Comparison and Interpretability Analysis of Deep Learning Models for Classifying the Manufacturing Process of Pigments Used in Cultural Heritage Conservation
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Overview
1.2. Related Work
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
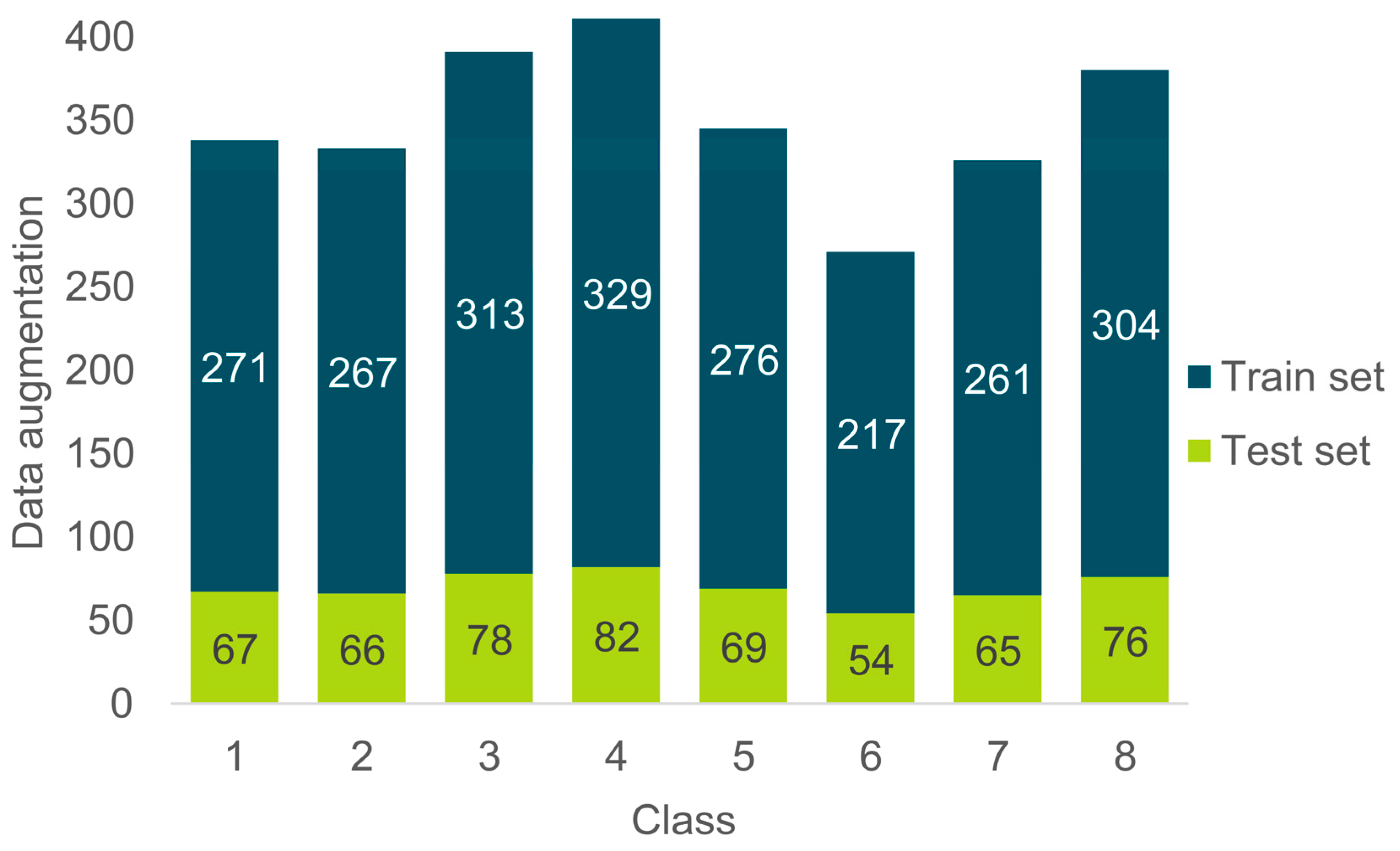
2.2. Dataset and Preprocessing
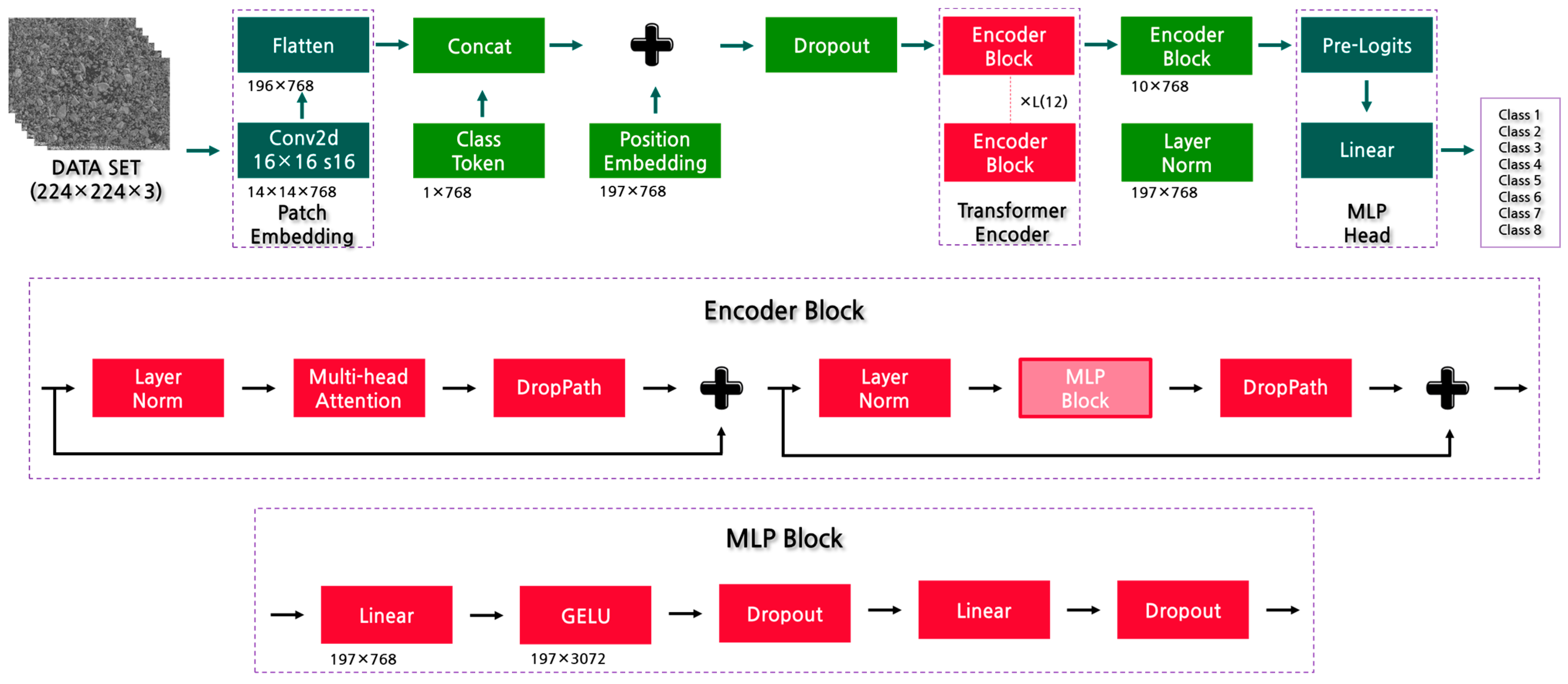
2.2.1. Proposed Approaches
2.2.2. Transfer Learning and Parameter Setting
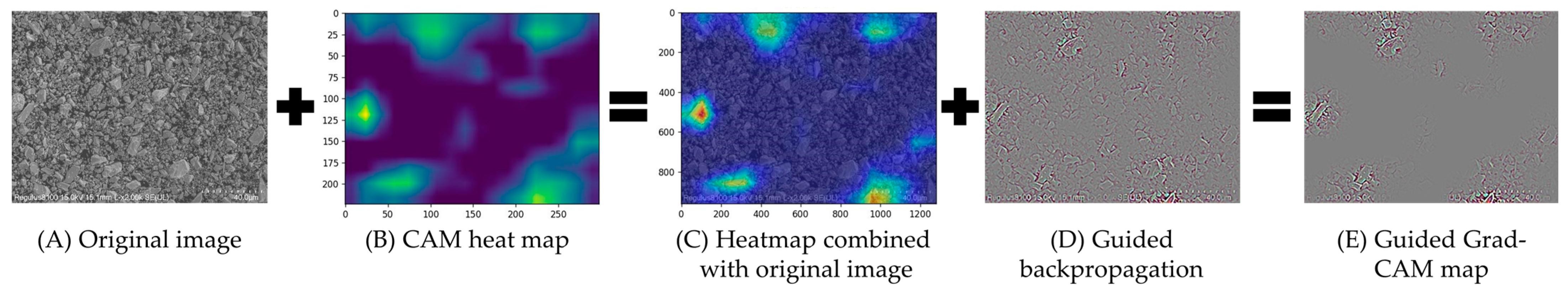
2.2.3. Visualization Method
2.2.4. Evaluation Measures
3. Results and Discussion
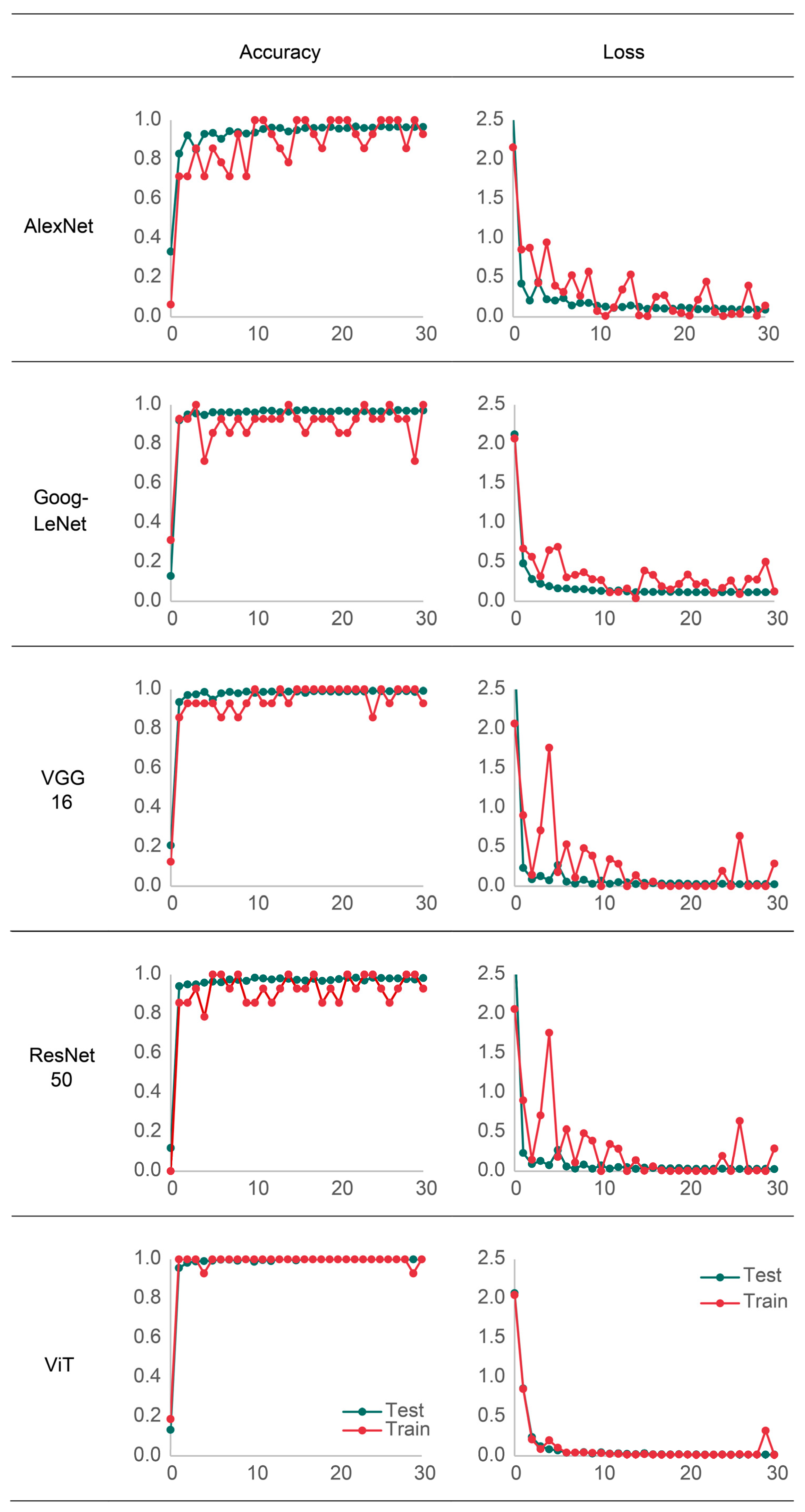
3.1. Evaluation of Deep Learning Models
3.2. ROC and PR Curves
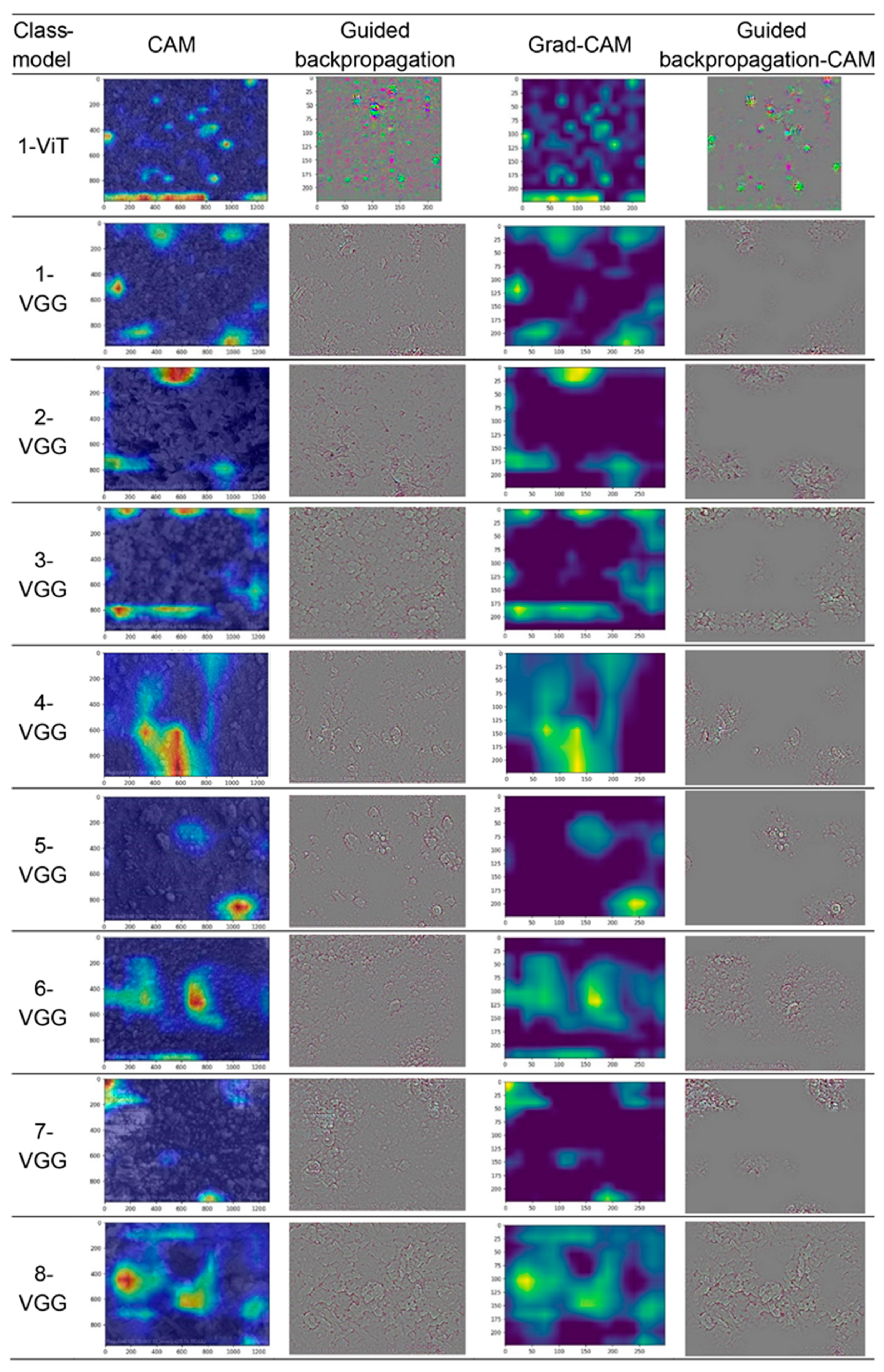
3.3. Interpretability Analysis
4. Conclusions
5. Patent
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CNN | Convolutional neural network |
| CAM | Class activation map |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| TP | True positive |
| TN | True negative |
| FP | False positive |
| FN | False negative |
| ROC | Receiver-operating characteristic |
| PR | Precision–recall |
| ViT | Vision transformer |
References
- Eastaugh, N.; Walsh, V.; Siddall, R. Pigment Compendium-Dictionary and Optical Microscopy of Historical Pigments; Routledge: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Go, I.; Ma, X.; Guo, H. CNN-based deep learning method for classifying micro-form images of pigments with different manufacturing processes. Herit. Sci. 2025, preprint. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, X.; Gallagher, B.; Eves, K.; Robertson, E.; Mundhenk, T.N.; Han, T.Y.-J. A study of real-world micrograph data quality and machine learning model robustness. Npj Comput. Mater. 2021, 7, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leksut, J.T.; Zhao, J.; Itti, L. Learning visual variation for object recognition. Image Vis. Comput. 2020, 98, 103912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćosović, M.; Rajković, J. CNN classification of the cultural heritage image. In Proceedings of the 19th International Symposium INFOTEH-JAHORINA, East Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina, 18–20 March 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, M.H.; Omer, Z.Q.; Aziz, B.B.; Abdulkareem, J.F.; Mahmood, T.M.A.; Kareem, F.A.; Mohammad, D.N. Convolutional neural network-based deep learning methods for skeletal growth prediction in dental patients. J. Imaging 2024, 10, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Z.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, P.; Qi, F.; Wang, N. CNN-based statistics and location estimation of missing components in routine inspection of historic buildings. J. Cult. Herit. 2019, 38, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Yu, J.M. Automatic surface damage classification developed based on deep learning for wooden architectural heritage. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci. 2023, X-M-1-2023, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andric, V.; Kvascev, G.; Cvetanovic, M.; Stojanovic, S.; Bacanin, N.; Gajic-Kvascev, M. Deep learning assisted XRF spectra classification. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.M.; Cho, K.H.; Park, S.; Kang, T.; Kim, M.S.; Nam, G.; Pyo, J. Estimation of cyanobacteria pigments in the main rivers of South Korea using spatial attention convolutional neural network with hyperspectral imagery. GISci. Remote Sens. 2022, 59, 547–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.; Daly, N.S.; Higgitt, C.; Rodrigues, M.R.D. Neural network-based classification of X-ray fluorescence spectra of artists’ pigments: An approach leveraging a synthetic dataset created using the fundamental parameters method. Herit. Sci. 2022, 10, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICOMOS. Venice Charter. Sci. J. 1994, 4, 110–112. [Google Scholar]
- Go, I.; Mun, S.; Lee, J.; Jeong, H. A case study on Hoeamsa Temple, Korea: Technical examination and identification of pigments and paper unearthed from the temple site. Herit. Sci. 2022, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaweel, M.; Khelifi, A.; Li, Z.; Squitieri, A.; Basmaji, T.; Ghazal, M. Automated archaeological feature detection using deep learning on optical UAV imagery: Preliminary results. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Orazio, M.; Gianangeli, A.; Monni, F.; Quagliarini, E. Automatic monitoring of the bio colonisation of historical building's facades through convolutional neural networks (CNN). J. Cult. Herit. 