Longitudinal Bending Stiffness Analysis of Composite Carbon Plates and Shoe Sole, Based on Three-Point Bending Test
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mechanical Test
2.2. Sole Model
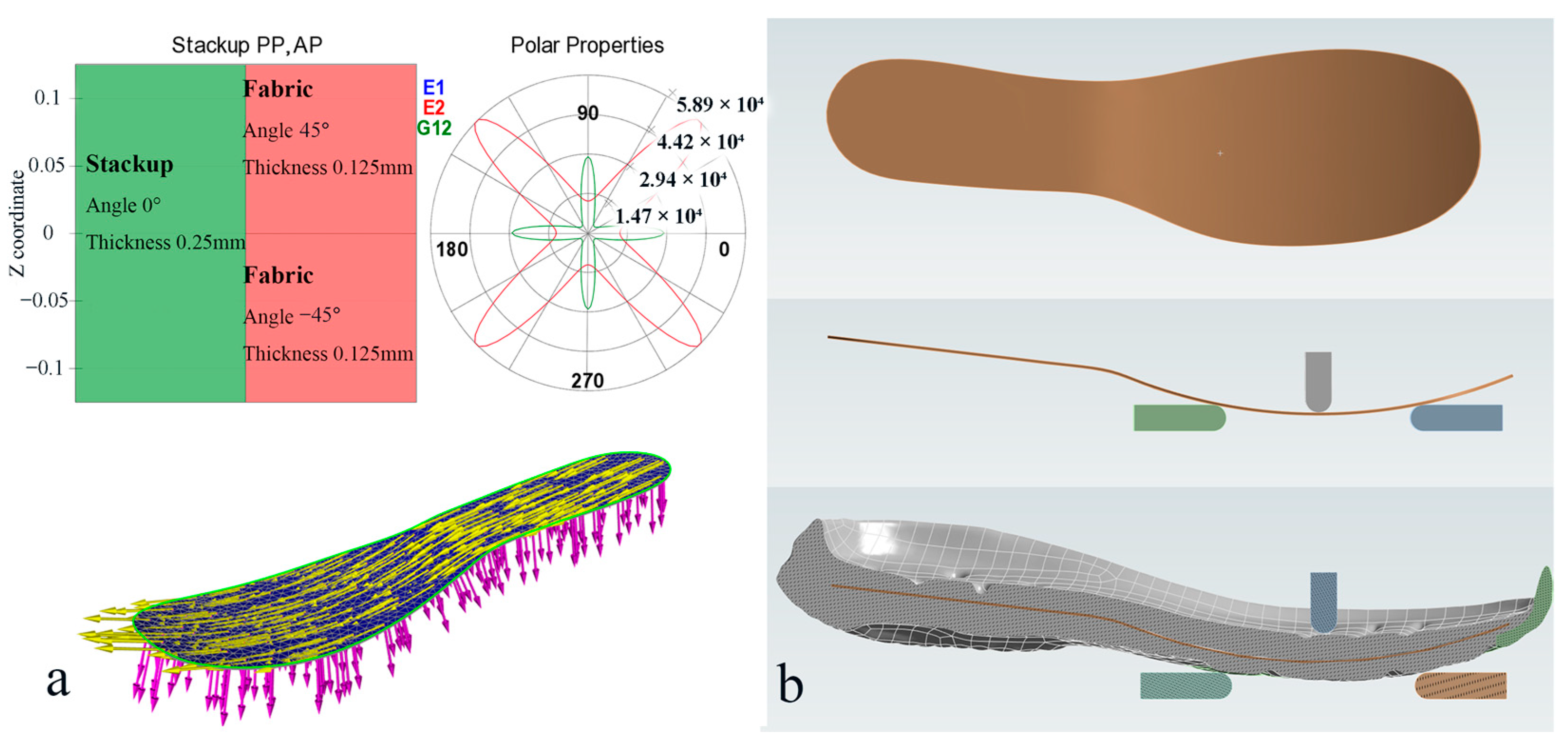
2.3. Plate and ‘Plate-Sole’ Models
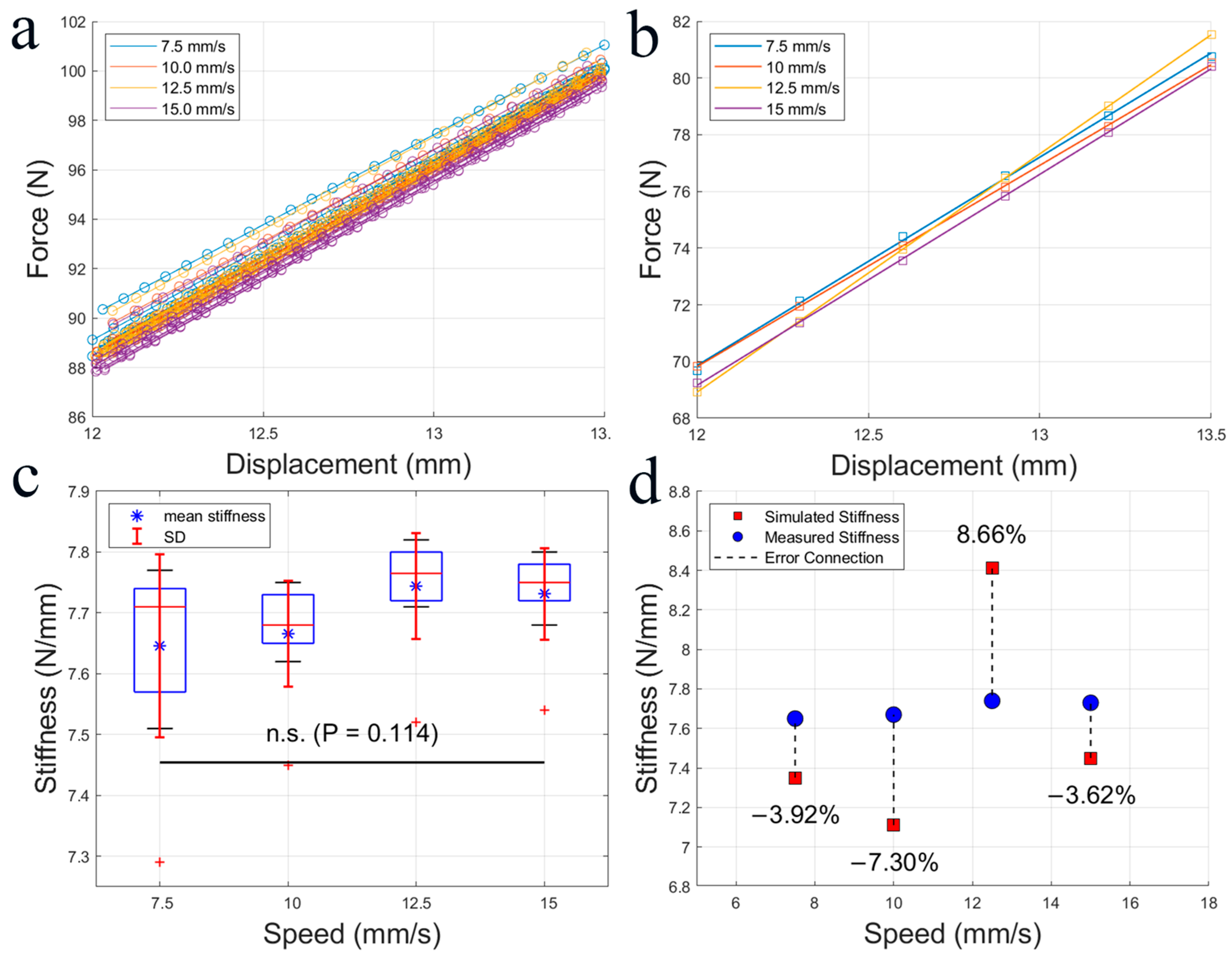
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Model Validation
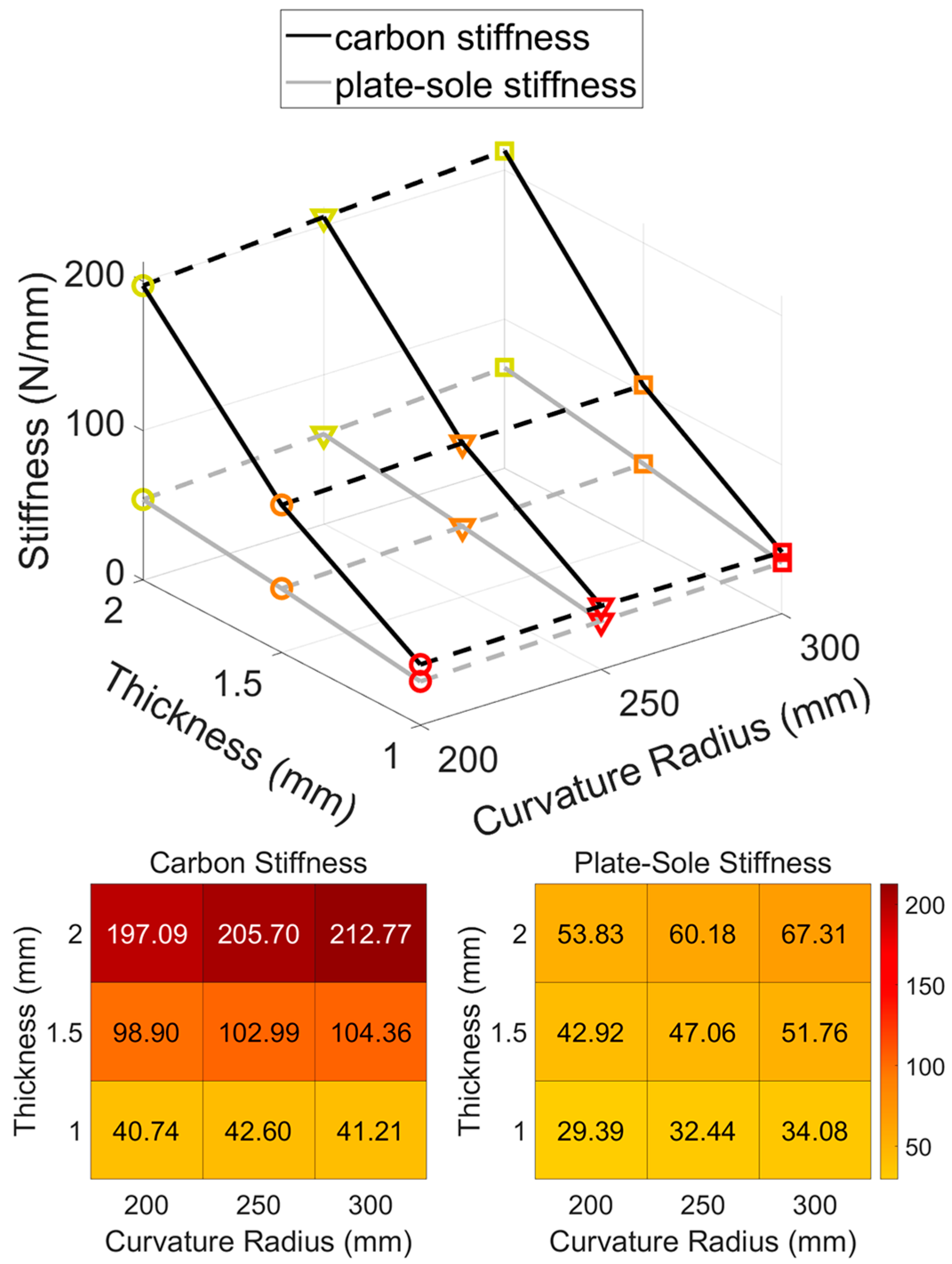
3.2. Plate Stiffness
3.3. ‘Plate-Sole’ Stiffness
3.4. Plate and ‘Plate-Sole’ Stiffness
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ortega, J.A.; Healey, L.A.; Swinnen, W.; Hoogkamer, W. Energetics and Biomechanics of Running Footwear with Increased Longitudinal Bending Stiffness: A Narrative Review. Sports Med. 2021, 51, 873–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, K.R.; Kilding, A.E. A Randomized Crossover Study Investigating the Running Economy of Highly-Trained Male and Female Distance Runners in Marathon Racing Shoes Versus Track Spikes. Sports Med. 2019, 49, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoogkamer, W.; Kipp, S.; Frank, J.H.; Farina, E.M.; Luo, G.; Kram, R. A Comparison of the Energetic Cost of Running in Marathon Racing Shoes. Sports Med. 2018, 48, 1009–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, I.; McLeod, A.; Valentine, D.; Low, T.; Ward, J.; Hager, R. Running economy, mechanics, and marathon racing shoes. J. Sports Sci. 2019, 37, 2367–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogkamer, W.; Kipp, S.; Kram, R. The Biomechanics of Competitive Male Runners in Three Marathon Racing Shoes: A Randomized Crossover Study. Sports Med. 2019, 49, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigoja, S.; Firminger, C.R.; Asmussen, M.J.; Fletcher, J.R.; Edwards, W.B.; Nigg, B.M. Does increased midsole bending stiffness of sport shoes redistribute lower limb joint work during running? J. Sci. Med. Sport 2019, 22, 1272–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willwacher, S.; König, M.; Potthast, W.; Brüggemann, G.P. Does specific footwear facilitate energy storage and return at the metatarsophalangeal joint in running? J. Appl. Biomech. 