Short-Term Photovoltaic Output Prediction Method Based on Data Decomposition and Error Correction
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- In the absence of auxiliary meteorological data, this article uses the STL method to decompose the historical data of photovoltaic output, obtaining more regular seasonal components, trend components, and residual terms.
- (2)
- By using different TCN models to mine the historical features of different components, accurate prediction of each component can be achieved, and the predicted value of the photovoltaic output can be obtained through superposition.
- (3)
- Considering the limitations of the prediction model, based on denoising the historical prediction error sequence, a deep neural network is used to explore the temporal patterns of prediction errors, and a photovoltaic output error correction method based on error prediction is proposed.
2. Data Analysis and Processing
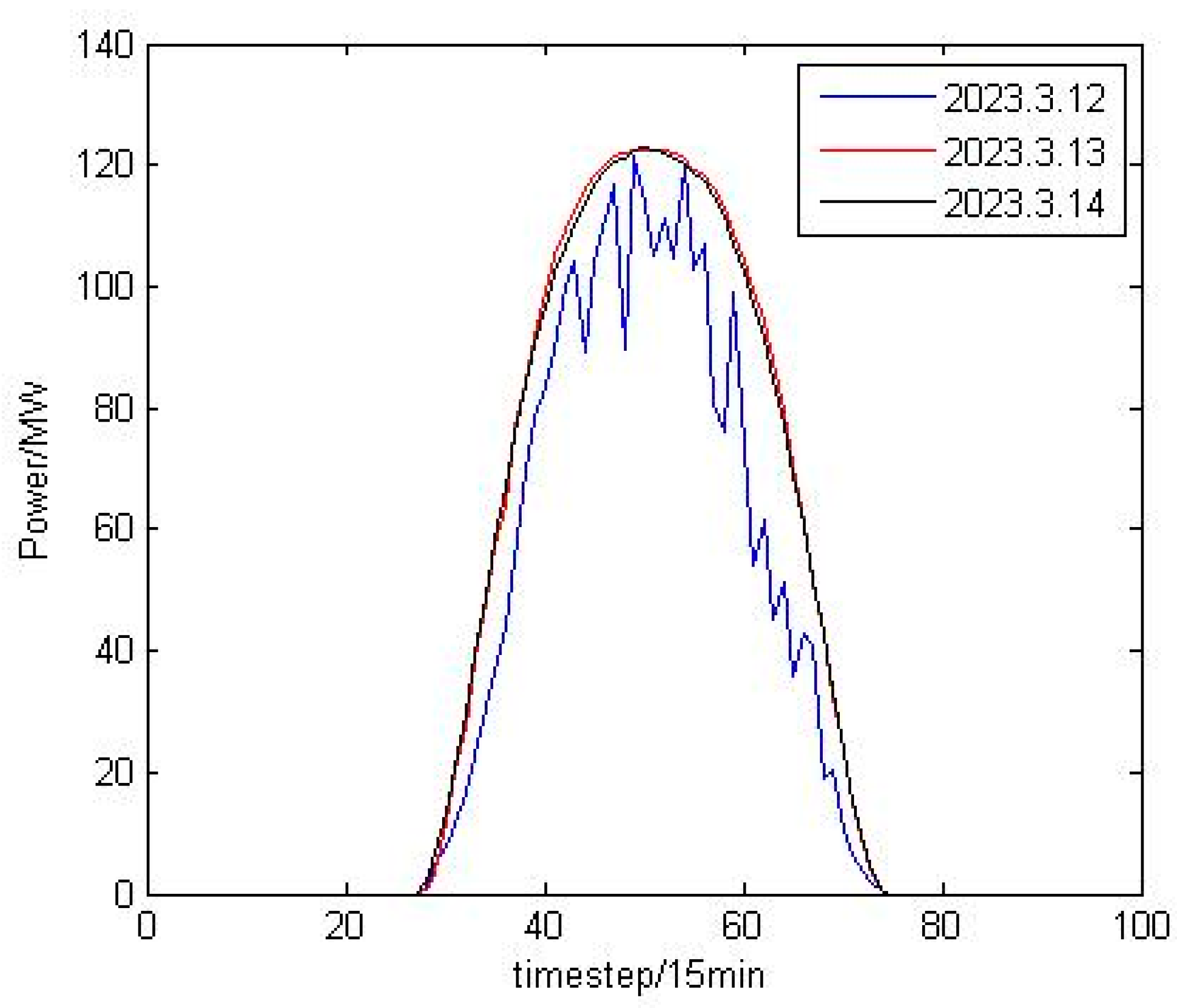
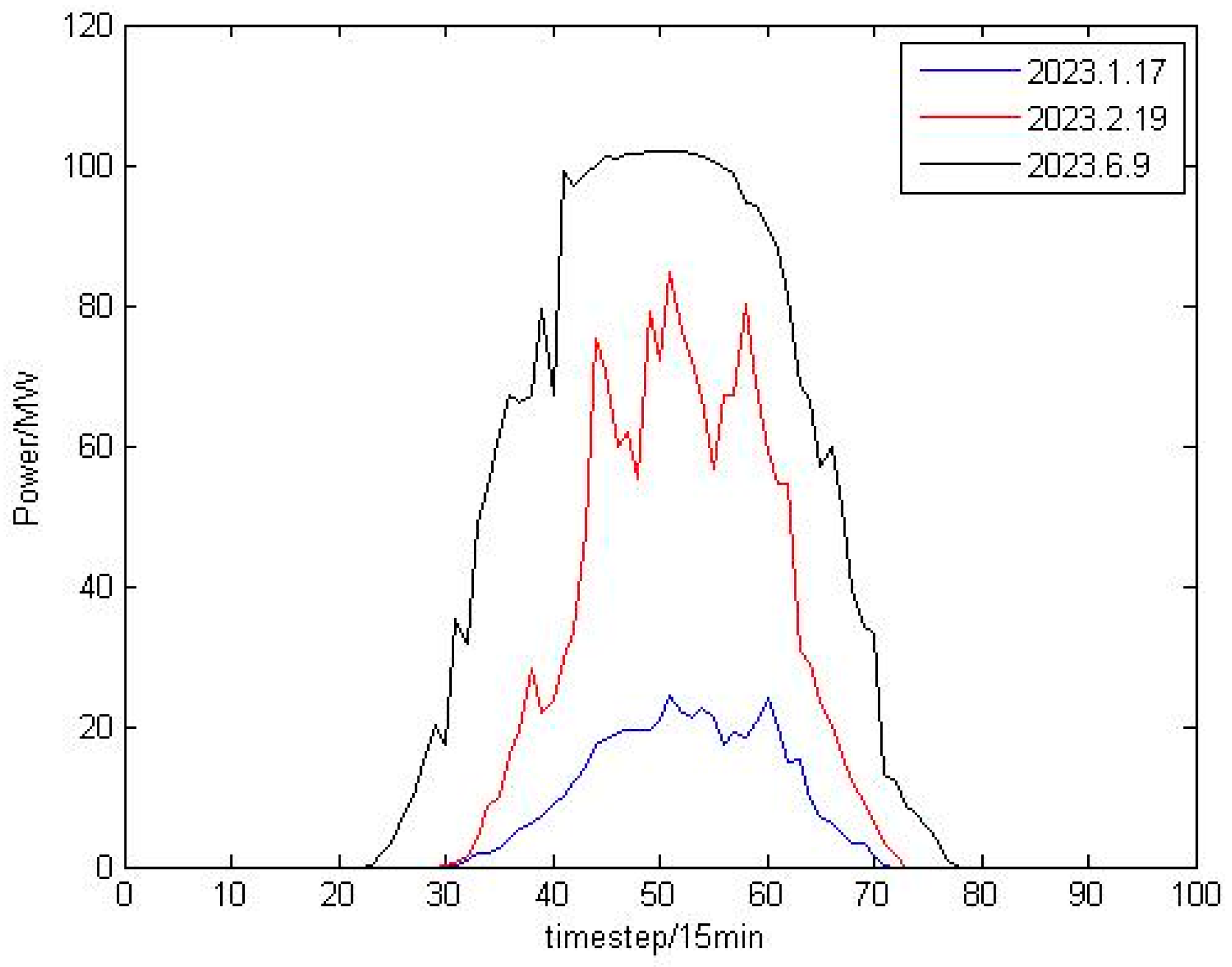
2.1. Data Analysis
2.2. Data Processing
3. Method
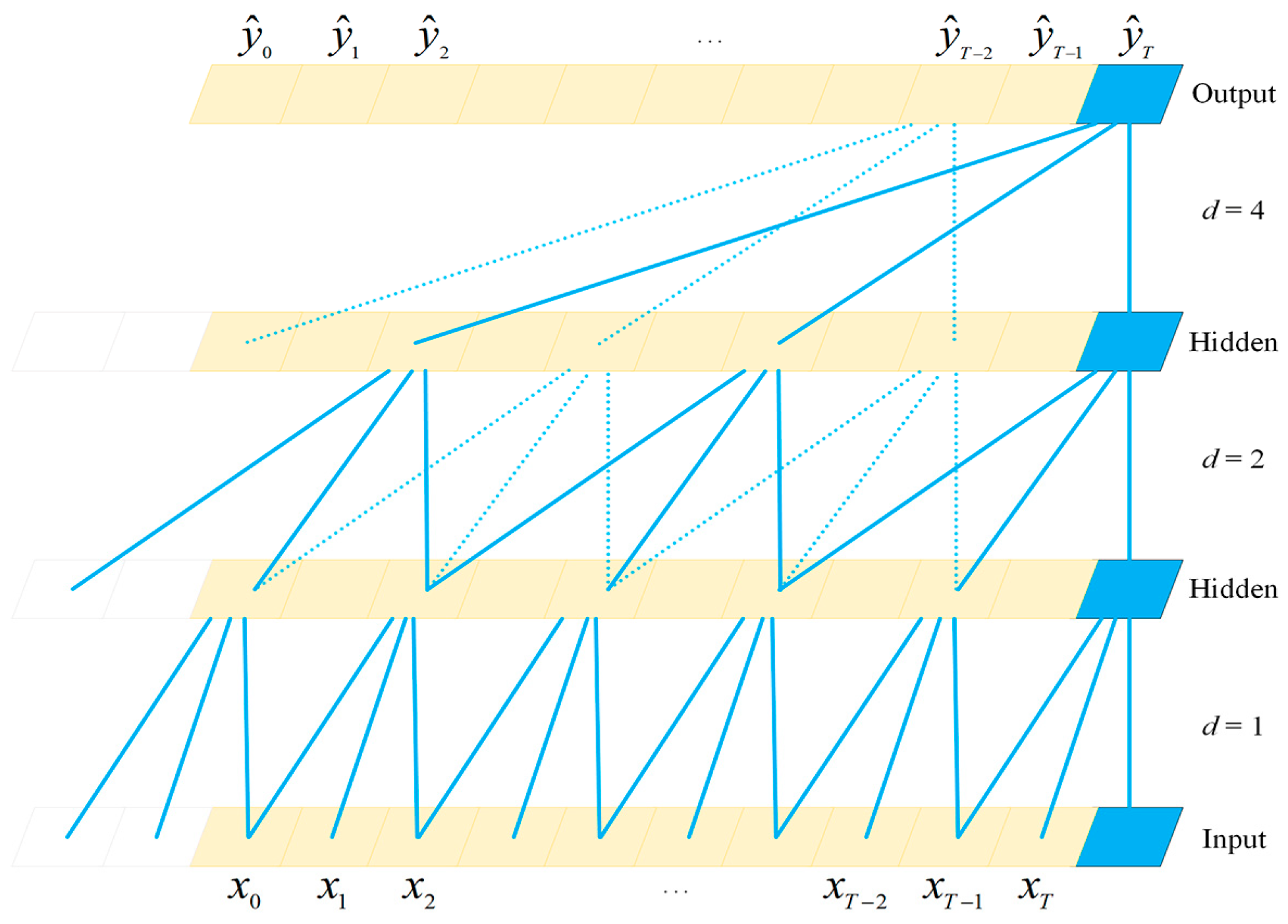
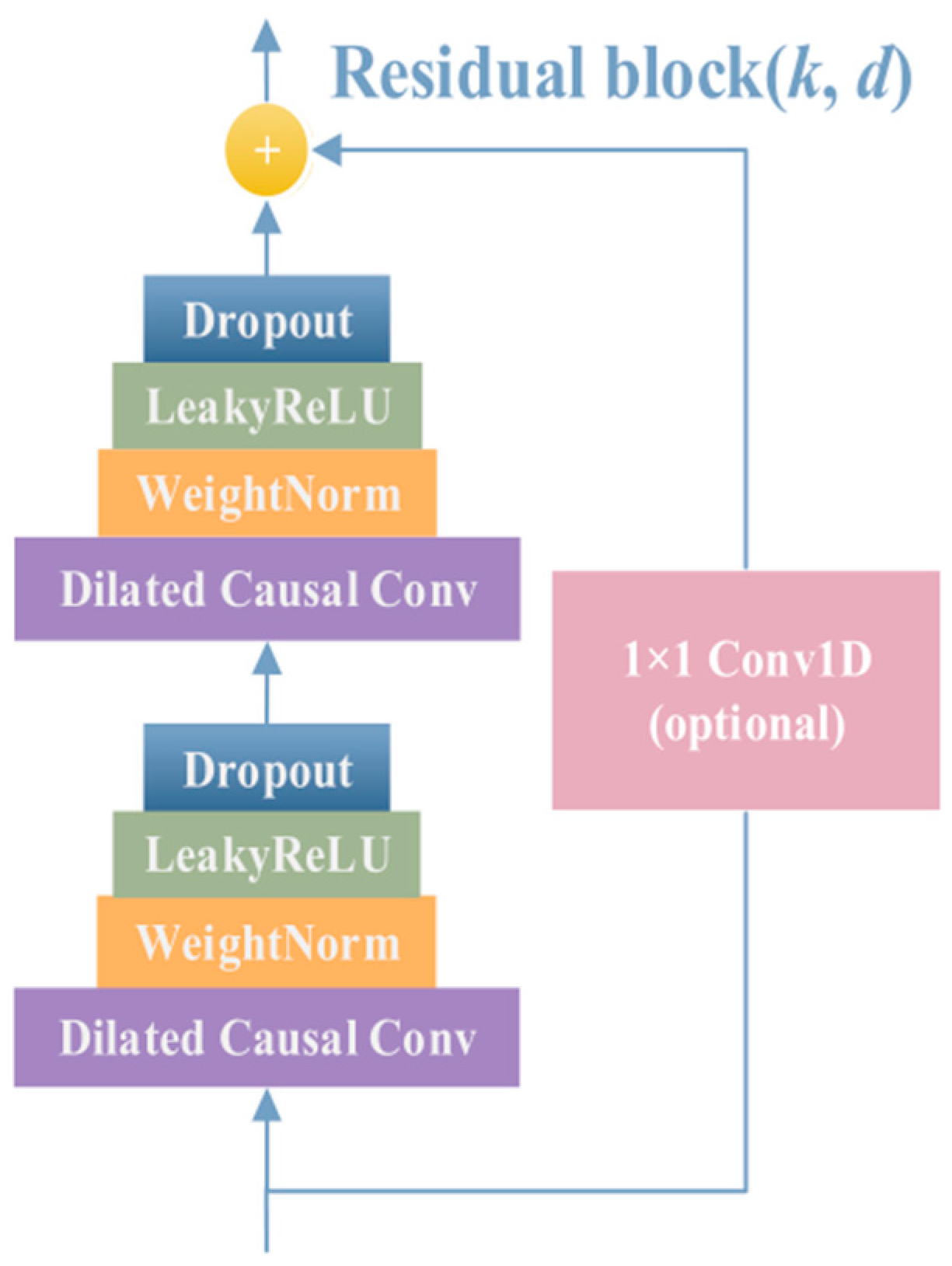
3.1. TCN Model Process
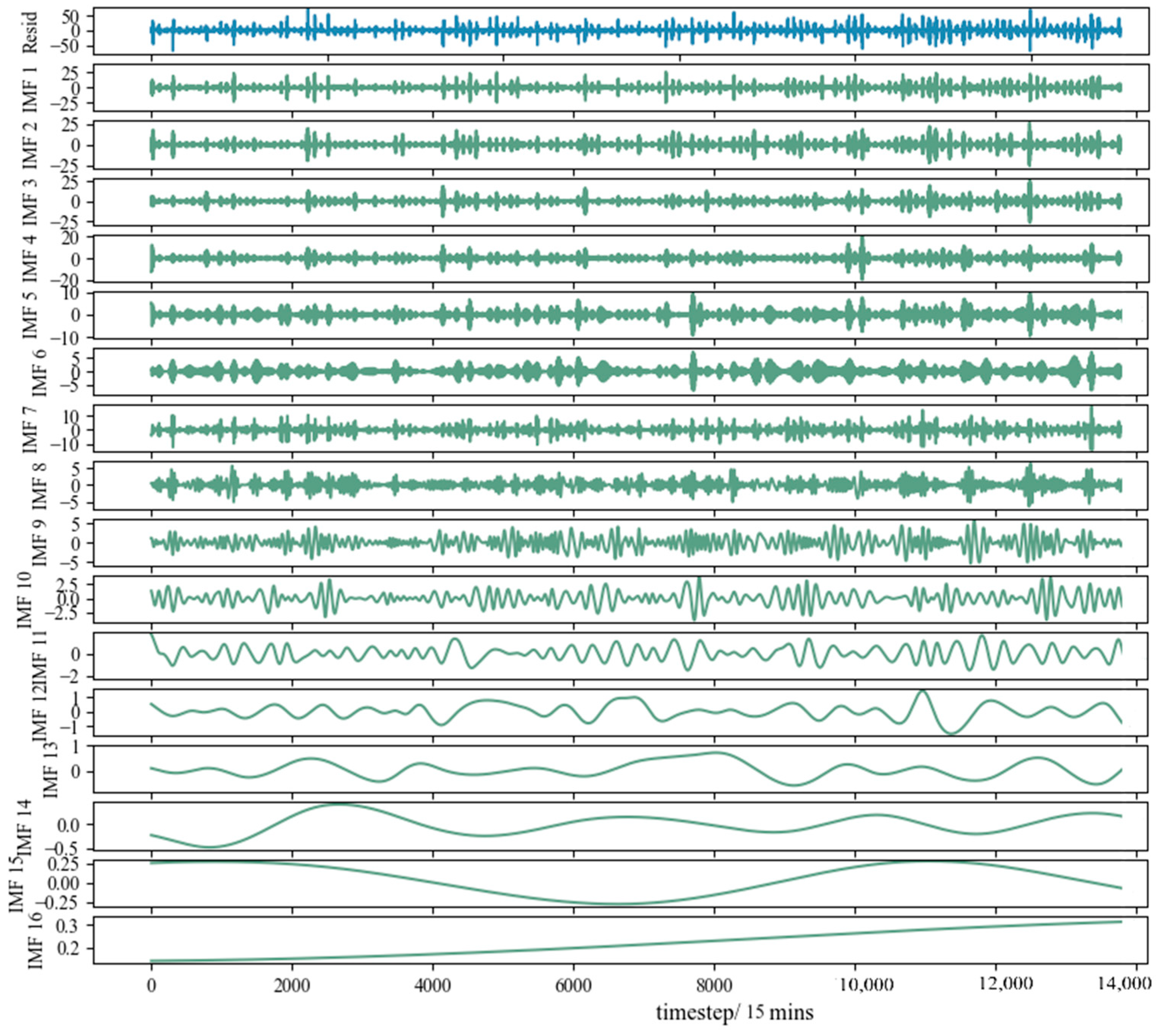
3.2. Error Correction Models
3.3. Performance Evaluation
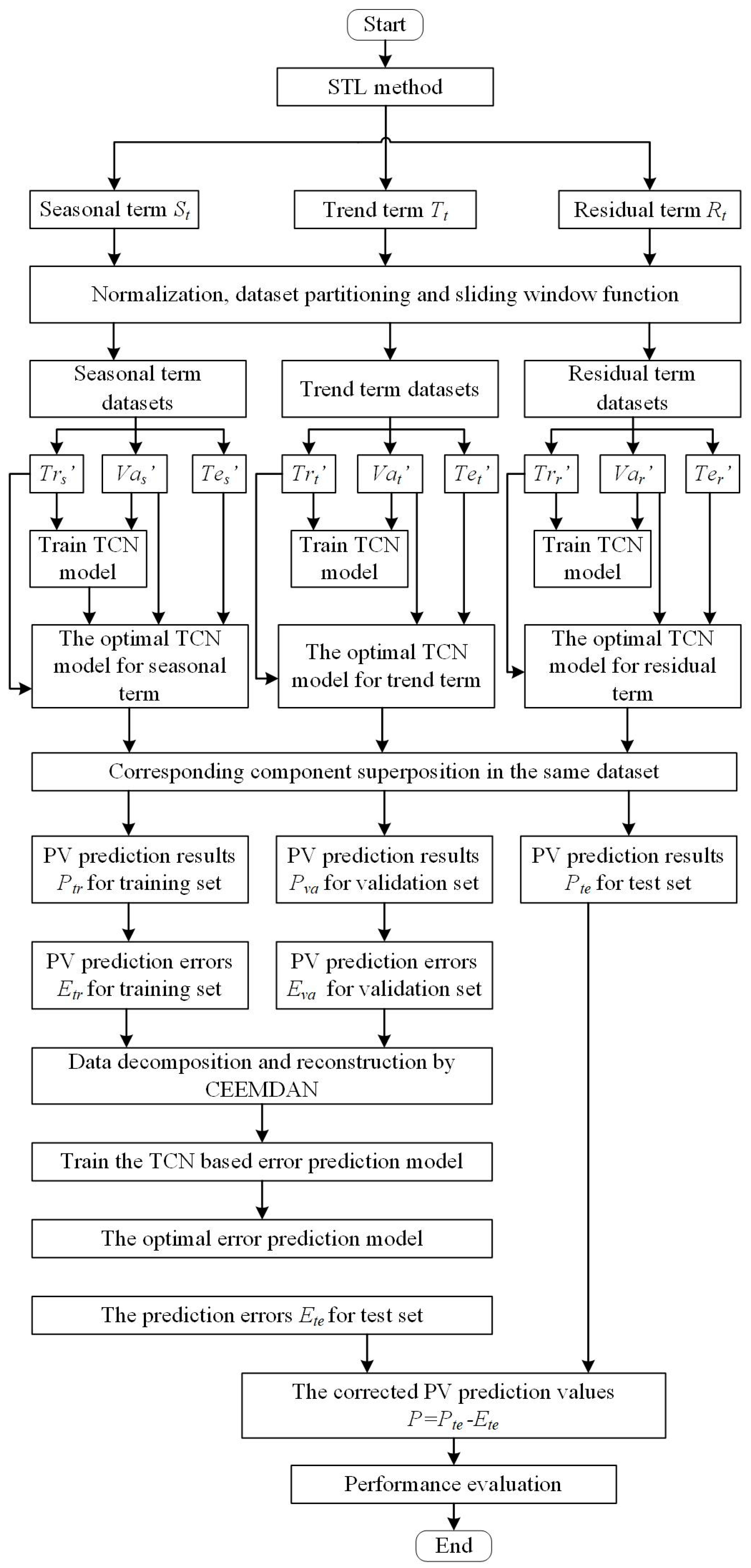
3.4. Workflow of the Proposed Methods
4. Analysis of the Experiments
4.1. Experimental Process
4.2. Ablation Experiments
4.3. Comparative Experiments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| STL | Seasonal and Trend decomposition using Loess |
