BWFER-YOLOv8: An Enhanced Cascaded Framework for Concealed Object Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Recent studies have demonstrated little emphasis on CWD performance for tiny weapons, allowing opportunity for improvement in the detection of concealed small weapons. The proposed study addresses the common CV challenges to improve CWD performance, such as low SNR, illumination, and view-point variations, concurrently. The above-mentioned issues have never been addressed concurrently.
- The proposed framework deploys an adaptive WF to remove noise in the CWD dataset. Moreover, the WF efficiently executes data enhancement by improving the SNR and reducing illumination problems. To the best of the authors’ knowledge, the adaptive WF has not yet been applied to CWD systems.
- A novel -R BRS method is introduced to expand the CWD dataset. The proposed preprocessing technique enhances the accuracy of the proposed CWD framework.
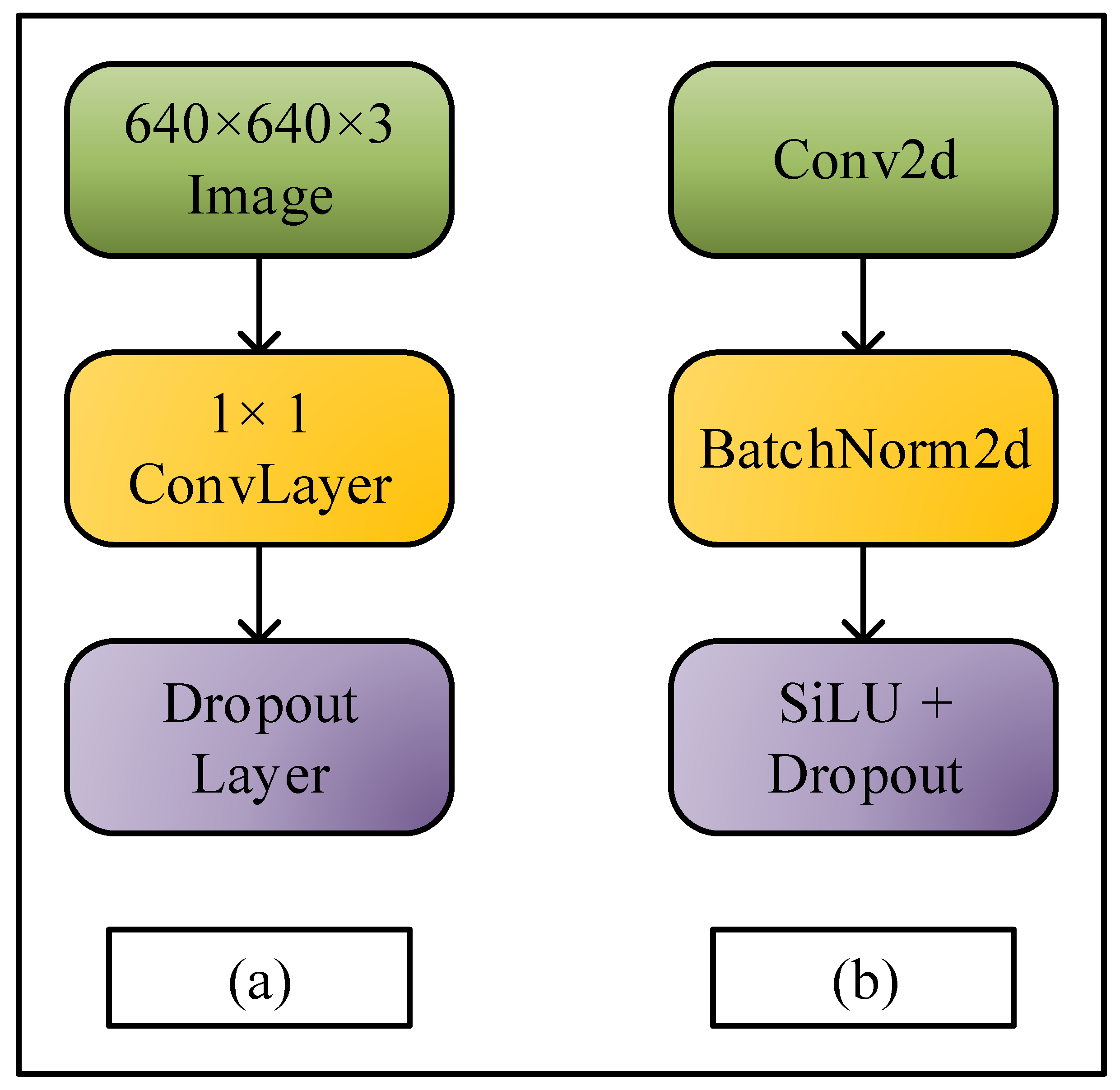
- The FER module has been added in the new enhanced YOLOv8 version, which comprises a 1 × 1 convolutional layer and dropout layer. The 1 × 1 convolutional layer is deployed to enhance the capability of feature extraction to detect small guns and to reduce the FP rate.
- ConvModule in the SOTA YOLOv8 has been replaced by the Conv_Reg module in the recommended FER-YOLOv8 algorithm. The Conv_Reg and FER modules efficiently address the overfitting issue in the detection of small weapons as a dropout layer is instigated in both modules.
- The proposed framework has been assessed on different evaluation metrics such as TP, FP, and mean average precision (mAP) to demonstrate the superiority of the proposed framework as compared to existing frameworks.
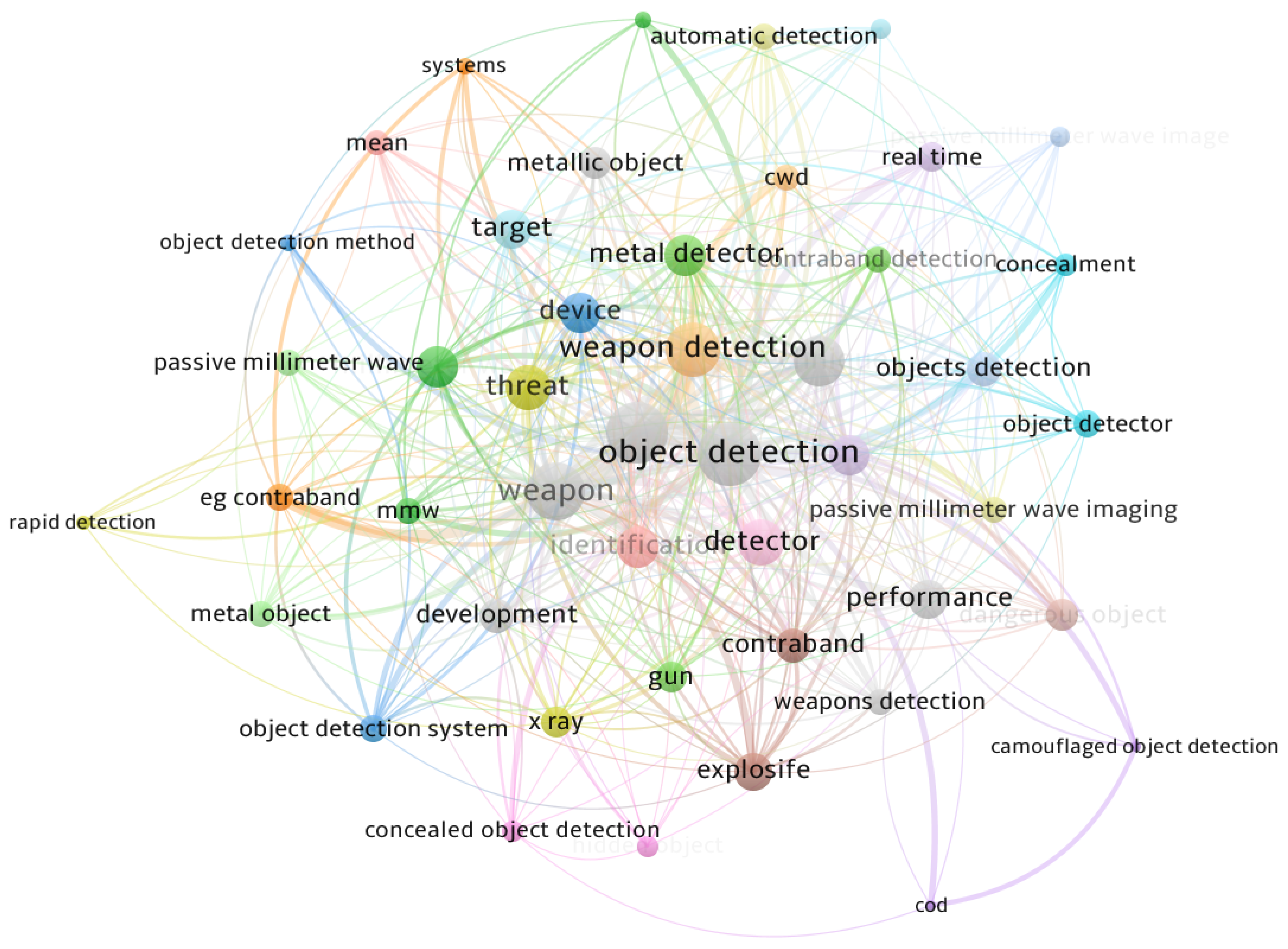
2. Related Work
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
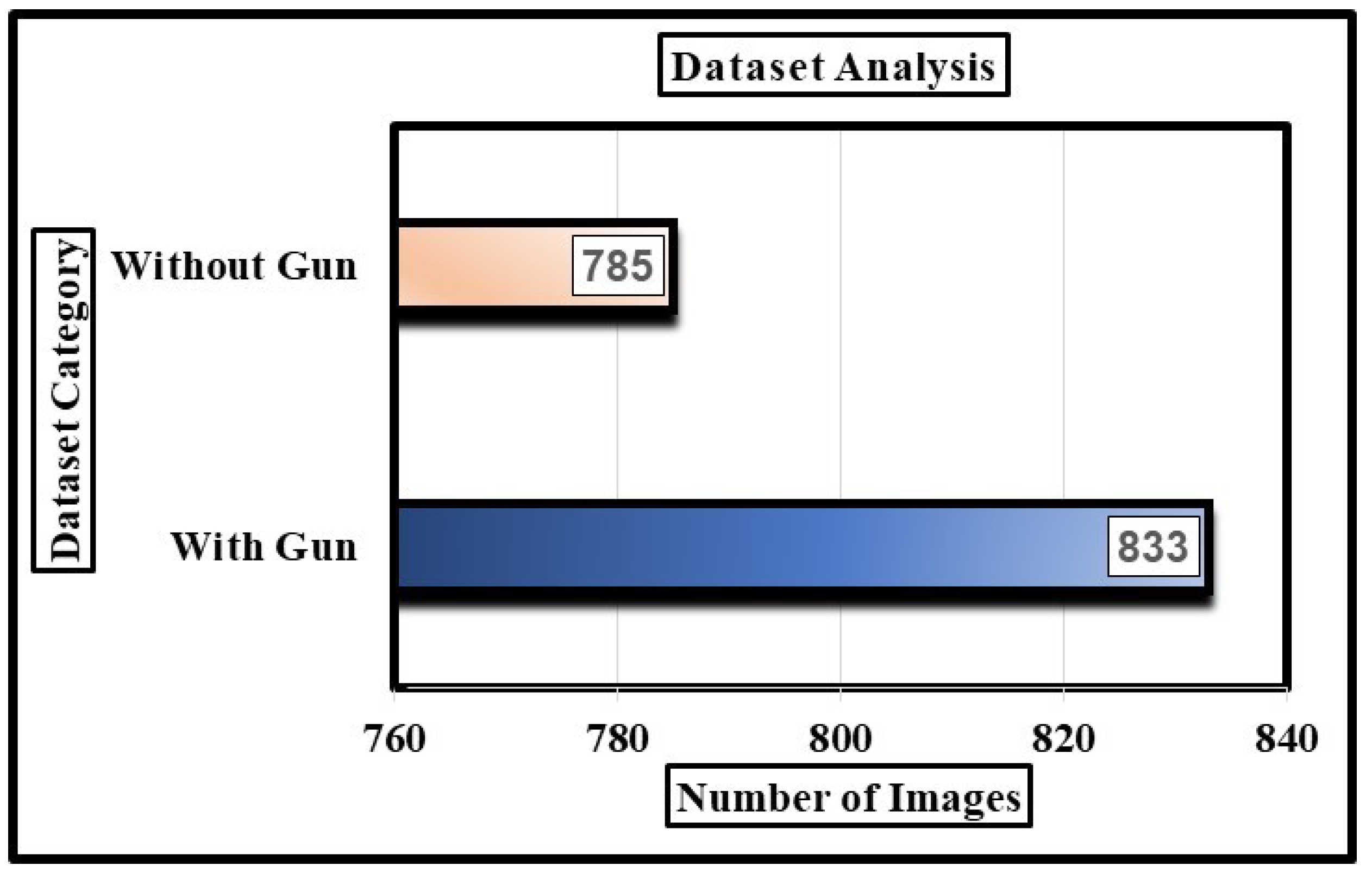
3.1.1. Dataset Overview
3.1.2. Data Preprocessing
| Algorithm 1 Class Balancing using Random Sampling |
|
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Problem Statement
3.2.2. Alpha-Reshuffled Bootstrap Random Sampling Method
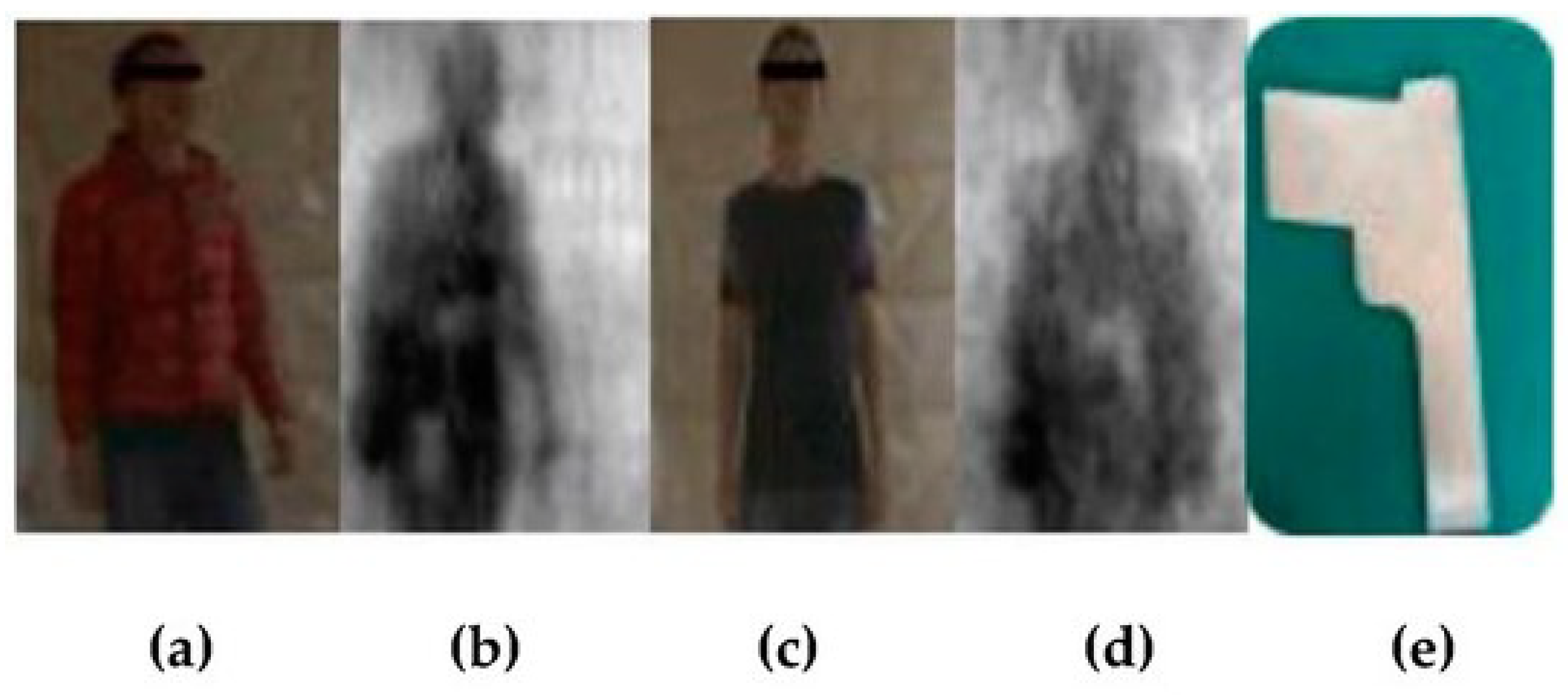
3.2.3. Adaptive Wiener Filter
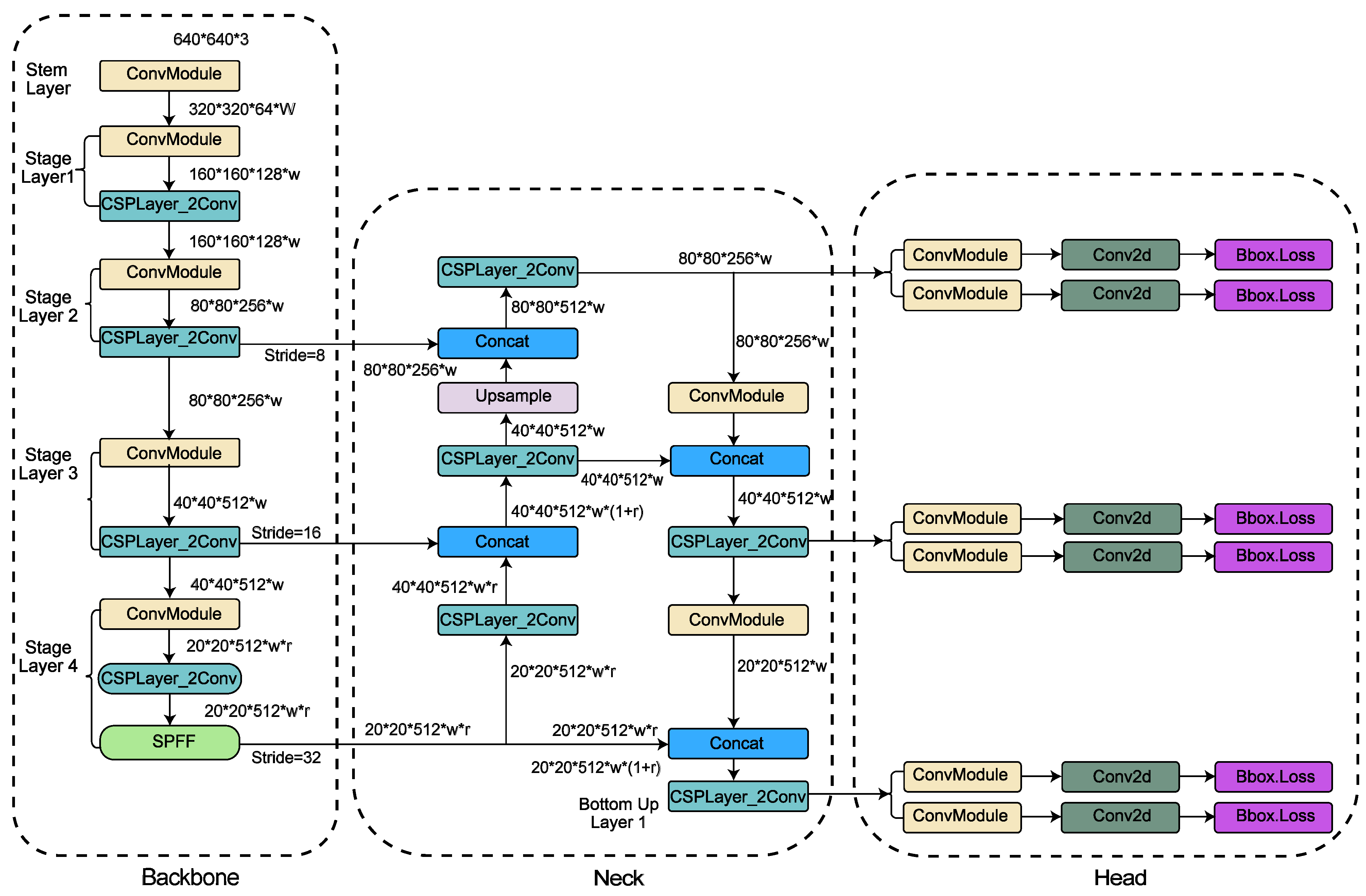
3.2.4. YOLOv8 Algorithm
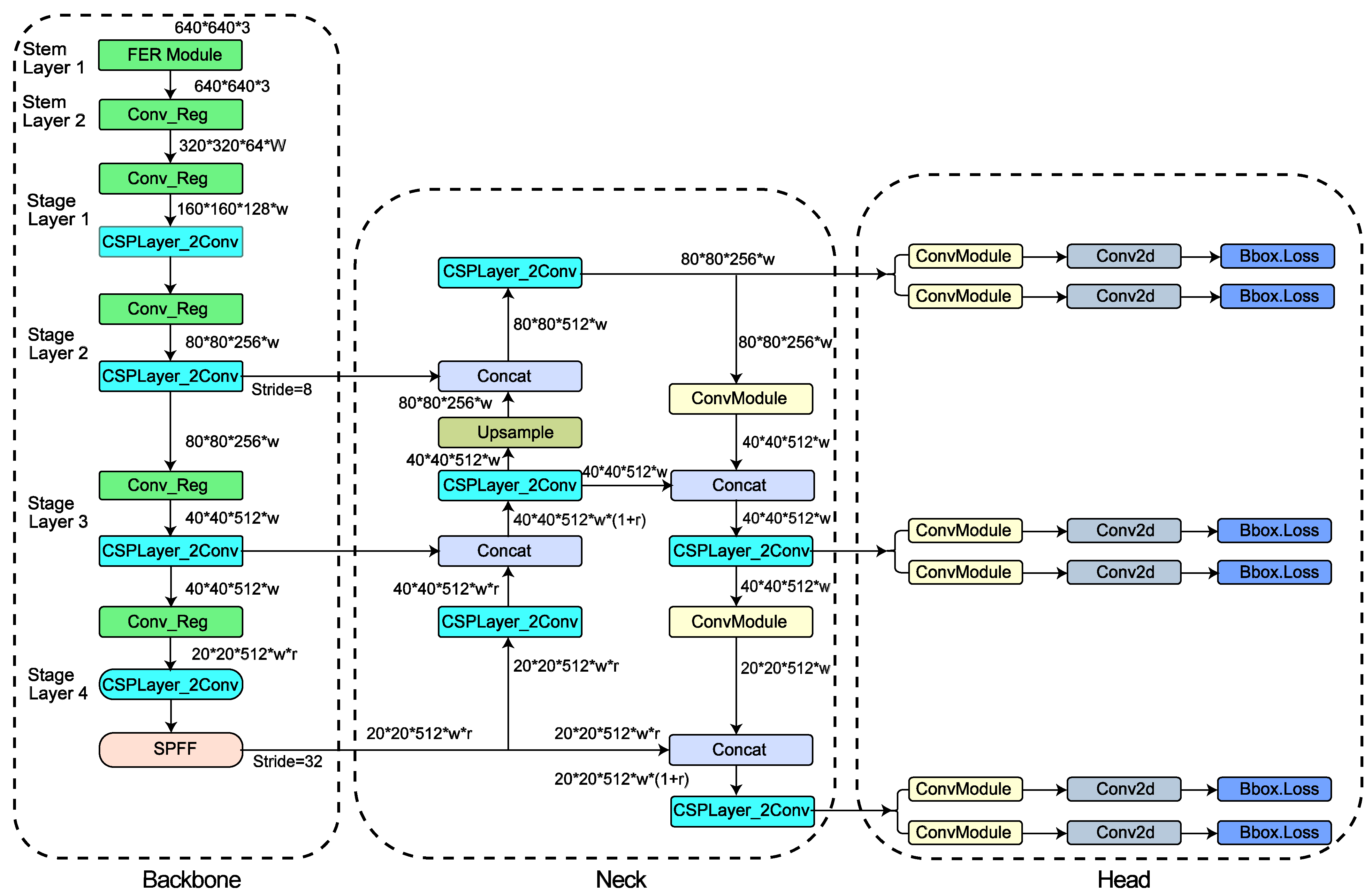
3.2.5. Proposed FER-YOLOv8 Algorithm
3.2.6. FER Module
3.2.7. Conv_Reg Module
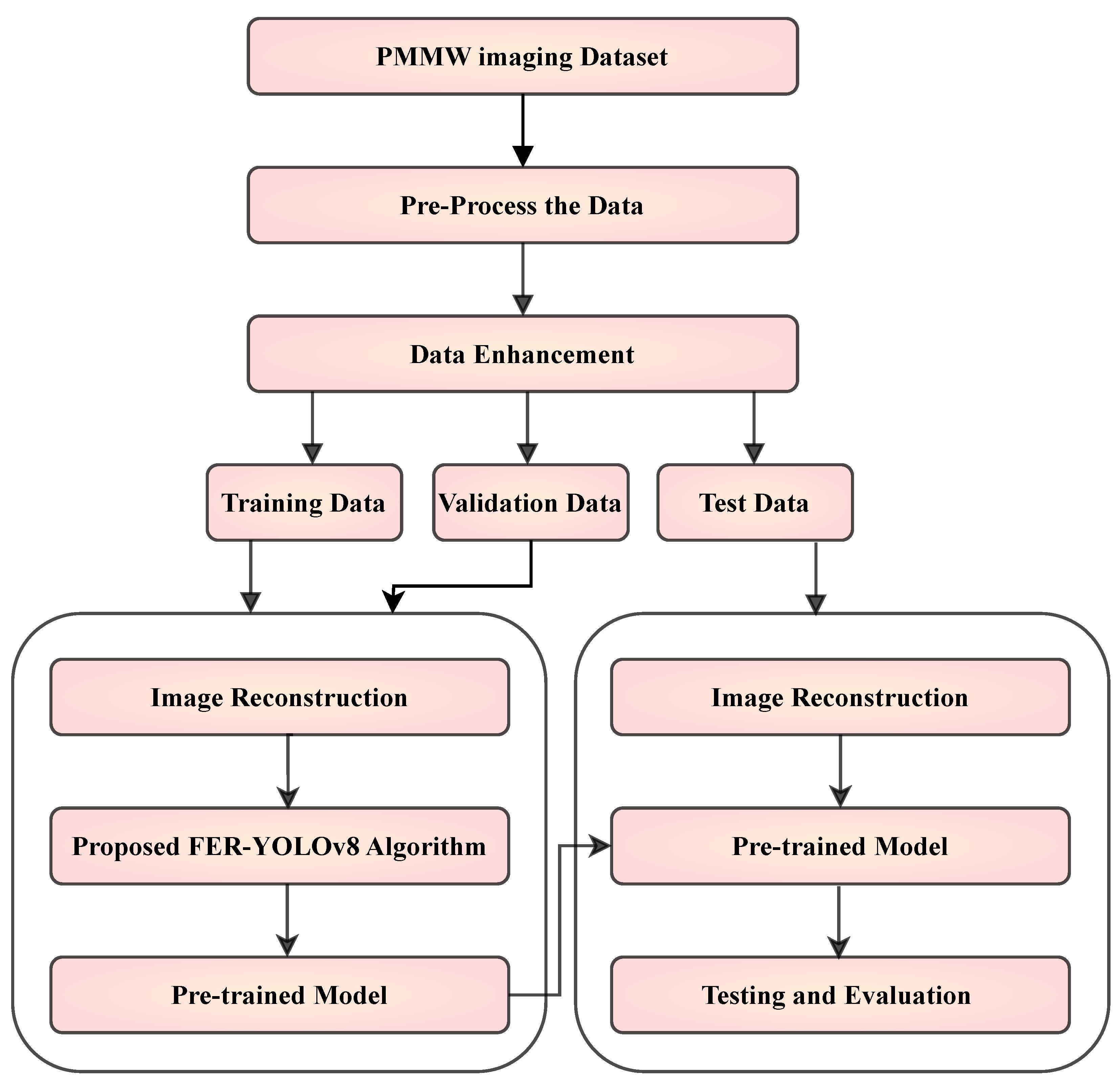
3.2.8. Proposed Research Framework
4. System Configuration with Simulation Setup
4.1. Hyperparameter Settings
4.2. Tiny YOLOv3, YOLOv8n, and YOLOv8m Configurations
4.3. Proposed FER-YOLOv8 Model Configuration
5. Evaluation Metrics
5.1. Evaluation Metrics for Quantitative Analysis
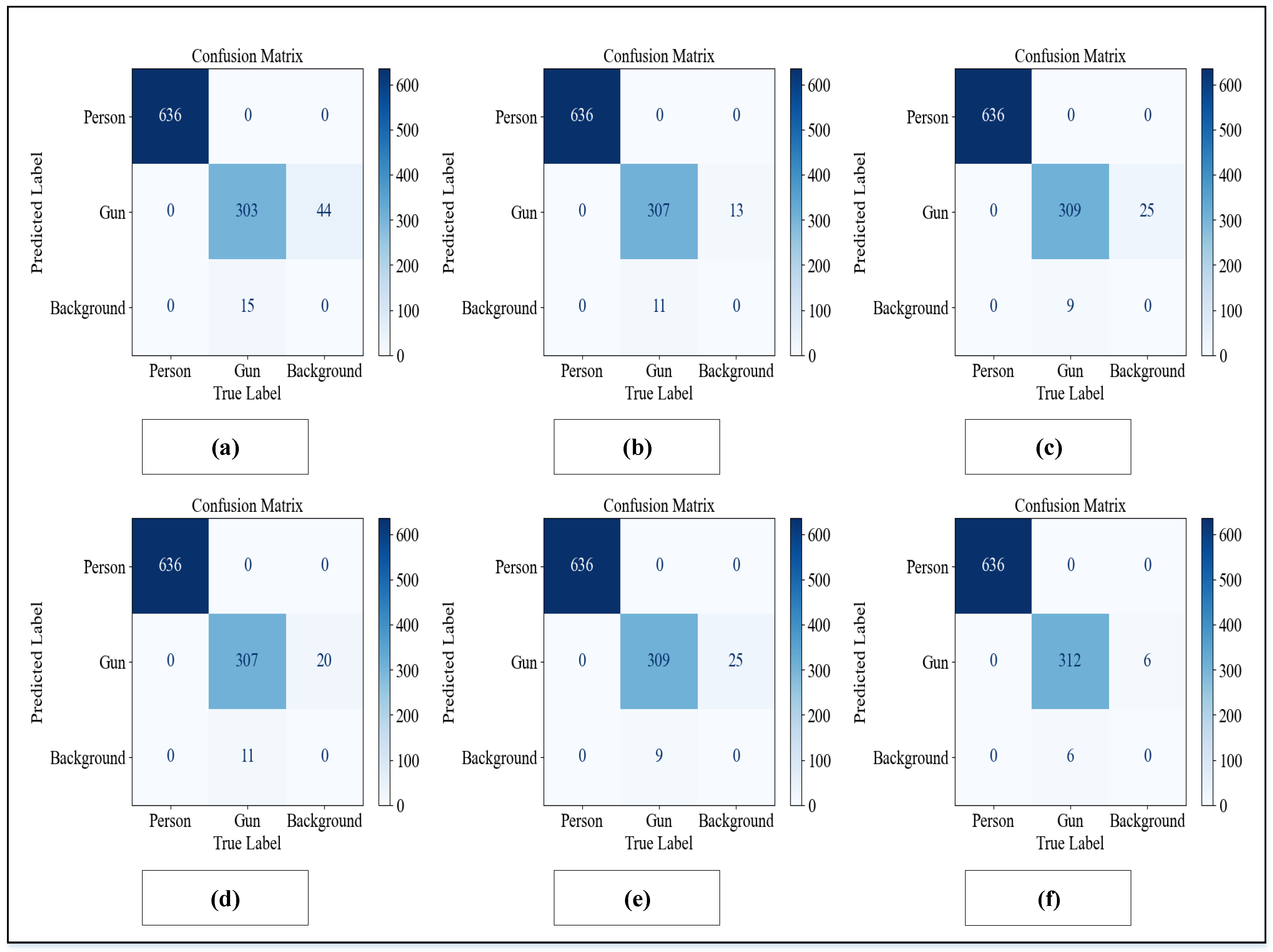
5.1.1. Confusion Matrix
5.1.2. Precision
5.1.3. Recall
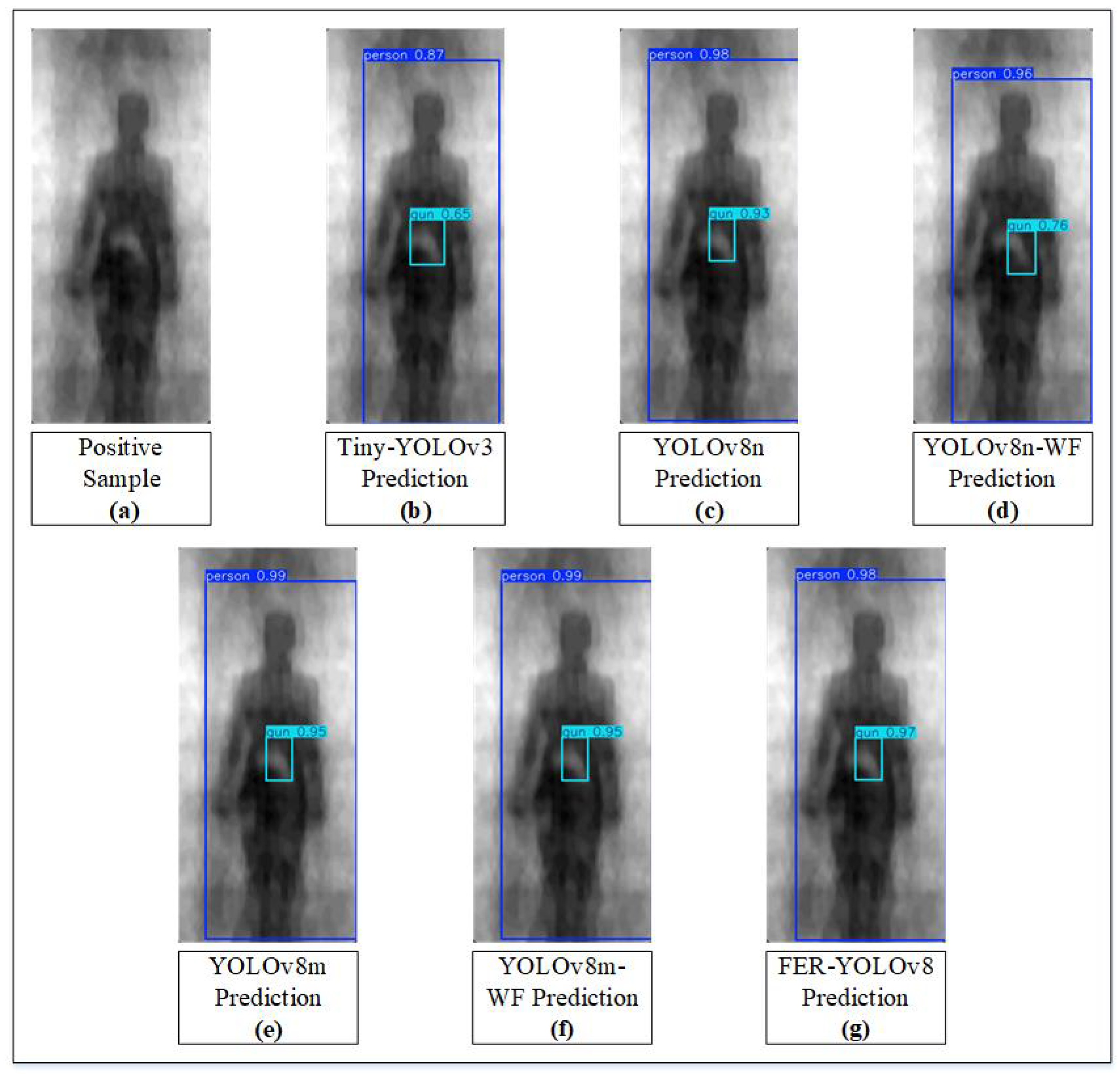
5.2. Qualitative Analysis
6. Simulation Results and Discussion
6.1. Qualitative Assessments
6.1.1. Error Evaluation
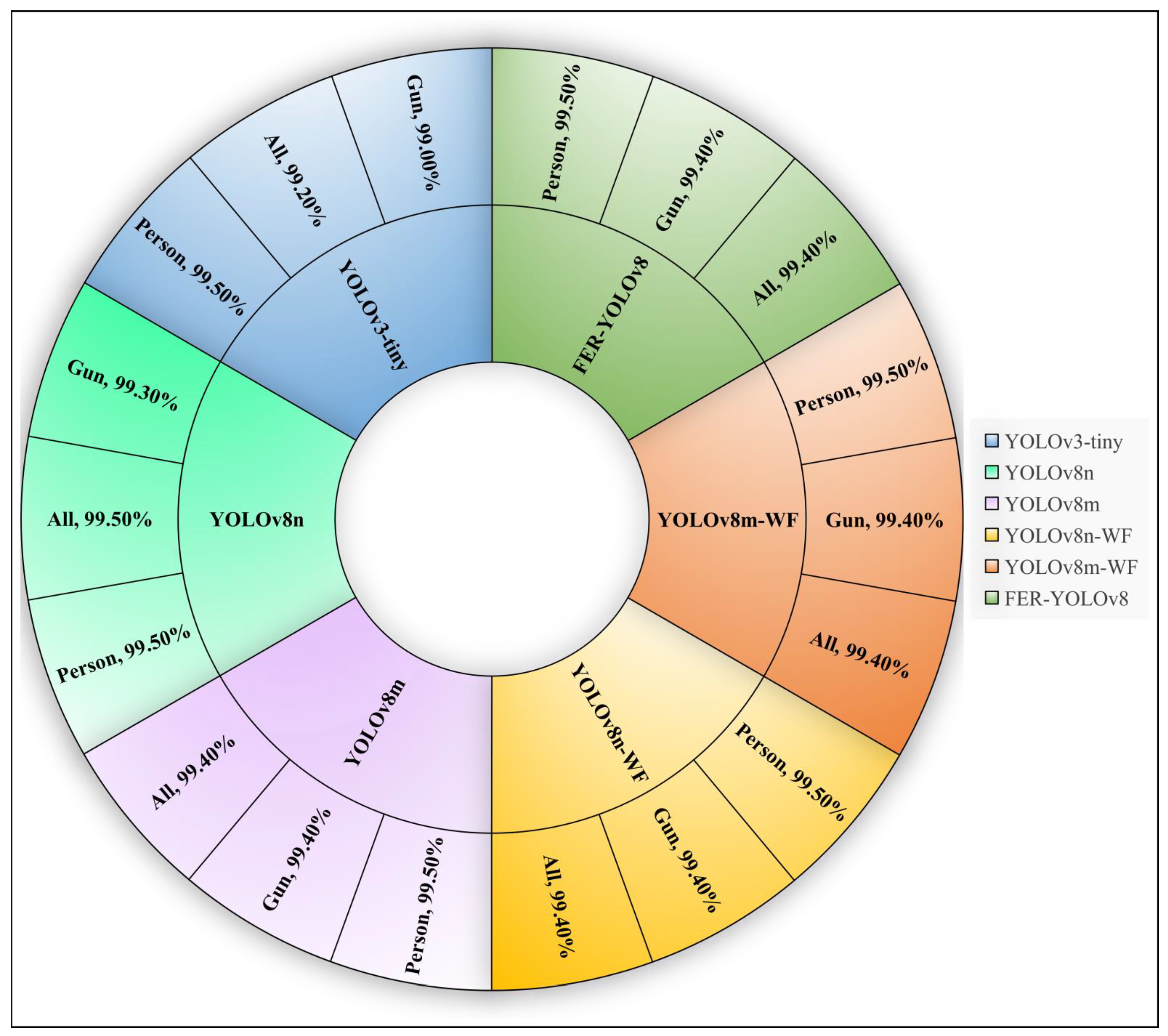
6.1.2. Precision Assessment
6.1.3. Recall Assessment
