Augmented Reality, Virtual Reality, and Intelligent Tutoring Systems in Education and Training: A Systematic Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
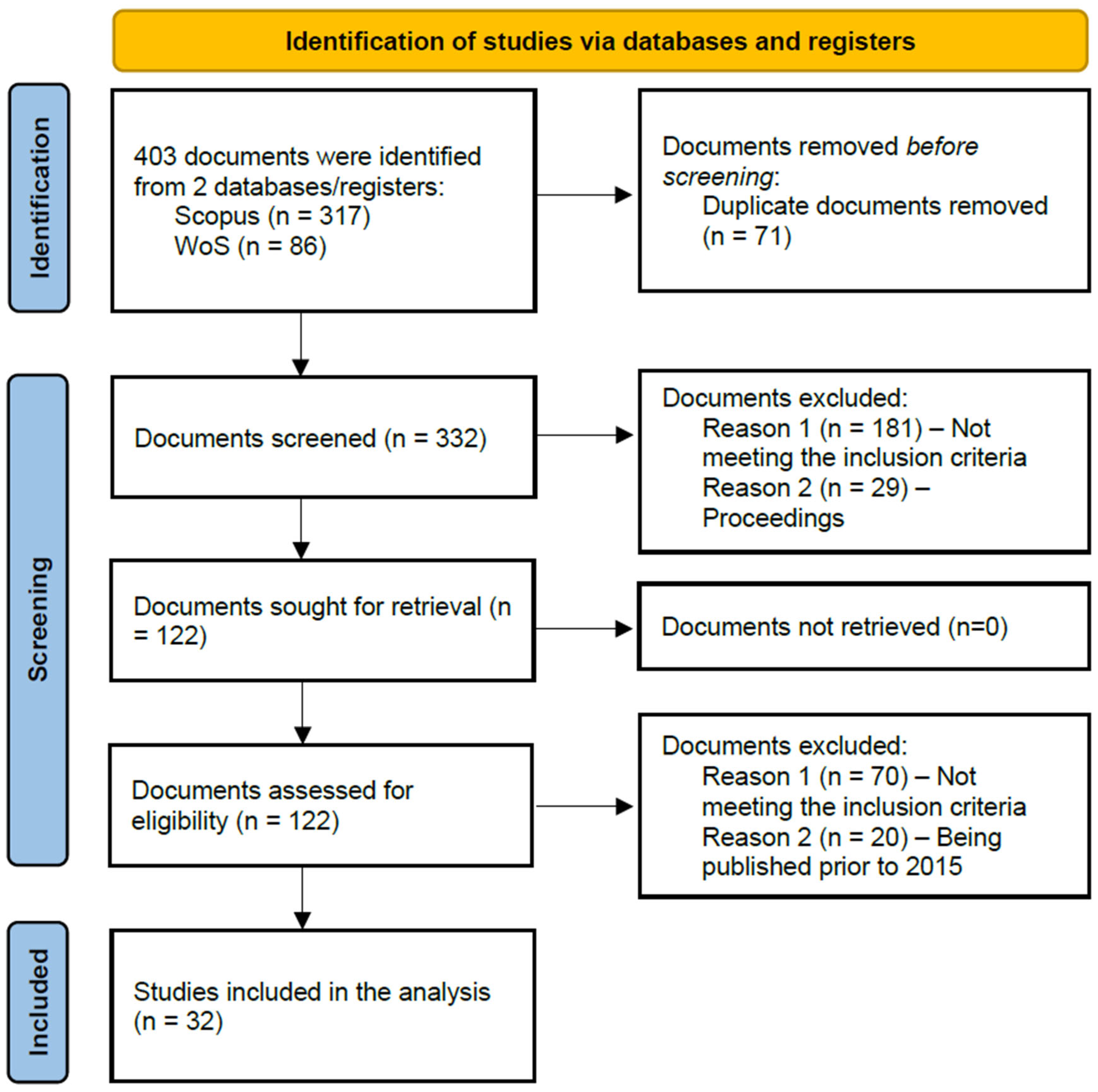
2. Materials and Methods
3. Result Analysis
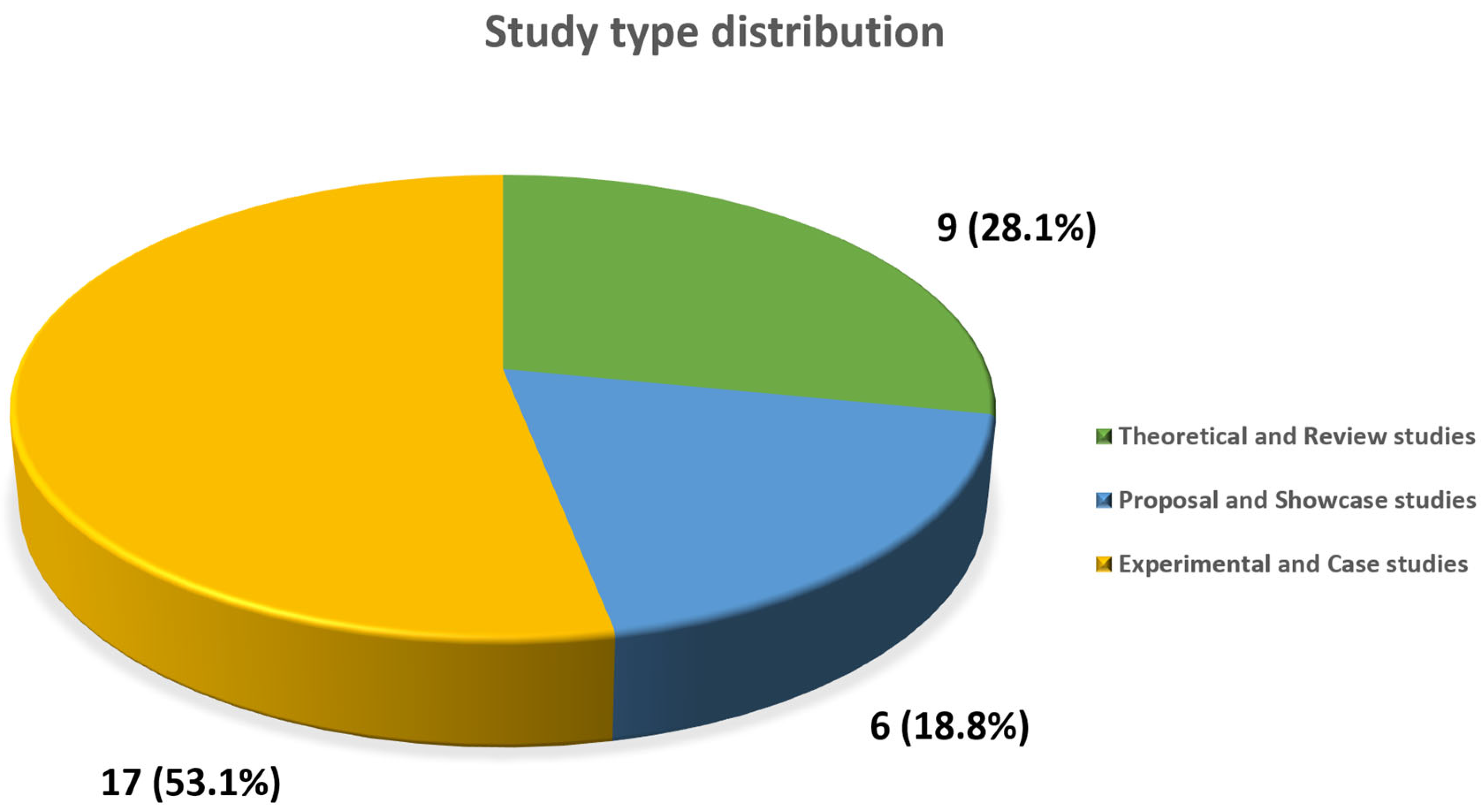
3.1. Document Collection Analysis
3.2. Theoretical and Review Study Analysis
3.3. Proposal and Showcase Studies Analysis
3.4. Experimental and Case Studies Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Synthesis of Outcomes
4.2. Thematic, Trend, and Topic Analysis
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mustafa, M.Y.; Tlili, A.; Lampropoulos, G.; Huang, R.; Jandrić, P.; Zhao, J.; Salha, S.; Xu, L.; Panda, S.; Kinshuk; et al. A systematic review of literature reviews on artificial intelligence in education (AIED): A roadmap to a future research agenda. Smart Learn. Environ. 2024, 11, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedro, F.; Subosa, M.; Rivas, A.; Valverde, P. Artificial Intelligence in Education: Challenges and Opportunities for Sustainable Development. 2019. Available online: https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000366994 (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Kaplan, A.; Haenlein, M. Rulers of the world, unite! The challenges and opportunities of artificial intelligence. Bus. Horiz. 2020, 63, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayeni, O.O.; Hamad, N.M.A.; Chisom, O.N.; Osawaru, B.; Adewusi, O.E. AI in education: A review of personalized learning and educational technology. GSC Adv. Res. Rev. 2024, 18, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampropoulos, G. Intelligent virtual reality and augmented reality technologies: An overview. Future Internet 2025, 17, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, F.; Chen, Y.; Moore, R.L.; Westine, C.D. Systematic review of adaptive learning research designs, context, strategies, and technologies from 2009 to 2018. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2020, 68, 1903–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, P. Adaptive learning. ELT J. 2016, 70, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattie, J. Visible Learning: A Synthesis of over 800 Meta-Analyses Relating to Achievement; Routledge: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bernacki, M.L.; Greene, M.J.; Lobczowski, N.G. A systematic review of research on personalized learning: Personalized by whom, to what, how, and for what purpose(s)? Educ. Psychol. Rev. 2021, 33, 1675–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemshack, A.; Spector, J.M. A systematic literature review of personalized learning terms. Smart Learn. Environ. 2020, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavinasab, E.; Zarifsanaiey, N.; Niakan Kalhori, S.R.; Rakhshan, M.; Keikha, L.; Ghazi Saeedi, M. Intelligent tutoring systems: A systematic review of characteristics, applications, and evaluation methods. Interact. Learn. Environ. 2021, 29, 142–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keleş, A.; Ocak, R.; Keleş, A.; Gülcü, A. ZOSMAT: Web-based intelligent tutoring system for teaching–learning process. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 1229–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shute, V.J.; Zapata-Rivera, D. Adaptive technologies. ETS Res. Rep. Ser. 2007, 2007, i-34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graesser, A.C.; Conley, M.W.; Olney, A. Intelligent tutoring systems. In APA Educational Psychology Handbook, Vol 3: Application to Learning and Teaching; American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; pp. 451–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Adesope, O.O.; Nesbit, J.C.; Liu, Q. Intelligent tutoring systems and learning outcomes: A meta-analysis. J. Educ. Psychol. 2014, 106, 901–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenbergen-Hu, S.; Cooper, H. A meta-analysis of the effectiveness of intelligent tutoring systems on college students’ academic learning. J. Educ. Psychol. 2014, 106, 331–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graesser, A.C.; Hu, X.; Sottilare, R. Intelligent tutoring systems. In International Handbook of the Learning Sciences; American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; pp. 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wijekumar, K.; Ramirez, G.; Hu, X.; Irey, R. The effectiveness of intelligent tutoring systems on k-12 students’ reading comprehension: A meta-analysis. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2019, 50, 3119–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conati, C. Intelligent tutoring systems: New challenges and directions. In Proceedings of the Twenty-First International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Pasadena, CA, USA, 14–16 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, J.R.; Boyle, C.F.; Reiser, B.J. Intelligent tutoring systems. Science 1985, 228, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleeman, D.; Brown, J.S. Intelligent Tutoring Systems; Academic Press: London, UK, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Kulik, J.A. Meta-analytic studies of findings on computer-based instruction. In Technology Assessment in Education and Training; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc.: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1994; pp. 9–33. [Google Scholar]
- VanLehn, K. The relative effectiveness of human tutoring, intelligent tutoring systems, and other tutoring systems. Educ. Psychol. 2011, 46, 197–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, S.; Mokbel, B.; Hammer, B.; Pinkwart, N. Learning feedback in intelligent tutoring systems. KI Künstliche Intell. 2015, 29, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulik, J.A.; Fletcher, J.D. Effectiveness of intelligent tutoring systems. Rev. Educ. Res. 2016, 86, 42–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas, S.; Rebolledo-Mendez, G.; Liarokapis, F.; Magoulas, G.; Poulovassilis, A. Learning as immersive experiences: Using the four-dimensional framework for designing and evaluating immersive learning experiences in a virtual world. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2010, 41, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrington, J.; Reeves, T.C.; Oliver, R. Immersive learning technologies: Realism and online authentic learning. J. Comput. High. Educ. 2007, 19, 80–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampropoulos, G.; Kinshuk. Virtual reality and gamification in education: A systematic review. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2024, 72, 1691–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakus, M.; Ersozlu, A.; Clark, A.C. Augmented reality research in education: A bibliometric study. EURASIA J. Math. Sci. Technol. Educ. 2019, 15, em1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Sánchez, M.A.; Palos-Sánchez, P.R.; Folgado-Fernández, J.A. Systematic literature review and bibliometric analysis on virtual reality and education. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2023, 28, 155–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lampropoulos, G. Combining artificial intelligence with augmented reality and virtual reality in education: Current trends and future perspectives. Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2025, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, R.T. A survey of augmented reality. Presence Teleoperators Virtual Environ. 1997, 6, 355–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K. Augmented reality in education and training. TechTrends 2012, 56, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipresso, P.; Giglioli, I.A.C.; Raya, M.A.; Riva, G. The past, present, and future of virtual and augmented reality research: A network and cluster analysis of the literature. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmigniani, J.; Furht, B. Augmented reality: An overview. In Handbook of Augmented Reality; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 3–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmigniani, J.; Furht, B.; Anisetti, M.; Ceravolo, P.; Damiani, E.; Ivkovic, M. Augmented reality technologies, systems and applications. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2011, 51, 341–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, W.R.; Craig, A.B. Understanding Virtual Reality: Interface, Application, and Design. Morgan Kaufmann: Burlington, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Burdea, G.C.; Coiffet, P. Virtual Reality Technology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Anthes, C.; Garcia-Hernandez, R.J.; Wiedemann, M.; Kranzlmuller, D. State of the art of virtual reality technology. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 5–12 March 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biocca, F.; Delaney, B. Immersive virtual reality technology. Commun. Age Virtual Real. 1995, 15, 127–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blascovich, J.; Bailenson, J. Infinite Reality: Avatars, Eternal Life, New Worlds, and the Dawn of the Virtual Revolution; William Morrow & Co: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lampropoulos, G. Augmented reality and artificial intelligence in education: Toward immersive intelligent tutoring systems. In Augmented Reality and Artificial Intelligence; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampropoulos, G.; Keramopoulos, E.; Diamantaras, K.; Evangelidis, G. Augmented reality and gamification in education: A systematic literature review of research, applications, and empirical studies. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzón, J. An overview of Twenty-Five years of augmented reality in education. Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2021, 5, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila-Garzon, C.; Bacca-Acosta, J.; Kinshuk; Duarte, J.; Betancourt, J. Augmented reality in education: An overview of Twenty-Five years of research. Contemp. Educ. Technol. 