| TCN | Temporal convolutional network |
| SVM | Support vector machine |
| ANNs | Artificial neural networks |
| PSO | Particle swarm optimization |
| BP | Backpropagation |
| RNN | Recurrent neural network |
| LSTM | Long short-term memory |
| CNN | Convolutional neural network |
| ACO | Ant colony optimization |
| WPD | Wavelet packet decomposition |
| CEEMDAN | Complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition with adaptive noise |
| EMD | Empirical mode decomposition |
| MAE | Mean absolute error |
| RMSE | Root mean square error |
References
- Ahmed, R.; Sreeram, V.; Mishra, Y.; Arif, M.D. A Review and Evaluation of the State-of-the-Art in PV Solar Power Forecasting: Techniques and Optimization. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 124, 109792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, U.K.; Tey, K.S.; Seyedmahmoudian, M.; Mekhilef, S.; Idris, M.Y.I.; Van Deventer, W.; Horan, B.; Stojcevski, A. Forecasting of Photovoltaic Power Generation and Model Optimization: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 912–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, M.J.; Gróf, G. Extensive Comparison of Physical Models for Photovoltaic Power Forecasting. Appl. Energy 2021, 283, 116239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, M.N.; Mekhilef, S.; Mokhlis, H.; Mohamed Shah, N. Review on Forecasting of Photovoltaic Power Generation Based on Machine Learning and Metaheuristic Techniques. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2019, 13, 1009–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böök, H.; Lindfors, A.V. Site-Specific Adjustment of a NWP-Based Photovoltaic Production Forecast. Sol. Energy 2020, 211, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, D.P.; Coimbra, C.F. Direct Power Output Forecasts from Remote Sensing Image Processing. J. Sol. Energy Eng. 2018, 140, 021011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedro, H.T.; Coimbra, C.F. Assessment of Forecasting Techniques for Solar Power Production with No Exogenous Inputs. Sol. Energy 2012, 86, 2017–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Thatte, A.A.; Xie, L. Multitime-Scale Data-Driven Spatio-Temporal Forecast of Photovoltaic Generation. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2014, 6, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, H.; Xiao, J.; Cheng, Y.; Ni, Q.; Wang, S. Short-Term Solar Power Forecasting Based on Weighted Gaussian Process Regression. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 65, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Long, H.; Zhang, Z.; Song, Z. Day-Ahead Prediction of Bi-Hourly Solar Radiance with a Markov Switch Approach. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM), Portland, OR, USA, 5–10 August 2018; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, S.; Li, R.; Tao, Z. A Novel Adaptive Discrete Grey Model with Time-Varying Parameters for Long-Term Photovoltaic Power Generation Forecasting. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 227, 113644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eseye, A.T.