Optimizing Growth Conditions and Biochemical Properties of Chondracanthus acicularis (Rhodophyta) in Laboratory Settings
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Acclimatization
2.2. Cultivation Methods
2.3. Growth Measurements
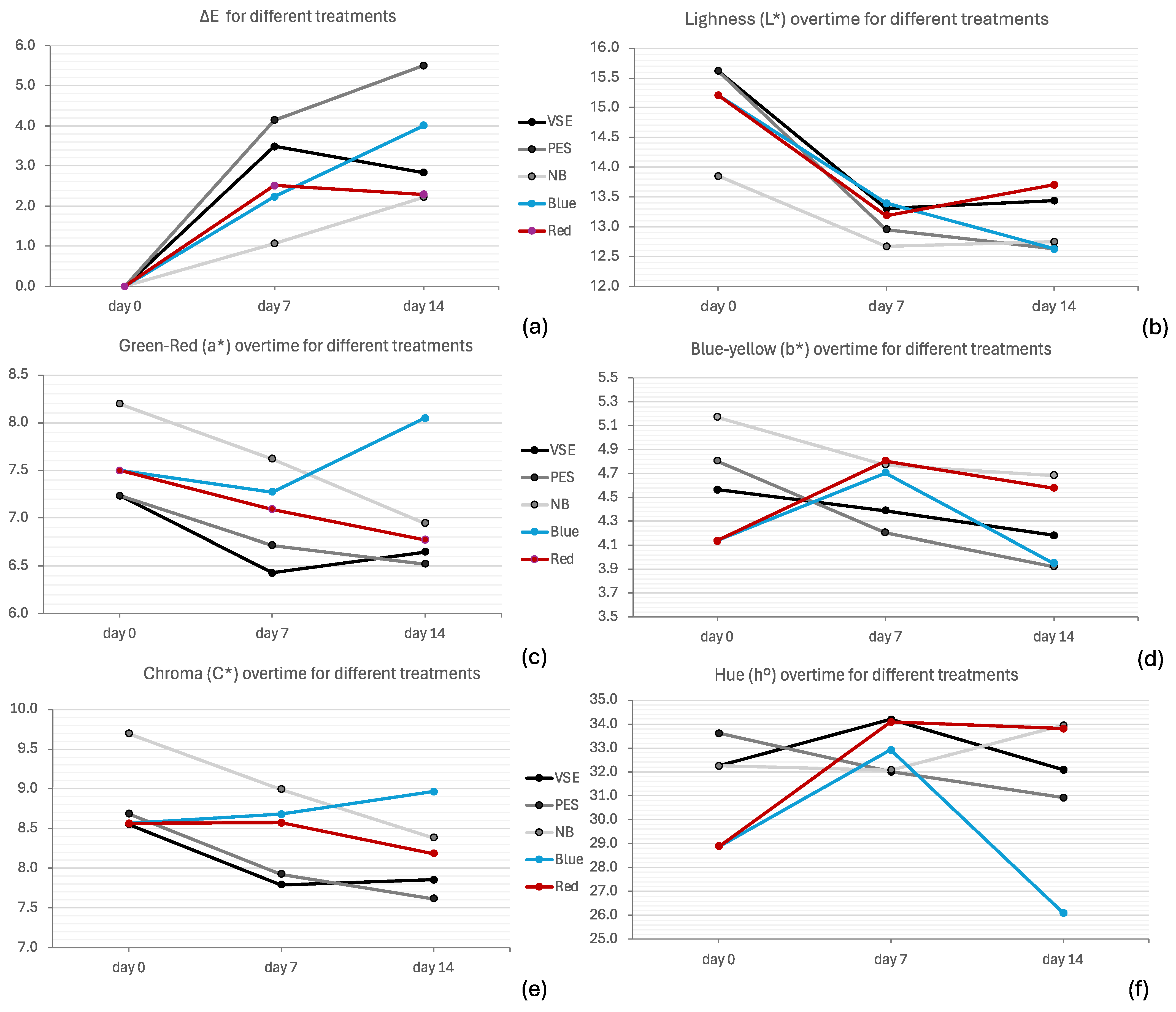
2.4. CIELAB Colour System
2.5. Biochemical Profiling
2.5.1. Moisture, Organic Matter, and Ash Content
2.5.2. Extraction and Quantification of Pigments
2.6. Statistical Analysis
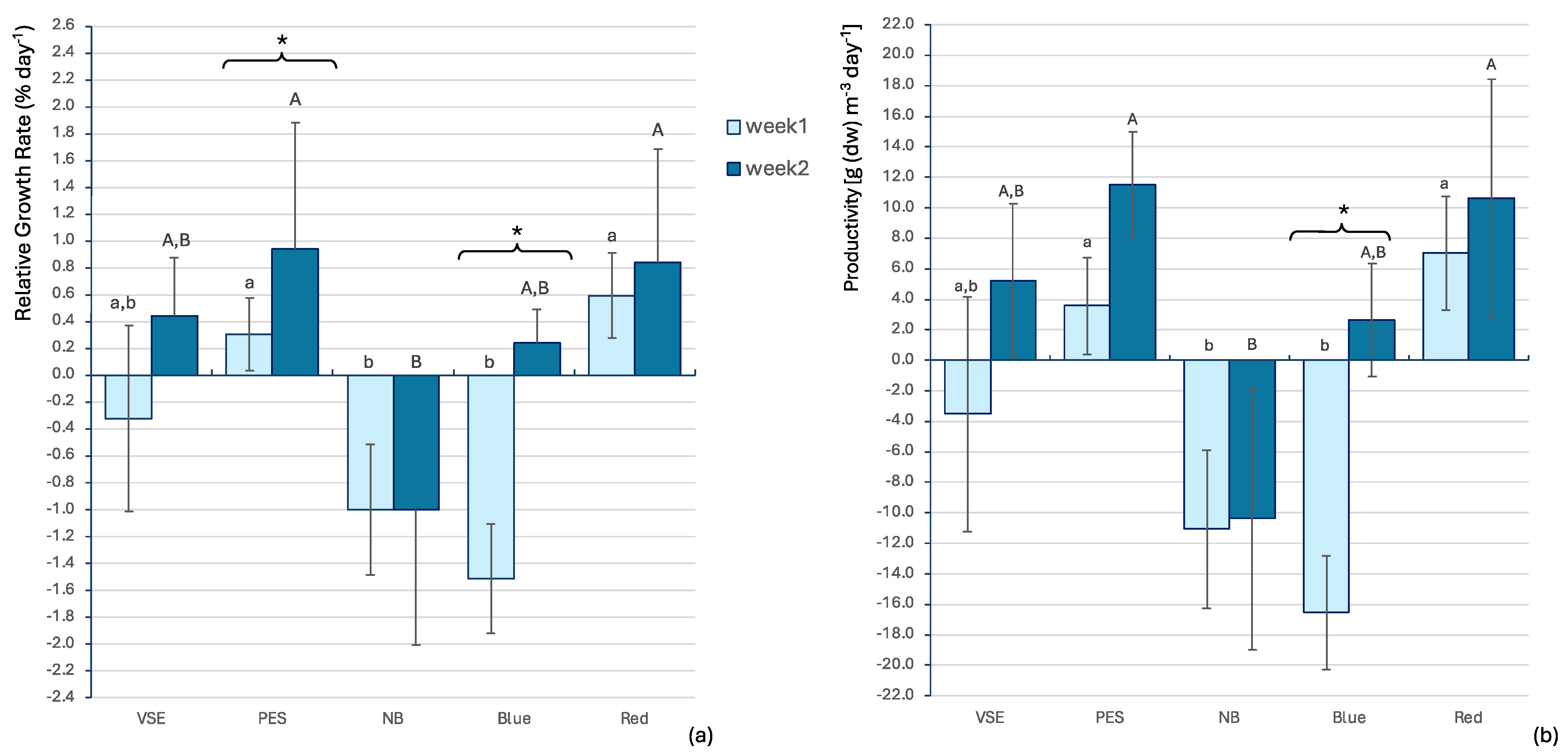
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Selnes, T.; Giesbers, E.; van den Burg, S.W.K. Innovation and Collaboration: Opportunities for the European Seaweed Sector in Global Value Chains. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Alalawy, A.I.; Almutairi, F.M.; Al-Duais, M.A.; Wang, J.; Salama, E.-S. Identification and Characterization of Marine Seaweeds for Biocompounds Production. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 101848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaco, M.; Duarte, A.; Bernardino, S.; Afonso, C.; Mouga, T. Sustainable Use of Seaweeds from S. Martinho Do Porto, Portugal–Past, Present, and Future Perspective. In Conference Proceedings ICoWEFS 2021, Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Water Energy Food and Sustainability (ICoWEFS 2021), Leiria, Portugal, 10–12 May 2021; da Costa Sanches Galvão, J.R., Duque de Brito, P.S., dos Santos Neves, F., da Silva Craveiro, F.G., de Amorim Almeida, H., Correia Vasco, J.O., Pires Neves, L.M., de Jesus Gomes, R., de Jesus Martins Mourato, S., Santos Ribeiro, V.S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Leiria, Portugal, 2021; pp. 216–226. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, L.; Cotas, J. Historical Use of Seaweed as an Agricultural Fertilizer in the European Atlantic Area. In Seaweeds as Plant Fertilizer, Agricultural Biostimulants and Animal Fodder; Pereira, L., Bahcevandziev, K., Joshi, N.H., Eds.; CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 1–22. ISBN 9781138597068. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, L. Edible Seaweeds of the World; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; ISBN 9780429154041. [Google Scholar]
- Flores-Molina, M.R.; Thomas, D.; Lovazzano, C.; Nez, A.N.; Zapata, J.; Kumar, M.; Correa, J.A.; Contreras-Porcia, L. Desiccation Stress in Intertidal Seaweeds: Effects on Morphology, Antioxidant Responses and Photosynthetic Performance. Aquat. Bot. 2014, 113, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampath-Wiley, P.; Neefus, C.D.; Jahnke, L.S. Seasonal Effects of Sun Exposure and Emersion on Intertidal Seaweed Physiology: Fluctuations in Antioxidant Contents, Photosynthetic Pigments and Photosynthetic Efficiency in the Red Alga Porphyra Umbilicalis Kützing (Rhodophyta, Bangiales). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2008, 361, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.; Sousa, A.; Coelho, H.; Amado, A.M.; Ribeiro-Claro, P.J.A. Use of FTIR, FT-Raman and 13C-NMR Spectroscopy for Identification of Some Seaweed Phycocolloids. Biomol. Eng. 2003, 20, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupert, R.; Rodrigues, K.F.; Thien, V.Y.; Yong, W.T.L. Carrageenan from Kappaphycus alvarezii (Rhodophyta, Solieriaceae): Metabolism, Structure, Production, and Application. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 859635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmawati, I.; Liviawaty, E.; Pratama, R.I. Carrageenan in Seaweed (Eucheuma sp.) and Use of Carrageenan in Fishery Food Products: A Review. Asian J. Fish. Aquat. Res. 2023, 23, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, S.S.M.; Carvalho, L.L.G.L.; Silva, P.P.J.; Rodrigues, M.S.M.; Pereira, O.; Pereira, L. Bioproducts From Seaweeds: A Review With Special Focus On The Iberian Peninsula. Curr. Org. Chem. 2014, 18, 896–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, M.V.; Inácio, L.G.; Martins, M.; Afonso, C.; Pereira, L.; Mouga, T. Primary Composition and Pigments of 11 Red Seaweed Species from the Center of Portugal. