A Thermodynamic Model for the Solubility of SO2 in Multi-Ion Electrolyte Solutions and Its Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Review of Experimental Data for SO2 Solubility in Pure Water and Aqueous Electrolyte Solutions
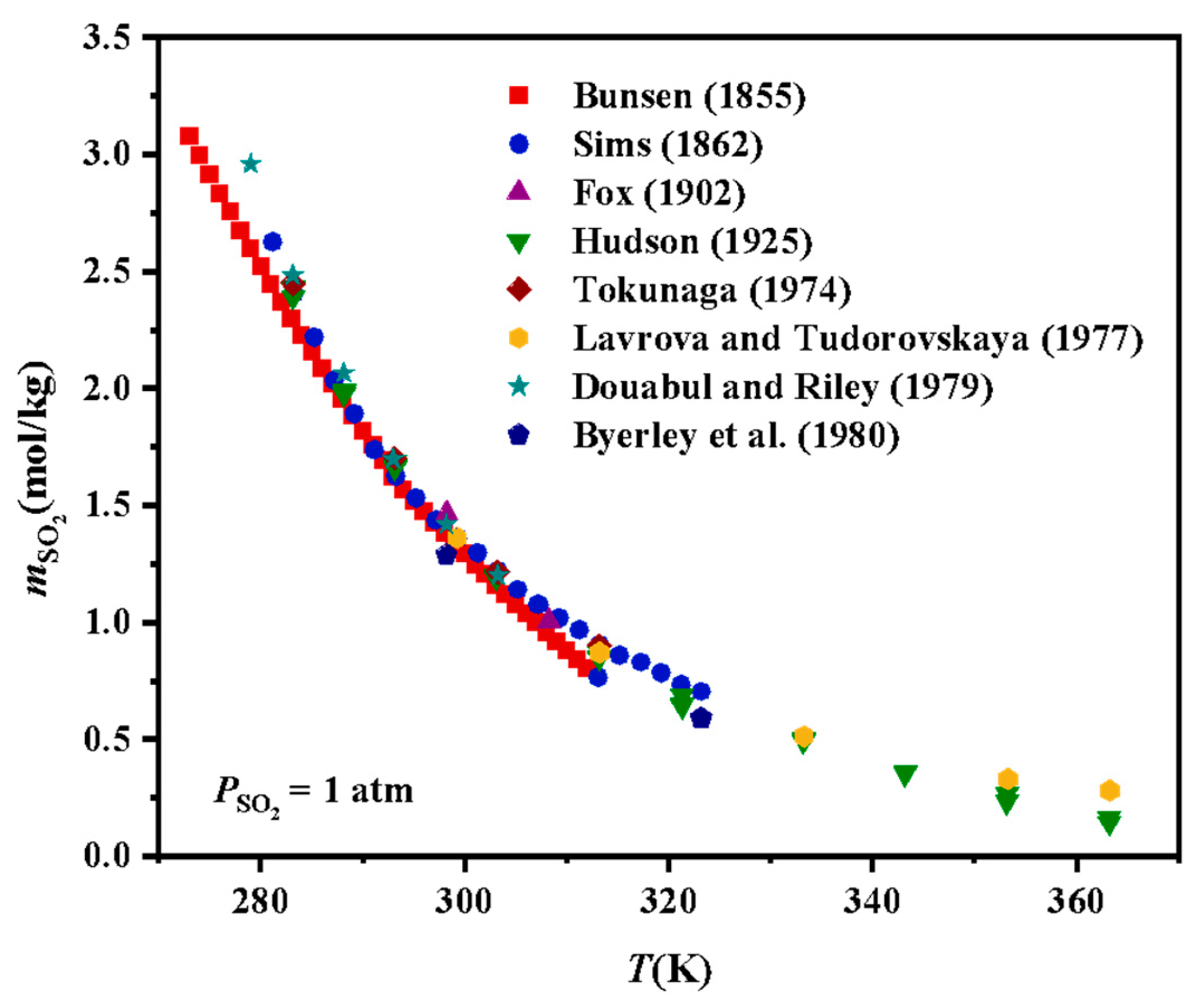
2.1. SO2-H2O Systems
2.2. SO2-NaCl-H2O Systems
2.3. SO2-KCl-H2O Systems
2.4. SO2-Na2SO4-H2O Systems
3. The Thermodynamic Model for SO2 Solubility in Multi-Ion Solutions and Parameterization
3.1. The Thermodynamic Model for SO2 Solubility in Multi-Ion Solutions
3.2. Parameterization
4. Comparison with Experimental Data
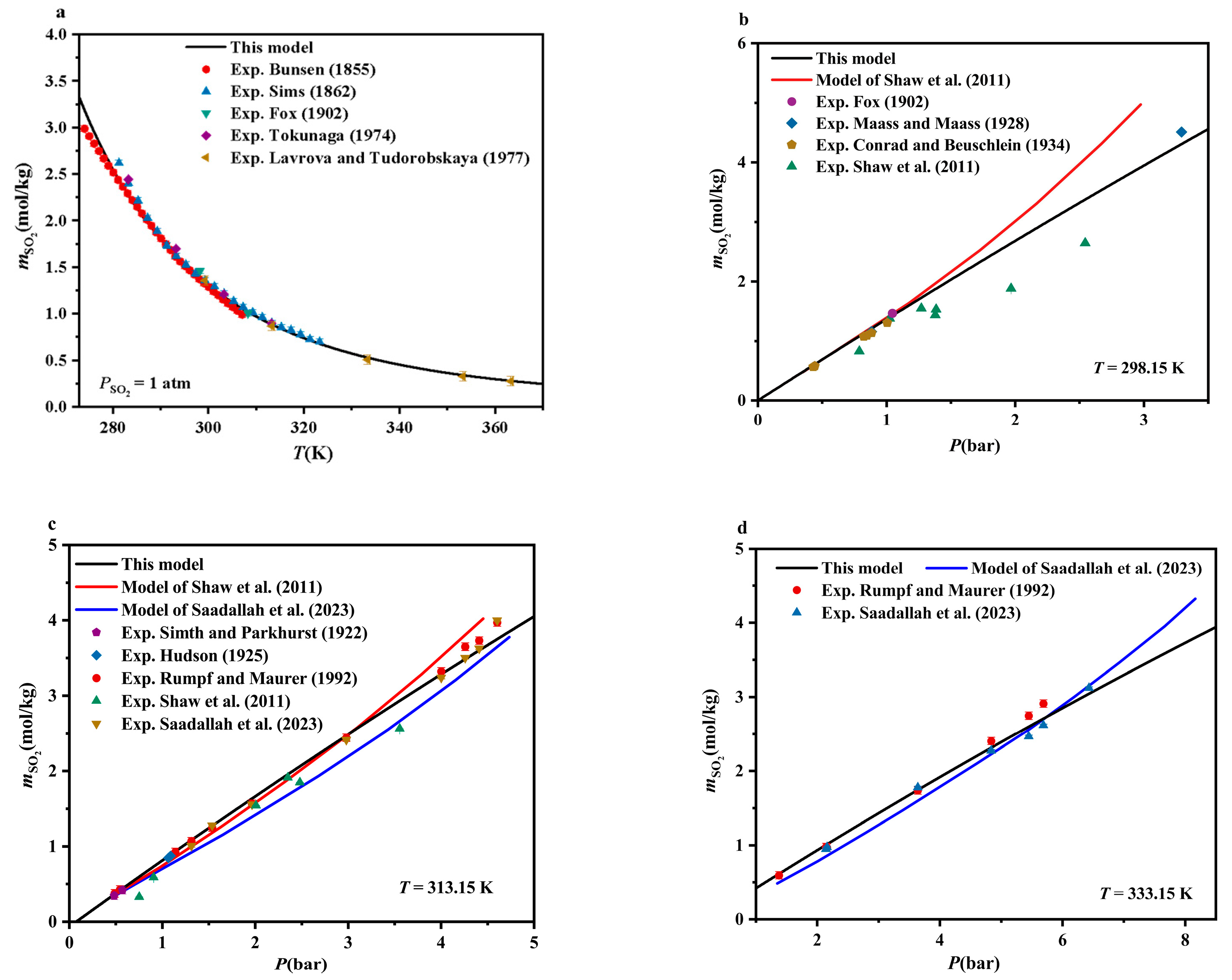
4.1. SO2-H2O Systems
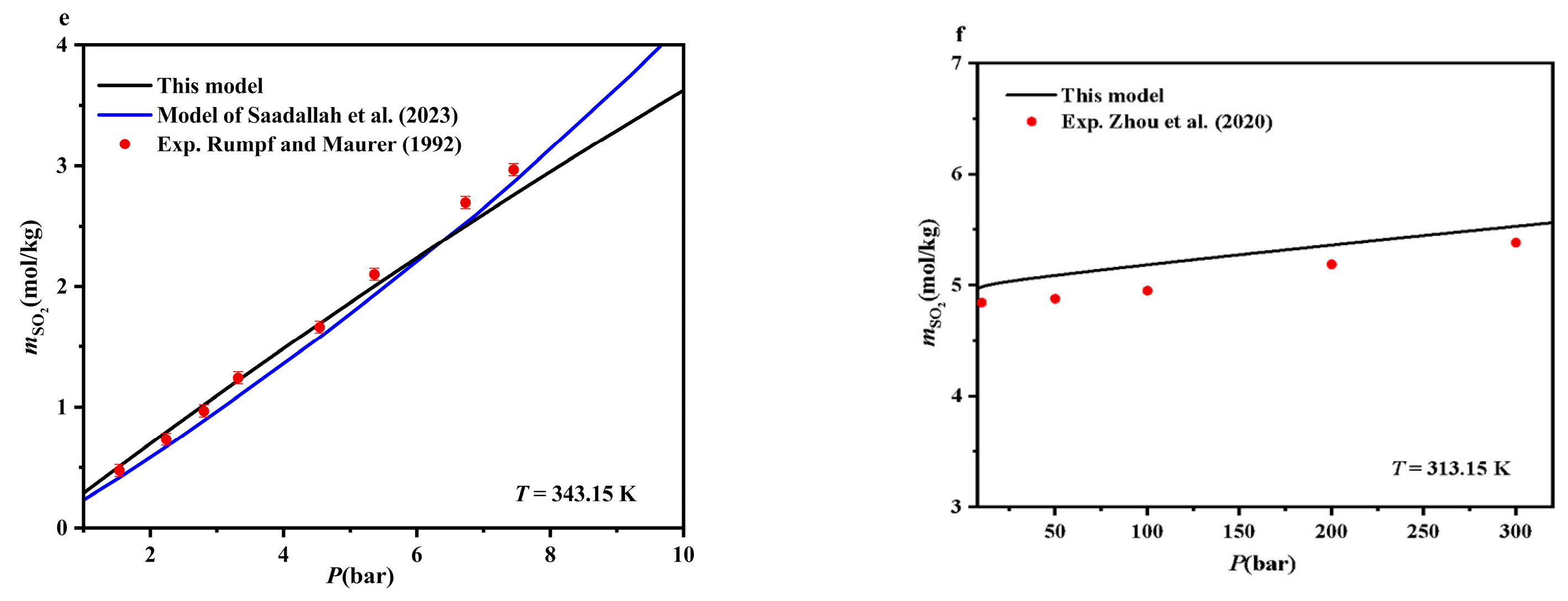
4.2. SO2-NaCl-H2O Systems

4.3. SO2-KCl-H2O Systems
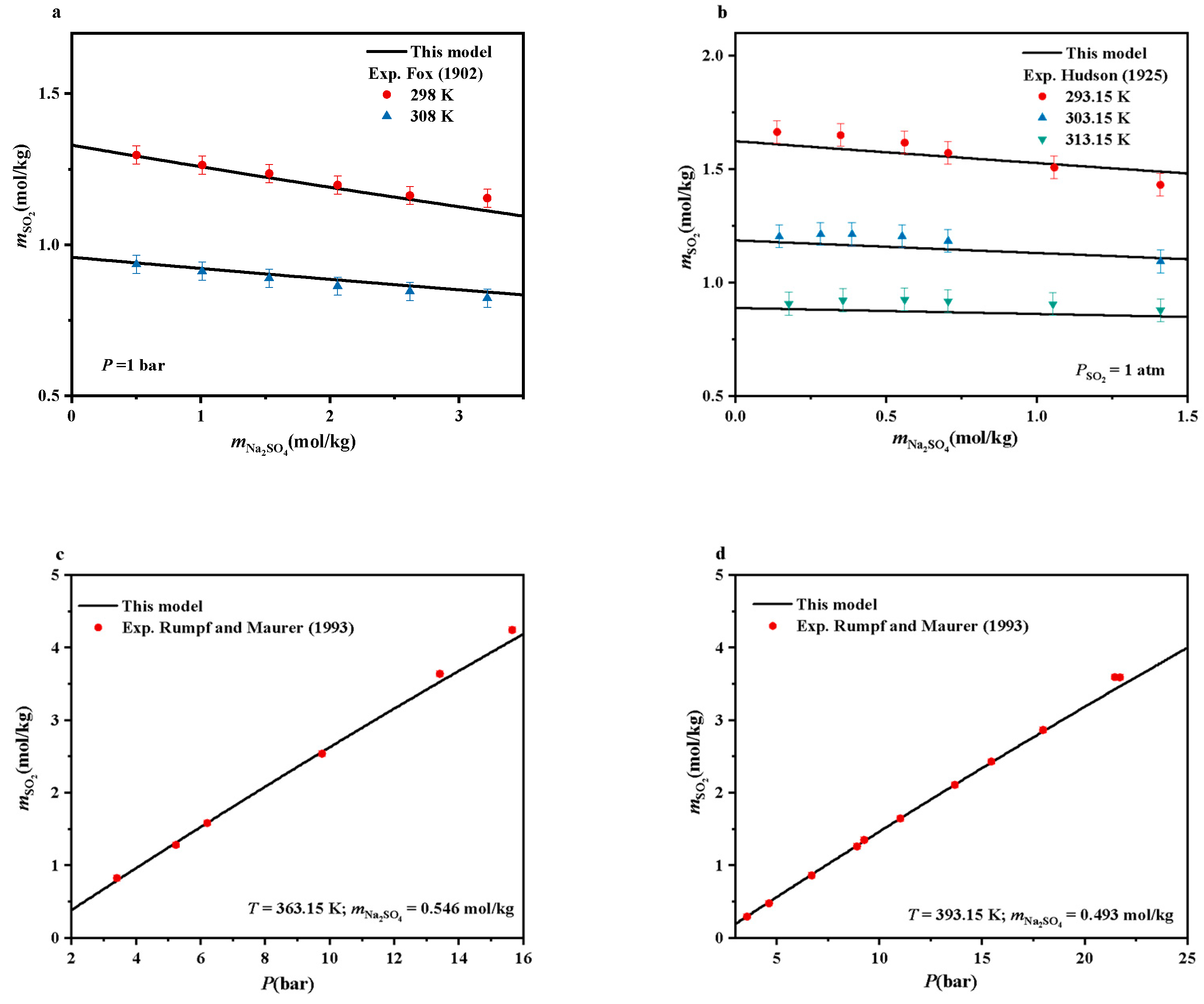
4.4. SO2-Na2SO4-H2O Systems
5. Applications of the Solubility Model
5.1. Prediction of SO2 Solubility in Seawater
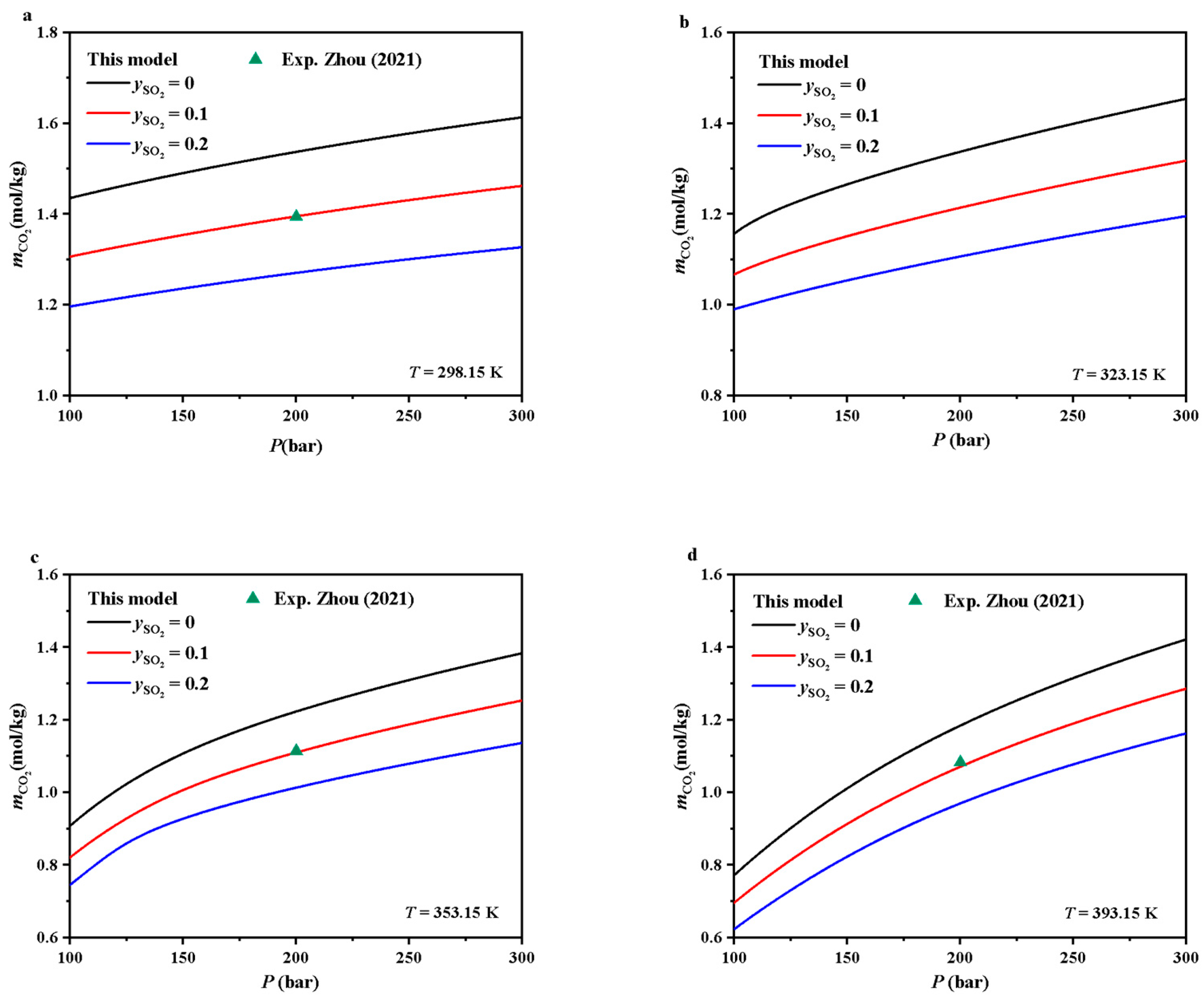
5.2. Prediction of CO2 Solubility of the CO2-SO2 Mixture in Pure Water
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| List of Symbols | |
| mi | molality (mol/kg) of component I in liquid phase |
| P | total pressure, that is in bar |
| Par | parameter |
| R | universal gas constant (83.14472 bar·cm3·mol−1·K−1) |
| T | absolute temperature in Kelvin |
| xi | mole fraction of component I in liquid phase |
| yi | mole fraction of component I in vapor phase |
| Greek letters | |
| α | activity |
| φ | fugacity coefficient |
| γ | activity coefficient |
| μ | chemical potential |
| ρ | density |
| interaction parameter | |
| interaction parameter | |
| Subscripts | |
| a | anion |
| c | cation |
| salt | salt solution |
| Superscripts | |
| v | vapor |
| l | liquid |
| (0) | standard state |
Appendix A. The EOS of Pure SO2
| m | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −1.6617272 × 10−1 | 1 | 1.5 | 0 |
| 2 | 9.3106614 × 10−1 | 1 | 0.25 | 0 |
| 3 | −1.9592419 × 100 | 1 | 1.25 | 0 |
| 4 | 6.1581150 × 10−2 | 3 | 0.25 | 0 |
| 5 | 1.7701346 × 10−4 | 7 | 0.875 | 0 |
| 6 | −5.9686148 × 10−4 | 2 | 1.375 | 0 |