2013, 29, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willwacher, S.; König, M.; Braunstein, B.; Goldmann, J.P.; Brüggemann, G.P. The gearing function of running shoe longitudinal bending stiffness. Gait Posture 2014, 40, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, J.P.R.; Stefanyshyn, D.J. Shoe midsole longitudinal bending stiffness and running economy, joint energy, and EMG. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2006, 38, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; He, Y.; Wang, S.; Meng, C. Ultimate Strength Study of Structural Bionic CFRP-Sinker Bolt Assemblies Subjected to Preload under Three-Point Bending. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, H.; Espino, D.M.; Shepherd, D.E.T. Fatigue strength of bovine articular cartilage-on-bone under three-point bending: The effect of loading frequency. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2017, 18, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, Y.; Miura, D.; Shinya, A. Application of fused deposition modeling technology for fabrication jigs of three-point bending test for dental composite resins. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2022, 130, 105172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Cheng, L.; Li, D. Experimental Study on Forged TC4 Titanium Alloy Fatigue Properties under Three-Point Bending and Life Prediction. Materials 2021, 14, 5329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biały, M.; Szust, A.; Napadłek, P.; Dobrzyński, M.; Więckiewicz, W. The three-point bending test of fiber-reinforced composite root canal posts. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2020, 29, 1111–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, N.; Rao, G.; Berton, E.; Delattre, N. The stiff plate location into the shoe influences the running biomechanics. Sports Biomech. 2021, 20, 815–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigo-Carranza, V.; Hoogkamer, W.; Salinero, J.J.; Rodríguez-Barbero, S.; González-Ravé, J.M.; González-Mohíno, F. Influence of Running Shoe Longitudinal Bending Stiffness on Running Economy and Performance in Trained and National Level Runners. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2023, 55, 2290–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo-Carranza, V.; Hoogkamer, W.; González-Ravé, J.M.; González-Mohíno, F. Relationship Between Advanced Footwear Technology Longitudinal Bending Stiffness and Energy Cost of Running. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2024, 34, e14687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, F.A.; Zehnter, F.; Yona, T.; Mai, P.; Willwacher, S.; Düking, P.; Sperlich, B. Acute physiological, biomechanical, and perceptual responses of runners wearing downward-curved carbon fiber insoles. Front. Sports Act. Living 2024, 6, 1340154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos-Salamanca, M.; Rodrigo-Carranza, V.; Rodríguez-Barbero, S.; Salinero, J.J.; González-Mohíno, F. Effects of the increase of longitudinal bending stiffness of advanced footwear technology on 3000 m performance, pacing strategy, and biomechanics. Footwear Sci. 2024, 16, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, K.; Park, S. The bending stiffness of shoes is beneficial to running energetics if it does not disturb the natural MTP joint flexion. J. Biomech. 2017, 53, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.; Forman, J.; Kim, T.; Panzer, M.B.; Crandall, J.R. Injury risk functions based on population-based finite element model responses: Application to femurs under dynamic three-point bending. Traffic Inj. Prev. 2018, 19 (Suppl. S1), S59–S64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridha, H.; Thurner, P.J. Finite element prediction with experimental validation of damage distribution in single trabeculae during three-point bending tests. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2013, 27, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Levadnyi, I.; Wang, J.; Xie, Z.; Fekete, G.; Cai, Y.; Gu, Y. Effect of the Construction of Carbon Fiber Plate Insert to Midsole on Running Performance. Materials 2021, 14, 5156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Chen, H.; Huang, J.; Ye, J.; Gao, L.; Liu, Q.; Quan, W.; Gu, Y. Biomechanical Investigation of Lower Limbs During Slope Transformation Running with Different Longitudinal Bending Stiffness Shoes. Sensors 2024, 24, 3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, S.; Harland, A.; Smith, P.; Lucas, T. A Study of Football Footwear Bending Stiffness. Procedia Eng. 2014, 72, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.Z.; Gross, M.T.; Van Werkhoven, H.; Piazza, S.J.; Sawicki, G.S. Adding Stiffness to the Foot Modulates Soleus Force-Velocity Behaviour during Human Walking. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagehorn, T.; Mai, P.; Bill, K.; Herbaut, A.; de Zee, M.; Kersting, U.G. Effect of increased shoe longitudinal bending stiffness on ankle and foot biomechanics in jump-cut movements of low and high degrees. Footwear Sci. 2024, 16, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wong, D.W.C.; Chen, T.L.W.; Chen, S.F.; Zhang, G.; Tan, Q.; Zhang, M. Different Design Feature Combinations of Flatfoot Orthosis on Plantar Fascia Strain and Plantar Pressure: A Muscle-Driven Finite Element Analysis With Taguchi Method. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 853085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Verma, S.; Jeng, J.Y. Supportless Lattice Structures for Energy Absorption Fabricated by Fused Deposition Modeling. 3d Print. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 7, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H. Effects of midsole hardness on the mechanical response characteristics of the plantar fascia during running. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; Deng, C.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, X. Cushioning mechanism of the metatarsals during landing for the skateboarding ollie maneuver. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1382161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amsalu, C.; Negasa, D.; Merga, A. Numerical analysis of fiber reinforced composite material for structural component application. Heliyon 2024, 10, e37698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiri, S. Comparative modal analysis on fishing rod made of functionally graded composite material using finite element analysis. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2022, 20, 22808000221089774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reda, R.; Khamis, M.; Ragab, A.E.; Elsayed, A.; Negm, A.M. Numerical analysis of the impact of winding angles on the mechanical performance of filament wound type 4 composite pressure vessels for compressed hydrogen gas storage. Heliyon 2024, 10, e33796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, W. Simulation and Analysis of the Damage of Carbon Fiber Composite Laminates Under Three Point