2021, 13, ep302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akçayır, M.; Akçayır, G. Advantages and challenges associated with augmented reality for education: A systematic review of the literature. Educ. Res. Rev. 2017, 20, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Liu, X.; Cheng, W.; Huang, R. A review of using augmented reality in education from 2011 to 2016. In Innovations in Smart Learning; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radianti, J.; Majchrzak, T.A.; Fromm, J.; Wohlgenannt, I. A systematic review of immersive virtual reality applications for higher education: Design elements, lessons learned, and research agenda. Comput. Educ. 2020, 147, 103778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavanagh, S.; Luxton-Reilly, A.; Wuensche, B.; Plimmer, B. A systematic review of virtual reality in education. Themes Sci. Technol. Educ. 2017, 10, 85–119. [Google Scholar]
- Freina, L.; Ott, M. A literature review on immersive virtual reality in education: State of the art and perspectives. In Proceedings of the International Scientific Conference Elearning and Software for Education, Bucharest, Romania, 23–24 April 2015; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.-C.; Huang, A.Y.Q.; Lu, O.H.T. Artificial intelligence in intelligent tutoring systems toward sustainable education: A systematic review. Smart Learn. Environ. 2023, 10, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Int. J. Surg. 2021, 88, 105906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusenbauer, M.; Haddaway, N.R. Which academic search systems are suitable for systematic reviews or meta-analyses? Evaluating retrieval qualities of google scholar, PubMed, and 26 other resources. Res. Synth. Methods 2020, 11, 181–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donthu, N.; Kumar, S.; Mukherjee, D.; Pandey, N.; Lim, W.M. How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 133, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aria, M.; Cuccurullo, C. Bibliometrix: An r-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J. Informetr. 2017, 11, 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellegaard, O.; Wallin, J.A. The bibliometric analysis of scholarly production: How great is the impact? Scientometrics 2015, 105, 1809–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eck, N.J.v.; Waltman, L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blei, D.M.; Ng, A.Y.; Jordan, M.I. Latent dirichlet allocation. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2003, 3, 993–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongeon, P.; Paul-Hus, A. The journal coverage of web of science and scopus: A comparative analysis. Scientometrics 2015, 106, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Liu, W. A tale of two databases: The use of web of science and scopus in academic papers. Scientometrics 2020, 123, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampropoulos, G.; Evangelidis, G. Learning analytics and educational data mining in augmented reality, virtual reality, and the metaverse: A systematic literature review, content analysis, and bibliometric analysis. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, S.; Dakua, S.P.; El Ansari, W.; Aboumarzouk, O.; Al Ansari, A. Novel applications of deep learning in surgical training. In Artificial Intelligence, Big Data, Blockchain and 5G for the Digital Transformation of the Healthcare Industry; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; pp. 301–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häfner, V.; Li, T.; Michels, F.L.; Häfner, P.; Yu, H.; Ovtcharova, J. Semantic Web-Enabled intelligent VR tutoring system for engineering education: A theoretical framework. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces Abstracts and Workshops (VRW), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–21 March 2024; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häfner, V.; Li, T.; Michels, F.; Häfner, P.; Yu, H.; Ovtcharova, J. A framework for intelligent virtual reality tutoring system using semantic web technology. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Computer Supported Education, Angers, France, 2–4 May 2024; pp. 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohil, M.K.; Mahajan, S.; Paul, T. An architecture to intertwine augmented reality and intelligent tutoring systems: Towards realizing technology-enabled enhanced learning. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2024, 30, 3279–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, A.; Mohanty, A. Educational technology: Exploring the convergence of technology and pedagogy through mobility, interactivity, AI, and learning tools. Cogent Eng. 2023, 10, 2283282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, T.; Lindqvist, T.; Laine, J.; Hakkarainen, K. Training hard skills in virtual reality: Developing a theoretical framework for AI-Based immersive learning. In AI in Learning: Designing the Future; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Swtizerland, 2023; pp. 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wild, F.; Whitelock, D. Design dimensions for holographic intelligent agents: A comparative analysis. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education (AIED’2021), Utrecht, The Netherlands, 14–18 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Herbert, B.; Ens, B.; Weerasinghe, A.; Billinghurst, M.; Wigley, G. Design considerations for combining augmented reality with intelligent tutors. Comput. Graph. 2018, 77, 166–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, M.; Mujika, I.; Arregi, A.; Aguirrezabal, P.; Custodio, D.; Pajares, M.; Gómez, J. EDUKA: Design and development of an intelligent tutor and author tool for the personalised generation of itineraries and training activities in immersive 3D and 360° educational environments. Int. J. Prod. Manag. Eng. 2023, 11, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thandapani, R.K.G.R.; Capel, B.; Lasnier, A.; Chatzigiannakis, I. INTERACT: An authoring tool that facilitates the creation of human centric interaction with 3d objects in virtual reality. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Mobile Human-Computer Interaction, Athens, Greece, 26–29 September 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schez-Sobrino, S.; Gmez-Portes, C.; Vallejo, D.; Glez-Morcillo, C.; Redondo, M.Á. An intelligent tutoring system to facilitate the learning of programming through the usage of dynamic graphic visualizations. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Tejwani, R.; Sundararajan, S.; Sipolins, A.; O’Hara, S.; Paul, A.; Kokku, R.; Kjallstrom, J.; Dang, N.H.; Huang, Y. Intelligent virtual reality tutoring system supporting open educational resource access. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Swtizerland, 2018; pp. 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaría-Bonfil, G.; Hernández, Y.; Pérez-Ramírez, M.; Arroyo-Figueroa, G. Bag of errors: Automatic inference of a student model in an electrical training system. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Swtizerland, 2018; pp. 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbert, B.m.; Weerasinghe, A.; Ens, B.; Billinghurst, M. An adaptive AR tutor for cabling a network topology. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Reality and Telexistence Eurographics Symposium on Virtual Environments, Adelaide, Australia, 22–24 November 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarshartehrani, F.; Mohammadrezaei, E.; Behravan, M.; Gracanin, D. Enhancing E-Learning experience through embodied AI tutors in immersive virtual environments: A approach for personalized educational adaptation. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 272–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ateş, H. Integrating augmented reality into intelligent tutoring systems to enhance science education outcomes. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2024, 30, 4435–4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezanson, K.; Soberanis, L.; Thomas, B.; Brooks, R.; Rojas-Muñoz, E. Towards an intelligent tutoring system for virtual reality learning environments. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference (FIE), College Station, TX, USA, 18–21 October 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uriarte-Portillo, A.; Zatarain-Cabada, R.; Barrón-Estrada, M.L.; Ibáñez, M.B.; González-Barrón, L.-M. Intelligent augmented reality for learning geometry. Information 2023, 14, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasin, M.; Utomo, R.A. Design of intelligent tutoring system (ITS) based on augmented reality (AR) for three-dimensional geometry material. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings, Zlín, Czech Republic, 26–27 July 2023; Volume 2569, p. 040001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, N.J.; Dutt, S.; Choudhary, S.l.; Kumar, M. Intelligent tutoring system in education for disabled learners using Human-Computer interaction and augmented reality. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Interact. 2022, 41, 1804–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbert, B.; Wigley, G.; Ens, B.; Billinghurst, M. Cognitive load considerations for augmented reality in network security training. Comput. Graph. 2022, 102, 566–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannaprathip, N.; Haddawy, P.; Schultheis, H.; Suebnukarn, S. Intelligent tutoring for surgical decision making: A Planning-Based approach. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 2022, 32, 350–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delamarre, A.; Shernoff, E.; Buche, C.; Frazier, S.; Gabbard, J.; Lisetti, C. The interactive virtual training for teachers (IVT-T) to practice classroom behavior management. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 2021, 152, 102646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menozzi, M.; Ropelat, S.; Köfler, J.; Huang, Y.-Y. Development of ophthalmic microsurgery training in augmented reality. Klin. Monatsblätter Für Augenheilkd. 2020, 237, 388–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ropelato, S.; Menozzi, M.; Michel, D.; Siegrist, M. Augmented reality microsurgery: A tool for training micromanipulations in ophthalmic surgery using augmented reality. Simul. Healthc. J. Soc. Simul. Healthc. 2020, 15, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Y.; Lai, A.-F.; Shen, R.-K.; Yang, C.-Y.; Shen, V.R.; Chu, Y.-H. Modeling and verification of an intelligent tutoring system based on petri net theory. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2019, 16, 4947–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Guo, D.; Weng, D. Improving authentic learning by AR-Based simulator. In Communications in Computer and Information Science; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holstein, K.; McLaren, B.M.; Aleven, V. Student learning benefits of a Mixed-Reality teacher awareness tool in AI-Enhanced classrooms. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Swtizerland, 2018; pp. 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ropelato, S.; Zünd, F.; Magnenat, S.; Menozzi, M.; Dinther, Y. van Adaptive tutoring on a virtual reality driving simulator. ETH ZurichInternational SERIES Inf. Syst. Manag. Creat. EMedia 2018, 2017, 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Longo, F.; Nicoletti, L.; Padovano, A. Smart operators in industry 4.0: A human-centered approach to enhance operators’ capabilities and competencies within the new smart factory context. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2017, 113, 144–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerfield, G.; Mitrovic, A.; Billinghurst, M. Intelligent augmented reality training for motherboard assembly. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 2015, 25, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-kfairy, M.; Ahmed, S.; Khalil, A. Factors Impacting Users’ Willingness to Adopt and Utilize the Metaverse in Education: A Systematic Review. Comput. Hum. Behav. Rep. 2024, 15, 100459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhan, Q.; Zhao, W. A Systematic Review of VR/AR Applications in Vocational Education: Models, Affects, and Performances. Interact. Learn. Environ. 2024, 32, 6375–6392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampropoulos, G.; Chen, N.S. Assessing the Educational Impact of Extended Reality Applications: Development and Validation of a Holistic Evaluation Tool. Educ. Inform. Technol. 2025, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crockett, K.; Latham, A.; Whitton, N. On predicting learning styles in conversational intelligent tutoring systems using fuzzy decision trees. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 2017, 97, 98–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutoria, A. Personalized education and artificial intelligence in the united states, china, and india: A systematic review using a Human-In-The-Loop model. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2022, 3, 100068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frasson, C.; Chalfoun, P. Managing learner’s affective states in intelligent tutoring systems. In Advances in Intelligent Tutoring Systems. Studies in Computational Intelligence; Nkambou, R., Bourdeau, J., Mizoguchi, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, G.-J. A conceptual map model for developing intelligent tutoring systems. Comput. Educ. 2003, 40, 217–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, Q.; Zheng, F.; Long, C.; Lu, Z.; Duan, Z. Comparing keywords plus of WOS and author keywords: A case study of patient adherence research. J. Assoc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2016, 67, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


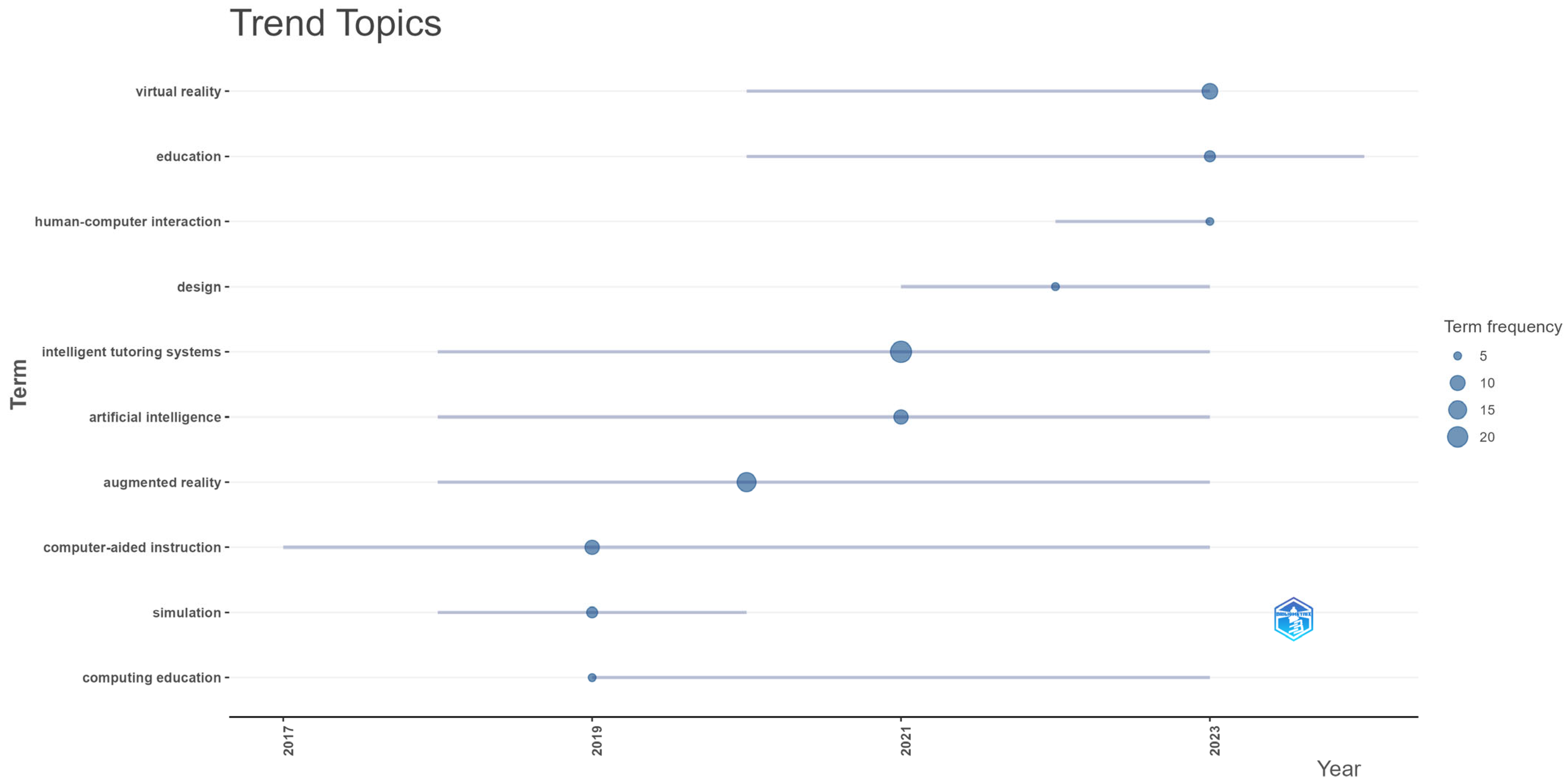
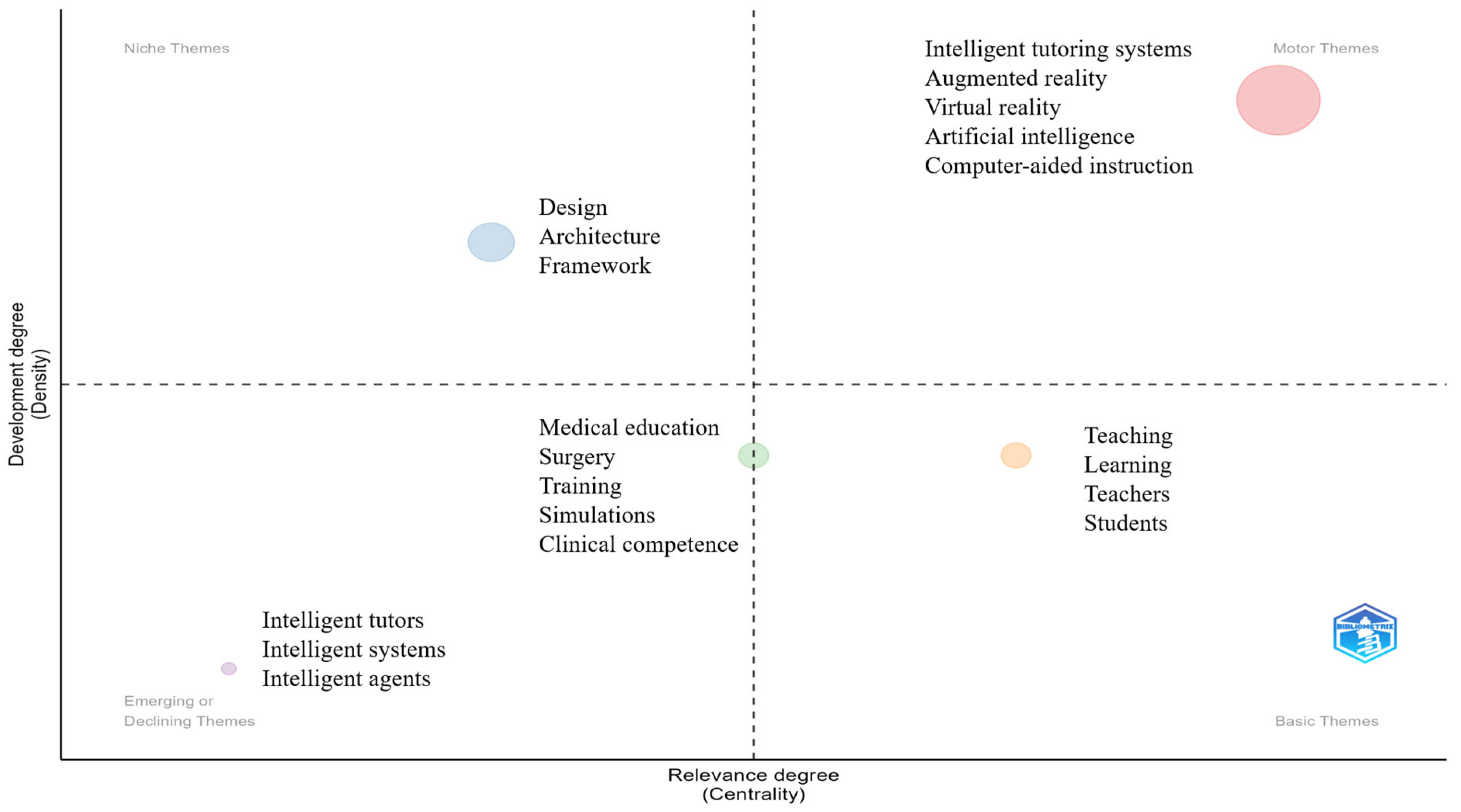
| Description | Results | Description | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Main information about data | Document types | ||
| Timespan | 2015:2024 | Journal Article | 16 |
