A Review on Landfill Leachate Treatment Technologies: Comparative Analysis of Methods and Process Innovation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Formation, Characteristics, and Composition of Landfill Leachate
2.1. Formation and Characteristics of Landfill Leachate
| Number | Parameters | Values (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | pH | 2.69–8.11 |
| 2 | BOD5 | 98–50,000 |
| 3 | COD | 140–157,200 |
| 4 | TOC | 3963–78,640 |
| 5 | NH3-N | 400–6000 |
| 6 | TN | 395–5332 |
| 7 | Calcium (Ca) | 69–2330 |
| 8 | Potassium (K) | 28–1700 |
| 9 | Magnesium (Mg) | 4–780 |
| 10 | Sodium (Na) | 85–3800 |
| 11 | Lead (Pb) | 0.001–5 |
| 12 | Arsenic (As) | 0.0001–0.578 |
| 13 | Chlorine (Cl−) | 47–6000 |
| 14 | Sulphate (SO42−) | 0.01–3240 |
| 15 | Volatile suspended solids (VSS) | 800–11,320 |
| 16 | Total Suspended Solids (TSS) | 930–13,333 |
| 17 | Volatile phenol | 1.3–800 |
| 18 | Total hardness | 15–2241 |
2.2. Composition of Landfill Leachate
2.3. Emerging Contaminants
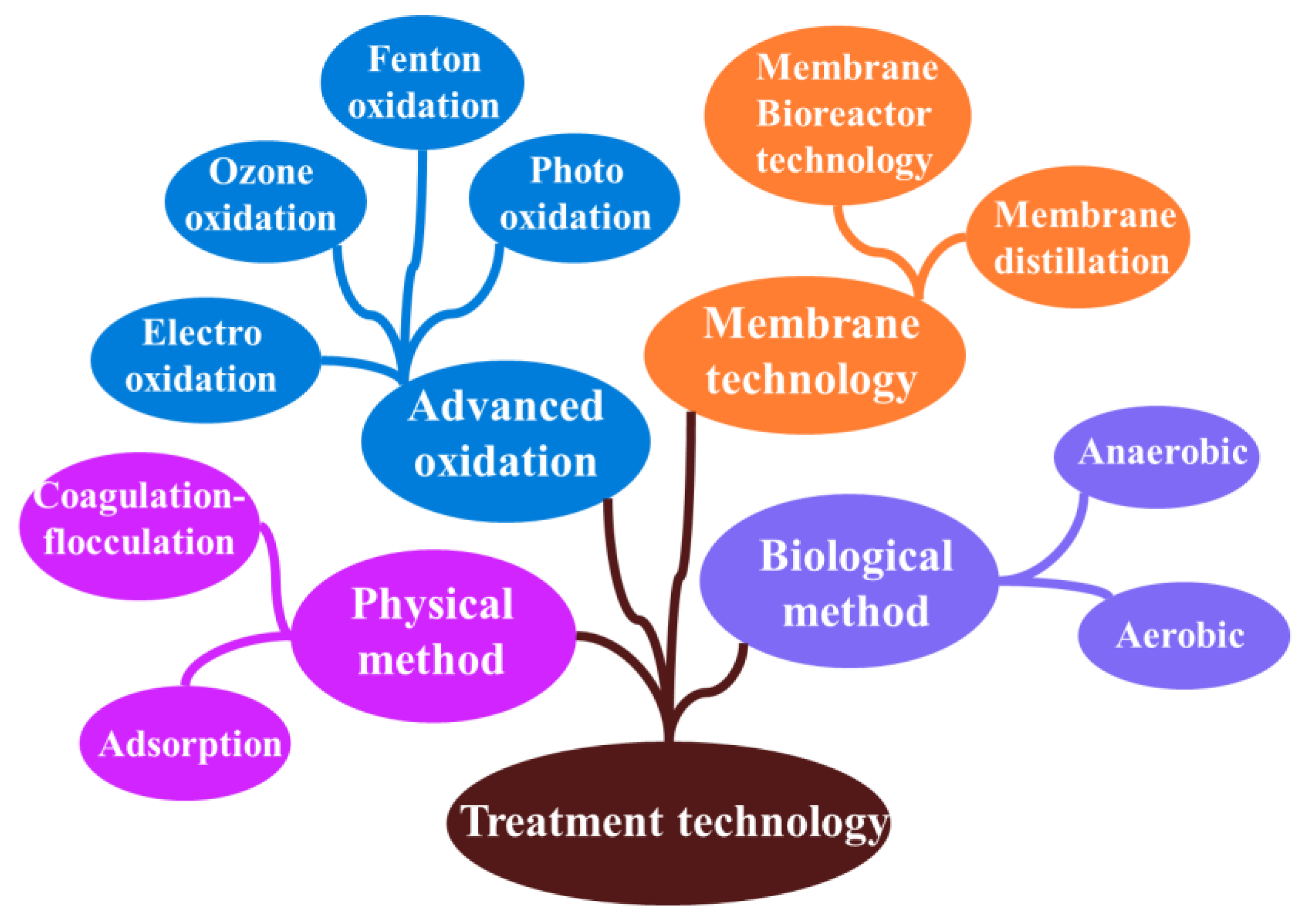
3. Technologies for Treating Landfill Leachate
3.1. Physical–Chemical Method
3.1.1. Adsorption
3.1.2. Coagulation–Flocculation Method
| Method | Adsorbent/ Coagulant | Dosage (g/L) | pH | Parameter | Concentration (mg/L) | Removal Rate (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADS | PAC | 0.1 | 7.8 | TOCi | 2.5 | 37.0 | [105] |
| TOCf | 1.6 | ||||||
| ADS | WoAC | 2.0 | 8.0 | DOCi | 197.5 | 70.8 | [104] |
| DOCf | 57.7 | ||||||
| ADS | CoAC | 2.0 | 8.0 | DOCi | 197.5 | 78.4 | [104] |
| DOCf | 42.7 | ||||||
| ADS | Palygorskite | 133.0 | 8.0 | CODi | 1998.0 | 54.7 | [111] |
| CODf | 905.0 | ||||||
| ADS | Palygorskite | 133.0 | 8.0 | NH3-Ni | 675.0 | 41.9 | [111] |
| NH3-Nf | 392.0 | ||||||
| CF | Na2FeO4 | 120.0 | 5.5 | CODi | 32,000.0 | 87.1 | [108] |
| CODf | 4144.0 | ||||||
| CF | FeCl3 | 34.8 | 7.6 | CODi | 22,000.0 | 50.0 | [109] |
| CODf | 11,000.0 | ||||||
| CF | Fe2 (SO4)3 | 0.2 | 7.6 | CODi | 3855.0 | 74.5 | [112] |
| CODf | 983.0 |
3.2. Advanced Oxidation Progresses
3.2.1. Electrooxidation
3.2.2. Ozone Oxidation
3.2.3. Fenton Oxidation
3.2.4. Photocatalytic Oxidation
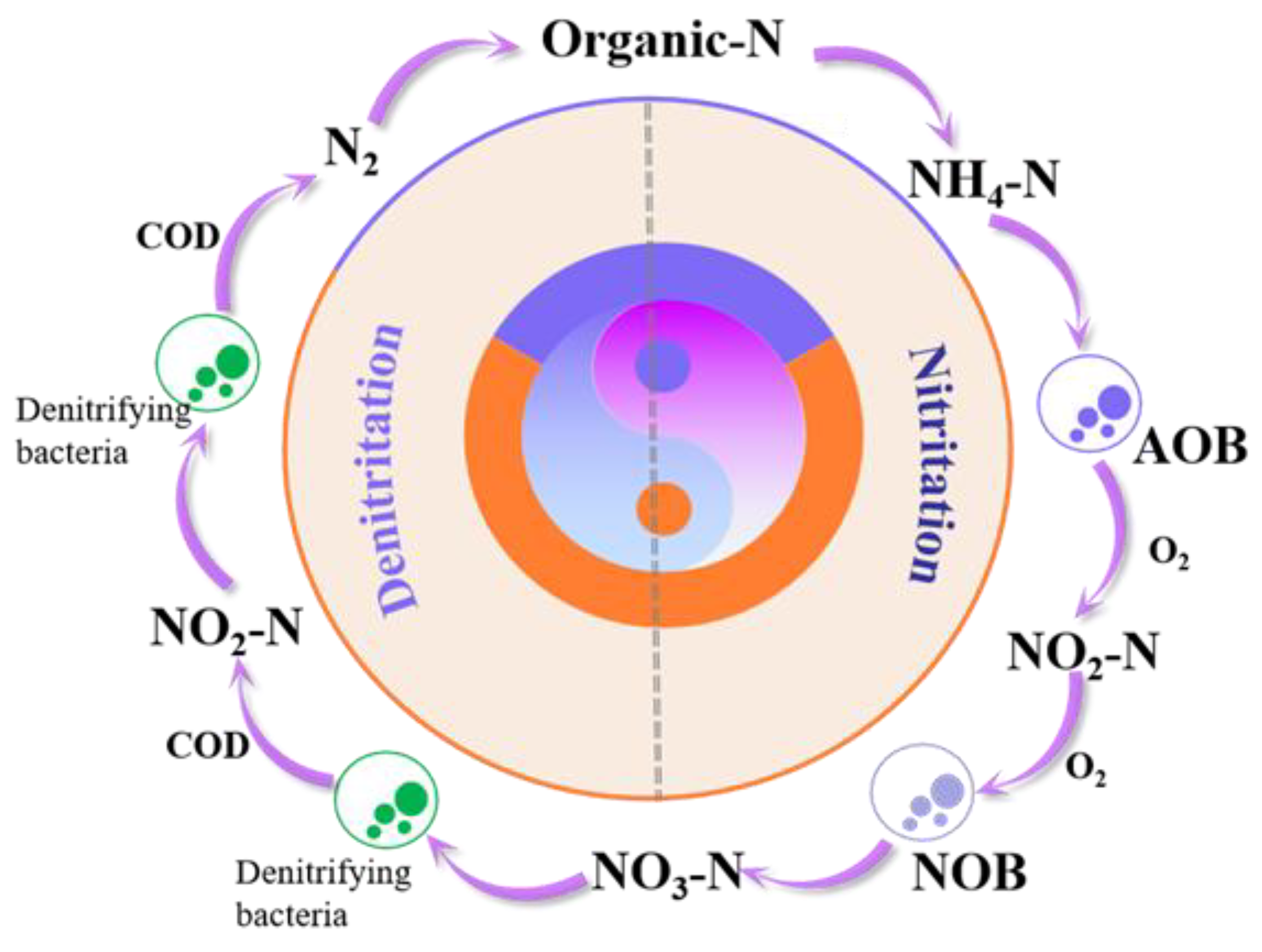
3.3. Biological Treatment Processes
3.3.1. Aerobic Treatment Processes
3.3.2. Anaerobic Treatment Processes
3.3.3. Constructed Wetlands
3.4. Membrane Technology
| Method | pH | Parameter | Concentration (mg/L) | Removal Rate (%) | Scale | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MBR-NF | / | CODi | 4670–6700 | 87% | Pilot | [151] |
| CODf | 800 | |||||
| AMBR | 7.1–8.3 | CODi | 2482.6 | 80.7 | Lab | [153] |
| CODf | 479.6 | |||||
| DCMD | 8.0 | CODi | 198.7 | 99.0 | Lab | [164] |
| CODf | 2.0 | |||||
| ITMD | 12.0 | CODi | 1291.8 | 99.9 | Lab | [162] |
| CODf | 0.5 | |||||
| MD | 7.0 | TOCi | 602.0 | 98.9 | Lab | [165] |
| TOCf | 6.5 | |||||
| PVDF | 8.3 | CODi | 1188.0 | 57.1 | Lab | [166] |
| CODf | 510.0 | |||||
| MBR | 8.0 | CODi | 5000.0 | 91.7 | Lab | [167] |
| CODf | 417.0 |
3.5. Leachate Recirculation
3.6. Cost of Technologies
3.7. Advantages and Disadvantages of Treatment Technologies
4. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miao, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, P. Review on manganese dioxide for catalytic oxidation of airborne formaldehyde. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 466, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotvajn, A.Ž.; Tišler, T.; Zagorc-Končan, J. Comparison of different treatment strategies for industrial landfill leachate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 162, 1446–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renou, S.; Givaudan, J.G.; Poulain, S.; Dirassouyan, F.; Moulin, P. Landfill leachate treatment: Review and opportunity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 150, 468–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Yang, W.; Liang, H.; Nabi, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Hu, J.; Chen, T.; Gao, D. Nitrogen removal from mature landfill leachate through enhanced Partial Nitrification-Anammox process in an innovative multi-stage fixed biofilm reactor. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 877, 162959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhada-Tata, P.; Hoornweg, D. What a Waste? A Global Review of Solid Waste Management; Urban Development Series; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Liu, J.; Gao, B.; Sillanpää, M. Landfill leachate treatment in-depth by bio-chemical strategy: Microbial activation and catalytic ozonation mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 444, 136464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauchert, E.; Schneider, S.; de Morais, J.L.; Peralta-Zamora, P. Photochemically-assisted electrochemical degradation of landfill leachate. Chemosphere 2006, 64, 1458–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, T.E.; Gouda, H.M.; Baloch, M.I.; Paul, P.; Javadi, A.A.; Alam, A. Literature review of baseline study for risk analysis—The landfill leachate case. Environ. Int. 2014, 63, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duyar, A.; Ciftcioglu, V.; Cirik, K.; Civelekoglu, G.; Uruş, S. Treatment of landfill leachate using single-stage anoxic moving bed biofilm reactor and aerobic membrane reactor. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 776, 145919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; He, L.; Dai, Z.; Sun, R.; Jiang, S.; Lu, Z.; Liang, Y.; Ren, L.; Sun, S.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Review on recent progress of bioremediation strategies in Landfill leachate—A green approach. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 50, 103229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, K.Y.; Hameed, B.H. An overview of landfill leachate treatment via activated carbon adsorption process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Cheng, L.; Liang, H.; Xu, A.; Li, Y.; Nabi, M.; Wang, H.; Hu, J.; Gao, D. Efficient nitrogen removal from mature landfill leachate by single-stage partial-nitritation anammox using expanded granular sludge bed. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 344, 118460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panizza, M.; Delucchi, M.; Sirés, I. Electrochemical process for the treatment of landfill leachate. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2010, 40, 1721–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Yang, P.; Wang, Z.; Ren, S.; Qiu, J.; Liang, H.; Peng, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q. Efficient and advanced nitrogen removal from mature landfill leachate via combining nitritation and denitritation with Anammox in a single sequencing batch biofilm reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 333, 125138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Liu, J.; Gao, B.; Sillanpää, M.; Al-Farraj, S. The effect of activated sludge treatment and catalytic ozonation on high concentration of ammonia nitrogen removal from landfill leachate. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 361, 127668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, V.; Kumar Padhi, S.; Kumar Dikshit, P.; Pattanaik, L. Recent developments in landfill leachate treatment: Aerobic granular reactor and its future prospects. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2022, 18, 100689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraume, M.; Drews, A. Membrane Bioreactors in Waste Water Treatment—Status and Trends. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2010, 33, 1251–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Fadel, M.; Sleem, F.; Hashisho, J.; Saikaly, P.E.; Alameddine, I.; Ghanimeh, S. Impact of SRT on the performance of MBRs for the treatment of high strength landfill leachate. Waste Manag. 2018, 73, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, C.; Guido, P.; Colin, J.; Le Dû-Delepierre, A. Estimation of the hazard of landfills through toxicity testing of leachates—I. Determination of leachate toxicity with a battery of acute tests. Chemosphere 1996, 33, 2303–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marttinen, S.K.; Kettunen, R.H.; Sormunen, K.M.; Soimasuo, R.M.; Rintala, J.A. Screening of physical–chemical methods for removal of organic material, nitrogen and toxicity from low strength landfill leachates. Chemosphere 2002, 46, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirbazari, M.; Ravindran, V.; Badriyha, B.N.; Kim, S.-H. Hybrid membrane filtration process for leachate treatment. Water Res. 1996, 30, 2691–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.C.; Dezotti, M.; Sant’Anna, G.L. Treatment and detoxification of a sanitary landfill leachate. Chemosphere 2004, 55, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisinno, C.L.; Oliveira-Filho, E.C.; Dufrayer, M.C.; Moreira, J.C.; Paumgartten, F.J. Toxicity evaluation of a municipal dump leachate using zebrafish acute tests. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2000, 64, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, S.; Xi, B.; Yu, H.; He, L.; Fan, S.; Liu, H. Characteristics of dissolved organic matter (DOM) in leachate with different landfill ages. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohdziewicz, J.; Bodzek, M.; Górska, J. Application of pressure-driven membrane techniques to biological treatment of landfill leachate. Process Biochem. 2001, 36, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargi, F.; Pamukoglu, M.Y. Aerobic biological treatment of pre-treated landfill leachate by fed-batch operation. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2003, 33, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uygur, A.; Kargı, F. Biological nutrient removal from pre-treated landfill leachate in a sequencing batch reactor. J. Environ. Manag. 2004, 71, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadi, S.; Karimi-Jashni, A.; Javadpour, S.; Amiri, H. Photocatalytic treatment of landfill leachate: A comparison between N-, P-, and N-P-type TiO2 nanoparticles. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 19, 100985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanmani, S.; Dileepan, A.G.B. Treatment of landfill leachate using photocatalytic based advanced oxidation process—A critical review. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wu, G.; Li, N.; Lu, X.; Zhao, J.; He, M.; Yan, B.; Zhang, H.; Duan, X.; Wang, S. Landfill leachate treatment by persulphate related advanced oxidation technologies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 418, 126355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Hsu, J.-Y.; Lin, Y.-C.; Chu, C.-J.; Lin, Y.-P.; Tsai, Y.-J.; Liao, P.-C. Nationwide suspect screening of new psychoactive substances (NPSs) and other controlled substances in Taiwan wastewater using liquid chromatography–High resolution mass spectrometry (LC-HRMS). Chemosphere 2025, 375, 144227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, M.; Gandhi, K.; Kumar, M.S. Emerging environmental contaminants: A global perspective on policies and regulations. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 332, 117344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shen, X.; Jiang, W.; Xi, Y.; Li, S. Comprehensive review of emerging contaminants: Detection technologies, environmental impact, and management strategies. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 278, 116420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Xu, H.; Zhong, C.; Liu, M.; Yang, L.; He, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, C.; Wang, D. Treatment of landfill leachate by coagulation: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Shafy, H.I.; Ibrahim, A.M.; Al-Sulaiman, A.M.; Okasha, R.A. Landfill leachate: Sources, nature, organic composition, and treatment: An environmental overview. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2024, 15, 102293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuabdou, S.M.A.; Ahmad, W.; Aun, N.C.; Bashir, M.J.K. A review of anaerobic membrane bioreactors (AnMBR) for the treatment of highly contaminated landfill leachate and biogas production: Effectiveness, limitations and future perspectives. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 255, 120215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Guidelines Approved by the Guidelines Review Committee. In Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: Fourth Edition Incorporating the First Addendum; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Aziz, H.A.; Ramli, S.F.; Hung, Y.-T. Physicochemical Technique in Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) Landfill Leachate Remediation: A Review. Water 2023, 15, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindamulla, L.; Nanayakkara, N.; Othman, M.; Jinadasa, S.; Herath, G.; Jegatheesan, V. Municipal Solid Waste Landfill Leachate Characteristics and Their Treatment Options in Tropical Countries. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2022, 8, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinedo-Hernández, J.; Marrugo-Negrete, J.; Pérez-Espitia, M.; Durango-Hernández, J.; Enamorado-Montes, G.; Navarro-Frómeta, A. A pilot-scale electrocoagulation-treatment wetland system for the treatment of landfill leachate. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 351, 119681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Białowiec, A.; Davies, L.; Albuquerque, A.; Randerson, P.F. The influence of plants on nitrogen removal from landfill leachate in discontinuous batch shallow constructed wetland with recirculating subsurface horizontal flow. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 40, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Liu, H.; Jiang, M.; Lin, J.; Ye, K.; Fang, S.