2024, 70, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nousias, S.; Arvanitis, G.; Lalos, A.S.; Pavlidis, G.; Koulamas, C.; Kalogeras, A.; Moustakas, K. A saliency aware CNN-based 3D model simplification and compression framework for remote inspection of heritage sites. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 169982–170001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Smith, K.; Wilder, C.; Wang, S. Curve-structure segmentation from depth maps: A CNN-based approach and its application to exploring cultural heritage objects. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2018, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonhage, A.; Eltaher, M.; Raab, T.; Breuß, M.; Raab, A.; Schneider, A. A modified mask region-based convolutional neural network approach for the automated detection of archaeological sites on high-resolution light detection and ranging-derived digital elevation models in the North German Lowland. Archaeol. Prospect. 2021, 28, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caspari, G.; Crespo, P. Convolutional neural networks for archaeological site detection—Finding “princely” tombs. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2021, 110, 104998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyot, A.; Lennon, M.; Hubert-Moy, L. Objective comparison of relief visualization techniques with deep CNN for archaeology. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2021, 38, 103027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazo, J.F. Detection of Archaeological Sites from Aerial Imagery Using Deep Learning; (Publication Number LU TP 19-09); LUND University: Lund, Sweden, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chane, S.; Mansouri, A.; Marzani, F.S.; Boochs, F. Integration of 3D and multispectral data for cultural heritage applications: Survey and perspectives. Image Vis. Comput. 