Influence of Local and Systemic Antibiotics in Non-Surgical Peri-Implantitis Treatment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Update
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Clinical Relevance of Dental Implants and the Emergence of Peri-Implantitis
1.2. Current Therapeutic Challenges and Approaches
1.3. Role of Antibiotics and Study Objective
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Study Selection
2.4. Data Extraction
2.5. Risk of Bias Assessment
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
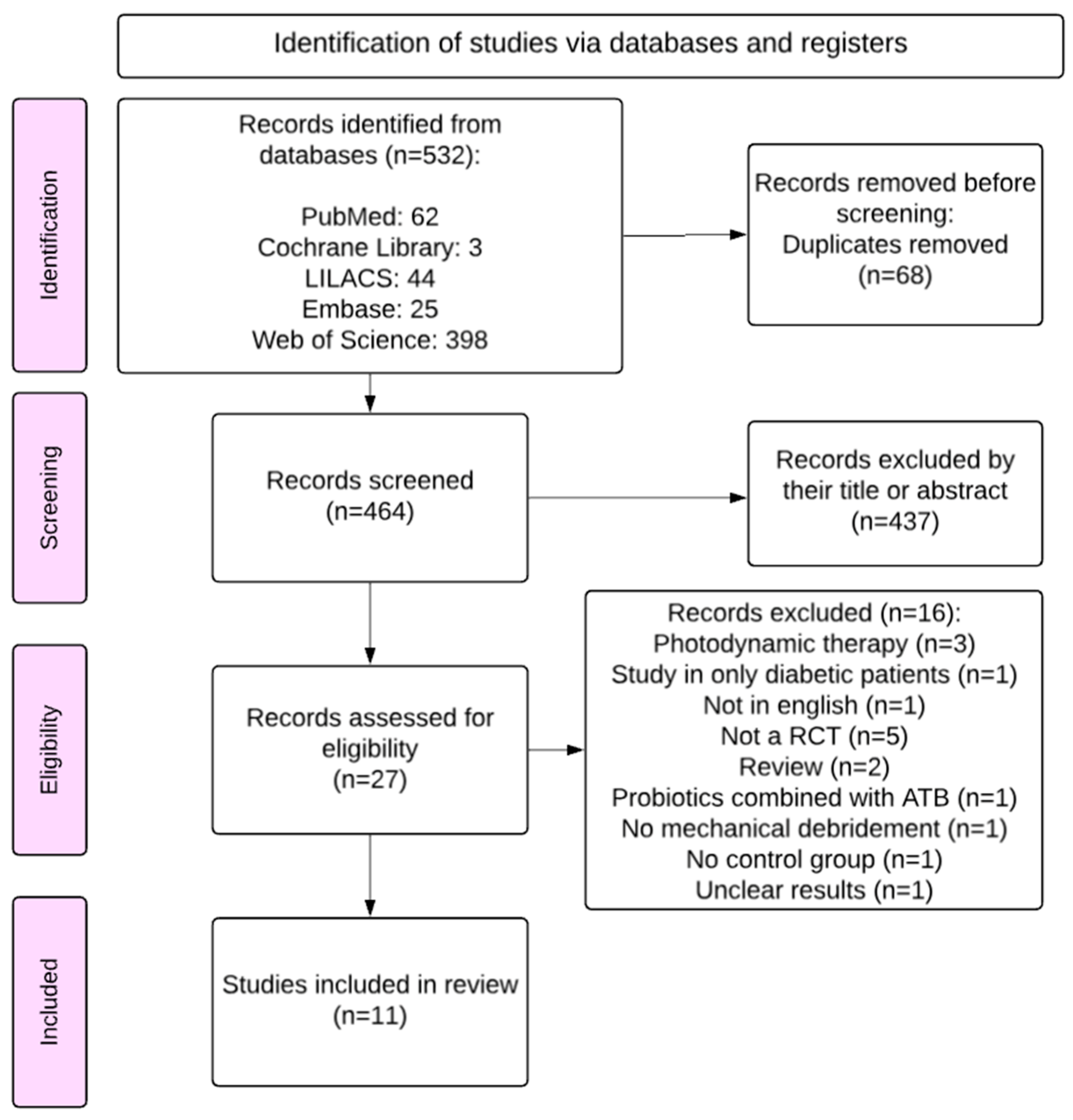
3.1. Search Results
3.2. Study Characteristics and Results of Individual Studies
3.3. Primary Clinical Outcomes
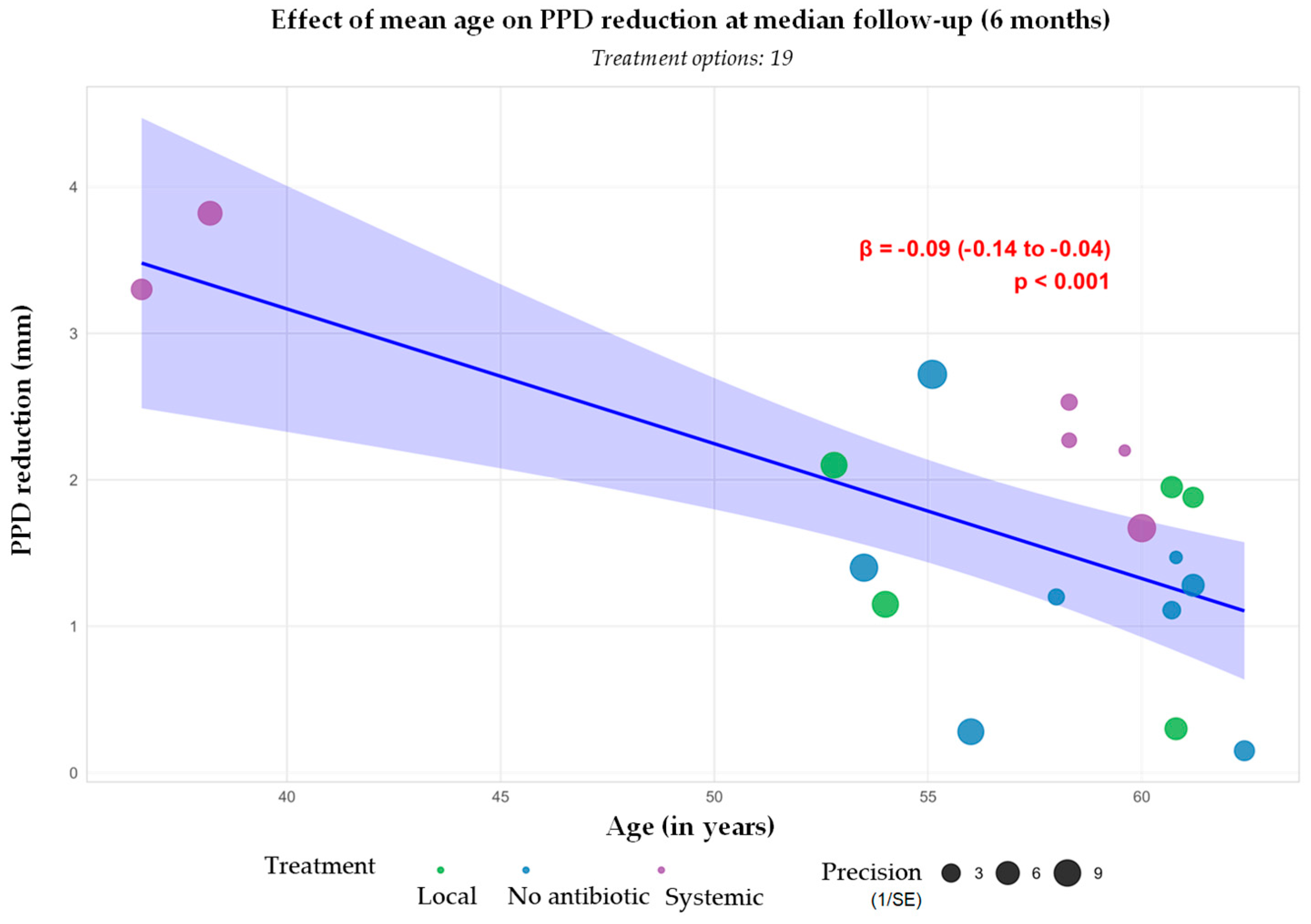
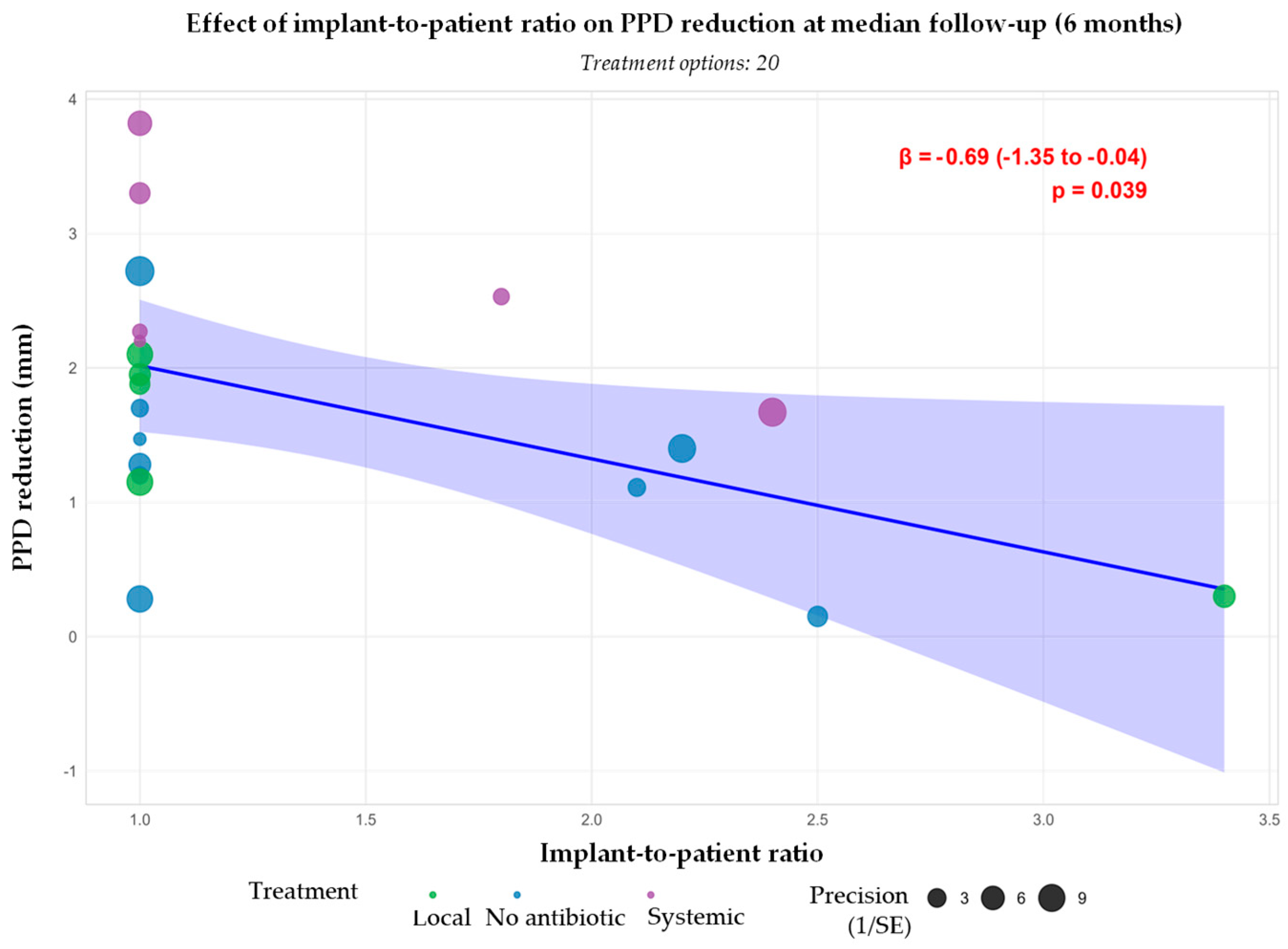
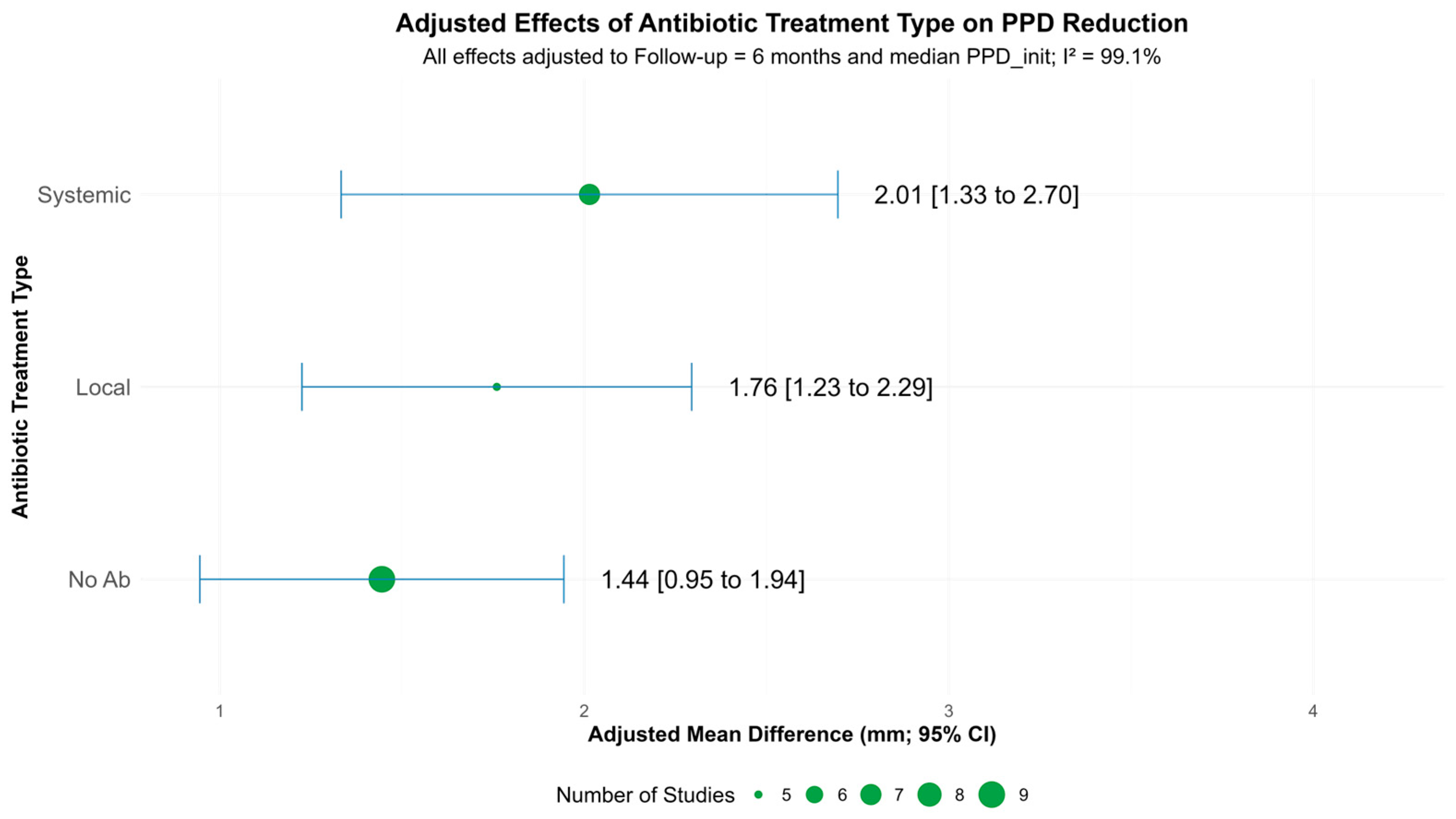
3.3.1. Probing Pocket Depth Reduction
3.3.2. Bleeding on Probing Reduction
3.4. Secondary Outcomes and Success Rates
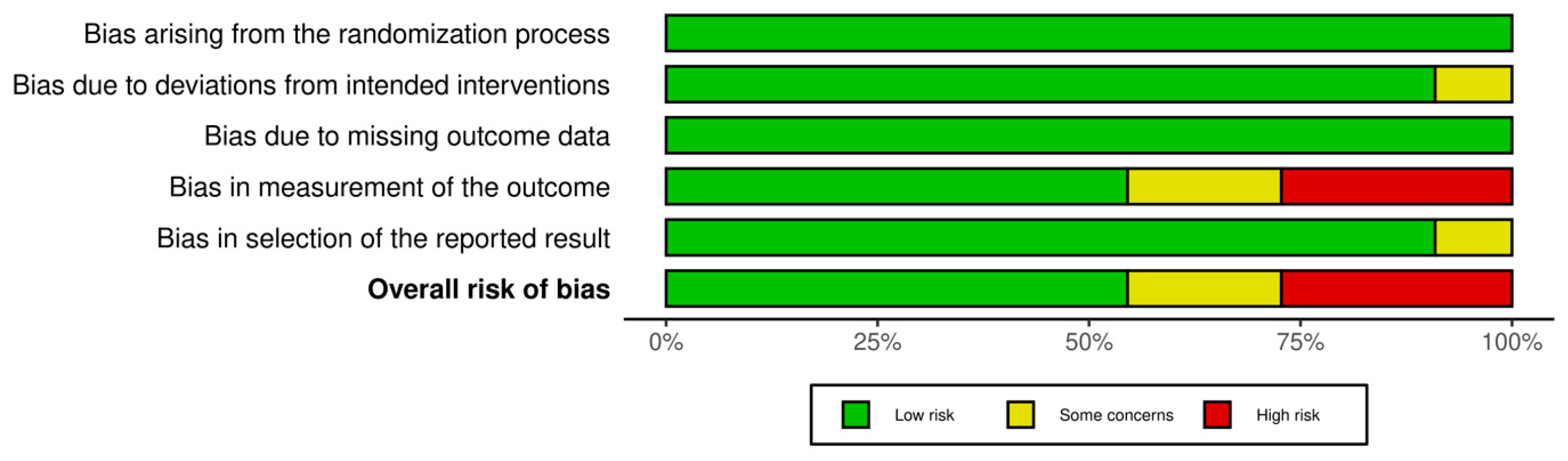
3.5. Risk of Bias Results
3.6. Summary of Evidence
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Glossary
| AMX | Amoxicillin |
| AMC | Amoxicillin–clavulanic acid |
| BID | Bis in die (twice daily) |
| BoP | Bleeding on probing |
| CD | Clindamycin |
| CHX | Chlorhexidine |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| DBL | Depth of bone lesion |
| DOX | Doxycycline |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| I2 | I-squared statistic |
| MD | Mechanical debridement |
| MH | Minocycline hydrochloride |
| MIN | Minocycline |
| MINm | Minocycline microspheres |
| MTZ | Metronidazole |
| PPD | Probing pocket depth |
| PRISMA 2020 | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses 2020 |
| PROSPERO | International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews |
| RCT | Randomised controlled trial |
| RoB 2.0 | Cochrane Risk of Bias 2.0 tool |
| SE | Standard error |
| Serratiopeptidase | Proteolytic enzyme with anti-inflammatory activity |
| TID | Ter in die (three times daily) |
| TNF-α | Tumour necrosis factor-alpha |
| t2 | Between-study variance |
| β | Regression coefficient |
| p-value | Probability value |
References
