Three-Dimensional Microstructure and Structural Representative Volume Element of the Intact and Remolded Loess
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. CT Scanning and 3D Reconstruction
2.3. Cube Partition
2.4. Data Processing
3. Results
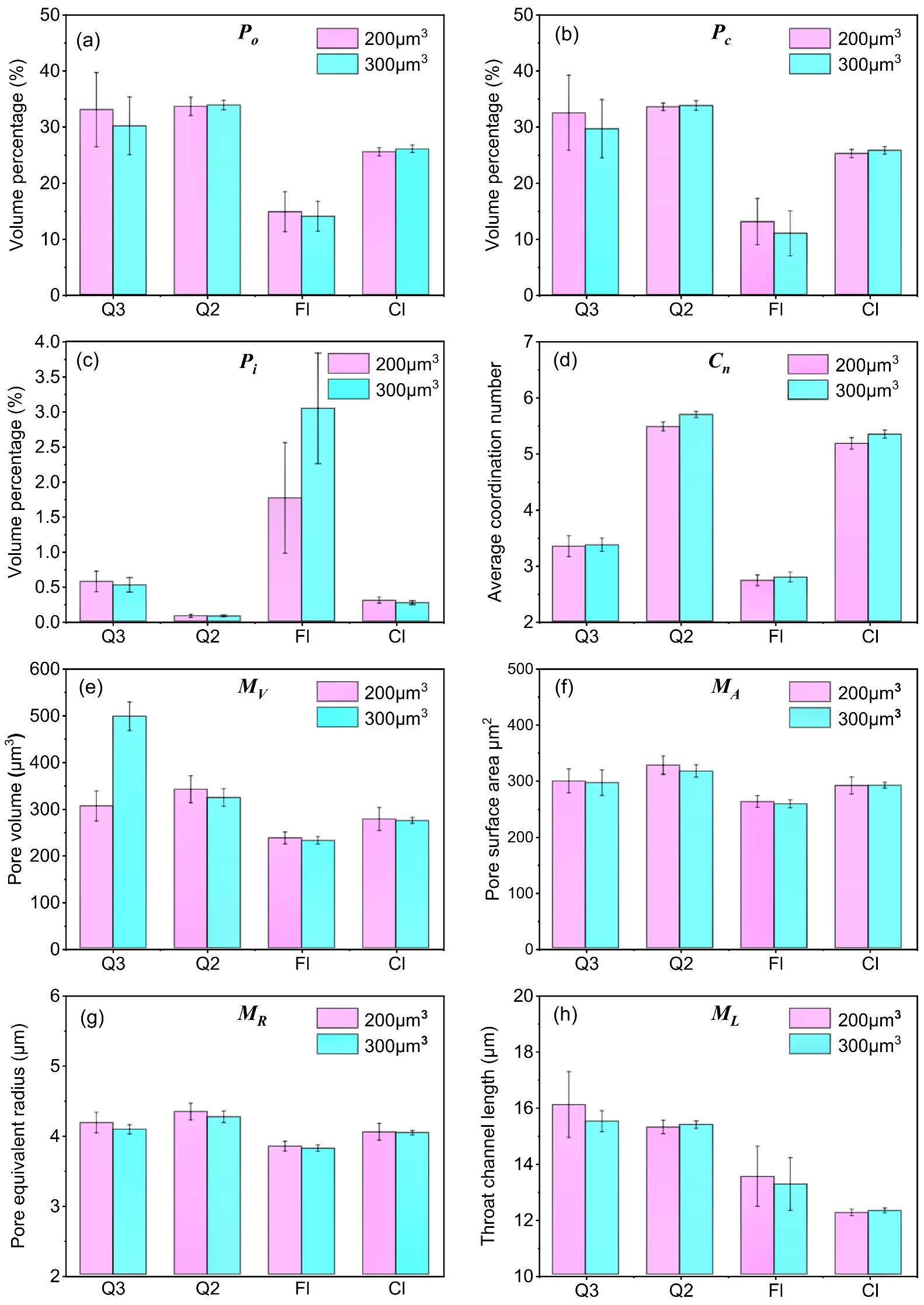
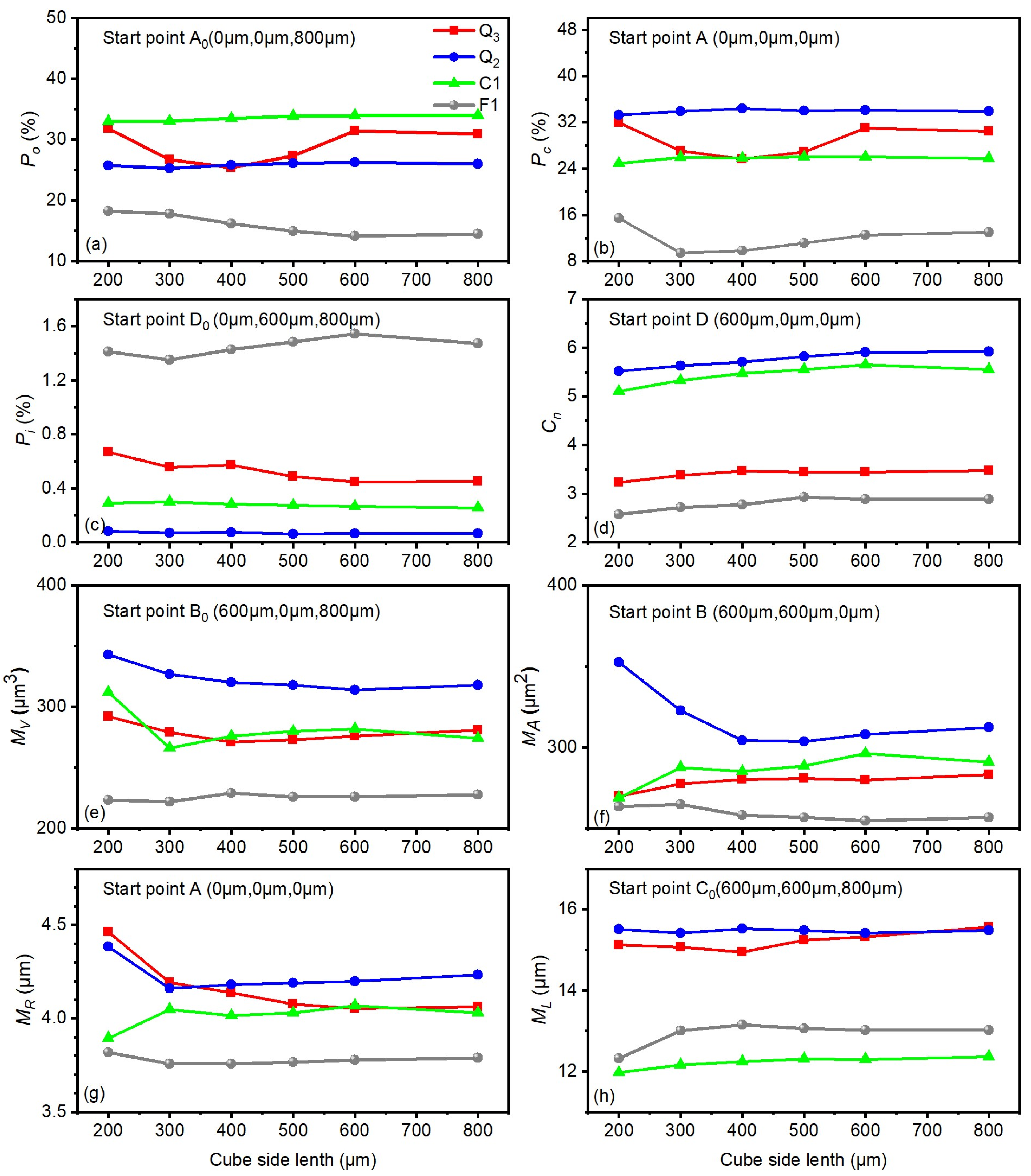
3.1. Pore Parameters’ Statistical Features of Cubes with Different Sizes
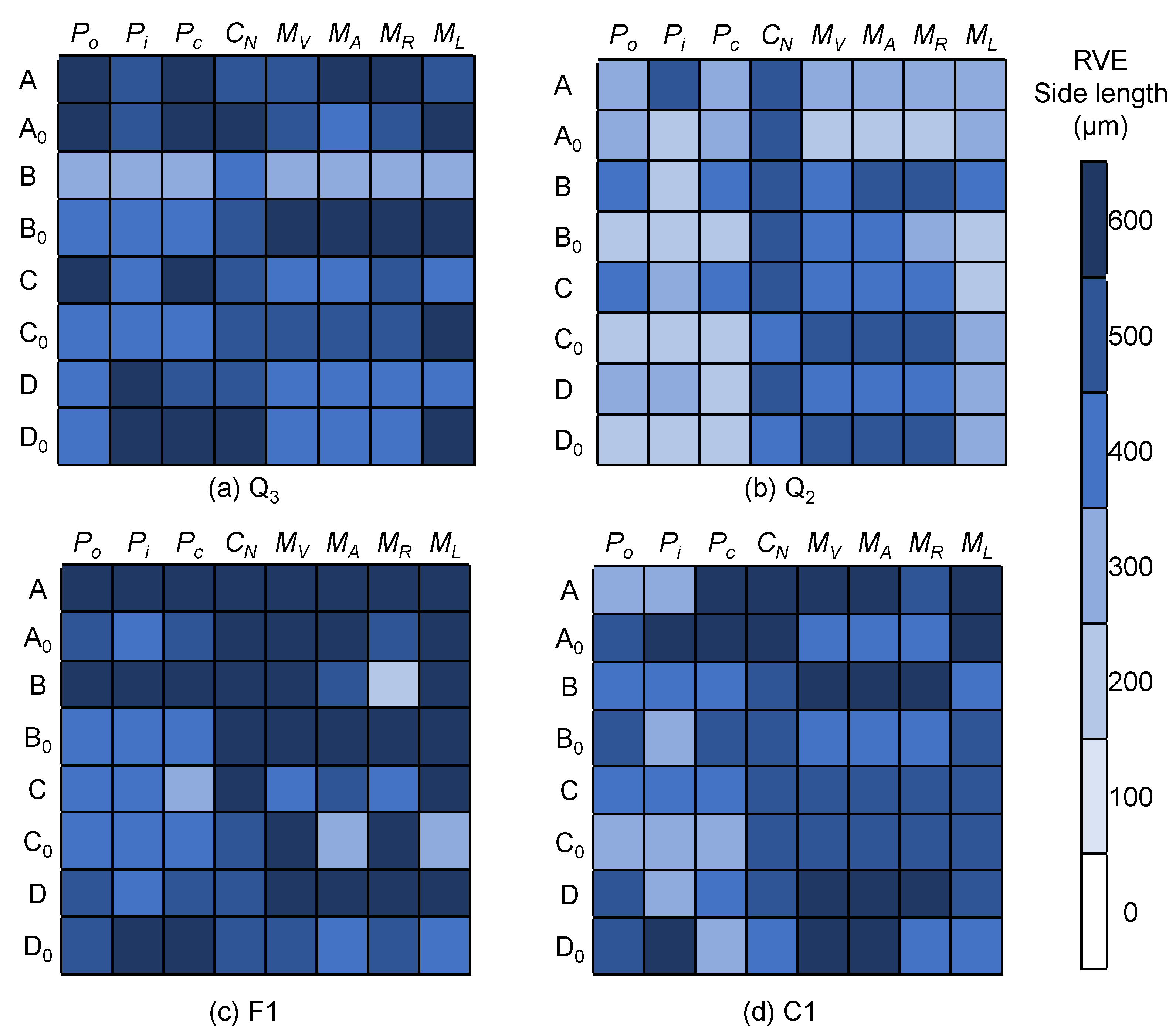
3.2. Determination of the REV Size
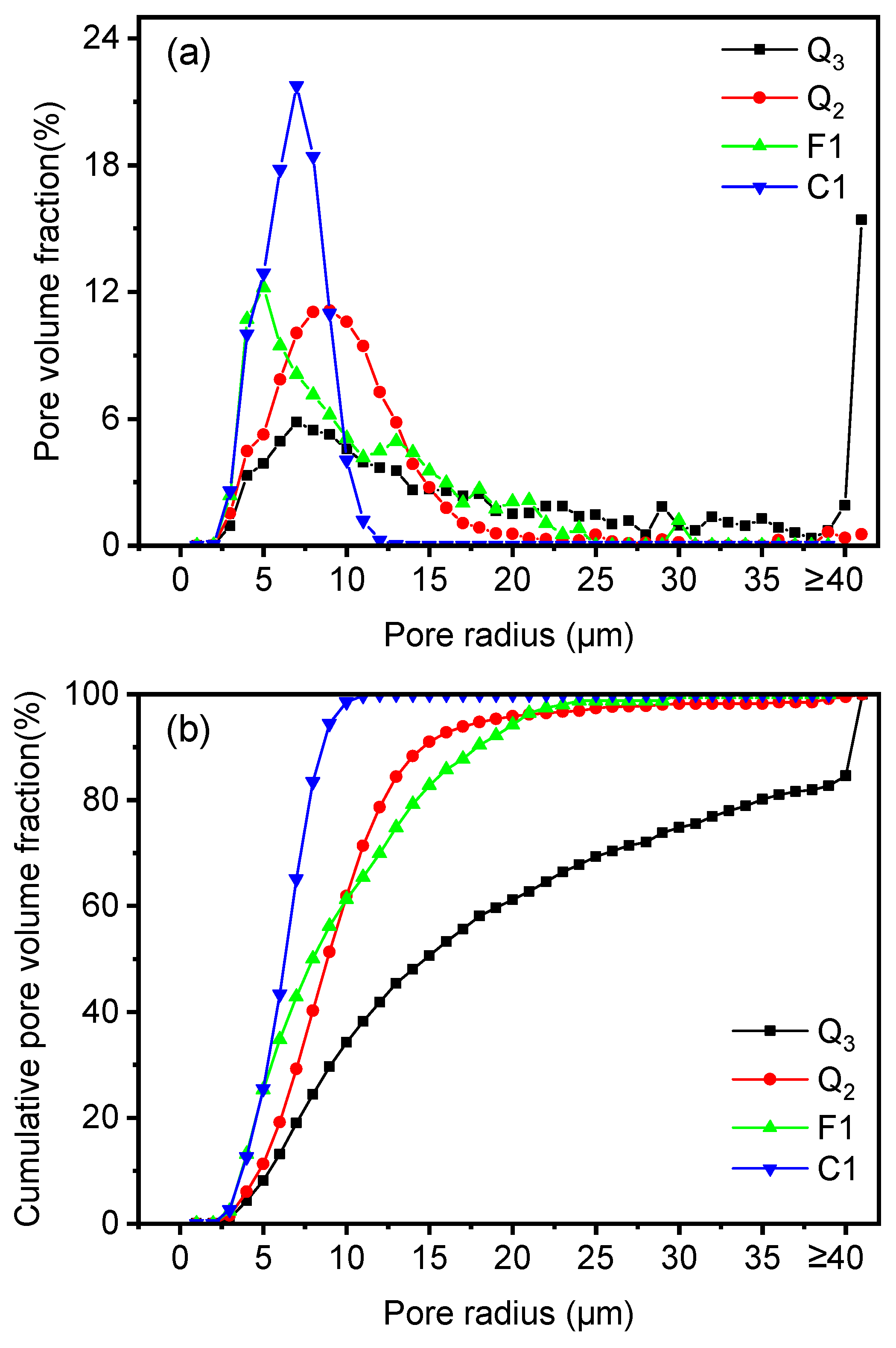
3.3. Pore Characteristics of the Intact and Remolded Loess
3.3.1. Pore Size Distribution
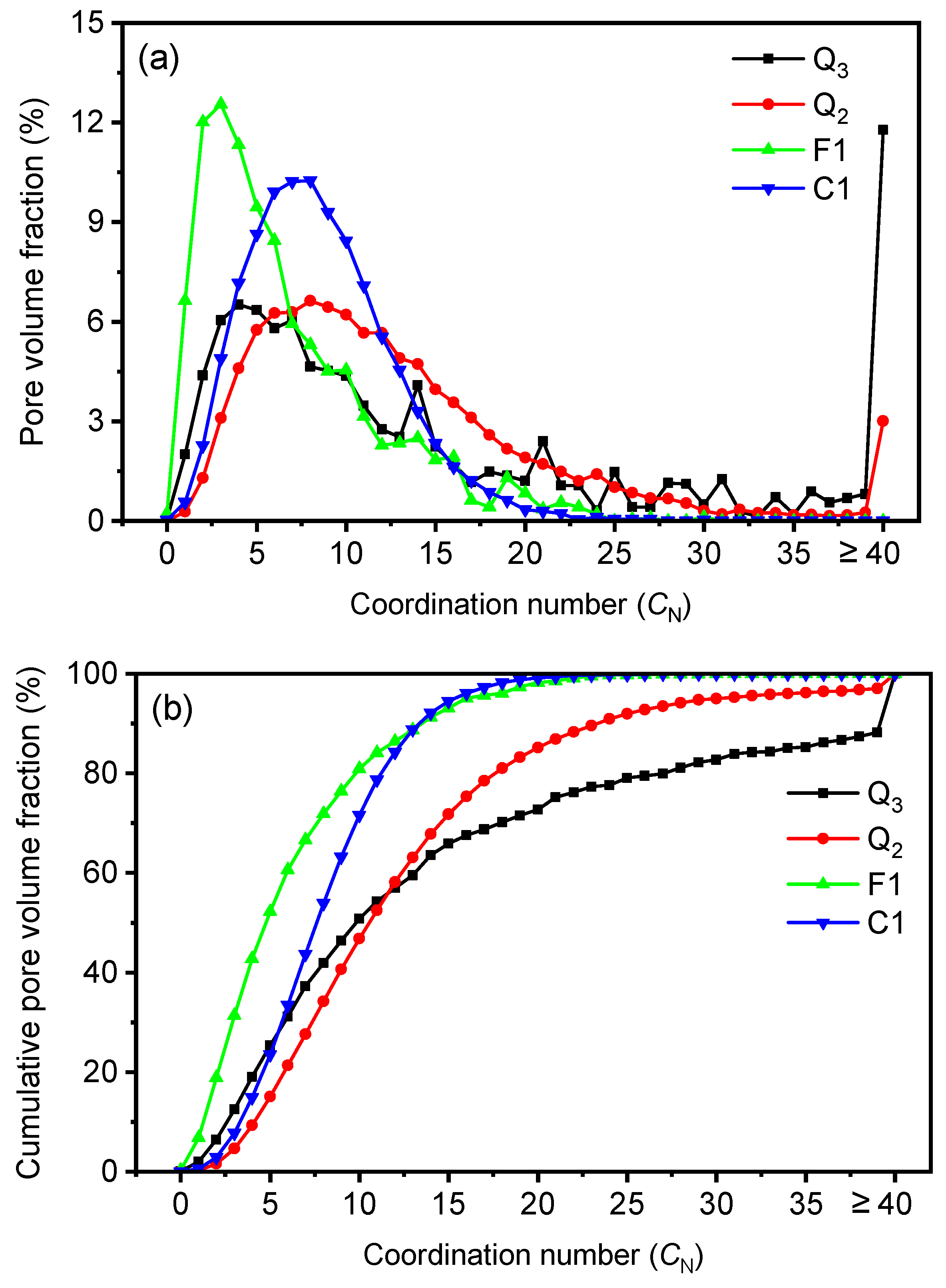
3.3.2. Pore Connectivity
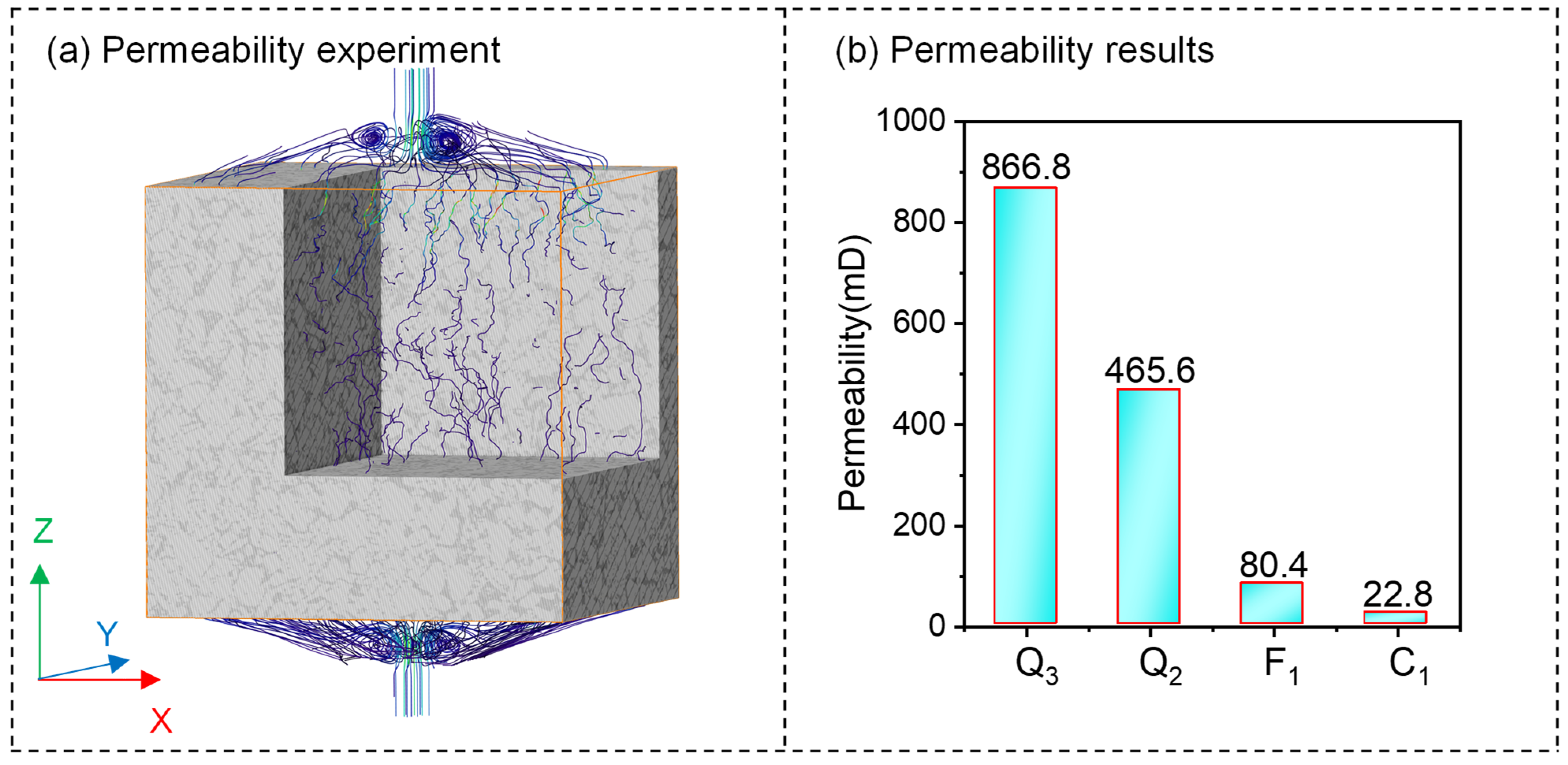
3.3.3. Permeability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- A robust workflow for determining the representative volume elements (RVE) of intact and remolded loess is introduced. In general, the intact loess has the smallest RVE size. 600 μm × 600 μm × 600 μm cube is the smallest size to analyze the 3D microstructure;
- Intact loess has more overhead pores, contributing to the formation of pore channels. Additionally, intact loess displays a more uniform microstructure and superior connectivity compared to remolded specimens;
- Remolded loess is much more compacted than intact loess, with the loess from the MBCC project showing greater uniformity than that from the GMRL project;
- The significant difference in the microstructure of intact and remolded loess is attributed to the substantial variations in their formation processes.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Derbyshire, E. Geological hazards in loess terrain, with particular reference to the loess regions of China. Earth Sci. Rev. 2001, 54, 231–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. A review of shear and tensile strengths of the Malan Loess in China. Eng. Geol. 2018, 236, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.H.; Peng, J.B.; Wang, Q.Y.; Zhuang, J.Q.; Zhang, F.Y. The mechanisms of a loess landslide triggered by diversion-based irrigation: A case study of the South Jingyang Platform, China. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2019, 78, 4945–4963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.S. Loess and Environment; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- He, C.X. How to develop modern agriculture on the basis of Gully management and land reclamation in Yan’an City. J. Yan’an Univ. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2013, 35, 60–63. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Qian, H.; Wu, J. Environment: Accelerate research on land creation. Nature 2013, 510, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Qi, S.; Guo, S.; Huang, Q.; Hou, X.; Zhang, L. Investigation on the Deformation and Failure Patterns of Loess Cut Slope Based on the Unsaturated Triaxial Test in Yan’an, China. J. Earth Sci. 2024, 35, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.W.; Hou, X.K.; Yu, Y.T.; Zhang, Y.G.; Hu, X.; Zhang, L.X.; Li, Z.Q.; Guo, S.F.; Zhang, F.Y.; Li, T.L.; et al. Collapse and subsidence mechanism of compacted loess and suitability of mountain bulldozing and city creation projects in the Loess Plateau of China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2023, 68, 1844–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.S.; Li, Y.R. Engineering philosophy and design scheme of gully land consolidation in Loess Plateau. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2017, 33, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, X.K.; Qi, S.W.; Yu, Y.T.; Zheng, J.G. Long-Term Settlement Characterization of High-Filling Foundation in the Mountain Excavation and City Construction Area of the Yan’an New District, China. J. Earth Sci. 2023, 34, 1908–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, C.H.; Dijkstra, T.; Wasowski, J.; Meng, X. Loess geohazards research in China: Advances and challenges for mega engineering projects. Eng. Geol. 2019, 251, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Qi, S.