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Van der Bruggen, B.; He, Z. Sustainable management of landfill leachate concentrate through recovering humic substance as liquid fertilizer by loose nanofiltration. Water Res. 2019, 157, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Guo, H.; Chen, Z.; Xu, Q.; Chen, L.; Bai, X. Analysis of landfill leachate promoting efficient application of weathered coal anaerobic fermentation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 273, 116151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandala, E.R.; Liu, A.; Wijesiri, B.; Zeidman, A.B.; Goonetilleke, A. Emerging materials and technologies for landfill leachate treatment: A critical review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 291, 118133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, T.; Wang, H.; Yang, K.; Fang, C.; Lv, B.; Yang, X. Study on treating old landfill leachate by Ultrasound–Fenton oxidation combined with MAP chemical precipitation. Chem. Speciat. Bioavailab. 2016, 27, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, C.; Zhou, K.; Peng, C.; Chen, W. Characterization and treatment of landfill leachate: A review. Water Res. 2021, 203, 117525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabaghian, Z.; Peyravi, M.; Jahanshahi, M.; Rad, A.S. Potential of Advanced Nano-structured Membranes for Landfill Leachate Treatment: A Review. ChemBioEng Rev. 2018, 5, 119–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.M.; Alfaia, R.G.d.S.M.; Campos, J.C. Landfill leachate treatment in Brazil—An overview. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 232, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Lu, X.-Q.; Luo, J.-H.; Liu, J.-Y.; Xu, Y.-F.; Zhao, A.-H.; Liu, F.; Tai, J.; Qian, G.-R.; Peng, B. Characterization of fresh leachate from a refuse transfer station under different seasons. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2013, 85, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Yang, G.; Tao, T.; Peng, Y. Recent advances in nitrogen removal from landfill leachate using biological treatments—A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 235, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.-H.; Shin, H.S.; Park, H. Characterization of humic substances present in landfill leachates with different landfill ages and its implications. Water Res. 2002, 36, 4023–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Xi, B.; Tan, W. Assessing the impacts and contamination potentials of landfill leachate on adjacent groundwater systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 930, 172664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagwar, P.P.; Dutta, D. Landfill leachate a potential challenge towards sustainable environmental management. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 171668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhamsaniya, M.; Sojitra, D.; Modi, H.; Shabiimam, M.A.; Kandya, A. A review of the techniques for treating the landfill leachate. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 77, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Wang, X.-G.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.-X.; Sha, H.-Q.; He, X.-S.; Sun, X.-J. Natural and anthropogenic dissolved organic matter in landfill leachate: Composition, transformation, and their coexistence characteristics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lv, J.; He, A.; Cao, D.; He, X.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, G. Investigation with ESI FT-ICR MS on sorbent selectivity and comprehensive molecular composition of landfill leachate dissolved organic matter. Water Res. 2023, 243, 120359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moravia, W.G.; Amaral, M.C.S.; Lange, L.C. Evaluation of landfill leachate treatment by advanced oxidative process by Fenton’s reagent combined with membrane separation system. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wu, W.; Shi, P.; Guo, J.; Cheng, J. Characterization of dissolved organic matter in landfill leachate during the combined treatment process of air stripping, Fenton, SBR and coagulation. Waste Manag. 2015, 41, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Y.; Hou, J.; Fang, C.; Tian, Y.; Naidu, R.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Cheng, Z.; He, J.; et al. Ultrasound-based advanced oxidation processes for landfill leachate treatment: Energy consumption, influences, mechanisms and perspectives. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 263, 115366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhuo, X.; He, C.; Shi, Q.; Li, Q. Molecular investigation into the transformation of dissolved organic matter in mature landfill leachate during treatment in a combined membrane bioreactor-reverse osmosis process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 397, 122759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Mao, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, S. Characterization of dissolved organic matter during the O3-based advanced oxidation of mature landfill leachate with and without biological pre-treatment and operating cost analysis. Chemosphere 2021, 271, 129810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarthi, A.; Bindhu, M.R.; Umadevi, M.; Parimaladevi, R.; Sathe, G.V.; Al-Mohaimeed, A.M.; Elshikh, M.S.; Balasubramanian, B. Evaluating the detection efficacy of advanced bimetallic plasmonic nanoparticles for heavy metals, hazardous materials and pesticides of leachate in contaminated groundwater. Environ. Res. 2021, 201, 111590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Yuan, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, H.; Si, Y.; Zhang, F. Removal of refractory organics and heavy metals in landfill leachate concentrate by peroxi-coagulation process. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 116, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojiri, A.; Zhou, J.L.; Ratnaweera, H.; Ohashi, A.; Ozaki, N.; Kindaichi, T.; Asakura, H. Treatment of landfill leachate with different techniques: An overview. Water Reuse 2020, 11, 66–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.; Pariatamby, A.; Ossai, I.C.; Hamid, F.S. Bioaugmentation assisted mycoremediation of heavy metal and/metalloid landfill contaminated soil using consortia of filamentous fungi. Biochem. Eng. J. 2020, 157, 107550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Coulon, F.; Wagland, S.T. Influence of pH, depth and humic acid on metal and metalloids recovery from municipal solid waste landfills. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, W.; Qiao, J.; Song, L. Occurrence and prevalence of antibiotic resistance in landfill leachate. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 12525–12533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Yang, S.; An, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lei, Y.; Song, L. Antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in landfills: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuansawan, N.; Witthayaphirom, C.; Sawasdee, A.; Chiemchaisri, C.; Shoda, M. Removals of endocrine disrupting compounds during landfill leachate treatment in two-stage aerobic sequential batch reactor: Effect of Alcaligenes faecalis no.4 bio-augmentation. Emerg. Contam. 2023, 9, 100223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Hu, P.; Lang-Yona, N.; Xu, M.; Guo, C.; Gu, J.-D. Global landfill leachate characteristics: Occurrences and abundances of environmental contaminants and the microbiome. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 461, 132446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibert, D.; Quesada, H.; Bergamasco, R.; Borba, F.H.; Pellenz, L. Presence of endocrine disrupting chemicals in sanitary landfill leachate, its treatment and degradation by Fenton based processes: A review. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 131, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Cheng, Z.; Yuan, H.; Zhu, N.; Lou, Z.; Otieno, P. Occurrence of banned and commonly used pesticide residues in concentrated leachate: Implications for ecological risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Wang, B.; Wang, H.; He, Z.; Pi, Y.; Zhou, J.; Liang, T.; Chen, M.; He, T.; Fu, T. Removal of organochlorine pesticides and metagenomic analysis by multi-stage constructed wetland treating landfill leachate. Chemosphere 2022, 301, 134761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laiju, A.R.; Gandhimathi, R.; Nidheesh, P.V. Removal of pharmaceutical and personal care products in landfill leachate treatment process. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2023, 31, 100434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Q.; Zhao, W.; Cao, X.; Lu, S.; Qiu, Z.; Gu, X.; Yu, G. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the leachates from a typical landfill reservoir of municipal solid waste in Shanghai, China: Occurrence and removal by a full-scale membrane bioreactor. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 323, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Tran, N.H.; Yin, T.; He, Y.; Gin, K.Y.-H. Removal of selected PPCPs, EDCs, and antibiotic resistance genes in landfill leachate by a full-scale constructed wetlands system. Water Res. 2017, 121, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatas, O.; Kobya, M.; Khataee, A.; Yoon, Y. Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) removal from real landfill leachate wastewater and simulated soil leachate by electrochemical oxidation process. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 28, 102954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierpaoli, M.; Szopińska, M.; Wilk, B.K.; Sobaszek, M.; Łuczkiewicz, A.; Bogdanowicz, R.; Fudala-Książek, S. Electrochemical oxidation of PFOA and PFOS in landfill leachates at low and highly boron-doped diamond electrodes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Brown, E.; Mededovic Thagard, S.; Holsen, T.M. Treatment of PFAS-containing landfill leachate using an enhanced contact plasma reactor. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 124452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Chen, L.; Shao, L.; Zhang, H.; Lü, F. Municipal solid waste (MSW) landfill: A source of microplastics? -Evidence of microplastics in landfill leachate. Water Res. 2019, 159, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, M.S.; Wang, H.; Luster-Teasley, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, R. Microplastics in landfill leachate: Sources, detection, occurrence, and removal. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2023, 16, 100256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Xiong, W.; Song, B.; Zhou, C.; Almatrafi, E.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, Y. Microplastics in landfill and leachate: Occurrence, environmental behavior and removal strategies. Chemosphere 2022, 305, 135325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, S.; Mishra, A.K.; Bhat, M.A.; Bhat, M.A.; Jan, A.T. Pollutants in aquatic system: A frontier perspective of emerging threat and strategies to solve the crisis for safe drinking water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 113242–113279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, M.M.; Tounsi, A.; Gomaa, H.; Hu, N.; Shenashen, M. Addressing emerging contaminants in wastewater: Insights from adsorption isotherms and adsorbents: A comprehensive review. Alex. Eng. J. 2024, 100, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Sánchez, I.M.; Tuberty, S.; Hambourger, M.; Bandala, E.R. Resource efficiency analysis for photocatalytic degradation and mineralization of estriol using TiO2 nanoparticles. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 1270–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadupudi, C.K.; Rice, L.; Xiao, L.; Kantamaneni, K. Endocrine Disrupting Compounds Removal Methods from Wastewater in the United Kingdom: A Review. Science 2021, 3, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, S.F.; Mofijur, M.; Nuzhat, S.; Chowdhury, A.T.; Rafa, N.; Uddin, M.A.; Inayat, A.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Ong, H.C.; Chia, W.Y.; et al. Recent developments in physical, biological, chemical, and hybrid treatment techniques for removing emerging contaminants from wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.-X.; Chen, Z.-Y.; Chen, C.H.; Hsieh, M.-F.; Lin, A.Y.-C.; Chen, S.S.; Wu, K.C.W. Efficient adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of water emerging contaminants through nanoarchitectonics of pore sizes and optical properties of zirconium-based MOFs. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 451, 131113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qiu, L.; Bao, S.; Tian, F.; Sheng, J.; Yang, W.; Yu, Y. Visible-light enhanced peroxymonosulfate activation on Co3O4/MnO2 for the degradation of tetracycline: Cooperation of radical and non-radical mechanisms. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 316, 123779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Cai, C.; Sun, F.; Ma, M.; An, T.; Chen, C. Advanced nitrogen removal of landfill leachate treatment with anammox process: A critical review. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 58, 104756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yan, Z.; Chang, H.; Wang, Q.; Fan, G.; Ye, J.; Xu, K.; Liang, H.; Qu, F. Enhancing membrane distillation efficiency in treating high salinity organic wastewater: A pressure-driven membrane electrochemical reactor approach. Desalination 2024, 582, 117619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amor, C.; Torres-Socías, E.D.; Peres, J.A.; Maldonado, M.I.; Oller, I.; Malato, S.; Lucas, M.S. Mature landfill leachate treatment by coagulation/flocculation combined with Fenton and solar photo-Fenton processes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 286, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.J.; Wu, C.