- Simonis, P.; Dufour, T.; Tenenbaum, H. Long-term implant survival and success: A 10–16-year follow-up of non-submerged dental implants. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2010, 21, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeets, R.; Henningsen, A.; Jung, O.; Heiland, M.; Hammächer, C.; Stein, J.M. Definition, etiology, prevention and treatment of peri-implantitis—a review. Head Face Med. 2014, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, D.; Berglundh, T.; Schwarz, F.; Chapple, I.; Jepsen, S.; Sculean, A.; Kebschull, M.; Papapanou, P.N.; Tonetti, M.S.; Sanz, M.; et al. Prevention and treatment of peri-implant diseases—The EFP S3 level clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2023, 50 (Suppl. S26), 4–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitz-Mayfield, L.J.A.; Salvi, G.E. Peri-implant mucositis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45 (Suppl. S20), S237–S245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglundh, T.; Armitage, G.; Araujo, M.G.; Avila-Ortiz, G.; Blanco, J.; Camargo, P.M.; Chen, S.; Cochran, D.; Derks, J.; Figuero, E.; et al. Peri-implant diseases and conditions: Consensus report of workgroup 4 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45 (Suppl. S20), S286–S291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mombelli, A.; Van Oosten, M.A.C.; Schürch, E.; Lang, N.P. The microbiota associated with successful or failing osseointegrated titanium implants. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 1987, 2, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levignac, J. [Periimplantation osteolysis- periimplantosis—periimplantitis]. Rev. Fr. Odontostomatol. 1965, 12, 1251–1260. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Albrektsson, T.; Isidor, F. Consensus Report of Session IV. In Proceedings of the First European Workshp on Periodontology; Lang, N.P., Karring, T., Eds.; Quintessence Publishing: London, UK, 1994; pp. 365–369. [Google Scholar]
- Uppala, S.; Parihar, A.; Modipalle, V.; Manual, L.; Oommen, V.; Karadiguddi, P.; Gupta, P. Crestal bone loss around dental implants after implantation of Tricalcium phosphate and Platelet- Rich Plasma: A comparative study. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2020, 9, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermejo, P.; Sánchez, M.C.; Llama-Palacios, A.; Figuero, E.; Herrera, D.; Sanz Alonso, M. Biofilm formation on dental implants with different surface micro-topography: An in vitro study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2019, 30, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, F.; Derks, J.; Monje, A.; Wang, H. Peri-implantitis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45 (Suppl. S20), S246–S266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prathapachandran, J.; Suresh, N. Management of peri-implantitis. Dent. Res. J. 2012, 9, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellado-Valero, A.; Buitrago-Vera, P.; Sola-Ruiz, M.; Ferrer-Garcia, J. Decontamination of dental implant surface in peri-implantitis treatment: A literature review. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cirugia Bucal 2013, 18, e869–e876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renvert, S.; Samuelsson, E.; Lindahl, C.; Persson, G.R. Mechanical non-surgical treatment of peri-implantitis: A double-blind randomized longitudinal clinical study. I: Clinical results. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2009, 36, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, F.; Sculean, A.; Rothamel, D.; Schwenzer, K.; Georg, T.; Becker, J. Clinical evaluation of an Er:YAG laser for nonsurgical treatment of peri-implantitis: A pilot study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2005, 16, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahm, N.; Becker, J.; Santel, T.; Schwarz, F. Non-surgical treatment of peri-implantitis using an air-abrasive device or mechanical debridement and local application of chlorhexidine: A prospective, randomized, controlled clinical study: Non-surgical therapy of peri-implantitis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2011, 38, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbato, L.; Cavalcanti, R.; Rupe, C.; Scartabelli, D.; Serni, L.; Chambrone, L.; Cairo, F. Clinical efficacy of adjunctive methods for the non-surgical treatment of peri-implantitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Oral Health 2023, 23, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barootchi, S.; Wang, H.-L. Peri-implant diseases: Current understanding and management. Int. J. Oral Implantol. Berl. Ger. 2021, 14, 263–282. [Google Scholar]
- Heitz-Mayfield, L.J.A.; Salvi, G.E.; Botticelli, D.; Mombelli, A.; Faddy, M.; Lang, N.P.; On Behalf of the Implant Complication Research Group (ICRG). Anti-infective treatment of peri-implant mucositis: A randomised controlled clinical trial: Treatment of peri-implant mucositis. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2011, 22, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.L.; Hiyari, S.; Yaghsezian, A.; Davar, M.; Lin, Y.-L.; Galvan, M.; Tetradis, S.; Camargo, P.M.; Pirih, F.Q. Comparing the Healing Potential of Late-Stage Periodontitis and Peri-Implantitis. J. Oral Implantol. 