Artificial Intelligence for Diagnosing Cranial Nerve III, IV, and VI Palsies Using Nine-Directional Ocular Photographs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Data Labeling
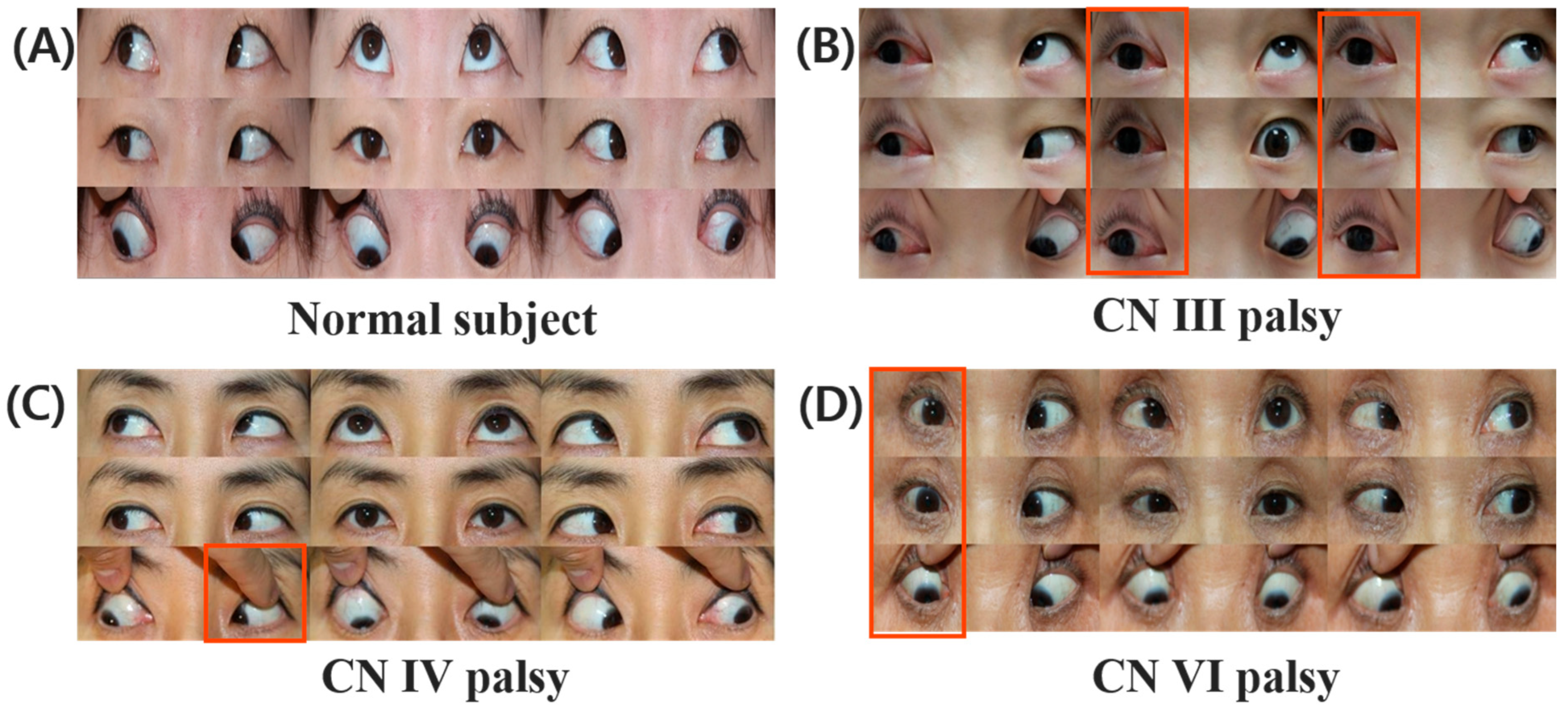
2.3. Characterization of CN III, IV, VI
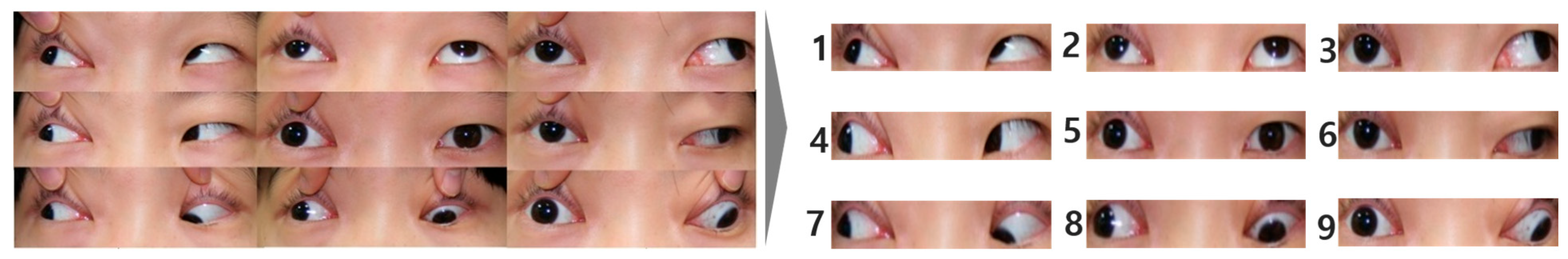
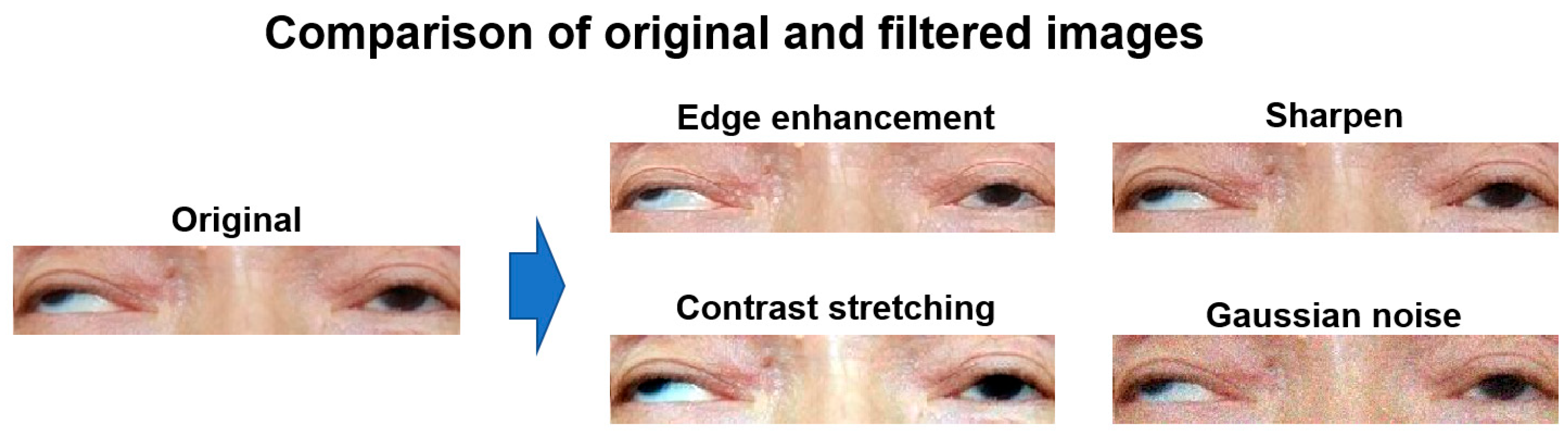
2.4. Data Augmentation of the Nine-Gaze Images
2.5. Construction of the CNN Model for CN Palsy Classification
3. Results
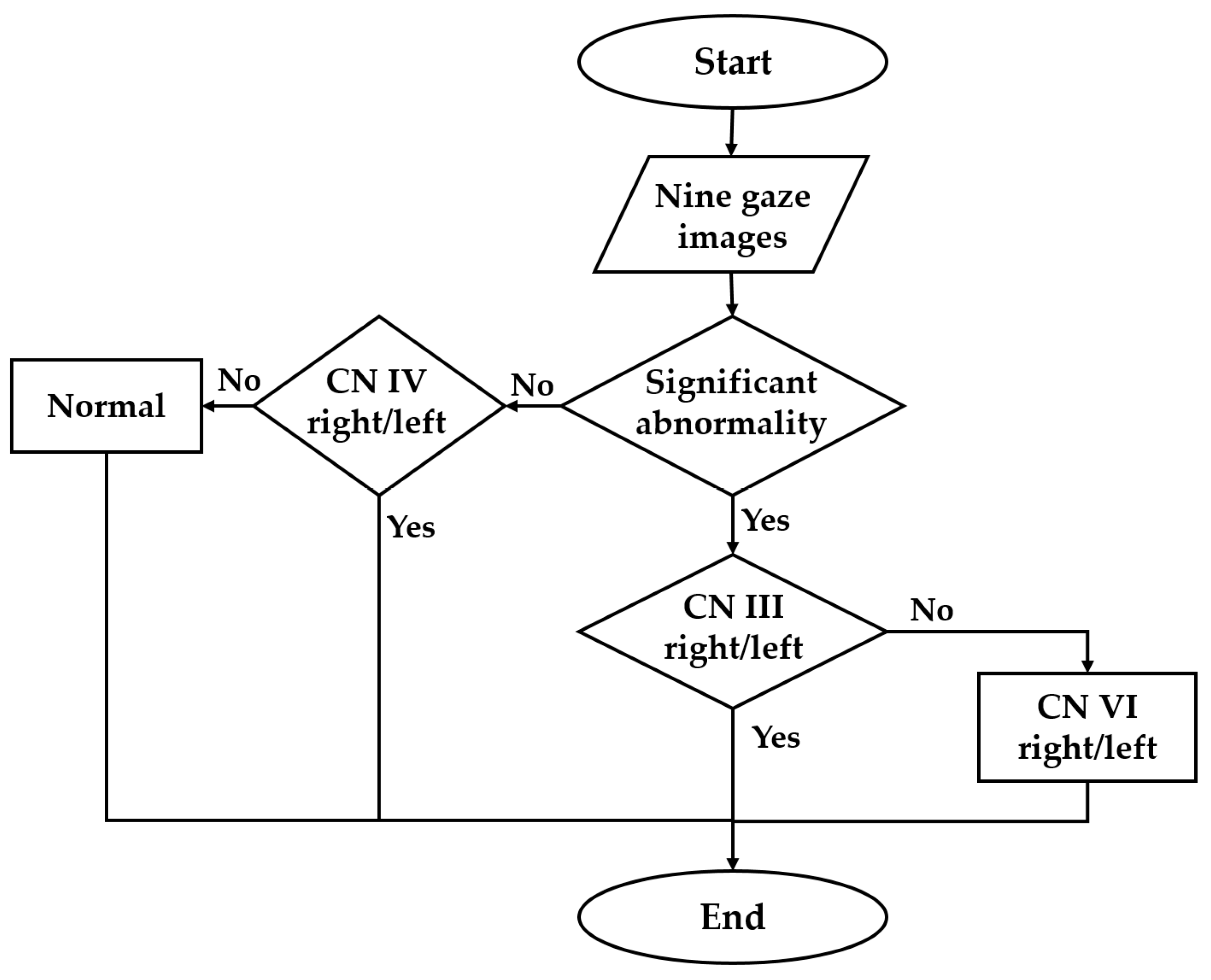
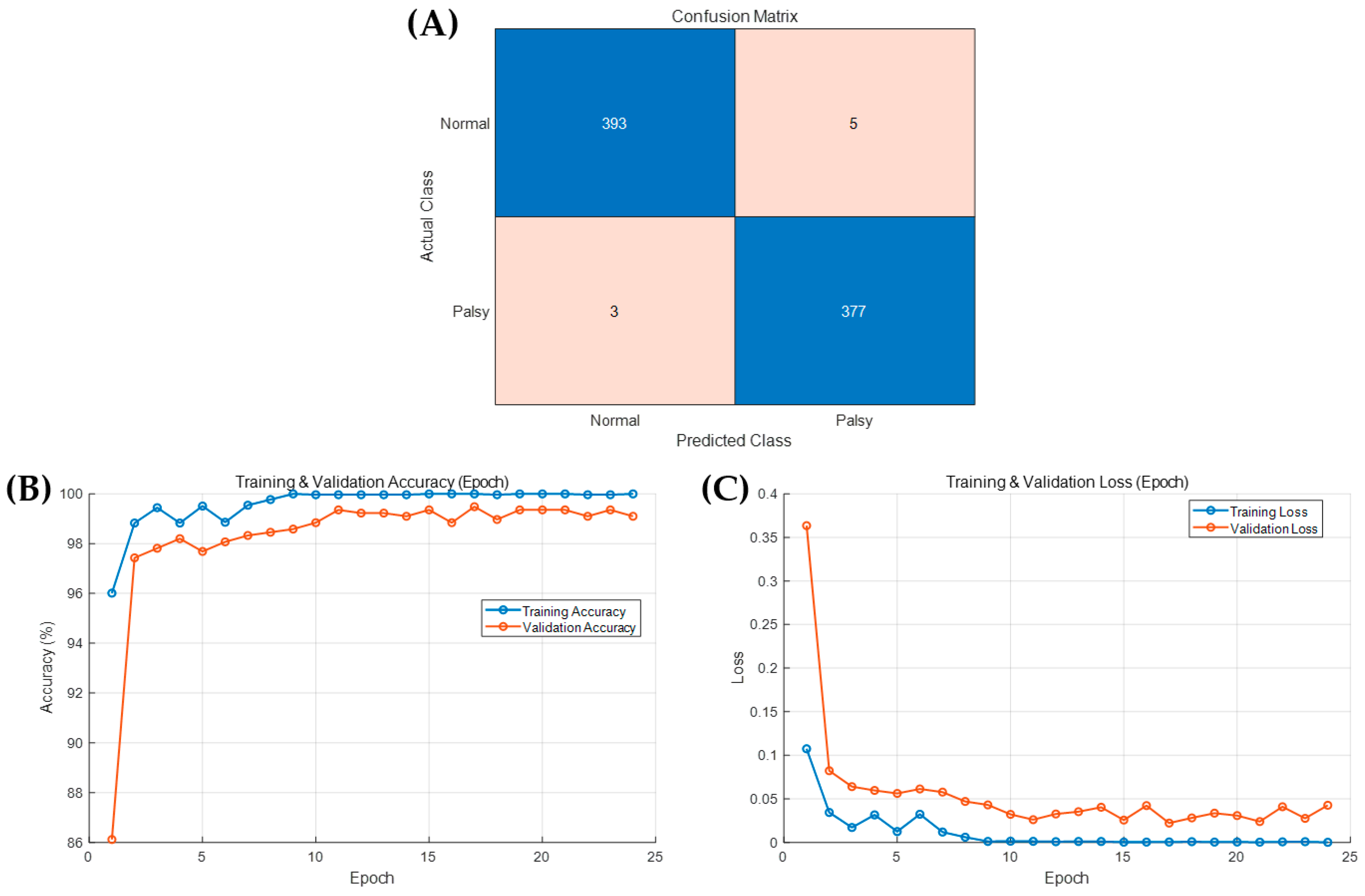
3.1. Abnormality Detection
3.2. Multinetwork CN Palsy Detection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shin, H.J.; Lee, S.J.; Oh, C.; Kang, H. Novel compact device for clinically measuring extraocular muscle (EOM) tension. J. Biomech. 2020, 26, 109955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Lee, S.; Oh, C.; Shin, H.J.; Lee, A.G. Quantitative measurement of passive duction force tension in intermittent exotropia and its clinical implications. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2021, 259, 1617–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.J.; Kim, S.; Kang, H.; Lee, A.G. Novel Instrument for Clinical Evaluations of Active Extraocular Muscle Tension. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.; Volpe, N.J. Paralytic strabismus: Third, fourth, and sixth nerve palsy. Neurol. Clin. 2010, 28, 803–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Choi, S. Third cranial nerve palsy and posterior communicating artery aneurysm. Clin. Exp. Emerg. Med. 2014, 1, 65–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuljhele, S.; Dhiman, R.; Sharma, M.; Kusiyaits, K.; Saxena, R.; Mahalingam, K.; Sharma, P. Acquired Ocular Motor Palsy: Current Demographic and Etiological Profile. Asia-Pac. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 9, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.W.; Lee, D.E.; Lee, J.W.; Kang, M.H.; Seong, M.; Cho, H.Y.; Oh, J.; Oh, S.Y. Clinical measurement of the angle of ocular movements in the nine cardinal positions of gaze. Ophthalmology 2014, 121, 870–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Lee, S.J.; Shin, H.J.; Lee, A.G. Measuring ocular torsion and its variations using different nonmydriatic fundus photographic methods. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0244230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoleta, A.; Catalin, L.; Bogdan, D.; Silvia, C.; Camelia, M.B.; Dorin, C.; Daniel, C.B.; Lonela, N.; Ovidiu-Dumitru, I.; Roxana, E.C. Use of Artificial Neural Networks to Predict the Progression of Glaucoma in Patients with Sleep Apnea. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, Z.; Mansoori, T. Artificial intelligence in glaucoma detection using color fundus photographs. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2024, 72, 408–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Fernandez-Loaiza, P.; Sauma, J.; Hernandez-Bogantes, E.; Masis, M. Classification of diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema. World J. Diabetes 2013, 4, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhale, R.; Hamideh, S.; Pooya, T.; Narges, B.; Mehdi, Y.; Mohadeseh, F.; Mohammad, F.; Kourosh, S. The relationship between abduction deficit and reoperation among patients with infantile esotropia. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 11, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Fu, H.; Li, R.; Lo, W.L.; Chi, Z.; Feng, D.D.; Song, Z.; Wen, D. Intelligent Evaluation of Strabismus in Videos Based on an Automated Cover Test. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q.V. EfficientNet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), PMLR, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; Volume 97, pp. 6105–6114. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, C.; Yao, Q.; Lu, J.; Xie, X.; Lin, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S.; Fan, Z.; Qiao, T. Detection of referable horizontal strabismus in children’s primary gaze photographs using deep learning. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2021, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaaslan, Ş.; Kobat, S.G. A new method based on deep learning and image processing for detection of strabismus with the Hirschberg test. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2023, 44, 103805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Figueiredo, L.A.; Dias, J.V.P.; Polati, M.; Carricondo, P.C.; Debert, I. Strabismus and artificial intelligence app: Optimizing diagnostic and accuracy. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2021, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.C.; Yang, H.K.; Kim, Y.J.; Hwang, J.; Kim, K.G. Automated Mathematical Algorithm for Quantitative Measurement of Strabismus Based on Photographs of Nine Cardinal Gaze Positions. Biomed. Res. Int. 2022, 24, 9840494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Li, Y.; Zeyi, Y.; Yin, T.; Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Shang, W.; Xie, B.; Yang, G.; Zhang, H.; et al. Deep Learning-Based Precision Cropping of Eye Regions in Strabismus Photographs: Algorithm Development and Validation Study for Workflow Optimization. J. Med. Internet Res. 2025, 27, e74402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarkheir, M.; Sadeghi, M.; Azarnoush, H.; Akbari, M.R.; Pour, E.K. Automated strabismus detection and classification using deep learning analysis of facial images. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, M.A.; Turner, A.W. Benefits of Integrating Telemedicine and Artificial Intelligence into Outreach Eye Care: Stepwise Approach and Future Directions. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 835804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Huang, X.; Chen, L.; Hou, P.; Liu, L.; Yang, G. Integrating artificial intelligence in strabismus management: Current research landscape and future directions. Exp. Biol. Med. 2024, 249, 10320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab Sait, A.R. Artificial Intelligence-Driven Eye Disease Classification Model. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, A.; Ugrin, M.C. Frequency of the superior rectus muscle overaction/contracture syndrome in unilateral fourth nerve palsy. J. AAPOS 2009, 13, 571–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Clark, R.A.; Demer, J.L. Can Binocular Alignment Distinguish Hypertropia in Sagging Eye Syndrome from Superior Oblique Palsy? Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2022, 63, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellahham, S. Artificial Intelligence: The Future for Diabetes Care. Am. J. Med. 2020, 133, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaniappan, K.; Lin, E.Y.T.; Vogel, S. Global Regulatory Frameworks for the Use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the Healthcare Services Sector. Healthcare 2024, 12, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Group | Control | C3-L | C3-R | C4-L | C4-R | C6-L | C6-R |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of cases | 242 | 23 | 47 | 14 | 15 | 33 | 25 |
