A Comprehensive Review of the Influence of Sensitizers on the Detonation Properties of Emulsion Explosives
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The reduction in matrix density through chemical means;
- The introduction of low-bulk-density substances to decrease overall density;
- The incorporation of solid inhomogeneities to promote localized energy release;
- The addition of high-energy explosives, such as 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (TNT), pentrite, nitrocellulose, smokeless powder, complex rocket fuels, hexogen, octogen, and their mixtures.
2. Review of Influence of Sensitizers on Detonation Properties of Emulsion Explosives
2.1. Chemical Density Reduction
2.2. Addition of Substances with Very Low Bulk Density
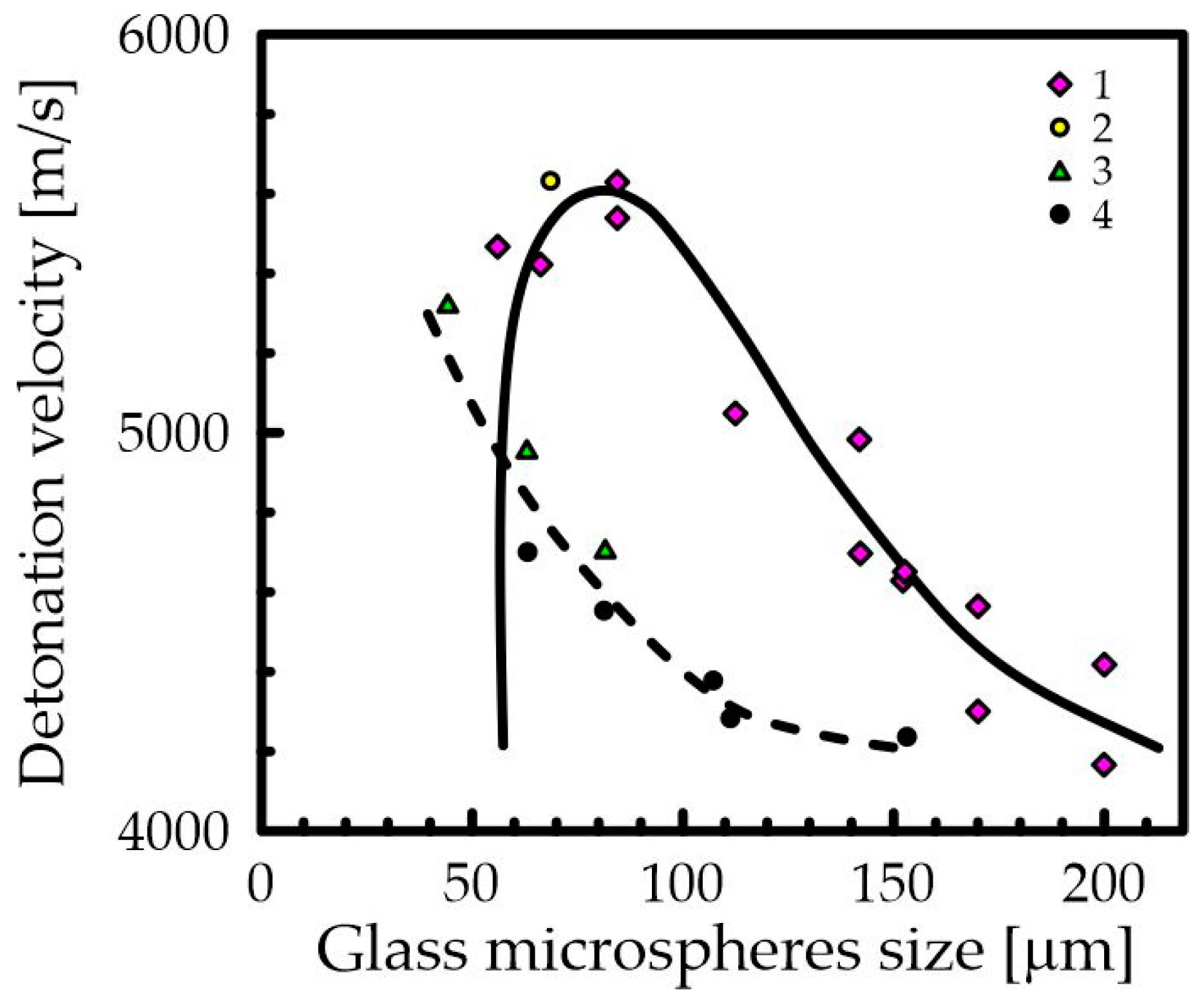
2.3. Introduction of Constant Inhomogeneities
2.4. Sensitization of EE Matrix with Explosives
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Behera, R.; Biswal, T.; Panda, R.B. Recent Progress in Explosives: A Brief Review. In Current Advances in Mechanical Engineering; Acharya, S.K., Mishra, D.P., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering; Springer: Singapore, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maranda, A.; Wachowski, L.; Kukfisz, B.; Markowska, D.; Paszula, J. Valorization of Energetic Materials from Obsolete Military Ammunition Through Life Cycle Assessment (LCA): A Circular Economy Approach to Environmental Impact Reduction. Sustainability 2025, 17, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Włodarczyk, E. Introduction to Explosion Mechanics; Wyd. Naukowe PWN: Warszawa, Poland, 1994; ISBN 83-01-11594-1. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Maranda, A.; Gołąbek, B.; Kasperski, J. Emulsion Explosives; Wyd. Naukowo-Techniczne: Warszawa, Poland, 2008; ISBN 978-83-204-1427-9. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Chaudri, M.; Field, J. The Role of Rapidly Compressed Gas Pockets in the Initiation of Explosives. Proc. R. Soc. A 1974, 340, 113–128. [Google Scholar]
- Bowden, A.D.; Yoffe, F.P. Initiation and Growth of Explosion in Liquids and Solids; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1952; ISBN 978-521-31233-2. [Google Scholar]
- Bowden, A.D.; Yoffe, F.P. Fast Reaction in Solids; Butterwoths Scientific Publications: London, UK, 1958; ISBN -10 1114784273. [Google Scholar]
- Marlow, J.M.; Bush, J.H. Thickened Emulsion Composition for Use a Propellants and Explosives. U.S. Patent 5,936,194, 10 August 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Chrisp, D.J. Formation of Foamed Emulsion-Type Blasting Agents. U.S. Patent 4,008,108, 15 February 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, A.K.; Rout, M.; Singh, D.R.; Jana, S.P. Influence of gassing Agent and Density on Detonation Velocity of Bulk Emulsion Explosives. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2018, 36, 89–94. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10706-017-0308-7 (accessed on 7 January 2025). [CrossRef]