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, M.V.; Pacheco, D.; Cotas, J.; Mouga, T.; Afonso, C.; Pereira, L. Red Seaweed Pigments from a Biotechnological Perspective. Phycology 2021, 2, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, T.; Barroso, S.; Mendes, S.; Amaral, R.A.; Dias, J.R.; Baptista, T.; Saraiva, J.A.; Alves, N.M.; Gil, M.M. Optimization of Phycobiliprotein Pigments Extraction from Red Algae Gracilaria gracilis for Substitution of Synthetic Food Colorants. Food Chem. 2020, 321, 126688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreto, J.I.; Carignan, M.O. Mycosporine-like Amino Acids: Relevant Secondary Metabolites. Chemical and Ecological Aspects. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 387–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chrapusta, E.; Kaminski, A.; Duchnik, K.; Bober, B.; Adamski, M.; Bialczyk, J. Mycosporine-Like Amino Acids: Potential Health and Beauty Ingredients. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McReynolds, C.; Adrien, A.; Silvestre de Ferron, A.; Boussetta, N.; Grimi, N.; Pecastaing, L.; Fernandes, S.C.M. Extraction of Mycosporine-like Amino Acids and Proteins from the Agarophyte Gelidium corneum Using Pulsed Power Techniques. Foods 2023, 12, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towle, G.A. Carrageenan. In Industrial Gums; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1973; pp. 83–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udo, T.; Mummaleti, G.; Mohan, A.; Singh, R.K.; Kong, F. Current and Emerging Applications of Carrageenan in the Food Industry. Food Res. Int. 2023, 173, 113369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, M.V.; Inácio, L.G.; Ruas, A.; Silva, I.A.; Mouga, T.; Pereira, L.; Afonso, C. Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties of Selected Red Seaweeds from Central Portugal. Appl. Sci. 2022, 13, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouga, T. Seaweed Harvesting and Aquaculture: An Overview of the Past 70 Years. In Conference Proceedings ICoWEFS 2023, Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Water Energy Food and Sustainability (ICoWEFS 2023), Leiria, Portugal, 10–12 May 2023; Galvão, J.R.D.C.S., Brito, P., Neves, F.D.S., Almeida, H.D.A., Mourato, S.D.J.M., Nobre, C., Eds.; Springer Nature: Castelo Branco, Portugal, 2024; pp. 365–375. ISBN 9783031485329. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2024; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2024; ISBN 978-92-5-138763-4. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.K.; Yarish, C.; Hwang, E.K.; Park, M.; Kim, Y. Seaweed Aquaculture: Cultivation Technologies, Challenges and Its Ecosystem Services. Algae 2017, 32, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreakis, N.; Schaffelke, B. Invasive Marine Seaweeds: Pest or Prize? In Seaweed Biology Novel Insights into Ecophysiology, Ecology and Utilization; Wiencke, C., Bischof, K., Eds.; Springer Nature: Berlin, Germany, 2012; pp. 235–262. [Google Scholar]