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Hou, X.; Ma, L.; Zou, Y.; Guo, S.; Peng, J. A comparative study on the physical properties of natural sedimentary loess and manual filling compacted loess. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.N.; Qi, S.W.; Zheng, B.W.; Guo, S.; Huang, Q.; Yu, X. Farming Influence on Physical-Mechanical Properties and Microstructural Characteristics of Backfilled Loess Farmland in Yan’an, China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng CW, W.; Kaewsong, R.; Zhou, C.; Alonso, E.E. Small strain shear moduli of unsaturated natural and compacted loess. Géotechnique 2017, 67, 646–651. [Google Scholar]
- Ng CW, W.; Mu, Q.Y.; Zhou, C. Effects of specimen preparation method on the volume change of clay under cyclic thermal loads. Géotechnique 2018, 69, 146–150. [Google Scholar]
- Ng CW, W.; Sadeghi, H.; Jafarzadeh, F.; Sadeghi, M.; Zhou, C.; Baghbanrezvan, S. Effect of microstructure on shear strength and dilatancy of unsaturated loess at high suctions. Can. Geotech. J. 2019, 57, 221–235. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Li, T.; Zhao, C.; Hou, X.; Li, P.; Zhang, Y. A study on the effect of pore and particle distributions on the soil water characteristic curve of compacted loess soil. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Qi, S.; Ma, L.; Guo, S.; Li, Z.; Li, G. Three-dimensional pore characterization of intact loess and compacted loess with micro-scale computed tomography and mercury intrusion porosimetry. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, X.; Qi, S.; Li, T.; Guo, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L. Microstructure and soil-water retention behavior of compacted and intact silt loess. Eng. Geol. 2020, 277, 105814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.K.; Qi, S.W.; Li, Y.; Liu, F.C.; Li, T.L.; Li, H. Hydraulic conductivity over a wide suction range of loess with different dry densities. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2024, 17, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.J.; Zhang, F.; Hu, H.; Cui, Y.; Peng, J. Structural characterization of natural loess and compacted loess under triaxial tests. Eng. Geol. 2014, 181, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Pan, Z.; Xiao, T.; Wang, J. Effects of molding water content and compaction degree on the microstructure and permeability of compacted loess. Acta Geotech. 2023, 18, 921–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Castelblanco, J.A.; Pereira, J.M.; Delage, P.; Cui, Y.J. The water retention properties of natural unsaturated loess from northern France. Géotechnique 2012, 62, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Zhang, H.; Tan, Y. Collapse behavior and microstructural alteration of remolded loess under graded wetting tests. Eng. Geol. 2018, 233, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Li, P.; Pan, Z.; Hou, Y.; Wang, J. Relationship between water retention capacity and pore-size distribution of compacted loess. J. Soils Sediments 2022, 22, 3151–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.L.; Zhang, D.F.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.B. Compression and wetting deformation behavior of intact loess under isotropic stresses. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2017, 36, 1736–1747. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G. Experimental study on collapsibility of compacted loess. Water Resour. Hydropower Eng. 1986, 06, 39–43. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Rogers CD, F.; Dijkstra, T.A.; Smalley, I.J. Hydroconsolidation and subsidence of loess: Studies from China, Russia, North America, and Europe: In memory of Jan Sajgalik. Eng. Geol. 1994, 37, 83–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, E.E.; Pinyol, N.M.; Gens, A. Compacted