| 7 | 1.7455469 × 10−3 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 8 | 2.1284330 × 10−1 | 1 | 2.375 | 1 |
| 9 | 5.0982105 × 10−1 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 10 | 1.0299522 × 10−2 | 5 | 2.125 | 1 |
| 11 | −2.5336956 × 10−1 | 1 | 3.5 | 2 |
| 12 | −5.4155817 × 10−2 | 1 | 6.5 | 2 |
| 13 | −5.9551762 × 10−2 | 4 | 4.75 | 2 |
| 14 | −1.6326078 × 10−2 | 2 | 12.5 | 3 |
References
- Guo, J.; Li, F.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Wu, K.; He, W. Retrieval of volcanic SO2 emission rate. J. Atmos. Environ. Opt. 2024, 19, 98–110. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Sun, G. Analysis of the relationship among thermal power Generation, coal-fired consumption and sulfur dioxide emission in China during 1991–2007. Resour. Sci. 2010, 32, 1230–1235. [Google Scholar]
- Krotkov, N.A.; McClure, B.; Dickerson, R.R.; Carn, S.A.; Li, C.; Bhartia, P.K.; Yang, K.; Krueger, A.J.; Li, Z.; Levelt, P.F. Validation of SO2 retrievals from the Ozone Monitoring Instrument over NE China. J. Geophy. Res.-Atmos. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; Liu, N. An improved model for calculating CO2 solubility in aqueous NaCl solutions and the application to CO2-H2O-NaCl fluid inclusions. Chem. Geol. 2013, 347, 43–58. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Mao, S. An improved model for CO2 solubility in aqueous electrolyte solution containing Na+, K+, Mg2+, Ca2+, Cl− and SO42− under conditions of CO2 capture and sequestration. Chem. Geol. 2017, 463, 12–28. [Google Scholar]
- Hunger, T.; Lapicque, F.; Storck, A. Thermodynamic equilibrium of diluted SO2 absorption into Na2SO4 or H2SO4 electrolyte solutions. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1990, 35, 453–463. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, J.; Rumpf, B.; Maurer, G. The solubility of sulfur dioxide in aqueous solutions of sodium chloride and ammonium chloride in the temperature range from 313 K to 393 K at pressures up to 3.7 MPa: Experimental results and comparison with correlations. Fluid Phase Equilib. 