Redefining Archaeological Research: Digital Tools, Challenges, and Integration in Advancing Methods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Traditional Methods vs. Digital Tools
2.1. Traditional Data Acquisition Methods in Archaeology
2.2. Advantages of Digital Tools in Data Acquisition
3. Types of Digital Tools
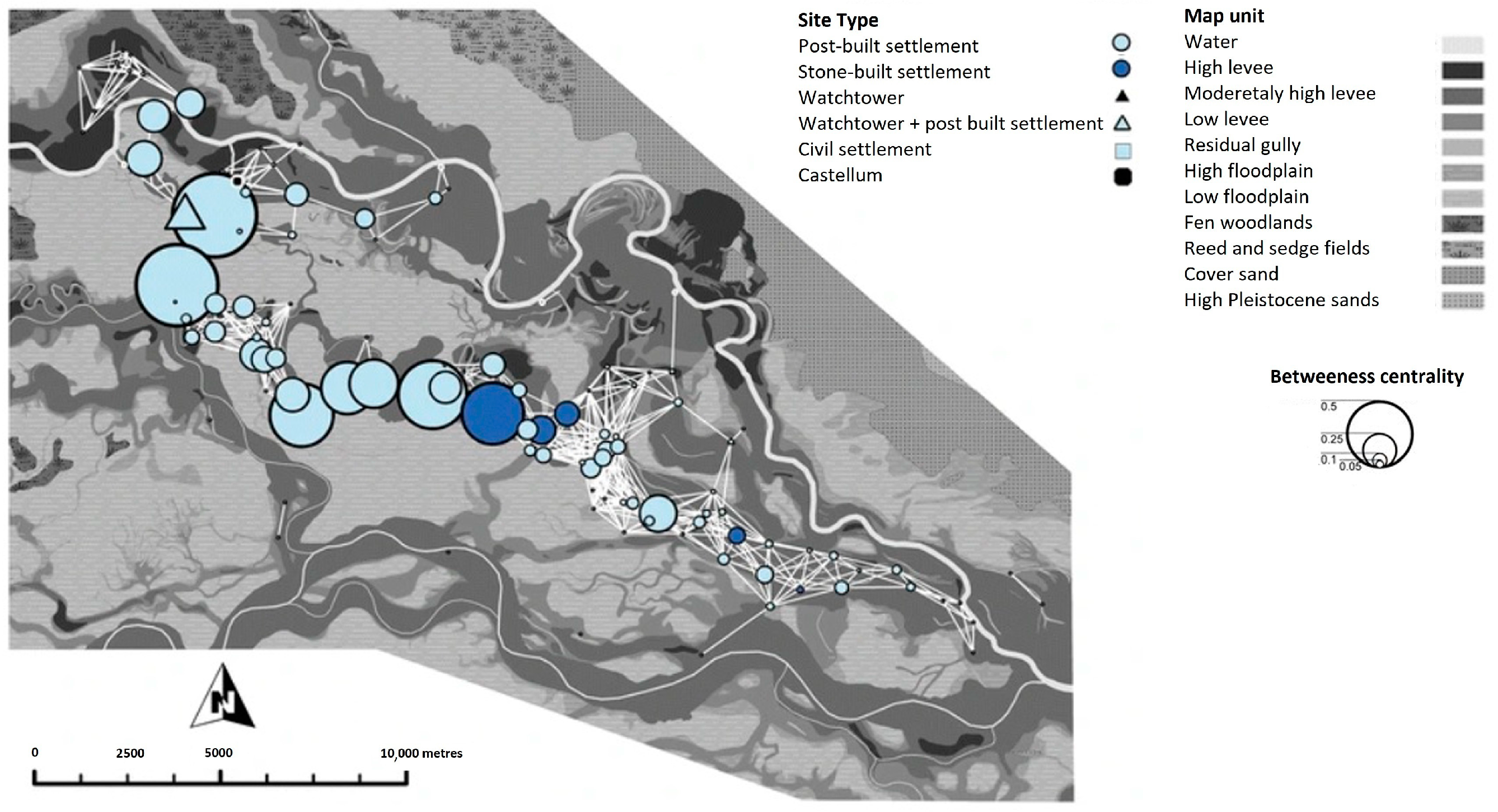
3.1. Geographic Information Systems (GISs)
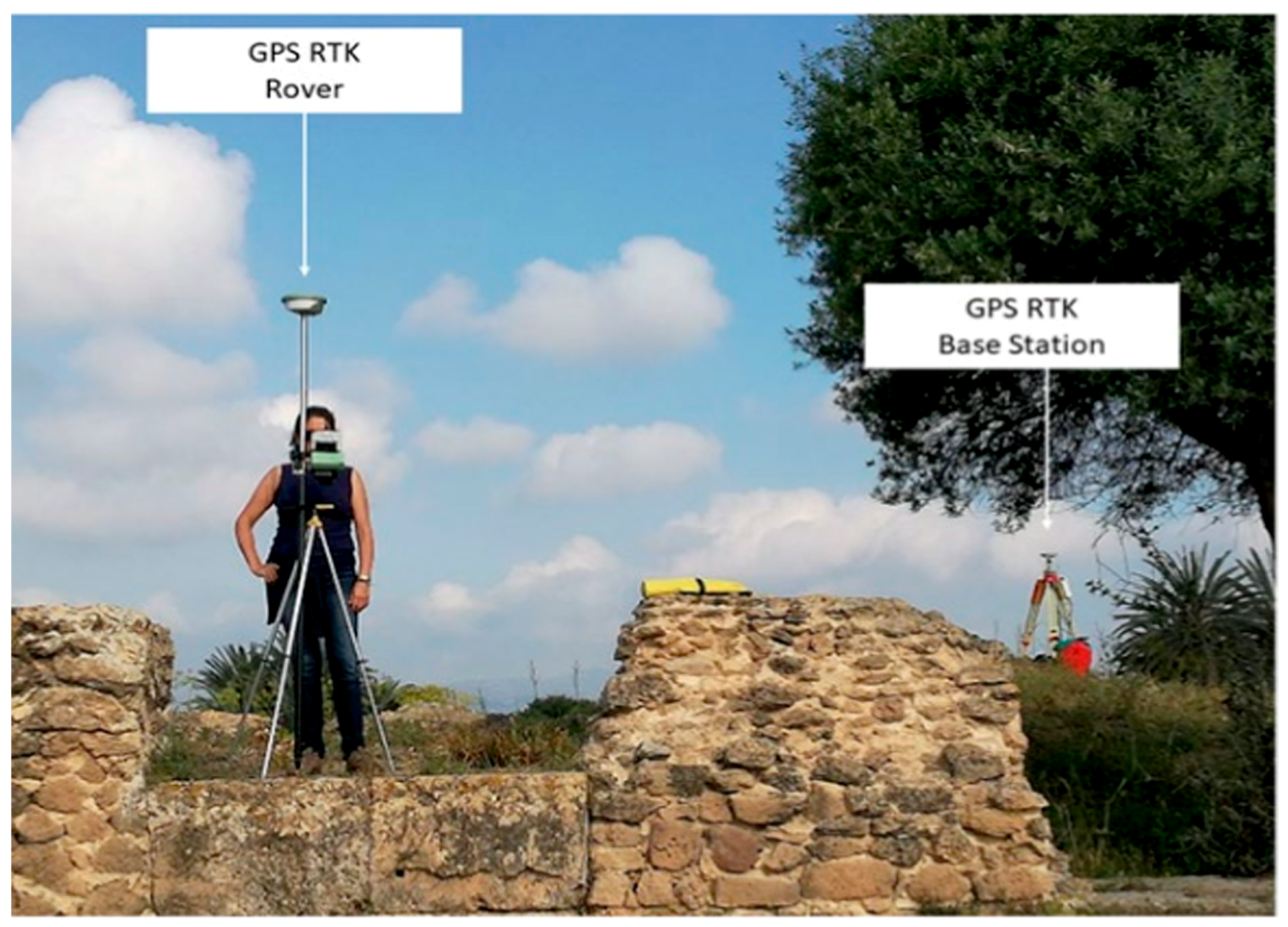
3.2. Global Positioning Systems (GPSs)
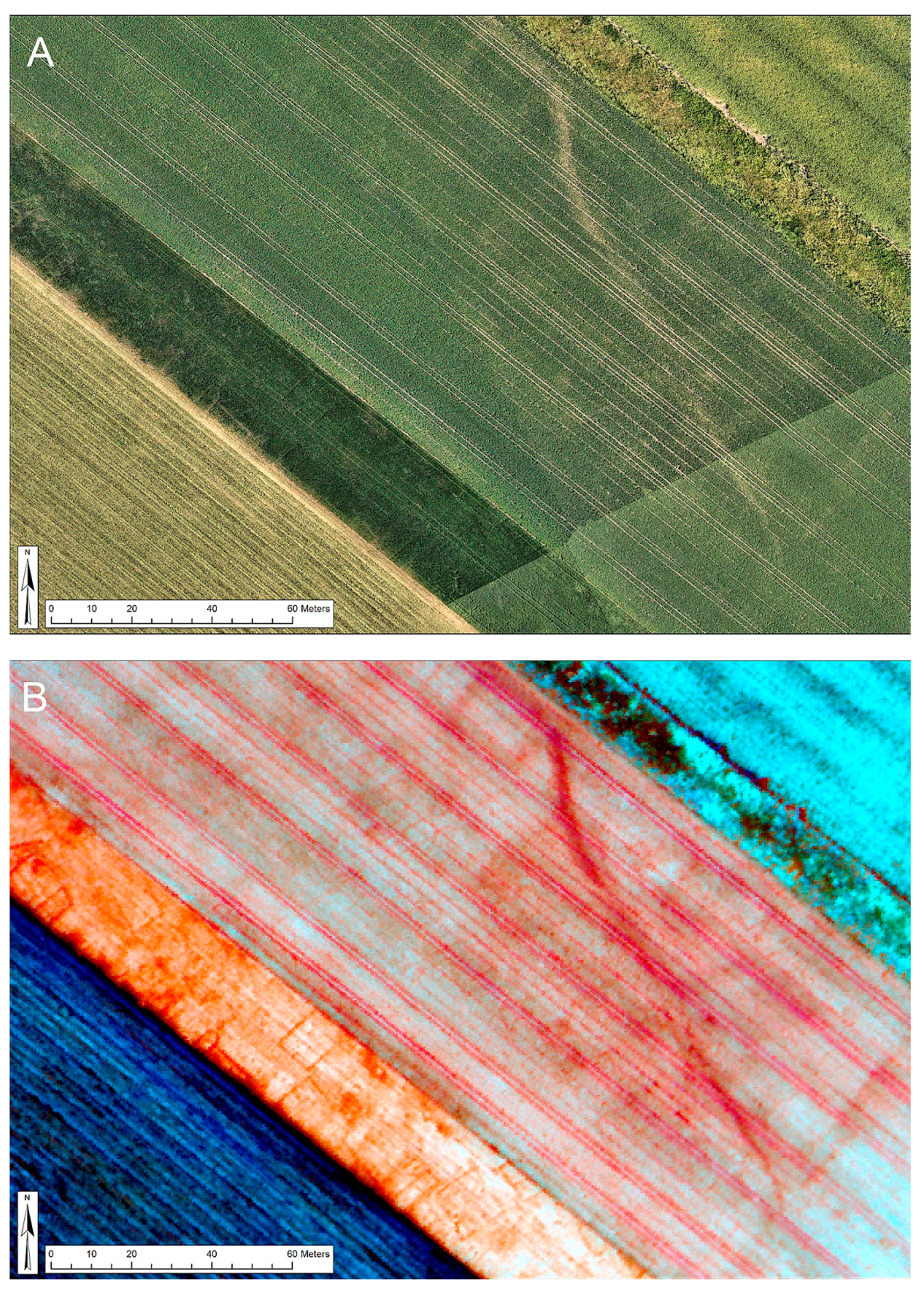
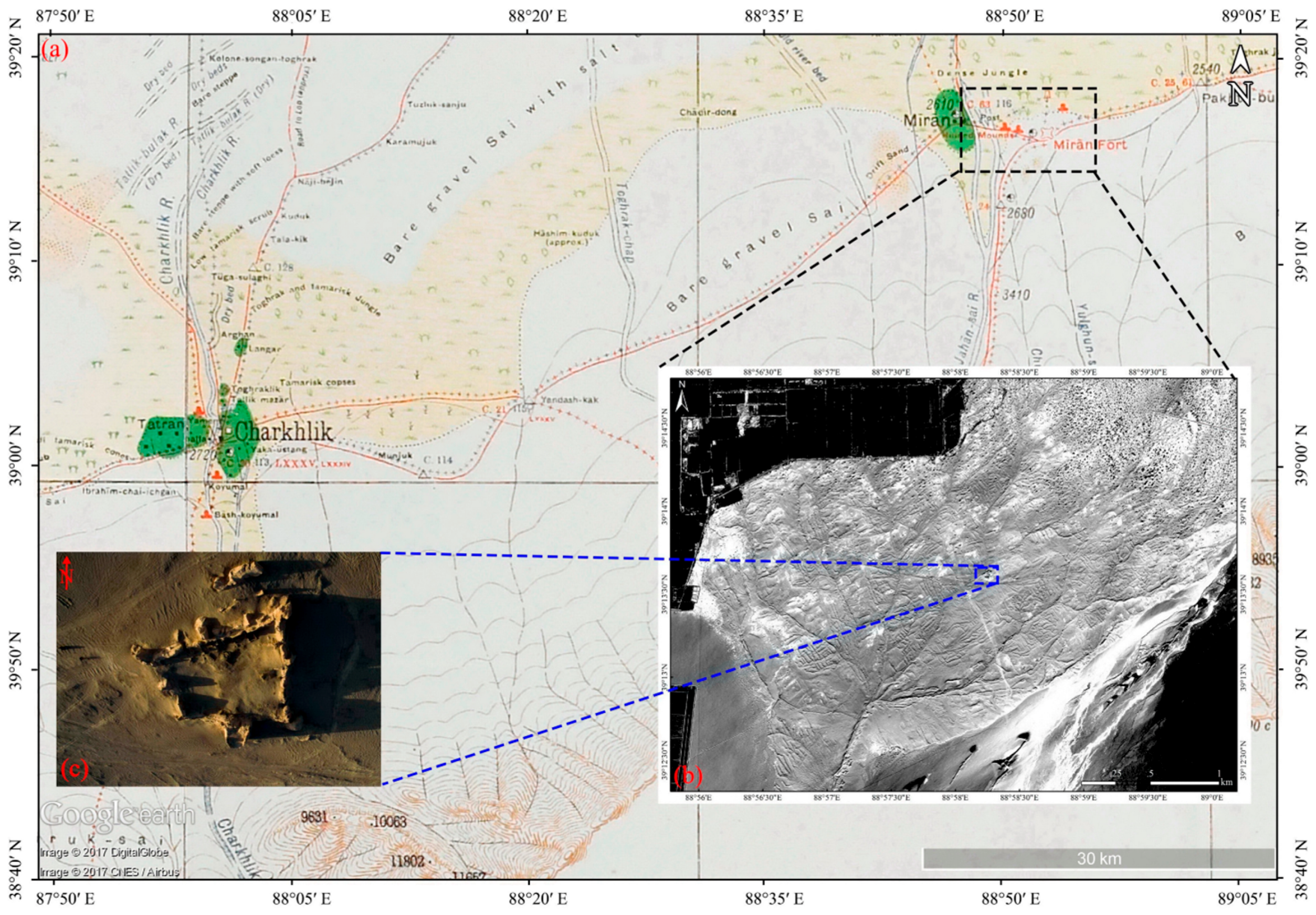
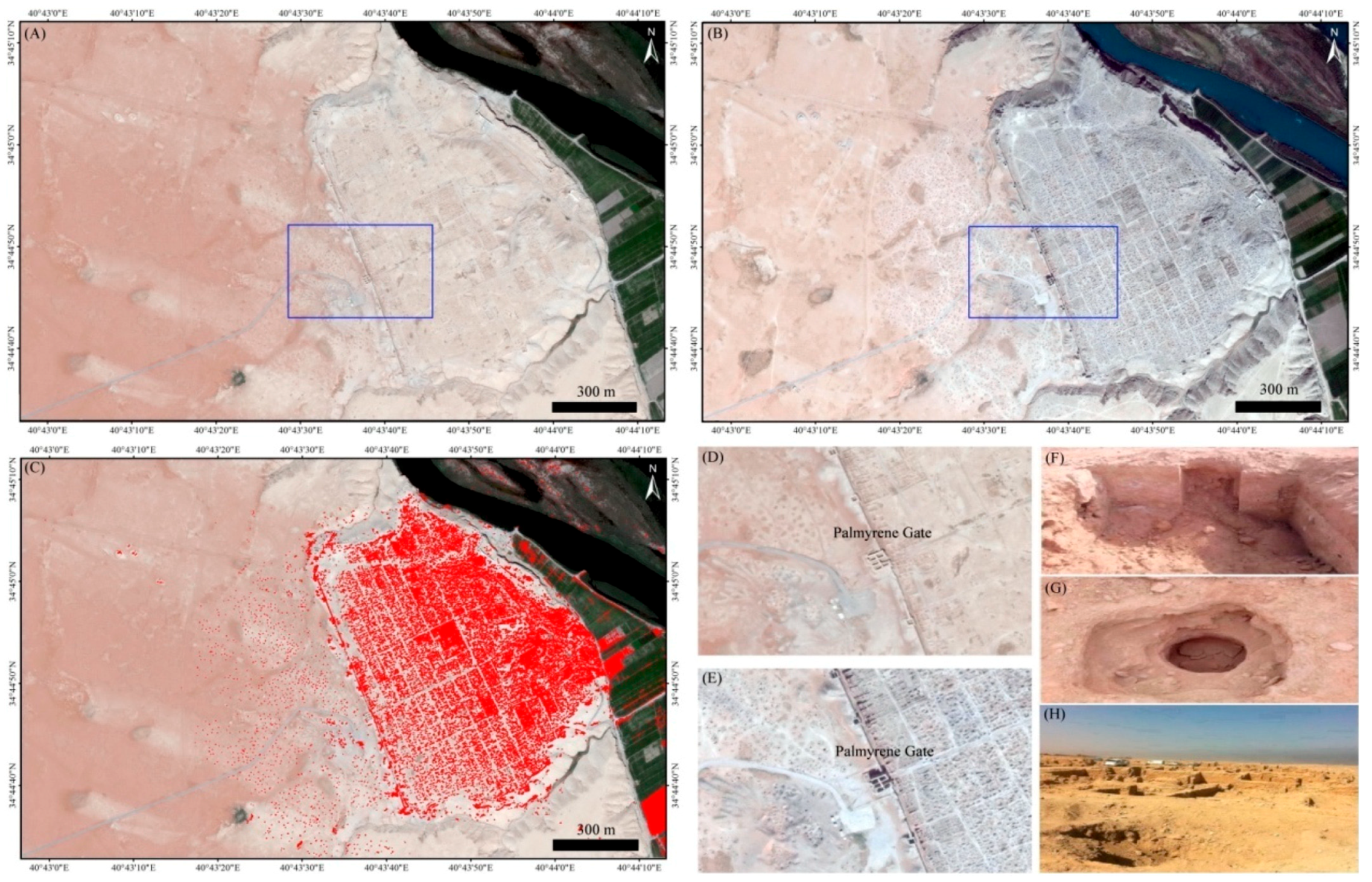
3.3. Remote Sensing Technologies
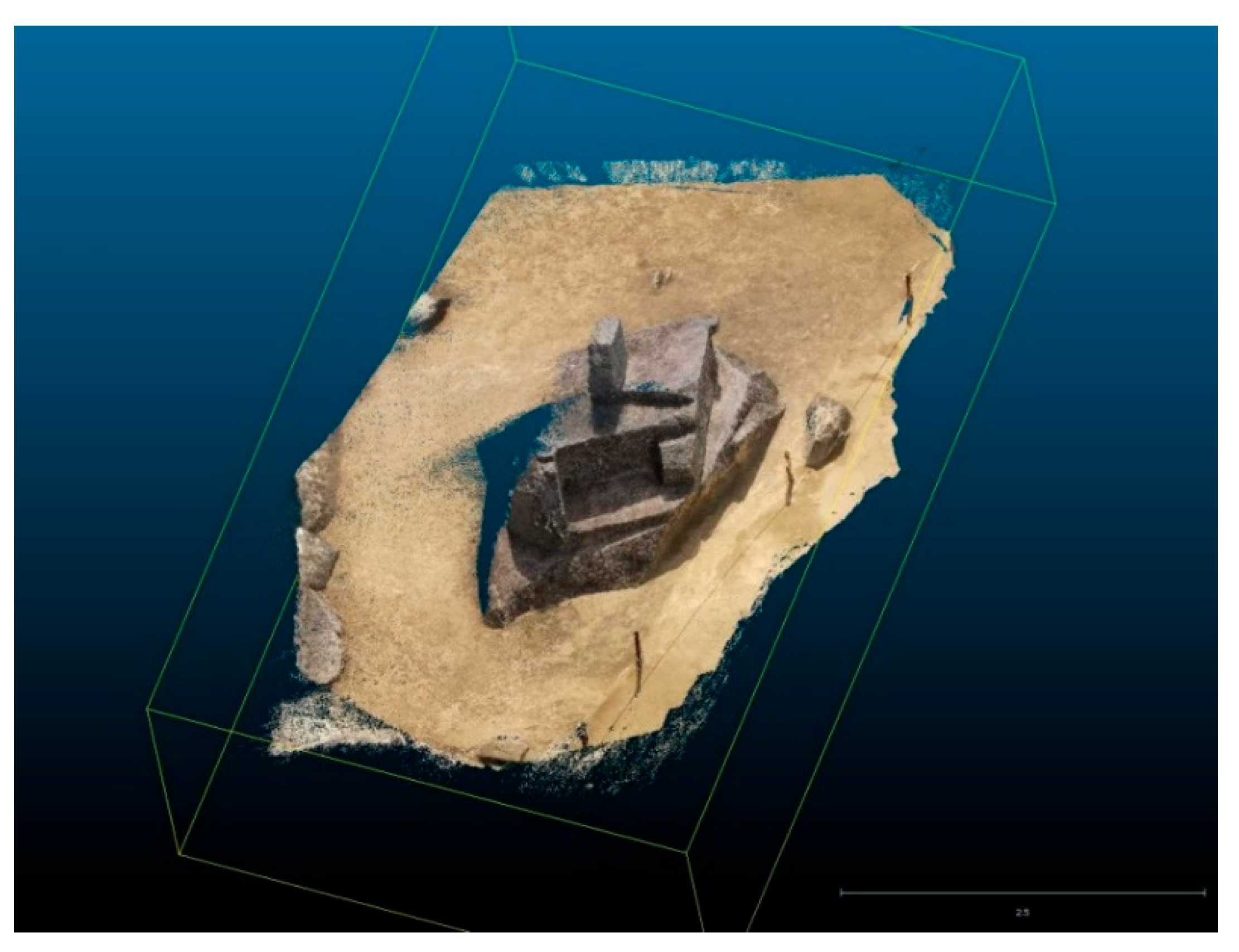
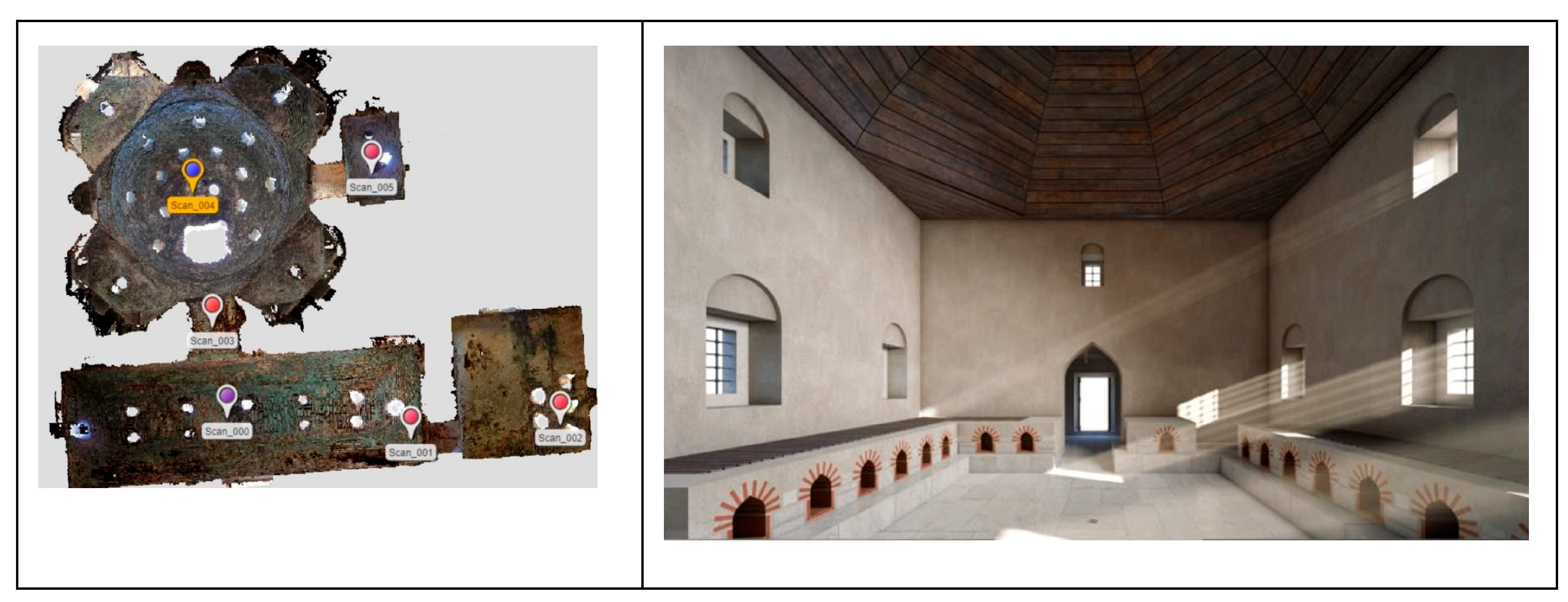
3.4. Three-Dimensional Scanning and Photogrammetry
3.5. Drones and Aerial Photography
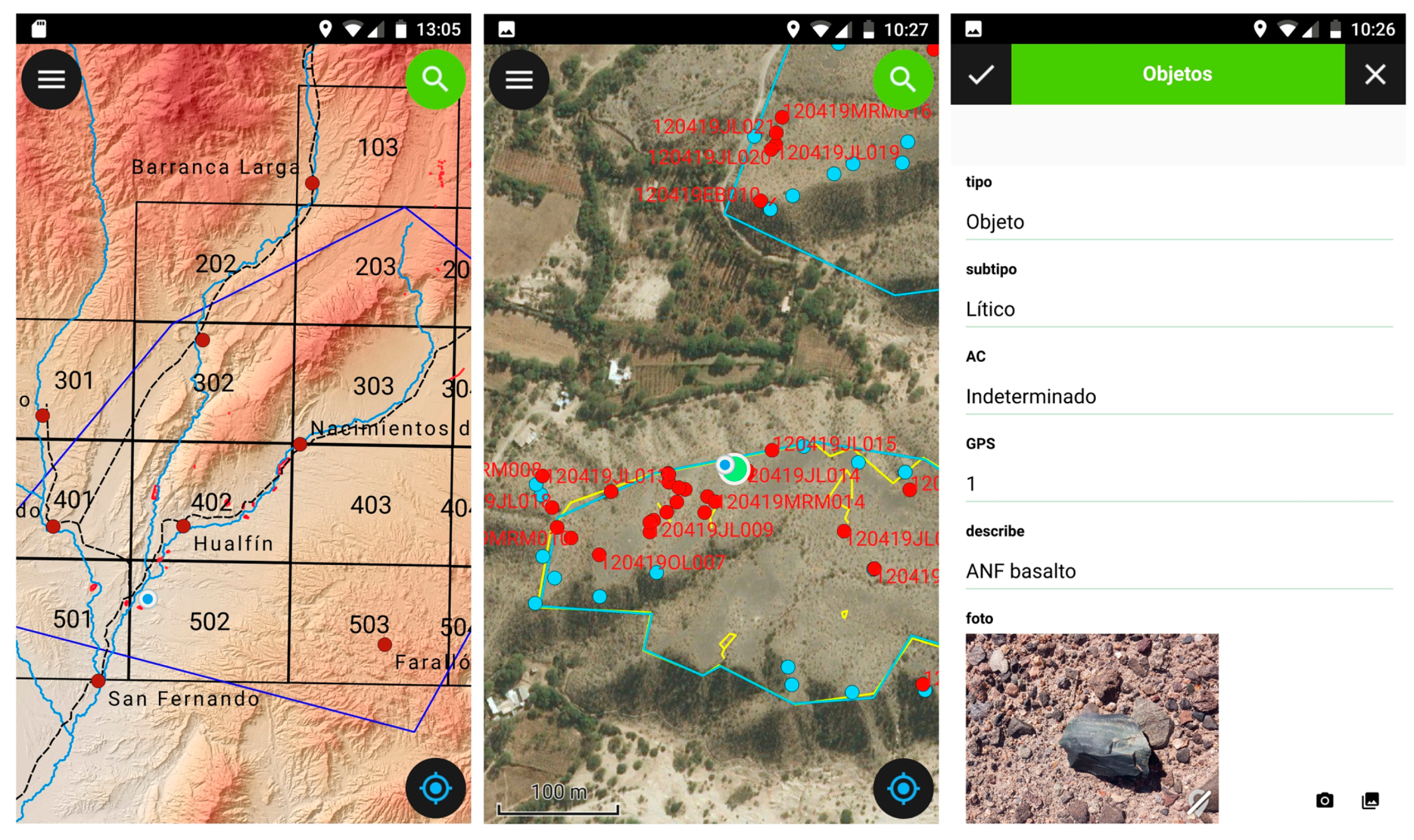
3.6. Mobile Applications and Digital Recording Systems
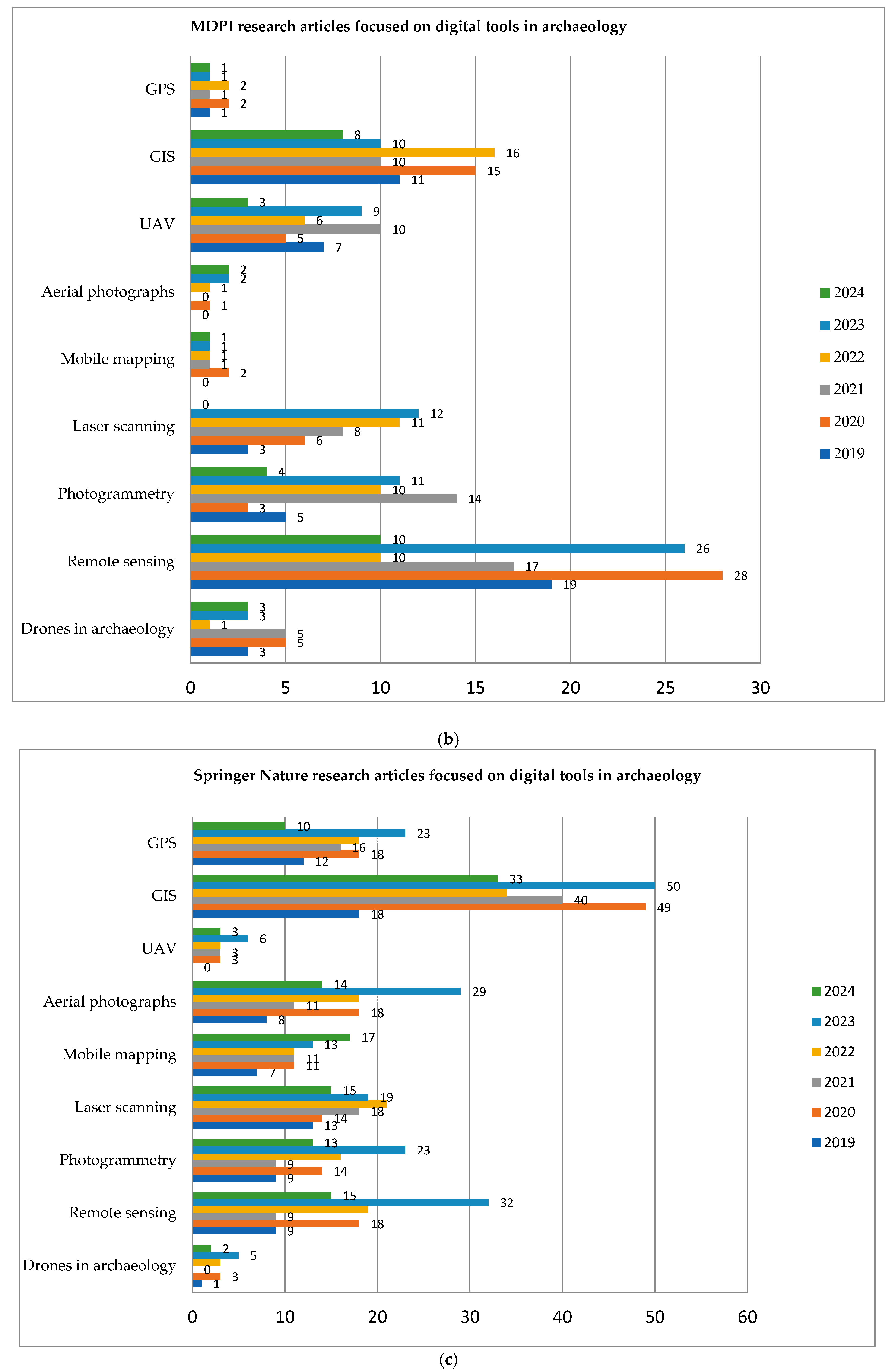
4. Trends in Digital Tools in Archaeology
5. Advancements and Challenges
5.1. Emerging Technologies and Innovations
5.2. Integration of Digital Tools with Traditional Methods
5.3. Challenges and Limitations
5.4. Future Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moullou, D.; Vital, R.; Sylaiou, S.; Ragia, L. Digital Tools for Data Acquisition and Heritage Management in Archaeology and Their Impact on Archaeological Practices. Heritage 2024, 7, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, V.; Mateus, L.; Aguiar, J. In Archaeology in the Digital Era Volume II. In Proceedings of the 40th Conference on Comput-er Applications and Quantitative Methods in Archaeology, Southampton, UK, 26–29 March 2012; Amsterdam University Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 2, p. 22, ISBN 978 90 4852 728 1. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Shi, Z.; Wang, B.; Yu, T. GPR Impedance Inversion for Imaging and Characterization of Buried Archaeological Remains: A Case Study at Mudu City Cite in Suzhou, China. J. Appl. Geophys. 