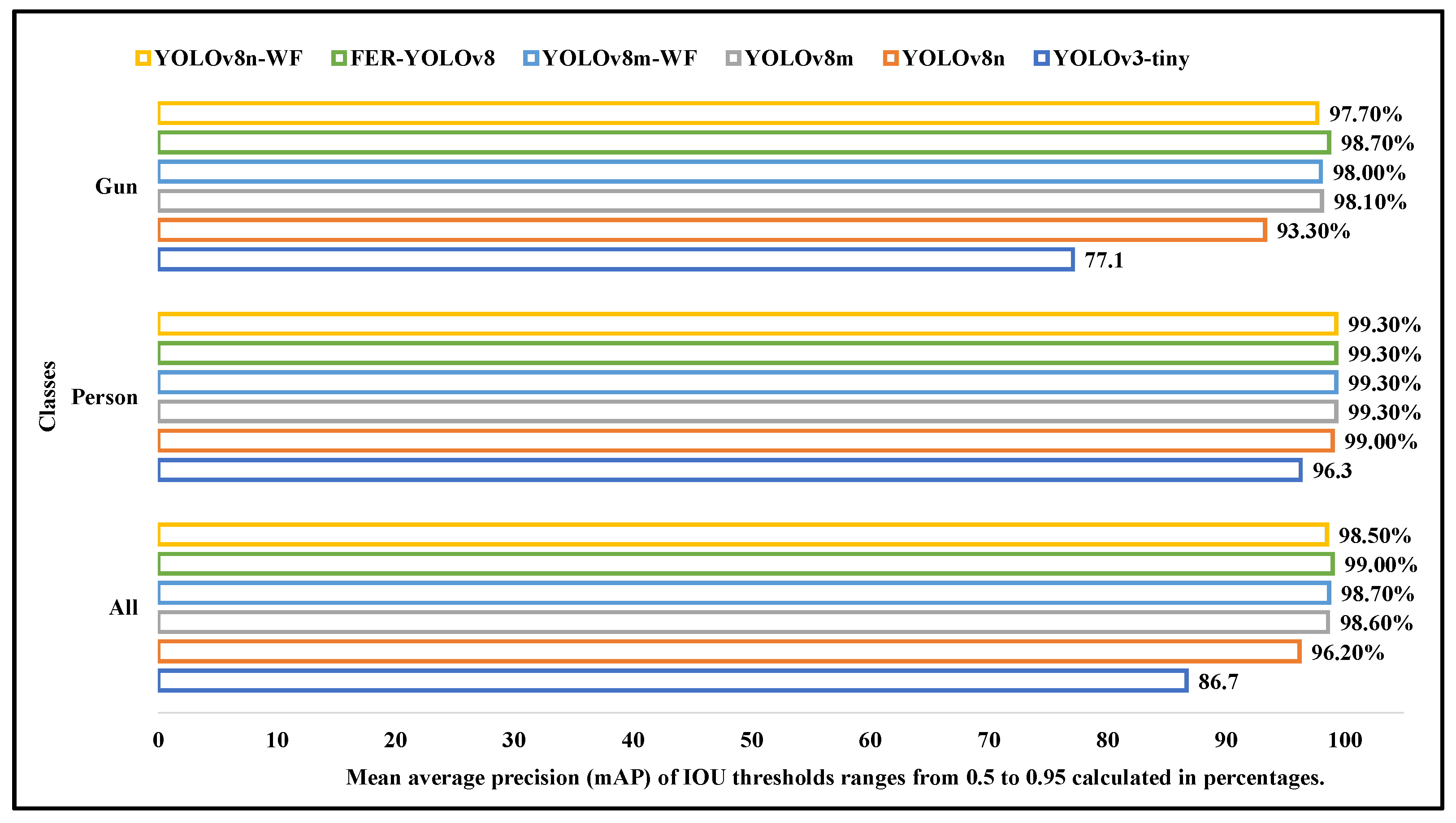
6.1.4. Mean Average Precision (mAP ⇒ 0.5)
6.1.5. Mean Average Precision (mAP ⇒ 0.5:0.95)
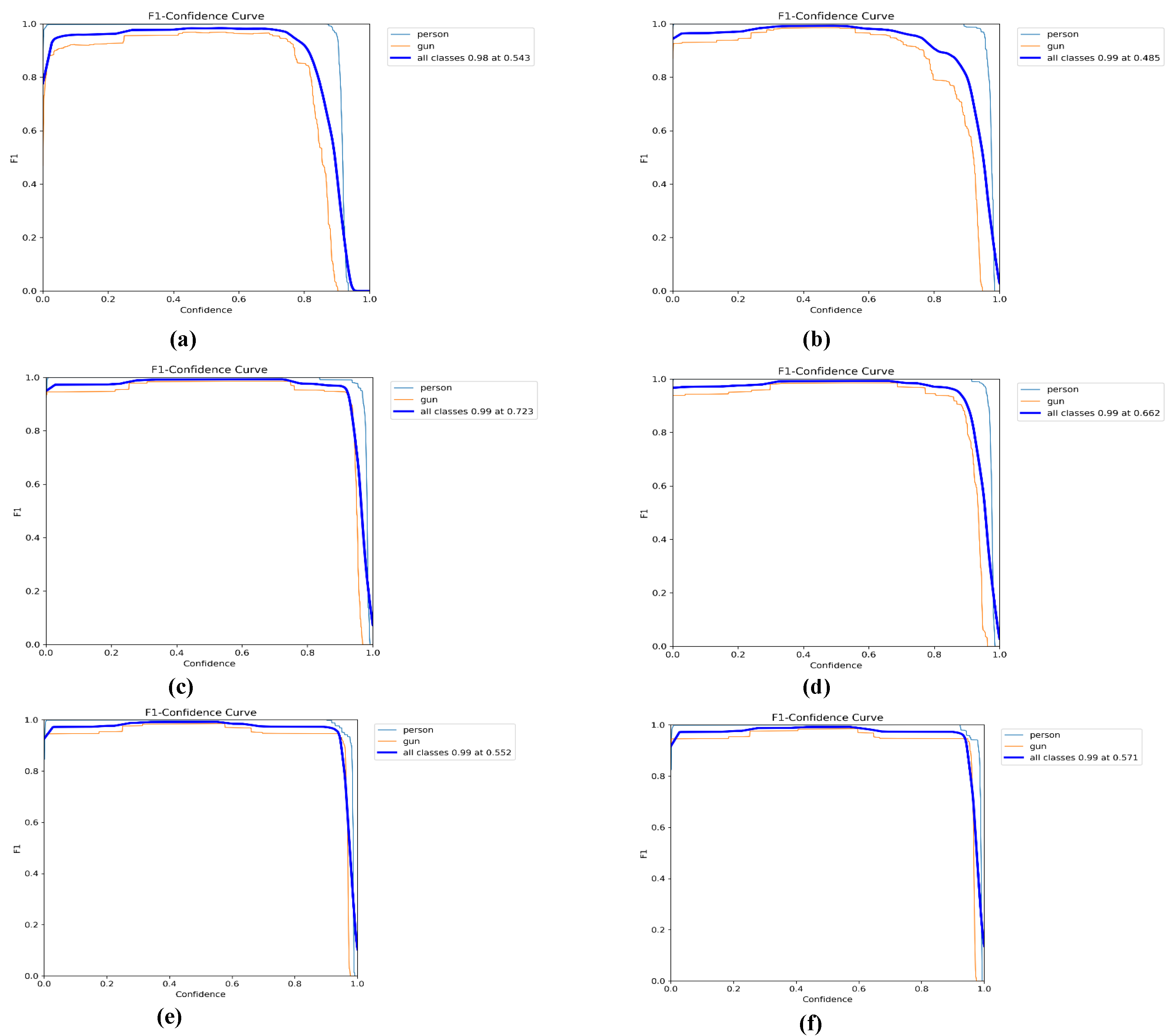
6.1.6. Comparison of F1-Confidence Curves
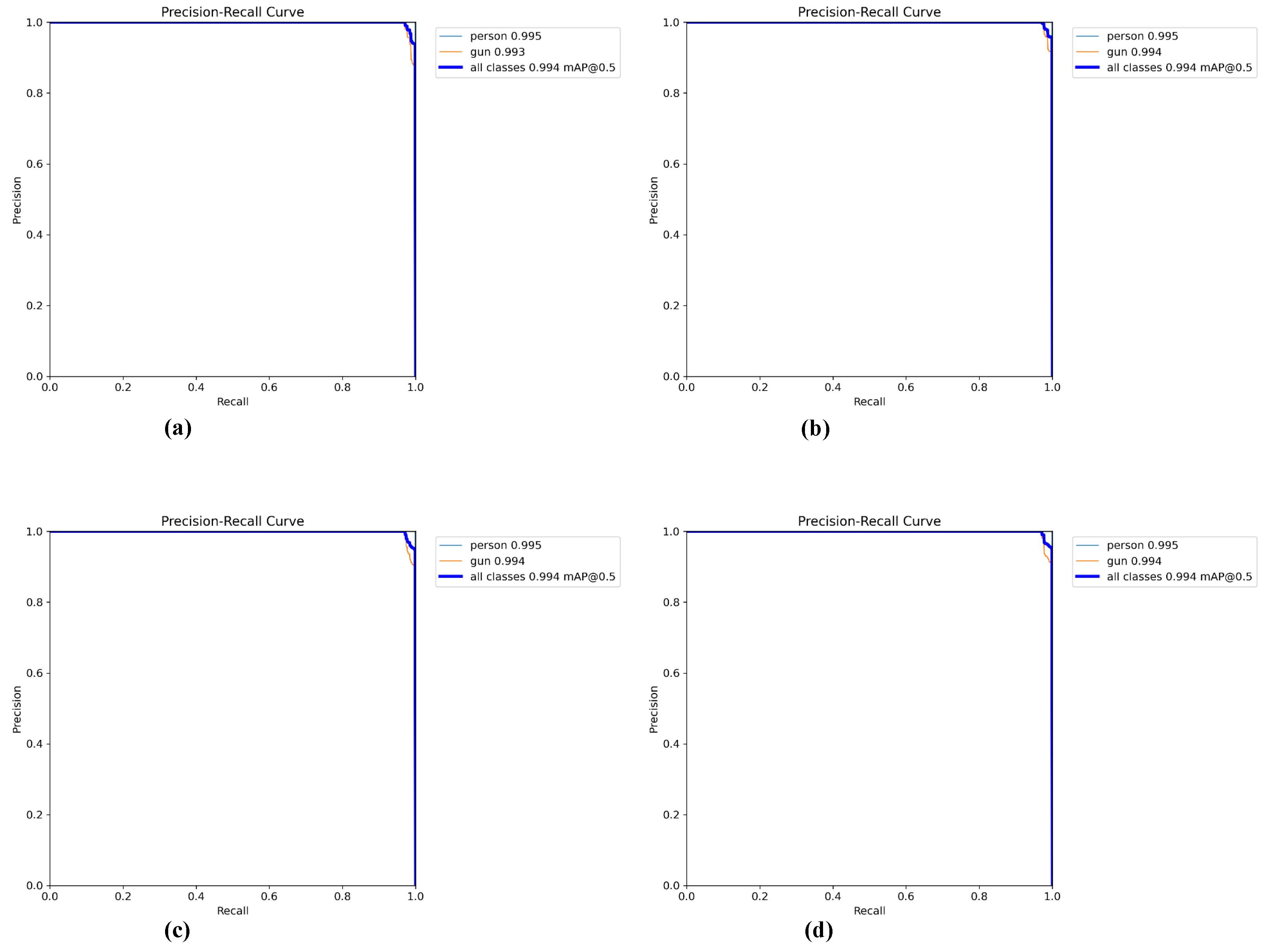
6.1.7. Comparison of Precision–Recall (PR) Curve
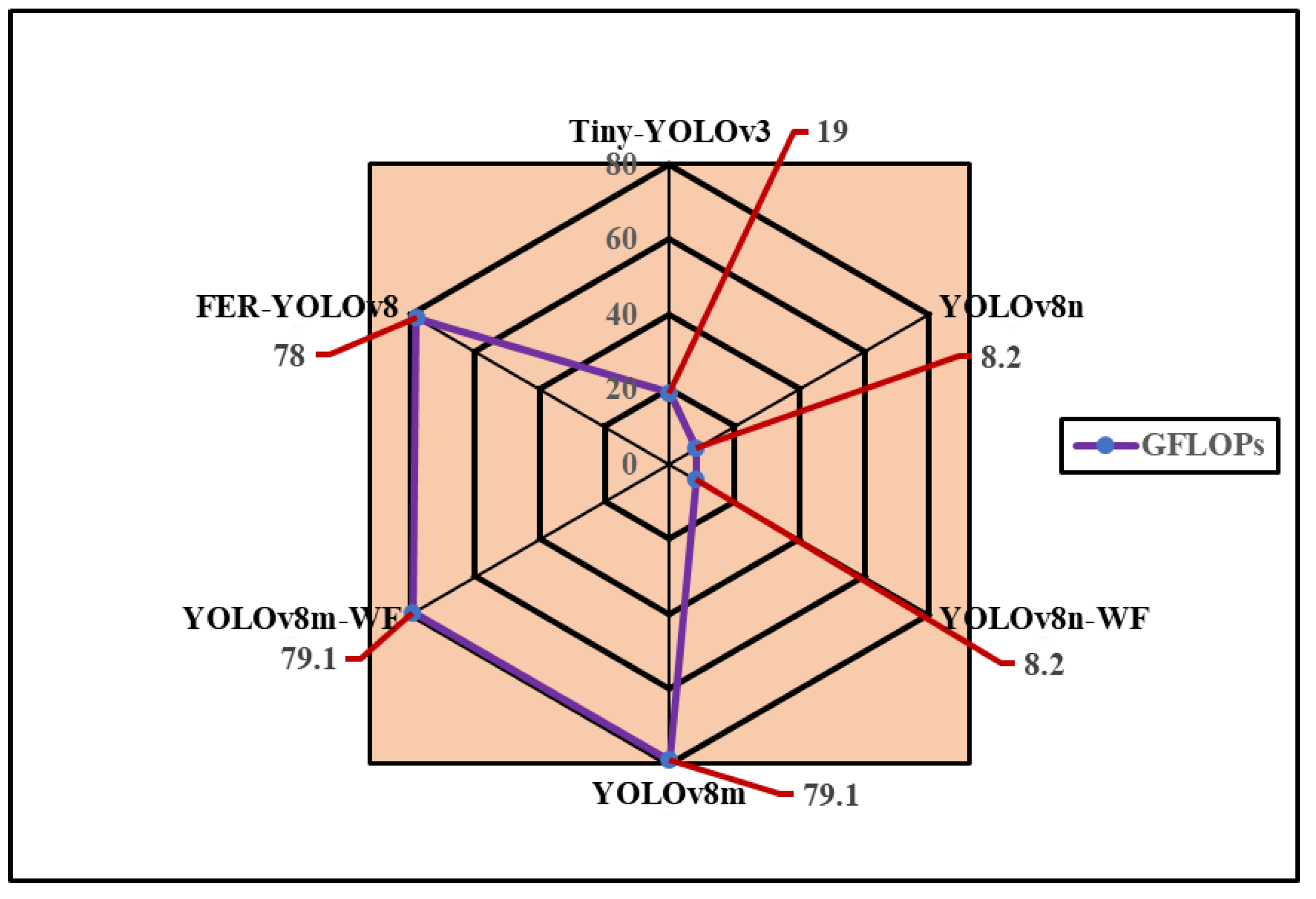
6.1.8. Computational Complexity
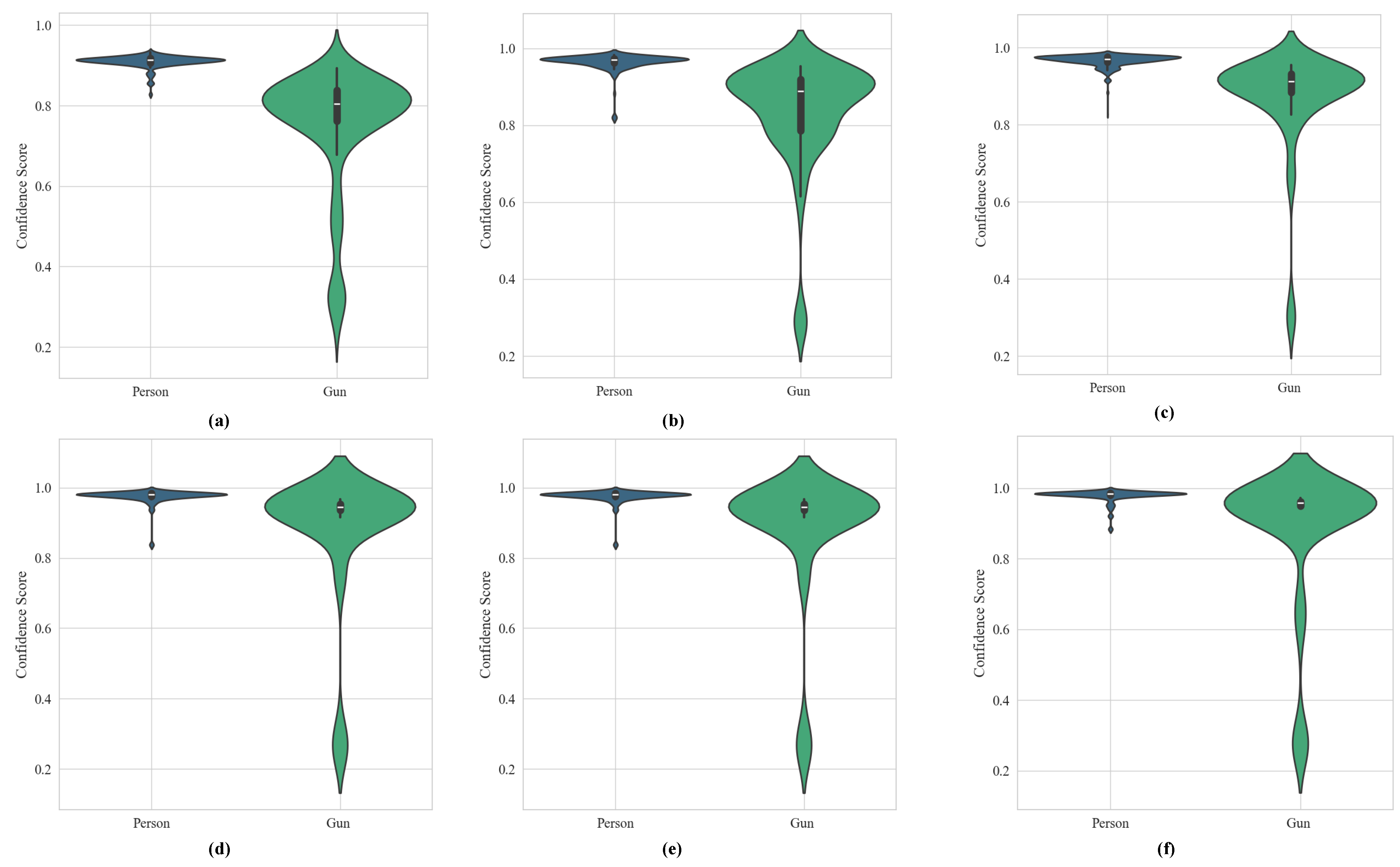
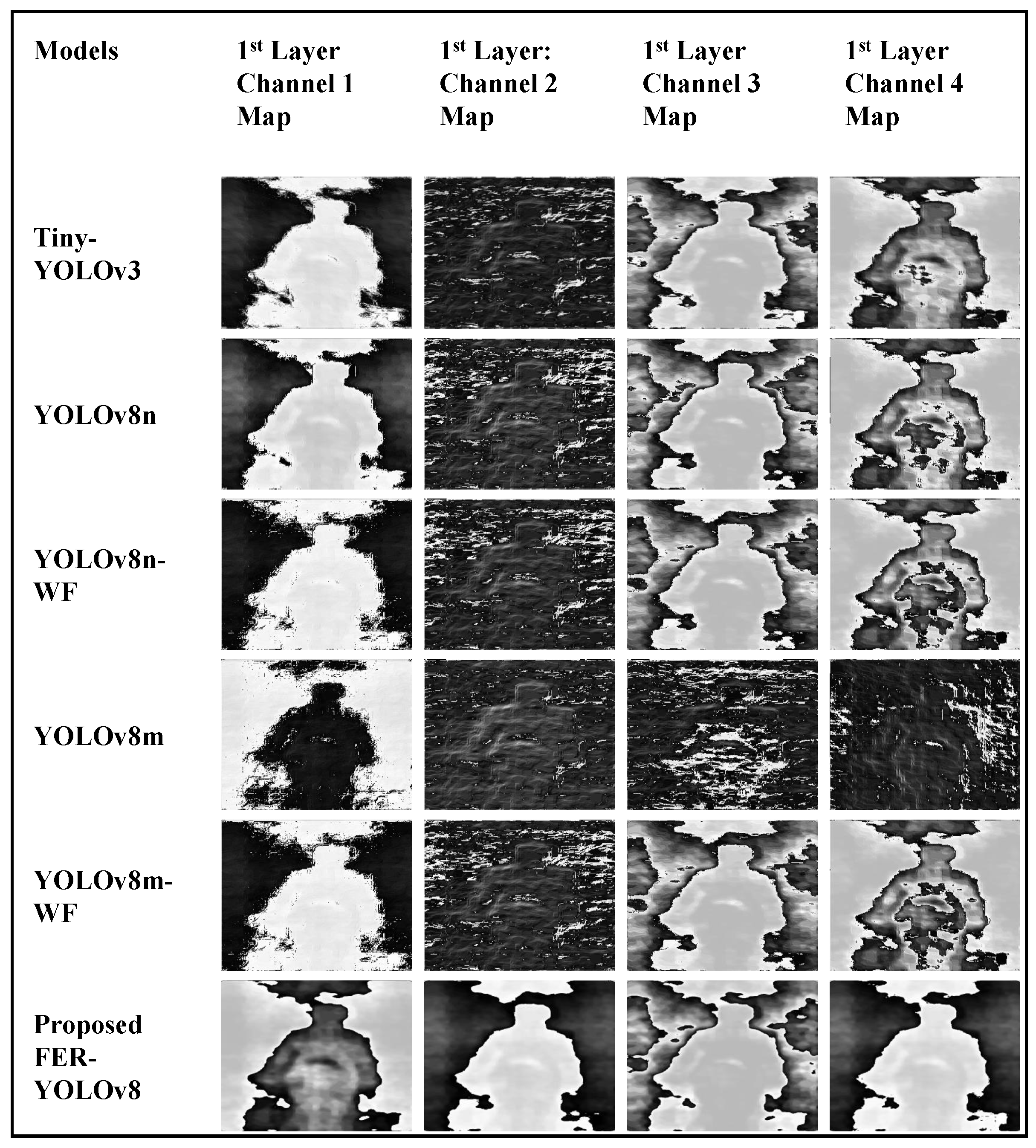
6.2. Qualitative Analysis
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, P.; Wei, R.; Su, Y.; Tan, W. Swin-YOLO for concealed object detection in millimeter wave images. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accardo, J.; Chaudhry, M.A. Radiation exposure and privacy concerns surrounding full-body scanners in airports. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2014, 7, 198–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Wei, Z.; Wang, N.; Song, B.; Gao, X. A novel deformable body partition model for MMW suspicious object detection and dynamic tracking. Signal Process. 2020, 174, 107627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golenkov, A.; Shevchik-Shekera, A.; Kovbasa, M.Y.; Lysiuk, I.; Vuichyk, M.; Korinets, S.; Bunchuk, S.; Dukhnin, S.; Reva, V.; Sizov, F. THz linear array scanner in application to the real-time imaging and convolutional neural network recognition. Semicond. Phys. Quantum Electron. Optoelectron. 2021, 24, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Terrorism Index 2024 Key Findings. Institute for Economics and Peace. Available online: https://www.visionofhumanity.org/7-key-findings-from-the-global-terrorism-index-2024 (accessed on 29 February 2024).
- Chen, H.M.; Lee, S.; Rao, R.M.; Slamani, M.A.; Varshney, P.K. Imaging for concealed weapon detection: A tutorial overview of development in imaging sensors and processing. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2005, 22, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agurto, A.; Li, Y.; Tian, G.Y.; Bowring, N.; Lockwood, S. A review of concealed weapon detection and research in perspective. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Networking, Sensing and Control, London, UK, 15–17 April 2007; pp. 443–448. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.M.; Li, N.; Ren, C.P.; Peng, Z.Y.; Lu, H.Z.; Li, D.; Wu, X.Y.; Zhou, Z.X.; Deng, J.Y.; Zheng, Z.H.; et al. Sterility of Aedes albopictus by X-ray Irradiation as an Alternative to γ-ray Irradiation for the Sterile Insect Technique. Pathogens 2023, 12, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riz à Porta, R.; Sterchi, Y.; Schwaninger, A. How realistic is threat image projection for x-ray baggage screening? Sensors 2022, 22, 2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velayudhan, D.; Hassan, T.; Ahmed, A.H.; Damiani, E.; Werghi, N. Baggage threat recognition using deep low-rank broad learning detector. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 21st Mediterranean Electrotechnical Conference (MELECON), Palermo, Italy, 14–16 June 2022; pp. 966–971. [Google Scholar]