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, D. Short-Term Photovoltaic Solar Power Forecasting Using a Hybrid Wavelet-PSO-SVM Model Based on SCADA and Meteorological Information. Renew. Energy 2018, 118, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, U.K.; Tey, K.S.; Seyedmahmoudian, M.; Idna Idris, M.Y.; Mekhilef, S.; Horan, B.; Stojcevski, A. SVR-Based Model to Forecast PV Power Generation under Different Weather Conditions. Energies 2017, 10, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paiva, G.M.; Pimentel, S.P.; Marra, E.G.; de Alvarenga, B.P.; Mussetta, M.; Leva, S. Intra-Day Forecasting of Building-Integrated PV Systems for Power Systems Operation Using ANN Ensemble. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Milan PowerTech, Milan, Italy, 23–27 June 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Fang, W.; Zhang, X.; Yang, C. An Improved Photovoltaic Power Forecasting Model with the Assistance of Aerosol Index Data. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2015, 6, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, K.; Azam, S.; Karim, A.; Zobaed, S.; Shanmugam, B.; Mathur, D. Machine Learning Based PV Power Generation Forecasting in Alice Springs. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 46117–46128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Yang, M.; Yu, Y. A Short-Term Forecasting Method for Photovoltaic Power Based on Ensemble Adaptive Boosting Random Forests. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/IAS 56th Industrial and Commercial Power Systems Technical Conference, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 29 June–28 July 2020; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Wang, H.; Zhang, S.; Xin, J.; Liu, H. Recurrent Neural Networks Based Photovoltaic Power Forecasting Approach. Energies 2019, 12, 2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garip, Z.; Ekinci, E.; Alan, A. Day-Ahead Solar Photovoltaic Energy Forecasting Based on Weather Data Using LSTM Networks: A Comparative Study for Photovoltaic (PV) Panels in Turkey. Electr. Eng. 2023, 105, 3329–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agga, A.; Abbou, A.; Labbadi, M.; El Houm, Y.; Ali, I.H.O. CNN-LSTM: An Efficient Hybrid Deep Learning Architecture for Predicting Short-Term Photovoltaic Power Production. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2022, 208, 107908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Qi, X.; Liu, H. Photovoltaic Power Forecasting Based LSTM-Convolutional Network. Energy 2019, 189, 116225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souhe, F.G.Y.; Mbey, C.F.; Kakeu, V.J.F.; Meyo, A.E.; Boum, A.T. Optimized Forecasting of Photovoltaic Power Generation Using Hybrid Deep Learning Model Based on GRU and SVM. Electr. Eng. 2024, 106, 7879–7898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhou, K.; Lu, X.; Yang, S. A Hybrid Deep Learning Model for Short-Term PV Power Forecasting. Appl. Energy 2020, 259, 114216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Peng, T.; Qian, S.; Ge, Y.; Wang, Z.; Nazir, M.S.; Zhang, C. An Error-Corrected