2017, 43, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, F.; Nuesry, E.; Bieling, K.; Herten, M.; Becker, J. Influence of an Erbium, Chromium-Doped Yttrium, Scandium, Gallium, and Garnet (Er,Cr:YSGG) Laser on the Reestablishment of the Biocompatibility of Contaminated Titanium Implant Surfaces. J. Periodontol. 2006, 77, 1820–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanos, G.E.; Nentwig, G.H. Regenerative therapy of deep peri-implant infrabony defects after CO2 laser implant surface decontamination. Int. J. Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2008, 28, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Faggion, C.M.; Listl, S.; Frühauf, N.; Chang, H.; Tu, Y. A systematic review and Bayesian network meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials on non-surgical treatments for peri-implantitis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2014, 41, 1015–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mombelli, A.; Lang, N.P. Antimicrobial treatment of peri-implant infections. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 1992, 3, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukumar, S.; Martin, F.; Hughes, T.; Adler, C. Think before you prescribe: How dentistry contributes to antibiotic resistance. Aust. Dent. J. 2020, 65, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Winkelhoff, A.J. Antibiotics in the treatment of peri-implantitis. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2012, 5, S43–S50. [Google Scholar]
- Busa, A.; Parrini, S.; Chisci, G.; Pozzi, T.; Burgassi, S.; Capuano, A. Local Versus Systemic Antibiotics Effectiveness: A Comparative Study of Postoperative Oral Disability in Lower Third Molar Surgery. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2014, 25, 708–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhumaidan, A.A.; Alrabiah, M.; Al-Aali, K.A.; Javed, F.; Vohra, F.; Abduljabbar, T. Efficacy of adjunct subgingival minocycline delivery for treatment of peri-implantitis in moderate cigarette smokers. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 26, 5698–5705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, C.; Pico, A.; Dopico, J.; Gándara, P.; Blanco, J.; Liñares, A. Adjunctive benefits of systemic metronidazole on non-surgical treatment of peri-implantitis. A randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2021, 49, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büchter, A.; Meyer, U.; Kruse-Lösler, B.; Joos, U.; Kleinheinz, J. Sustained release of doxycycline for the treatment of peri-implantitis: Randomised controlled trial. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2004, 42, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Waal, Y.C.M.; Vangsted, T.E.; Van Winkelhoff, A.J. Systemic antibiotic therapy as an adjunct to non-surgical peri-implantitis treatment: A single-blind RCT. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2021, 48, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liñares, A.; Dopico, J.; Blanco, C.; Pico, A.; Sobrino, T.; Blanco, J.; Leira, Y. The systemic impact of non-surgical treatment of peri-implantitis with or without adjunctive systemic metronidazole: Secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2024, 35, 1519–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Song, Y.W.; Cha, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.; Shin, H.; Lee, D.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, C. Adjunctive use of metronidazole-minocycline ointment in the nonsurgical treatment of peri-implantitis: A multicenter randomized controlled trial. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2021, 23, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passariello, C.; Lucchese, A.; Pera, F.; Gigola, P. Clinical, Microbiological and Inflammatory Evidence of the Efficacy of Combination Therapy Including Serratiopeptidase in the Treatment of Periimplantitis. Eur. J. Inflamm. 2012, 10, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polymeri, A.; Van Der Horst, J.; Anssari Moin, D.; Wismeijer, D.; Loos, B.G.; Laine, M.L. Non-surgical peri-implantitis treatment with or without systemic antibiotics: A randomized controlled clinical trial. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2022, 33, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renvert, S.; Lessem, J.; Dahlén, G.; Lindahl, C.; Svensson, M. Topical minocycline microspheres versus topical chlorhexidine gel as an adjunct to mechanical debridement of incipient peri-implant infections: A randomized clinical trial. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2006, 33, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renvert, S.; Lessem, J.; Dahlén, G.; Renvert, H.; Lindahl, C. Mechanical and Repeated Antimicrobial Therapy Using a Local Drug Delivery System in the Treatment of Peri-Implantitis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Periodontol. 