1999, 165, 99–119. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Sevilla, J.; Álvarez, M.; Díaz, M.C.; Marrero, M.C. Absorption equilibria of dilute SO2 in seawater. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2004, 49, 1710–1716. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, M.K. Experimental determination of dissociation constant, Henry’s constant, heat of reactions, SO2 absorbed and gas bubble–liquid interfacial area for dilute sulphur dioxide absorption into water. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2007, 253, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, K.; Pasel, C.; Luckas, M.; Herbell, J.-D. Solubility of sulphur dioxide in aqueous electrolyte solutions at higher ionic strengths-Chloride and bromide containing systems. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2009, 279, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.C.; Romero, M.A.; Elder, R.H.; Ewan, B.C.R.; Allen, R.W.K. Measurements of the solubility of sulphur dioxide in water for the sulphur family of thermochemical cycles. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 4749–4756. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, S.P.; Yao, Y.; Piri, M. Modeling the solubility of SO2 + CO2 mixtures in brine at elevated pressures and temperatures. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 10864–10872. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, C.; Pasel, C.; Luckas, M.; Bathen, D. Absorption of SO2 in different electrolyte solutions, seawater and brine. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2015, 402, 89–101. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Guo, H.; Yang, P.; Wang, Z. Solubility of SO2 in water from 263.15 to 393.15 K and from 10 to 300 bar: Quantitative Raman spectroscopic measurements and PC-SAFT prediction. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 12855–12861. [Google Scholar]