soil behavior: Initial state, structure, and constitutive modeling. Géotechnique 2013, 63, 463–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanit, T.; Forest, S.; Galliet, I.; Mounoury, V.; Jeulin, D. Determination of the size of the representative volume element for random composites: Statistical and numerical approach. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2003, 40, 3647–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, E. A microstructural insight into compacted clayey soils and their hydraulic properties. Eng. Geol. 2013, 165, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delage, P.; Audiguier, M.; Cui YJ Howat, M.D. Microstructure of compacted silt. Can. Geotech. J. 1996, 33, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koliji, A.; Vulliet, L.; Laloui, L. Structural characterization of unsaturated aggregated soil. Can. Geotech. J. 2010, 47, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, E.; Simms, P.H. Microstructure investigation in unsaturated soils: A review with special attention to the contribution of mercury intrusion porosimetry and environmental scanning electron microscopy. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2008, 26, 705–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.P.; Yan, Y.J. Influence of structure on shear characteristics of the unsaturated loess in Lanzhou, China. Eng. Geol. 2014, 168, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assallay, A.M.; Rogers CD, F.; Smalley, I.J. Formation and collapse of metastable particle packings and open structures in loess deposits. Eng. Geol. 1997, 48, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.D.; Li, P.; Ma, Y.; Vanapalli, S.K. Evolution of pore-size distribution of intact loess and remolded loess due to consolidation. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 1226–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.T.; Fan, W.; Yuan, W.; Wei, Y.N.; Yu, B. Three-dimensional pore network characterization of loess and paleosol stratigraphy from South Jingyang Plateau, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Shao, S. Can X-ray computed tomography (CT) be used to determine the pore-size distribution of intact loess? Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; He, S.; Deng, X.; Xu, Y. Characterization of macropore structure of Malan loess in NW China based on 3D pipe models constructed by using computed tomography technology. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2018, 154, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.N.; Fan, W.; Yu, B.; Deng LS Wei, T. Characterization and evolution of three-dimensional microstructure of Malan loess. Catena 2020, 192, 104585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.N.; Fan, W.; Yu, N.; Deng, L.S.; Wei, T. Permeability of loess from the South Jingyang Plateau under different consolidation pressures in terms of the three-dimensional microstructure. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2020, 79, 4841–4857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Fan, W.; Fan, J.H.; Dijkstra, T.A.; Wei, Y.N.; Wei, T.T. X-ray micro-computed tomography (μ-CT) for 3D characterization of particle kinematics representing water-induced loess micro-fabric collapse. Eng. Geol. 2020, 279, 105895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Fan, W.; Dijkstra, T.A.; Wei, Y.N.; Deng, L.S. Heterogeneous evolution of pore structure during loess collapse: Insights from X-ray micro-computed tomography. Catena 2021, 201, 105206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Wang, J. 3D quantitative shape analysis on form, roundness, and compactness with μCT. Powder Technol. 2016, 291, 262–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargmann, S.; Klusemann, B.; Markmann, J.; Schnabel, J.E.; Schneider, K.; Soyarslan, C.; Wilmers, J. Generation of 3D representative volume elements for heterogeneous materials: A review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2018, 96, 322–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, J.P.; Liu, C.; Huang, R.