2018, 148, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garstki, K. Digital Innovations in European Archaeology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pechunov, N.; Taipova, E. Digital tools in a clil context of teaching english to archaeology students. In Proceedings of the ADVED 2022- 8th International Conference on Advances in Education, Istanbul, Turkey, 10–12 October 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perfetti, L.; Fassi, F.; Rossi, C. Low-Cost Digital Tools for Archaeology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaeva, Z.; Hochschild, V.; Märker, M.; Sommer, C. Digital Data and Tools in Archaeology: The ROCEEH Out of Africa Database (ROAD). GI_Forum 2018, 6, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menéndez-Marsh, F.; Al-Rawi, M.; Fonte, J.; Dias, R.; Gonçalves, L.J.; Seco, L.G.; Hipólito, J.; Machado, J.P.; Medina, J.; Moreira, J.; et al. Geographic Information Systems in Archaeology: A Systematic Review. J. Comput. Appl. Archaeol. 2023, 6, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, A. Mobilizing Archaeologists: Increasing the Quantity and Quality of Data Collected in the Field with Mobile Technology. Adv. Archaeol. Pract. 2014, 2, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Guo, H.; Du, X. Integrated RS, GIS and GPS approaches to archaeological prospecting in the Hexi Corridor, NW China: A case study of the royal road to ancient Dunhuang. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2014, 50, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, F. A GIS-Based Digital Documentation Protocol for High-Resolution Documentation of Paleolithic Sites. J. Paleolit. Archaeol. 