| Sources (Journals, Books, etc.) | 29 | Book Chapter | 3 |
| Documents | 32 | Conference/Proceedings Paper | 13 |
| Annual Growth Rate % | 22.03 | Authors | |
| Document Average Age | 4.03 | Authors | 114 |
| Average Citations per Document | 25.38 | Authors of Single-Authored Docs | 2 |
| References | 1223 | Author collaboration | |
| Document contents | Single-Authored Docs | 2 | |
| Keywords Plus (ID) | 144 | Co-Authors per Doc | 4.03 |
| Author’s Keywords (DE) | 103 | International Co-Authorships % | 21.88 |
| Year | MeanTCperDoc | n | MeanTCperYear | CitableYears |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 202 | 1 | 18.36 | 11 |
| 2017 | 120 | 3 | 13.33 | 9 |
| 2018 | 25.6 | 5 | 3.2 | 8 |
| 2019 | 8 | 1 | 1.14 | 7 |
| 2020 | 14.67 | 3 | 2.44 | 6 |
| 2021 | 6 | 2 | 1.2 | 5 |
| 2022 | 7.67 | 3 | 1.92 | 4 |
| 2023 | 4 | 8 | 1.33 | 3 |
| 2024 | 0.5 | 6 | 0.25 | 2 |
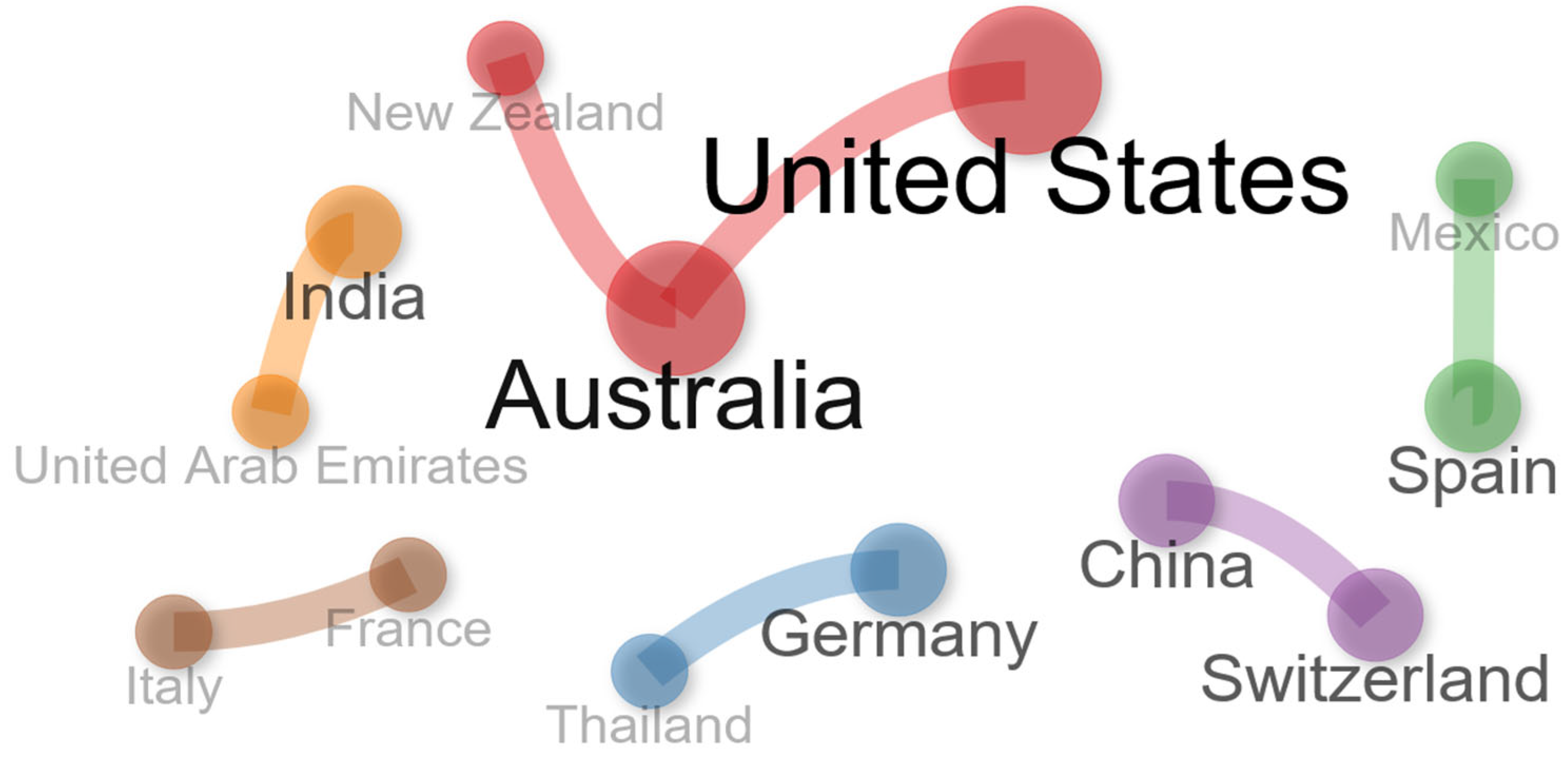
| Country | Documents | SCP | MCP | Freq. | MCP_Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| United States | 5 | 4 | 1 | 0.156 | 0.2 |
| Australia | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0.094 | 0.333 |
| India | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0.094 | 0.333 |
| Spain | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0.094 | 0.333 |
| Switzerland | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0.094 | 0.333 |
| Germany | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0.063 | 0 |
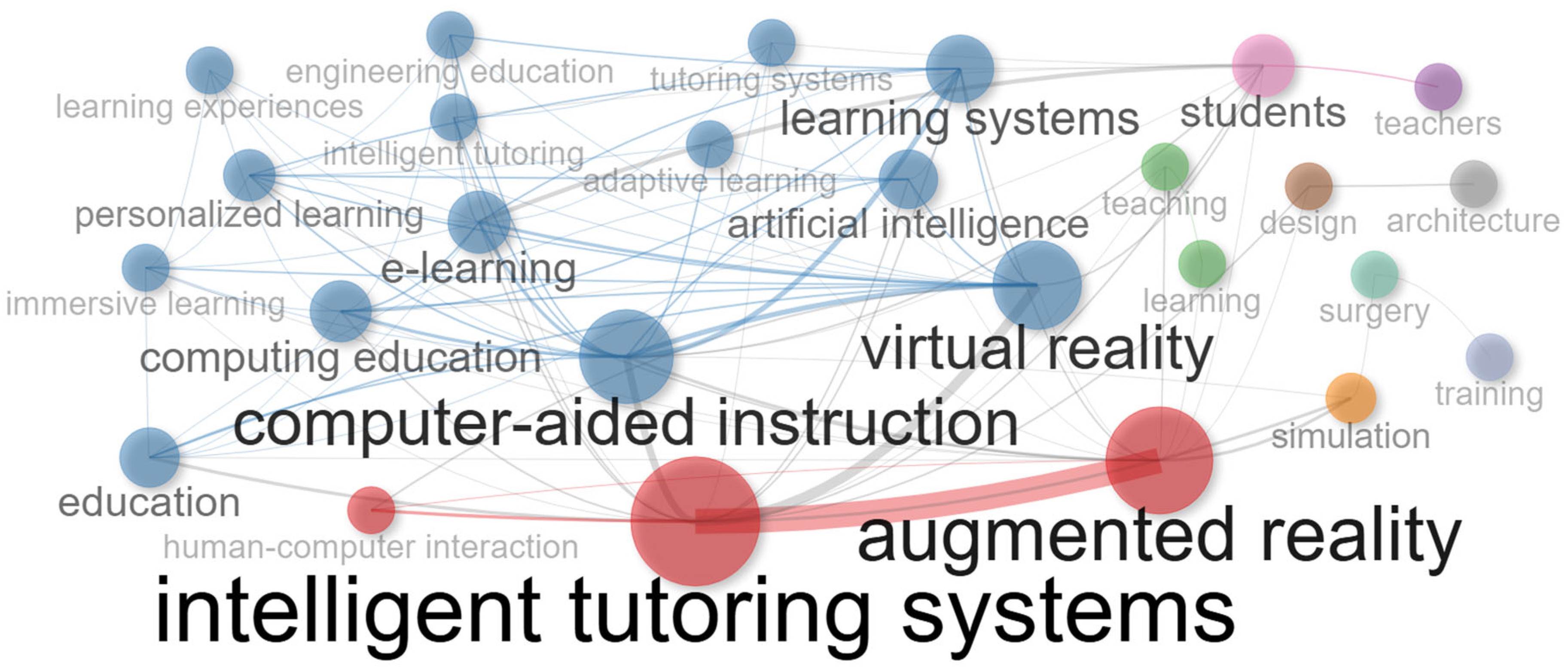
| Keyword | Total Link Strength | Keyword | Total Link Strength | Keyword | Total Link Strength |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| intelligent tutoring systems | 90 | training | 37 | design | 22 |
| augmented reality | 76 | personalized learning | 33 | learning systems | 22 |
| computer-aided instruction | 65 | human-computer interaction | 29 | learning experiences | 21 |
| virtual reality | 64 | engineering education | 28 | teachers | 17 |
| students | 44 | simulation | 28 | architecture | 16 |
| learning systems | 43 | teaching | 28 | framework | 14 |
| artificial intelligence | 42 | immersive learning | 27 | surgery | 14 |
| e-learning | 41 | intelligent tutoring | 26 | head-mounted displays | 13 |
| education | 41 | tutoring systems | 23 | environments | 12 |
| computing education | 38 | adaptive learning | 22 | intelligent tutors | 7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lampropoulos, G. Augmented Reality, Virtual Reality, and Intelligent Tutoring Systems in Education and Training: A Systematic Literature Review. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3223. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063223
Lampropoulos G. Augmented Reality, Virtual Reality, and Intelligent Tutoring Systems in Education and Training: A Systematic Literature Review. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(6):3223. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063223
Chicago/Turabian StyleLampropoulos, Georgios. 2025. "Augmented Reality, Virtual Reality, and Intelligent Tutoring Systems in Education and Training: A Systematic Literature Review" Applied Sciences 15, no. 6: 3223. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063223
APA StyleLampropoulos, G. (2025). Augmented Reality, Virtual Reality, and Intelligent Tutoring Systems in Education and Training: A Systematic Literature Review. Applied Sciences, 15(6), 3223. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063223