- Kovbasa, M.; Golenkov, A.; Sizov, F. Neural network application to the postal terahertz scanner for automated detection of concealed items. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Ukrainian Microwave Week (UkrMW), Kharkiv, Ukraine, 21–25 September 2020; pp. 870–873. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Ouyang, W.; Wang, X.; Fieguth, P.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Pietikäinen, M. Deep learning for generic object detection: A survey. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2020, 128, 261–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadrado-Calle, D.; Piironen, P.; Ayllon, N. Solid-state diode technology for millimeter and submillimeter-wave remote sensing applications: Current status and future trends. IEEE Microw. Mag. 2022, 23, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Qiao, L.; Zhu, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Z. Passive polarimetric imaging of millimeter and terahertz waves for personnel. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 46, 1233–1236. [Google Scholar]
- Owda, A.Y. Passive millimeter-wave imaging for burns diagnostics under dressing materials. Sensors 2022, 22, 2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gou, S.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Jiao, C.; Mao, S. Self-paced feature attention fusion network for concealed object detection in millimeter-wave image. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 32, 224–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, F.; Pu, Z.; Huang, X.; Chen, J.; Shao, S. AC-SDBSCAN: Toward concealed object detection of passive terahertz images. IET Image Process. 2022, 16, 839–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danso, S.A.; Liping, S.; Deng, H.; Odoom, J.; Chen, L.; Xiong, Z.g. Optimizing YOLOv3 detection model using terahertz active security scanned low-resolution images. Theor. Appl. Sci. 2021, 95, 235–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovbasa, M.; Golenkov, A.; Shevchik-Shekera, A.; Sizov, F. Study of object detection in linear terahertz imaging systems. Opt. Eng. 2023, 62, 083104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danso, S.A.; Liping, S.; Hu, D.; Afoakwa, S.; Badzongoly, E.L.; Odoom, J.; Muhammad, O.; Mushtaq, M.U.; Qayoom, A.; Zhou, W. An optimal defect recognition security-based terahertz low resolution image system using deep learning network. Egypt. Inform. J. 2023, 24, 100384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haworth, C.D.; Gonzalez, B.G.; Tomsin, M.; Appleby, R.; Coward, P.R.; Harvey, A.R.; Lebart, K.; Petillot, Y.R.; Trucco, E. Image analysis for object detection in millimetre-wave images. In Proceedings of the Passive Millimetre-Wave and Terahertz Imaging and Technology, London, UK, 27–28 October 2004; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2004; Volume 5619, pp. 117–128. [Google Scholar]