2023, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Unto, N.; Landeschi, G. Archaeological 3D GIS; Routledge: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhagen, P. Spatial Analysis in Archaeology: Moving into New Territories. In Digital Geoarchaeology: New Techniques for Interdisciplinary Human-Environmental Research; Siart, C., Forbriger, M., Bubenzer, O., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howland, M.D.; Liss, B.; Najjar, M.; Levy, T.E. GIS-based mapping of archaeological sites with low-altitude aerial photography and structure from Motion: A case study from Southern Jordan. In 2015 Digital Heritage; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Wang, X.; Lasaponara, R.; Xiang, B.; Zhen, J.; Zhu, L.; Yang, R.; Liu, D.; Liu, C. Auto-Extraction of Linear Archaeological Traces of Tuntian Irrigation Canals in Miran Site (China) from Gaofen-1 Satellite Imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenhuijzen, M.R.; Verhagen, P. Exploring the dynamics of transport in the Dutch limes. eTopoi J. Anc. Stud. 2015, 4. Available online: https://www.topoi.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/09/eTopoi_Sp4_Verhagen_etal.pdf (accessed on 25 December 2024).
- Katsamudanga, S. GIS Applications in Southern African Archaeology; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buławka, N.; Chyla, J. Mobile GIS—Current Possibilities, Future Needs. Position Paper. In Digital Archaeologies, Material Worlds (Past and Present), Proceedings of the 45rd Annual Conference on Computer Applications and Quantitative Methods in Archaeology, Atlanta, GA, USA, 14–16 March 2017; Tübingen University Press: Tübingen, Germany, 2020; pp. 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiocchi, V.; Del Pizzo, S.; Pugliano, G.; Onori, M.; Robustelli, U.; Troisi, S.; Vatore, F.; Trujillo, F.L. Use of the sensors of a latest generation mobile phone for the three-dimensional reconstruction of an archaeological monument: The survey of the Intihuatana stone in