Abstract
A Knowledge Graph (KG), which structurally represents entities (nodes) and relationships (edges), offers a powerful and flexible approach to knowledge representation in the field of Artificial Intelligence (AI). KGs have been increasingly applied in various domains—such as natural language processing (NLP), recommendation systems, knowledge search, and medical diagnostics—spurring continuous research on effective methods for their construction and maintenance. Recently, efforts to combine large language models (LLMs), particularly those aimed at managing hallucination symptoms, with KGs have gained attention. Consequently, new approaches have emerged in each phase of KG development, including Extraction, Learning Paradigm, and Evaluation Methodology. In this paper, we focus on major publications released after 2022 to systematically examine the process of KG construction along three core dimensions: Extraction, Learning Paradigm, and Evaluation Methodology. Specifically, we investigate (1) large-scale data preprocessing and multimodal extraction techniques in the KG Extraction domain, (2) the refinement of traditional embedding methods and the application of cutting-edge techniques—such as Graph Neural Networks, Transformers, and LLMs—in the KG Learning domain, and (3) both intrinsic and extrinsic metrics in the KG Evaluation domain, as well as various approaches to ensure interpretability and reliability.
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
Knowledge Graphs (KGs) were initially popularized by Google as a means to enhance search capabilities. Subsequently, the rise of Large Language Models (LLMs) has positioned KGs as a robust method for organizing large-scale heterogeneous data, and they have been applied in semantic search, recommendation systems, and question answering [,,]. By representing entities (nodes) and their interlinked relationships (edges), KGs improve data retrieval efficiency and the interpretability of trained models, and even mitigate the hallucination effects often associated with LLMs []. However, constructing high-quality KGs remains complex due to diverse data sources, nuanced relationship learning, and the need for rigorous enhancement and evaluation.
This survey provides an overview of research from 2022 to 2024 on KG construction—covering extraction, learning, and evaluation—and examines recent work addressing hallucinations and knowledge gaps in various LLM-driven tasks. Through this exploration, we identify key challenges and unresolved issues in the current knowledge graph landscape, offering insights for future innovation.
1.2. Survey Taxnomy
Figure 1 provides a high-level overview of the proposed research framework for knowledge graph construction, visually representing the three core phases—Extraction, Learning, and Evaluation—along with their key sub-components. This figure is crucial not only for understanding the logical progression of each phase but also for situating the various methodologies discussed in this paper. The diverse methodologies presented in the main text are sometimes reiterated to help the readers better comprehend the content. By aligning the surveyed taxonomy with the structure shown in Figure 1, readers can easily understand how foundational extraction techniques, advanced machine learning approaches, and rigorous evaluation protocols collectively form a cohesive pipeline. In particular, the sub-stages within each phase (e.g., Pre-Construction Preparation for Extraction, Graph Neural Network-Based Learning, Qualitative Evaluation methods, etc.) reflect the positioning of the various research threads synthesized in this paper, thereby clarifying how each method and reference discussed in the following sections fits into the broader knowledge graph construction roadmap.
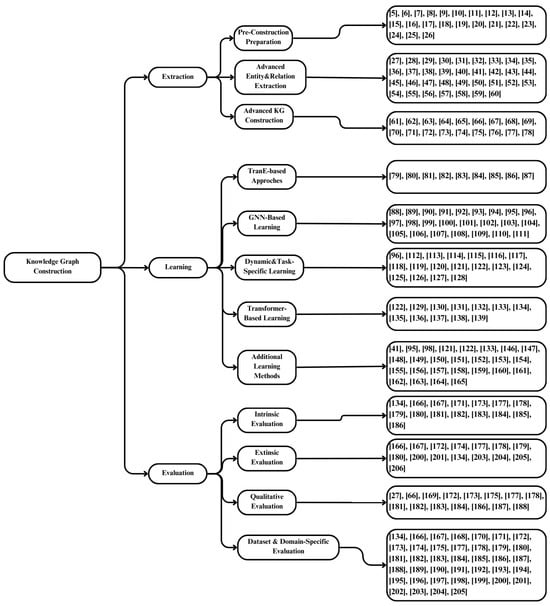
Figure 1.
A systematic overview of the key stages of knowledge graph construction (Extraction, Learning, Evaluation) and the reference numbers allocated to each sub-section.
Extraction. Section 2 discusses the various processes involved in collecting and transforming raw data into structured data to construct knowledge graphs. This includes a range of extraction techniques, from rule-based and machine learning-based methods for foundational entity and relationship extraction to approaches that enhance extraction accuracy using LLMs (e.g., transformer-based models). By analyzing diverse methods, from traditional rule-based approaches to deep learning architectures, this section aims to provide an understanding of both conventional techniques and the latest advancements.
Learning. Section 3 focuses on machine learning techniques that infer and refine relational patterns within knowledge graphs. The discussion begins by exploring traditional embedding models and relation learning algorithms—such as TransE and DistMult—that provide a foundational framework for representing entities and their interconnections in a low-dimensional space. Building on these established methods, this section then delves into recent developments that utilize Graph Neural Networks, attention-based architectures, and contrastive learning techniques to capture complex interactions and higher-order structures. Additionally, it highlights advanced strategies, including transfer learning and various few-shot, one-shot, and zero-shot approaches that address data sparsity and enhance the generalization and robustness of the knowledge graph models.
Evaluation. Section 4 examines the various metrics and evaluation frameworks used to assess the performance of Knowledge Graphs (KGs). The evaluation process consists of intrinsic and extrinsic evaluations. Intrinsic evaluation measures the internal quality of a knowledge graph by focusing on three key aspects: First, accuracy evaluates whether the entities and relationships are correctly identified. Second, coverage indicates the extent to which a KG represents a relevant domain. Third, consistency ensures that the information in the KG is maintained without contradictions. In contrast, extrinsic evaluation measures how effectively a KG can be utilized in practical downstream tasks such as information retrieval and question answering. Furthermore, this section provides a comparative analysis of various evaluation benchmarks, including widely used datasets and challenge tasks, to comprehensively highlight the strengths and limitations of current approaches.
In summary, this survey aims to integrate the recent research landscape surrounding knowledge graph construction into a coherent roadmap, providing a reference for researchers and practitioners seeking to transcend the current limitations of the field. By comprehensively exploring extraction, learning, enhancement, and evaluation, we aim to lay a foundation for future innovations. The following sections will delve into each aspect in detail, thoroughly reviewing the methodologies, challenges, and emerging trends in this domain.
1.3. Semi-Automatic Paper Selection Process
In this paper, a semi-automatic survey process was implemented to rapidly and systematically synthesize research trends on Knowledge Graphs spanning 2022 to 2024. The overall procedure comprises four key steps.
Collection Articles. The Web of Science (WOS) database was utilized to automatically collect approximately 4000 articles related to Knowledge Graphs. This approach enabled the systematic acquisition of a vast body of literature, providing a robust foundation for subsequent evaluation and analysis.
Relevance Assessment. Each collected article was evaluated for alignment with the survey objectives using a predefined evaluation prompt. Specifically, GPT-4o mini and GPT-4o were employed to automatically generate relevance scores based on the content and research direction of the articles. This objective assessment facilitated the selection of articles most pertinent to the survey, ensuring an unbiased and systematic review process.
As a result of this scoring process, the number of papers in Knowledge Graph (KG) research was determined across three major categories: Extraction, Learning, and Evaluation. Figure 2 presents the distribution of these papers, with 74, 87, and 40 papers in each category, respectively. These values reflect the assessed relevance and suitability of each paper for this study, providing a structured overview of the research landscape.
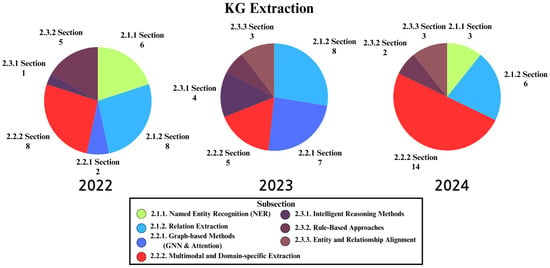
Figure 2.
Yearly paper distribution in KG extraction subsections (2022–2024). This figure presents the annual number of research papers across different subsections within the KG extraction domain from 2022 to 2024.
Category Generation. Guided by the relevance scores, the articles were initially clustered into three primary themes—Extraction, Learning, and Evaluation. Subsequent analysis refined these broad categories, yielding three distinct sub-categories within each theme. While automated methods—such as keyword matching and topic modeling—helped identify candidate labels, researchers manually finalized and validated these sub-themes, ensuring their conceptual alignment with the broader survey goals.
By incorporating these semi-automated and human-centered measures, this study efficiently handled a large volume of literature while maintaining methodological rigor and transparency. Automated scoring (via GPT-4o mini and GPT-4o) proved valuable for initial filtering; however, the writing phase prioritized manual composition and expert review. Consequently, the final survey manuscript combines the speed and breadth of automation with the depth, reliability, and nuanced perspectives of human oversight.
2. KGs Extraction
This illustration details the annual distribution of research papers across various subfields of KG extraction from 2022 to 2024. This highlights that while some areas—such as relation extraction and multimodal/domain-specific extraction—maintain steady, high levels of scholarly activity, other subsections, like graph-based methods and intelligent reasoning, experience significant surges in certain years.
Steady or Growing Areas. Multimodal and Domain-Specific Extraction (Section 2.2.2) and Relation Extraction (Section 2.1.2) appear to maintain consistently high interest. This sustained attention could be driven by the increasing need to handle diverse data formats—such as images, videos, and specialized domain texts—and the growing importance of accurate entity-to-entity linking in complex applications.
Peaks and Surges in Specific Years. Topics like Graph-based Methods (Section 2.2.1) and Intelligent Reasoning (Section 2.3.1) show marked surges in certain years. These spikes may be attributed to breakthroughs in neural architectures (e.g., attention-based GNNs) or new reasoning paradigms that have temporarily shifted the research focus. Additionally, improvements in computational hardware and libraries can accelerate development in these areas, causing sudden increases in publication volume.
Fluctuations and Declines. Some subsections experienced sporadic peaks followed by rapid declines, suggesting that research efforts in those areas either reached a saturation point or were eclipsed by more innovative methods. Shifting priorities—such as the rise of end-to-end extraction pipelines or more advanced reasoning techniques—can lead to a decrease in traditional rule-based or less flexible approaches.
Emerging Use Cases and Practical Constraints. Real-world applications requiring scalable, domain-specific extraction solutions often motivate the research community to refine existing methods and explore novel frameworks. For instance, heightened interest in industry adoption might sustain certain topics for longer, whereas academic research might pivot quickly if a method shows diminishing returns or new challenges arise.
Overall, the trends in KG extraction highlight how some techniques remain stable focal points, whereas others gain or lose prominence in response to new methodological breakthroughs, changing computational capabilities, and domain-driven requirements.
2.1. Pre-Construction Preparation
2.1.1. Named Entity Recognition (NER)
In the initial stage of KG construction, it is essential to identify key terms (entities) from unstructured text and consistently map them to predefined ontologies or schemas. Approaches that leverage pretrained language models, such as BERT, have been shown to effectively improve NER precision when processing large corpora []. By combining statistical distributions with language graphs, these methods can extend not only commonsense knowledge but also domain-specific information.
In the relation extraction stage, techniques such as dependency parsing, semantic feature extraction, multi-head stacked graph convolution networks (GCN), and attention mechanisms are widely used []. For example, the entities identified by NER are embedded using a Bi-LSTM model, and methods such as Simplified Graph Convolution Networks (SGC) are then applied to optimize relational information, thereby enhancing the accuracy of relation extraction. Research has also been conducted on combining BERT-based NER with rule-learning methods (e.g., the Open Path or OPRL algorithms) to generate extraction queries and complete the KG [].
Another study applied a supervised information extraction model based on a BERT transformer to perform tokenization, contextual embedding, and entity classification, and then fine-tuned it on a domain-specific dataset to improve its accuracy []. BERT’s core strength lies in its exceptional contextual understanding at the token level, which surpasses traditional approaches.
The entities identified by NER are then mapped to a predefined ontology or set of labels, which is a critical process for ensuring the consistency of KG creation []. This mapping is further reinforced by combining the statistical distributions with the language graph information. In addition, some studies have optimized KG performance using multi-relational graph attention networks or embedding-based models that reflect the importance or attention weights of adjacent nodes [].
2.1.2. Relation Extraction
Relation extraction identifies the semantic connections between entities to generate triple structures (subject–relation–object), which form the basic structure of the knowledge graph. Techniques such as bidirectional relation-guided attention have been used to create a complementary effect between entity recognition and relation extraction []. In the cybersecurity domain, a method combining BERT-based NER with a GCN to extract attack behaviors significantly improved the accuracy of threat behavior recognition []. In various domains (e.g., healthcare, security, software, and education), BERT-based NER has become a core technology for KG construction.
Recent approaches have incorporated Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) into KG applications to integrate engineering knowledge from texts. This method employs token classification and sequence-to-sequence (Seq2Seq) models to extract explicit engineering facts from the KG []. In contrast, the AutoAlign technique leverages large language models to automate the alignment process of knowledge graphs, significantly reducing the need for manual intervention [].
Domain-specific studies include methods for extracting the relationships between ketamine and the gut microbiota from the literature and pathway data [], approaches that capture diverse features using multi-channel convolutions in triple embeddings [], methods for constructing a processed knowledge graph [], approaches based on hierarchical transformers and dual quaternions [], and triple extraction via sentence transformers utilizing dependency parsing [].
Generative approaches extend and refine the KG by directly generating triple structures from learned data distributions, while sampling techniques effectively extract sub-structures from large graphs to balance accuracy and computational cost. For example, a multi-information preprocessing event extraction approach using BiLSTM-CRF with attention extracts events from academic texts to construct a KG []. Document-level dynamic graph attention integrates distributed information from an entire document using a two-stage graph strategy to improve the relation accuracy []. Seq2EG employs a sequence-to-sequence transformer to generate event graphs and incorporate complex event structures into the KG []. In addition, methods such as biomedical relation comparison, cognitively inspired multi-task frameworks [], and KG linking through self-supervised learning have been proposed. SelfKG [] leverages a novel self-supervised contrastive learning strategy that does not require labeled entity pairs by focusing on pushing away many negative samples. By employing a relative similarity metric along with self-negative sampling and multiple negative queues (inspired by momentum contrast techniques), SelfKG demonstrates that accurate entity alignment across different KGs can be achieved without any manual supervision. This approach not only reduces the labeling cost, but also achieves performance comparable to that of state-of-the-art supervised methods. along with the ERGM method—a multi-stage joint extraction technique that includes global entity matching []—and KG-based methods for automating complex scenarios, such as emergency planning or water resource management [].
While Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated state-of-the-art performance in extracting entity-relation tuples, they can occasionally generate “hallucinated” relationships that are not grounded in the source text. For example, a model may infer a causal link between two entities that are merely co-mentioned but lack any actual causal or logical connection. To mitigate such issues, recent studies have explored automated validation steps—such as cross-referencing extracted relationships against an external knowledge base or domain-specific rules—to filter out spurious links. Furthermore, incorporating fine-grained attention mechanisms and contrastive learning approaches can help ensure that relation extraction remains faithful to the available evidence, thereby reducing the risk of erroneously generated triples.
2.2. Advanced Entity and Relation Extraction
In some domain-specific corpora, LLM-driven extraction pipelines have generated “hallucinated” triples, such as attributing non-existent functions to certain genes or synthesizing medical relations (e.g., drug–condition links) that are not supported by clinical evidence. These errors typically arise when the training data are sparse, ambiguous or contradictory. To address this, researchers have proposed post-processing heuristics—using either knowledge graph consistency checks or multimodal cross-validation (e.g., text plus imaging data)—to detect and remove unsubstantiated relationships before finalizing the KG.
2.2.1. Graph-Based Methods (GNN and Attention)
Graph-based extraction methods organize the analysis results (entities and relations) from text into a graph structure and use Graph Neural Networks (GNN) and attention mechanisms to infer and validate information. For example, one approach achieved high precision by combining NER with a deep learning transformer to verify the entities and relations extracted at the sentence level [].
In the biological domain, studies have combined BERT-based NER with topological clustering to learn the gene interaction structures within protein networks. In addition, research has been conducted on extracting drug–drug interactions by integrating heterogeneous knowledge graphs [] and methods that extract relationships by merging web tables []. Other approaches include graph-based methods using multimodal learning [], research on expanding KGs from large heterogeneous data sources [], and comprehensive information extraction pipelines, where BERT-based NER plays a core role [].
Studies have reported the use of multi-task graph convolution networks (MGCN) to extract entities and relations. For example, by integrating dependency trees into a GCN, structure information can be captured while simultaneously learning node and edge features, effectively handling overlapping or complex relation labels []. Furthermore, various methods have been employed, such as combining BERT-based NER with translation-based frameworks like TransE for accurate extraction from domain datasets [] and constructing KGs using multimodal educational data [].
Other approaches include using BiLSTM-CRF models to extract named entities and adding entity type information through unsupervised learning to reduce false positives [] and employing TrellisNet-CRF to complement the accuracy of BERT-based NER []. Strategies that integrate graph structure learning, attention-based BERT NER, and automated feature generation (combining deep learning with graph learning) further enhance KG extraction performance []. Finally, a strategy was developed that uses BERT-based NER to automatically extract triple structures from geological reports and link them to a predefined ontology [].
2.2.2. Multimodal and Domain-Specific Extraction
Multimodal and domain-specific approaches are designed to handle various data types—not only text but also images, audio, and sensor data—thus enabling the high-precision extraction of entities and relations in specific industries. For instance, the GridOnto system integrates fault events from power grids into a KG, demonstrating its effective application in the energy sector []. In the security domain, LLM-TIKG utilizes large language models to construct a threat intelligence KG that enhances the extraction of security-related events []. Additionally, causal relation extraction methods focus on deriving deep causal relationships from long texts, thereby enriching the KG with explicit engineering and domain-specific facts []. Knowledge Guided Attention focuses on chemical–disease relationships by combining attention mechanisms with GCN to reduce noise []. Methods that use distant supervision to incorporate the global context and suppress errors have also been proposed []. The Experiencer-Driven Graph approach captures deep semantic information in emotion-cause relationships [], and dual-fusion models that combine text with equipment sensor data have been developed to simultaneously analyze logs and documents []. An automated clinical knowledge graph framework that integrates clinical records and literature to support evidence-based medicine (EBM) is also included [].
Additional domain-specific improvement techniques include progressive entity type assignment methods to effectively learn domain-specific ontologies [] and the CG-JKNN model, which integrates image and graph data to form medical relations for tuberculosis diagnosis []. In the industrial and healthcare sectors, systems such as the Novel Rational Medicine Use System [], semantic-spatial aware data integration for place KGs [], relation labeling in product KGs for e-commerce [], pipelines for extracting relations using transportation authority data [], and task-centric KG construction based on multimodal representation learning for industrial maintenance automation [] have been proposed. For geological data, approaches include deep learning-based methods that combine text and images to extract entities [], methods that fuse entity descriptions with type information to enhance the completeness of a medical KG [], joint extraction approaches for geological reports [], BDCore, which uses bidirectional decoding and joint graph representations [], prompt learning for biomedical relation extraction using GCN [], and NER for equipment fault diagnosis that combines RoBERTa-wwm-ext with deep learning [].
2.3. Advanced Knowledge Graph Construction
2.3.1. Intelligent Reasoning Methods
KG construction is increasingly leveraging advanced techniques to automatically extend complex domain knowledge. In particular, methods such as multi-hop reasoning, causal reasoning, and quantum embeddings are being integrated to enhance knowledge representation. For example, PharmKE is a knowledge extraction platform that applies transfer learning to pharmaceutical texts to automatically extract various medical entities and relations (e.g., drug names, drug–drug interactions (DDI), adverse drug reactions (ADR), and indications) within an integrated environment []. By fine-tuning a BERT-like model on pharmaceutical corpora, it accurately recognizes specialized terms, such as drug codes and clinical names, and integrates them into the KG using subsequent pipelines. Similarly, an event ontology-based knowledge-enhanced event relation method actively leverages domain ontologies [].
In addition, the Learning Relation Prototype maps long-tail relations with few labels in an unsupervised manner using prototype embeddings []. In software project KGs, the CAJP technique has been utilized [], and Query Path Generation—performing bidirectional inference to handle complex question-answering tasks—has been applied []. The MHlinker model, which integrates the extraction of fault entity relations in mine hoists, has also been reported [], as has a novel joint extraction approach that combines interactive encoding with visual attention to extract entities and relations simultaneously [].
2.3.2. Rule-Based Approaches
Rule-based approaches achieve high precision by utilizing predefined rules and patterns established by domain experts, although they may be somewhat vulnerable to new variations. For example, the Heterogeneous Affinity Graph Inference method proposes a way to reduce noise when constructing document-level entity relations []. In addition, Image2Triplets combines BERT-based NER with computer vision techniques to extract relations simultaneously from images and text, applying specific rules (e.g., focus targets) to improve accuracy [].
In the medical field, joint models that combine sequence labeling, GCN, and transformers have been proposed to extract adverse drug event (ADE) relationships from complex pharmaceutical texts []. QLogicE integrates BERT-based NER with quantum embeddings and translation-based models to enhance the efficiency of entity and relationship representations []. A generative model called KGGen manages the quality of the generated triple structures through adversarial learning, which combines negative sampling and quality control rules []. Furthermore, an improved attention network that combines deep learning with rule-based techniques enhances the accuracy of equipment used for KG construction []. AtenSy-SNER utilizes syntactic features and semantic augmentation for entity extraction in the software domain and reduces false positives using rule-based validation [].
2.3.3. Entity and Relationship Alignment
Recent studies addressing the problem of entity and relation alignment have proposed various approaches aimed at effectively modeling complex contextual information and mitigating noise. One notable model is the Dual Attention Graph Convolutional Network (DAGCN) [], which combines local attention and global attention to capture both local structural information around entities (e.g., neighboring nodes, adjacent words, attributes, etc.) and long-range dependencies arising from global contextual and syntactic relationships within sentences. By modeling both local and global contexts, DAGCN achieves high accuracy for complex sentences, as shown by benchmarks like TACRED and SemEval.
The Contextual Dependency-Aware GCN [] integrates dependency-based graph structures with contextual information by segmenting sentences at the token level to build and process a dependency graph with a GCN. Unlike earlier methods that only consider simple dependency relations, it incorporates contextual embeddings to resolve polysemy and ambiguity, thereby enhancing entity and relation extraction, even in complex sentences.
Another notable line of research focuses on extracting and aligning relationships between objects and their corresponding actions and states in knowledge graphs. A proposed approach [] automatically identifies and connects object-action and object-state relationships in knowledge graphs—such as linking “cup” with “drink” or “cup” with “fragile”. This method applies a sophisticated matching algorithm that enables the effective association of actions or states with objects, even in noisy or structurally complex contexts. By enriching the knowledge graph information with object-centric features and their associated attributes and actions, this approach enhances the graph’s semantic richness and utility.
Furthermore, an Interactive Optimization approach [] has been introduced to incrementally improve model performance by incorporating continuous user or expert feedback during the relation extraction and alignment process. In this framework, misclassified cases or additional information identified during human inspection are fed back into the model, which adjusts its knowledge graph representation learning based on the feedback. Through repeated cycles of interaction and adjustment, the model gradually refines its alignment capabilities, enhancing its accuracy and reliability, even in complex domains where fully automated systems might struggle.
In summary, approaches based on attention-based modeling, dependency graph integration, object-action/state extraction, and interactive feedback have significantly improved the accuracy and robustness of entity alignment and relationship alignment. Specifically, the DAGCN [] and Contextual Dependency-Aware GCN [] effectively integrate diverse contextual information, achieving superior performance even in complex sentence structures. The object-action/state extraction technique [] robustly captures intricate relationships in noisy environments, while the Interactive Optimization approach [] leverages continuous feedback to iteratively refine model performance, ensuring higher reliability in challenging domains.
2.4. Final Summary
In the Pre-Construction Preparation phase, the focus is on laying a robust foundation for KG construction through two key steps. First, Named Entity Recognition employs advanced techniques such as BERT-based models, Bi-LSTM, CRF, and graph-based methods to accurately identify key entities and map them to predefined ontologies [,,,,,]. Next, Relation Extraction leverages methods like dependency parsing, semantic feature extraction, multi-head graph convolution networks, and attention mechanisms to extract subject–relation–object triples from unstructured text [,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,]
Building on these initial tasks, the Advanced Extraction stage further refines the process. In this stage, Graph-based Methods—using graph neural networks (GNNs) and attention mechanisms—organize entities and relations into structured graphs [,,,,,,,,,,,,]. Additionally, Multimodal and Domain-Specific Extraction integrates diverse data sources (including text, images, and sensor inputs) to enhance precision in specialized fields such as healthcare, cybersecurity, and industrial applications [,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,].
Finally, during the Construction phase, the process is extended and automated by incorporating Intelligent Reasoning Methods—such as multi-hop reasoning, causal inference, and quantum embeddings—to support complex inference tasks [,,,,]. This is complemented by Rule-based Approaches that utilize predefined rules, knowledge-guided attention, and logic-based models to further refine extraction accuracy in specialized domains [,,,,,,]. Moreover, advanced techniques for Entity and Relationship Alignment ensure consistency and seamless integration across heterogeneous knowledge graphs [,,,,,].
3. KGs Learning
This section provides a structured guide to various methodologies in Knowledge Graph (KG) learning, covering foundational techniques, advanced models, and other learning methods. The emphasis lies on how these approaches contribute to tasks such as link prediction, relational inference, and structured data analysis. In the subsections that follow, key models and enhancements are described with both theoretical insights and practical examples drawn from diverse application domains.
Figure 3 illustrates the annual distribution of research papers on KG learning from 2022 to 2024, offering a closer look at how interest in specific subsections fluctuated over time. Overall, the learning domain exhibits patterns in which certain areas undergo substantial surges in 2023 or 2024, while others remain steady or even decline. Several potential reasons and driving factors are outlined below:
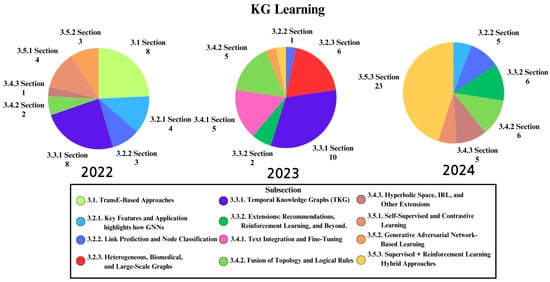
Figure 3.
The graph illustrates the distribution of research papers across different subsections in the knowledge graph (KGs) learning domain over three years (2022–2024). This includes re-cited papers, excluding reference [].
Notable surges in 2022–2024. Supervised plus Reinforcement Learning Hybrid Approach (Section 3.5.3): A dramatic increase in 2024 could stem from breakthroughs in reinforcement learning frameworks and the growing availability of large-scale data. Researchers have been motivated by the promise of achieving more robust and adaptive link prediction or reasoning tasks by combining supervised signals with reinforcement-based explorations.
Text Integration (Section 3.4.1) and Fusion of Topology with Logical Rules (Section 3.4.2): These areas display either steady growth or a marked resurgence. This uptake may be attributed to the release of more powerful natural language processing models (e.g., large language models) and an expanding set of well-structured corpora. As a result, integrating textual information with topological or logical features has become more feasible, thereby driving further research.
Consistent or Gradual Growth. Certain subfields (e.g., Heterogeneous Graphs or Temporal Knowledge Graphs) may show incremental increases in research output. This trend is often fueled by improvements in computational resources and an industry-wide shift toward real-time, dynamic KG applications—leading to a steady demand for incremental or temporal modeling approaches.
Fluctuations and Declines. Some subsections (e.g., Section 3.2.3 and Section 3.5.2) exhibit a concentration of research in a single year, followed by a sharp decrease. Such sporadic peaks may reflect shifting priorities—perhaps due to the saturation of certain methods, a pivot toward more promising alternatives, or newly emerging challenges that redirect attention. Additionally, competition from advanced approaches (like reinforcement learning hybrids or deep generative models) can overshadow previously popular techniques.
Overall, the observed trends highlight how KG learning research has evolved in response to novel techniques, growing computational capabilities, and increasing availability of domain-specific datasets. As new methodologies prove their value (e.g., reinforcement learning hybrids or improved NLP integration), they spur a surge of interest, whereas areas that face fewer unresolved challenges may experience relative decline.
3.1. TransE-Based Approaches
TransE [] learns embeddings for triples (h, r, t) by representing entities (h, t) and relations (r) as low-dimensional vectors that ideally satisfy using a margin-based ranking loss that pulls real triples closer while pushing negative (corrupted) triples apart. Its simplicity, rapid training on large datasets, and scalability have made it a popular foundational method.
h + r ≈ t
However, a single-vector operation often struggles to capture complex relational patterns. In particular, one-to-many or many-to-one relationships pose a significant challenge. For example, by constructing a KG from patent and technical report data, basic embeddings are obtained with TransE and then enhanced by training additional diffusion and absorption vectors to predict “how ideas flow between technological domains” in Technological Knowledge Flow models []. To further improve accuracy, the Multi-Filter Soft Shrinkage technique combines convolutional layers with TransE embeddings as initialization, suppressing noise while modeling higher-order interactions [].