Bending Load. J. Mech. Eng. 2019, 55, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeod, A.R.; Bruening, D.; Johnson, A.W.; Ward, J.; Hunter, I. Improving running economy through altered shoe bending stiffness across speeds. Footwear Sci. 2020, 12, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healey, L.A.; Hoogkamer, W. Longitudinal bending stiffness does not affect running economy in Nike Vaporfly Shoes. J. Sport Health Sci. 2022, 11, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanyshyn, D.J.; Nigg, B.M. Influence of midsole bending stiffness on joint energy and jump height performance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2000, 32, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Shao, E.; Sun, D.; Xuan, R.; Baker, J.S.; Gu, Y. Effects of footwear with different longitudinal bending stiffness on biomechanical characteristics and muscular mechanics of lower limbs in adolescent runners. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 907016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Cen, X.; Chen, H.; Sun, D.; Munivrana, G.; Bálint, K.; Bíró, I.; Gu, Y. The influence of running shoe with different carbon-fiber plate designs on internal foot mechanics: A pilot computational analysis. J. Biomech. 2023, 153, 111597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Cen, X.; Sun, D.; Bálint, K.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Gao, S.; Bíró, I.; Zhang, M.; Gu, Y. Curved carbon-plated shoe may further reduce forefoot loads compared to flat plate during running. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farina, E.M.; Haight, D.; Luo, G. Creating footwear for performance running. Footwear Sci. 2019, 11 (Suppl. S1), S134–S135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isherwood, J.; Woo, S.; Cho, M.; Cha, M.; Park, S.; Kim, S.; Han, S.; Jun, J.; Sung, N.; Sterzing, T. Advanced footwear technology and its impacts on running mechanics, running economy and perception of male and female recreational runners. Footwear Sci. 2024, 16, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Part | Density (kg/m3) | Young’s Modulus (MPa) | Poisson’s Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fixture | 7850 | 200,000 | 0.3 |
| Midsole | 2300 | 1.2 | 0.365 |
| Outsole [30] | 2300 | 8 | 0.47 |
