi, N.; Rezaei, M. The Influence of Organic Amendment Source on Carbon and Nitrogen Mineralization in Different Soils. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2020, 20, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Li, L.; Friman, V.-P.; Guo, J.; Guo, S.; Shen, Q.; Ling, N. Organic Amendments Increase Crop Yields by Improving Microbe-Mediated Soil Functioning of Agroecosystems: A Meta-Analysis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 124, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Herrera, M.d.R.; Negrete-Rodríguez, M.d.l.L.X.; Álvarez-Trejo, J.L.; Samaniego-Hernández, M.; González-Cruz, L.; Bernardino-Nicanor, A.; Conde-Barajas, E. Evaluation of Non-Conventional Biological and Molecular Parameters as Potential Indicators of Quality and Functionality of Urban Biosolids Used as Organic Amendments of Agricultural Soils. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedolla-Rivera, H.I.; Xochilt Negrete-Rodríguez, M.d.l.L.; Medina-Herrera, M.d.R.; Gámez-Vázquez, F.P.; Álvarez-Bernal, D.; Samaniego-Hernández, M.; Gámez-Vázquez, A.J.; Conde-Barajas, E. Development of a Soil Quality Index for Soils under Different Agricultural Management Conditions in the Central Lowlands of Mexico: Physicochemical, Biological and Ecophysiological Indicators. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, M.; Ansari, A.A.; Gill, S.S. (Eds.) Contaminants in Agriculture: Sources, Impacts and Management; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; ISBN 978-3-030-41551-8. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Liu, S.; Gong, Y. Evaluation of Soil Quality and Maize Growth in Different Profiles of Reclaimed Land with Coal Gangue Filling. Land 2021, 10, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assunção, S.J.R.; Pedrotti, A.; Gonzaga, M.I.S.; Nobrega, J.C.A.; Holanda, F.S.R. Soil Quality Index of an Ultisol under Long-Term Plots in the Coastal Tablelands in Northeastern Brazil. Rev. Caatinga 2023, 36, 432–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, H.C.; Ashworth, A.J.; Wienhold, B.J.; Savin, M.C.; Allen, F.L.; Saxton, A.M.; Curi, N. Soil Quality Indices Based on Long-Term Conservation Cropping Systems Management. Agrosyst. Geosci. Environ. 2020, 3, e20036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
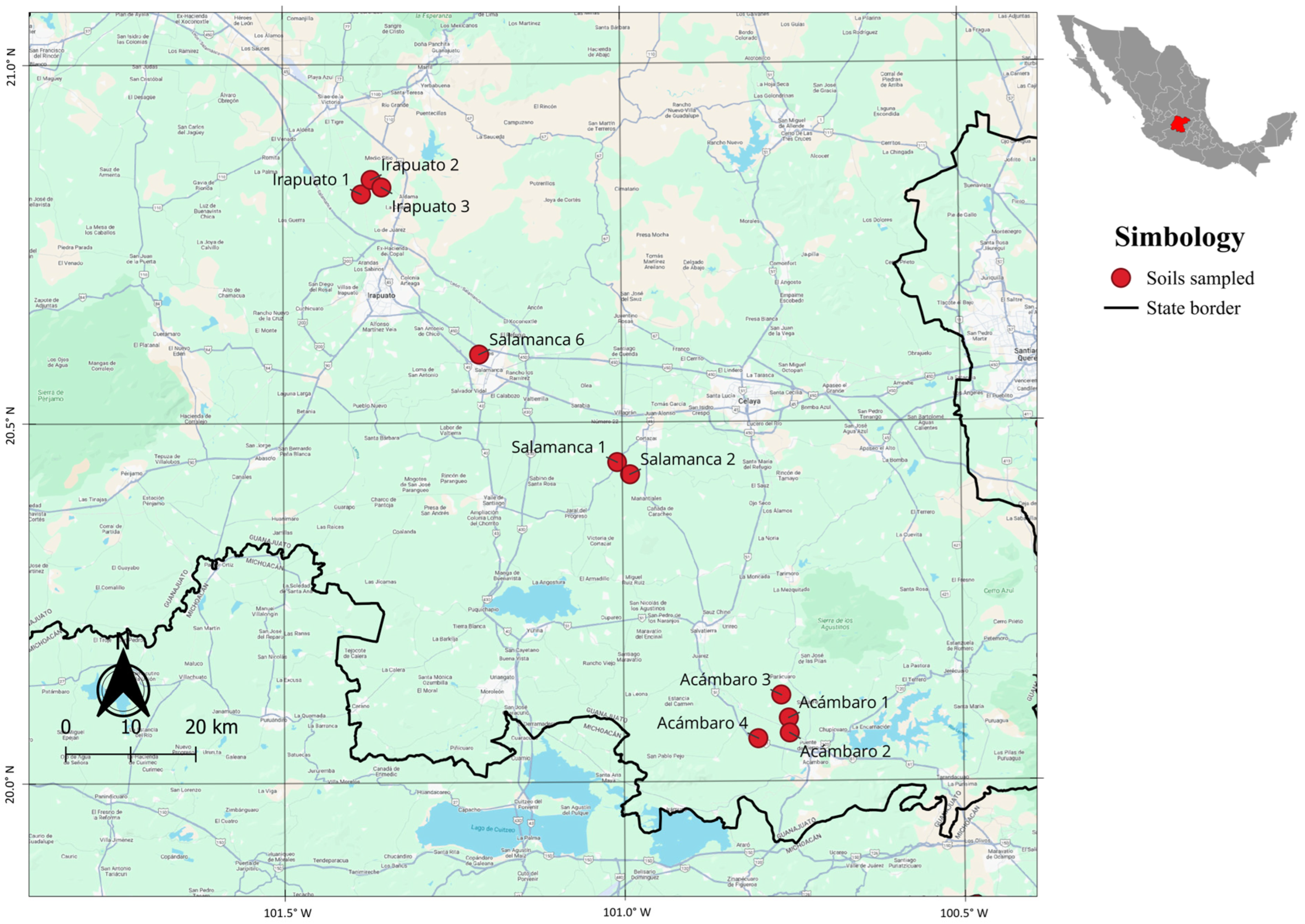

| Municipality | Soil | Type of Irrigation | Fertilization (NPK) | Tillage | Yield | Localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acámbaro | Ac1 | Rolled | 240-40-00 | Conventional | 8.5–12.0 t ha−1 | 20°05′13.32″ N, 100°45′25.62″ W |
| Ac2 | Rolled | 240-40-00 | Conventional | 8.5–12.0 t ha−1 | 20°03′57.77″ N, 100°45′20.95″ W | |
| Ac3 | Rolled | 240-40-00 | Conventional | 8.5–12.0 t ha−1 | 20°03′31.20″ N, 100°48′07.58″ W | |
| Ac4 | Rolled | 240-40-00 | Conventional | 8.5–12.0 t ha−1 | 20°04′36.31″ N, 100°44′37.74″ W | |
| Salamanca | Sa1 | Rolled | 240-40-00 | Conventional | 8.5–12.0 t ha−1 | 20°26′38.56″ N, 101°00′26.72″ W |
| Sa2 | Rolled | 240-40-00 | Conventional | 8.5–12.0 t ha−1 | 20°25′37.58″ N, 100°59′18.57″ W | |