Deep Autoformer Model via Bayesian Optimization Algorithm and Secondary Decomposition for Photovoltaic Power Prediction. Appl. Energy 2025, 377, 124738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, K.; Zhao, J.; Tao, Y.; Qi, Q.; Tian, Y. Operational Day-Ahead Photovoltaic Power Forecasting Based on Transformer Variant. Appl. Energy 2024, 373, 123825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, F.; Jia, Y. Combined Ultra-Short-Term Photovoltaic Power Prediction Based on CEEMDAN Decomposition and RIME Optimized AM-TCN-BiLSTM. Energy 2025, 318, 134847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, R.B.; Cleveland, W.S. STL: A Seasonal-Trend Decomposition Procedure Based on Loess. J. Off. Stat. 1990, 6, 3–73. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, S.; Kolter, J.Z.; Koltun, V. An Empirical Evaluation of Generic Convolutional and Recurrent Networks for Sequence Modeling. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.01271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.E.; Colominas, M.A.; Schlotthauer, G.; Flandrin, P. A Complete Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition with Adaptive Noise. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Prague, Czech Republic, 22–27 May 2011; pp. 4144–4147. [Google Scholar]
- Krevnevičiūtė, J.; Mitkevičius, A.; Naujokaitis, D.; Lagzdinytė-Budnikė, I.; Marčiukaitis, M. The Forecast of the Wind Turbine Generated Power Using Hybrid (LTC + XGBoost) Model. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhu, R.; Yu, C.; Mi, X. DHGAR: Multi-Variable-Driven Wind Power Prediction Model Based on Dynamic Heterogeneous Graph Attention Recurrent Network. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkelund, Y. Numerical Weather Modelling and Large Eddy Simulations of Strong-Wind Events in Coastal Mountainous Terrain. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Hyperparameters | Values |
|---|---|
| batch_size | 16 |
| epochs | 100 |
| learning rate | 0.001 |
| patience | 10 |
| Dropout | 0.1 |
| Dense | 4 |
| Loss | MSE |
| filter_nums | 12 |
| kernel_size | 8 |
| nb_stacks | 2 |
| Model | Hyperparameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| LSTM | units | 12, 10, 8 |
| GRU | units | 16, 12, 8 |
| CNN | filters | 16, 10, 8 |
| BPNN | dense | 16, 12, 8 |
| Method | nMAE | nRMSE | R2 | Training Time | Params |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCN | 0.0732 | 0.1940 | 0.854 | 163.13 | 29,164 |
| TCN + STL | 0.0599 | 0.0991 | 0.884 | 888.89 | 29,164 |
| TCN + STL + ECM | 0.0571 | 0.0917 | 0.922 | 484.41 | 59,684 |
| LSTM | 0.1675 | 0.1883 | 0.867 | 138.86 | 2236 |
| LSTM + STL | 0.1923 | 0.1842 | 0.883 | 516.33 | 2236 |
| LSTM + STL + ECM | 0.0632 | 0.0888 | 0.912 | 97.77 | 2236 |
| GRU | 0.0965 | 0.1842 | 0.871 | 157.89 | 2556 |
| GRU + STL | 0.0897 | 0.1116 | 0.876 | 561.97 | 2556 |
| GRU + STL + ECM | 0.0594 | 0.1081 | 0.907 | 287.46 | 2556 |
| CNN | 0.1958 | 0.2837 | 0.857 | 28.74 | 1242 |
| CNN + STL | 0.1802 | 0.2097 | 0.870 | 124.99 | 1242 |
| CNN + STL + ECM | 0.1412 | 0.1627 | 0.910 | 29.95 | 1242 |
| BPNN | 0.1802 | 0.2853 | 0.874 | 12.32 | 872 |