- Valero, M.; Guillemin, M.; Destombe, C.; Gachon, C.M.M.; Badis, Y.; Buschmann, A.H.; Camus, C.; Faugeron, S. Perspectives on Domestication Research for Sustainable Seaweed Aquaculture. Perspect. Phycol. 2017, 1, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumford, T.W.J.R. Progress and Prospects for Field Cultivation of Iridaea cordata and Gigartina exasperata. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Seaweeds in the Warm Pacific, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 6 March 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Bulboa, C.R.; Macchiavello, J.E.; Oliveira, E.C.; Fonck, E. First Attempt to Cultivate the Carrageenan-Producing Seaweed Chondracanthus chamissoi (C. Agardh) Kutzing (Rhodophyta; Gigartinales) in Northern Chile. Aquac. Res. 2005, 36, 1069–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschmann, A.H.; Varela, D.; Cifuentes, M.; Del Carmen Hernández-González, M.; Henríquez, L.; Westermeier, R.; Correa, J.A. Experimental Indoor Cultivation of the Carrageenophytic Red Alga Gigartina skottsbergii. Aquaculture 2004, 241, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Campos, M.; Pérez-Lloréns, J.L.; Barrena, F.; Pérez-González, C.M.; Hernández, I. Culture of Gracilaria gracilis and Chondracanthus teedei from Vegetative Fragments in the Field and Carpospores in Laboratory. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.; Amado, A.M.; Critchley, A.T.; van de Velde, F.; Ribeiro-Claro, P.J.A. Identification of Selected Seaweed Polysaccharides (Phycocolloids) by Vibrational Spectroscopy (FTIR-ATR and FT-Raman). Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 1903–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L. Population Studies and Carrageenan Properties in Eight Gigartinales (Rhodophyta) from Western Coast of Portugal. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 939830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco, D.; Cotas, J.; Domingues, A.; Ressurreição, S.; Bahcevandziev, K.; Pereira, L. Chondracanthus teedei var. lusitanicus: The Nutraceutical Potential of an Unexploited Marine Resource. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, F.; Fernandes, C.; Silva, P.; Pereira, L.; Gonçalves, T. Antifungal Activity of Carrageenan Extracts from the Red Alga Chondracanthus teedei var. lusitanicus. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 2991–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vásquez, V.; Martínez, R.; Rodríguez-Núñez, K.; Bernal, C. Angiotensin-I Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Bioaccessible Peptides Obtained from Protein Extracts of Macrocystis pyrifera and Chondracanthus chamissoi Seaweeds. Algal. Res. 2024, 81, 103575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares Pessoa Pinho de Vasconcelos, E.R.; Vasconcelos, J.B.; de Vasconcelos Reis, T.N.; de Lourdes Montenegro Cocentino, A.; Mallea, A.J.A.; Martins, G.M.; Neto, A.I.; Fujii, M.T. Macroalgal Responses to Coastal Urbanization: Relative Abundance of Indicator Species. J. Appl. Phycol. 2019, 31, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, A.I. Observations on the Biology and Ecology of Selected Macroalgae from the Littoral of São Miguel (Azores). Bot. Mar. 2000, 43, 483–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulboa Contador, C.; Massad, I.P.; Contreras-Porcia, L.; Zapata, J.; Castañeda, F.; Ramírez, M.E.; Gil-Kodaka, P. Concise Review of Genus Chondracanthus (Rhodophyta: Gigartinales). J. Appl. Phycol. 2020, 32, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiry, M.D. Photoperiodic and Temperature Responses in the Growth and Tetrasporogenesis of Gigartina acicularis (Rhodophyta) from Ireland. Helgol. Meeresunters. 1984, 1, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santelices, B. Patterns of Reproduction, Dispersal and Recruitment in Seaweeds. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 1990, 28, 177–276. [Google Scholar]