- Kramarczyk, B.; Pytlik, M.; Mertuszka, P.; Jaszcz, K.; Jarosz, T. Novel Sensitizing Agent Formulation for Bulk Emulsion Explosives with Improved Energetic Parameters. Materials 2022, 75, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramarczyk, B.; Suda, K.; Kowalik, P.; Świątek, K.; Jaszcz, K.; Jarosz, T. Emulsion Explosives: A Tutorial Review and Highlight of Recent Progress. Materials 2022, 15, 4952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.F.; Ma, H.H.; Shen, Z.W. Detonation Characteristic of Emulsion Explosives Sensitized by MgH2. Combust. Explos. Shock Waves 2013, 49, 614–619. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1134/S0010508213050134 (accessed on 7 January 2025). [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.F.; Ma, H.H.; Liu, R.; Shen, Z.W. Explosion Power and Pressure Desensitization Resisting Property of Emulsion Explosives Sensitized by MgH2. J. Energetic Mater. 2014, 32, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.F.; Ma, H.H.; Liu, R.; Shen, Z.W. Pressure Desensitization Influential Factors and Mechanism of Magnesium Hydride Sensitized Emulsion Explosives. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2014, 39, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.F.; Wang, Q.; Liu, F.; Ma, H.H.; Shen, Z.W.; Guo, Z.R.; Liu, R. The Effect of Energetic Additive Coated MgH2 on the Power of Emulsion Explosives Sensitized by Glass Microballoons. Cent. Eur. J. Energetic Mater. 2016, 73, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.F.; Yan, S.L.; Ma, H.H.; Shen, Z.W.; Liu, R. A New Type of Functional Chemical Sensitizer MgH2 for Improving Pressure Desensitization Resistance for Emulsion Explosives. Shock Waves 2016, 26, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wu, H.; Yan, Y. Relationship Research between Crystallization Quantity of Emulsion Explosive and Desensitization Degree under Dynamic Pressure. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 393–395, 1389–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluhm, H.F. Ammonium Nitrate Emulsion Blasting Agents and Method of Preparing Same. U.S. Patent 3,447,978, 3 June 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Wade, C. Water-In-Oil Emulssion Explosive Containing Entrapped Gas. U.S. Patent 3,715,247, 3 September 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Persson, P.A. Detonation Behavior Emulsion Explosives. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 1990, 75, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuguang, W. Emulsion Explosives; Metallurgical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 1993; ISBN 75-02-41574-2. [Google Scholar]