-C.; Ma, H.-W.; Chang, C.-C. Treatment of landfill leachate by ozone-based advanced oxidation processes. Chemosphere 2004, 54, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Mirino, M.W.; Yuan, Y. Partial nitrification and denitrification of mature landfill leachate using a pilot-scale continuous activated sludge process at low dissolved oxygen. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 218, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikowska, D.; Bernat, K.; Konopka, K. Kinetics of denitrification with crude glycerine as a carbon source in landfill leachate treatment. Desalination Water Treat. 2018, 116, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagni, A.; Marsili-Libelli, S. Nitrogen removal via nitrite in a sequencing batch reactor treating sanitary landfill leachate. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foo, K.Y.; Lee, L.K.; Hameed, B.H. Batch adsorption of semi-aerobic landfill leachate by granular activated carbon prepared by microwave heating. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 222, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, F.J.; Beltrán, F.J.; Gimeno, O.; Frades, J.; Carvalho, F. Adsorption of landfill leachates onto activated carbon: Equilibrium and kinetics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 131, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikowska, D.; Bernat, K.; Parszuto, K.; Sułek, P. Efficiency and kinetics of organics removal from landfill leachate by adsorption onto powdered and granular activated carbon. Desalination Water Treat. 2014, 57, 4458–4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, L.B.; Murthy, Z.V.P. Treatment of landfill leachates by nanofiltration. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 1209–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, H.A.; Feng, C.T.; Bashir, M.J.K. Advanced Treatment of Landfill Leachate Effluent Using Membrane Filtration. Int. J. Sci. Res. Environ. Sci. 2013, 1, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydın Temel, F.; Cağcağ Yolcu, Ö.; Kuleyin, A. A multilayer perceptron-based prediction of ammonium adsorption on zeolite from landfill leachate: Batch and column studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 410, 124670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Li, R.; Sun, X.; Liu, X.; Li, D. The roles of phosphorus species formed in activated biochar from rice husk in the treatment of landfill leachate. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 288, 121533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, S.; Liao, X.; Shi, H.; Huang, J. Unveiling the molecular responses of dissolved organic matter in landfill leachate to activated carbon adsorption. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 330, 125335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Siddique, M.S.; Graham, N.J.D.; Yu, W. Removal of Small-Molecular-Weight Organic Matter by Coagulation, Adsorption, and Oxidation: Molecular Transformation and Disinfection Byproduct Formation Potential. ACS EST Eng. 2022, 2, 886–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Shi, A.; Shi, Y.; Yue, D.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Cui, D. An innovative approach for landfill leachate treatment based on selective adsorption of humic acids with carbon nitride. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 461, 142090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawakkoly, B.; Alizadehdakhel, A.; Dorosti, F. Evaluation of COD and turbidity removal from compost leachate wastewater using Salvia hispanica as a natural coagulant. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 137, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbabi, M.; Tousizadeh, S.; Tondro, E.; Sedehi, M.; Arbabi, A. Evaluation of chemical oxygen demand and color removal from leachate using coagulation/flocculation combined with advanced oxidation process. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2022, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaouki, Z.; Hadri, M.; Nawdali, M.; Benzina, M.; Zaitan, H. Treatment of a landfill leachate from Casablanca city by a coagulation-flocculation and adsorption process using a palm bark powder (PBP). Sci. Afr. 2021, 12, e00721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyakhsass, R.; Souabi, S.; Rifi, S.K.; Bouaouda, S.; Taleb, A.; Madinzi, A.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Anouzla, A. Applicability of central composite design and response surface methodology for optimizing treatment of landfill leachate using coagulation-flocculation. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2023, 197, 669–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genethliou, C.; Lazaratou, C.V.; Triantaphyllidou, I.E.; Xanthaki, E.; Mourgkogiannis, N.; Sygellou, L.; Tekerlekopoulou, A.G.; Koutsoukos, P.; Vayenas, D.V. Adsorption studies using natural palygorskite for the treatment of real sanitary landfill leachate. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Gu, Z.; Wen, P.; Li, Q. Degradation of refractory organic contaminants in membrane concentrates from landfill leachate by a combined coagulation-ozonation process. Chemosphere 2019, 217, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanbari, F.; Wu, J.; Khatebasreh, M.; Ding, D.; Lin, K.-Y.A. Efficient treatment for landfill leachate through sequential electrocoagulation, electrooxidation and PMS/UV/CuFe2O4 process. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 242, 116828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, M.T.; Torres, I.M.S.; Ruggeri, H.; Scalize, P.; Albuquerque, A.; Gil, E.d.S. Application of Electrocoagulation with a New Steel-Swarf-Based Electrode for the Removal of Heavy Metals and Total Coliforms from Sanitary Landfill Leachate. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Wang, J.; Shen, Z.; Yan, W.; Nengzi, L.; Feng, C.; Lei, X.; Yu, L.; Hu, J. Efficiently removing dissolved organic pollutants in landfill leachate concentrate using dual-anode Fe2+/HClO system: The significance of insolubilization based on oxidative coupling of organics. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 344, 127244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chen, W.; Gu, Z.; Li, Q. A review of the characteristics of Fenton and ozonation systems in landfill leachate treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 143131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, W.; Wang, Z.; Guo, M.; Jin, X.; Jin, P.; Wang, X. Unveiling the transformation of organics in leachate during the composite anode-supported electro-hybrid ozonation-coagulation (CA-E-HOC) treatment: Significance of synergy among chlorine, coagulant, and ozone. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 496, 154213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Liu, J.; Gao, B.; Hao, J. Ozone direct oxidation pretreatment and catalytic oxidation post-treatment coupled with ABMBR for landfill leachate treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 794, 148557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scandelai, A.P.J.; Cardozo Filho, L.; Martins, D.C.C.; Freitas, T.K.F.d.S.; Garcia, J.C.; Tavares, C.R.G. Combined processes of ozonation and supercritical water oxidation for landfill leachate degradation. Waste Manag. 2018, 77, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Luo, H.; Wang, T.; Zhou, J.; Zhu, Y.; Hou, J. Advanced treatment of landfill leachate by catalytic ozonation with MnCeOx/γ-Al2O3 catalyst. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 46, 104113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; He, C.; Shan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J. Catalytic ozonation of atenolol by Mn-Ce@Al2O3 catalysts: Efficiency, mechanism and degradation pathways. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Wu, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, B.; Wen, C.; Hu, C.; Liu, C.; Liu, Q. Enhancing levoglucosan production from waste biomass pyrolysis by Fenton pretreatment. Waste Manag. 2020, 108, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jegadeesan, C.; Somanathan, A.; Jeyakumar, R.B. Sanitary landfill leachate treatment by aerated electrochemical Fenton process. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 337, 117698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wu, S.; Sun, H.; Arhin, S.G.; Papadakis, V.G.; Goula, M.A.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Wang, W. Efficient degradation of organic compounds in landfill leachate via developing bio-electro-Fenton process. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 319, 115719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jiang, H.; Wang, H.; Show, P.L.; Ivanets, A.; Luo, D.; Wang, C. MXenes as heterogeneous Fenton-like catalysts for removal of organic pollutants: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, S.; Chi, C.; Wang, Y.; Gao, X.; Li, P.; Wang, Y.; Wan, C.; Wu, S. Treatment of mature landfill leachate using chemical and electrical Fenton with novel Fe-loaded GAC heterogeneous catalysts. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 60, 105169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandran Loganayagi, P.A. Ramsathyajayanthi Landfill leachate degradation using zinc oxide under direct sunlight. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2017, 8, 3039–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa Filho, B.M.; Vilar, V.J.P. Strategies for the intensification of photocatalytic oxidation processes towards air streams decontamination: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 391, 123531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, X.; Yang, Y.; Niu, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Lai, C.; Yi, H.; Li, M.; An, Z.; Huang, D.; et al. A direct Z-scheme oxygen vacant BWO/oxygen-enriched graphitic carbon nitride polymer heterojunction with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 403, 126363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadi, S.; Karimi-Jashni, A.; Javadpour, S.; Mahmoudian-Boroujerd, L. Photocatalytic landfill leachate treatment using P-type TiO2 nanoparticles under visible light irradiation. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 23, 6047–6065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Kumar Naini, P.; Sundaram, B. Photocatalytic treatment of landfill leachate using CaTiO3 nanoparticles. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2023, 20, 100904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhao, R. Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) in Wastewater Treatment. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2015, 1, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, M.N.; Jin, B.; Chow, C.W.K.; Saint, C. Recent developments in photocatalytic water treatment technology: A review. Water Res. 2010, 44, 2997–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Chon, K.; Ren, X.; Kou, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Hwang, M.-H.; Chae, K.-J. The role of beneficial microorganisms in an anoxic-oxic (AO) process for treatment of ammonium-rich landfill leachates: Nitrogen removal and excess sludge reduction. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bove, D.; Merello, S.; Frumento, D.; Arni, S.A.; Aliakbarian, B.; Converti, A. A Critical Review of Biological Processes and Technologies for Landfill Leachate Treatment. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2015, 38, 2115–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagaba, A.H.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Lawal, I.M.; Abubakar, S.; Hassan, I.; Zubairu, I.; Umaru, I.; Abdurrasheed, A.S.; Adam, A.A.; Ghaleb, A.A.S.; et al. Sequencing batch reactor technology for landfill leachate treatment: A state-of-the-art review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 282, 111946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonnorat, J.; Honda, R.; Panichnumsin, P.; Boonapatcharoen, N.; Yenjam, N.; Krasaesueb, C.; Wachirawat, M.; Seemuang-on, S.; Jutakanoke, R.; Teeka, J.; et al. Treatment efficiency and greenhouse gas emissions of non-floating and floating bed activated sludge system with acclimatized sludge treating landfill leachate. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 330, 124952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmaadawy, K.; Liu, B.; Hassan, G.K.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Hu, J.; Hou, H.; Yang, J.; Wu, X. Microalgae-assisted fixed-film activated sludge MFC for landfill leachate treatment and energy recovery. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 160, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Ferraz, F.; Lashkarizadeh, M.; Yuan, Q. Comparing young landfill leachate treatment efficiency and process stability using aerobic granular sludge and suspended growth activated sludge. J. Water Process Eng. 2017, 17, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, V.; Padhi, S.K.; Pattanaik, L.; Bhatt, R. Simultaneous removal of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus from landfill leachate using an aerobic granular reactor. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 28, 102657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Peng, Y. Efficient nitrogen removal from mature landfill leachate in a step feed continuous plug-flow system based on one-stage anammox process. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 347, 126676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Xue, F.; Wang, W.; Huang, X.; Wang, Z. Partial nitrification coupled with denitrification and anammox to treat landfill leachate in a tower biofilter reactor (TBFR). J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 42, 102155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, L.-L.; Yang, T.; Zhang, J.; Li, X. The configuration, purification effect and mechanism of intensified constructed wetland for wastewater treatment from the aspect of nitrogen removal: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 293, 122086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, D.A.D.; Soda, S.; Machimura, T.; Ike, M. Removal of phenol, bisphenol A, and 4-tert-butylphenol from synthetic landfill leachate by vertical flow constructed wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 578, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, Z.J.; Bashir, M.J.K.; Ng, C.A.; Sethupathi, S.; Lim, J.-W. A sequential treatment of intermediate tropical landfill leachate using a sequencing batch reactor (SBR) and coagulation. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 205, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; He, C.; Tian, T.; Liu, Z.; Gu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Wang, W. UASB-modified Bardenpho process for enhancing bio-treatment efficiency of leachate from a municipal solid waste incineration plant. Waste Manag. 2020, 102, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Mu, Y.; Cheng, X.; Sun, D. Treatment of fresh leachate with high-strength organics and calcium from municipal solid waste incineration plant using UASB reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 5498–5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolar, D.; Košutić, K.; Strmecky, T. Hybrid processes for treatment of landfill leachate: Coagulation/UF/NF-RO and adsorption/UF/NF-RO. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 168, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfahani, A.R.; Zhai, L.; Sadmani, A.H.M.A. Removing heavy metals from landfill leachate using electrospun polyelectrolyte fiber mat-laminated ultrafiltration membrane. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.N.; Lan, C.Q. Treatment of landfill leachate using membrane bioreactors: A review. Desalination 2012, 287, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, W.; Du, Q. Applicability of nanofiltration for the advanced treatment of landfill leachate. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 116, 2343–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiemchaisri, C.; Chiemchaisri, W.; Nindee, P.; Chang, C.Y.; Yamamoto, K. Treatment performance and microbial characteristics in two-stage membrane bioreactor applied to partially stabilized leachate. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 64, 1064–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindamulla, L.M.L.K.B.; Jayawardene, N.K.R.N.; Wijerathne, W.S.M.S.K.; Othman, M.; Nanayakkara, K.G.N.; Jinadasa, K.B.S.N.; Herath, G.B.B.; Jegatheesan, V. Treatment of mature landfill leachate in tropical climate using membrane bioreactors with different configurations. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 136013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Li, N.; Guo, W.; Wang, R.; Yan, Y.; Shao, S. Removing refractory organic substances from landfill leachate using a nanofiltration membrane bioreactor: Performance and mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 484, 149704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, A.; Boo, C.; Karanikola, V.; Lin, S.; Straub, A.P.; Tong, T.; Warsinger, D.M.; Elimelech, M. Membrane distillation at the water-energy nexus: Limits, opportunities, and challenges. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 1177–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, L.; Hou, D.; Wu, X.; Li, K.; Wang, J. Fenton pretreatment to mitigate membrane distillation fouling during treatment of landfill leachate membrane concentrate: Performance and mechanism. Water Res. 2023, 244, 120517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, S.S.; Chen, S.-S.; Sangeetha, D.; Chang, H.-M.; Thanh, C.N.D.; Le, Q.H.; Ku, H.-M. Developments in forward osmosis and membrane distillation for desalination of waters. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 16, 1247–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Lu, Z.; Chen, X.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Liu, L.; Fan, G.; Chang, H.; Qu, F.; Liang, H. Membrane distillation treatment of landfill leachate: Characteristics and mechanism of membrane fouling. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 289, 120787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhong, L.; Horseman, T.; Liu, Z.; Zeng, G.; Li, Z.; Lin, S.; Wang, W. Superhydrophobic-omniphobic membrane with anti-deformable pores for membrane distillation with excellent wetting resistance. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 620, 118768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Wu, B.; Jeong, S.; Jeong, S.; Kim, M. Recent advances of membrane-based hybrid membrane bioreactors for wastewater reclamation. Front. Membr. Sci. Technol. 2024, 3, 1361433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoungrana, A.; Zengin, İ.H.; Elcik, H.; Özkaya, B.; Çakmakci, M. The treatability of landfill leachate by direct contact membrane distillation and factors influencing the efficiency of the process. Desalination Water Treat. 2017, 71, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liu, Q.; Shu, X.; Yu, H.; Rong, H.; Qu, F.; Liang, H. Simultaneous ammonium and water recovery from landfill leachate using an integrated two-stage membrane distillation. Water Res. 2023, 240, 120080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aftab, B.; Yin, G.; Maqbool, T.; Hur, J.; Wang, J. Enhanced landfill leachate treatment performance by adsorption-assisted membrane distillation. Water Res. 2024, 250, 121036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Lin, S.; Ye, L.; Qu, D.; Yang, H.; Chang, H.; Yu, H.; Yan, Z.; Rong, H.; Qu, F. Landfill leachate treatment by direct contact membrane distillation: Impacts of landfill age on contaminant removal performance, membrane fouling and scaling. Desalination 2024, 577, 117407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, X.; Lu, Z.; Wei, Z.; Fan, G.; Liang, H.; Qu, F. Evaluation of applying membrane distillation for landfill leachate treatment. Desalination 2021, 520, 115358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuabdou, S.M.A.; Bashir, M.J.K.; Aun, N.C.; Sethupathi, S.; Yong, W.L. Development of a novel polyvinylidene fluoride membrane integrated with palm oil fuel ash for stabilized landfill leachate treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 311, 127677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohdziewicz, J.; Neczaj, E.; Kwarciak, A. Landfill leachate treatment by means of anaerobic membrane bioreactor. Desalination 2008, 221, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval-Cobo, J.; Caicedo-Concha, D.; Marmolejo-Rebellón, L.; Torres-Lozada, P.; Fellner, J. Evaluation of Leachate Recirculation as a Stabilisation Strategy for Landfills in Developing Countries. Energies 2022, 15, 6494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, E. Wastewater Treatment: An Overview. In Green Adsorbents for Pollutant Removal: Fundamentals and Design; Crini, G., Lichtfouse, E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, E. Advantages and disadvantages of techniques used for wastewater treatment. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