- Saadallah, K.; Lachet, V.; Creton, B.; Caumon, M.-C.; Randi, A.; Sterpenich, J. Solubility study of binary systems containing sulfur dioxide and water: A combination of Raman spectroscopy and Monte Carlo molecular simulation. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2023, 574, 113901. [Google Scholar]
- Meissner, H.P.; Kusik, C.L. Activity coefficients of strong electrolytes in multicomponent aqueous solutions. AIChE J. 1972, 18, 294–298. [Google Scholar]
- Meissner, H.P.; Tester, J.W. Activity coefficients of strong electrolytes in aqueous solutions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Process Des. Dev. 1972, 11, 128–133. [Google Scholar]
- Bromley, L.A. Thermodynamic properties of strong electrolytes in aqueous solution. AICHE J. 1973, 19, 313–320. [Google Scholar]
- Bromley, L.A. Approximate individual ion values of β (or B) in extended Debye-Hückel theory for uni-univalent aqueous solutions at 298.15 K. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 1972, 4, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitzer, K.S. Thermodynamics of electrolytes. I. Theoretical basis and general equations. J. Phys. Chem. 1973, 77, 268–277. [Google Scholar]
- Weisenberger, S.; Schumpe, D.A. Estimation of gas solubilities in salt solutions at temperatures from 273 K to 363 K. AIChE J. 1996, 42, 298–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miri, R.; Aagaard, P.; Hellevang, H. Examination of CO2–SO2 solubility in water by SAFT1. Implications for CO2 transport and storage. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 10214–10223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunsen, R. Ueber das Gesetz der Gasabsorption. Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1855, 93, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, T.H. Contributions to the knowledge of the laws of gas-absorption. Q. J. Chem. Soc. Lond. 1862, 14, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, C.J.J. Über die löslichkeit des schwefeldioxyds in wässerigen salzlösungen und seine wechselwirkung mit den salzen. Z. Phys. Chem. 1902, 41, 458–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simth, W.T.; Parkhurst, R.B. The