Therapeutic Potential and Challenges of Pioglitazone in Cancer Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Overview of Pioglitazone
3. Therapeutic Use of Pioglitazone
3.1. Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 (T2DM)
3.2. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH)
3.3. Cardiovascular Protection
3.4. Neurodegenerative Diseases (NDs)
3.5. Anticancer Properties
3.5.1. Overview
3.5.2. Molecular Pharmacology
3.6. Therapeutic Effect on Different Types of Cancer
3.6.1. Breast Cancer
3.6.2. Lung Cancer
- The use with EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors such as gefitinib for NSCLC, as it was found that PPAR-γ mediated upregulation of phosphate, and tensin homolog (PTEN) downregulated the PI3K/Akt pathway that is correlated to resistance to said TKIs [70].
- Combination of pioglitazone with clarithromycin and a relatively small dose of chemotherapeutic agent was compared against nivolumab in the ModuLung trial by Heudobler et al. (2021) [75]. This trial was terminated early due to the approval of checkpoint inhibitors as first line treatment, with the conclusion that nivolumab was superior to this combination therapy; however, with a difference in the overall survival rate and quality of life between the two regimens being similar, the latter seems to be a viable alternative to be assessed in future trials and be considered in cases with few other options [75].
3.6.3. Renal Cancer
3.6.4. Hepatocellular Carcinoma
3.6.5. Colorectal Cancer
3.6.6. Thyroid Cancer
3.6.7. Glioma
3.6.8. Hematological Malignancies
3.6.9. Pancreatic Cancer
3.7. Immunotherapy
3.8. Clinical Evidence
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mal, S.; Dwivedi, A.R.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, N.; Kumar, B.; Kumar, V. Role of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma (PPARγ) in Different Disease States: Recent Updates. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 3193–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza-Tavares, H.; Miranda, C.S.; Macedo, I.; Sandoval, C.; Santana-Oliveira, D.A.; Silva-Veiga, F.M.; Fernandes-da-Silva, A.; Souza-Mello, V. Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors as Targets to Treat Metabolic Diseases: Focus on the Adipose Tissue, Liver, and Pancreas. World J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 29, 4136–4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixit, G.; Prabhu, A. The Pleiotropic Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptors: Regulation and Therapeutics. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2022, 124, 104723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qaoud, M.T.; Al-masri, I.; Önkol, T. Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors as Superior Targets for Treating Diabetic Disease, Design Strategies—Review Article. Turk. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 19, 353–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dana, N.; Ferns, G.A.; Nedaeinia, R.; Javanmard, S.H. Leptin Signaling in Breast Cancer and Its Crosstalk with Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors α and γ. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2022, 25, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, A.; Kaur, P.; Sahu, S.K.; Mittal, A. A New Insight into the Treatment of Diabetes by Means of Pan PPAR Agonists. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2022, 100, 947–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staels, B.; Butruille, L.; Francque, S. Treating NASH by Targeting Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 1302–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, N.; Genda, K. Pioglitazone (Actos, Glustin). In Drug Discovery in Japan; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlén, A.D.; Dashi, G.; Maslov, I.; Attwood, M.M.; Jonsson, J.; Trukhan, V.; Schiöth, H.B. Trends in Antidiabetic Drug Discovery: FDA Approved Drugs, New Drugs in Clinical Trials and Global Sales. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 12, 807548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.K.; Singh, R.; Chakraborty, P.P. Diabetes Monotherapies versus Metformin-Based Combination Therapy for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2021, 14, 3833–3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency. Actos: EPAR—Product Information. 2024. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/actos-epar-product-information_en.pdf (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Papaetis, G.S. Pioglitazone, Bladder Cancer, and the Presumption of Innocence. Curr. Drug Saf. 2022, 17, 294–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanis, S.P.; Parker, T.T.; Colca, J.R.; Fisher, R.M.; Kletzein, R.F. Synthesis and Biological Activity of Metabolites of the Antidiabetic, Antihyperglycemic Agent Pioglitazone. J. Med. Chem. 1996, 39, 5053–5063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, T.; Patel, V. Thiazolidinediones: Recent Development in Analytical Methodologies. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2023, 62, 789–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltanpour, S.; Zohrabi, F.; Bastami, Z. Thermodynamic Solubility of Pioglitazone HCl in Polyethylene Glycols 200, 400 or 600+Water Mixtures at 303.2 and 308.2K—Data Report and Modeling. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2014, 379, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beloshe, S.P.; Chougule, D.D.; Shah, R.R.; Ghodke, D.S.; Pawar, N.D.; Ghaste, R.P. Effect of Method of Preparation on Pioglitazone HCl-β-Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes. Asian J. Pharm. 2010, 4, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faiz, S.; Arshad, S.; Kamal, Y.; Imran, S.; Asim, M.H.; Mahmood, A.; Inam, S.; Irfan, H.M.; Riaz, H. Pioglitazone-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers: In-Vitro and In-Vivo Evaluation for Improved Bioavailability. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 79, 104041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Matzger, A.J. A Newly Discovered Racemic Compound of Pioglitazone Hydrochloride Is More Stable than the Commercial Conglomerate. Cryst. Growth Des. 2017, 17, 414–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckland, D.; Danhof, M. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Pioglitazone. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2000, 108, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.I.; Yazdi, Z.S.; Beitelshees, A.L. Pharmacological Treatment of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e142243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, G.; Kumar, R.; Desna, D.S.; Chaudhary, M.; Kaur, C.; Khurrana, N. Thiazolidinedione as a Promising Medicinal Scaffold for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2023, 20, e201023222411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maheshwari, A.; Dhoat, P. USE, Safety and Adverse Effects of Thiazolidinediones—A Review. World J. Pharm. Res. 2023, 12, 111–119. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, W.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Bu, H.; Takahashi, H. Pioglitazone on Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 15 RCTs. Medicine 2022, 101, e31508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Du, H.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, Y.; Ma, C.; Chen, H.; Li, M.; Tian, J.; Xue, C.; Long, G.; et al. Response to Pioglitazone in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Patients with vs. without Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1111430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Pepa, G.; Russo, M.; Vitale, M.; Carli, F.; Vetrani, C.; Masulli, M.; Riccardi, G.; Vaccaro, O.; Gastaldelli, A.; Rivellese, A.A.; et al. Pioglitazone Even at Low Dosage Improves NAFLD in Type 2 Diabetes: Clinical and Pathophysiological Insights from a Subgroup of the TOSCA.IT Randomised Trial. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 178, 108984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazhar, I.; Yasir, M.; Sarfraz, S.; Shlaghya, G.; Narayana, S.; Mushtaq, U.; Ameen, B.S.; Nie, C.; Nechi, D.; Penumetcha, S. Vitamin E and Pioglitazone: A Comprehensive Systematic Review of Their Efficacy in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Cureus 2023, 15, e43635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanyal, A.J.; Chalasani, N.; Kowdley, K.V.; McCullough, A.; Diehl, A.M.; Bass, N.M.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Lavine, J.E.; Tonascia, J.; Unalp, A.; et al. Pioglitazone, Vitamin E, or Placebo for Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1675–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesti, L.; Tricò, D.; Mengozzi, A.; Natali, A. Rethinking Pioglitazone as a Cardioprotective Agent: A New Perspective on an Overlooked Drug. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2021, 20, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spence, J.D.; Viscoli, C.; Kernan, W.N.; Young, L.H.; Furie, K.; DeFronzo, R.; Abdul-Ghani, M.; Dandona, P.; Inzucchi, S.E. Efficacy of Lower Doses of Pioglitazone after Stroke or Transient Ischaemic Attack in Patients with Insulin Resistance. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2022, 24, 1150–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camafort, M.; Yang, E.; Ponte, C.I.; Coca, A. Therapeutic Strategies to Prevent Recurrent Stroke. In Hypertension and Brain Damage. Updates in Hypertension and Cardiovascular Protection; Springer: Cham, Swizterland, 2024; pp. 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.M.; Liu, W.Z.; Yang, L. Pioglitazone Ameliorates Hypertension Induced Cardiac Hypertrophy and down Regulates Cardiac Hypoxia Inducible Factor-l α in Rats. Pak. J. Zool. 2023, 55, 1657–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.D.; Sun, G.X.; Guo, J.J.; Hu, C.C.; Sun, R.C.; Yu, H.C. Effects of PPARγ agonist pioglitazone on cardiac fibrosis in diabetic mice by regulating PTEN/AKT/FAK pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 25, 812–819. [Google Scholar]
- Mannucci, E.; Giaccari, A.; Gallo, M.; Targher, G.; Pintaudi, B.; Candido, R.; Monami, M. Effects of Pioglitazone on Cardiovascular Events and All-Cause Mortality in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 32, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhowail, A.; Alsikhan, R.; Alsaud, M.; Aldubayan, M.; Rabbani, S.I. Protective Effects of Pioglitazone on Cognitive Impairment and the Underlying Mechanisms: A Review of Literature. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2022, 16, 2919–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, A.M.; Burns, D.K.; Gottschalk, W.K. Reassessment of Pioglitazone for Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 666958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamanian, M.Y.; Terefe, E.M.; Taheri, N.; Kujawska, M.; Tork, Y.J.; Abdelbasset, W.K.; Shoukat, S.; Jade, M.; Heidari, M.; Alesaeidi, S. Neuroprotective and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Pioglitazone on Parkinson’s Disease: A Comprehensive Narrative Review of Clinical and Experimental Findings. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2023, 22, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, M.; Zhang, L.; Huo, J.; Fu, Y.; Huang, T.; Fan, D. Genetic Variation in Targets of Antidiabetic Drugs and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Risk. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamu, A.; Li, S.; Gao, F.; Xue, G. The Role of Neuroinflammation in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Current Understanding and Future Therapeutic Targets. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2024, 16, 1347987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.; Choi, D.W.; Kim, K.J.; Kim, K.Y.; Nam, C.M.; Kim, E. Pioglitazone Use and Reduced Risk of Dementia in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus with a History of Ischemic Stroke. Neurology 2023, 100, e1799–e1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Tao, Y.; Li, J.; Kang, M. Pioglitazone Use Is Associated with Reduced Risk of Parkinson’s Disease in Patients with Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2022, 106, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra, B.; Hiteshi, P.; Khalkho, P.; Malik, R.; Bhadada, S.K.; Bhansali, A.; Shafiq, N.; Malhotra, S.; Kumar, N.; Rajput, R.; et al. Bladder Cancer with Pioglitazone: A Case-Control Study. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2022, 16, 102637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashmi, A. Pioglitazone Suspension and Its Aftermath: A Wake up Call for the Indian Drug Regulatory Authorities. J. Pharmacol. Pharmacother. 2013, 4, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morones, J.; Pérez, M.; Muñoz, M.; Sánchez, E.; Ávila, M.; Topete, J.; Ventura, J.; Martínez, S. Evaluation of the Effect of an α-Adrenergic Blocker, a PPAR-γ Receptor Agonist, and a Glycemic Regulator on Chronic Kidney Disease in Diabetic Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousefnia, S.; Momenzadeh, S.; Forootan, F.S.; Ghaedi, K.; Nasr-Esfahani, M.H. The Influence of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor γ (PPARγ) Ligands on Cancer Cell Tumorigenicity. Gene 2018, 649, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lei, F.; Lin, Y.; Han, Y.; Yang, L.; Tan, H. Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors as Therapeutic Target for Cancer. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2023, 28, 17931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, T.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Yang, K.; Xie, F.; Liao, Z.; Wei, P. PPAR-γ Modulators as Current and Potential Cancer Treatments. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 737776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.X.; Lin, S.Y.; Lian, S.X.; Qiu, Y.R.; Li, Z.H.; Chen, Z.H.; Lu, W.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, L.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Inhibition of the Breast Cancer by PPARγ Agonist Pioglitazone through JAK2/STAT3 Pathway. Neoplasma 2020, 67, 834–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olatunde, A.; Nigam, M.; Singh, R.K.; Panwar, A.S.; Lasisi, A.; Alhumaydhi, F.A.; Jyoti kumar, V.; Mishra, A.P.; Sharifi-Rad, J. Cancer and Diabetes: The Interlinking Metabolic Pathways and Repurposing Actions of Antidiabetic Drugs. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.H.; Han, S.H.; Park, J.I. Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor γ and PGC-1α in Cancer: Dual Actions as Tumor Promoter and Suppressor. PPAR Res. 2018, 2018, 6727421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wang, H.; Cui, Q.; Shi, J.; Hou, Y. Dual Function of Activated PPARγ by Ligands on Tumor Growth and Immunotherapy. Med. Oncol. 2024, 41, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goleij, P.; Amin, M.; Rabie, A.; Mohamed, L.; Hamed, A.; Abdu, M.; Moahmmednoor, M.; Khan, H. Molecular Secrets Revealed: How Diabetes May Be Paving the Way for Leukemia. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2024, 25, 1563–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsubaki, M.; Takeda, T.; Tomonari, Y.; Kawashima, K.; Itoh, T.; Imano, M.; Satou, K.; Nishida, S. Pioglitazone Inhibits Cancer Cell Growth through STAT3 Inhibition and Enhanced AIF Expression via a PPARγ-Independent Pathway. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017, 233, 3638–3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elrod, H.A.; Sun, S.-Y. PPARγ and Apoptosis in Cancer. PPAR Res. 2008, 2008, 704165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.H.; Lee, T.J.; Sung, E.G.; Song, I.H.; Kim, J.Y. Pioglitazone Mediates Apoptosis in Caki Cells via Downregulating C-FLIP(L) Expression and Reducing Bcl-2 Protein Stability. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 22, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, H.S. Preclinical Drug Discovery in Colorectal Cancer: A Focus on Natural Compounds. Curr. Drug Targets 2021, 22, 977–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballav, S.; Biswas, B.; Sahu, V.K.; Ranjan, A.; Basu, S. PPAR-γ Partial Agonists in Disease-Fate Decision with Special Reference to Cancer. Cells 2022, 11, 3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Yu, L.; Qu, X.; Huang, T. The Role of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors in the Tumor Microenvironment, Tumor Cell Metabolism, and Anticancer Therapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1184794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dicitore, A.; Caraglia, M.; Gaudenzi, G.; Manfredi, G.; Amato, B.; Mari, D.; Persani, L.; Arra, C.; Vitale, G. Type I Interferon-Mediated Pathway Interacts with Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor-γ (PPAR-γ): At the Cross-Road of Pancreatic Cancer Cell Proliferation. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Rev. Cancer 2014, 1845, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joharapurkar, A.; Patel, V.; Kshirsagar, S.; Patel, M.S.; Savsani, H.; Jain, M. Effect of Dual PPAR-α/γ Agonist Saroglitazar on Diabetic Retinopathy and Oxygen-Induced Retinopathy. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 899, 174032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Quiles, M.; Broekema, M.F.; Kalkhoven, E. PPARgamma in Metabolism, Immunity, and Cancer: Unified and Diverse Mechanisms of Action. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 624112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, S.; Safaroghli-Azar, A.; Pourbagheri-Sigaroodi, A.; Salari, S.; Gharehbaghian, A.; Hamidpour, M.; Bashash, D. Stimulation of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-Gamma (PPARγ) Using Pioglitazone Decreases the Survival of Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia Cells through Up-Regulation of PTEN Expression. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2020, 21, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.; Qian, J.; Chen, H.; Liu, Q.; Hussain, S.; Jin, J.; Shi, J.; Hou, Y. PPARγ Agonist Pioglitazone Enhances Colorectal Cancer Immunotherapy by Inducing PD-L1 Autophagic Degradation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 950, 175749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciaramella, V.; Sasso, F.C.; Liello, R.D.; Della, M.; Barra, G.; Viscardi, G.; Esposito, G.; Sparano, F.; Troiani, T.; Martinelli, E.; et al. Activity and Molecular Targets of Pioglitazone via Blockade of Proliferation, Invasiveness and Bioenergetics in Human NSCLC. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, C.H. Pioglitazone and Breast Cancer Risk in Female Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, Q.H.; Alkharashi, L.A.; Alajami, H.; Alkharashi, I.; Alkharashi, L.; Alhinti, S.N. Pioglitazone Enhances Cisplatin’s Impact on Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Role of PPARγ in Cell Apoptosis. Saudi Pharm. J. 2024, 32, 102059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakouti, P.; Mohammadi, M.; Boshagh, M.A.; Amini, A.; Rezaee, M.A.; Rahmani, M.R. Combined Effects of Pioglitazone and Doxorubicin on Migration and Invasion of MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells. J. Egypt. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2022, 34, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, S.Y.; Syn, N.L.; Koh, A.P.-F.; Teng, J.C.-F.; Deivasigamani, A.; Tan, T.Z.; Thike, A.A.; Vali, S.; Kapoor, S.; Wang, X.; et al. Epigenetic Derepression Converts PPARγ into a Druggable Target in Triple-Negative and Endocrine-Resistant Breast Cancers. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augimeri, G.; Bonofiglio, D. PPARgamma: A Potential Intrinsic and Extrinsic Molecular Target for Breast Cancer Therapy. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Xin, Z.; Ren, P.; Wu, H. The Role of PPARs in Breast Cancer. Cells 2022, 12, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Tang, M.; Shang, J. PPARγ Modulators in Lung Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms, Clinical Prospects, and Challenges. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho, M.V.; Gonçalves-de-Albuquerque, C.F.; Silva, A.R. PPAR Gamma: From Definition to Molecular Targets and Therapy of Lung Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keith, R.L.; Blatchford, P.J.; Merrick, D.T.; Bunn, P.A.; Bagwell, B.; Dwyer-Nield, L.D.; Jackson, M.K.; Geraci, M.W.; Miller, Y.E. A Randomized Phase II Trial of Pioglitazone for Lung Cancer Chemoprevention in High-Risk Current and Former Smokers. Cancer Prev. Res. 2019, 12, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seabloom, D.E.; Galbraith, A.R.; Haynes, A.M.; Antonides, J.D.; Wuertz, B.R.; Miller, W.A.; Miller, K.A.; Steele, V.E.; Miller, M.S.; Clapper, M.L.; et al. Fixed-Dose Combinations of Pioglitazone and Metformin for Lung Cancer Prevention. Cancer Prev. Res. 2017, 10, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seabloom, D.E.; Galbraith, A.R.; Haynes, A.M.; Antonides, J.D.; Wuertz, B.R.; Miller, W.A.; Miller, K.A.; Steele, V.E.; Suen, C.S.; O’Sullivan, M.G.; et al. Safety and Preclinical Efficacy of Aerosol Pioglitazone on Lung Adenoma Prevention in A/J Mice. Cancer Prev. Res. 2017, 10, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heudobler, D.; Schulz, C.; Fischer, J.R.; Staib, P.; Wehler, T.; Südhoff, T.; Schichtl, T.; Wilke, J.; Hahn, J.; Lüke, F.; et al. A Randomized Phase II Trial Comparing the Efficacy and Safety of Pioglitazone, Clarithromycin and Metronomic Low-Dose Chemotherapy with Single-Agent Nivolumab Therapy in Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treated in Second or Further Line (ModuLung). Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 599598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, A.V.V.V.R.; Kumari, G.K.; Krishnamurthy, P.T. Preliminary Evaluation of Anticancer Efficacy of Pioglitazone Combined with Celecoxib for the Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Investig. New Drugs 2022, 40, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Luo, X.; Ye, X.; Li, H.; Liu, H.; Du, Q.; Zhai, Q. SIRT1/PGC-1α/PPAR-γ Correlate with Hypoxia-Induced Chemoresistance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 682762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.H. Pioglitazone Does Not Affect the Risk of Kidney Cancer in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Metabolism 2014, 63, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piątkowska-Chmiel, I.; Gawrońska-Grzywacz, M.; Natorska-Chomicka, D.; Herbet, M.; Sysa, M.; Iwan, M.; Korga, A.; Dudka, J. Pioglitazone as a Modulator of the Chemoresistance of Renal Cell Adenocarcinoma to Methotrexate. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 43, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, M.; Mahmoud, M.A.; Alshammari, A.; Almutairi, M.M.; Al-Ghamdi, J.M.; Alsabhan, J.F.; Shabanah, O.A.; Alshalawi, N.A.; Alzarea, S.I.; Alasmari, A.F. The Ameliorative Effect of Pioglitazone against Colistin-Induced Nephrotoxicity Is Mediated by Inhibition of NF-ΚB and Restoration of Nrf2 Signaling: An Integrative Bioinformatics Prediction-Guided in Vitro Study. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0314092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, D.S.; Jerkins, T. In Praise of Pioglitazone: An Economically Efficacious Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes and Other Manifestations of the Metabolic Syndrome. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2023, 25, 3093–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ghoshal, S.; Sojoodi, M.; Arora, G.; Masia, R.; Erstad, D.J.; Lanuti, M.; Hoshida, Y.; Baumert, T.; Tanabe, K.K.; et al. Pioglitazone Reduces Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development in Two Rodent Models of Cirrhosis. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2019, 23, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, L.H.; Huang, B.; Wang, R.Y.; Yuan, S.X.; Tao, Q.F.; Xu, Y.; Sun, H.Y.; Lin, C.; Zhou, W.P. Pioglitazone, a PPARγ Agonist, Inhibits Growth and Invasion of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Blockade of the Rage Signaling. Mol. Carcinog. 2014, 54, 1584–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.; Zhang, M.; Wang, M.; Xu, W.; Duan, X.; Han, X.; Ren, J. Pioglitazone, a Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor γ Agonist, Induces Cell Death and Inhibits the Proliferation of Hypoxic HepG2 Cells by Promoting Excessive Production of Reactive Oxygen Species. Oncol. Lett. 2024, 27, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.H.; Li, S.-F.; Wei, R.; Jiang, Z. Diabetes and Colorectal Cancer Risk: Clinical and Therapeutic Implications. J. Diabetes Res. 2022, 2022, 1747326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, S.; Valente, S.; Chaimbault, P.; Schohn, H. Evaluation of Δ2-Pioglitazone, an Analogue of Pioglitazone, on Colon Cancer Cell Survival: Evidence of Drug Treatment Association with Autophagy and Activation of the Nrf2/Keap1 Pathway. International J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouya, F.D.; Salehi, R.; Rasmi, Y.; Kheradmand, F.; Fathi-Azarbayjani, A. Combination Chemotherapy against Colorectal Cancer Cells: Co-Delivery of Capecitabine and Pioglitazone Hydrochloride by Polycaprolactone-Polyethylene Glycol Carriers. Life Sci. 2023, 332, 122083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushchayeva, Y.; Kushchayev, S.; Jensen, K.; Brown, R.J. Impaired Glucose Metabolism, Anti-Diabetes Medications, and Risk of Thyroid Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, K.; Okiyama, Y.; Tanaka, S. In Silico Search for Drug Candidates Targeting the PAX8–PPARγ Fusion Protein in Thyroid Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; O’Donnell, M.; O’Donnell, J.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sartor, M.A.; Koenig, R.J. Adipogenic Differentiation of Thyroid Cancer Cells through the Pax8-PPARγ Fusion Protein Is Regulated by Thyroid Transcription Factor 1 (TTF-1). J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 19274–19286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, A.; Coperchini, F.; Croce, L.; Magri, F.; Teliti, M.; Rotondi, M. Drug Repositioning in Thyroid Cancer Treatment: The Intriguing Case of Anti-Diabetic Drugs. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1303844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, T.J.; Haugen, B.R.; Sherman, S.I.; Shah, M.H.; Caoili, E.M.; Koenig, R.J. Pioglitazone Therapy of PAX8-PPARγ Fusion Protein Thyroid Carcinoma. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 1277–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir Kutbay, N.; Biray Avci, C.; Sarer Yurekli, B.; Caliskan Kurt, C.; Shademan, B.; Gunduz, C.; Erdogan, M. Effects of Metformin and Pioglitazone Combination on Apoptosis and AMPK/MTOR Signaling Pathway in Human Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer Cells. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2020, 34, e22547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basilotta, R.; Lanza, M.; Casili, G.; Chisari, G.; Munao, S.; Colarossi, L.; Cucinotta, L.; Campolo, M.; Esposito, E.; Paterniti, I. Potential Therapeutic Effects of PPAR Ligands in Glioblastoma. Cells 2022, 11, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grommes, C.; Karlo, J.C.; Caprariello, A.; Blankenship, D.; DeChant, A.; Landreth, G.E. The PPARγ Agonist Pioglitazone Crosses the Blood–Brain Barrier and Reduces Tumor Growth in a Human Xenograft Model. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2013, 71, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtor, T.; Spagnolo, A.; Glick, R.P.; Feinstein, D.L. PPAR—Thiazolidinedione Agonists and Immunotherapy in the Treatment of Brain Tumors. PPAR Res. 2008, 2008, 547470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching, J.; Amiridis, S.; Stylli, S.S.; Morokoff, A.P.; O’Brien, T.J.; Kaye, A.H. A Novel Treatment Strategy for Glioblastoma Multiforme and Glioma Associated Seizures: Increasing Glutamate Uptake with PPARγ Agonists. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2015, 22, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, G.; Ranjan, S.; Sunita, P.; Pattanayak, S.P. Thiazolidinedione Derivatives in Cancer Therapy: Exploring Novel Mechanisms, Therapeutic Potentials, and Future Horizons in Oncology. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2024, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vasconcelos, A.; Boeira, A.J.Z.; Drawanz, B.B.; Pedra, N.S.; Bona, N.P.; Stefanello, F.M.; Cunico, W. 2,4-Thiazolidinedione as Precursor to the Synthesis of Compounds with Anti-Glioma Activities in C6 and GL261 Cells. Med. Chem. 2021, 17, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biegański, M.; Szeliga, M. Disrupted Glutamate Homeostasis as a Target for Glioma Therapy. Pharmacol. Rep. 2024, 76, 1305–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilibrasi, C.; Butta, V.; Riva, G.; Bentivegna, A. Pioglitazone Effect on Glioma Stem Cell Lines: Really a Promising Drug Therapy for Glioblastoma? PPAR Res. 2016, 2016, 7175067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapia-Pérez, J.H.; Kirches, E.; Mawrin, C.; Firsching, R.; Schneider, T. Cytotoxic Effect of Different Statins and Thiazolidinediones on Malignant Glioma Cells. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2010, 67, 1193–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia-Pérez, J.H.; Preininger, R.; Kirches, E.; Reinhold, A.; Butzmann, J.; Prilloff, S.; Mawrin, C.; Schneider, T. Simultaneous Administration of Statins and Pioglitazone Limits Tumor Growth in a Rat Model of Malignant Glioma. Anticancer Res. 2016, 36, 6357–6365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cramer, C.K.; Alphonse-Sullivan, N.K.; Isom, S.; Metheny-Barlow, L.J.; Cummings, T.L.; Page, B.R.; Brown, D.; Blackstock, A.W.; Peiffer, A.M.; Strowd, R.E.; et al. Safety of Pioglitazone during and after Radiation Therapy in Patients with Brain Tumors: A Phase I Clinical Trial. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 145, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaeili, S.; Salari, S.; Kaveh, V.; Ghaffari, S.H.; Bashash, D. Alteration of PPAR-GAMMA (PPARG.; PPARγ) and PTEN Gene Expression in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patients and the Promising Anticancer Effects of PPARγ Stimulation Using Pioglitazone on AML Cells. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2021, 9, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiki, M.; Hatta, Y.; Yamazaki, T.; Itoh, T.; Enomoto, Y.; Takeuchi, J.; Sawada, U.; Aizawa, S.; Horie, T. Pioglitazone Inhibits the Growth of Human Leukemia Cell Lines and Primary Leukemia Cells While Sparing Normal Hematopoietic Stem Cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2006, 29, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Póvoa, V.M.O.; Delafiori, J.; Dias-Audibert, F.L.; de Oliveira, A.N.; Lopes, A.B.P.; de Paula, E.V.; Pagnano, K.B.B.; Catharino, R.R. Metabolic Shift of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients under Imatinib–Pioglitazone Regimen and Discontinuation. Med. Oncol. 2021, 38, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hijazi, Μ.A.; Gessner, A.; El-Najjar, Ν. Repurposing of Chronically Used Drugs in Cancer Therapy: A Chance to Grasp. Cancers 2023, 15, 3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, H.; Jamshidi, A.; Ghatee, M.A.; Mazhab-Jafari, K.; Khorasani, M.; Rahmati, M.; Mohammadi, S. PPARγ Activation by Pioglitazone Enhances the Anti-Proliferative Effects of Doxorubicin on Pro-Monocytic THP-1 Leukemia Cells via Inducing Apoptosis and G2/M Cell Cycle Arrest. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. Res. 2021, 42, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.; Kim, D.S.; Lee, M.W.; Lee, J.W.; Sung, K.W.; Koo, H.H.; Yoo, K.H. Anti-Leukemic Effects of PPARγ Ligands. Cancer Lett. 2018, 418, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okabe, S.; Tauchi, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Ohyashiki, K. Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors: Targets for the Treatment of Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Leukemia Cells. Blood 2017, 130, 5241. [Google Scholar]