2012, 31, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Passos, D.; Marini, F.; Xu, J.; Amigo, J.M.; Gowen, A.A.; Jansen, J.J.; Biancolillo, A.; Roger, J.M.; Rutledge, D.N.; et al. Deep learning for near-infrared spectral data modelling: Hypes and benefits. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 157, 116804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhi, A.; Bouras, A.; Al-Ali, A.K.; Foufou, S. A machine learning framework for enhancing digital experiences in cultural heritage. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 2020, 36, 734–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cheng, P.; Li, J. Application interface design of Chongqing intangible cultural heritage based on deep learning. Heliyon 2023, 9, e22242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z. The construction of a digital dissemination platform for the intangible cultural heritage using convolutional neural network models. Heliyon 2025, 11, e40986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, R. The practice and exploration of deep learning algorithm in the creation and realization of intangible cultural heritage animation. Appl. Math. Nonlinear Sci. 2024, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liarokapis, F.; Voulodimos, A.; Doulamis, N.; Doulamis, A. Visual Computing for Cultural Heritage; Liarokapis, F., Voulodimos, A., Doulamis, N., Doulamis, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.S. Real-time recognition of Korean traditional dance movements using BlazePose and a metadata-enhanced framework. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego, J.; Pedraza, A.; Lopez, S.; Steiner, G.; Gonzalez, L.; Laurinavicius, A.; Bueno, G. Glomerulus classification and detection based on convolutional neural networks. J. Imaging 2018, 4, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Wu, Y.; Yang, T.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, Z. Research on image classification and retrieval using deep learning with attention mechanism on diaspora Chinese architectural heritage in Jiangmen, China. Buildings 2023, 13, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X. A framework for promoting sustainable development in rural ecological governance using deep convolutional neural networks. Neural Netw. 2024, 28, 3683–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bani Baker, Q.; Hammad, M.; Al-Smadi, M.; Al-Jarrah, H.; Al-Hamouri, R.; Al-Zboon, S.A. Enhanced COVID-19 detection from X-ray images with convolutional neural network and transfer learning. J. Imaging 2024, 10, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swarna, R.A.; Hossain, M.M.; Khatun, M.R.; Rahman, M.M.; Munir, A. Concrete crack detection and segregation: A feature fusion, crack isolation, and explainable AI-based approach. J. Imaging 2024, 10, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, A.E.; Warner, T.A.; Guillén, L.A. Accuracy assessment in convolutional neural network-based deep learning remote sensing studies—Part 1: Literature review. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurício, J.; Domingues, I.; Bernardino, J. Comparing vision transformers and convolutional neural networks for image classification: A literature review. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
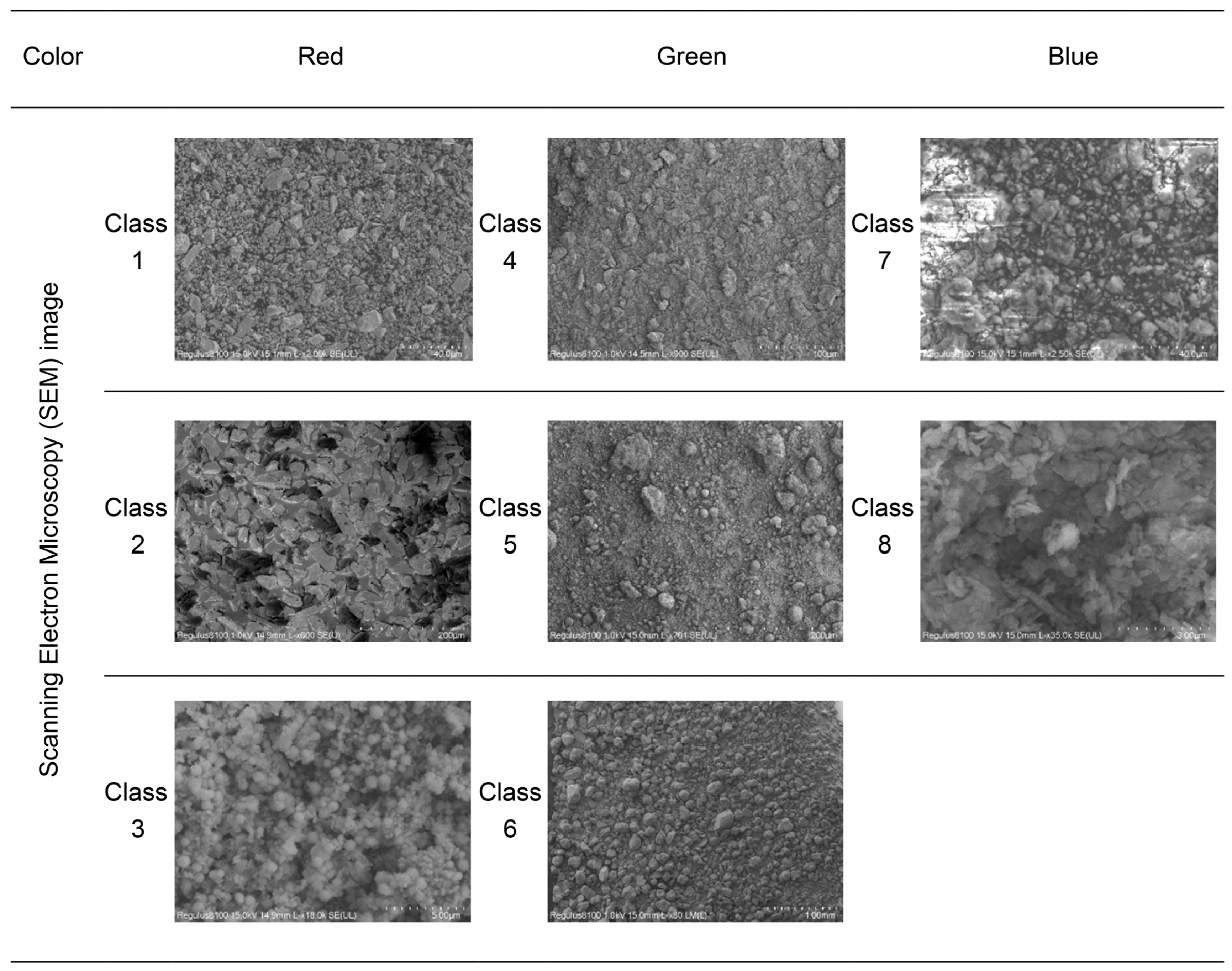


| Class | Color (Source) | Manufacturer | Common Name (Chemical Structure) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Red (traditional) | Suzhou Jiang Sixu Tang Chinese Painting Pigment Co., Ltd. (Suzhou, China) | Cinnabar (HgS) |
| 2 | Red (traditional) | GAIRART (Goyang-si, Republic of Korea) | Cinnabar (HgS) |
| 3 | Red (industrial) | GAIRART (made in Japan) | Vermillion (HgS) |
| 4 | Green (traditional) | National Research Institute of Cultural Heritage (Daejeon, Republic of Korea) | Atacamite (Cu2Cl(OH)3) |
| 5 | Green (traditional) | Atacamite (Cu2Cl(OH)3) | |
| 6 | Green (industrial) | Kremer (Bad Soden-Salmünster, Germany) | Verdigris (Cu(CH3COO)2 |
| 7 | Blue (traditional) | Korean traditional indigo (Republic of Korea) | Indigo + Calcite (C16H10N2O2 + CaCO3) |
| 8 | Blue (industrial) | ChemFaces (Wuhan, China) | Indigo (C16H10N2O2) |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| RandomResizedCrop | 224 |
| Normalization | [0.485, 0.456, 0.406] |
| [0.229, 0.224, 0.225] | |
| Batch size | 16 |
| Number of workers | 8 |
| Optimizer | Adam |
| Criterion | Cross-entropy loss |
| Epochs | 30 |
| Step size | 5 |
| Gamma | 0.5 |