2008, 79, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibli, J.A.; Ferrari, D.S.; Siroma, R.S.; Figueiredo, L.C.D.; Faveri, M.D.; Feres, M. Microbiological and clinical effects of adjunctive systemic metronidazole and amoxicillin in the non-surgical treatment of peri-implantitis: 1 year follow-up. Braz. Oral Res. 2019, 33 (Suppl. S1), e080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanauskaite, A.; Fretwurst, T.; Schwarz, F. Efficacy of alternative or adjunctive measures to conventional non-surgical and surgical treatment of peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2021, 7, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledano-Osorio, M.; Vallecillo, C.; Toledano, R.; Aguilera, F.S.; Osorio, M.T.; Muñoz-Soto, E.; García-Godoy, F.; Vallecillo-Rivas, M. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Systemic Antibiotic Therapy in the Treatment of Peri-Implantitis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 6502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barootchi, S.; Ravidà, A.; Tavelli, L.; Wang, H.-L. Nonsurgical treatment for peri-implant mucositis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Oral Implantol. Berl. Ger. 2020, 13, 123–139. [Google Scholar]
- Grusovin, M.G.; Pispero, A.; Del Fabbro, M.; Sangiorgi, M.; Simion, M.; Stefanini, M.; Varoni, E.M. Antibiotics as Adjunctive Therapy in the Non-Surgical Treatment of Peri-Implantitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, M.; Grusovin, M.G.; Worthington, H.V. Treatment of peri-implantitis: What interventions are effective? A Cochrane systematic review. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2012, 5, S21–S41. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Crespi, R.; Marconcini, S.; Crespi, G.; Giammarinaro, E.; Menchini Fabris, G.B.; Barone, A.; Covani, U. Nonsurgical Treatment of Peri-implantitis Without Eliminating Granulation Tissue: A 3-Year Study. Implant Dent. 2019, 28, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosola, S.; Oldoini, G.; Giammarinaro, E.; Covani, U.; Genovesi, A.; Marconcini, S. The effectiveness of the information-motivation model and domestic brushing with a hypochlorite-based formula on peri-implant mucositis: A randomized clinical study. Clin. Exp. Dent. Res. 2022, 8, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, M.; Herrera, D.; Kebschull, M.; Chapple, I.; Jepsen, S.; Berglundh, T.; Sculean, A.; Tonetti, M.S.; EFP Workshop Participants and Methodological Consultants. Treatment of stage I–III periodontitis—The EFP S3 level clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2020, 47 (Suppl. S22), 4–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