| Sa6 | Rolled | 240-40-00 | Conventional | 8.5–12.0 t ha−1 | 20°35′42.42″ N, 101°12′37.97″ W | |
| Irapuato | Ir1 | Rolled | 240-40-00 | Conventional | 8.5–12.0 t ha−1 | 20°49′08.48″ N, 101°23′02.82″ W |
| Ir2 | Rolled | 240-40-00 | Conventional | 8.5–12.0 t ha−1 | 20°50′21.64″ N, 101°22′10.45″ W | |
| Ir3 | Rolled | 240-40-00 | Conventional | 8.5–12.0 t ha−1 | 20°49′42.58″ N, 101°21′13.54″ W |
| Soil Quality | Very High | High | Moderate | Low | Very Low |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scale | 0.80–1.00 | 0.60–0.79 | 0.40–0.59 | 0.20–0.39 | 0.00–0.19 |
| Class | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Indicators | Soils | p | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ac1 | Ac2 | Ac3 | Ac4 | Ir1 | Ir2 | Ir3 | Sa1 | Sa2 | Sa6 | ||
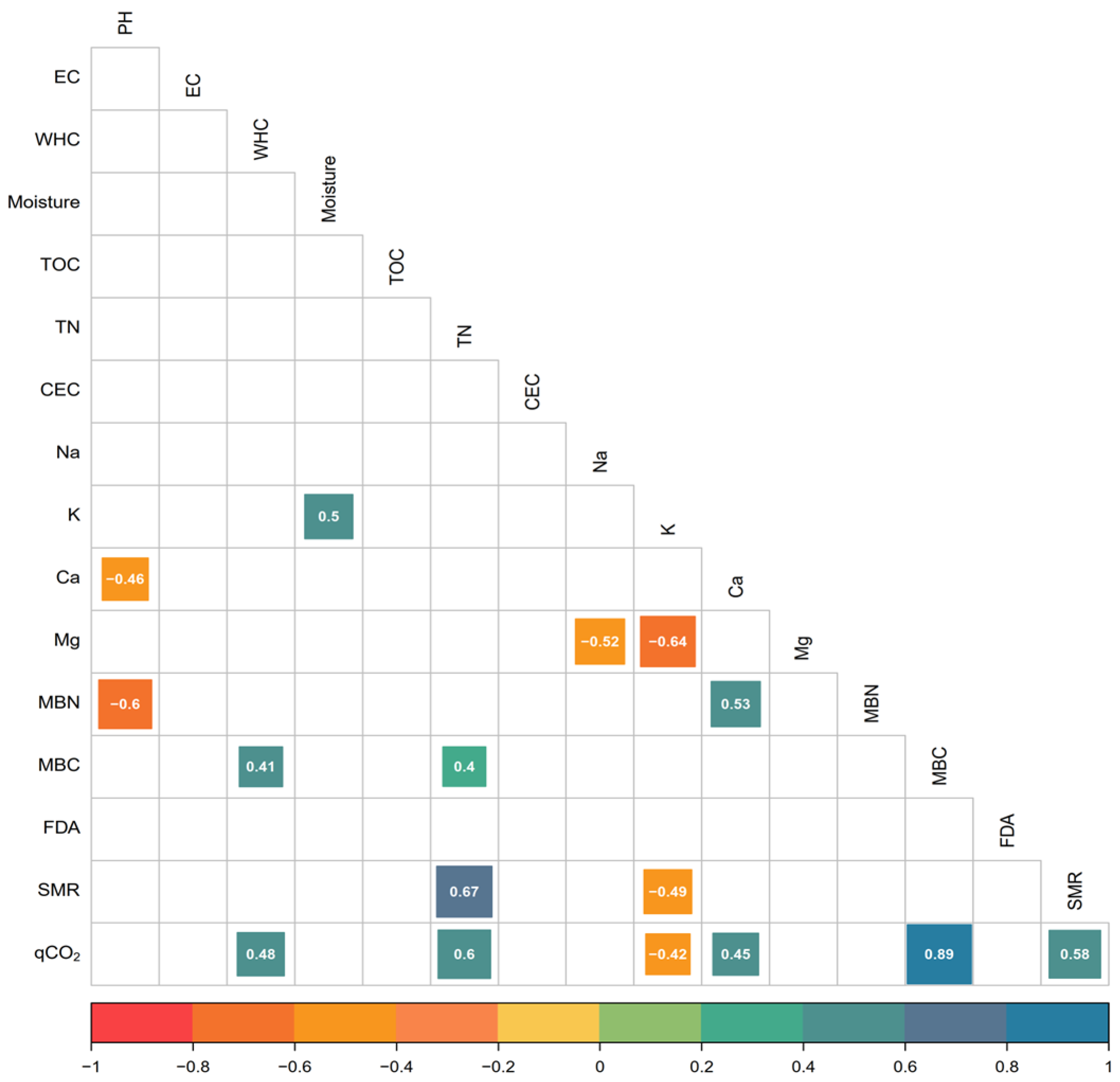
| pH | 7.29a | 6.27cd | 6.07de | 5.89e | 6.97b | 6.29cd | 6.96b | 6.40c | 6.91b | 6.17cde | <0.01 |
| EC | 0.24a | 0.24a | 0.14a | 0.22a | 0.18a | 0.21a | 0.24a | 0.32a | 0.28a | 0.20a | ns |
| WHC | 89a | 72a | 120a | 81a | 82a | 77a | 75a | 92a | 96a | 101a | ns |
| Moisture | 20.1de | 29.5ab | 19.8e | 23.7cde | 27.6abc | 32.5a | 26.2bc | 25.6bcd | 28.9abc | 29.0abc | <0.01 |
| TOC | 2.50ab | 2.74ab | 2.50ab | 2.20b | 2.27b | 1.87b | 2.96ab | 2.49ab | 3.68a | 2.64ab | <0.01 |
| TN | 0.161g | 0.159h | 0.181a | 0.171f | 0.177b | 0.172e | 0.173d | 0.176c | 0.176c | 0.172e | <0.01 |
| CEC | 6.00a | 5.24cd | 5.80ab | 5.58abc | 5.36bc | 5.83ab | 4.76d | 5.18cd | 5.82ab | 5.40bc | <0.01 |
| Na | 2.32a | 1.74cd | 1.19e | 2.11ab | 2.21a | 1.66d | 0.93f | 1.21e | 1.95bc | 2.17ab | <0.01 |