Because TransE embeddings can degrade on sparse or incomplete graphs, iterative rule-guided reasoning methods employing reinforcement learning (RL) have been proposed to dynamically supplement “missing paths” and update embeddings []. The SSKGE framework integrates structural reinforcement and semantic guidance to reduce the training time and improve link prediction performance []. HolmE extends TransE by capturing compositional patterns in Riemannian space, providing a generalized embedding framework that encompasses models like TransE and RotatE [].
Another extension employs TransE as the embedding backbone with a two-level RL mechanism for multi-hop reasoning. In this hierarchical RL approach, a high-level agent decides which relation to explore while a low-level agent selects the appropriate node for that relation, effectively compressing the action space and updating the model end-to-end []. To handle continuously emerging entities and relations, embedding generators are trained to create vectors dynamically from side information (e.g., text or attributes), preserving the overall vector space structure for real-time or online KG completion [].
Finally, for temporal knowledge graphs (TKGs), techniques such as the Temporal-Structural Adaptation Network (TSA-Net) incorporate specialized embedding modules or recurrent mechanisms to capture complex temporal dependencies among temporal, relational, and entity representations [].
Collectively, these studies demonstrate that while TransE [] provides a simple and scalable foundation for knowledge graph embedding, its inherent limitations—such as difficulty in capturing complex relational patterns and sensitivity to data sparsity—have spurred various enhancements. For example, hierarchical and convolutional extensions [,] improve the modeling of knowledge flow and noise suppression, whereas iterative rule-guided reasoning frameworks using reinforcement learning [,] effectively supplement the missing paths in sparse graphs. Additionally, approaches for open-world and temporal graph completion [,] have been developed to dynamically adapt to emerging entities and time-dependent data.
3.2. Graph Neural Network (GNN)-Based Learning
GNNs learn node embeddings by iteratively aggregating and transforming information from nodes, edges, and their neighbors using message passing. When applied to KGs, GNNs can flexibly handle heterogeneous graphs with diverse nodes and relationship types.
3.2.1. Key Features and Application Highlights How GNNs
Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) learn embeddings for each node by iteratively aggregating and transforming the structure of the nodes, edges, and their neighbors using message-passing techniques. When applied to knowledge graphs, GNNs exhibit the following characteristics: First, heterogeneous graphs with diverse types of nodes and relationships can be flexibly handled using techniques like meta-paths or attention mechanisms. Second, while iterative structural learning enables information from neighboring nodes to propagate into deeper layers, allowing higher-order structure learning, caution is required to avoid over-smoothing. Multi-Grained Semantics-Aware Graph Neural Networks [] proposed a GNN that effectively learns the rich semantic information of knowledge graphs by considering multi-grained semantics. Furthermore, the Graph Relearn Network [] introduced methods to mitigate performance fluctuations in GNNs and improve prediction accuracy. Recent work has further expanded the application scope of GNNs. For instance, ref. [] leveraged spatiotemporal scene graph embeddings—where GNNs are combined with LSTM layers—to predict autonomous vehicle collisions by capturing dynamic inter-object relationships in complex traffic scenes. Similarly, ref. [] demonstrated that integrating Graph Convolutional Neural Networks with Label Propagation can significantly enhance node classification performance by adaptively learning edge weights based on node label information.
The GNN-based Imbalanced Node Classification Model (GNN-INCM) [] is designed to address class imbalance issues by applying loss balancing along with node sampling strategies to enhance performance in minority classes. Specifically, it selects nodes based on importance and utilizes the structural characteristics of graph networks to effectively learn from minority class data. This leads to a robust node classification performance, even in datasets with severe class imbalances. INS-GNN [], which integrates self-supervised learning into GNNs, ensures stable node classification performance on imbalanced datasets. By autonomously learning the characteristics of graph data, this model alleviates the problem of under-learning in minority class nodes, achieving practical performance improvements in various real-world networks. GNNs have emerged as a powerful paradigm for learning structured graph data by leveraging both node attributes and underlying graph topology to generate informative embeddings []. By aggregating information from neighbors, GNNs capture complex dependencies within graphs, making them highly effective for tasks like node classification and link prediction. The Graph Convolutional Network (GCN), an early GNN framework, introduced convolution-like operations tailored for graph-structured data [].
The Graph Attention Network (GAT) architecture refines this process by incorporating an attention mechanism to assign adaptive weights to neighbor information []. The same GAT architecture leverages a specialized relational aggregator that captures nuanced interactions associated with various entity and relationship types, making it well-suited for heterogeneous graphs [,]. The Dynamic Representation of Relations and global information (DRR-GAT) [] extends the existing GAT by applying dynamic relation-specific weights, effectively modeling complex graph structures. Iterative Graph Self-Distillation (IGSD) [] employs an iterative self-distillation technique to enhance the prediction stability of GNN models by refining the latent representation of nodes. At each iteration, it generates new embeddings to improve the model prediction accuracy, particularly in large graph datasets, reducing the model variance and delivering more precise results.
Beyond general graph analytics, GNNs serve as the cornerstone of knowledge graph (KG) learning, supporting various tasks such as entity classification, relationship prediction, and KG completion [,]. In this context, GNNs leverage node embeddings to exploit relational information, uncovering complex semantic patterns encoded in KGs. The integration of contrastive learning techniques within GNN frameworks is especially noteworthy, as it promotes the alignment of embeddings with meaningful semantic subspaces. This alignment aids in distinguishing relational patterns, ultimately enhancing the performance of KG completion and other downstream tasks []. Additionally, the flexibility of GNNs has spurred the emergence of advanced architectures, such as higher-order models that capture multi-hop dependencies and path-based models that incorporate longer relational contexts to further refine these relationships []. These diverse approaches underscore the adaptability of GNNs, highlighting their capability to tackle various learning scenarios and enhance the utility of knowledge graphs in real-world applications.
Compared to TransE-based methods, GNN-based approaches leverage iterative message passing to capture both local and higher-order relational structures. This makes them particularly effective for heterogeneous graphs, where diverse node types and complex interactions are prevalent [,,,,,,,,,,,,,,]. In particular, architectures such as the Graph Relearn Network [] and Graph Attention Network [,] have been shown to mitigate issues like over-smoothing and performance fluctuations, resulting in more robust performance in tasks such as node classification and link prediction.
3.2.2. Link Prediction and Node Classification
In Graph Neural Network (GNN)-based learning, link prediction and node classification are two key tasks that leverage the inherent structure of graphs. Link prediction infers missing or potential future connections by analyzing the relational patterns among nodes, while node classification assigns labels to nodes by considering both their individual features and the influence of their neighboring nodes. Together, these tasks empower various applications, such as recommendation systems, network analysis, and anomaly detection, by effectively capturing the underlying connectivity within the graph.
By representing objects such as vehicles, pedestrians, and road facilities as a graph and combining it with a temporal LSTM, SG2VEC [] can predict future collision events. Node embeddings are directly optimized for the downstream task of “collision likelihood” and are lightweight for fast inference on actual AV (autonomous vehicle) edge hardware. MuCoMiD [] addresses biological knowledge graphs (genes, miRNAs, diseases, proteins, etc.) using GNN-based multi-task learning. It addresses challenges such as data scarcity and noise by enabling automatic feature extraction and integrating more than five different biological data sources. The GNN layers learn the interactions between nodes (biomolecules), demonstrating robust predictions even with limited labeled data.
The heterogeneous graph-based knowledge tracing method with spatiotemporal evolution (TSKT) [] is designed to learn from graph data containing heterogeneous nodes and relationships. This model captures complex interactions among various node and relationship types through meta-paths and meta-graphs, achieving excellent performance in modeling learners’ learning patterns. The Graph Structure Self-Contrasting (GSSC) [] approach enhances graph-based learning performance by integrating graph structures into a multilayer perceptron (MLP). By incorporating graph structures into the input layer of the MLP, this model effectively learns the nonlinear interactions between nodes, significantly improving the node classification performance.
The Graph-Aware Tensor Factorization Convolutional Network (GATFCN) [] combines tensor factorization with graph convolution (GCN). By integrating graph structural information into the tensor factorization process, this model learns more precise interactions between nodes and relationships, achieving outstanding performance in tasks like link prediction. Ref. [] combined a GNN with self-supervised learning to detect adverse effects in drug−drug interactions. This model learns complex relationships from large-scale drug datasets and captures patterns of drug−drug similarities, interactions, and side effects. It predicts potential side effects based on real clinical data, aiding in drug safety evaluation and clinical trial design. GraphX-Net [], a GNN model designed for cancer survival prediction, represents patient data as nodes and similarities as edges to construct the graph structure. This model evaluates the contribution of each sample (patient) within the graph and accurately predicts the probability of survival in patients with cancer. By leveraging geometric features and graph structural information, advanced cancer survival predictions are supported, significantly contributing to personalized treatment design and survival analysis.
3.2.3. Heterogeneous, Biomedical, and Large-Scale Graphs
In heterogeneous information networks (HINs) containing different types of nodes and relationships (e.g., person-organization, paper-author, drug-disease), GNNs leverage meta-paths and meta-graphs to learn diverse proximities []. For example, HIGCN (Heterogeneous graph convolutional network with local influence) calculates the local importance of each node to extract multi-faceted semantics within heterogeneous graphs. GNNs are actively utilized to predict the survival rates of patients with cancer, drug−drug interaction (DDI) predictions, and hospital knowledge graph expansions []. Advanced variants like Graph Neural Topic Models and Bayesian GNNs, have also emerged to address challenges in medical data, such as uncertainty, heterogeneity, and scalability. For instance, the Geometric GNN [], used for cancer survival prediction based on omics data, calculates node embeddings by considering the geometric features of the data (e.g., curvature and Ricci curvature). A comprehensive survey of graph embedding techniques tailored for biomedical data [] provides an overview of graph-specific embedding methods for biomedical applications.
For large-scale knowledge graphs (KGs) containing hundreds of millions to billions of nodes, the cost of message passing becomes a significant bottleneck, leading to research on distributed implementations or model parallelization []. For example, the distributed non-negative RESCAL algorithm integrates GNN-like operations to maximize the efficiency. Moreover, automatic model selection in large-scale environments is a critical issue. The distributed non-negative RESCAL with automatic model selection for exascale data [] introduces a distributed RESCAL embedding method suitable for exascale datasets, enabling the efficient learning of large-scale knowledge graphs.
3.3. Dynamic and Task-Specific Learning
3.3.1. Temporal Knowledge Graphs (TKG)
Research is being conducted on GNNs that learn temporal knowledge graphs (TKGs) that change over time, enabling the inference of future facts from past data. When tracking structural changes over time, the GNN layers update the node representations by integrating the current timestamp graph with past (or neighboring) timestamps. For example, SFTe [] predicts future interactions by embedding the structure, factuality, and temporality individually.
To adapt quickly, even with few-shot training samples for new relations or entities, research is exploring GNNs with meta-learning to dynamically adjust parameters []. Models like MTRN (task-related network based on meta-learning) employ specialized components, such as neighbor-aware encoders and self-attention encoders, to sensitively respond to task transitions. Knowledgebra [] proposed an embedding method that optimizes the model performance by leveraging the algebraic structure of KGs to enhance global consistency. Dynamic relation learning for link prediction in knowledge hypergraphs [] improves the link prediction performance in hypergraphs through dynamic relation learning.
T-GAE [] utilizes temporal information in graphs to learn the interactions between nodes. It employs a graph attention mechanism to integrate spatiotemporal dependencies, which allows the model to capture dynamic changes in temporal graphs, predict future interactions from past data and handle complex temporal patterns efficiently. The Bayesian hierarchical graph neural network (BHGNN) [] incorporates uncertainty in graph data into the learning process to produce highly reliable results. It is particularly effective in tasks where reliability is crucial, such as industrial fault diagnosis, in which uncertainty feedback is used to simultaneously improve prediction accuracy and model confidence. This approach contributes to error detection and refinement in several scenarios.
CDRGN-SDE [] employs a cross-dimension network to model interactions across multiple dimensions when learning temporal data. The model captures changing graph structures along the temporal axis and learns complex dependencies in temporal graphs to make accurate predictions. This enables effective learning, even in large-scale temporal graphs. Ref. [] proposed a model that simultaneously learns multiple graph structures along the temporal axis and infers relationships and patterns in TKGs. This model efficiently captures time-dependent patterns and reflects interactions across the past, present, and future.
Dynamic learning approaches in temporal knowledge graphs not only adapt to evolving data but also help mitigate issues such as hallucinated relationships. For instance, models like T-GAE adjust node representations over time to reduce the occurrence of spurious or unsupported links. For example, models like T-GAE [] incorporate temporal-structural adaptations to adjust node representations over time, reducing the occurrence of spurious or unsupported relations. Additionally, frameworks that integrate reinforcement learning [] provide mechanisms to continuously refine the graph structure, ensuring that errors due to hallucination are minimized in real-world applications.
3.3.2. Extensions: Recommendations, Reinforcement Learning, and Beyond
When user-item, item-attribute, or item-item interactions are represented as a graph and GNNs are used to learn node embeddings, the recommendation accuracy improves significantly []. EMKR employs multi-task learning (recommendation + KGE) to enhance the performance of both tasks. Reinforcement Negative Sampling (KGRec-RNS) uses reinforcement learning (RL) to identify “meaningful” negative samples [], which provide far more informative negatives than random sampling, improving training efficiency and interpretability.
For fully inductive learning in evolving KGs, one method has been proposed to classify or predict links using GNNs on sampled subgraphs rather than the entire graph []. Techniques such as personalized PageRank (PPR) are employed to extract neighboring nodes, which helps mitigate over-smoothing and enables flexible inductive reasoning. Ref. [] proposed a sequential recommendation system based on knowledge graphs and transformers, and ref. [] introduced an enhanced multi-task learning framework that integrates recommendation and KG embedding tasks. Additionally, some approaches combine first-order neuro-symbolic and logic rule embeddings to improve the explainability of recommendation tasks []. For example, logical rules such as “If X is related to Y, and Y is similar to Z, then X is related to Z” can be used in conjunction with neural embeddings. Moreover, BiG-Fed [] further enhances the recommendation performance by combining hierarchical optimization with federated learning.
Ref. [] introduced a method for extracting local subgraphs from large-scale graphs to reduce the training time and improve prediction accuracy. This approach performs link prediction based on subgraphs, achieving high efficiency and performance without requiring the entire graph to be trained, making it particularly useful for large-scale datasets like recommendation systems. Ref. [] proposed a model for knowledge graph-based question generation using subgraphs. By focusing on specific nodes and relationships, the model generates questions that reflect the structural information from the graph, enabling more precise responses in question-answering systems.
Global-Local Anchor Representation (GLAR) [] is an inductive link prediction model centered on subgraphs, capable of effectively predicting links in dynamic environments where new nodes and relationships are continuously added. This model leverages the properties of local subgraphs to enable scalability and achieves high performance with an efficient computation.
In summary, dynamic and task-specific learning models offer significant advantages over static embedding methods by adapting to new data using meta-learning and dynamic relation learning. This adaptability not only improves the overall accuracy but also enhances the robustness of the knowledge graphs by reducing errors, such as hallucinated relationships.