- Haworth, C.D.; Petillot, Y.R.; Trucco, E. Image processing techniques for metallic object detection with millimetre-wave images. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2006, 27, 1843–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, O.; Ferraz, L.; Binefa, X.; Gómez, I.; Dorronsoro, C. Concealed object detection and segmentation over millimetric waves images. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition-Workshops, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Li, Y. A multi-class classification system for passive millimeter-wave image. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Microwave and Millimeter Wave Technology (ICMMT), Chengdu, China, 7–11 May 2018; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski, M. Real-time concealed object detection and recognition in passive imaging at 250 GHz. Appl. Opt. 2019, 58, 3134–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maqueda, I.G.; De La Blanca, N.P.; Molina, R.; Katsaggelos, A.K. Fast millimeter wave threat detection algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2015 23rd European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Nice, France, 31 August–4 September 2015; pp. 599–603. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Chen, X.; Wu, L. Segmentation of concealed objects in passive millimeter-wave images based on the Gaussian mixture model. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2015, 36, 400–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeom, S.; Lee, D.; Son, J. Shape feature analysis of concealed objects with passive millimeter wave imaging. Prog. Electromagn. Res. Lett. 2015, 57, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gou, S.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L. Patch-Based Gaussian Mixture Model for Concealed Object Detection in Millimeter-Wave images. In Proceedings of the TENCON 2018—2018 IEEE Region 10 Conference, Jeju, Republic of Korea, 28–31 October 2018; pp. 2522–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Pang, L.; Liu, H.; Xu, X. Wavelet fusion for concealed object detection using passive millimeter wave sequence images. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, XLII-3, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ye, W.; Chen, J.F.; Gong, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F. A Visible and Passive Millimeter Wave Image Fusion Algorithm Based on Pulse-Coupled Neural Network in Tetrolet Domain for Early Risk Warning. Math. Probl. Eng. 2018, 2018, 4205308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Işıker, H.; Özdemir, C. A Multi-Thresholding Method Based on Otsu’s Algorithm for the Detection of Concealed Threats in Passive Millimeter-Wave Images. Frequenz 2019, 73, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Niu, Y.; Zhao, Z. Concealed object enhancement using multi-polarization information for passive millimeter and terahertz wave security screening. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 6350–6366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Tapia, S.; Molina, R.; de la Blanca, N.P. Using machine learning to detect and localize concealed objects in passive millimeter-wave images. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2018, 67, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.P.; Ji, G.P.; Cheng, M.M.; Shao, L. Concealed Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 44, 6024–6042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-J.; Sun, X.-W.; Yang, K.-H. A low-complexity method for concealed object detection in active millimeter-wave images. J. Infrared Millim. Waves 2019, 38, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, J.; Han, Y. Understanding the effective receptive field in semantic image segmentation. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2018, 77, 22159–22171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Tapia, S.; Molina, R.; de la Blanca, N.P. Deep CNNs for object detection using passive millimeter sensors. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2017, 29, 2580–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, M. Hidden object detection and recognition in passive terahertz and mid-wavelength infrared. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2019, 40, 1074–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Cui, J.; Chen, Z.; Wen, X. Concealed threat detection based on multi-view millimeter wave imaging for human body. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Signal, Information and Data Processing (ICSIDP), Chongqing, China, 11–13 December 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, R. A review of terahertz detectors. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2019, 52, 433001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yang, K.; Sun, X. Precise localization of concealed objects in millimeter-wave images via semantic segmentation. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 121246–121256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, H.; Wu, Q.; Ngan, K.N.; Xu, L. High-quality R-CNN object detection using multi-path detection calibration network. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2020, 31, 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, M.T.; Khan, M.G.; Aslam, M.; Fiaz, M.J. Weapon detection in real-time cctv videos using deep learning. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 34366–34382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Xing, G.; Roy, S.; Liu, H. Ramp-cnn: A novel neural network for enhanced automotive radar object recognition. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 21, 5119–5132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yu, J.; Kong, S.; Wu, Z.; Wen, L. Joint anchor-feature refinement for real-time accurate object detection in images and videos. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2020, 31, 594–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Liu, T.; Chen, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, S. Multi-source aggregation transformer for concealed object detection in millimeter-wave images. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 32, 6148–6159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, K.; Sun, Z.; Wu, Q.; He, W.; Wang, H. Concealed object detection and recognition system based on millimeter wave FMCW radar. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Liu, H.; Roy, S.; Xing, G.; Alansari, A.; Luo, Y. Learning to detect open carry and concealed object with 77 GHz radar. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2022, 16, 791–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuravlev, A.; Razevig, V.; Rogozin, A.; Chizh, M. Microwave imaging of concealed objects with linear antenna array and optical tracking of the target for high-performance security screening systems. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2022, 71, 1326–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Huang, X.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Shang, Z.; Zhang, Y. YOLO-MSFG: Toward real-time detection of concealed objects in passive terahertz images. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 22, 520–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yang, Z.; Hu, A.; Liu, C.; Cui, T.J.; Miao, J. Unifying convolution and transformer for efficient concealed object detection in passive millimeter-wave images. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 33, 3872–3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.B.; Lee, J.Y. TCU-Net: Transformer and Convolutional Neural Network-Based Advanced U-Net for Concealed Object Detection. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 122347–122360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Hu, F.; Hu, Y. Concealed object detection for passive millimeter-wave security imaging based on task-aligned detection transformer. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amadi, L.; Agam, G. Weakly supervised 2D pose adaptation and body part segmentation for concealed object detection. Sensors 2023, 23, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Shi, J.; Tao, C.; Xu, F.; Tang, X.; Li, L.; Zhou, Y.; Tian, B.; Wei, S.; Zhang, X. Multitype label noise modeling and uncertainty-weighted label correction for concealed object detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yang, Z.; Hu, A.; Liu, C.; Cui, T.J.; Miao, J. Source-free domain adaptive detection of concealed objects in passive millimeter-wave images. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veranyurt, O.; Sakar, C.O. Concealed pistol detection from thermal images with deep neural networks. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 44259–44275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandel, S.; Bhatnagar, G.; Kowalski, M. Saliency and superpixel improved detection and segmentation of concealed objects for passive terahertz images. Opt. Eng. 2023, 62, 023101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardar, S.; Assi, S.; Zolkifly, I.A.; Jayabalan, M.; Alsaleem, M.; Mohammed, A.H.; Al-Jumeily OBE, D. Application of Deep Learning Algorithms to Terahertz Images for Detection of Concealed Objects. In Data Science and Emerging Technologies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 279–289. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, X.T.; Do, T.T.T.; Lin, C.T. Early Detection of Human Decision-Making in Concealed Object Visual Searching Tasks: An EEG-BiLSTM Study. In Proceedings of the 2023 45th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Sydney, Australia, 24–27 July 2023; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Khor, W.; Chen, Y.K.; Roberts, M.; Ciampa, F. Infrared Thermography as a Non-Invasive Scanner for Concealed Weapon Detection. Cranfield Online Research Data (CORD) 2024. Available online: https://dspace.lib.cranfield.ac.uk/handle/1826/21320 (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- He, C.; Li, K.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, G.; Tang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Li, X. Weakly-supervised concealed object segmentation with sam-based pseudo labeling and multi-scale feature grouping. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 36, 30726–30737. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.; Tan, W.; Dong, Y.; Xu, W.; Huang, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, D. Enhancing concealed object detection in Active Millimeter Wave Images using wavelet transform. Signal Process. 2024, 216, 109303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.; Lucyszyn, S. Few-shot concealed object detection in sub-THz security images using improved pseudo-annotations. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, K.; Benecchi, A.; Bourlai, T. Passive Millimeter Wave Concealed Object Detection Using YOLOv8. In Proceedings of the SoutheastCon 2024, Atlanta, GA, USA, 15–24 March 2024; pp. 884–889. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Jia, Z.; Wang, H.; Jia, K. Deep-learning-based method for concealed object detection in terahertz (THz) images. In Proceedings of the Advanced Fiber Laser Conference (AFL2023), Shenzhen, China, 10–12 November 2024; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2024; Volume 13104, pp. 268–274. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Asif, M.; Hu, A.; Miao, J. Design of a low-cost cross-correlation system for aperture synthesis passive millimeter wave imager. In Proceedings of the Millimetre Wave and Terahertz Sensors and Technology XI, Berlin, Germany, 10–11 September 2018; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2018; Volume 10800, p. 1080003. [Google Scholar]
- Ansel, J.; Yang, E.; He, H.; Gimelshein, N.; Jain, A.; Voznesensky, M.; Bao, B.; Bell, P.; Berard, D.; Burovski, E.; et al. PyTorch 2: Faster Machine Learning Through Dynamic Python Bytecode Transformation and Graph Compilation. In Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Architectural Support for Programming Languages and Operating Systems, ASPLOS ’24, New York, NY, USA, 27 April–1 May 2024; Volume 2, pp. 929–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ultralytics. YOLOv3 in PyTorch. 2024. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3 (accessed on 15 October 2024).