- Deribas, A.A.; Medvedev, A.E.; Reshetnyak, A.Y.; Fomin, V.M. Detonation of Emulsion Explosives Containing Hollow Microspheres. Dokl. Phys. 2003, 48, 163–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, D. Contrasting Pattems in Behavior of High Explosives. In Symposium (International) on Combustion; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1967; Volume 77, pp. 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, M.; Lida, M.; Tanaka, K.; Fujiwara, S.; Kusakabe, M.; Shiino, K. Detonation Behavior of Emulsion Explosives Containng Glass Microballoons. In Proceedings of the 8th Symposium (International) on Detonation, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 15–19 July 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Sumiya, F.; Hirosaki, Y.; Kato, Y. Detonability of Emulsion Explosives Precompressed by Dynamie Pressure. Sci. Tech. Energetic Mater. 2004, 65, 88–93. [Google Scholar]
- Sumiya, F.; Hirosaki, Y.; Kato, Y. Influence of Pressure Wave Propagating in Compressed Emulsion Explosives on Detonator. Sci. Tech. Energetic Mater. 2005, 66, 266–273. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, S.H.; Wu, H.; Liu, F. Influence of Sensitizing Method on Crystallization of Emulsion Explosives under Dynamic Pressure. In Proceedings of the International Autum Semina on Propellants, Explosives and Pyrotechnics. Theory and Practice of Energetic Materials, Kunming, China, 22–25 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sil’vestrov, V.V.; Plastinin, A.V. Investigation of Low Detonation Velocity Emulsion Explosives. Combust. Expl. Shock Waves 2009, 45, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Meng, X.R.; Feng, C.T.; Wang, Q.; Wu, S.S.; Ma, H.H.; Shen, Z.W. The Effect of the Hydrogen Containing Material TiH2 on the Detonation Characteristics of Emulssion Explosives. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2017, 42, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsi, K.; Daoush, W.M. Al-TiH2 Composite Particles as Foaming Precursors for Metallic Foams. Scr. Mater. 2015, 705, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajak, D.K.; Kumaraswamidhas, L.A.; Das, S. Investigation and Characterization of Aluminium Alloy Foams with TiH2 as a Foaming Agent. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 1338–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjarholt, G. Expansion Works in Underwater Detonation. In Proceedings of the 6th Symposium (International) on Detonation, San Diego, CA, USA, 24–27 August 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Maranda, A.; Włodarczyk, E.; Serafmowicz, J. Analysis of Detonation Parameters of Emulsion Explosives Sensitized with Glass Microspheres Enveloping Air. Biul. WAT 1986, 35, 25–38. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Anshits, A.G.; Anshits, N.N.; Deribas, A.A.; Kasatkina, N.S.; Plastinin, A.V.; Reshetnyak, A.Y.; Sil’vestrov, V.V. Detonation Velocity of Emulsion Explosives Containing Cenospheres. Combust. Expl. Shock Waves 2005, 47, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Cheng, Y.-F.; Tao, C.; Su, H.; Gong, Y.; Chen, Y.; Shen, Z.-W. Effects of Content and Particle Size of Cenospheres on the Detonation Characteristics of Emulsion Explosive. J. Energetic Mater. 2021, 39, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhri, M.M.; Almgren, L.A.; Persson, A. Detonation Behaviour of a „Water-In-Oil” Type Emulsion Explosives Containing Glass Microballoons of Selcted Sizes. In Proceedings of the 10th Symposium (International) on Detonation, Boston, MA, USA, 12–16 July 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Vattipalli, M.R.; Ghosh, P.K. Elastomeric Polymers as Potent Additives for Emulsion Explosives. In Proceedings of the 27th International Annual Conference of ICT. Energetic Materials-Technology, Manufacturing and Processing, Karlsruhe, Germany, 25–28 June 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Hirosaki, Y.; Murata, K.; Kato, Y.; Itoh, S. Detonation Behavior of Emulsion Explosives. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Annual Conference of ICT. Ignition, Combustion and Detonation, Karsluhe, Germany, 3–6 July 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hirosaki, Y.; Murata, K.; Kato, Y.; Itoh, S. Detonation Characteristics of Emulsion Explosives as Functions of Void Size and Volume. In Proceedings of the 12th Symposium (International) on Detonation, San Diego, CA, USA, 1 July 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Mendes, R.; Ribeiro, J.; Plaksin, I.; Campos, J.; Tavaras, B. Differences between the Detonation Behavior of Emulsion Explosives Sensitized with Glass or with Polymeric Microballoons. J. Phys. Conf. Series 2014, 500, 052030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarczyk, E.; Maranda, A.; Paszula, J.; Papliński, A. Studies of Effect of Aluminium Powder on Selected Parameters of Emulsion Explosives Sensitized with Microballoons. Chemik 2016, 70, 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- Bordzilovski, S.A.; Karakhanov, S.M.; Plastinin, A.V.; Rafeichik, S.I.; Yunoshev, A.S. Detonation Temperature of Emulsion Explosive with a Polymer Sentizier. Combust. Expl. Shock Waves 2017, 53, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunoshev, A.S.; Plastinin, A.V.; Rafeichik, S.I. Detonation Velocity of an Emulsion Explosive Sensitized with Polymer Microballoons. Combust. Expl. Shock Waves 2017, 53, 738–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunoshev, A.S.; Bordzilovski, S.A.; Voronin, M.S.; Karakhanov, S.M.; Makarov, S.N.; Plastinin, A.V. Detonation Pressure of an Emulsion Explosive Sensitized by Polymer Microballoons. Combust. Expl. Shock Waves 2019, 55, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurbangalina, R.K.H. Dependence of the Critical Diameter of Liquid Explosives on the Powder Content. Prik. Mekh. Tekh. Fiz. 1969, 4, 133–138. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Mullay, J. Solid Sensitizer for Water-In-Oil Emulsion Explosives. U.S. Patent 4,453,989, 12 June 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Tomic, E.A. Emulsion Type Explosives Composition Containing Ammonium Stearate or Alkali Metal Stearate. U.S. Patent 3,770,522, 6 November 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Machacek, O.; Eck, G.R. Waste Propellants and Smokeless Powders as Ingredients in Commercial Watergel Explosives. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Annual Conference of ICT, Waste Management of Energetic Materials and Polymers, Karlsruhe, Germany, 30 June–3 July 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Rosa, P.C.; Walter, B.G.; Machacek, O. Solid Sensitizer for Beneficial of Containing Wastes. U.S. Patent 5,612,507, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Munson, W.O. Demilitarization of Large Rocket Motors and Propellant Utilization. In Application of Demilitarized Gun and Rocket Propellants in Commercial Explosives; Machacek, O., Ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dortrecht, The Netherlands; Boston, MA, USA; London, UK, 1999; ISBN 0-793-6697-2. [Google Scholar]
- Matseevich, B.V.; Mokhova, N.V.; Malygin, N.K. Used of Converted High Energy Value Explosive Materials as Industrial Energetic Materias. In Application of Demilitarized Gun and Rocket Propellants in Commercial Explosives; Machacek, O., Ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dortrecht, The Netherlands; Boston, MA, USA; London, UK, 1999; ISBN 0-793-6697-2. [Google Scholar]
- Glinskiy, V.P.; Mardasov, O.F.; Mochova, M.V.; Shalygin, N.K.; Obrazcova, B.F. Creation of Safe on Manipulation Industrial Explosives and Products for Mining Industry on the Basis of Gunpowder. In Application of Demilitarized Gun and Rocket Propellants in Commercial Explosives; Machacek, O., Ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dortrecht, The Netherlands; Boston, MA, USA; London, UK, 1999; ISBN 0-793-6697-2. [Google Scholar]