- Bertocci, I.; Araújo, R.; Incera, M.; Arenas, F.; Pereira, R.; Abreu, H.; Larsen, K.; Sousa-Pinto, I. Benthic Assemblages of Rock Pools in Northern Portugal: Seasonal and between-Pool Variability. Sci. Mar. 2011, 76, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.; Mesquita, J.F. Carrageenophytes of Occidental Portuguese Coast: 1-Spectroscopic Analysis in Eight Carrageenophytes from Buarcos Bay. Biomol. Eng. 2003, 20, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.; Van De Velde, F. Portuguese Carrageenophytes: Carrageenan Composition and Geographic Distribution of Eight Species (Gigartinales, Rhodophyta). Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Ordóñez, E.; Rupérez, P. FTIR-ATR Spectroscopy as a Tool for Polysaccharide Identification in Edible Brown and Red Seaweeds. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 1514–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Guo, C.; Guo, H. Progress of Carrageenan-Based Films and Coatings for Food Packaging Applications. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2024, 37, 533–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mzibra, A.; Aasfar, A.; Benhima, R.; Khouloud, M.; Boulif, R.; Douira, A.; Bamouh, A.; Meftah Kadmiri, I. Biostimulants Derived from Moroccan Seaweeds: Seed Germination Metabolomics and Growth Promotion of Tomato Plant. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2021, 40, 353–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mzibra, A.; Aasfar, A.; El Arroussi, H.; Khouloud, M.; Dhiba, D.; Kadmiri, I.M.; Bamouh, A. Polysaccharides Extracted from Moroccan Seaweed: A Promising Source of Tomato Plant Growth Promoters. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 2953–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.M.; Sultana, F.; Khan, S.; Nayeema, J.; Mostafa, M.; Ferdus, H.; Tran, L.S.P.; Mostofa, M.G. Carrageenans as Biostimulants and Bio-Elicitors: Plant Growth and Defense Responses. Stress Biol. 2024, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montanha, J.A.; Bourgougnon, N.; Boustie, J.; Amoros, M. Antiviral Activity of Carrageenans from Marine Red Algae. Am. J. Pharm. 2009, 28, 443–451. [Google Scholar]
- Vrinda, S.K.; Niharika, A.S.; Ligin, M.; Sabitha, M. Carrageenan for Drug Delivery and Biomedical Applications. Nat. Biopolym. Drug Deliv. Tissue Eng. 2023, 57–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodian, M.Y.; Lafontaine, N.; Matard, M.; Mussio, I.; Rusig, A.M. Evaluation of the in Vitro Methods for Micropropagation of Chondracanthus acicularis (Roth) Fredericq (Gigartinales, Rhodophyta): Tissue Culture and Production of Protoplasts. J. Appl. Phycol. 2013, 25, 1835–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmond, S.; Green, L.; Yarish, C.; Kim, J.; Neefus, C. New England Seaweed Culture Handbook-Nursery Systems; Redmond, S., Green, L., Yarish, C., Kim, J., Neefus, C., Eds.; Connecticut Sea Grant CTSG-14-01; Connecticut Sea Grant: Groton, CT, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, L.B.; Barufi, J.B.; Plastino, E.M. Growth of Red and Green Strains of the Tropical Agarophyte Gracilaria cornea J. Agardh (Gracilariales, Rhodophyta) in Laboratory. Rev. Bras. Bot. 2006, 29, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concórdio-Reis, P.; Cardeira, M.; Macedo, A.C.; Ferreira, S.S.; Serra, A.T.; Coimbra, M.A.; Amorim, A.; Reis, M.A.M.; Freitas, F. Novel Exopolysaccharide Produced by the Marine Dinoflagellate Heterocapsa AC210: Production, Characterization, and Biological Properties. Algal. Res. 2023, 70, 103014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patarra, R.F.; Carreiro, A.S.; Lloveras, A.A.; Abreu, M.H.; Buschmann, A.H.; Neto, A.I. Effects of Light, Temperature and Stocking Density on Halopteris scoparia Growth. J. Appl. Phycol. 2017, 29, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellar, M.; Obón, J.; Fernández-López, J. The Isolation and Properties of a Concentrated Red-purple Betacyanin Food Colourant from Opuntia stricta Fruits. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2006, 86, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 20th ed.; Latimer, G.W., Jr., Ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2016; ISBN 0935584870. [Google Scholar]