solubility of sulfur dioxide in suspensions of calcium and magnesium hydroxides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1922, 44, 1918–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hudson, J.C. The solubility of sulphur dioxide in water and in aqueous solutions of potassium chloride and sodium sulphate. J. Chem. Soc. 1925, 127, 1332–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwood, T.K. Solubilities of sulfur dioxide and ammonia in water. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1925, 17, 745–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maass, C.E.; Maass, O. Sulfur dioxide and its aqueous solutions. I. Analytical methods, vapor density and vapor pressure of sulfur dioxide. Vapor pressure and concentrations of the solutions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1928, 50, 1352–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, W.B.; Maass, O. Equilibria in sulphur dioxide solutions. Can. J. Res. 1930, 2, 42–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, O.M.; Maass, O. An investigation of the equilibria existing in gas-water systems forming electrolytes. Can. J. Res. 1931, 5, 162–199. [Google Scholar]
- Conrad, F.H.; Beuschlein, W.L. Some equilibrium relations in the system calcium oxide-sulfur dioxide-water (acid region) at pressures below atmospheric. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1934, 56, 2554–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, H.F.; Leppla, P.W. The solubility of sulfur dioxide at low partial pressures. The Ionization constant and heat of Ionization of sulfurous acid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1934, 56, 2233–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, C.L. Sulfur Dioxide, Chlorine, Fluorine and Chlorine Oxides, Solubility Data Series; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Beuschlein, W.L.; Simenson, L.O. Solubility of sulfur dioxide in water. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1940, 62, 610–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, R.V. The solubility of sulfur dioxide in water and sulfuric acid. Tappi J. 1956, 39, 517–519. [Google Scholar]