| Epoxy Carbon Woven (230 GPa) Wet | |
|---|---|
| Density (kg/m3) | 1451 |
| Young’s Modulus X direction (MPa) | 59,160 |
| Young’s Modulus Y direction (MPa) | 59,160 |
| Young’s Modulus Z direction (MPa) | 7500 |
| Poisson’s Ratio XY | 0.04 |
| Poisson’s Ratio YZ | 0.3 |
| Poisson’s Ratio XZ | 0.3 |
| Shear Modulus XY (MPa) | 3300 |
| Shear Modulus YZ (MPa) | 2700 |
| Shear Modulus XZ (MPa) | 2700 |
| Size (mm) | Average Quality | Nodes | Elements |
|---|---|---|---|
| 16 | 0.61 | 17,538 | 9256 |
| 8 | 0.71 | 29,249 | 16,570 |
| 4 | 0.82 | 131,961 | 84,760 |
| 2 | 0.84 | 878,940 | 611,511 |
| Plate Thickness (mm) | Curvature Radius (mm) | Reduction Percentage (%) | Curvature Radius (mm) | Plate Thickness (mm) | Reduction Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 200 | 27.86 | 200 | 1 | 27.86 |
| 250 | 23.85 | 1.5 | 56.61 | ||
| 300 | 17.29 | 2 | 72.69 | ||
| 1.5 | 200 | 56.61 | 250 | 1 | 23.85 |
| 250 | 54.31 | 1.5 | 54.31 | ||
| 300 | 50.41 | 2 | 70.75 | ||
| 2 | 200 | 72.69 | 300 | 1 | 17.29 |
| 250 | 70.75 | 1.5 | 50.41 | ||
| 300 | 68.37 | 2 | 68.37 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Y.; Jia, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, X. Longitudinal Bending Stiffness Analysis of Composite Carbon Plates and Shoe Sole, Based on Three-Point Bending Test. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2785. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15052785
Guo Y, Jia Y, Wu Y, Zhu X. Longitudinal Bending Stiffness Analysis of Composite Carbon Plates and Shoe Sole, Based on Three-Point Bending Test. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(5):2785. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15052785
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Yangyu, Yunlong Jia, Yusen Wu, and Xiaolan Zhu. 2025. "Longitudinal Bending Stiffness Analysis of Composite Carbon Plates and Shoe Sole, Based on Three-Point Bending Test" Applied Sciences 15, no. 5: 2785. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15052785
APA StyleGuo, Y., Jia, Y., Wu, Y., & Zhu, X. (2025). Longitudinal Bending Stiffness Analysis of Composite Carbon Plates and Shoe Sole, Based on Three-Point Bending Test. Applied Sciences, 15(5), 2785. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15052785