- Beer, S.; Eshel, A. Determining Phycoerythrin and Phycocyanin Concentrations in Aqueous Crude Extracts of Red Algae. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1985, 36, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osório, C.; Machado, S.; Peixoto, J.; Bessada, S.; Pimentel, F.B.; Alves, R.C.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P. Pigments Content (Chlorophylls, Fucoxanthin and Phycobiliproteins) of Different Commercial Dried Algae. Separations 2020, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, J.T.O.; Allen, R.L. Dependence of Chloroplast Pigment Synthesis on Protein Synthesis: Effect of Actidione. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1965, 21, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.K.; Mao, Y.; Kraemer, G.; Yarish, C. Growth and Pigment Content of Gracilaria tikvahiae McLachlan under Fluorescent and LED Lighting. Aquaculture 2015, 436, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, F.L.; Aguilera, J.; Niell, F.X. Red and blue light regulation of growth and photosynthetic metabolism in Porphyra umbilicalis (Bangiales, Rhodophyta). Eur. J. Phycol. 1995, 30, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.M.; El-Sheekh, M. Enhancement of Biochemical and Nutritional Contents of Some Cultivated Seaweeds Under Laboratory Conditions. J. Diet. Suppl. 2018, 15, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, M.; Correia, A.; Pereira, C.; Santos, J.; Baptista, T.; Afonso, C.; Gil, M.; Pombo, A.; Tecelão, C.; Mendes, S.; et al. The Influence of Light and Culture Media on the Growth of the Red Seaweed Gracilaria gracilis (Rhodophyta, Gracilariales) under Laboratory Conditions. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurd, C.L.; Harrison, P.J.; Bischof, K.; Lobban, C.S. Seaweed Ecology and Physiology, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014; ISBN 9780521145954. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Lan, L.; Li, H.; Gong, Q.; Gao, X. Effects of Nitrogen Source and Concentration on the Growth and Biochemical Composition of the Red Seaweed Grateloupia turuturu (Halymeniaceae, Rhodophyta). Sustainability 2023, 15, 4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubsch, A.; Lansbergen, R.A. Seaweed Factsheet: Nutrient Uptake and Requirements; Wageningen University & Research: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, P.J.; Hurd, C.L. Nutrient Physiology of Seaweeds: Application of Concepts to Aquaculture. Cah. Biol. Mar. 2001, 42, 71–82. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, M.; Huang, X.; Luo, Z. Effects of Nitrogen to Phosphorus Ratios on Algal Growth and Arsenate Metabolism by Microcystis aeruginosa with Dissolved Organic Phosphorus and Nitrate as Nutrients. Algal Res 2023, 69, 102922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, M.; Meena, R.; Siddhanta, A.K.; Selvaraj, K.; Chithra, K. Culture of the Red Alga Sarconema filiforme in Open Waters and Hybrid Carrageenan from the Cultivated Seaweeds. J. Appl. Phycol. 2015, 27, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakaki, N.; Flores Ramos, L.; Oscanoa Huaynate, A.I.; Ruíz Soto, A.; Ramírez, M.E. Biochemical and Nutritional Characterization of Edible Seaweeds from the Peruvian Coast. Plants 2023, 12, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, M.V.; Mouga, T.; Correia, A.P.; Afonso, C.; Baptista, T. New Insights on the Sporulation, Germination, and Nutritional Profile of Gracilaria gracilis (Rhodophyta) Grown under Controlled Conditions. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, D.; Freitas, A.C.; Pereira, L.; Rocha-Santos, T.A.P.; Vasconcelos, M.W.; Roriz, M.; Rodríguez-Alcalá, L.M.; Gomes, A.M.P.; Duarte, A.C. Chemical Composition of Red, Brown and Green Macroalgae from Buarcos Bay in Central West Coast of Portugal. Food Chem. 2015, 183, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, L.; Lima, E.; Neto, A.I.; Marcone, M.; Baptista, J. Nutritional and Functional Bioactivity Value of Selected Azorean Macroalgae: Ulva compressa, Ulva rigida, Gelidium microdon, and Pterocladiella capillacea. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 1757–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tibbetts, S.M.; Milley, J.E.; Lall, S.P. Nutritional Quality of Some Wild and Cultivated Seaweeds: Nutrient Composition, Total Phenolic Content and in Vitro Digestibility. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 3575–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidigare, R.R.; Ondrusek, M.E.; Morrow, J.H.; Kiefer, D.A. In-Vivo Absorption Properties of Algal Pigments. Conf. Proc. SPIE 1990, 1302, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voerman, S.E.; Ruseckas, A.; Turnbull, G.A.; Samuel, I.D.W.; Burdett, H.L. Red Algae Acclimate to Low Light by Modifying Phycobilisome Composition to Maintain Efficient Light Harvesting. BMC Biol. 2022, 20, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Li, K.; Pan, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wernberg, T.; de Bettignies, T.; Wu, J.; Zhou, C.; Huang, Z.; Xiao, X. Artificial Light Source Selection in Seaweed Production: Growth of Seaweed and Biosynthesis of Photosynthetic Pigments and Soluble Protein. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, R.; Campos, A.M.; Goldman, J.; Barrote, I.; Mata, L.; Silva, J. Effects of Light Quality and Intensity on Growth and Bromoform Content of the Red Seaweed Asparagopsis taxiformis. J. Appl. Phycol. 2024, 36, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dishon, G.; Resetarits, H.M.; Tsai, B.; Jones, A.L.; Agarwal, V.; Smith, J.E. The Effect of Light Intensity, Spectrum, and Photoperiod on the Physiological Performance of Asparagopsis taxiformis Tetrasporophytes. Algal. Res. 2023, 76, 103304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona, R.; Vergara, J.J.; Lahaye, M.; Niell, F.X. Light Quality Affects Morphology and Polysaccharide Yield and Composition of Gelidium sesquipedale. J. Appl. Phycol. 1998, 10, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yago, T.; Arakawa, H.; Shigeto, S.; Ito, R.; Matsumoto, A.; Okumura, Y. Effects of Light Conditions on the Growth of Commercial Seaweed Undaria pinnatifida. Afr. J. Plant Sci. 2017, 11, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ak, I.; Yücesan, M. Effect of Light Intensity on the Pigment Composition of Gracilaria verrucosa (Rhodophyta). Fres. Environ. Bull. 2012, 21, 2126–2131. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.P.; Singh, P. Effect of Temperature and Light on the Growth of Algae Species: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 50, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, K.C.; Simpson, F.J. The Cultivation of Palmaria palmata. Effect of Light Intensity and Temperature on Growth and Chemical Composition. Bot. Mar. 1981, 24, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghedifa, A.B.; Vega, J.; Korbee, N.; Mensi, F.; Figueroa, F.L.; Sadok, S. Effects of Light Quality on the Photosynthetic Activity and Biochemical Composition of Gracilaria gracilis (Rhodophyta). J. Appl. Phycol. 2021, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delta E, Delta H, Delta T: What does it mean? Available online: https://help.fiery.com/fieryxf/KnowledgeBase/color/Delta%20E_H_T.pdf (accessed on 3 December 2024).