3.4. Transformer-Based Learning
Transformers have demonstrated exceptional performance in natural language processing, leading to a significant increase in research combining Transformers with knowledge graphs (KGs). For KGs that extensively utilize textual information from documents, the self-attention mechanism allows modeling of long-range dependencies and subtle contextual relationships between entities. This capability has positioned Transformers as an increasingly influential approach to KG learning [].
3.4.1. Text Integration and Finetuning
Research such as MHAVGAE [] combines weakly supervised learning with a Multi-head Attention Variational Graph Auto-Encoder, integrating Transformer-style multi-head attention into a VAE to automatically learn prerequisite relationships in large-scale conceptual graphs. Metrics like Resource-Prerequisite Reference Distance (RPRD) are used to augment incomplete labels, significantly reducing the need for manual labeling.
Pretrained text-based models (e.g., BERT) have inspired dual attention structures in graph layers, assigning different attention channels based on the importance of the relations []. For instance, the Dual-AEN model independently updates entities and relations while facilitating their interactions.
Methods like SATrans [] inject structural information from tables and graphs directly into the attention mask of a Transformer encoder, mitigating structural loss caused by “flattening” data into plain text. The lower layers of self-attention focus on local information, while the upper layers emphasize global information, achieving high accuracy in tasks that reflect local-global structures, such as validation and question answering. Fine-tuning these models on domain-specific KG data enables the capture of nuanced semantic features that facilitate tasks like relation extraction and entity linking [].
Ref. [] proposed a technique to expand knowledge graphs (KGs) using pretrained language models (e.g., BERT, GPT). This approach extracts entities and relationships from text data and integrates them into the KG, thereby enriching its representation. By leveraging the strong language understanding capabilities of pretrained models, this method adds new information that existing KGs may lack and enhances the semantics of the existing relationships. The synergy between NLP and KG in this approach improves performance across various applications, including question answering and recommendation systems.
Transformer architectures (e.g., BERT) have become the dominant paradigm in knowledge graph construction, particularly due to their ability to capture long-range dependencies. However, traditional recurrent neural networks (RNNs), such as LSTM or GRU models, can still offer advantages in terms of computational efficiency for shorter sequences. Table 1 summarizes the key differences between these methods in terms of accuracy, efficiency, and practical applicability.

Table 1.
Comparison of RNN-based methods vs. transformer-based methods.
3.4.2. Fusion of Topology and Logical Rules
The Fuse Topology contexts and Logical rules in Language Model (FTL-LM) [] enhances knowledge graph (KG) learning by combining graph topology information (structural relationships between nodes) with logical rules. This model imposes constraints on relationships within the graph through logical rules while learning the structural interactions of nodes and edges via topology information. For instance, it improves the reliability of relation prediction using rules like “If X is related to Y, and Y is related to Z, then X is also related to Z”. This approach excels in domains where logical consistency is critical, such as healthcare and the law.
The Medical Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (MCBERT) [] system learns the relationships among diseases, drugs, and symptoms using domain-specific KGs. By modeling complex relationships in medical data using KGs, MCBERT facilitates efficient analysis and prediction. It is particularly useful for tasks such as drug-disease interactions, prescription suitability evaluations, and patient profiling, supporting medical professionals in decision-making.
The Adaptive Hierarchical Transformer with Memory (AHTM) [] combines a hierarchical Transformer architecture with model compression techniques to effectively generate KG embeddings for large-scale medical datasets. This method accounts for the high-dimensional nature of medical data and learns key patterns and relationships while reducing memory usage and computational costs. For example, it processes extensive medical datasets, including patient records, pharmaceutical databases, and genomic information to produce embeddings that maintain predictive accuracy while enhancing computational efficiency.
Ref. [] explored the potential of integrating large language models (LLMs) with graph data to expand and utilize KGs. This survey proposes methods for combining LLMs’ language understanding and generation capabilities with graph-based learning to effectively learn new entities and relationships. By merging the structural information of graph data with the rich textual representations of LLMs, this approach achieves strong performance in various tasks, such as KG-based question answering, summarization, and relation prediction.
The Unsupervised Semantics and Syntax into heterogeneous Graphs (USS-Graph) [] adopts unsupervised learning techniques to efficiently learn from graph data. This model simultaneously captures the structural features and syntactic semantics of a graph and models node and edge interactions with precision. By automatically learning significant patterns and relationships in the graph without explicit labels, it demonstrates high scalability, even with large datasets. This approach is applicable to graph-based text classification, relation extraction, and other similar tasks.
3.4.3. Hyperbolic Space, IRL, and Other Extensions
Traditional Transformers often assume Euclidean space; however, many studies suggest that hyperbolic space (curvature < 0) is better suited for hierarchical KGs (e.g., tree-structured or layered graphs). For instance, HyGGE [] performs graph attention in a hyperbolic space to capture complex neighbor structures and relationship patterns more effectively, while DeER [] adopts a trainable curvature mechanism that automatically adjusts geometric properties to fit the data. Similarly, RpHGNN [] refines embeddings in heterogeneous graphs via an iterative “propagation-update” cycle, thus reducing information loss and preserving hidden relationships across multi-type nodes. Each of these methods demonstrates how hyperbolic embeddings can offer more nuanced representations than standard Euclidean approaches, particularly for KGs with strongly hierarchical features.
Beyond the choice of embedding space, AInvR [] integrates IRL (Inverse Reinforcement Learning) with a Transformer-based inference module to automatically learn reward functions—thereby tackling the sparse reward issues frequently seen in multi-hop reasoning tasks. This IRL-based approach can also be combined with meta-learning strategies (discussed in Section 3.5.4) to further address data sparsity or dynamically adapt to new reasoning paths. Meanwhile, ref. [] models user-item interactions for sequential recommendation tasks, highlighting how Transformers handle temporal or sequential dependency in KGs, and ref. [] processes object-region relationships within video data to enhance interpretability in Video QA. Furthermore, HG-SCM [] adopts a structural causal model perspective to identify events and their causes in a human-like manner, emphasizing causal inference from graph data. Lastly, ref. [] proposed a graph-augmented MLP-based parallel learning model that employs quantization and parallelized processes—allowing real-time training and inference for massive graph datasets.
3.5. Additional Learning Methods
3.5.1. Self-Supervised and Contrastive Learning
Techniques for self-supervised learning of embeddings by constructing pairs of nodes or subgraphs within graphs are emerging []. Implicit GCL (iGCL) constructs augmentations in the latent space, avoiding excessive random edge deletion/addition to balance structural preservation and training stability. Fine-Grained GCL (FSGCL) [] enhances representation learning by contrasting meanings across graph motifs and meta-paths. Dynamic attention networks adaptively focus on different parts of the graph based on task requirements, helping to better distinguish between entities and relationships []. This approach emphasizes context-specific features, enabling models to better understand the significance of entities and their relationships.
TCKGE [] combines contrastive learning with Transformers to enhance embedding performance, while Clustering Enhanced Multiplex Graph Contrastive Representation Learning [] improves clustering performance across multiple graphs using contrastive learning. Graph Contrastive Learning with Implicit Augmentations [] proposes contrastive learning leveraging implicit augmentations, and [] improves knowledge graph completion performance by separating relational GNNs through contrastive learning. Graph Contrastive Learning with Personalized Augmentation [] introduced contrastive learning with personalized augmentations, and LLM-TIKG [] proposed the generation of threat intelligence knowledge graphs based on large language models using contrastive learning. In addition, one method [] shows that self-attention mechanisms can generate low-dimensional knowledge graph embeddings by dynamically adjusting inter-node interactions, thereby enhancing the link prediction performance. Ref. [] introduced a multi-level graph knowledge contrastive learning framework that effectively integrates both local and global graph information for superior representation learning. Ref. [] proposed a method that leverages self-attention mechanisms to generate low-dimensional embeddings, thereby dynamically adjusting inter-node interactions and significantly enhancing link prediction performance.
3.5.2. Generative Adversarial Network (GAN)-Based Learning
In KGE models, generating negative triples by random replacement is often too easy, which allows the model to quickly distinguish them. To address this, GANs are used to generate plausible negative triples, while a discriminator simultaneously classifies real/fake triples and learns embeddings []. After training with Generative Adversarial Graph Embedding, the generator effectively restores the distribution of the training data, and the discriminator acquires expressive capabilities for triple classification or link prediction []. Moreover, one study [] proposed a GAN-based framework that effectively models complex relational patterns—such as one-to-many and many-to-one—thus overcoming the limitations of traditional single-vector representations.
3.5.3. Integrating Supervised and Reinforcement Learning
Traditional supervised learning excels at learning from labeled triples and node annotations, ensuring stable and reliable embeddings. However, supervised methods alone may miss latent or less frequent relationships, especially in sparse regions. Reinforcement learning (RL) addresses this limitation by dynamically exploring the graph to discover additional link candidates and multi-hop paths. By integrating both approaches—as exemplified in RD-MPNN []—the model benefits from the strengths of each method. Specifically, supervised learning provides a solid foundation by reliably learning known relationships, while RL complements this by continuously exploring and validating new connections in underrepresented areas. This hybrid strategy leads to higher-quality embeddings that are both robust and comprehensive.
In recommendation systems, for example, KGRec-RNS [] leverages RL to model user activity as a Markov Decision Process. This approach identifies “meaningful” negative samples that are more informative than random negatives, thereby enhancing the learning efficiency and interpretability. Additionally, in multi-hop reasoning tasks, using Inverse Reinforcement Learning (IRL) [] to learn reward parameters from real data allows the model to better prioritize correct paths and mitigate over-rewarding of incorrect routes. The combination of supervised learning and RL thus achieves a balanced trade-off between stability and dynamic exploration, resulting in improved overall performance.
3.5.4. Hyperbolic and Geometric Learning, and Meta-Learning
Building on the hyperbolic concepts introduced in Section 3.4.3, more advanced hyperbolic and non-Euclidean geometric learning methods further exploit the properties of curved spaces to model hierarchical and complex relationships in KGs. For example, one approach [] leverages Poincaré geometry to enhance link prediction by capturing intricate interactions between entities and relations, while another [] proposes a deep hyperbolic convolutional model that expands the expressive power of KG embeddings. CoPEs (Composition-based Poincaré embeddings) [] similarly use hyperbolic geometry to preserve distance relationships in large-scale or deeply hierarchical graphs, improving generalization and interpretability []—a critical advantage when dealing with real-world KGs that often contain multi-level hierarchies.
Meanwhile, meta-learning techniques address the challenges of data sparsity and frequent domain shifts by focusing on both the global graph structure and local few-shot scenarios []. Approaches such as MAML [] and Prototypical Networks [] enable learning from minimal examples [], offering robust KG completion in environments with limited or intermittently available data. Building on these fundamentals, ref. [] introduced the selective transfer of KG embeddings for few-shot relation prediction, while ref. [] applied multi-granularity meta-learning to tackle long-tail classification—a scenario in which many entities or relations appear infrequently. Furthermore, ref. [] integrated dynamic prompt learning with meta-learning for multi-label disease diagnosis, swiftly adapting to newly introduced diseases and label structures by modeling disease-symptom relationships within a KG. This approach ensures high diagnostic accuracy in data-sparse conditions and is extendable to personalized diagnostic systems, underscoring the potential synergy between hyperbolic embedding methods and meta-learning for real-world medical applications.
3.6. Final Summary
KG learning encompasses a broad range of methodologies that enable effective link prediction, relational inference, and structured data analysis. Foundational approaches, such as TransE-based embeddings [,,,,,,,,], efficiently represent entities and relations, while GNN-based methods [,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,] capture complex, heterogeneous interactions—supporting tasks like node classification and link prediction. Dynamic and task-specific strategies leverage temporal modeling and meta-learning to adapt to evolving graph structures and further enhance recommendation systems and reinforcement learning [,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,]. Transformer-based approaches—notably those incorporating pretrained text models []—integrate textual and structural information via self-attention [,,,,,] and improve relational consistency by fusing topology with logical rules [,,,,]. Finally, additional learning methods—including self-supervised/contrastive learning, GAN-based negative sampling, and supervised plus reinforcement learning hybrids—address challenges such as few-shot and long-tail learning [,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,]. Together, these diverse strategies form a comprehensive framework that drives significant advancements in KG learning in various domains.
4. KGs Evaluation
Intrinsic Evaluation (Section 4.1), Extrinsic Evaluation (Section 4.2), Qualitative Evaluation (Section 4.3), and Dataset and Domain-Specific Evaluation (Section 4.4). Overall, the number of publications peaks in 2023 before declining in 2024, but each sub-section follows its own trajectory.
Steady or Growing Areas Intrinsic Evaluation (Section 4.1) gradually increases and stabilizes over time. This steady rise may be attributed to the ongoing need for robust internal metrics—such as accuracy, consistency, and completeness—that allow researchers to benchmark KG models in controlled settings.
Peaks and Surges in Specific Years Extrinsic Evaluation (Section 4.2) and Dataset and Domain-Specific Evaluation (Section 4.4) show a marked surge in 2023, possibly reflecting a heightened focus on real-world applications and specialized datasets during that period. As industries and academic communities sought more tangible results and domain-aligned benchmarks, publications in these areas spiked to address the practical constraints.
Fluctuations and Declines Qualitative Evaluation (Section 4.3) reaches its highest point in 2023, then experiences a decline in 2024. This decline may indicate a shift in research priorities toward more standardized or quantifiable metrics or the saturation of existing qualitative methods. Over time, as certain qualitative approaches mature, interest may wane in favor of new, data-intensive evaluation techniques.
Overall, these trends underscore how the KG Evaluation landscape evolves in tandem with methodological advances and the practical demands of specific domains. While some approaches—like intrinsic metrics—remain consistently relevant, others experience spikes or dips as researchers adapt to changing expectations for rigorous, real-world performance and domain-driven requirements.
4.1. Intrinsic Evaluation
4.1.1. What Is an Intrinsic Evaluation?
Intrinsic evaluation offers a suite of quantitative metrics that assess the quality and performance of the outputs generated by a knowledge graph model, and each metric is particularly well-suited to different tasks and application scenarios. For example, classification metrics such as Precision, Recall, and F1-Score are advantageous when evaluating discrete prediction tasks—like determining whether a predicted RDF triple correctly represents the relationship between entities. In contexts where false positives are especially detrimental, a high Precision is critical, while Recall becomes paramount when it is crucial to capture all relevant relations. The F1-Score then serves as a balanced indicator when both types of errors are equally consequential.
In contrast, rank-based metrics, such as Mean Reciprocal Rank (MRR) and Hits@K, are more appropriate for tasks involving link prediction or information retrieval, where the model generates a ranked list of candidate relations. MRR is beneficial because it captures the average rank of the first correct answer, thereby favoring models that bring correct candidates to the top, while Hits@K focuses on the proportion of cases in which the correct answer appears within the top K predictions—making these metrics particularly useful in systems that can operate effectively on a shortlist of candidates.