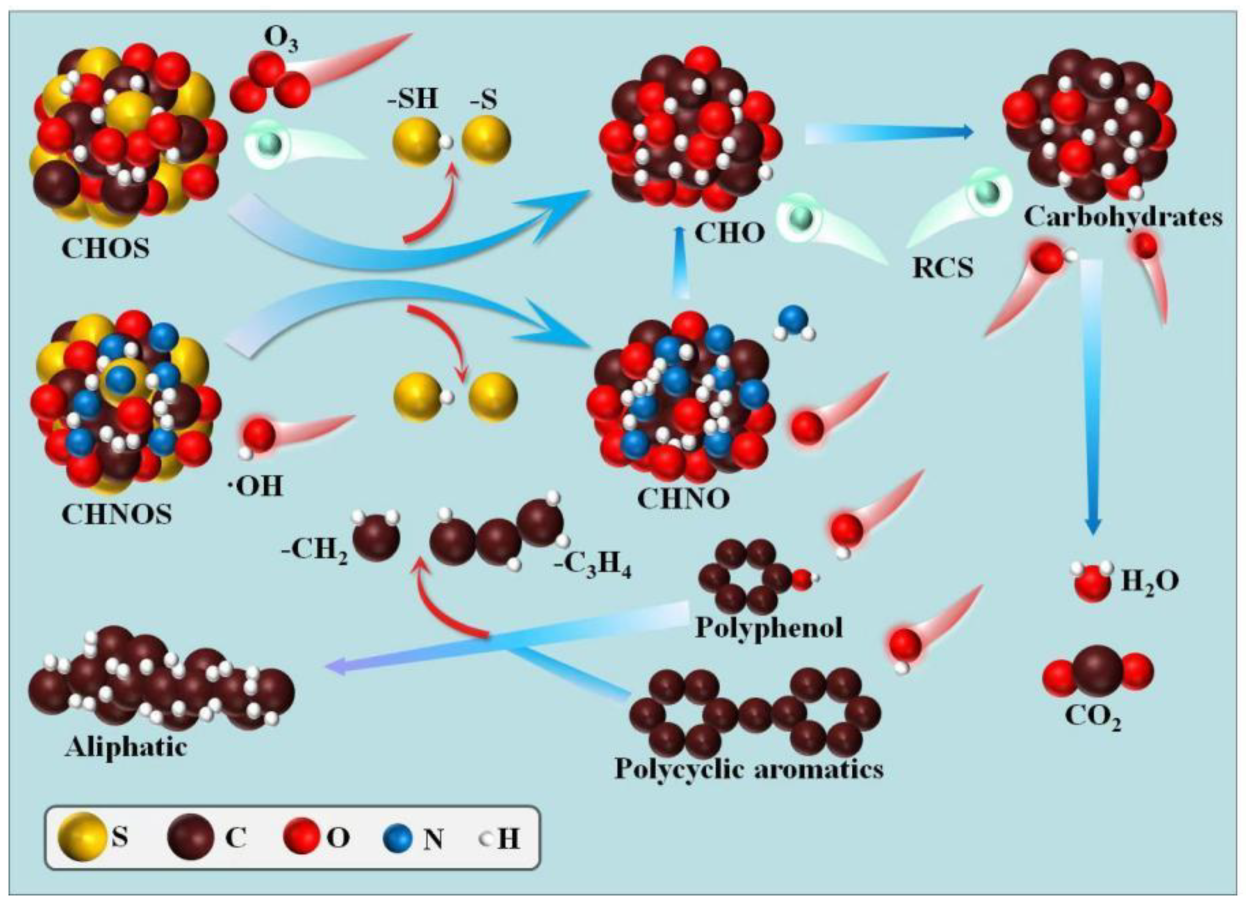
| Species | Examples | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Dissolved organic matter | Organic acid | [56,60,61] |
| Humic acid-like compounds | ||
| Fulvic acid-like compounds | ||
| Metal ions | Fe2+, Fe3+, Mn2+, Zn2+, Pb2+, Cr3+, Cr6+, Ni2+ | [62,63,64] |
| Metalloid ions | Cl−, PO43−, SO42−, As3+, As5+ | [65,66] |
| Antibiotics | Macrolides | [67,68] |
| Quinolones | ||
| Sulfonamides | ||
| Tetracyclines | ||
| Endocrine disrupters | Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons | [69,70,71] |
| Polychlorinated biphenyls | ||
| Bisphenol A | ||
| Pesticides | Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane | [72,73] |
| Hexachlorocyclohexane | ||
| Pharmaceutical and personal care products | Bezafibrate | [74,75,76] |
| Carbamazepine | ||
| Sulfamethoxazole | ||
| Metoprolol | ||
| Commercial organic matter | Perfluoroalkyl acids | [77,78,79] |
| Perfluorooctane sulphonate | ||
| Microplastics | Polystyrene | [80,81,82] |
| Polypropylene | ||
| Polyethylene | ||
| Polyvinyl chloride |
| Method | pH | Parameter | Concentration (mg/L) | Removal Rate (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EO | 7.3 | CODi | 3400.0 | 50.0 | [113] |
| CODf | 1700.0 | ||||
| EO | 3.0 | CODi | 3015.7 | 90.1 | [115] |
| CODf | 297.7 | ||||
| O3 | 7.2 | CODi | 12,320.0 | 80.4 | [118] |
| CODf | 2417.0 | ||||
| O3 | 7.6 | CODi | 1062.0 | 55.8 | [120] |
| CODf | 469.0 | ||||
| Fenton | 2.0 | CODi | 970.0 | 70.0 | [124] |
| CODf | 291.0 | ||||
| Fenton | 5.0 | CODi | 1851.0 | 97.4 | [126] |
| CODf | 48.0 | ||||
| Photocatalytic | 6.0 | CODi | 600.0 | 85.0 | [130] |
| CODf | 90.0 | ||||
| Photocatalytic | 6.0 | CODi | 47,089.0 | 72.0 | [131] |
| CODf | 13,185.0 |
| Method | pH | Parameter | Concentration (mg/L) |
Removal Rate (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASP | 7.85 | CODi | 950.0 | 69.9 | [138] |
| CODf | 286.0 | ||||
| SBR | 8.4 | CODi | 4975.0 | 50.0 | [145] |
| CODf | 2487.0 | ||||
| GSBR | 7.5 | TANi | 498.0 | 99.0 | [139] |
| TANf | 5.0 | ||||
| GSBR | 7.5 | CODi | 810.0 | 67.0 | [139] |
| CODf | 267.0 | ||||
| AGR | 7.5 | CODi | 1149.0 | 75.0 | [140] |
| CODf | 287.0 | ||||
| A/O | 8.2 | CODi | 3387.7 | 52.9 | [141] |
| CODf | 1605.6 | ||||
| USAB | 7.5 | CODi | 6000.0 | 85.0 | [146] |
| CODf | 900.0 | ||||
| USAB | 7.1 | CODi | 73,000.0 | 82.4 | [147] |
| CODf | 12,848.0 | ||||
| TBFR | 7.6 | CODi | 2360.8 | 88.5 | [142] |
| CODf | 272.7 |
| Treatment Process | Technologies | Equipment Investment (CNY/ton·Day) | Operational Cost (CNY/ton) | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physicochemical treatment | Coagulation sedimentation, adsorption, membrane separation (ultrafiltration, reverse osmosis) | 500–2000 | 10–30 | Suitable for small-scale treatment; low initial investment but high maintenance costs for membrane separation in later stages. |
| Biological treatment | Aerobic, anaerobic, MBR (Membrane Bio-Reactor) | 2000–5000 | 20–50 | Effective for refractory organic compounds; high operational costs. |
| Advanced oxidation | Fenton oxidation, ozone oxidation, photocatalytic oxidation | 5000–10,000 | 50–100 | Suitable for high-concentration leachate; high energy consumption and capital/operational costs. |
| Technologies | Advantages | Disadvantages | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical method | Adsorption |
• Simple operation • Adsorbent reusability • Effective for low-concentration organics and heavy metals |
• High adsorbent costs • Complex regeneration protocols • Limited efficacy for high-concentration wastewater |
| Coagulation–flocculation method |
• Cost-effective • Minimal infrastructure requirements • Efficient removal of suspended solids and select organics |
• Limited effectiveness against soluble organic compounds • Generates sludge requiring additional treatment | |
| Advanced oxidation progress |
• Rapid degradation of refractory organics • High reaction efficiency |
• Elevated operational costs • Secondary pollution risks | |
| Biological method | Aerobic |
• Low operational costs • Effective organic matter and ammonia nitrogen removal |
• Inefficient for refractory organics • Performance instability under fluctuating water quality |
| Anaerobic |
• Suitable for high-organic wastewater • Energy-efficient with biogas recovery potential |
• Prolonged startup period • Sensitive to temperature/pH variations • Post-treatment effluent requirements | |
| Membrane technology |
• High separation efficiency • Superior effluent quality • Adaptable to high-concentration wastewater |
• Membrane fouling susceptibility • High membrane replacement costs • Significant energy demand | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiang, R.; Wei, W.; Mei, T.; Wei, Z.; Yang, X.; Liang, J.; Zhu, J. A Review on Landfill Leachate Treatment Technologies: Comparative Analysis of Methods and Process Innovation. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3878. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073878
Xiang R, Wei W, Mei T, Wei Z, Yang X, Liang J, Zhu J. A Review on Landfill Leachate Treatment Technologies: Comparative Analysis of Methods and Process Innovation. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(7):3878. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073878
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiang, Rongcheng, Wugan Wei, Tianhong Mei, Zihan Wei, Xiaorui Yang, Jinhua Liang, and Jianliang Zhu. 2025. "A Review on Landfill Leachate Treatment Technologies: Comparative Analysis of Methods and Process Innovation" Applied Sciences 15, no. 7: 3878. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073878
APA StyleXiang, R., Wei, W., Mei, T., Wei, Z., Yang, X., Liang, J., & Zhu, J. (2025). A Review on Landfill Leachate Treatment Technologies: Comparative Analysis of Methods and Process Innovation. Applied Sciences, 15(7), 3878. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073878