- Idowu, A.T.; Amigo-Benavent, M.; Whelan, S.; Edwards, M.D.; FitzGerald, R.J. Impact of Different Light Conditions on the Nitrogen, Protein, Colour, Total Phenolic Content and Amino Acid Profiles of Cultured Palmaria palmata. Foods 2023, 12, 3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawes, C.J. The Effect of Nutrient and Photon Fluence on the Photosynthetic Responses of Red and Green Pigmented Cultivars of Eucheuma denticulatum. Bot. Mar. 1995, 38, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simko, I. Predictive Modeling of a Leaf Conceptual Midpoint Quasi-Color (CMQ) Using an Artificial Neural Network. Sensors 2020, 20, 3938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleitas, A.G.; Sardar, S.; Arnould-Pétré, M.M.; Murace, M.; Vignolini, S.; Brodie, J.; Lanzani, G.; D’Andrea, C. Influence of Structural Colour on the Photoprotective Mechanism in the Gametophyte Phase of the Red Alga Chondrus crispus. J. R. Soc. Interface 2024, 21, 20230676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawes, C.; Kovach, C.; Friedlander, M. Exposure of Gracilaria to Various Environmental Conditions. II. The Effect on Fatty Acid Composition. Bot. Mar. 1993, 36, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomi Barufi, J.; Figueroa, F.L.; Plastino, E.M. Effects of Light Quality on Reproduction, Growth and Pigment Content of Gracilaria birdiae (Rhodophyta: Gracilariales). Sci. Mar. 2015, 79, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
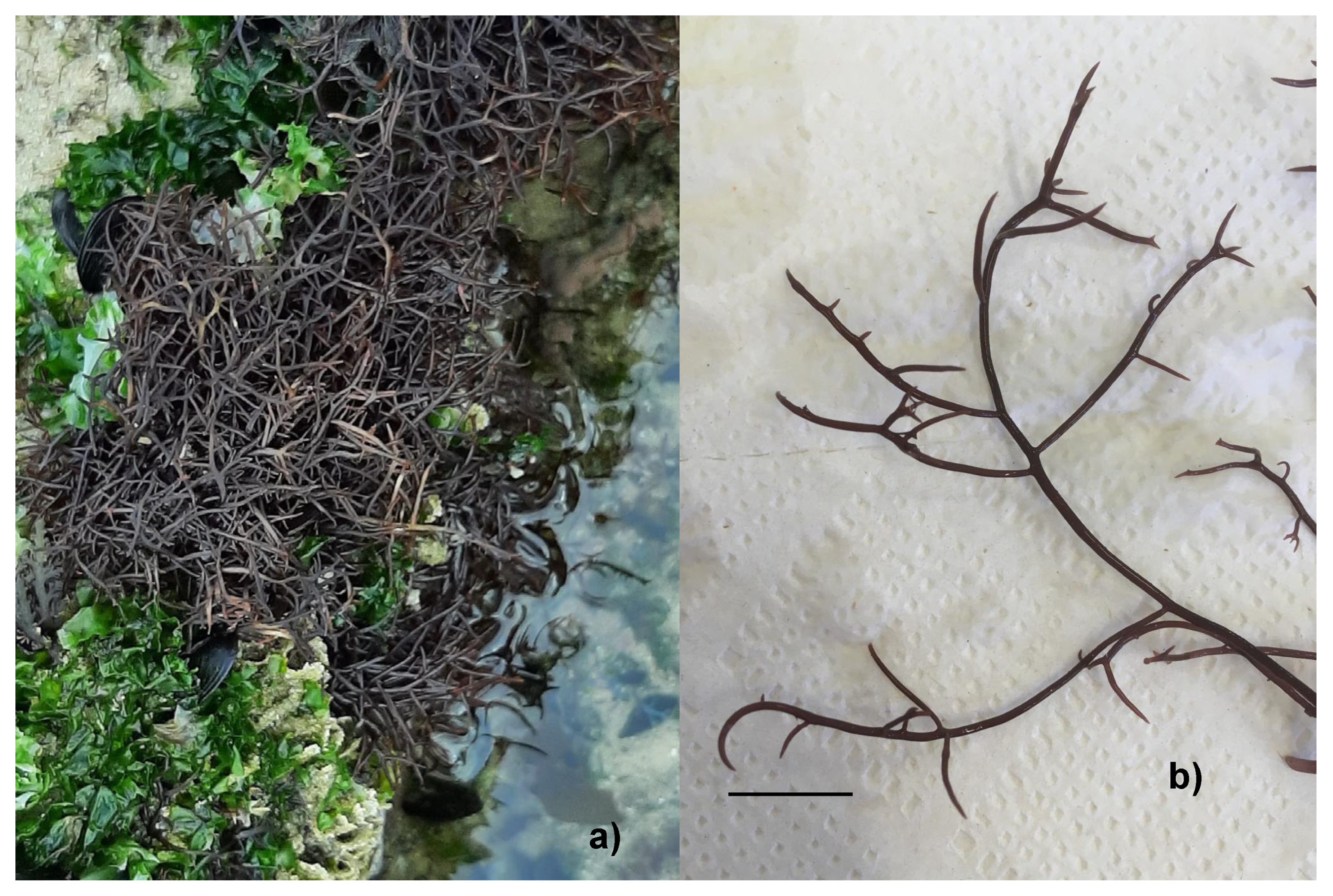




| Essay | Culture Media | Light |
|---|---|---|
| A | Von Stosch Enriched (VSE) | White LED |
| B | Provasoli Enriched Seawater (PES) | White LED |
| C | Nutribloom plus® (NB) | White LED |
| D | Provasoli Enriched Seawater (PES) | Red LED |
| E | Provasoli Enriched Seawater (PES) | Blue LED |
| Dry Weight | Organic Matter | Ash | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VSE, day7 | 27.01 | ± | 0.82 | 73.00 | ± | 2.68 a | 27.00 | ± | 2.68 b |