- Esmaeili, S.; Yousefi, A.-M.; Delshad, M.; Bashash, D. Synergistic Effects of PI3K Inhibition and Pioglitazone against Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia Cells. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2022, 11, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, Y.; Yousefi, A.-M.; Bashash, D. Inhibition of PI3K Signaling Intensified the Antileukemic Effects of Pioglitazone: New Insight into the Application of PPARγ Stimulators in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Indian J. Hematol. Blood Transfus. 2023, 39, 546–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghadiany, M.; Tabarraee, M.; Salari, S.; Haghighi, S.; Rezvani, H.; Ghasemi, S.N.; Karimi-Sari, H. Adding Oral Pioglitazone to Standard Induction Chemotherapy of Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2019, 19, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, S.; Safaroghli-azar, A.; Pourbagheri-Sigaroodi, A.; Salari, S.; Gharehbaghian, A.; Hamidpour, M.; Bashash, D. Activation of PPARγ Intensified the Effects of Arsenic Trioxide in Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia through the Suppression of PI3K/Akt Pathway: Proposing a Novel Anticancer Effect for Pioglitazone. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2020, 122, 105739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glodkowska-Mrowka, E.; Manda-Handzlik, A.; Stelmaszczyk-Emmel, A.; Seferynska, I.; Stoklosa, T.; Przybylski, J.; Mrowka, P. PPARγ Ligands Increase Antileukemic Activity of Second- and Third-Generation Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Cells. Blood Cancer J. 2016, 6, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazi, M.S.; Mohammadi, S.; Yazdani, Y.; Sedighi, S.; Memarian, A.; Aghaei, M. Effects of Valproic Acid and Pioglitazone on Cell Cycle Progression and Proliferation of T-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Jurkat Cells. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2016, 19, 779. [Google Scholar]
- Rousselot, P.; Prost, S.; Guilhot, J.; Roy, L.; Etienne, G.; Legros, L.; Charbonnier, A.; Coiteux, V.; Cony-Makhoul, P.; Huguet, F.; et al. Pioglitazone Together with Imatinib in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Proof of Concept Study. Cancer 2016, 123, 1791–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beatriz, A.; Miranda, E.C.; Oliveira, M.; Vergílio, B.R.; Pavan, C.; Delamain, M.T.; Duarte, G.B.; Souza, C.A.; De, E.V.; Pagnano, K.B. Pioglitazone Did Not Affect PPAR-Γ, STAT5, HIF2α and CITED2 Gene Expression in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients with Deep Molecular Response. Blood 2019, 134, 1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; He, X.; Sun, Y. Hypoglycemic Agents and Incidence of Pancreatic Cancer in Diabetic Patients: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1193610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y. Diabetes Medication Use and Risk of Breast, Colorectal, and Pancreatic Cancer: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Mushashi, F.; Son, S.; Bhatti, P.; Dummer, T.; Murphy, R.A. Diabetes Medications and Cancer Risk Associations: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Evidence over the Past 10 Years. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- See, L.-C.; Wu, C.-Y.; Tsai, C.-Y.; Lee, C.-C.; Chen, J.-J.; Jenq, C.-C.; Chen, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-C.; Yen, C.-L.; Yang, H.-Y. PPAR-γ Agonist Pioglitazone and the Risks of Malignancy among Type2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients. Acta Diabetol. 2024. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ninomiya, I.; Yamazaki, K.; Oyama, K.; Hayashi, H.; Tajima, H.; Kitagawa, H.; Fushida, S.; Fujimura, T.; Ohta, T. Pioglitazone Inhibits the Proliferation and Metastasis of Human Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Oncol. Lett. 2014, 8, 2709–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, H. PPARγ Potentiates Anticancer Effects of Gemcitabine on Human Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2011, 40, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sisi, A.E.; Sokar, S.S.; Salem, T.A.; Abu, S.E. PPARγ-Dependent Anti-Tumor and Immunomodulatory Actions of Pioglitazone. J. Immunotoxicol. 2014, 12, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahrambeigi, S.; Molaparast, M.; Sohrabi, F.; Seifi, L.; Faraji, A.; Fani, S.; Shafiei-Irannejad, V. Targeting PPAR Ligands as Possible Approaches for Metabolic Reprogramming of T Cells in Cancer Immunotherapy. Immunol. Lett. 2020, 220, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Chan, S.L.; Zhou, J.; Joaquim; Kwong, T.T.; Zeng, X.; Wu, H.; Cao, J.; Tu, Y.; Feng, Y.; et al. Targeting PPAR-Gamma Counteracts Tumour Adaptation to Immune-Checkpoint Blockade in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Study of Pioglitazone and Carboplatin in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors—Full Text View. 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02133625?cond=cancer%20&intr=pioglitazone&rank=3 (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Pioglitazone Hydrochloride in Preventing Head and Neck Cancer in Patients with Oral Leukoplakia—Full Text View. 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT00099021?cond=cancer%20&intr=pioglitazone&rank=4 (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- A Phase II Study of Pioglitazone for Patients with Cancer of the Pancreas—Full Text View. 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT01838317?cond=cancer%20&intr=pioglitazone&rank=9 (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Preventing Squamous Cell Skin Cancer—Full Text View. 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02347813?cond=cancer%20&intr=pioglitazone&rank=10 (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Pioglitazone to Treat Adults Undergoing Surgery for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer—Full Text View. 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT00923949?cond=cancer%20&intr=pioglitazone&page=2&rank=11 (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Study of Imatinib Discontinuation in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia with Deep Molecular Response (EDI-PIO)—Full Text View. 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02852486?cond=cancer%20&intr=pioglitazone&page=2&rank=13 (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Pioglitazone Hydrochloride in Treating Patients with Stage IA-IIIA Non-small Cell Lung Cancer—Full Text View. 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT01342770?cond=cancer%20&intr=pioglitazone&page=2&rank=15 (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Study on Trabectedin in Combination with Pioglitazone in Patients Myxoid Liposarcomas with Stable Disease After T Alone. (TRABEPIO)—Full Text View. 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04794127?cond=cancer%20&intr=pioglitazone&page=2&rank=1 (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Pioglitazone-Metformin Combination Treatment for High Risk Oral Preneoplasia—Full Text View. 