- Rabe, A.E.; Harris, J.F. Vapor liquid equilibrium data for the binary system sulfur dioxide and water. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1963, 8, 333–336. [Google Scholar]
- Vosolsobe, J.; Simecek, A.; Michalek, J. Rozpusnost kyslíku siričiného ve vodě. Chem. Prum. 1965, 15, 401. [Google Scholar]
- Tokunaga, J. Solubilities of sulfur dioxide in aqueous alcohol solutions. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1974, 19, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrova, E.M.; Tudorovskaya, G.L. Solubility of sulfur dioxide in aqueous hydrochloric acid solutions. J. Appl. Chem. USSR 1977, 50, 1102–1106. [Google Scholar]
- Douabul, A.; Riley, J. Solubility of sulfur dioxide in distilled water and decarbonated seawater. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1979, 24, 274–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byerley, J.J.; Rempel, G.L.; Thang, V. Solubility of sulfur dioxide in water-acetonitrile solutions. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1980, 25, 55–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumpf, B.; Maurer, G. Solubilities of hydrogen cyanide and sulfur dioxide in water at temperatures from 293.15 to 413.15 K and pressure up to 2.5 MPa. Fluid Phase Equilib. 1992, 81, 241–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, M.A.; Krissmann, J.; Petersgerth, P.; Luckas, M.; Luckas, K. Spectrophotometric measurement of the vapor-liquid equilibris of (sulphur dioxide + water). J. Chem. Thermodyn. 1996, 28, 685–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millero, F.J.; Hershey, J.P.; Johnson, G. The solubility of SO2 of and the dissociation of H2SO3 in NaCl solutions. J. Atmos. Chem. 1989, 8, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumpf, B.; Maurer, G. Solubility of sulfur dioxide in aqueous solutions of sodium and ammonium sulfate at temperatures from 313.15 K to 393.15 K and pressures up to 3.5 MPa. Fluid Phase Equilib. 1993, 91, 113–131. [Google Scholar]