- Nemec, O.; Novotny, M.; Yungova, M.; Zeman, S. Preliminary Verification of Fortification of W/O Type Emulsion with Demilitarized Explosives Based on TNT. In Proceedings of the 14th Seminar on New Tends in Research of Energetic Materials, Part II, Pardubice, Czech Republic, 13–15 April 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Nemec, O.; Yungova, M.; Zeman, S. Modification of W/O Emulsions by Demilitarized Composition B. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2013, 38, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renick, J.D.; Persson, P.A.; Sanchez, J.A. Detonation Properties of Mixtures of HMX and Emulsion Explosives. In Proceedings of the 9th Symposium (International) on Detonation, Portland, OR, USA, 28 August–1 September 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Lipińska, K.; Lipiński, M.; Maranda, A. Demilitarized Double Base Propellants as Ingredients of Commercial Explosives. Cent. Eur. J. Energetic Mater. 2005, 2, 69–78. [Google Scholar]
- Biegańska, J. Using Nitrocellulose Powder in Emulsion Explosives. Combust. Expl. Shock Waves 2011, 47, 366–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunzel, M.; Nemec, U.; Matys, R. Erythritol Tetranitrate as a Sensitizer in Ammonium Nitratebased Explosives. Cent. Eur. J. Energetic Mater. 2013, 70, 351–358. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Ma, H.; Shen, Z.H. Effects of RDX Powders on Detonation Characteristics of Emulsion Explosives. J. Energetic Mater. 2019, 37, 459–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.M.; Zhao, H.R. Historical Perspective. Perspectives in the Stability of Emulsion Explosives. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 307, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.M.; Xu, M.X.; Hao, X.; Zhao, H.R. Peculiarities of Rheological Behavior of Highly Concentrated Water-In-Oil Emulsion: The Role of Droplet Size, Surfactant, Oil and Ammonium Nitrate Content. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 272, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gołąbek, B.; Kasperski, J. The Influence of the Composition and Structure of Emulsion Explosives on Their Detonation Parameters. Ph.D. Thesis, Central Institute of Mining, Katowice, Poland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hypex Bio. Sustainable Mining Explosive. Available online: https://www.swedishmininginnovation.se/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/HypexBio.pdf (accessed on 28 January 2025).
- Araos, M. Improved Explosive Composition. Patent WO 2013/0132272, 31 January 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Araos, M.; Onederra, I. Detonation Characteristics of Alternative Mining Explosives Based on Hydrogen Peroxide as the Oxidizing Agent. In Proceedings of the 7th EFEE World Conference on Explosives and Blasting, Moscow, Russia, 15–17 September 2013; pp. 182–188. [Google Scholar]
- Araos, M.; Onederra, I. Development of a Novel Mining Explosive Formulation to Eliminate Nitrogen Oxide Fumes. Min. Technol. 2015, 124, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araos, M.; Onederra, I. Detonation Characteristics of a NOx-Free Mining Explosive Based on a Sensitized Mixture of Low-Concentration Hydrogen Peroxide and Fuel. Cent. Eur. J. Energetic Mater. 2017, 14, 759–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