| K | 1.88a | 1.92a | 1.37b | 1.99a | 2.02a | 2.07a | 1.98a | 1.84a | 2.03a | 1.84a | ns |
| Ca | 0.27cd | 0.24d | 0.42b | 0.48a | 0.28cd | 0.47ab | 0.49a | 0.30c | 0.29cd | 0.49a | <0.01 |
| Mg | 1.54d | 1.49d | 2.84a | 1.11f | 0.99g | 1.74c | 1.38e | 1.75c | 1.88b | 1.09f | <0.01 |
| Indicators | Soils | p | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ac1 | Ac2 | Ac3 | Ac4 | Ir1 | Ir2 | Ir3 | Sa1 | Sa2 | Sa6 | ||
| MBN | 163de | 190c | 220ab | 244a | 119f | 194c | 210bc | 187cd | 159e | 159e | <0.01 |
| MBC | 144abcd | 36d | 144ab | 96abcd | 132abc | 72bcd | 114abcd | 60cd | 114abcd | 168a | <0.01 |
| FDA | 103a | 40b | 68ab | 67ab | 38b | 59ab | 65ab | 40b | 56ab | 65ab | <0.01 |
| SMR | 144b | 108b | 216a | 162ab | 144ab | 144ab | 168ab | 168ab | 150ab | 138b | <0.01 |
| qco2 | 30bc | 11c | 84a | 39bc | 54ab | 29bc | 56ab | 26bc | 41bc | 67ab | <0.01 |
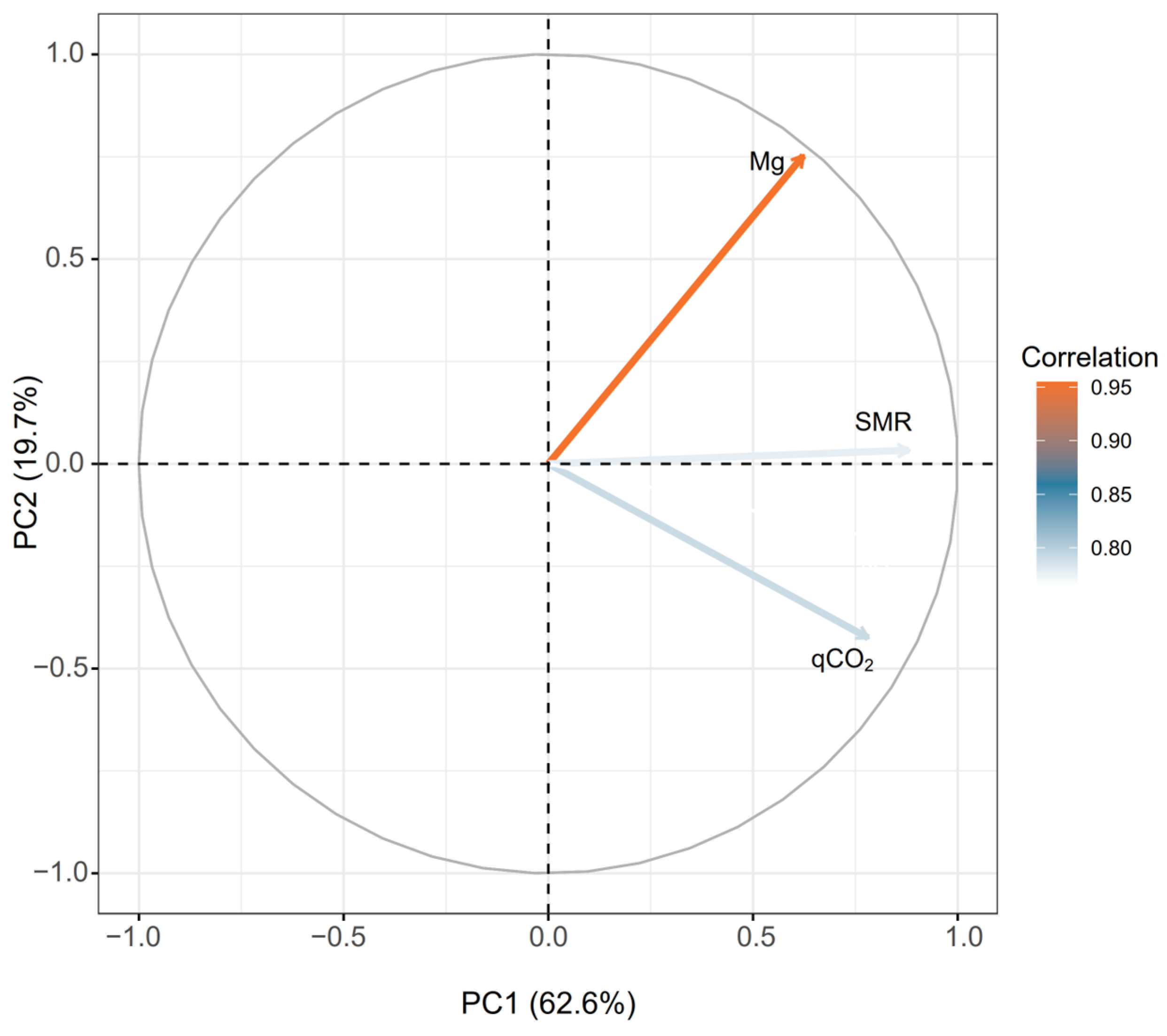
| Indicator | PC1 | PC2 |
|---|---|---|
| TN | 0.85 | --- |
| Mg | --- | 0.75 |
| SMR | 0.88 | --- |
| qCO2 | 0.78 | --- |
| Soil | SQI | Quality | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ac1 | 0.43ab | Moderate | <0.001 |
| Ac2 | 0.59ab | Moderate | <0.001 |
| Ac3 | 0.48ab | Moderate | <0.001 |
| Ac4 | 0.53ab | Moderate | <0.001 |
| Ir1 | 0.45ab | Moderate | <0.001 |
| Ir2 | 0.57ab | Moderate | <0.001 |
| Ir3 | 0.52ab | Moderate | <0.001 |
| Sa1 | 0.63a | High | <0.001 |
| Sa2 | 0.54ab | Moderate | <0.001 |