- Denbigh, K. The Principles of Chemical Equilibrium; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X. The Prediction of PVTx and Vapor-Liquid Equilibrium (VLE) Properties of C-H-O-N-S Fluid Mixtures. Master’s Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, W.; Kretzschmar, H. IAPWS industrial formulation 1997 for the thermodynamic properties of water and steam. In International Steam Tables: Properties of Water Steam Based on the Industrial Formulation IAPWS-IF97; Springer Vieweg: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 7–150. [Google Scholar]
- Pitzer, K.S.; Peiper, J.C.; Busey, R.H. Thermodynamic properties of aqueous sodium chloride solutions. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1984, 13, 1–102. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Z.; Sun, R. An improved model calculating CO2 solubility in pure water and aqueous NaCl solutions from 273 to 533 K and from 0 to 2000 bar. Chem. Geol. 2003, 193, 257–271. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Z.; Sun, R.; Liu, R.; Zhu, C. Accurate thermodynamic model for the calculation of H2S solubility in pure water and brines. Energy Fuels 2007, 21, 2056–2065. [Google Scholar]
- Harvie, C.E.; Møller, N.; Weare, J.H. The prediction of mineral solubilities in natural waters: The Na-K-Mg-Ca-H-Cl-SO4-OH-HCO3-CO3-CO2-H2O system to high ionic strengths at 25 °C. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1984, 48, 723–751. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q. Quantitative Raman Spectroscopic Investigation on Non-Equilibrium Dissolution and Water-Rock Reaction of SO2-CO2 Co-Injection into Pore Space. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Ely, J.F. Universal equation of state for engineering application: Algorithm and application to non-polar and polar fluids. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2004, 222–223, 107–118. [Google Scholar]