| Option | Optimizer | Initial LR | LR Drop Period | Mini-Batch Size | Macro Precision | Macro Recall | Macro F1 Score | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Adam | 1 × 10−3 | 5 | 32 | 0.9832 | 0.9829 | 0.9829 | 0.9848 |
| 2 * | Adam | 5 × 10−4 | 5 | 32 | 0.9805 | 0.9864 | 0.9829 | 0.9841 |
| 3 | Adam | 1 × 10−3 | 8 | 32 | 0.9813 | 0.9833 | 0.9821 | 0.9832 |
| 4 | Sgdm a | 1 × 10−3 | 5 | 32 | 0.9312 | 0.9079 | 0.9155 | 0.9229 |
| 5 | Rmsprop b | 1 × 10−3 | 5 | 32 | 0.9777 | 0.9803 | 0.9784 | 0.9808 |
| 6 | Adam | 1 × 10−3 | 5 | 64 | 0.9742 | 0.9781 | 0.9751 | 0.9763 |
| 7 | Adam | 1 × 10−3 | 5 | 16 | 0.9872 | 0.977 | 0.981 | 0.9837 |
| Class | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| ‘Normal’ | 0.9924 | 0.9874 | 0.9899 |
| ‘Palsy’ | 0.9869 | 0.9921 | 0.9895 |
| Class | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| ‘C3-L-1’ | 0.8684 | 0.75 | 0.8049 |
| ‘C3-L-2’ | 0.8431 | 0.9772 | 0.9053 |
| ‘C3-L-4’ | 0.8913 | 0.9318 | 0.9111 |
| ‘C3-L-7’ | 0.8542 | 0.8542 | 0.8542 |
| ‘C3-L-8’ | 0.8864 | 0.8864 | 0.8864 |
| ‘C3-R-2’ | 0.8537 | 0.7955 | 0.8236 |
| ‘C3-R-3’ | 0.8571 | 0.875 | 0.866 |
| ‘C3-R-6’ | 0.9574 | 0.9375 | 0.9474 |
| ‘C3-R-8’ | 0.8409 | 0.8409 | 0.8409 |
| ‘C3-R-9’ | 0.8864 | 0.8864 | 0.8864 |
| ‘C4-L-7’ | 1 | 0.75 | 0.8571 |
| ‘C4-R-9’ | 0.8636 | 0.95 | 0.9048 |
| ‘C6-L-3’ | 0.9487 | 0.925 | 0.9367 |
| ‘C6-L-6’ | 0.9302 | 1 | 0.9639 |
| ‘C6-L-9’ | 0.9556 | 0.9773 | 0.9663 |
| ‘C6-R-1’ | 1 | 0.975 | 0.9873 |
| ‘C6-R-4’ | 0.8649 | 0.8 | 0.8312 |
| ‘C6-R-7’ | 0.7885 | 0.9318 | 0.8542 |
| ‘N-1’ | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| ‘N-2’ | 0.976 | 1 | 0.9877 |
| ‘N-3’ | 0.9535 | 0.9762 | 0.9647 |
| ‘N-4’ | 1 | 0.9783 | 0.989 |
| ‘N-5’ | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| ‘N-6’ | 1 | 0.9535 | 0.9762 |