Machu Picchu (Peru’). IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 949, 012106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín-Buzón, C.; Pérez-Romero, A.; López-Castro, J.L.; Jerbania, I.B.; Manzano-Agugliaro, F. Photogrammetry as a New Scientific Tool in Archaeology: Worldwide Research Trends. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limp, W.F.; Barnes, A. Solving the Grid-to-Ground Problem when Using High Precision GNSS in Archaeological Mapping. Adv. Archaeol. Pract. 2014, 2, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fábrega-Álvarez, P.; Lynch, J. Archaeological Survey Supported by Mobile GIS: Low-Budget Strategies at the Hualfín Valley (Catamarca, Argentina). Adv. Archaeol. Pract. 2022, 10, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topouzi, S.; Tripolitsiotis, A.; Sarris, A.; Mertikas, S. Errors & Inaccuracies in Repositioning of Archaeological Sites. In Computer Applications and Quantitative Methods in Archaeology, Proceedings of the 29th Conference, Gotland, Sweden, 25–29 April 2001; Archaeopress: Oxford, UK, 2001; pp. 559–566. [Google Scholar]
- Rowan, Y.M.; Kersel, M.M.; Hill, A.C.; Urban, T.M. Late Prehistory of the Lower Galilee: Multi-Faceted Investigations of Wadi el-Ashert. Bull. Am. Sch. Orient. Res. 2021, 385, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavantzis, I.; Tsifodimou, Z.E.; Skalidi, I.; Karachaliou, E.; Giannaris, I.; Bakousi, A.; Skondras, A.; Katakalos, K.; Stylianidis, E. Restoration workflows by means of photogrammetry: The case study of pashas bridge. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2023, 48, 1543–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schowengerdt, R.A. Remote Sensing: Models and Methods for Image Processing; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; Available online: https://books.google.gr/books?id=KQXNaDH0X-IC (accessed on 25 December 2024).