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05727761?cond=cancer%20&intr=pioglitazone&page=2&rank=20 (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Pioglitazone for Oral Premalignant Lesions—Full Text View. 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT00951379?cond=cancer%20&intr=pioglitazone&page=3&rank=21 (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- A Trial With Metronomic Low-Dose Treosulfan, Pioglitazone and Clarithromycin Versus Standard Treatment in NSCLC (ModuLung)—Full Text View. 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02852083?cond=cancer%20&intr=pioglitazone&page=3&rank=22 (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Value of Using Pioglitazone in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Treatment—Full Text View. 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04883125?cond=cancer%20&intr=pioglitazone&page=3&rank=27 (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Pioglitazone for Lung Cancer Chemoprevention—Full Text View. 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT00780234?cond=cancer%20&intr=pioglitazone&page=3&rank=28 (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Safety and Efficiency Study of Pioglitazone in Combination with Imatinib Mesylate to Treat Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (SESPI)—Full Text View. 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02687425?cond=cancer%20&intr=pioglitazone&page=3&rank=30 (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Therapies in Combination or Sequentially with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (TKIs) in Chronic Phase Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Patients in CCR (ACTIW) (ACTIW)—Full Text View. 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02767063?cond=cancer%20&intr=pioglitazone&page=4&rank=31 (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Second STOP After Pioglitazone Priming in CML Patients (PIO2STOP)—Full Text View. 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02889003?cond=cancer%20&intr=pioglitazone&page=4&rank=32 (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Combined Antiinflammatory and Angiostatic Therapy in Patients with Hormone-refractory Prostate Cancer (INV342)—Full Text View. 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT00427999?cond=cancer%20&intr=pioglitazone&page=4&rank=33 (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Pioglitazone as Second-Line in Patients with Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer After Treatment With Gemcitabine—Full Text View. 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT00867126?cond=cancer%20&intr=pioglitazone&page=4&rank=37 (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Pioglitazone and Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor in Treating Patients with Relapsed Chronic Myeloid Leukemia—Full Text View. 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02730195?cond=cancer%20&intr=pioglitazone&page=4&rank=38 (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Phase I and Consecutive Phase II, Two-arm, Randomized Multi-center Trial in Patients with Advanced Melanoma—Full Text View. 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT01614301?cond=cancer%20&intr=pioglitazone&page=5&rank=43 (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- ACTOplus Met XR in Treating Patients with Stage I-IV Oral Cavity or Oropharynx Cancer Undergoing Definitive Treatment—Full Text View. 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02917629?cond=cancer%20&intr=pioglitazone&page=5&rank=44 (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Third-line Therapy of Multiple Myeloma a Prospective Phase I/II Trial (MM03). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT01010243?cond=cancer%20&intr=pioglitazone&page=5&rank=46 (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Modulatory Effect of Prodigiosin or Pioglitazone on TIME and the Crosstalk to Immune-Checkpoint Protein(s)—Full Text View. 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06502249?cond=cancer%20&intr=pioglitazone&page=5&rank=48 (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Pioglitazone and Imatinib for CML Patients (ACTIM)—Full Text View. 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02888964?cond=cancer%20&intr=pioglitazone&page=5&rank=50 (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- A Study of Perpetrator Drug Interactions of Enasidenib in AML Patients—Full Text View. 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03720366?cond=cancer%20&intr=pioglitazone&page=6&rank=53&tab=table (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Pioglitazone in Thyroid Cancers—Full Text View. 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT01655719?cond=cancer%20&intr=pioglitazone&rank=1&tab=results (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Incretin-based Drugs and Pancreatic Cancer—Full Text View. 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02475499?cond=cancer%20&intr=pioglitazone&page=6&rank=57 (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Moghareabed, R.; Hemati, S.; Akhavan, A.; Emami, H.; Farghadani, M.; Roayaei, M.; Tavajoh, S.; Feizi, A. Randomized Phase II Clinical Trial of Pioglitazone plus Chemotherapy versus Chemotherapy Alone in Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer. J. Glob. Oncol. 2019, 5, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agulló-Ortuño, M.T.; Pérez, C.; Díaz-García, C.V.; Homet, B.; Agudo-López, A.; Rodríguez Garzotto, A.; Prieto-García, E.; Adeva, J.; Riesco, M.C.; Rodríguez, R.; et al. Abstract 2575: Pharmacodynamic Evaluation of the Combination of Carboplatin and Paclitaxel Associated with Either Pioglitazone or Hydroxyurea, within a Randomized Phase 1 Dose Escalation Clinical Trial in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.H.; Kwon, S.Y.; Kim, J.; Na, C.J.; Choi, S.; Min, J.J.; Bom, H.S.; Kim, Y.C.; Oh, I.J.; Chae, H.J.; et al. A Phase II Clinical Trial to Investigate the Effect of Pioglitazone on 18F-FDG Uptake in Malignant Lesions. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Med. 2015, 5, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamtani, R.; Haynes, K.; Bilker, W.B.; Vaughn, D.J.; Strom, B.L.; Glanz, K.; Lewis, J.D. Association between Longer Therapy with Thiazolidinediones and Risk of Bladder Cancer: A Cohort Study. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2012, 104, 1411–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, A.; Weill, A.; Ricordeau, P.; Fagot, J.P.; Alla, F.; Allemand, H. Pioglitazone and Risk of Bladder Cancer among Diabetic Patients in France: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 1953–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Shi, W.; Fu, S.; Wang, T.; Zhai, S.; Song, Y.; Han, J. Pioglitazone and Bladder Cancer Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 1070–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wu, J.; Mao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Xu, X.; Lin, Y.; Chen, H.; Zheng, X.; Qin, J.; et al. Diabetes Mellitus and Risk of Bladder Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