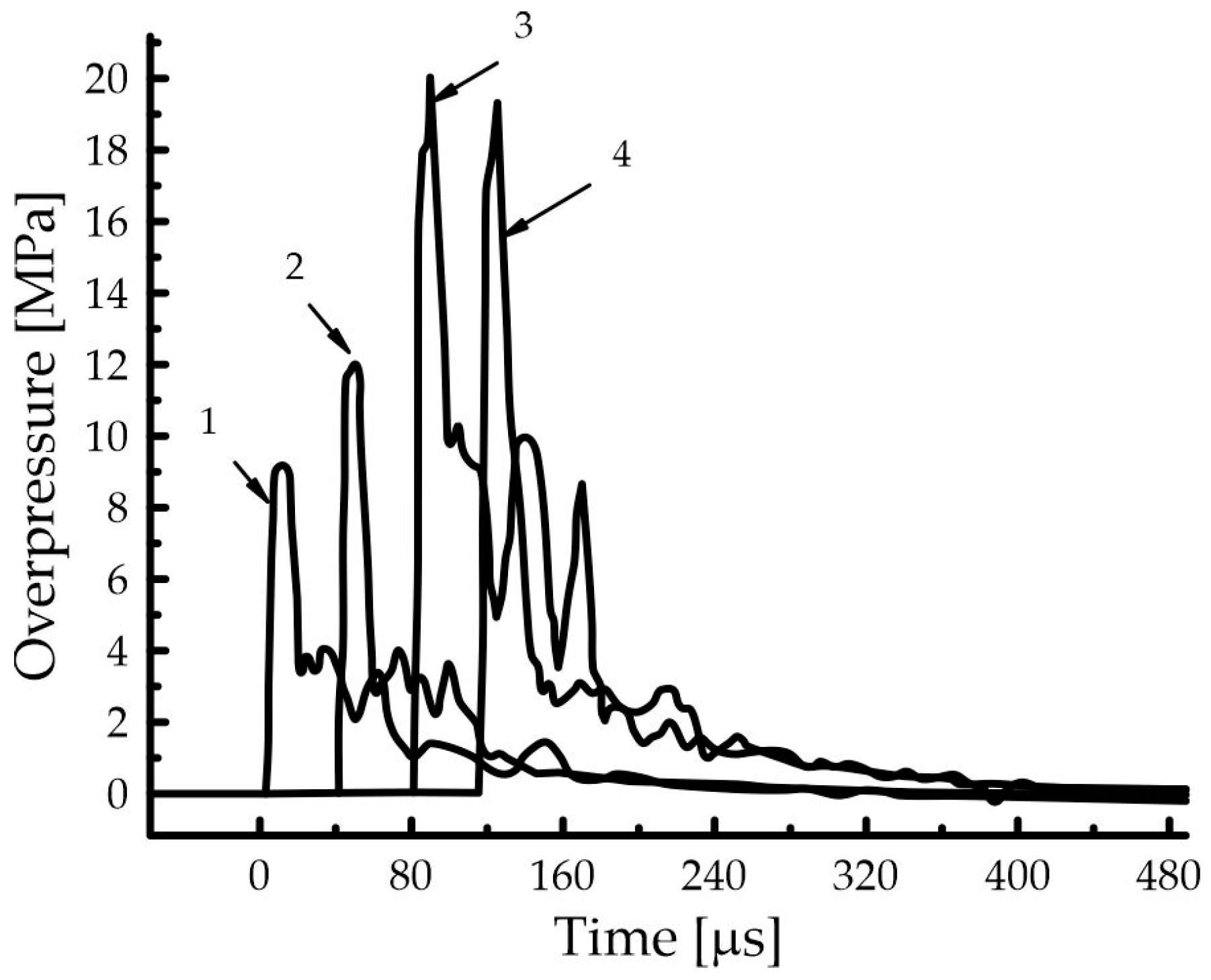
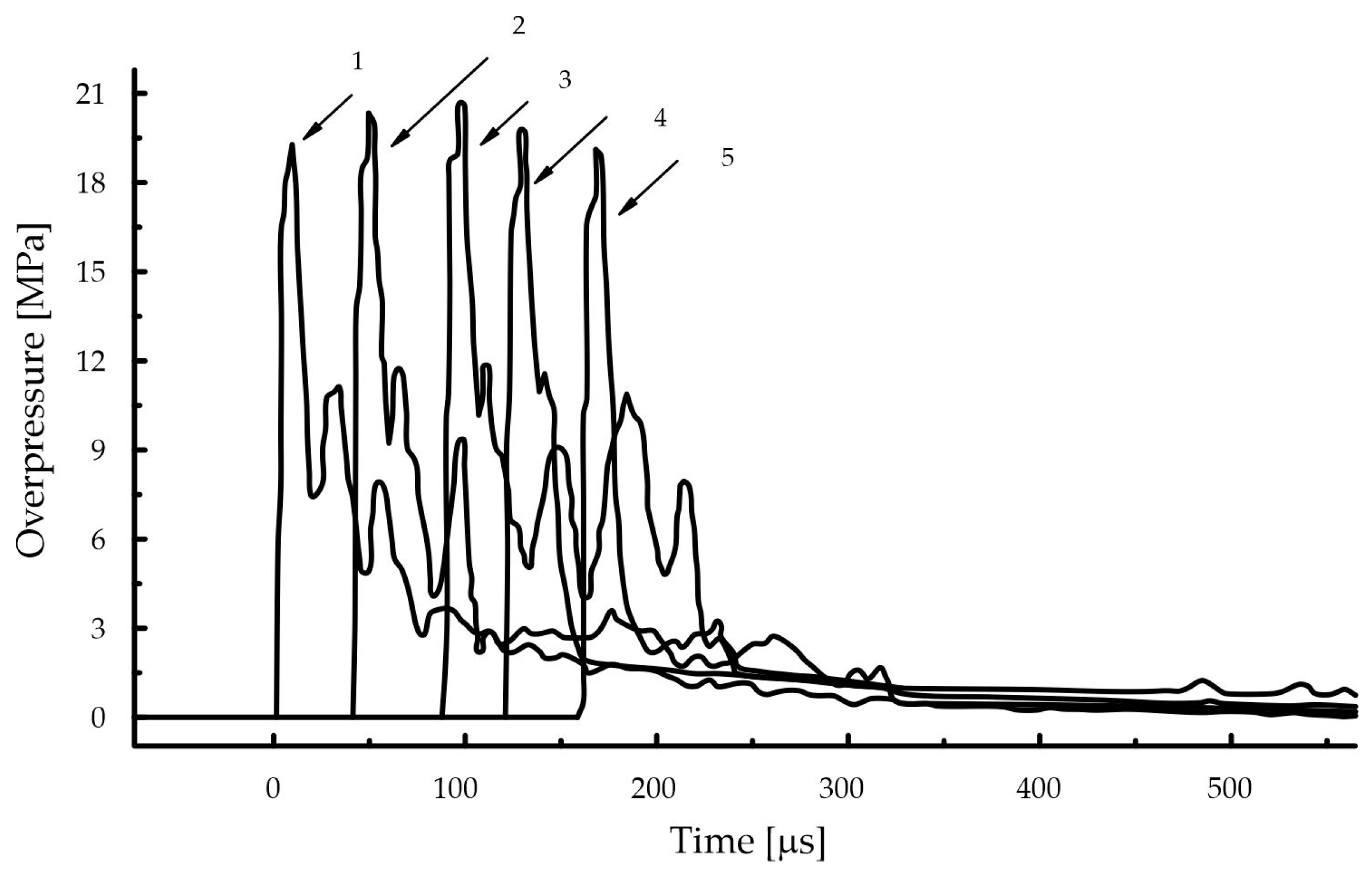
| Component | Sensitizer | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| EE | BK-1 | BK-2 | |
| Component Content [wt. %] | |||
| Ammonium nitrate | - | 30.0 | 47.1 |
| Water | 95.45 | 61.6 | 41.0 |
| Sodium perchlorate | - | 4.0 | 8.0 |
| Sodium nitrite | 4.50 | 3.0 | 3.3 |
| pH modifier | 0.05 | 1.5 | 0.7 |
| Sensitizer | Detonation Velocity [m/s] | Peak Overpressure 1 [kPa] | Impulse ABV 1 [Pa∙s] | Explosive Gas Content [kg/dm3] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOx | CO | ||||
| EE | 4233 | 123.73 | 57.20 | 0.55 | 4.11 |
| BK-1 | 4647 | 127.13 | 57.53 | 0.33 | 2.51 |
| BK-2 | 5033 | 131.20 | 58.60 | 0.31 | 3.45 |
| Component | Sensitizer | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GMs | GMs/Al | MgH2 | NaNO2 | |
| [wt.%] | ||||
| Matrix | 96.0 | 92.0 | 98.0 | 99.8 |
| GMs | 4.0 | 4.0 | - | - |
| Aluminum dust | - | 4.0 | - | - |
| MgH2 | - | - | 2 | - |
| NaNO2 | - | - | - | 0.2 |
| Parameter | ||||
| Density [g/cm3] | 1.21 | 1.24 | 1.29 | 1.24 |
| Underwater test | 10.89 | 10.72 | 13.12 | - |
| maximum overpressure [MPa] | ||||
| Energy [kJ/kg] | 2871 | 3187 | 3762 | - |
| Detonation energy [kJ/kg] | ||||
| Theoretical | 3297 | 3684 | 3530 | 3297 |
| Experimental | 2728 | 3028 | 3574 | 2835 |
| Detonation velocity [m/s] | 4434 | 4389 | 5552 | - |
| Brisance [mm] | 16.1 | 16.2 | 19.1 | 16.85 |
| Sensitizer | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GMs | NaNO2 | MgH2 | ||
| Component | [wt.%] | |||
| Matrix | 96.0 | 99.8 | 98.0 | 99.0 |
| GMs | 4.0 | - | - | - |
| NaNO2 | - | 0.2 | - | - |
| MgH2 | - | - | 2.0 | 1.0 |
| Distance [mm] | Sensitization degree [%] | |||
| 25 | 100 | 88.12 | 38.97 | 38.97 |
| 40 | 86.41 | 84.47 | 18.89 | 18.89 |
| 50 | 79.82 | 71.63 | 12.11 | 12.11 |
| 60 | 73.67 | 53.47 | 10.45 | 10.45 |
| 75 | 63.34 | 15.59 | 11.76 | 11.76 |
| GMs Size [μm] | GMs Content [%] | Density [g/cm3] | Detonation Velocity [m/s] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 153 | 5.359 | 0.909 | 3891 |
| 3.874 | 1.003 | 4218 | |
| 2.135 | 1.100 | 4214 | |
| 1.724 | 1.210 | 3754 | |
| 108 | 8.985 | 0.900 | 3837 |
| 6.645 | 0.998 | 4165 | |
| 4.586 | 1.103 | 4374 | |
| 3.014 | 1.202 | 4120 | |
| 82 | 9.916 | 0.895 | 3779 |
| 8.289 | 0.992 | 4203 | |
| 5.870 | 1.097 | 4551 | |
| 3.876 | 1.205 | 4615 | |
| 64 | 11.972 | 0.891 | 3781 |
| 9.030 | 0.999 | 4244 | |
| 6.544 | 1.112 | 4695 | |
| 4.321 | 1.204 | 4711 |
| No | Component [%] | Maximum Overpressure [MPa] | Energy [MJ/kg] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Matrix | GM | TiH2 | SW * | GB ** | Total | ||