| ‘N-7’ | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| ‘N-8’ | 0.9767 | 1 | 0.9882 |
| ‘N-9’ | 1 | 0.9149 | 0.9556 |
| Group | No. of CNNs | Macro Precision | Macro Recall | Macro F1-Score | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C3 | 10 | 0.9932 ± 0.0095 | 0.9931 ± 0.0094 | 0.9931 ± 0.0096 | 0.9931 ± 0.0096 |
| C4 | 2 | 0.9654 ± 0.0153 | 0.9834 ± 0.0066 | 0.9736 ± 0.0116 | 0.9770 ± 0.0097 |
| C6 | 6 | 0.9829 ± 0.0155 | 0.9826 ± 0.0163 | 0.9822 ± 0.0167 | 0.9822 ± 0.0167 |
| Average | 0.9867 ± 0.0147 | 0.9885 ± 0.0125 | 0.9873 ± 0.0138 | 0.9877 ± 0.0133 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shin, H.J.; Kim, S.J.; Park, S.H.; Kim, M.S.; Kang, H. Artificial Intelligence for Diagnosing Cranial Nerve III, IV, and VI Palsies Using Nine-Directional Ocular Photographs. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 11174. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011174
Shin HJ, Kim SJ, Park SH, Kim MS, Kang H. Artificial Intelligence for Diagnosing Cranial Nerve III, IV, and VI Palsies Using Nine-Directional Ocular Photographs. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(20):11174. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011174
Chicago/Turabian StyleShin, Hyun Jin, Seok Jin Kim, Sung Hyun Park, Min Seok Kim, and Hyunkyoo Kang. 2025. "Artificial Intelligence for Diagnosing Cranial Nerve III, IV, and VI Palsies Using Nine-Directional Ocular Photographs" Applied Sciences 15, no. 20: 11174. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011174
APA StyleShin, H. J., Kim, S. J., Park, S. H., Kim, M. S., & Kang, H. (2025). Artificial Intelligence for Diagnosing Cranial Nerve III, IV, and VI Palsies Using Nine-Directional Ocular Photographs. Applied Sciences, 15(20), 11174. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011174