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y. Determination of geometrical and structural representative volume elements at the Baihetan dam site. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2012, 45, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, Y.; Wu, K. Imaged-based fractal characterization of micro-fracture structure in coal. Fuel 2019, 239, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Yao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Qiu, F. Analyses of representative elementary volume for coal using X-ray μ-CT and FIB-SEM and its application in permeability prediction model. Fuel 2019, 254, 115563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Sun, X.; Li, D.; Ryu, S.; Khaleel, M.A. Mechanism-based representative volume elements (RVEs) for predicting property degradations in multiphase materials. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2013, 68, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, A.; Hohenbrink, T.L.; Iden, S.C.; van Genuchten, M.T.; Durner, W. Prediction of the absolute hydraulic conductivity function from soil water retention data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2023, 27, 1565–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Vanapalli, S.; Li, T. Review of collapse triggering mechanism of collapsible soils due to wetting. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2016, 8, 256–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilek, V. The loess deposits of the Bohemian Massif: Silt provenance, palaeometeorology, and loessification processes. Quat. Int. 2001, 76, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; He, S.; Aydin, A. Wetting-driven formation of present-day loess structure. Geoderma 2020, 377, 114564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, L.; Xu, L.; Baudet, B.A.; Gao, C.; Huang, C. The structure degradation of silty loess induced by long-term water seepage. Eng. Geol. 2020, 272, 105634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