- Campana, S. Remote Sensing in Archaeology. In Encyclopedia of Geoarchaeology; Gilbert, A.S., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 703–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Wang, X.; Guo, H.; Lasaponara, R.; Zong, X.; Masini, N.; Wang, G.; Shi, P.; Khatteli, H.; Chen, F.; et al. Airborne and spaceborne remote sensing for archaeological and cultural heritage applications: A review of the century (1907–2017). Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 232, 111280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasaponara, R.; Masini, N. (Eds.) Remote Sensing in Archaeology: From Visual Data Interpretation to Digital Data Manipulation. In Satellite Remote Sensing: A New Tool for Archaeology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agapiou, A.; Alexakis, D.D.; Lysandrou, V.; Sarris, A.; Cuca, B.; Themistocleous, K.; Hadjimitsis, D.G. Impact of urban sprawl to cultural heritage monuments: The case study of Paphos area in Cyprus. J. Cult. Herit. 2015, 16, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bewley, R.H. Aerial survey for archaeology. Photogramm. Rec. 2003, 18, 273–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeven, G.; Sevara, C. Trying to Break New Ground in Aerial Archaeology. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolis, O.; Gonzalez, C. 19—Wavelet-based fractal and multifractal analysis for detecting mineral deposits using multispectral images taken by drones. In Methods and Applications in Petroleum and Mineral Exploration and Engineering Geology; Gaci, S., Hachay, O., Nicolis, O., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucci, C.; Picollo, M.; Chiarantini, L.; Uda, G.; Fiori, L.; De Nigris, B.; Osanna, M. Remote-sensing hyperspectral imaging for applications in archaeological areas: Non-invasive investigations on wall paintings and on mural inscriptions in the Pompeii site. Microchem. J. 2020, 158, 105082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doneus, M.; Verhoeven, G.; Atzberger, C.; Wess, M.; Ruš, M. New ways to extract archaeological information from hyperspectral pixels. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2014, 52, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, E.; Freeman, T.; Hensley, S. Spaceborne and Airborne Radar at Angkor: Introducing New Technology to the Ancient Site. In Remote Sensing in Archaeology; Wiseman, J., El-Baz, F., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 185–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balz, T.; Caspari, G.; Fu, B.; Liao, M. Discernibility of Burial Mounds in High-Resolution X-Band SAR Images for Archaeological Prospections in the Altai Mountains. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casana, J.; Laugier, E.J.; Hill, A.C.; Reese, K.M.; Ferwerda, C.; McCoy, M.D.; Ladefoged, T. Exploring archaeological landscapes using drone-acquired lidar: Case studies from Hawai’i, Colorado, and New Hampshire, USA. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2021, 39, 103133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opitz, R.S.; Ryzewski, K.; Cherry, J.F.; Moloney, B. Using Airborne LiDAR Survey to Explore Historic-Era Archaeo-logical Landscapes of Montserrat in the Eastern Caribbean. J. Field Archaeol. 2015, 40, 523–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brivio, P.A.; Pepe, M.; Tomasoni, R. Multispectral and multiscale remote sensing data for archaeological prospecting in an alpine alluvial plain. J. Cult. Herit. 2000, 1, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, I.; Mkrtchyan, A. Free and Low-Cost Aerial Remote Sensing in Archaeology. Adv. Archaeol. Pract. 2023, 11, 164–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anschuetz, K.F.; Wilshusen, R.H.; Scheick, C.L. An archaeology of landscapes: Perspectives and directions. J. Archaeol. Res. 2001, 9, 157–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saturno, W.; Sever, T.L.; Irwin, D.E.; Howell, B.F.; Garrison, T.G. Putting Us on the Map: Remote Sensing Investigation of the Ancient Maya Landscape. In Remote Sensing in Archaeology; Wiseman, J., El-Baz, F., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 137–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughn, S.; Crawford, T. A predictive model of archaeological potential: An example from northwestern Belize. Appl. Geogr. 