| Sa6 | 0.39b | Low | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sánchez-Guzmán, A.; Bedolla-Rivera, H.I.; Conde-Barajas, E.; Negrete-Rodríguez, M.d.l.L.X.; Lastiri-Hernández, M.A.; Gámez-Vázquez, F.P.; Álvarez-Bernal, D. Corn Cropping Systems in Agricultural Soils from the Bajio Region of Guanajuato: Soil Quality Indexes (SQIs). Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2858. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14072858
Sánchez-Guzmán A, Bedolla-Rivera HI, Conde-Barajas E, Negrete-Rodríguez MdlLX, Lastiri-Hernández MA, Gámez-Vázquez FP, Álvarez-Bernal D. Corn Cropping Systems in Agricultural Soils from the Bajio Region of Guanajuato: Soil Quality Indexes (SQIs). Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(7):2858. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14072858
Chicago/Turabian StyleSánchez-Guzmán, Alejandra, Héctor Iván Bedolla-Rivera, Eloy Conde-Barajas, María de la Luz Xochilt Negrete-Rodríguez, Marcos Alfonso Lastiri-Hernández, Francisco Paúl Gámez-Vázquez, and Dioselina Álvarez-Bernal. 2024. "Corn Cropping Systems in Agricultural Soils from the Bajio Region of Guanajuato: Soil Quality Indexes (SQIs)" Applied Sciences 14, no. 7: 2858. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14072858
APA StyleSánchez-Guzmán, A., Bedolla-Rivera, H. I., Conde-Barajas, E., Negrete-Rodríguez, M. d. l. L. X., Lastiri-Hernández, M. A., Gámez-Vázquez, F. P., & Álvarez-Bernal, D. (2024). Corn Cropping Systems in Agricultural Soils from the Bajio Region of Guanajuato: Soil Quality Indexes (SQIs). Applied Sciences, 14(7), 2858. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14072858