| BPNN + STL | 0.1730 | 0.1826 | 0.881 | 46.72 | 872 |
| BPNN + STL + ECM | 0.1436 | 0.1382 | 0.913 | 26.50 | 872 |
| Method | nMAE | nRMSE | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| TCN + STL + ECM | 0.0571 | 0.0917 | 0.922 |
| LSTM + STL + ECM | 0.0632 | 0.0888 | 0.912 |
| GRU + STL + ECM | 0.0594 | 0.1081 | 0.907 |
| CNN + STL + ECM | 0.1412 | 0.1627 | 0.910 |
| BPNN + STL + ECM | 0.1436 | 0.1382 | 0.913 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhu, L.; Tang, J. Short-Term Photovoltaic Output Prediction Method Based on Data Decomposition and Error Correction. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 11089. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011089
Liang C, Zhang Y, Zhao Z, Zhu L, Tang J. Short-Term Photovoltaic Output Prediction Method Based on Data Decomposition and Error Correction. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(20):11089. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011089
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Chen, Yilin Zhang, Ziwei Zhao, Liu Zhu, and Junjie Tang. 2025. "Short-Term Photovoltaic Output Prediction Method Based on Data Decomposition and Error Correction" Applied Sciences 15, no. 20: 11089. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011089
APA StyleLiang, C., Zhang, Y., Zhao, Z., Zhu, L., & Tang, J. (2025). Short-Term Photovoltaic Output Prediction Method Based on Data Decomposition and Error Correction. Applied Sciences, 15(20), 11089. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011089