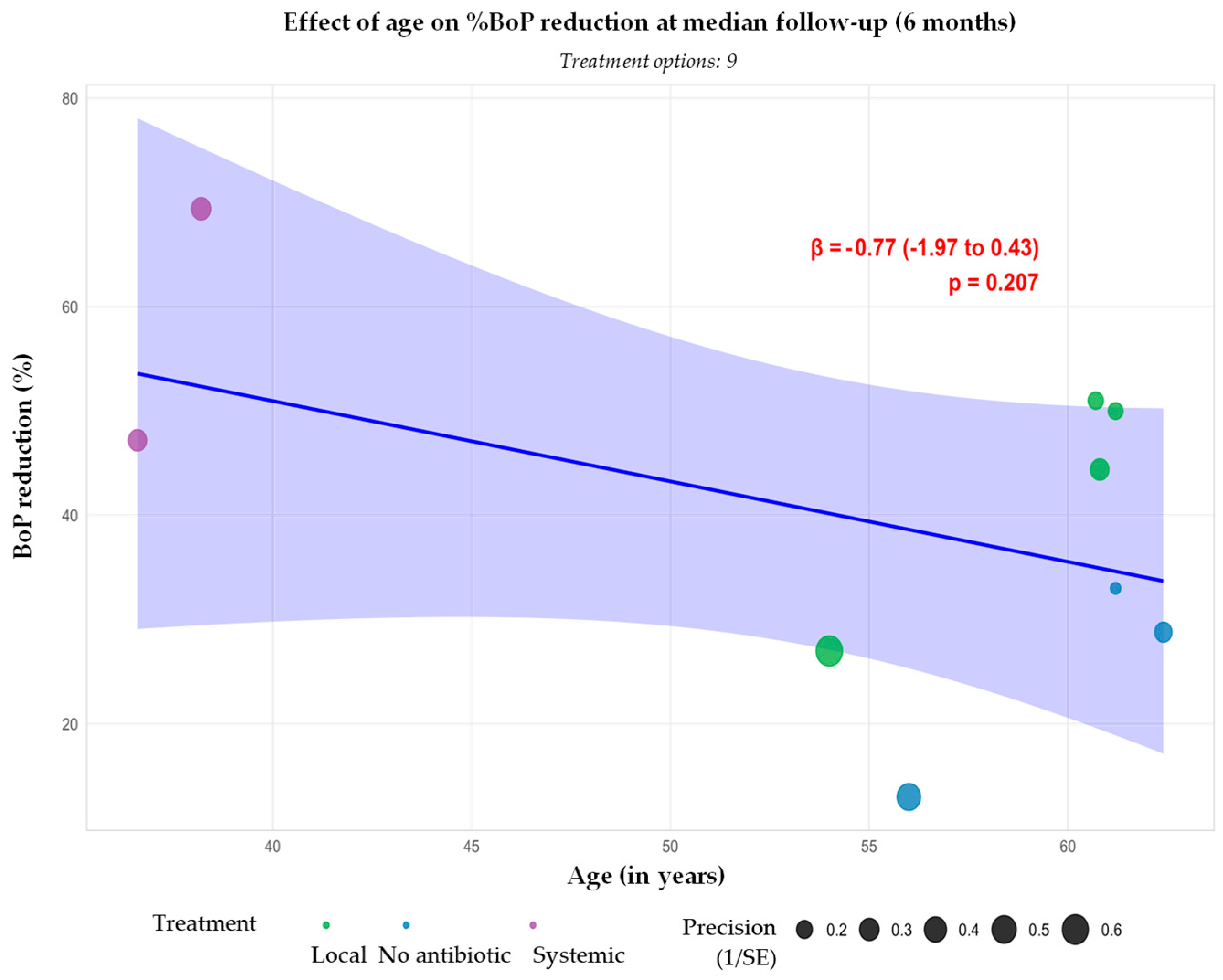
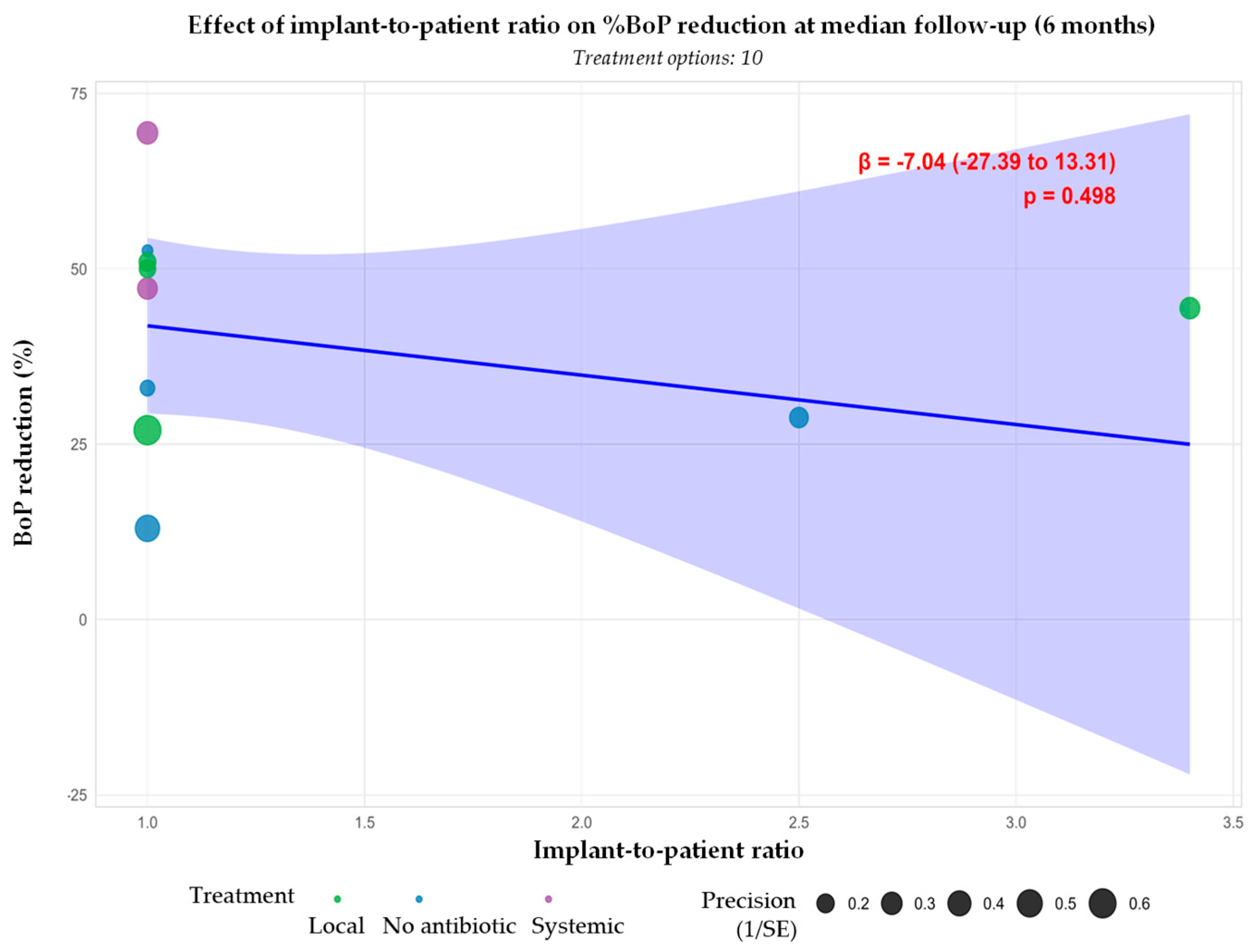
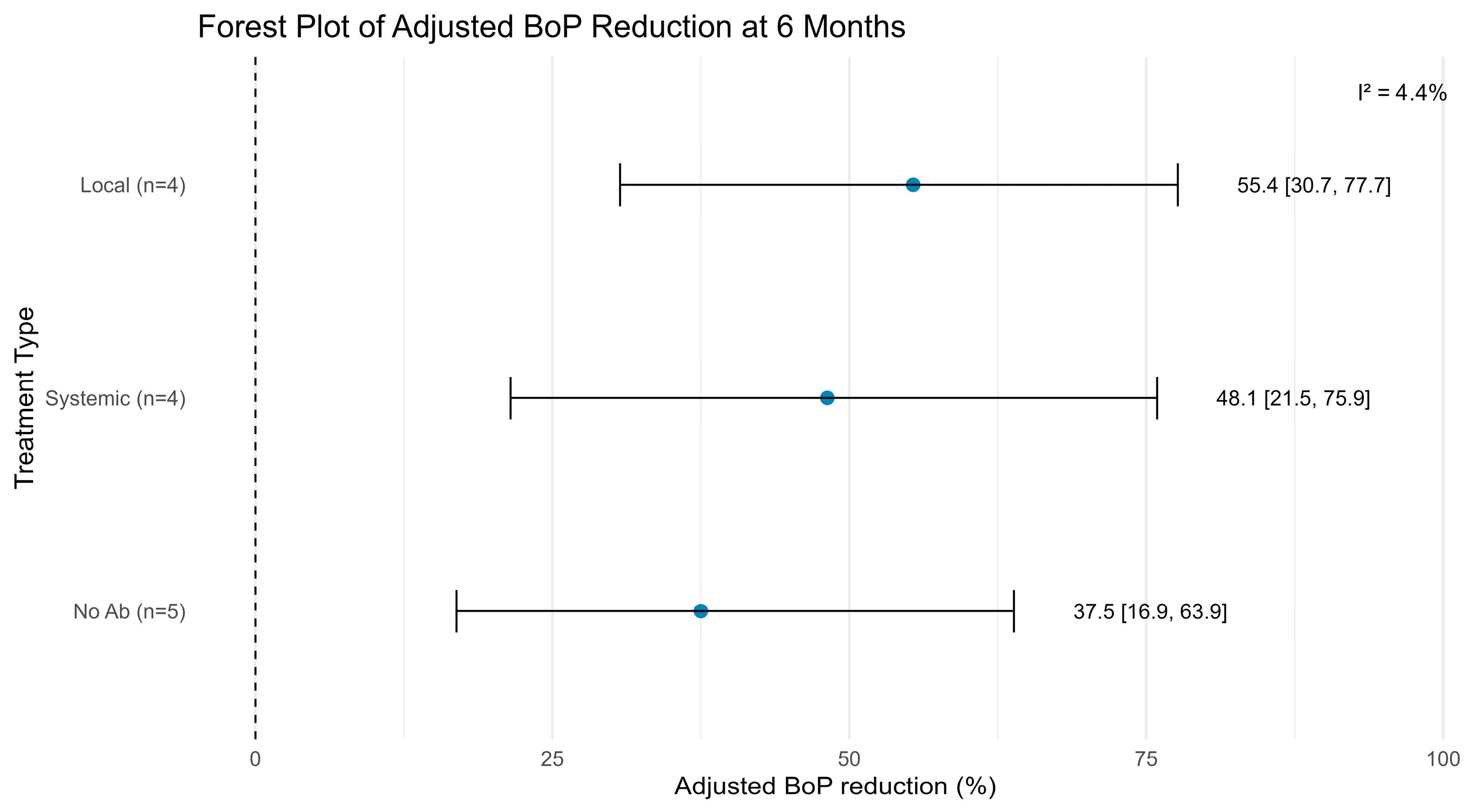
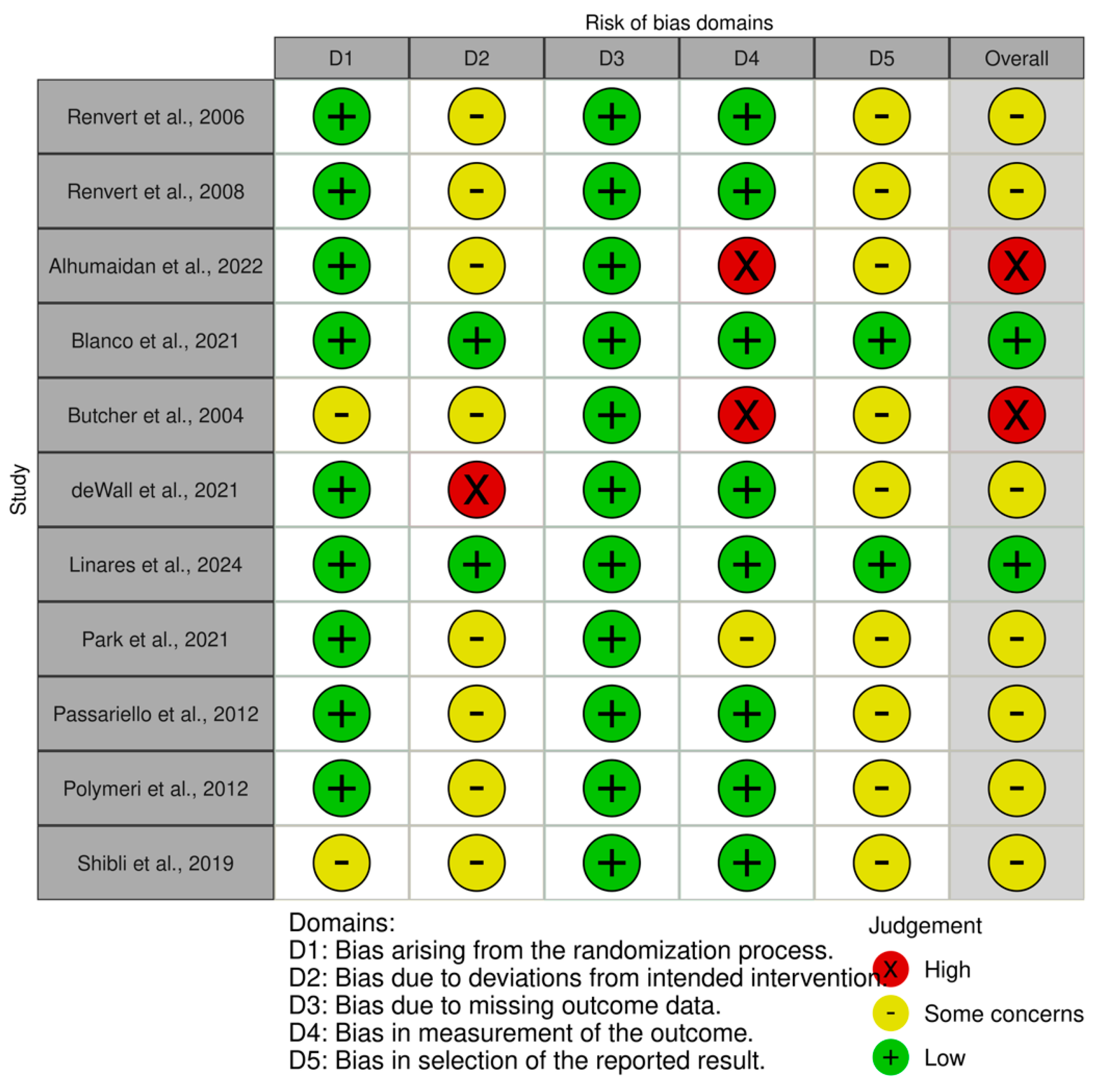
| Authors | Treatment Patients (Implants) | Location | Follow-Up (Months) | Type of Treatment | Evaluated Measures | Conclusions | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Test | ||||||
| Büchter et al., 2004 [31] | MD 14 | MD + DOX 14 | Germany | 4 | Local | PPD reduction (mm), BoP reduction (%) | Adjunctive local antimicrobial treatment gave good results in the short term, with a reduction in pocket probing depth and probing attachment levels. |
| Renvert et al., 2006 [37] | MD + CHX 14 | MD + MINm 16 | Sweden | 12 | Local | PPD reduction (mm), BoP reduction (%) | The use of adjunctive minocycline microspheres resulted in improvements in both probing depths and bleeding scores. |
| Renvert et al., 2008 [38] | MD + CHX 15 (38) | MD + MINm 17 (57) | Sweden | 12 | Local | PPD reduction (mm), BoP reduction (%) | Adjunctive use of minocycline microspheres is beneficial in the treatment of peri-implant lesions, but the treatment may have to be repeated. |
| Passarielo et al., 2012 [35] | MD + AMC or CD 64 (64) | MD + AMC or CD + serratiopeptidase/ 64 (64) | Italy | 6 | Systemic | PPD reduction (mm), BoP reduction (%), DBL (mm) | Combined systemic administration of antibiotics and serratiopeptidase associated with MD significantly enhances success rates. |
| Shibli et al., 2019 [39] | MD 20 | MD + AMX + MTZ 20 | Brazil | 12 | Systemic | PPD reduction (mm), BoP reduction (%) | The results of this study do not support the adjunctive use of systemic MTZ + AMX to the non-surgical treatment of peri-implantitis. |
| De Waal et al., 2021 [32] | MD + CHX 29 (64) | MD + AMX + MTZ 28 (68) | Netherlands | 3 | Systemic | PPD reduction (mm), DBL (mm) | Adjunctive systemic antibiotic therapy of AMX and MTZ does not improve clinical and microbiological outcomes and should not be recommended. |
| Park et al., 2021 [34] | MD 37 (37) | MD + MTZ + MIN 38 (38) | China | 3 | Local | PPD reduction (mm), BoP reduction (%) | Local adjunctive use of minocycline, either with or without the addition of metronidazole, results in significantly higher treatment success rates compared to non-surgical treatment. The combination of metronidazole might enhance the PPD reduction in pockets ≥8 mm. |
| MD + MIN 39 (39) | |||||||