2009, 29, 542–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymański, J.; Misiewicz, K.; Mieszkowski, R.; Martecki, J. Regional patterns, local techniques. Remote sensing and archaeology at prehispanic site of San Isidro, El Salvador. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2022, 45, 103628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeazzi, F.; Callieri, M.; Dellepiane, M.; Charno, M.; Richards, J.; Scopigno, R. Web-based visualization for 3D data in archaeology: The ADS 3D viewer. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2016, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stylianidis, E.; Evangelidis, K.; Vital, R.; Dafiotis, P.; Sylaiou, S. 3D Documentation and Visualization of Cultural Heritage Buildings through the Application of Geospatial Technologies. Heritage 2022, 5, 2818–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelli, A.; Achille, C.; Tommasi, C.; Fassi, F. Integration of 3D models and diagnostic analyses through a conservation-oriented information system. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2017, 42, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galantucci, R.A.; Fatiguso, F. Advanced damage detection techniques in historical buildings using digital photogrammetry and 3D surface anlysis. J. Cult. Herit. 2019, 36, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakoumaki, M.C.; Lala, D.M.; Tsaroucha, A.; Psalti, A. Advanced Digitization Methods for the Protection and Dissemination of Cultural Heritage towards Digital transformation: The Archaeological Museum of Delphi. Procedia CIRP 2023, 118, 1056–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Ibáñez, L.A.; Barneche-Naya, V. Assisted navigation and natural interaction for virtual archaeological heritage. implementation of an attractor-based approach using a game engine. Mediterr. Archaeol. Archaeom. 2016, 16, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzado-Martínez, A.; García-Fernández, Á.-L.; Ortega-Alvarado, L.M. Accessing interactively the spatio-temporal data-model of an archaeological site through its 3D virtual reconstruction. Digit. Appl. Archaeol. Cult. Herit. 2022, 26, e00235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vital, R.; Sylaiou, S. Digital survey: How it can change the way we perceive and understand heritage sites. Digit. Appl. Archaeol. Cult. Herit. 2022, 24, e00212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croix, S.; Deckers, P.; Sindbæk, S.M. Recasting a Viking warrior woman from Ribe: 3D digital image reconstruction compared. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2020, 32, 102455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, M.M.; Ribeiro, G.; Paulo, R.; Bessa, M.; Sousa, F.R.; Moreira, E.; Mesquita, E. Strategy for HBIM implementation using high-resolution 3D architectural documentation based on laser scanning and photogrammetry of the José de Alencar theatre. Digit. Appl. Archaeol. Cult. Herit. 2023, 30, e00287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Maida, G.; Hattermann, M.; Delpiano, D. 3D models of lithic artefacts: A test on their efficacy. Digit. Appl. Archaeol. Cult. Herit. 2023, 30, e00279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, I.; Lindenbergh, R.; Watson, L.; Shelton, K. Building a Mycenaean chamber tomb catalogue from terrestrial laser scan data. Digit. Appl. Archaeol. Cult. Herit. 2024, 32, e00319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiabrando, F.; Nex, F.; Piatti, D.; Rinaudo, F. UAV and RPV systems for photogrammetric surveys in archaelogical areas: Two tests in the Piedmont region (Italy). J. Archaeol. Sci. 2011, 38, 697–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casana, J.; Fowles, S.; Montgomery, L.M.; Mermejo, R.; Ferwerda, C.; Hill, A.C.; Adler, M. Multi-sensor drone survey of ancestral agricultural landscapes at Picuris Pueblo, New Mexico. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2023, 157, 105837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stek, T.D. Drones over Mediterranean landscapes. The potential of small UAV’s (drones) for site detection and heritage management in archaeological survey projects: A case study from Le Pianelle in the Tappino Valley, Molise (Italy). J. Cult. Herit. 2016, 22, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiz, J.I.; Martín, P.M.; Cuesta, R.; Subías, E.; Codina, D.; Cartes, A. Examples and Results of Aerial Photogrammetry in Archeology with UAV: Geometric Documentation, High Resolution Multispectral Analysis, Models and 3D Printing. Drones 2022, 6, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canicattì, M.; Vallone, M. Drones in vegetable crops: A systematic literature review. Smart Agric. Technol. 