| VSE, day 14 | 29.00 | ± | 0.56 | 71.31 | ± | 1.38 | 28.69 | ± | 1.38 |
| PES, day 7 | 28.88 | ± | 1.62 | 72.52 | ± | 0.92 a | 27.48 | ± | 0.92 b |
| PES, day 14 | 28.39 | ± | 1.05 | 73.33 | ± | 1.04 a | 26.67 | ± | 1.04 b |
| NB, day7 | 31.21 | ± | 1.01 | 73.26 | ± | 0.16 a | 26.74 | ± | 0.16 b |
| NB, day 14 | 29.14 | ± | 0.86 | 71.24 | ± | 0.78 | 28.76 | ± | 0.78 |
| Blue LED, day7 | 27.43 | ± | 0.95 | 71.69 | ± | 0.06 | 28.31 | ± | 0.06 |
| Blue LED, day 14 | 28.06 | ± | 0.63 | 71.24 | ± | 0.22 | 28.76 | ± | 0.22 |
| Red LED, day7 | 26.35 | ± | 0.99 | 71.12 | ± | 0.24 | 28.88 | ± | 0.24 |
| Red LED, day 14 | 26.12 | ± | 0.01 | 68.06 | ± | 0.29 b | 31.94 | ± | 0.29 a |
| Wild | 29.47 | ± | 0.20 | 69.20 | ± | 0.86 b | 30.80 | ± | 0.86 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mouga, T.; Sousa, A.; Freitas, M.V.; Afonso, C. Optimizing Growth Conditions and Biochemical Properties of Chondracanthus acicularis (Rhodophyta) in Laboratory Settings. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 810. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15020810
Mouga T, Sousa A, Freitas MV, Afonso C. Optimizing Growth Conditions and Biochemical Properties of Chondracanthus acicularis (Rhodophyta) in Laboratory Settings. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(2):810. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15020810
Chicago/Turabian StyleMouga, Teresa, Andreia Sousa, Marta V. Freitas, and Clélia Afonso. 2025. "Optimizing Growth Conditions and Biochemical Properties of Chondracanthus acicularis (Rhodophyta) in Laboratory Settings" Applied Sciences 15, no. 2: 810. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15020810
APA StyleMouga, T., Sousa, A., Freitas, M. V., & Afonso, C. (2025). Optimizing Growth Conditions and Biochemical Properties of Chondracanthus acicularis (Rhodophyta) in Laboratory Settings. Applied Sciences, 15(2), 810. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15020810