For continuous numerical prediction tasks, regression metrics like Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE), Mean Absolute Error (MAE), and Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE) are used. RMSE is especially sensitive to large errors, which is advantageous in applications where significant deviations can have a profound impact, whereas MAE provides a straightforward average error measure that is easier to interpret. MAPE, which expresses errors as percentages relative to true values, is particularly useful in scenarios in which the relative scale of error is more informative than the absolute difference.
Additionally, when assessing the quality of the learned embeddings, methods such as the Pearson correlation coefficient can quantify the linear relationship between embedding similarities and ground-truth semantic relationships. In some cases, an F1-Score is also computed for clustering or classification tasks performed on embedding spaces, providing further insight into the expressive power of the representations.
Finally, evaluating algorithm optimization and efficiency through measures like average effectiveness, standard deviation, execution time, and memory usage is essential when scaling models to large datasets or deploying them in real-time applications. These metrics not only reflect the model’s internal optimization and stability across various runs but also determine its practical viability in resource-constrained environments.
By carefully selecting and interpreting these intrinsic evaluation metrics in accordance with the specific requirements and constraints of the knowledge graph application, researchers can gain a comprehensive understanding of the model performance and make informed decisions regarding further optimization and deployment strategies. Through Table 2, we can see how the evaluation metrics are assessed.

Table 2.
Comprehensive overview of intrinsic evaluation metrics and their mathematical definitions.
4.1.2. Intrinsic Evaluation: Metrics, Methods, and Case Studies
In a study based on the public standard for public transportation data, researchers used the GTFS Madrid benchmark to precisely measure how well a CSV-based RML mapping tool produced results that matched public transportation data and to evaluate the impact of data types (e.g., differences in handling xsd:long versus xsd:integer) on mapping errors and attribute matching success rates []. Additionally, a study was conducted that rigorously evaluated the performance differences among link prediction techniques using various knowledge graph datasets under the same preprocessing conditions and demonstrated the statistical significance between methods using the Wilcoxon test and the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test []. In the Chinese domain, intrinsic performance was systematically verified by quantitatively evaluating the embedding representation and the effect of negative samples in an entity linking model using the FB15K237, WN18RR, and SCWS datasets, measured using the Pearson correlation coefficient and F1-Score [].
Furthermore, a study evaluating the effect of mutation operators introduced several metrics—including average effectiveness, average n-step effectiveness, standard deviation of effectiveness, and execution time—to quantify the algorithm optimization performance []. Another research compared the performance of entity-relation extraction using the New York Times, WebNLG, and ADE datasets with Micro-F1 and Macro-F1 metrics []. In an air quality prediction task, the KnowAir and UrbanAir (North) datasets were used to quantitatively evaluate prediction errors with RMSE, MAE, and MAPE [], and a study on patient similarity search based on medical data reported excellent performance in terms of Accuracy and F1-Score using the MIMIC-III and MIMIC-IV datasets []. Additionally, research utilizing datasets that include spatiotemporal information employed Mean Reciprocal Rank, Hit@1, and Hit@10 to demonstrate performance improvements exceeding three times that of TransE [], and another study analyzed the effect of text embeddings and graph neural network layer tuning in multilingual entity alignment using the DBP15K dataset []. Studies evaluating the effect of temporal logical rules using the ICEWS and GDELT datasets [,] have provided valuable insights; furthermore, an iterative approach for applying temporal logical rules to improve reasoning performance was proposed in []. Finally, research that quantitatively evaluated performance in fields such as legal judgment prediction, link prediction, KG generation, and railway defect detection in the domains of law, biomedicine, agriculture, and railway fault detection further exemplifies intrinsic evaluation [,,,].
4.2. Extrinsic Evaluation
4.2.1. What Is an Extrinsic Evaluation?
Extrinsic evaluation goes beyond assessing a model’s internal consistency or predictive accuracy by quantifying its practical value in real-world application environments. This evaluation framework examines how effectively a knowledge graph (KG) model performs in operational settings, considering factors such as processing speed, usability of the outputs, and performance improvements over existing systems when integrated into tasks like question answering, recommendation, ranking, legal judgment prediction, medical diagnosis, code mapping, and more.
For example, in the public transportation domain, extrinsic evaluation may involve comparing a CSV-based mapping tool with systems like Morph-KGC and SPARQL Anything using GTFS data, to verify whether they produce identical results. In question-answering tasks, the integration of large-scale language models with KGs has been shown to enhance metrics such as Mean Average Precision and Mean Reciprocal Rank, demonstrating the model’s ability to rank and retrieve correct answers effectively.
In medical applications, studies leveraging datasets such as MIMIC-III and MIMIC-IV have shown that patient similarity search models can achieve high accuracy and F1-Scores, while in multilingual entity alignment, improvements are quantified using datasets like DBP15K. Similarly, in the legal domain, judgment prediction models based on datasets like ECHR and CAIL2018 have attained superior Accuracy and AUC-ROC compared to traditional legal AI systems. Other studies in biomedical, agricultural, and railway defect detection applications have demonstrated tangible performance benefits—such as improved link prediction accuracy and reduced query response times—when KG models are applied in real-world scenarios.
Overall, extrinsic evaluation provides an objective measure of how well a KG model performs in practical settings, highlighting its benefits in operational environments and its advantages over conventional methods through measurable improvements in various application-specific metrics.
Knowledge graphs constructed or refined using LLM-based systems can exhibit hallucinated relationships that degrade the overall performance. For instance, a clinical decision-support application may rely on KG-based inferences only to discover that certain predictive links between symptoms and diagnoses are fabricated by the generative model. Extrinsic evaluation thus benefits from dedicated error-detection strategies—such as outlier analysis or correlation checks with trusted medical databases—to ensure that the discovered relationships are both accurate and clinically valid. By incorporating such validation layers, practitioners can reduce erroneous recommendations and maintain higher reliability in domains where trust is essential.
4.2.2. Extrinsic Evaluation Across Diverse Knowledge Graph Applications
In the field of public transportation, a quantitative analysis was conducted comparing a CSV-based mapping tool with Morph-KGC and SPARQL Anything, using GTFS public transportation data to determine whether the same results were generated []. Another study constructed an application pipeline that evaluated various link prediction techniques under the same conditions to analyze their impact on a real-world knowledge graph evaluation workflow []. In the question-answering task, the integration of large-scale language models with knowledge graphs was shown to improve Mean Average Precision and Mean Reciprocal Rank using both Chinese and English QA datasets (NLPCC2017, cMedQA, TREC-QA, and WikiQA) [].
In the medical application field, the use of the MIMIC-III and MIMIC-IV datasets demonstrated that a patient similarity search model achieved high accuracy and F1-score [], while in multilingual entity alignment, performance improvements across languages were quantitatively verified using the DBP15K dataset []. In the legal domain, a judgment prediction model based on the ECHR and CAIL2018 datasets achieved superior Accuracy and Area Under the Curve for Receiver Operating Characteristic (AUC-ROC) compared to conventional legal AI models []. In the biomedical field, studies using the KEGG50k, Hetionet, SuppKG, and ADInt datasets have demonstrated improved link prediction performance []. In agricultural applications, research based on Bangladesh agricultural data (BBS) reported that after KG generation, OLAP queries and business intelligence analyses experienced significantly reduced query response times [], and in railway defect detection, evaluations using the NEU RSDDS-AUG dataset quantitatively verified the benefits of external applications []. Additionally, evaluations through RDF triple store benchmarks [] and open-world KG completion assessment via extended pretrained language models [], as well as multilingual KG alignment performance evaluation [] and studies that quantitatively analyzed the effects of relation-based graph attention and mutual information maximization techniques [,,] are presented as extensive applications of extrinsic evaluation.
Other applications, such as software bug triaging, clinical decision support, mobile app recommendation, literature-based research hypothesis generation, cybersecurity, federated learning in healthcare, link prediction under few-shot conditions, and storage space savings through normalization techniques, have also been evaluated.
4.3. Qualitative Evaluation
Qualitative evaluation is a method that deeply analyzes the internal decision-making process and inference mechanisms of a knowledge graph model through case studies, capturing aspects such as interpretability and transparency, which are difficult to assess through numerical evaluation. Through such evaluations, one can understand how the model processes information and makes decisions and identify the causes of errors. This, in turn, provides important insights into model improvement and optimization strategies.
For example, in a study that evaluated internal optimization performance, the validity and completeness of the mutation operator were observed to affect the model performance. This study qualitatively analyzed the efficiency trade-offs to explain how each component of the algorithm contributes to the overall performance []. In another study, by incorporating a visual attention mechanism, the evaluation focused on which parts of the input sentence the model concentrated on during the entity-relation extraction process, thereby greatly enhancing the intuitiveness of the result interpretation []. A study that qualitatively interpreted the phenomenon in which a Sub-Entity Embedding model consistently outperformed existing methods contributed to a better understanding of the subtle performance differences between models []. Additionally, research that strengthened the transparency of the model’s decision-making process through a balance between text embeddings and internal information provided a qualitative analysis of how the model reached its decisions [].
A study that deeply analyzed the use of temporal logical rules and reliability through cases using the ICEWS and GDELT datasets offered qualitative insights into the inference process of the model and the impact of errors []. Another study, through a multi-stage inference technique, qualitatively evaluated the interpretability of legal judgment prediction, clearly revealing the decision-making process in practical applications []. In the domain of biomedical relationship extraction, research that analyzed the effects of integrating large-scale language model-based text embeddings with domain knowledge on a case-by-case basis provided intuitive insights into the model’s internal workings []. Furthermore, a study evaluating the readability of community structures and node layouts in graph exploration and visualization through user studies and case analyses qualitatively demonstrated the model’s interpretability in applied settings [].
In the e-commerce field, the role of a language model that exhibits high relationship labeling performance, even with limited data, was qualitatively analyzed []. In a question-answering task, a study qualitatively discussed the strengths and limitations of the system based on the inclusion of SPARQL modifiers []. Additionally, research evaluating the results of EHR data integration among medical institutions alongside domain experts [] and a study analyzing the interpretability of information extraction after generating a large-scale scientific KG [] have contributed to an in-depth understanding of the model’s practical usability. Moreover, studies that qualitatively interpreted the bias of commonsense knowledge models [], discussed the challenges of classifying sensitive data with domain expert evaluations [], and assessed the stability of dynamic KG refinement through case studies [] are important examples of qualitative evaluation. Finally, diverse qualitative analyses have been conducted in various studies on topics such as clinical data integration, semantic relevance evaluation, enhanced path inference for medical diagnosis, AMR parsing, complex entity resolution, fall risk detection, hydraulic engineering, community exploration, cybersecurity, reverse-engineering question generation, and IoT applications.
4.4. Dataset and Domain-Specific Evaluation
In studies evaluating industry and multilingual scenarios, one research work utilized the GTFS Madrid benchmark to assess the consistency and coherence of mapping tools based on the public standard for transit data []. Another study compared various link prediction techniques across different knowledge graph datasets under identical preprocessing conditions []. Some studies have evaluated entity linking performance in the Chinese domain using the FB15K237, WN18RR, and SCWS datasets [], as well as a study that verified model performance in multilingual knowledge graph alignment tasks—considering the language-specific characteristics—based on the DBP15K series datasets []. Evaluations using large-scale healthcare and medical datasets, such as Yago (ST), DBpedia (ST), and Wikidata (ST), have also been conducted [], along with research that quantitatively assessed storage space and complex query performance in industrial settings using various RDF triple store benchmarks []. Lastly, a study evaluating the interpretability and alignment performance of multilingual KGs also falls under this category [].
In the domains of medicine, law, biomedicine, agriculture, and air quality prediction, one study used the KnowAir and UrbanAir (North) datasets for an air quality prediction task to evaluate the prediction accuracy and computational efficiency []. In the context of patient similarity search based on medical data, research employing the MIMIC-III and MIMIC-IV datasets evaluated model performance according to domain-specific characteristics []. Moreover, studies evaluating link prediction and completion performance in spatiotemporal knowledge graphs using the Yago (ST), DBpedia (ST), and Wikidata (ST) datasets [], as well as research evaluating the application performance of judgment prediction models in the legal domain using the ECHR and CAIL2018 datasets [] have been conducted. In biomedicine, link prediction evaluations using datasets such as KEGG50k, Hetionet, SuppKG, and ADInt have been carried out []. Additionally, research based on Bangladesh agricultural data (BBS) evaluated the completeness, currency, and OLAP compatibility of fisheries, forestry, and agriculture data after KG generation [], and a study using the NEU RSDDS-AUG dataset analyzed the extrinsic application effects in the railway defect detection field []. Finally, a study on the open-world KG completion task utilizing various KG benchmark datasets [] also falls into this category.
In the fields of science, commonsense, clinical, natural language processing, entity resolution, human activity monitoring, hydraulic engineering, community exploration, cybersecurity, reverse-engineering question generation, and IoT applications, research using the ICEWS and GDELT datasets evaluated the effects of temporal events and logical rules on event data []. Additionally, studies on graph exploration and visualization using the Les Misérables and Graph of Science datasets [], as well as research evaluating relationship-labeling performance in product knowledge graphs using the Electronics and Instacart datasets in the e-commerce domain [] have been conducted. There is research quantitatively evaluating the effect of SPARQL modifier handling in question-answering tasks using the MQALD dataset [] and studies assessing data integration and code mapping performance between medical institutions using real EHR data and medical codes (RxNorm, VA codes) [].
Other examples include a study that evaluated scientific KG generation and information extraction performance using a large-scale computer science paper dataset (6.7 million papers, 10 million entities, and 41 million triples) [], and research that assessed the bias in commonsense knowledge models using the ConceptNet and Wikidata-CS datasets []. There has also been work on data privacy evaluation using DPV-based sensitive personal data []. In addition, studies using datasets such as FB15K, NELL, WN18, and YAGO3-10 evaluated the performance of dynamic KG refinement and continuous updates [], and research based on cerebral aneurysm and COVID-19 datasets evaluated clinical data integration and evidence-based medicine support performance []. Evaluations of semantic relevance have been carried out using DBpedia and 14 benchmark datasets [], and research utilizing the MIMIC-III, MIMIC-IV, and eICU datasets evaluated the interpretability of medical diagnosis and disease prediction through path inference []. There are also evaluations in natural language processing using the AMR2.0 and AMR3.0 datasets [], studies on complex entity resolution tasks using seven real-world industrial and domain-specific datasets [], and evaluations of fall risk detection and human activity monitoring using everyday activity and event data []. Research based on a dedicated hydraulic engineering dataset to assess KG embedding and link prediction performance in the field of hydraulic engineering has been conducted []. Other examples include studies on edge attribute-based community exploration using standard graph datasets [], evaluations of KG construction and quality in cybersecurity using datasets such as FB15K [], assessments of reverse-engineering question generation, question quality, and filtering performance using a Wikidata-based KG [], and research on collision detection and context recognition in the IoT field using trigger-action programming-related datasets []. In the question-answering field, there is research evaluating extrinsic QA performance using the NLPCC2017, cMedQA, TREC-QA, and WikiQA datasets [], as well as studies that quantitatively evaluated the effects of relation-based graph attention and mutual information maximization techniques using the FB15K-237 dataset [,,].