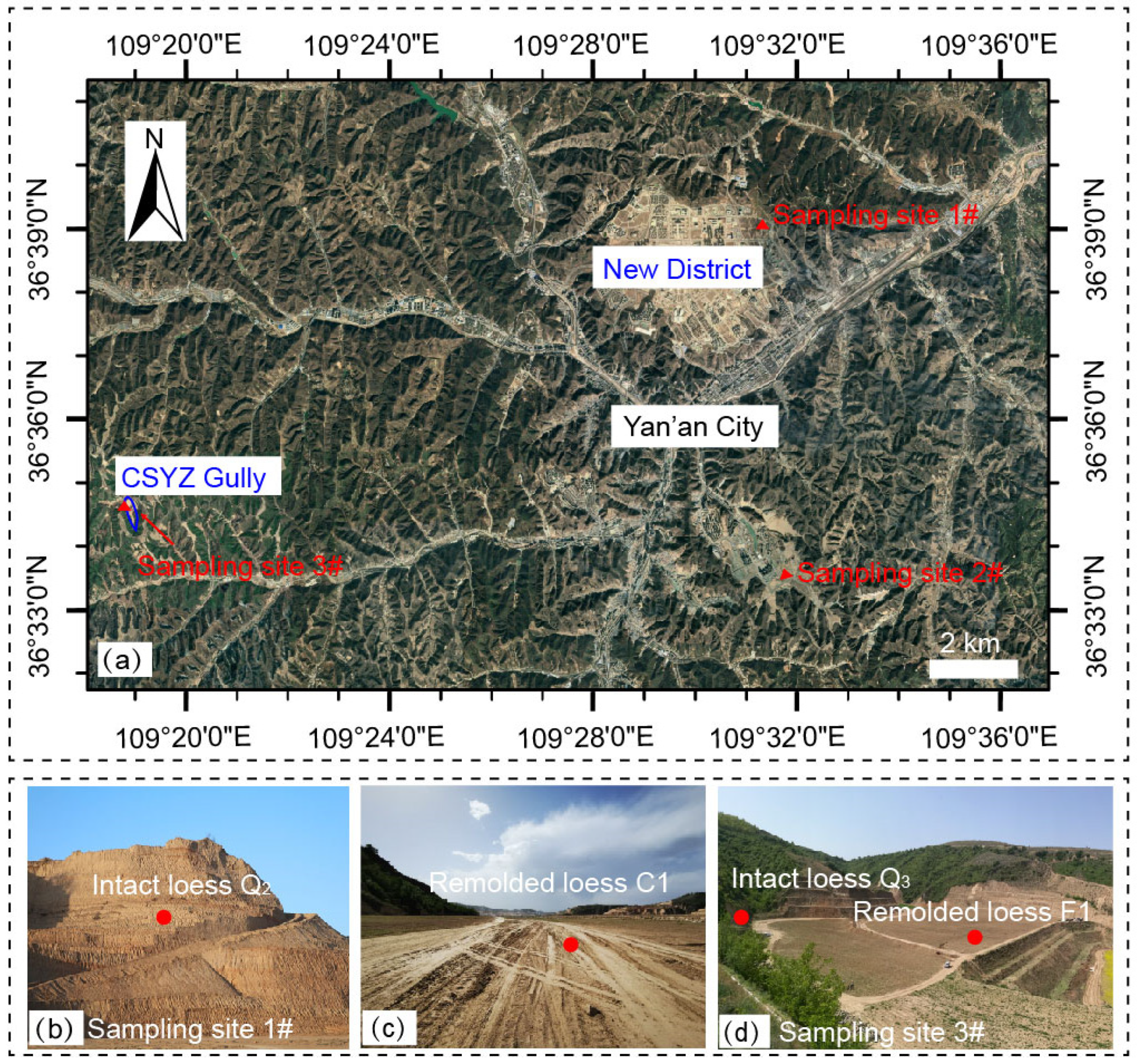

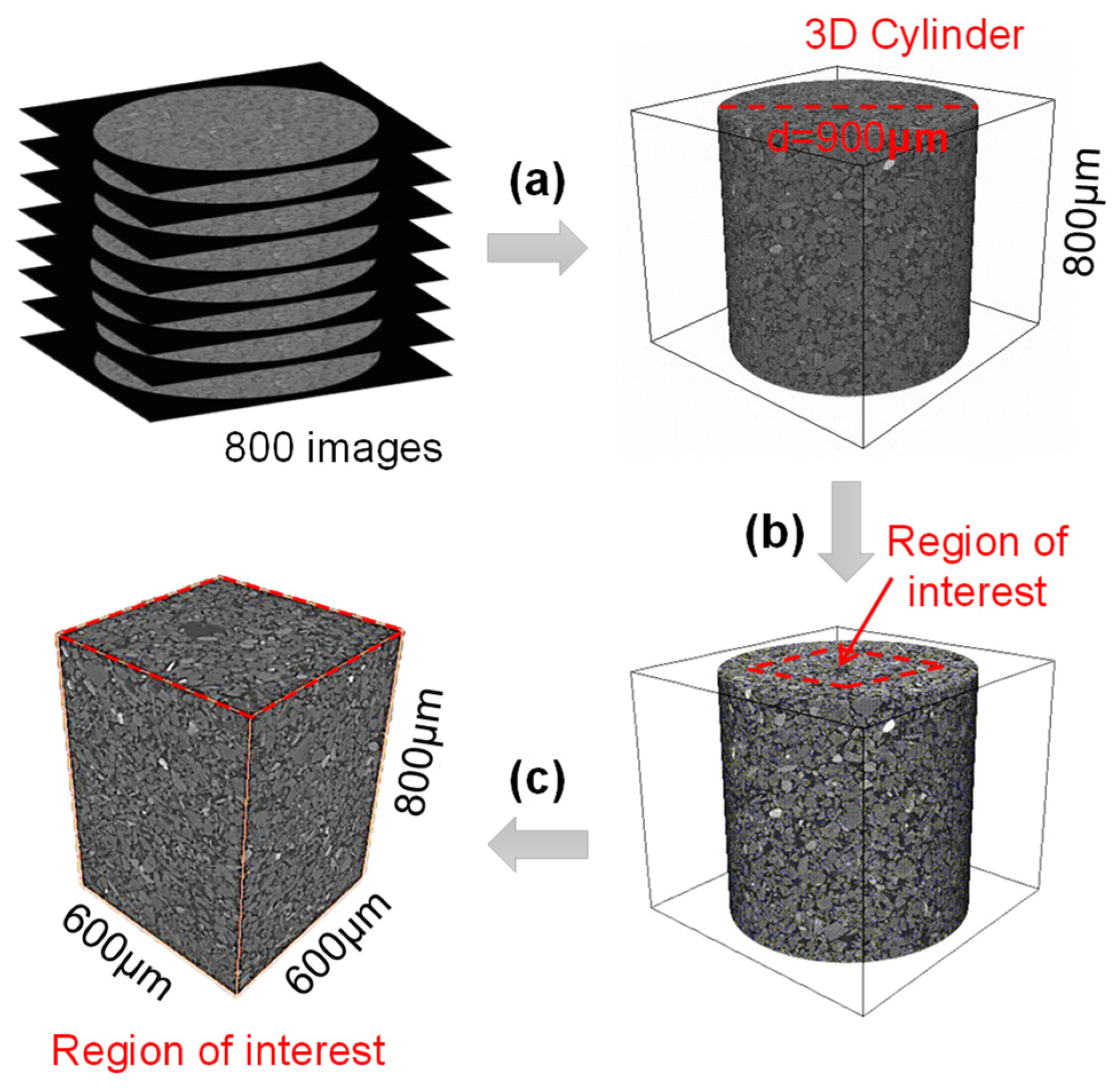
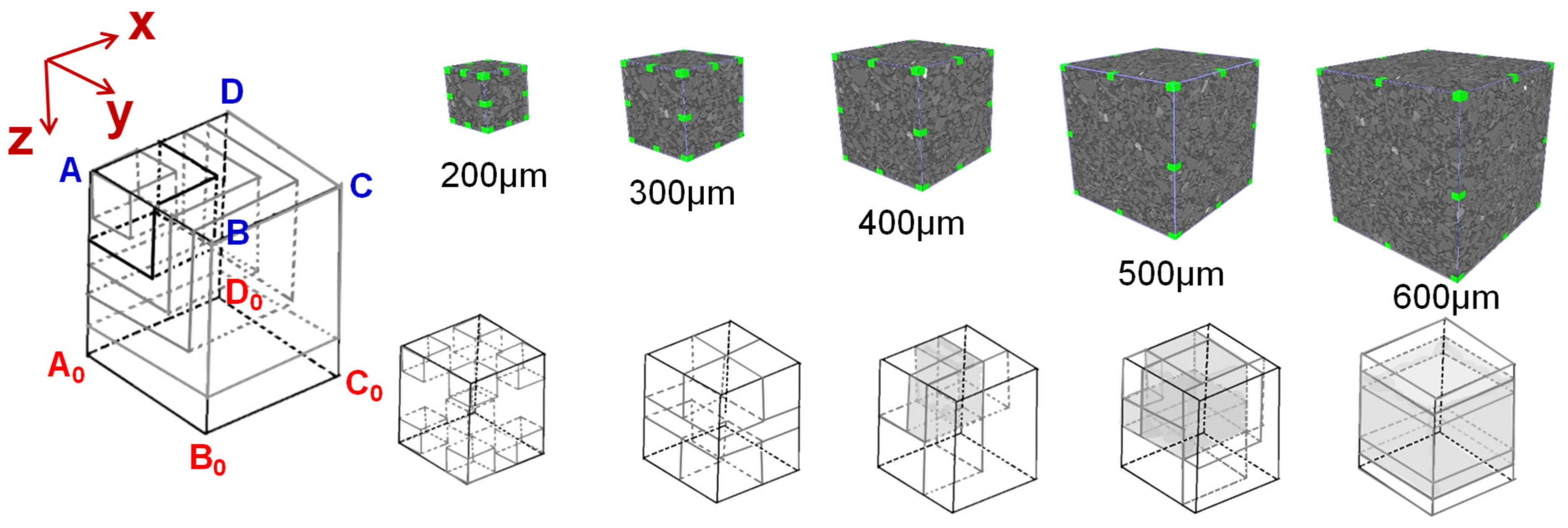
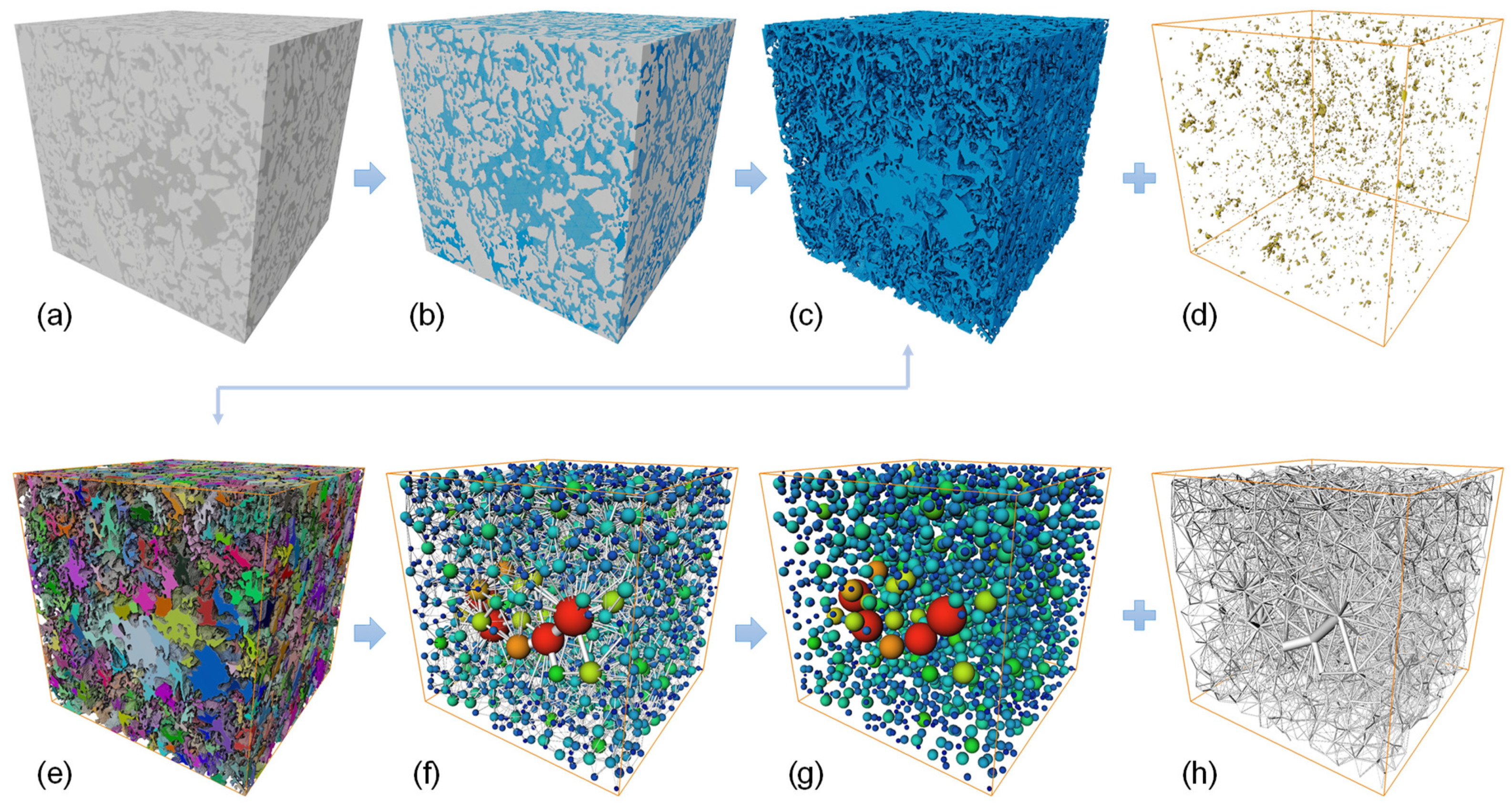


| Specimens | Dry Density (g/cm3) | In-Situ Water Content (%) | Void Ratio | Atterberg Limits | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plastic Limit | Liquid Limit | Plastic Index | ||||
| Q3 | 1.37 | 9.7% | 0.97 | 17.8 | 27.6 | 9.8 |
| Q2 | 1.54 | 13.9% | 0.75 | 18.5 | 28.5 | 10.0 |
| F1 | 1.61 | 16.5% | 0.68 | 17.4 | 26.8 | 9.4 |
| C1 | 1.66 | 13.9% | 0.63 | 18.5 | 28.5 | 10.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, L.; Zhang, L.; Hou, X.; Guo, S.; Qi, S. Three-Dimensional Microstructure and Structural Representative Volume Element of the Intact and Remolded Loess. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3120. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063120
Ma L, Zhang L, Hou X, Guo S, Qi S. Three-Dimensional Microstructure and Structural Representative Volume Element of the Intact and Remolded Loess. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(6):3120. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063120
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Lina, Linxin Zhang, Xiaokun Hou, Songfeng Guo, and Shengwen Qi. 2025. "Three-Dimensional Microstructure and Structural Representative Volume Element of the Intact and Remolded Loess" Applied Sciences 15, no. 6: 3120. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063120
APA StyleMa, L., Zhang, L., Hou, X., Guo, S., & Qi, S. (2025). Three-Dimensional Microstructure and Structural Representative Volume Element of the Intact and Remolded Loess. Applied Sciences, 15(6), 3120. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063120