| Model | AlexNet | GoogLeNet | VGG16 | ResNet50 | ViT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | 0.969 | 0.973 | 0.993 | 0.984 | 1 |
| Precision | 0.970 | 0.973 | 0.993 | 0.984 | 1 |
| Recall | 0.969 | 0.973 | 0.993 | 0.984 | 1 |
| F1-score | 0.970 | 0.973 | 0.993 | 0.984 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Go, I.; Fu, Y.; Ma, X.; Guo, H. Comparison and Interpretability Analysis of Deep Learning Models for Classifying the Manufacturing Process of Pigments Used in Cultural Heritage Conservation. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3476. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073476
Go I, Fu Y, Ma X, Guo H. Comparison and Interpretability Analysis of Deep Learning Models for Classifying the Manufacturing Process of Pigments Used in Cultural Heritage Conservation. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(7):3476. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073476
Chicago/Turabian StyleGo, Inhee, Yu Fu, Xi Ma, and Hong Guo. 2025. "Comparison and Interpretability Analysis of Deep Learning Models for Classifying the Manufacturing Process of Pigments Used in Cultural Heritage Conservation" Applied Sciences 15, no. 7: 3476. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073476
APA StyleGo, I., Fu, Y., Ma, X., & Guo, H. (2025). Comparison and Interpretability Analysis of Deep Learning Models for Classifying the Manufacturing Process of Pigments Used in Cultural Heritage Conservation. Applied Sciences, 15(7), 3476. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073476