Finally, in Section 4.4. Dataset and Domain-Specific Evaluation, the Evaluation Metrics/Considerations are summarized in Table 3 and Table 4.

Table 3.
Datasets used in knowledge graphs across various domains.

Table 4.
Summary of evaluation metrics and considerations for various datasets in knowledge graph applications.
4.5. Final Summary
Intrinsic evaluation, as addressed in studies [,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,], shows that it is a method of evaluating the internal outputs generated by a knowledge graph model—such as data processing, entity and relation inference, and spatiotemporal prediction—using quantitative metrics (e.g., precision, recall, F1-score, mean reciprocal rank, root mean square error) to assess consistency, accuracy, embedding representation, algorithm optimization, and efficiency.
Extrinsic evaluation, as demonstrated in studies [,,,,,,,,,,,,,,], quantitatively proves the practical value provided by the model in real industrial data and application tasks (e.g., question-answering, recommendation, judgment prediction, medical diagnosis, and code mapping).
Qualitative evaluation, as carried out in studies [,,,,,,,,,,,,,,], assesses the interpretability and transparency of the model by deeply analyzing its internal decision-making process, inference mechanisms, and usability in application environments through case studies.
Finally, Dataset and Domain-Specific Evaluations have been demonstrated through studies in the first paragraph using [,,,,,,], in the second paragraph using [,,,,,,,], and in the third paragraph using [,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,]. These studies objectively evaluate the model’s performance and potential for application across various fields, including industry, multilingual contexts, healthcare, law, biomedicine, agriculture, air quality prediction, spatiotemporal analysis, science, commonsense reasoning, data privacy, dynamic knowledge graph refinement, clinical integration, natural language processing, entity resolution, human activity monitoring, hydraulic engineering, community exploration, cybersecurity, reverse-engineering question generation, and IoT applications.
5. Conclusions
This study comprehensively examines trends in knowledge graph (KG) research from 2022 to 2024, focusing on three main areas: extraction (2.x), learning (3.x), and evaluation (4.x). The findings indicate that KG research is progressing rapidly, driven by advancements in deep learning and natural language processing and the growing importance of hybrid approaches and domain-specific techniques.
First, KG extraction (2.x) showed notable fluctuations in research interest over time. In 2022, foundational studies focused on improving basic models for extracting entities and relations from textual and unstructured data, as well as accelerating large-scale data preprocessing. In 2023, attention shifted toward multimodal and domain-specific extraction (Section 2.2.2), particularly in the context of large-scale patent and technical documents. By 2024, extraction research had taken another leap, focusing on automated pipelines capable of handling complex contexts and multiple domains, resulting in a marked increase in more sophisticated methods.
In the KG Learning (3.x) domain, the focus also varied by year. In 2022, enhancements to classical embedding methods such as TransE took center stage. Moving into 2023, Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) and Transformer-based models gained traction for tasks like node classification and link prediction. Then in 2024, there was a surge in novel methods that integrated large language models (LLMs) and applied hybrid approaches combining supervised and reinforcement learning (Section 3.5.3). These approaches enabled more accurate modeling of complex relational structures, significantly improving performance in specialized fields dealing with large-scale data, such as patents and technical reports.
Lastly, KG Evaluation (4.x) peaked in 2023 before showing some decline in 2024. In 2022, intrinsic evaluation (Section 4.1) played a central role in establishing accuracy and precision metrics for early-stage models. In 2023, a spike was observed in extrinsic evaluation (Section 4.2) and Dataset/Domain-Specific Evaluation (Section 4.4), reflecting an increasing need to validate KG models for real-world applications in industry, healthcare, law, the Internet of Things (IoT), and more. While 2024 saw growing interest in interpretability and qualitative evaluation (Section 4.3), the overall research volume slightly decreased, likely due to concurrent efforts emphasizing quantitative metrics.
Reflecting these year-to-year shifts in research priorities, this study provides a holistic review of the latest methods and trends in KG extraction, learning, and evaluation. In particular, 2022 featured substantial work on improving classical embeddings and intrinsic metrics, while 2023 saw an expansion into multimodal/domain-specific extraction, GNN/Transformer-based embeddings, and extrinsic evaluation. Subsequently, 2024 brought LLM integration, supervised + reinforcement learning hybrids, renewed attention to advanced extraction methods, and greater emphasis on interpretability and qualitative metrics. These developments highlight the simultaneous pursuit of broader applications and higher performance, implying that adaptive and integrated approaches are vital as data scales and complexities increase. This trajectory suggests that knowledge graphs will continue to serve as a foundational infrastructure in diverse areas—from industry to healthcare and law—while also demanding solutions for challenges in scalability, complexity, and reliability.
6. Future Work
Despite continuous and rapid advancements in knowledge graph (KG) construction methodologies, a universally recognized standard encompassing the entire KG development pipeline remains elusive. This methodological gap arises from the complex interactions among diverse factors, including domain-specific requirements, data heterogeneity, and algorithmic complexity. Each stage—from initial data preprocessing and entity-relationship extraction to multimodal integration of diverse data types, such as text, images, and videos—necessitates tailored strategies and sophisticated technical choices, presenting researchers with significant challenges.
Future KG research should explicitly focus on several promising areas. First, developing advanced techniques for robust multimodal data integration, including the efficient extraction and accurate alignment of entities and relations across heterogeneous sources (e.g., text, images, and videos), remains critically important. Establishing standardized, scalable, and reproducible methodologies for multimodal data integration will significantly enhance the usability and applicability of KG across domains.
Second, addressing the current limitations of KG Evaluation methodologies through comprehensive and robust evaluation frameworks is essential. Future evaluations should expand beyond traditional intrinsic metrics (accuracy, precision, recall) and integrate more sophisticated metrics and benchmarks inspired by recent advancements in language model evaluation, such as F-score-based measures and metrics emphasizing interpretability, consistency, and domain-specific applicability. Such multidimensional evaluation frameworks will provide more reliable assessments of the quality and practical effectiveness of KG.
Third, establishing real-time dynamic knowledge updates and self-maintenance mechanisms represents a significant research opportunity. Many existing KGs rely primarily on static datasets, limiting their applicability in dynamic and evolving domains. Designing automated pipelines capable of continuously integrating and updating information from rapidly changing external sources (e.g., news streams, social media, and scientific publications) will ensure that KGs remain current, accurate, and highly relevant for downstream applications.
Finally, leveraging KG structures to enhance model explainability and interpretability remains a critical, yet relatively underexplored, area. Utilizing structured relational information within KGs to produce transparent, interpretable explanations of AI predictions—independent of specific model architectures—constitutes an essential step toward more trustworthy and transparent AI systems. Further research in this direction will significantly contribute to the broader acceptance and deployment of AI in sensitive or high-stakes contexts.
Funding
This work was supported by the IITP(Institute of Information & Coummunications Technology Planning & Evaluation)-ICAN (ICT Challenge and Advanced Network of HRD) grant funded by the Korea government (Ministry of Science and ICT) (IITP-2025-2022-00156394*).
Acknowledgments
In this study, AI-assisted technology (ChatGPT) was used as a supplementary tool for writing assistance and for initial data filtering. However, all content has been reviewed and revised by the authors to ensure its accuracy and integrity. AI was not involved in the interpretation of the results or the formulation of the final conclusions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wang, Q.; Mao, Z.; Wang, B.; Guo, L. Knowledge graph embedding: A survey of approaches and applications. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2017, 29, 2724–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Chen, C.; He, C.; Li, Y.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, W. Can LLMs be Good Graph Judger for Knowledge Graph Construction? arXiv 2024, arXiv:2411.17388. [Google Scholar]
- Du, X.; Li, N. Academic Paper Knowledge Graph, the Construction and Application. In Proceedings of the ICBASE, Guangzhou, China, 21–23 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hofer, M.; Obraczka, D.; Saeedi, A.; Köpcke, H.; Rahm, E. Construction of knowledge graphs: Current state and challenges. Information 2024, 15, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Pan, H.; Ke, H.; Ou, J.; Fang, T.; Song, Y. ASER: Towards large-scale commonsense knowledge acquisition via higher-order selectional preference over eventualities. Artif. Intell. 2022, 309, 103740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K.; Yang, B.; Wang, S.; Chang, Y.; Li, S.; Yi, G. Relation extraction for manufacturing knowledge graphs based on feature fusion of attention mechanism and graph convolution network. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 255, 109703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omran, P.G.; Taylor, K.; Mendez, S.R.; Haller, A. Active knowledge graph completion. Inf. Sci. 2022, 604, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, D.; Bensmann, F.; Dietze, S.; Krüger, F. The role of software in science: A knowledge graph-based analysis of software mentions in PubMed Central. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2022, 8, e835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, F.; Jiang, H.; Feng, D.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, G. Random walk on node cliques for high-quality samples to estimate large graphs with high accuracies and low costs. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 2022, 64, 1909–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, G.; Wang, X.; Zou, X.; Liu, C.; Cen, S. MRGAT: Multi-relational graph attention network for knowledge graph completion. Neural Netw. 2022, 154, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Liu, Y. Bidirectional relation-guided attention network with semantics and knowledge for relational triple extraction. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 224, 119905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Wang, J.; Qiu, H.; Yu, J.; Yu, Z.; Liu, S. Attack Behavior Extraction Based on Heterogeneous Cyberthreat Intelligence and Graph Convolutional Networks. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2023, 74, 235–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddharth, L.; Luo, J. Retrieval augmented generation using engineering design knowledge. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2024, 303, 112410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Su, Y.; Trisedya, B.D.; Zhao, X.; Yang, M.; Cheng, H.; Qi, J. Autoalign: Fully automatic and effective knowledge graph alignment enabled by large language models. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2023, 36, 2357–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Feenstra, K.A.; Huang, Z.; Heringa, J. Mining literature and pathway data to explore the relations of ketamine with neurotransmitters and gut microbiota using a knowledge-graph. Bioinformatics 2024, 40, btad771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Chen, Q.; Hao, M.; Li, Y.; Sun, B. Mconvkgc: A novel multi-channel convolutional model for knowledge graph completion. Computing 2024, 106, 915–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Li, X.; Yan, F.; Lu, Y.; Shen, W. A method for constructing a machining knowledge graph using an improved transformer. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 237, 121448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liang, X. An radicals construction technique based on dual quaternions and hierarchical transformers. Neurocomputing 2024, 604, 128315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottersen, S.G.; Pinheiro, F.; Bação, F. Triplet extraction leveraging sentence transformers and dependency parsing. Array 2024, 21, 100334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Tang, Y.; Long, Y.; Hu, K.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, C.-D. Multi-information preprocessing event extraction with BiLSTM-CRF attention for academic knowledge graph construction. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2022, 10, 2713–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Zhang, K.; Huang, K.; Xu, T.; Li, X.; Liu, Y. Document-level relation extraction with two-stage dynamic graph attention networks. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2023, 267, 110428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhou, J.; Kong, L.; Gu, Y.; Qu, W. Seq2EG: A novel and effective event graph parsing approach for event extraction. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 2023, 65, 4273–4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Tuan, L.A. A novel, cognitively inspired, unified graph-based multi-task framework for information extraction. Cogn. Comput. 2023, 15, 2004–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hong, H.; Wang, X.; Chen, Z.; Kharlamov, E.; Dong, Y.; Tang, J. Selfkg: Self-supervised entity alignment in knowledge graphs. In Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2022, Virtual, 25–29 April 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, C.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Zhu, R.; Du, K.; Ma, Q. ERGM: A multi-stage joint entity and relation extraction with global entity match. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2023, 271, 110550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassiliades, A.; Symeonidis, S.; Diplaris, S.; Tzanetis, G.; Vrochidis, S.; Bassiliades, N.; Kompatsiaris, I. XR4DRAMA Knowledge Graph: A Knowledge Graph for Disaster Management. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 17th International Conference on Semantic Computing (ICSC), Laguna Hills, CA, USA, 1–3 February 2023; pp. 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessí, D.; Osborne, F.; Recupero, D.R.; Buscaldi, D.; Motta, E. SCICERO: A deep learning and NLP approach for generating scientific knowledge graphs in the computer science domain. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 258, 109945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asada, M.; Miwa, M.; Sasaki, Y. Integrating heterogeneous knowledge graphs into drug–drug interaction extraction from the literature. Bioinformatics 2023, 39, btac754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzuriaga, J.; Munoz, E.; Rosales-Mendez, H.; Hogan, A. Merging Web Tables for Relation Extraction with Knowledge Graphs. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2023, 35, 1803–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Lu, K.; Yu, S.; Cai, T.; Zitnik, M. Multimodal learning on graphs for disease relation extraction. J. Biomed. Inform. 2023, 143, 104415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, E.; Jozashoori, S.; Vidal, M.E. Scaling up knowledge graph creation to large and heterogeneous data sources. J. Web Semant. 2023, 75, 100755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaradeh, M.Y.; Singh, K.; Stocker, M.; Both, A.; Auer, S. Information extraction pipelines for knowledge graphs. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 2023, 65, 1989–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Zhang, K.; Lv, L.; Li, X.; Huang, K.; Zhang, T. Joint extraction of entities and overlapping relations by improved graph convolutional networks. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 5212–5224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Shang, Y.-M.; Sun, X.; Wei, W.; Mao, X. Three birds, one stone: A novel translation based framework for joint entity and relation extraction. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 236, 107677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Shen, Q.; Song, R.; Chi, Y.; Xu, H. MEduKG: A deep-learning-based approach for multi-modal educational knowledge graph construction. Information 2022, 13, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, M.; Bansal, C.; Kumar, S.; Rao, N.; Nagappan, N. SoftNER: Mining knowledge graphs from cloud incidents. Empir. Softw. Eng. 2022, 27, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wei, Z.; Jia, D.; Dou, X.; Tang, H.; Li, N. Constructing marine expert management knowledge graph based on Trellisnet-CRF. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2022, 8, e1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Xi, X.; He, J. AFGSL: Automatic feature generation based on graph structure learning. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 238, 107835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wu, L.; Xie, Z.; Qiu, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, K.; Tao, L. Understanding geological reports based on knowledge graphs using a deep learning approach. Comput. Geosci. 2022, 168, 105229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Li, G.; Gu, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L. GridOnto: Knowledge representation and extraction for fault events in power grid. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 58863–58878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zou, F.; Han, J.; Sun, X.; Wang, Y. Llm-tikg: Threat intelligence knowledge graph construction utilizing large language model. Comput. Secur. 2024, 145, 103999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershowitz, B.; Hodkiewicz, M.; Bikaun, T.; Stewart, M.; Liu, W. Causal knowledge extraction from long text maintenance documents. Comput. Ind. 2024, 161, 104110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Lin, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z. Knowledge Guided Attention and Graph Convolutional Networks for Chemical-Disease Relation Extraction. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2022, 20, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wan, H.; Lin, Y. Exploiting global context and external knowledge for distantly supervised relation extraction. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2023, 261, 110195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhao, H.; Gu, T.; Ying, D. Experiencer-driven and knowledge-aware graph model for emotion–cause pair extraction. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2023, 278, 110703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W.; Chu, X.; Jiang, W.; Li, Z. A multimodal dual-fusion entity extraction model for large and complex devices. Comput. Commun. 2023, 210, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, F.; Giglou, H.B.; Malik, K.M. Automated clinical knowledge graph generation framework for evidence based medicine. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 233, 120964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Huang, R.; Zhai, M.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, B. A performant and incremental algorithm for knowledge graph entity typing. World Wide Web 2023, 26, 2453–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, V.; Choi, D.; Yener, B.; Beamer, G. Prediction of tuberculosis from lung tissue images of diversity outbred mice using jump knowledge based cell graph neural network. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 17164–17194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Liu, L.; Xiao, F.; Han, Y. A Novel Rational Medicine Use System Based on Domain Knowledge Graph. Electronics 2024, 13, 3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, R. A Semantic-Spatial Aware Data Conflation Approach for Place Knowledge Graphs. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2024, 13, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ma, L.; Li, X.; Xu, J.; Cho, J.H.D.; Nag, K.; Korpeoglu, E.; Kumar, S.; Achan, K. Relation labeling in product knowledge graphs with large language models for e-commerce. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2024, 15, 5725–5743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukumar, S.T.; Lung, C.-H.; Zaman, M.; Panday, R. Knowledge Graph Generation and Application for Unstructured Data Using Data Processing Pipeline. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 136759–136770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lu, Y. A task-centric knowledge graph construction method based on multi-modal representation learning for industrial maintenance automation. Eng. Rep. 2024, 6, e12952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tian, M.; Wu, Q.; Tao, L.; Jiang, T.; Qiu, Q.; Huang, H. A deep learning-based method for deep information extraction from multimodal data for geological reports to support geological knowledge graph construction. Earth Sci. Inform. 2024, 17, 1867–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, B.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, X. Medical knowledge graph completion via fusion of entity description and type information. Artif. Intell. Med. 2024, 151, 102848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, M.; Ma, K.; Wu, Q.; Qiu, Q.; Tao, L.; Xie, Z. Joint extraction of entity relations from geological reports based on a novel relation graph convolutional network. Comput. Geosci. 2024, 187, 105571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.; Zhao, C.; Li, D.; Dai, J. Bdcore: Bidirectional decoding with co-graph representation for joint entity and relation extraction. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2024, 294, 111781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Meng, J.; Zhao, D.; Jia, X.; Chu, Y.; Lin, H. Integrating graph convolutional networks to enhance prompt learning for biomedical relation extraction. J. Biomed. Inform. 2024, 157, 104717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, B.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Xie, L. Named Entity Recognition for Equipment Fault Diagnosis Based on RoBERTa-wwm-ext and Deep Learning Integration. Electronics 2024, 13, 3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jofche, N.; Mishev, K.; Stojanov, R.; Jovanovik, M.; Zdravevski, E.; Trajanov, D. Pharmke: Knowledge extraction platform for pharmaceutical texts using transfer learning. Computers 2023, 12, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knez, T.; Žitnik, S. Event-centric temporal knowledge graph construction: A survey. Mathematics 2023, 11, 4852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Deng, B.W.Y.; Wang, Z.H.B.; Hua, Y.X.Z.; Xiao, X.L.Y. A Knowledge Graph Construction Method for Software Project Based on CAJP. J. Internet Technol. 2023, 24, 1229–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, J.; Zhou, G.; Xie, Z.; Yu, X.; Cui, X. Query path generation via bidirectional reasoning for multihop question answering from knowledge bases. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2022, 15, 1183–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, X.; Deng, H.; Dong, X.; Zhu, Z.; Li, F.; Wang, L. MHlinker: Research on a Joint Extraction Method of Fault Entity Relationship for Mine Hoist. Electronics 2023, 12, 3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhu, S. A Novel Joint Extraction Model for Entity Relations Using Interactive Encoding and Visual Attention. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 132567–132575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhong, J.; Xue, Z.; Dai, Q.; Li, X. Heterogenous affinity graph inference network for document-level relation extraction. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 250, 109146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Su, C.; Deng, Y.; Cheng, J. Image2Triplets: A computer vision-based explicit relationship extraction framework for updating construction activity knowledge graphs. Comput. Ind. 2022, 137, 103610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Allaly, E.-D.; Sarrouti, M.; En-Nahnahi, N.; El Alaoui, S.O. An attentive joint model with transformer-based weighted graph convolutional network for extracting adverse drug event relation. J. Biomed. Inform. 2022, 125, 103968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Wang, Y.; Yu, X.; Feng, R. Qlogice: Quantum logic empowered embedding for knowledge graph completion. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 239, 107963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Yu, P.S.; Jing, N. KGGen: A Generative Approach for Incipient Knowledge Graph Population. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2022, 34, 2254–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Yang, M.; Jiang, P. Improving attention network to realize joint extraction for the construction of equipment knowledge graph. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 125, 106723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Li, T.; Gao, W.; Xia, Y. AttenSy-SNER: Software knowledge entity extraction with syntactic features and semantic augmentation information. Complex Intell. Syst. 2023, 9, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Qian, L.; Zhao, X.; Tao, B. The construction of knowledge graphs in the aviation assembly domain based on a joint knowledge extraction model. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 26483–26495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, Z.; Jia, W.; Wu, F.; Liu, H.; Tan, J. Dual attention graph convolutional network for relation extraction. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2023, 36, 530–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Du, Y.; Hu, J.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Chen, X. A contextual dependency-aware graph convolutional network for extracting entity relations. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 239, 122366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassiliades, A.; Patkos, T.; Efthymiou, V.; Bikakis, A.; Bassiliades, N.; Plexousakis, D. Extraction of object-action and object-state associations from Knowledge Graphs. J. Web Semant. 2024, 81, 100816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, R.; Zhang, Z.; Meng, Y.; Zhou, Z. Interactive optimization of relation extraction via knowledge graph representation learning. J. Vis. 2024, 27, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordes, A.; Usunier, N.; Garcia-Duran, A.; Weston, J.; Yakhnenko, O. Translating embeddings for modeling multi-relational data. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2013, 26. Available online: https://papers.nips.cc/paper_files/paper/2013/file/1cecc7a77928ca8133fa24680a88d2f9-Paper.pdf (accessed on 24 March 2025).
- Liu, H.; Wu, H.; Zhang, L.; Yu, R.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, M.; Liu, Q.; Chen, E. A hierarchical interactive multi-channel graph neural network for technological knowledge flow forecasting. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 2022, 64, 1723–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zu, L.; Yan, Y.; Zuo, J.; Sang, B. Multi-filter soft shrinkage network for knowledge graph embedding. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 250, 123875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Lan, M.; Luo, J.; Chen, X.; Zhou, G. Iterative rule-guided reasoning over sparse knowledge graphs with deep reinforcement learning. Inf. Process. Manag. 2022, 59, 103040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Shen, B.; Zhong, Y. SSKGE: A time-saving knowledge graph embedding framework based on structure enhancement and semantic guidance. Appl. Intell. 2023, 53, 25171–25183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Zhou, B.; Yang, H.; Tan, Z.; Sun, Z.; Li, C.; Waaler, A.; Kharlamov, E.; Soylu, A. Knowledge graph embedding closed under composition. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2024, 38, 3531–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.; Ouyang, D.; Liang, S.; Shao, J. Step by step: A hierarchical framework for multi-hop knowledge graph reasoning with reinforcement learning. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 248, 108843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, B.; Seo, S.; Hwang, J.; Lee, D.; Lee, K.-H. Open-world knowledge graph completion for unseen entities and relations via attentive feature aggregation. Inf. Sci. 2022, 586, 468–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Ruan, K.; Huang, B.; Yu, W.; Xiao, J.; Huang, J. TSA-Net: A temporal knowledge graph completion method with temporal-structural adaptation. Appl. Intell. 2024, 54, 10320–10332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Li, C.T.; Pang, J. Multi-grained semantics-aware graph neural networks. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2022, 35, 7251–7262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Li, K.; Jiang, Y.; Jia, Z.; Lv, L.; Ma, Y. Graph Relearn Network: Reducing performance variance and improving prediction accuracy of graph neural networks. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2024, 301, 112311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malawade, A.V.; Yu, S.-Y.; Hsu, B.; Muthirayan, D.; Khargonekar, P.P.; Al Faruque, M.A. Spatiotemporal scene-graph embedding for autonomous vehicle collision prediction. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 9379–9388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Leskovec, J. Combining Graph Convolutional Neural Networks and Label Propagation. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. 2022, 40, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Tang, Y.; Chen, Y. A graph neural network-based node classification model on class-imbalanced graph data. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 244, 108538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, X.; Zhou, F.; Wang, W.; Jin, W.; Tang, J.; Wang, X. INS-GNN: Improving graph imbalance learning with self-supervision. Inf. Sci. 2023, 637, 118935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zheng, T.; Hao, Q. HIRE: Distilling high-order relational knowledge from heterogeneous graph neural networks. Neurocomputing 2022, 507, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.-J.; Lu, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J. Heterogeneous graph convolutional network with local influence. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 236, 107699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Si, G.; Li, J.; An, Z.; Tian, P.; Zhou, F. Fully-inductive link prediction with path-based graph neural network: A comparative analysis. Neurocomputing 2024, 609, 128484. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Guo, J.; Peng, C.; Niu, Z.; Wu, X. Graph attention network with dynamic representation of relations for knowledge graph completion. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 219, 119616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lin, S.; Liu, W.; Zhou, P.; Tang, J.; Liang, X.; Xing, E.P. Iterative graph self-distillation. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2023, 36, 1161–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, W.; Xiao, B.; Liu, X.; Zhou, S.; Cai, Z.; Cheng, J. Revisiting initializing then refining: An incomplete and missing graph imputation network. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2024, 36, 3244–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yang, D.; Wang, P.; Rosso, P.; Cudre-Mauroux, P. Schema-aware hyper-relational knowledge graph embeddings for link prediction. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2023, 36, 2614–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Zhong, J.; Li, R.; Li, X. Disentangled Relational Graph Neural Network with Contrastive Learning for knowledge graph completion. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2024, 295, 111828. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Yang, L.; Wang, Z.; Gong, M. Higher-order GNN with Local Inflation for entity alignment. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2024, 293, 111634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.; Mücke, S.; Khosla, M. Mucomid: A multitask graph convolutional learning framework for miRNA-disease association prediction. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2022, 19, 3081–3092. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Hu, S.; Geng, J.; Huang, T.; Hu, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, Q. Heterogeneous graph-based knowledge tracing with spatiotemporal evolution. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 238, 122249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Lin, H.; Zhao, G.; Tan, C.; Li, S.Z. Learning to Model Graph Structural Information on MLPs via Graph Structure Self-Contrasting. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Yang, L. Graph-aware tensor factorization convolutional network for knowledge graph completion. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2024, 15, 1755–1766. [Google Scholar]
- ChandraUmakantham, O.; Srinivasan, S.; Pathak, V. Detecting Side Effects of Adverse Drug Reactions Through Drug-Drug Interactions Using Graph Neural Networks and Self-Supervised Learning. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 93823–93840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basaad, A.; Basurra, S.; Vakaj, E.; Aleskandarany, M.; Abdelsamea, M.M. GraphX-Net: A Graph Neural Networkbased Shapley Values for Predicting Breast Cancer Occurrence. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 93993–94007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Oh, J.H.; Simhal, A.K.; Elkin, R.; Norton, L.; Deasy, J.O.; Tannenbaum, A. Geometric graph neural networks on multi-omics data to predict cancer survival outcomes. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 163, 107117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yin, Z.; Ding, W.; King, I. A survey on graph embedding techniques for biomedical data: Methods and applications. Inf. Fusion 2023, 100, 101909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, M.; Kharat, N.; Boureima, I.; Skau, E.; Nebgen, B.; Djidjev, H.; Rajopadhye, S.; Smith, J.P.; Alexandrov, B. Distributed non-negative rescal with automatic model selection for exascale data. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2023, 179, 104709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Ma, R.; Niu, W.; Yan, L.; Ma, Z. SFTe: Temporal knowledge graphs embedding for future interaction prediction. Inf. Syst. 2024, 125, 102423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.-H.; Wei, D.; Zhang, L.; Ma, G.-F.; Xu, X.-L.; Long, H.-X. Task-related network based on meta-learning for few-shot knowledge graph completion. Appl. Intell. 2024, 54, 5961–5975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Wang, Y.; Sha, L.; Engelbrecht, J.; Hong, P. Knowledgebra: An Algebraic Learning Framework for Knowledge Graph. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Extr. 2022, 4, 432–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Hui, B.; Zeira, I.; Wu, H.; Tian, L. Dynamic relation learning for link prediction in knowledge hypergraphs. Appl. Intell. 2023, 53, 26580–26591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Ma, R.; Yan, L.; Ma, Z. T-GAE: A timespan-aware graph attention-based embedding model for temporal knowledge graph completion. Inf. Sci. 2023, 642, 119225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Xie, Z.; Liu, R.; Yu, W.; Hu, Q.; Li, X.; Ding, S.X. Bayesian hierarchical graph neural networks with uncertainty feedback for trustworthy fault diagnosis of industrial processes. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 35, 18635–18648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Feng, W.; Wu, Z.; Li, G.; Ning, B. CDRGN-SDE: Cross-dimensional recurrent graph network with neural stochastic differential equation for temporal knowledge graph embedding. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 247, 123295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hui, B.; Mu, C.; Tian, L. Learning multi-graph structure for Temporal Knowledge Graph reasoning. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 255, 124561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, J.-T. A neighborhood-aware graph self-attention mechanism-based pre-training model for Knowledge Graph Reasoning. Inf. Sci. 2023, 647, 119473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Xun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y. Reinforcement negative sampling recommendation based on collaborative knowledge graph. J. Intell. Inf. Syst. 2024, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Meng, S.; Li, Q.; Zhou, X.; Qi, L.; Xu, X. Edge-enabled federated sequential recommendation with knowledge-aware Transformer. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2023, 148, 610–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Li, J.-Y.; Chen, C.-H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhan, Z.-H. Enhanced multi-task learning and knowledge graph-based recommender system. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2023, 35, 10281–10294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spillo, G.; Musto, C.; de Gemmis, M.; Lops, P.; Semeraro, G. Recommender systems based on neuro-symbolic knowledge graph embeddings encoding first-order logic rules. User Model. User-Adapt. Interact. 