2024, 7, 100396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona, J.Á.S.; Quirós, E.; Mayoral, V.; Charro, C. Assessing the potential of multispectral and thermal UAV imagery from archaeological sites. A case study from the Iron Age hillfort of Villasviejas del Tamuja (Cáceres, Spain). J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2020, 31, 102312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, H. Quantitative Analysis of Two Low-Cost Aerial Photography Platforms: A Case Study of the Site of Zagora, Andros, Greece. J. Field Archaeol. 2016, 41, 660–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campiani, A.; McAvoy, S.; Lercari, N.; Stuardo, R.L.; Delgado, G.J.; Mejía, J.L.; Rissolo, D.; Kuester, F. Developing an interoperable cloud-based visualization workflow for 3D archaeological heritage data: The Palenque 3D Archaeological Atlas. Digit. Appl. Archaeol. Cult. Herit. 2023, 31, e00293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lercari, N.; Tanasi, D.; Sonnemann, T.; Hassam, S.; Calderone, D.; Trapani, P.; Ruider, L.; Lanteri, R. Archaeology of Archaeology at Heloros: Re-Interpreting the Urban Layout of a Complex Greek Settlement in Sicily Using Prox-imal Sensing and Data Fusion. Digit. Appl. Archaeol. Cult. Herit. 2024, 33, e00327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orengo, H.A.; Garcia-Molsosa, A. A brave new world for archaeological survey: Automated machine learning-based potsherd detection using high-resolution drone imagery. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2019, 112, 105013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Materazzi, F.; Pacifici, M. Archaeological crop marks detection through drone multispectral remote sensing and vegetation indices: A new approach tested on the Italian pre-Roman city of Veii. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2022, 41, 103235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, K. Heritage at risk: Digital preservation of traditional cultural heritage (TCH) in Sri Lanka. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2023, 48, 1197–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
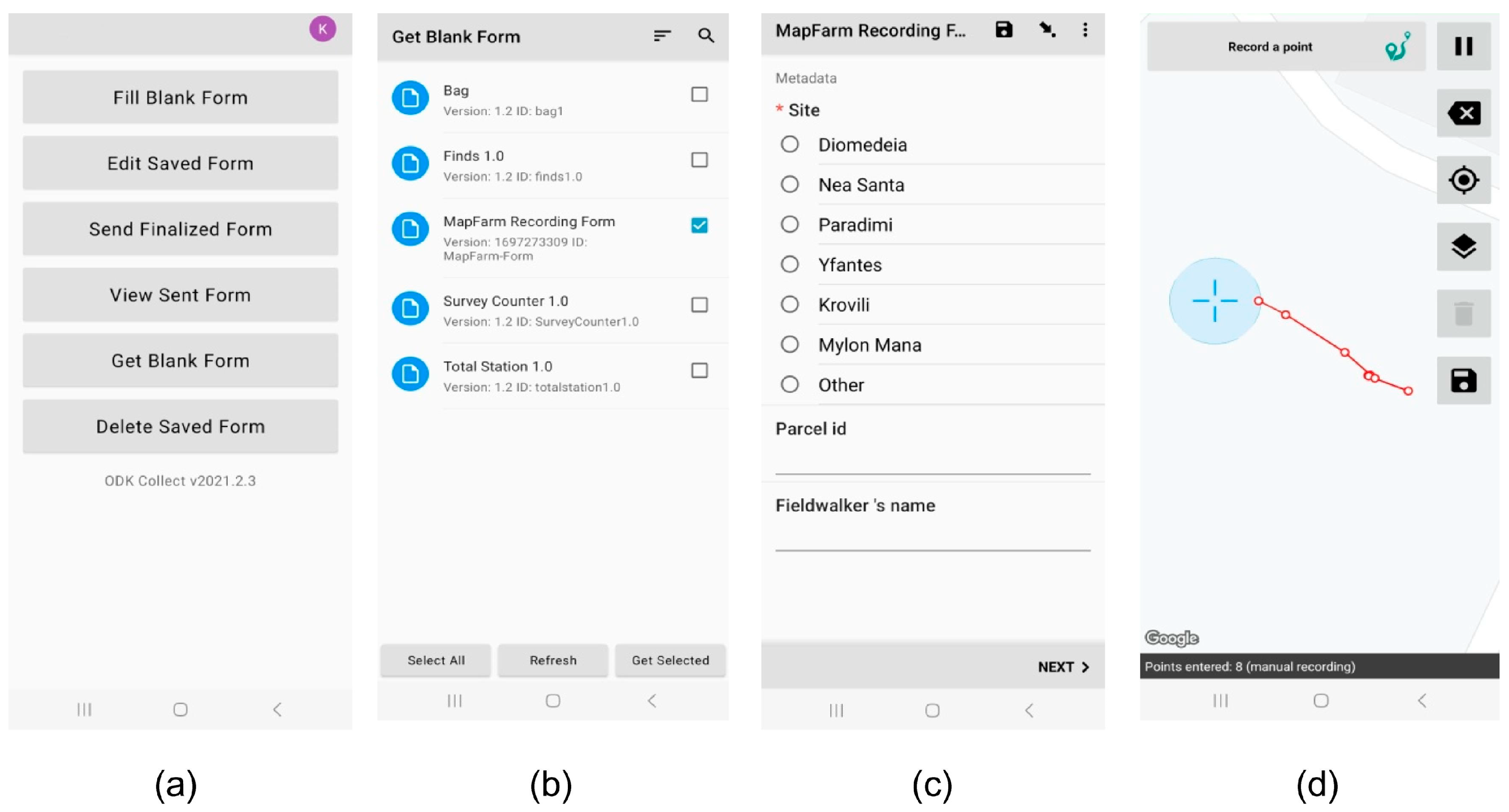
- Sgouropoulos, K.; Urem-Kotsou, D.; Chrysafakoglou, P. Application of mobile digital recording and GIS analysis of archaeological surface survey finds in the MapFarm project. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2024, 53, 104331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, S.; Ballsun-Stanton, B.; Cassidy, S.; Crook, P.; Klump, J.; Sobotkova, A. FAIRer Data through Digital Recording: The FAIMS Mobile Experience. J. Comput. Appl. Archaeol. 2022, 5, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballsun-Stanton, B.; Ross, S.A.; Sobotkova, A.; Crook, P. FAIMS Mobile: Flexible, open-source software for field research. SoftwareX 2018, 7, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urem-Kotsou, D.; Sgouropoulos, K.; Kotsos, S.; Chrysafakoglou, P.; Chrysaphi, M.; Skoulariki, D. Surveying the Neolithic farmers in Aegean Thrace with digital technologies. Stud. Praehist. 2022, 16, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyrou, A.; Agapiou, A. A Review of Artificial Intelligence and Remote Sensing for Archaeological Research. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küçükdemirci, M.; Sarris, A. GPR Data Processing and Interpretation Based on Artificial Intelligence Approaches: Future Perspectives for Archaeological Prospection. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venditti, C.P.; Mele, P. Digital Transformation and Archaeology. In Developing Effective Communication Skills in Archaeology; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 224–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamitrou, A.; Sturt, F.; Bogiatzis, P.; Beresford-Jones, D. Towards the use of artificial intelligence deep learning networks for detection of archaeological sites. Surf. Topogr. Metrol. Prop. 2022, 10, 044001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Alvarado, L.M.; García-Fernández, Á.L.; Conde-Rodríguez, F.