| Blanco et al., 2021 [30] | MD 16 (34) | MD + MTZ 16 (28) | Spain | 12 | Systemic | PPD reduction (mm), BoP reduction (%) | The adjunctive use of systemic metronidazole as an adjunct to non-surgical treatment resulted in additional improvements in clinical, radiographic and microbiologic parameters. |
| Polymeri et al., 2022 [36] | MD + CHX 19 | MD + CHX + MTZ + AMX 18 | Netherlands | 3 | Systemic | PPD reduction (mm), DBL (mm) | No clinical benefit from the adjunctive use of systemic AMX and MTZ in the non-surgical treatment of peri-implantitis, suggesting that the routine use of systemic antibiotics is not recommended. |
| Alhumaidan et al., 2022 [29] | MD (current smokers) 12 (12) | MD + MH (current smokers) 12 (12) | United States of America | 6 | Local | PPD reduction (mm) | A single subgingival delivery of minocycline hydrochloride (MH) is as effective as non-surgical MD alone. |
| MD (non-smokers) 12 (12) | MD + MH (non-smokers) 12 (12) | ||||||
| Liñares et al., 2024 [33] | MD 11 | MD + MTZ 10 | Spain | 6 | Systemic | PPD reduction (mm), BoP reduction (%) | Systemic anti-inflammatory impact with reduction in peripheral levels of CRP, IL-6 and TNF-α was observed regardless of the use of systemic metronidazole. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meném, M.; Estácio, C.; Mascarenhas, P.; Santos, A. Influence of Local and Systemic Antibiotics in Non-Surgical Peri-Implantitis Treatment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Update. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 11422. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111422
Meném M, Estácio C, Mascarenhas P, Santos A. Influence of Local and Systemic Antibiotics in Non-Surgical Peri-Implantitis Treatment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Update. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(21):11422. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111422
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeném, Madalena, Catarina Estácio, Paulo Mascarenhas, and Alexandre Santos. 2025. "Influence of Local and Systemic Antibiotics in Non-Surgical Peri-Implantitis Treatment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Update" Applied Sciences 15, no. 21: 11422. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111422
APA StyleMeném, M., Estácio, C., Mascarenhas, P., & Santos, A. (2025). Influence of Local and Systemic Antibiotics in Non-Surgical Peri-Implantitis Treatment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Update. Applied Sciences, 15(21), 11422. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111422