- Koech, K.E. On Object Detection Metrics with Worked Example. 2023. Available online: https://towardsdatascience.com/on-object-detectionmetrics-with-worked-example-216f173ed31e (accessed on 15 October 2024).
- Chang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Bu, Z.; Cui, H.; Ding, L. Three-Dimensional Millimeter-Wave Object Detector Based on the Enhancement of Local-Global Contextual Information. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 130963–130971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Models | Hyperparameter |
|---|---|
| Tiny YOLOv3, YOLOv8n, and YOLOv8m | Epoch: 100 |
| Batch size: 16 | |
| Learning rate: 0.01 | |
| Final learning rate: 0.01 | |
| Momentum: 0.9 | |
| weight_decay = 0.0005 | |
| Optimizer: AdamW | |
| Patience: 100 | |
| Proposed FER-YOLOv8 | Dropout rate: 20% |
| Epoch: 100 | |
| Batch size: 16 | |
| Learning rate: 0.01 | |
| Final learning rate: 0.01 | |
| Momentum: 0.9 | |
| weight_decay = 0.0005 | |
| Optimizer: AdamW | |
| Patience: 100 |
| Module | Layer | Input Channels | Output Channels | Parameters | Size/Stride | Output |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FER | Convolutional | 3 | 8 | 40 | 1 × 1/1 | 640 × 640 |
| Dropout | - | - | 0 | - | 640 × 640 | |
| Conv_Reg | Convolutional | 8 | 48 | 3552 | 3 × 3/2 | 320 × 320 |
| Dropout | - | - | 0 | - | 320 × 320 |
| Model | Overall Precision (%) | Macro-Averaging Precision (%) | Precision for Person Class (%) | Precision for Gun Class (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tiny YOLOv3 | ||||
| YOLOv8n | ||||
| YOLOv8m | ||||
| YOLOv8n-WF | ||||
| YOLOv8m-WF | ||||
| Proposed FER-YOLOv8 |
| Model | Overall Recall (%) | Macro-Averaging Recall (%) | Recall for Person Class (%) | Recall for Gun Class (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tiny YOLOv3 | ||||
| YOLOv8n | ||||
| YOLOv8m | ||||
| YOLOv8n-WF | ||||
| YOLOv8m-WF | ||||
| Proposed FER-YOLOv8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ijaz, K.; Khosa, I.; Ansari, E.A.; Ali, S.F.; Hussain, A.; Butt, F.A. BWFER-YOLOv8: An Enhanced Cascaded Framework for Concealed Object Detection. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15020690
Ijaz K, Khosa I, Ansari EA, Ali SF, Hussain A, Butt FA. BWFER-YOLOv8: An Enhanced Cascaded Framework for Concealed Object Detection. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(2):690. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15020690
Chicago/Turabian StyleIjaz, Khalid, Ikramullah Khosa, Ejaz A. Ansari, Syed Farooq Ali, Asif Hussain, and Faran Awais Butt. 2025. "BWFER-YOLOv8: An Enhanced Cascaded Framework for Concealed Object Detection" Applied Sciences 15, no. 2: 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15020690
APA StyleIjaz, K., Khosa, I., Ansari, E. A., Ali, S. F., Hussain, A., & Butt, F. A. (2025). BWFER-YOLOv8: An Enhanced Cascaded Framework for Concealed Object Detection. Applied Sciences, 15(2), 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15020690