2024, 34, 2039–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, P.; Lu, S.; Wu, L.; Yu, H. Big-fed: Bilevel optimization enhanced graph-aided federated learning. IEEE Trans. Big Data 2022, 10, 903–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, H.A.; Pilutti, D.; James, S.; Del Bue, A.; Pelillo, M.; Vascon, S. Locality-aware subgraphs for inductive link prediction in knowledge graphs. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2023, 167, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, L.; Zaki, M.J. Toward subgraph-guided knowledge graph question generation with graph neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 35, 12706–12717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, G.; Liu, J.; Tu, X.; Huang, J.X. One Subgraph for All: Efficient Reasoning on Opening Subgraphs for Inductive Knowledge Graph Completion. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2024, 36, 8914–8927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Tiwari, P.; Ananiadou, S. Knowledge-enhanced graph topic transformer for explainable biomedical text summarization. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2023, 28, 1836–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lan, H.; Yang, X.; Zhang, S.; Song, W.; Peng, Z. Weakly supervised setting for learning concept prerequisite relations using multi-head attention variational graph auto-encoders. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 247, 108689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Z.; Ye, Y. Learning knowledge graph embedding with a dual-attention embedding network. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 212, 118806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Duan, C.; Zhao, T. Local-to-Global Structure-Aware Transformer for Question Answering over Structured Knowledge. IEICE Trans. Inf. Syst. 2023, 106, 1705–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tan, Q.; Huang, X.; Li, B. Graph contrastive learning with personalized augmentation. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2024, 36, 6305–6316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.; Ko, Y. Knowledge graph extension with a pre-trained language model via unified learning method. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2023, 262, 110245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Mao, R.; Liu, J.; Xu, F.; Cambria, E. Fusing topology contexts and logical rules in language models for knowledge graph completion. Inf. Fusion 2023, 90, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querfurth, B.V.; Lohmoeller, J.; Pennekamp, J.; Bleckwehl, T.; Kramann, R.; Wehrle, K.; Hayat, S. mcBERT: Patient-Level Single-cell Transcriptomics Data Representation. bioRxiv 2024. bioRxiv:2024-11. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Yang, H.; Yang, C.; Zhang, W. Efficient Medical Knowledge Graph Embedding: Leveraging Adaptive Hierarchical Transformers and Model Compression. Electronics 2023, 12, 2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.; Liu, G.; Han, C.; Jiang, M.; Ji, H.; Han, J. Large language models on graphs: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2024, 36, 8622–8642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Fu, X.; Liu, X.; Wu, J. Deeply integrating unsupervised semantics and syntax into heterogeneous graphs for inductive text classification. Complex Intell. Syst. 2024, 10, 1565–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Lu, W.; Yan, Y. HyGGE: Hyperbolic graph attention network for reasoning over knowledge graphs. Inf. Sci. 2023, 630, 190–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhu, K.; Chang KC, C.; Xiong, J.; Hwu, W.M. DEER: Descriptive Knowledge Graph for Explaining Entity Relationships. In Proceedings of the 2022 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 7–11 December 2022; Association for Computational Linguistics; pp. 6686–6698. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Hooi, B.; He, B. Efficient heterogeneous graph learning via random projection. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2024, 36, 8093–8107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lu, G.; Qin, K.; Du, K. AInvR: Adaptive learning rewards for knowledge graph reasoning using agent trajectories. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 2023, 28, 1101–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Song, K.; Jiang, Z.; Kang, Y.; Yuan, W.; Li, X.; Sun, C.; Huang, C.; Liu, X. Towards human-like perception: Learning structural causal model in heterogeneous graph. Inf. Process. Manag. 2024, 61, 103600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, H.; Chai, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, L. Toward quantized model parallelism for graph-augmented mlps based on gradient-free admm framework. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 35, 4491–4501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Shu, L.; Chen, C.; Zheng, Z. Fine-Grained Semantics Enhanced Contrastive Learning for Graphs. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2024, 36, 8238–8250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zheng, J.; Jin, B.; Zhu, H. Adaptive Knowledge Contrastive Learning with Dynamic Attention for Recommender Systems. Electronics 2024, 13, 3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Fang, Q.; Hu, J.; Qian, S.; Xu, C. TCKGE: Transformers with contrastive learning for knowledge graph embedding. Int. J. Multimed. Inf. Retr. 2022, 11, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, R.; Tang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, W. Clustering enhanced multiplex graph contrastive representation learning. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 36, 1341–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Du, X.; Zhu, B.; Ma, Z.; Chen, K.; Gao, J. Graph contrastive learning with implicit augmentations. Neural Netw. 2023, 163, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Chen, H.; Yin, H.; Li, Q.; Xu, G. Multi-level Graph Knowledge Contrastive Learning. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2024, 36, 8829–8841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghershahi, P.; Hosseini, R.; Moradi, H. Self-attention presents low-dimensional knowledge graph embeddings for link prediction. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2023, 260, 110124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Tang, J.; Peng, Z.; Wang, Y. Relation correlations-aware graph convolutional network with text-enhanced for knowledge graph embedding. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2024, 15, 4659–4668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zeng, J.; Zheng, X. Learning structured embeddings of knowledge graphs with generative adversarial framework. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 204, 117361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yan, X.; Jin, Y. An edge-aware graph autoencoder trained on scale-imbalanced data for traveling salesman problems. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2024, 291, 111559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, A.; Saif, S.; Chen, J.; Yu, J.J.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, D. CoPE: Composition-based Poincaré embeddings for link prediction in knowledge graphs. Inf. Sci. 2024, 662, 120197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ren, H.; Zhang, X. Deep hyperbolic convolutional model for knowledge graph embedding. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2024, 300, 112183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Gu, L.; Kobayashi, K.; Liu, L.; Zhang, M.; Harada, T.; Summers, R.M.; Zhu, Y. Interpretable medical image visual question answering via multi-modal relationship graph learning. Med. Image Anal. 2024, 97, 103279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Zhao, H. Hierarchical long-tailed classification based on multi-granularity knowledge transfer driven by multi-scale feature fusion. Pattern Recognit. 2024, 145, 109842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Li, X.; Yuan, Y.; Guan, Y.; Jiang, J.; Guo, X.; Peng, X. Knowledge-based dynamic prompt learning for multi-label disease diagnosis. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2024, 286, 111395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakken, M. maplib: Interactive, literal RDF model mapping for industry. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 39990–40005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sola, F.; Ayala, D.; Ayala, R.; Hernández, I.; Rivero, C.R.; Ruiz, D. AYNEXT-tools for streamlining the evaluation of link prediction techniques. SoftwareX 2023, 23, 101474. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.-B.; Zhong, Z.-M.; Yuan, P.-P.; Jin, H. Improving entity linking in Chinese domain by sense embedding based on graph clustering. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 2023, 38, 196–210. [Google Scholar]
- John, S.; Kosiol, J.; Lambers, L.; Taentzer, G. A graph-based framework for model-driven optimization facilitating impact analysis of mutation operator properties. Softw. Syst. Model. 2023, 22, 1281–1318. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, J. Adaptive scalable spatio-temporal graph convolutional network for PM2. 5 prediction. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 126, 107080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Luo, F.; Wang, X.; Di, Z.; Li, B.; Luo, B. A one-size-fits-three representation learning framework for patient similarity search. Data Sci. Eng. 2023, 8, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, G.; Zhou, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Du, B. Sub-Entity Embedding for inductive spatio-temporal knowledge graph completion. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2023, 148, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Bao, T.; Liu, L.; Han, J.; Wang, J.; Peng, T. Cross-lingual knowledge graph entity alignment based on relation awareness and attribute involvement. Appl. Intell. 2023, 53, 6159–6177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadhassanzadeh, H.; Abidi, S.S.R. Plausible reasoning over large health datasets: A novel approach to data analytics leveraging semantics. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2024, 289, 111493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Hoo, V.; Shao, Z.; Zhang, X. LegalReasoner: A Multi-Stage Framework for Legal Judgment Prediction via Large Language Models and Knowledge Integration. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 166843–166854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, H.; Li, M.; Yang, H.; Zhang, R. FuseLinker: Leveraging LLM’s pre-trained text embeddings and domain knowledge to enhance GNN-based link prediction on biomedical knowledge graphs. J. Biomed. Inform. 2024, 158, 104730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nath, R.P.D.; Das, T.R.; Das, T.C.; Raihan, S.S. Knowledge Graph Generation and Enabling Multidimensional Analytics on Bangladesh Agricultural Data. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 87512–87531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Sun, X.; Qian, X.; Fang, M. Asymmetrical Contrastive Learning Network via Knowledge Distillation for No-Service Rail Surface Defect Detection. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Tai, Z.; Shen, E.; Wang, J. Graph exploration with embedding-guided layouts. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2023, 30, 3693–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Bao, J.; Li, H.; He, C.; Chen, F. A multi-view temporal knowledge graph reasoning framework with interpretable logic rules and feature fusion. Electronics 2024, 13, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Yu, W.; Chai, D.; Zhao, W.; Chen, M. Temporal knowledge graphs reasoning with iterative guidance by temporal logical rules. Inf. Sci. 2023, 621, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siciliani, L.; Basile, P.; Lops, P.; Semeraro, G. MQALD: Evaluating the impact of modifiers in question answering over knowledge graphs. Semant. Web 2022, 13, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Gan, Z.; Shi, X.; Patwari, A.; Rush, E.; Bonzel, C.-L.; Panickan, V.A.; Hong, C.; Ho, Y.-L.; Cai, T.; et al. Multiview Incomplete Knowledge Graph Integration with application to cross-institutional EHR data harmonization. J. Biomed. Inform. 2022, 133, 104147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melotte, S.; Ilievski, F.; Zhang, L.; Malte, A.; Mutha, N.; Morstatter, F.; Mehrabi, N. Where Does Bias in Common Sense Knowledge Models Come From? IEEE Internet Comput. 2022, 26, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambarelli, G.; Gangemi, A. PRIVAFRAME: A frame-based knowledge graph for sensitive personal data. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2022, 6, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huseynli, A.; Akcayol, M.A. Continuous Knowledge Graph Refinement With Confidence Propagation. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 59226–59237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuoda, G.; Aebeloe, C.; Dell’Aglio, D.; Keen, A.; Hose, K. StarBench: Benchmarking RDF-star triplestores. In QuWeDa 2023: 7th Workshop on Storing, Querying and Benchmarking Knowledge Graphs; CEUR Workshop Proceedings: Kyiv, Ukraine, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Formica, A.; Taglino, F. Semantic relatedness in DBpedia: A comparative and experimental assessment. Inf. Sci. 2023, 621, 474–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Lin, Y.; Xu, Y.; Hu, J.; Dong, S. Interpretable Disease Prediction via Path Reasoning over medical knowledge graphs and admission history. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2023, 281, 111082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sataer, Y.; Gao, Z.; Fan, Y.; Li, B.; Gao, M.; Shi, C. Exploration and comparison of diverse approaches for integrating syntactic knowledge into AMR parsing. Appl. Intell. 2023, 53, 30757–30777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirielle, N.; Christen, P.; Ranbaduge, T. Unsupervised graph-based entity resolution for complex entities. ACM Trans. Knowl. Discov. Data 2023, 17, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egami, S.; Ugai, T.; Oono, M.; Kitamura, K.; Fukuda, K. Synthesizing event-centric knowledge graphs of daily activities using virtual space. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 23857–23873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsaneva, S. Evaluating Knowledge Graphs with Hybrid Intelligence. In The Semantic Web: ESWC 2023 Satellite Events; Pesquita, C., Skaf-Molli, H., Efthymiou, V., Kirrane, S., Ngonga, A., Collarana, D., Cerqueira, R., Alam, M., Trojahn, C., Hertling, S., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; Volume 13998, pp. 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, K.; Tian, Y.; Shang, Y.; Zhou, T.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Yao, X.; Zhang, P.; Chen, J.; Li, J. Causal knowledge graph construction and evaluation for clinical decision support of diabetic nephropathy. J. Biomed. Inform. 2023, 139, 104298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, Y.; Beck, D.; Verspoor, K. Graph embedding-based link prediction for literature-based discovery in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Biomed. Inform. 2023, 145, 104464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, S.; Wang, G.; Wang, Z. Efficient community search in edge-attributed graphs. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2023, 35, 10790–10806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shi, Z.; Pan, C.; Zhao, D.; Sun, N. Cybersecurity knowledge graphs construction and quality assessment. Complex Intell. Syst. 2024, 10, 1201–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciroku, F.; de Berardinis, J.; Kim, J.; Meroño-Peñuela, A.; Presutti, V.; Simperl, E. RevOnt: Reverse engineering of competency questions from knowledge graphs via language models. J. Web Semant. 2024, 82, 100822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Hu, L.; Du, X.; Shen, Z.; Hu, J.; Wang, F. CCDF-TAP: A Context-Aware Conflict Detection Framework for IoT Trigger-Action Programming With Graph Neural Network. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 31534–31544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Wang, J. Knowledge enhanced graph inference network based entity-relation extraction and knowledge graph construction for industrial domain. Front. Eng. Manag. 2024, 11, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, S.; Wu, S.; Gu, Z.; Tian, Y. Performance benchmark on semantic web repositories for spatially explicit knowledge graph applications. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2022, 98, 101884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tian, J.; Liu, X.; Tao, T.; Ren, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y. Research on a knowledge graph embedding method based on improved convolutional neural networks for hydraulic engineering. Electronics 2023, 12, 3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trisedya, B.D.; Salim, F.D.; Chan, J.; Spina, D.; Scholer, F.; Sanderson, M. i-Align: An interpretable knowledge graph alignment model. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2023, 37, 2494–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Shao, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, J.; Cui, B. DRGI: Deep Relational Graph Infomax for Knowledge Graph Completion: (Extended Abstract). In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 38th International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 9–12 May 2022; pp. 1499–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinou, A.C.; Guo, Z.; Kitson, N.K. The impact of prior knowledge on causal structure learning. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 2023, 65, 3385–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanourakis, N.; Efthymiou, V.; Kotzinos, D.; Christophides, V. Knowledge graph embedding methods for entity alignment: Experimental review. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2023, 37, 2070–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Ma, Y.; Xiang, Z.; Yang, C.; He, K. A spatial–temporal graph neural network framework for automated software bug triaging. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 241, 108308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, W.; Xing, X.; Yuan, Y. Medical federated learning with joint graph purification for noisy label learning. Med. Image Anal. 2023, 90, 102976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Zhou, G.; Liu, J.; Huang, J.X. Incorporating global–local neighbors with Gaussian mixture embedding for few-shot knowledge graph completion. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 234, 121086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, Z.; Cai, J.; Ji, S.; Wu, F. Duality-induced regularizer for semantic matching knowledge graph embeddings. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 45, 1652–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).