| 1 | 95 | 4 | 1 | 19.01 | 0.658 | 1.63 | 2.69 |
| 2 | 94 | 4 | 2 | 20.58 | 0.712 | 1.68 | 2.83 |
| 3 | 92 | 4 | 4 | 20.72 | 0.695 | 1.66 | 2.79 |
| 4 | 90 | 4 | 6 | 19.92 | 0.681 | 1.64 | 2.74 |
| 5 | 88 | 4 | 8 | 19.46 | 0.679 | 1.65 | 2.75 |
| 6 | 96 | 4 | - | 21.77 | 0.704 | 1.50 | 2.58 |
| 7 | 94 | 4 | 2 *** | 19.16 | 0.665 | 1.58 | 2.63 |
| No | Component [%] | Density [g/cm3] | Detonation Velocity [m/s] | Brisance [mm] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Matrix | GM | TiH2 | ||||
| 1 | 96 | 4 | - | 1.18 | 4534 | 16.1 |
| 2 | 94 | 4 | 2 | 1.11 | 2659 | 23.8 |
| Content [%] | Density [g/cm3] | Brisance [mm] | Detonation Velocity [m/s] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSs | GMs | |||
| 2 | - | 1.24 | 9.9 | ND |
| 4 | - | 1.21 | 10.7 | ND |
| 6 | - | 1.18 | 13.0 | 3027 |
| 8 | - | 1.17 | 13.3 | 3367 |
| 10 | - | 1.16 | 13.4 | 4138 |
| 12 | - | 1.15 | 14.7 | 4616 |
| 14 | - | 1.13 | 14.4 | 4137 |
| 16 | - | 1.11 | 13.9 | 4053 |
| - | 2 | 1.20 | 18.7 | 3653 |
| - | 3 | 1.18 | 19.7 | 4950 |
| - | 4 | 1.12 | 20.6 | 5176 |
| - | 5 | 1.10 | 20.2 | 4789 |
| Content [%] | Grain Size [μm] | Density [g/cm3] | Brisance [mm] | Detonation Velocity [m/s] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSs | GMs | |||||
| 12 | - | 26 | - | 1.23 | 11.2 | ND |
| 12 | - | 58 | - | 1.15 | 14.7 | 4616 |
| 12 | - | 83 | - | 1.18 | 18.3 | 4970 |
| 12 | - | 142 | - | 1.20 | 13.8 | 3862 |
| - | 4 | - | 18 | 1.16 | 4.8 | ND |
| - | 4 | - | 35 | 1.14 | 14.5 | 4541 |
| - | 4 | - | 57 | 1.12 | 20.6 | 5176 |
| - | 4 | - | 102 | 1.09 | 14.7 | 4563 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maranda, A.; Markowska, D.; Kukfisz, B.; Jakubczak, W. A Comprehensive Review of the Influence of Sensitizers on the Detonation Properties of Emulsion Explosives. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2417. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15052417
Maranda A, Markowska D, Kukfisz B, Jakubczak W. A Comprehensive Review of the Influence of Sensitizers on the Detonation Properties of Emulsion Explosives. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(5):2417. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15052417
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaranda, Andrzej, Dorota Markowska, Bożena Kukfisz, and Weronika Jakubczak. 2025. "A Comprehensive Review of the Influence of Sensitizers on the Detonation Properties of Emulsion Explosives" Applied Sciences 15, no. 5: 2417. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15052417
APA StyleMaranda, A., Markowska, D., Kukfisz, B., & Jakubczak, W. (2025). A Comprehensive Review of the Influence of Sensitizers on the Detonation Properties of Emulsion Explosives. Applied Sciences, 15(5), 2417. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15052417