-A.; Jurado-Rodríguez, J.M. Integrated and interactive 4D system for archaeological stratigraphy. Archaeol. Anthropol. Sci. 2022, 14, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsianis, M.; Kalayci, T.; Sarris, A. Bridging Digital Approaches and Legacy in Archaeology. Digital 2022, 2, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, E.C. Creating a Software Methodology to Analyze and Preserve Archaeological Legacy Data. Adv. Archaeol. Pract. 2023, 11, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhard, A. Archaeology of Digital Environments: Tools, Methods, and Approaches. Doctoral Dissertation, University of York, York, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Giuliani, F.; Gaglio, F.; Martino, M.; De Falco, A. A HBIM pipeline for the conservation of large-scale architectural heritage: The city Walls of Pisa. Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delpozzo, E.; Balletti, C. Bridging the gap: An open-source gis+bim system for archaeological data. the case study of altinum, Italy. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2023, 48, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovell, L.J.; Davies, R.J.; Hunt, D.V.L. The Application of Historic Building Information Modelling (HBIM) to Cultural Heritage: A Review. Heritage 2023, 6, 6691–6717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
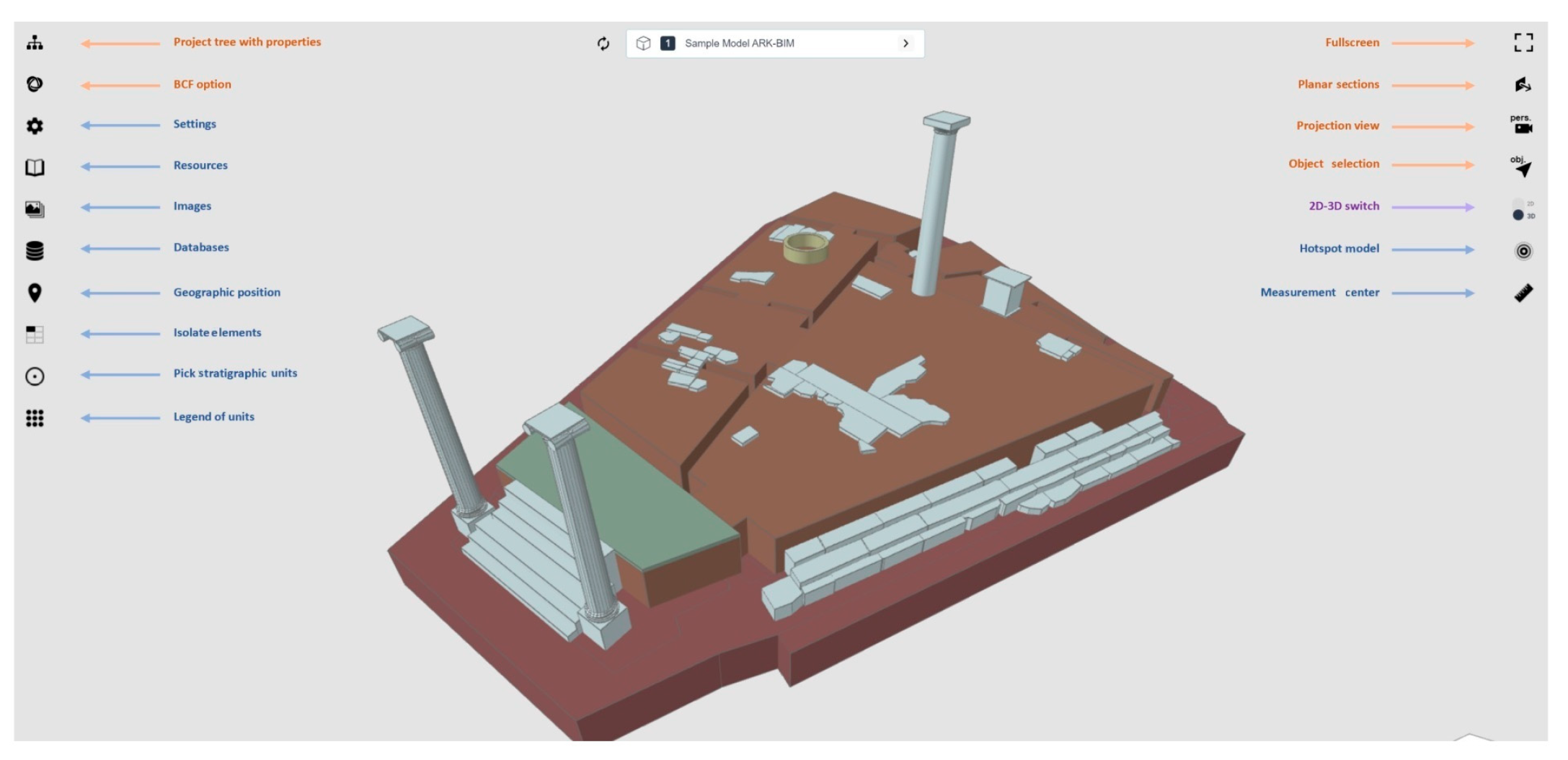
- Diara, F.; Rinaudo, F. ARK-BIM: Open-Source Cloud-Based HBIM Platform for Archaeology. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorenza, J.; Rimella, N.; Calandra, D.; Osello, A.; Lamberti, F. Enhancing HBIM-to-VR workflows: Semi-automatic generation of virtual heritage experiences using enriched IFC files. Digit. Appl. Archaeol. Cult. Herit. 2025, 36, e00391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klehm, C.E. The Use and Challenges of Spatial Data in Archaeology. Adv. Archaeol. Pract. 2023, 1, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervolarakis, Z.; Zidianakis, E.; Katzourakis, A.; Evdaimon, T.; Partarakis, N.; Zabulis, X.; Stephanidis, C. Three-Dimensional Digitization of Archaeological Sites—The Use Case of the Palace of Knossos. Heritage 2023, 6, 904–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauro, V.; Lombardo, V. The Cataloging and Conservation of Digital Survey in Archaeology: A Photogrammetry Protocol in the Context of Digital Data Curation. Heritage 2023, 6, 3113–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, C.L. Current Digital Archaeology. Annu. Rev. Anthropol. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Kansa, E.; Kansa, S.W. Digital Data and Data Literacy in Archaeology Now and in the New Decade. Adv. Archaeol. Pract. 2021, 9, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, C.; Fernandez, R.; Irwin, J. Digital Archaeological Data in the Wild West: The challenge of practising responsible digital data archiving and access in the United States. Internet Archaeol. 2021, 58, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
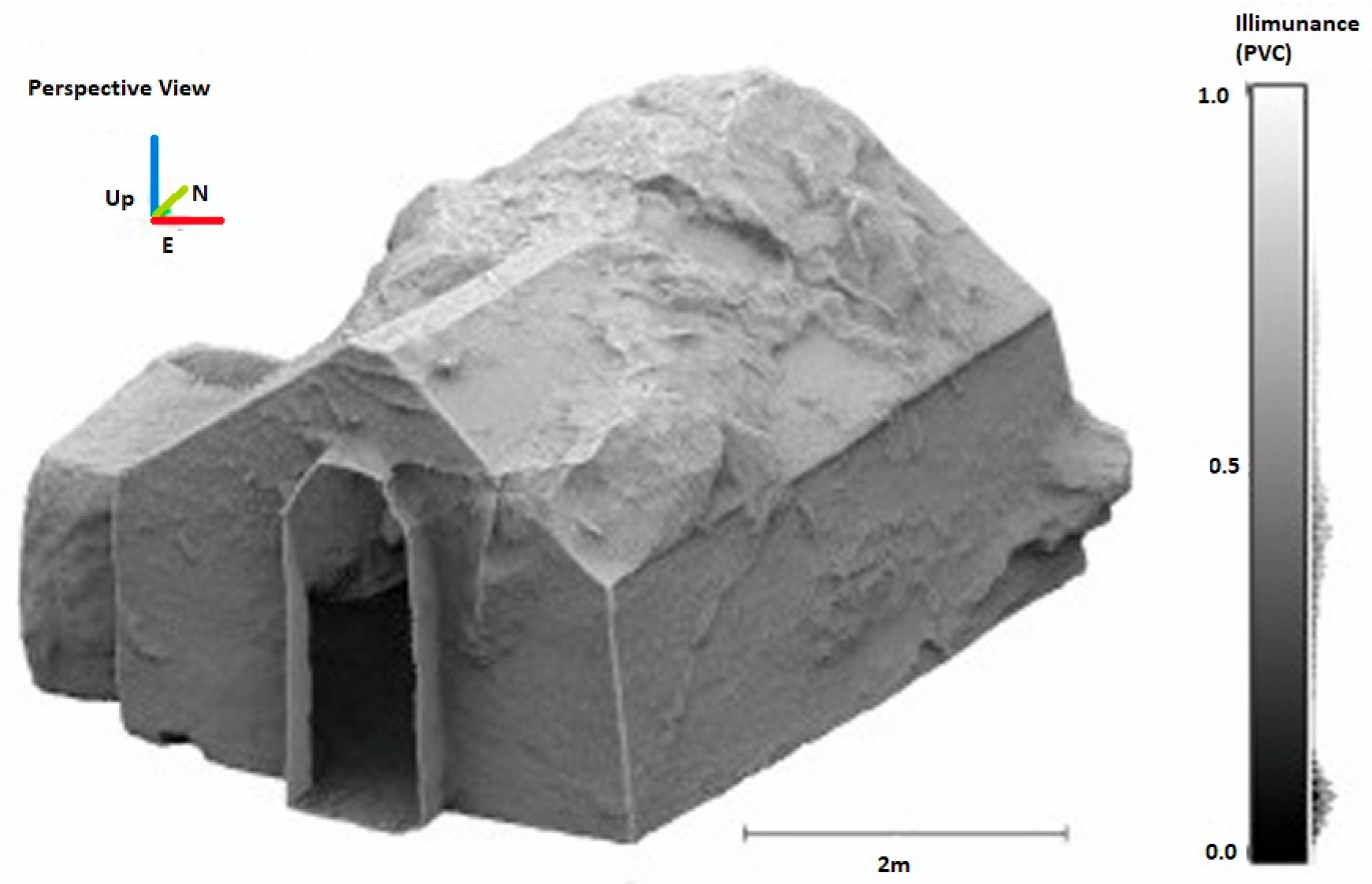
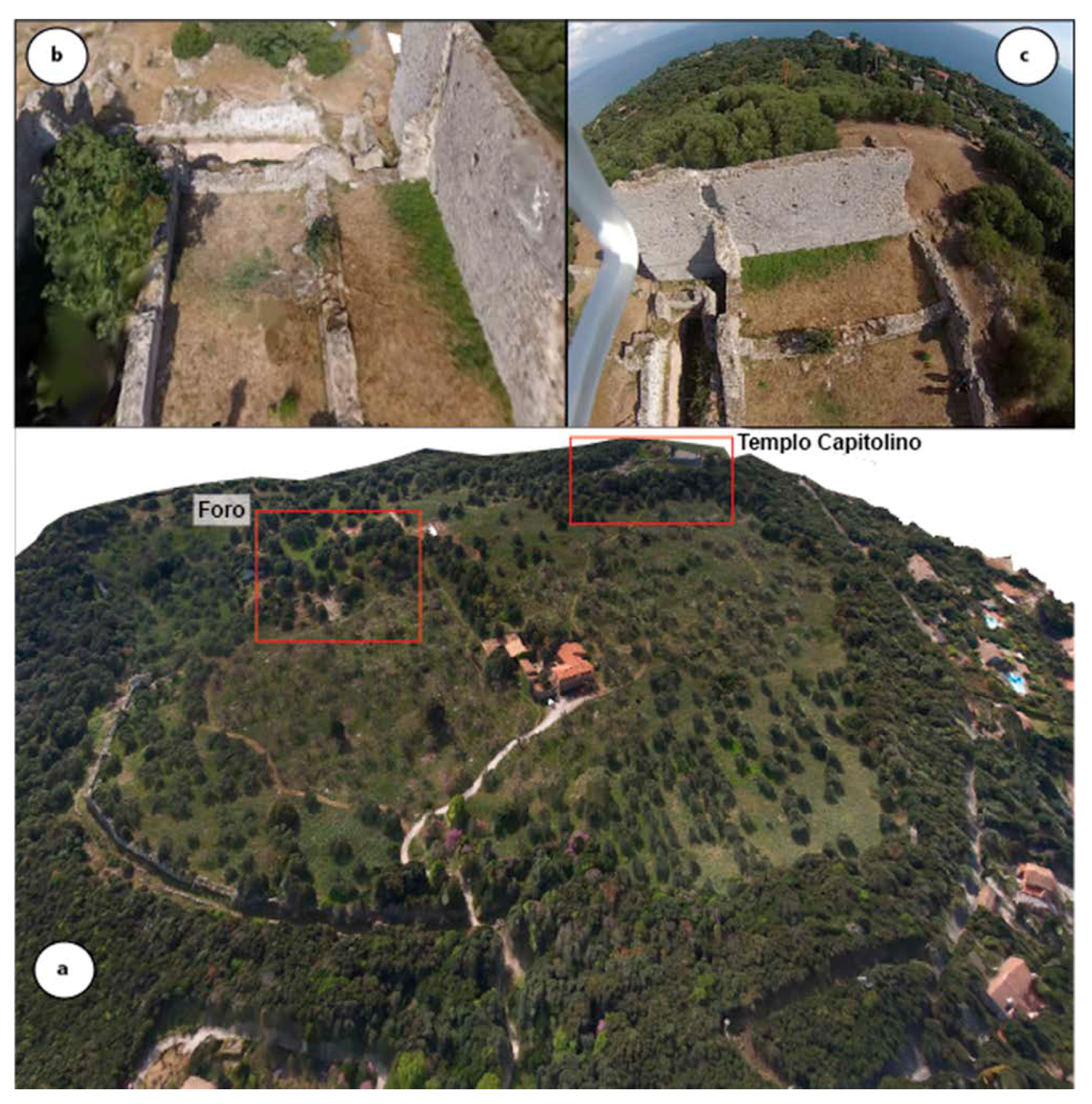













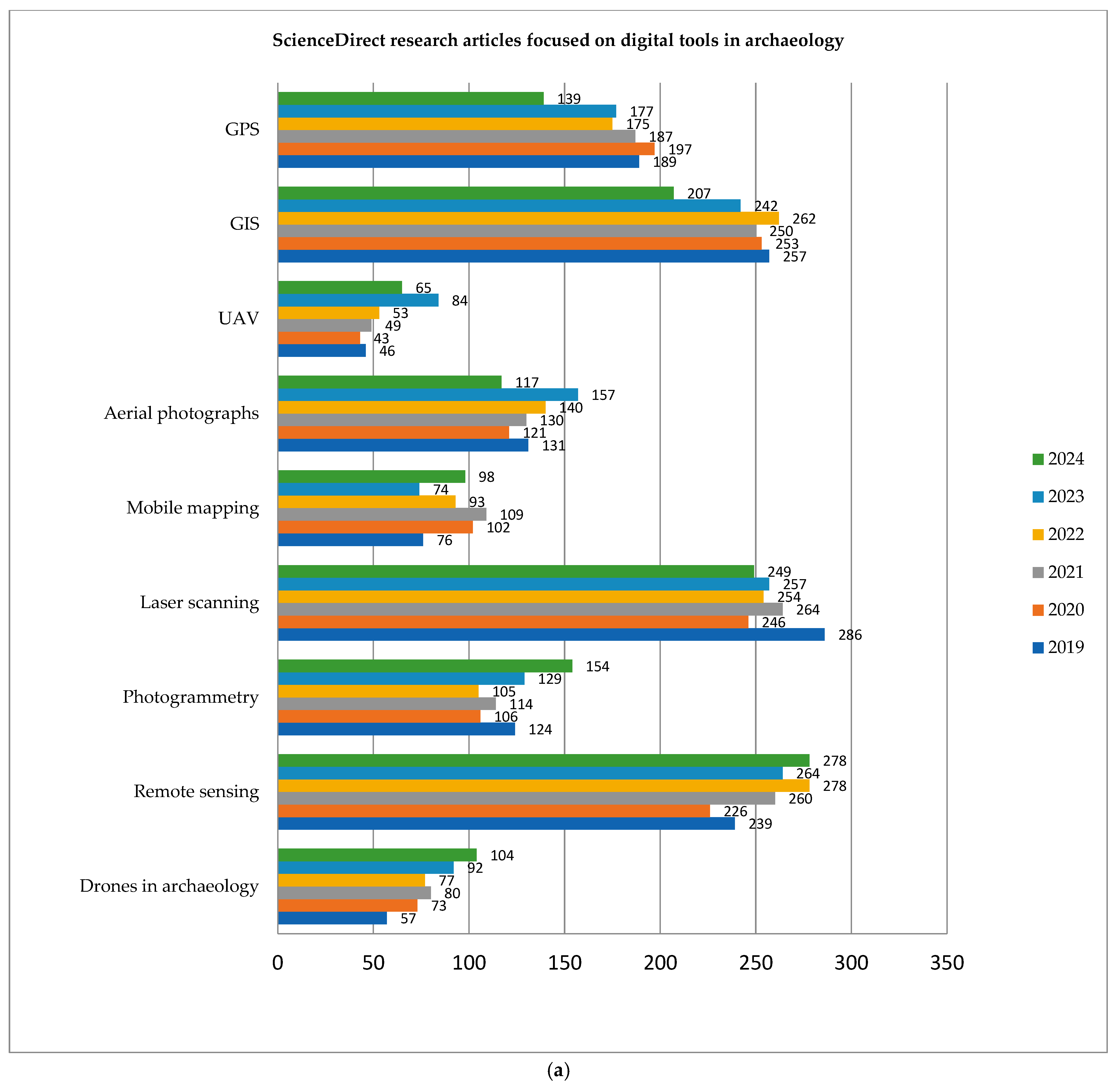
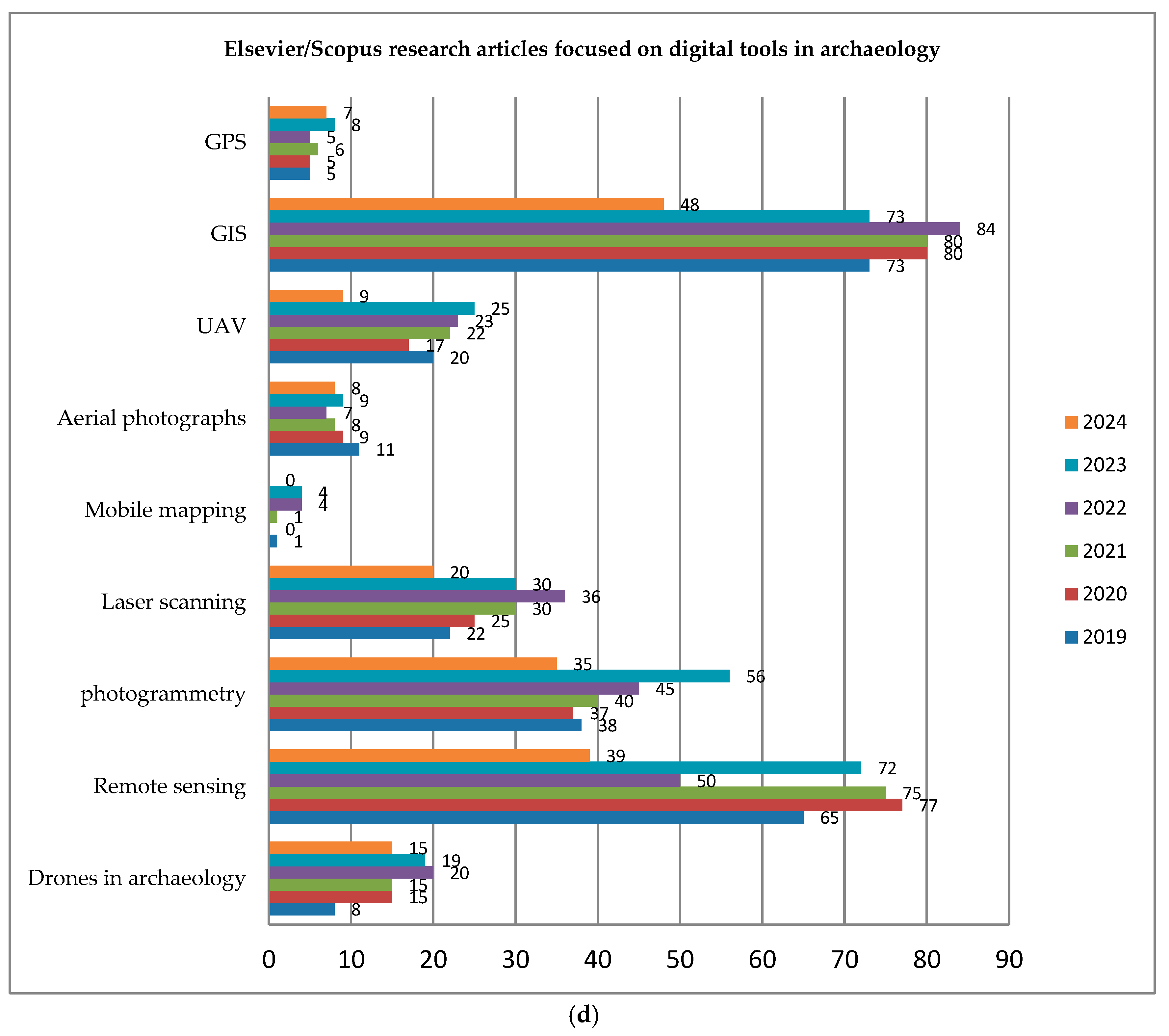

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sylaiou, S.; Tsifodimou, Z.-E.; Evangelidis, K.; Stamou, A.; Tavantzis, I.; Skondras, A.; Stylianidis, E. Redefining Archaeological Research: Digital Tools, Challenges, and Integration in Advancing Methods. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2495. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15052495
Sylaiou S, Tsifodimou Z-E, Evangelidis K, Stamou A, Tavantzis I, Skondras A, Stylianidis E. Redefining Archaeological Research: Digital Tools, Challenges, and Integration in Advancing Methods. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(5):2495. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15052495
Chicago/Turabian StyleSylaiou, Stella, Zoi-Eirini Tsifodimou, Konstantinos Evangelidis, Aikaterini Stamou, Ioannis Tavantzis, Alexandros Skondras, and Efstratios Stylianidis. 2025. "Redefining Archaeological Research: Digital Tools, Challenges, and Integration in Advancing Methods" Applied Sciences 15, no. 5: 2495. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15052495
APA StyleSylaiou, S., Tsifodimou, Z.-E., Evangelidis, K., Stamou, A., Tavantzis, I., Skondras, A., & Stylianidis, E. (2025). Redefining Archaeological Research: Digital Tools, Challenges, and Integration in Advancing Methods. Applied Sciences, 15(5), 2495. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15052495