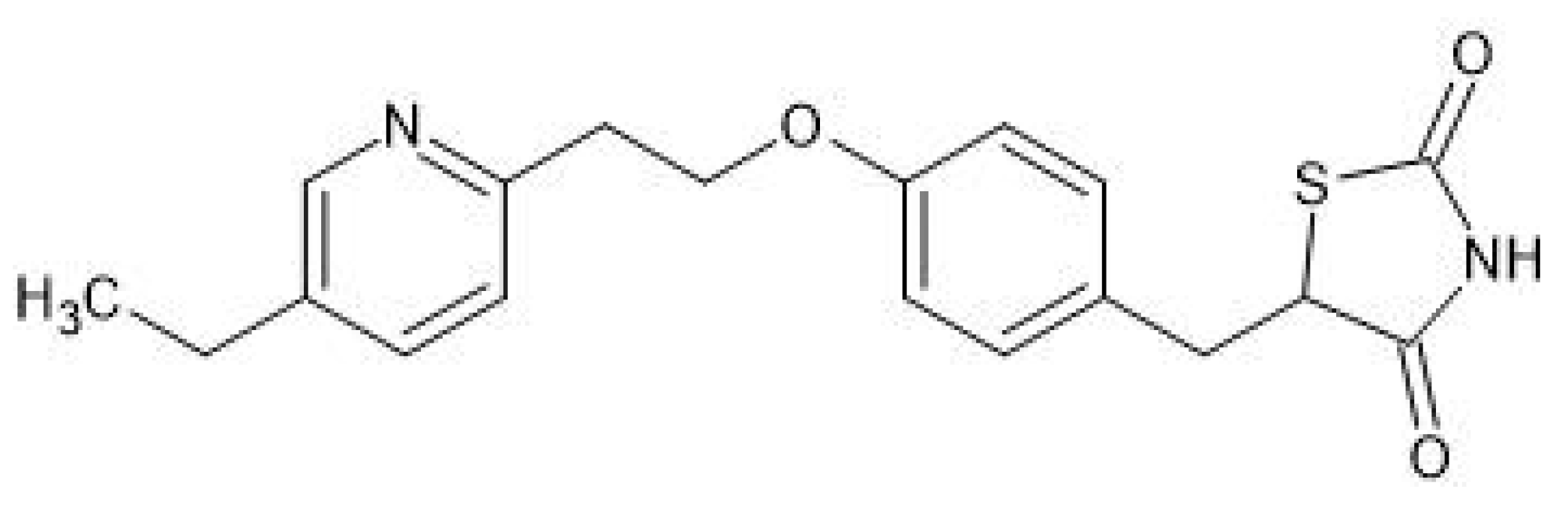


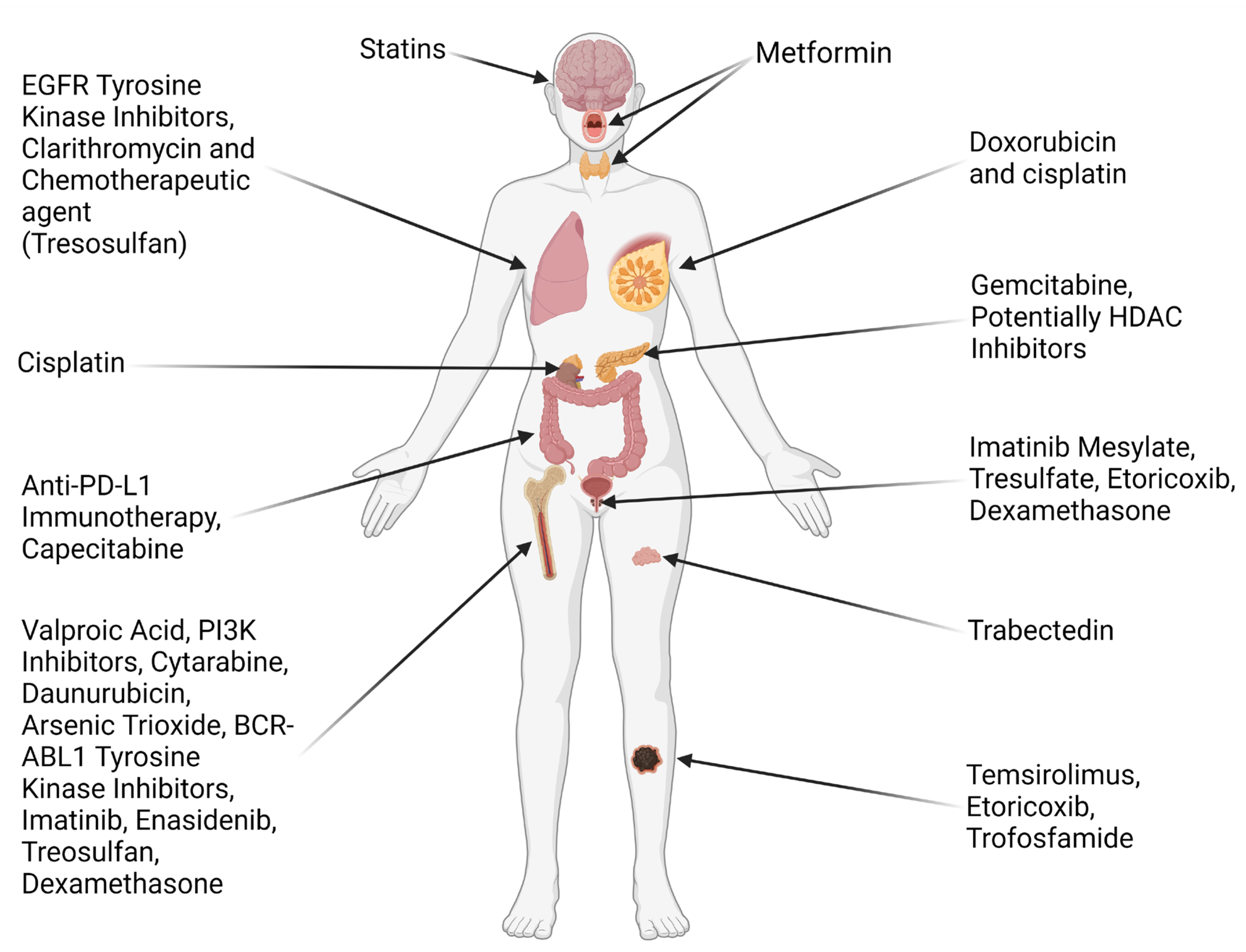
| Process | Mechanism | Cancer Type |
|---|---|---|
| Reduced cell proliferation | Increased expression of excitatory amino acid transporter 2 [44]. | Neuroblastoma |
| Increased activity of p-Akt and p-GSK-3β [44]. | ||
| Redifferentiation of tumor associated adipocytes [44]. | ||
| Inhibited cell growth via mTOR and STAT5 pathway tampering by retinoid X receptor agonists [45]. | Glioma | |
| Inhibited expression of estrogen receptor and aromatase via PGE2 and BRCA1 pathways [46]. | Breast cancer | |
| Inhibition of JAK2/STAT3 pathway [47]. | ||
| Increased expression of p21 and MAPK activity [48]. | ||
| Inhibited CSC proliferation due to decreased STAT5 and HIF-2α levels [49]. | Chronic myeloid leukemia | |
| Downregulated MAPK, RAS, MYC gene expression and phosphorylation of MAPK pathway proteins [50]. | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
| Increased apoptosis | Downregulation of BCL2 and SCD1 [44]. | Leukemia |
| Reduced expression phosphorylation of MEK1 and ERK phosphorylation [51]. | ||
| Downregulation of STAT3 with ERK1/2, NF-κβ and p38MAPK molecules unaffected [49,52]. | ||
| Reduced expression of Survivin [49,52]. | ||
| Increased expression of TRAIL death ligand and apoptosis inducing factor [49,53]. | ||
| Downregulation of BCLXL/BCL2 in a PPAR-γ and caspase-independent manner [51]. | Prostate cancer, squamous cell cancer (SCC) | |
| Induction of apoptosis in a caspase-dependent manner assisted by downregulation of c-FLIP, leading to BCL2 downregulation and instability [54]. | Caki cells | |
| Downregulation of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) [55]. | Colorectal cancer | |
| Upregulation of cyclinB1, CDC2, p21 and alteration of BAX/BCL2 ratio [55]. | ||
| Reduced angiogenesis [44,45,46,56,57,58] | Reduced expression of matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP2), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), COX-2. | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| Inhibition of fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF-2) and urokinase plasminogen activator. | ||
| Apoptosis of endothelial cells. | ||
| Combined downregulation of COX-2 and VEGF when coupled with clofibric acid [45]. | Ovarian cancer | |
| Reduction of bFGF- and VEGF-initiated angiogenesis [59]. | Chick chorioallantoic membrane model | |
| Drug Sensitization | Reduced expression of metallothionein and endorphin connected to S273 phosphorylation [60]. | Pancreatic cancer |
| Enhanced type I Interferon activity due to inhibition of the STAT-3 pathway [58]. | ||
| Increased arsenic trioxide induced tumor toxicity through inhibition of the PI3K/AKT pathway [45]. | Leukemia | |
| Doxorubicin sensitization via modulation of P-glycoprotein [56]. | Osteosarcoma | |
| Reduced resistance to cisplatin [46]. | ||
| Cell Cycle Modification | Increased cisplatin and oxiplatin efficacy. | Thyroid, lung, prostate, breast, kidney, esophageal and urothelial cancer |
| Inhibited EGFR/MDM2 mediated chemoresistance and PPAR-γ degradation [50]. | ||
| Downregulation of cyclin dependent kinase 4 (CDK4). | ||
| Upregulation of CDK inhibitors including p19, p21, p27 and rho-related GTP binding protein. | ||
| Activation of Rb protein [51,60]. | ||
| Downregulation of cyclins D, cyclin E, CDK2, CDK4, proliferating nuclear antigen and retinoblastoma protein [58]. | Breast and colorectal cancer | |
| Induction of G1-arrest through the activation of p21 along with the upregulation of FOXO3a [61]. | Acute promyelotic leukemia (NB4 cells) | |
| Accelerated differentiation | Induced adipogenesis [57]. | Melanoma |
| Immunomodulation | Increased β3 and α5 integrin expression [57]. | Colorectal cancer |
| Reduced PD-L1 levels due to autophagy [62]. | Lung, colorectal cancer | |
| Bioenergetic disruption | Reduced pyruvate oxidation and glutathione levels. | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| ROS-induced stress mediated by HIF-1 and NF-κβ signaling. | ||
| Reduced metastasis and invasiveness | Downregulation of smad family member 3 (SMAD3), PDK1 and MCT-1. | Breast cancer |
| Upregulation of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1). | ||
| Downregulation of NF-κβ, eIF2α, MMP9 and fibronectin [46]. | Lung cancer | |
| Upregulation of CXCR4, CXCR7, E-cadherin [47]. | ||
| Downregulation of TGF-β. | Glioma | |
| Reduced expression and invasiveness of β-cantenin [46]. | Breast cancer | |
| Downregulation of TGFβR1 and SMAD3 associated with epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) [63]. | Non-small cell lung cancer | |
| Increased autophagy | Upregulation of HIF-1 and BNIP3 [51]. | Breast and prostate cancer |
| Activation of PI3K [61]. | Acute promyelotic leukemia (NB4 cells) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vasileiou, M.; Diamantoudis, S.C.; Tsianava, C.; Nguyen, N.P. Therapeutic Potential and Challenges of Pioglitazone in Cancer Treatment. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1925. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15041925
Vasileiou M, Diamantoudis SC, Tsianava C, Nguyen NP. Therapeutic Potential and Challenges of Pioglitazone in Cancer Treatment. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(4):1925. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15041925
Chicago/Turabian StyleVasileiou, Maria, Sotirios Charalampos Diamantoudis, Christina Tsianava, and Nam P. Nguyen. 2025. "Therapeutic Potential and Challenges of Pioglitazone in Cancer Treatment" Applied Sciences 15, no. 4: 1925. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15041925
APA StyleVasileiou, M., Diamantoudis, S. C., Tsianava, C., & Nguyen, N. P. (2025). Therapeutic Potential and Challenges of Pioglitazone in Cancer Treatment. Applied Sciences, 15(4), 1925. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15041925