| References | Salt | T (K) | P (bar) | (mol/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hunger et al. [6] | H2SO4, Na2SO4 | 298–323 | 10−4–0.1 | 0-saturation |
| Xia et al. [7] | NaCl, NH4Cl | 313–393 | 0–37 | 0–6 |
| Rodríguez-Sevilla et al. [8] | seawater | 278.15–318.15 | 0.976 | unstated |
| Mondal [9] | water | 293–333 | 0–0.01 * | 0 |
| Zimmermann et al. [10] | HCl, NaCl, HBr, NaBr | 298 | 1.015 | 0–4.613 |
| Shaw et al. [11] | water | 298–313 | 0.2–3.6 | 0 |
| Tan et al. [12] | water, NaCl | 313–393 | 0–40 | 0–6 |
| Cox et al. [13] | seawater, brine | 298.15–323.15 | unstated | 0–1 |
| Zhou et al. [14] | water | 263.15–393.15 | 10–300 | 0 |
| Saadallah et al. [15] | water | 293–393 | 0–25 | 0 |
| References | Solution | T (K) | P (bar) | Nd |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bunsen [23] | water | 273.00–313.00 | 1+ | 41 |
| Sims [24] | water | 281.20–323.20 | 1+ | 22 |
| Fox [25] | water | 298.20–308.20 | 1+ | 2 |
| Simth and Parkhurst [26] | water | 278.20–333.20 | 0.20–1.60 | 8 |
| Hudson [27] | water | 283.15–363.15 | 1+ | 42 |
| Sherwood [28] | water | 273.15–323.15 | 0.00–1.00 | 109 |
| Maass and Maass [29] | water | 283.20–300.20 | 0.00–3.50 | 29 |
| Campbell and Maass [30] | water | 298.15–383.15 | 0.14–4.50 | 55 |
| Morgan and Maass [31] | water | 273.00–298.00 | 0.00–1.20 | 38 |
| Conrad and Beuschlein [32] | water | 298.20 | 0.40–1.00 | 6 |
| Johnstone and Leppla [33] | water | 298.20–323.20 | 0.00–0.20 | 16 |
| Young [34] | water | 373.00–423.00 | 1.70–7.20 | 22 |
| Beuschlein and Simenson [35] | water | 296.40–386.15 | 0.12–2.11 | 53 |
| Parkinson [36] | water | 263.00–294.00 | 0.00–0.06 | 42 |
| Rabe and Harris [37] | water | 303.15–353.15 | 0.09–1.20 | 43 |
| Vosolsobe et al. [38] | water | 293.20–333.20 | 0.04–0.34 | 35 |
| Tokunaga [39] | water | 283.15–313.15 | 1+ | 4 |
| Lavrova and Tudorovskaya [40] | water | 299.15–363.15 | 1+ | 5 |
| Douabul and Riley [41] | water | 278.97–303.25 | 1+ | 6 |
| Byerley et al. [42] | water | 298.15–323.15 | 1+ | 2 |
| Rumpf and Maurer [43] | water | 293.14–393.33 | 0.35–25.09 | 66 |
| Siddiqi et al. [44] | water | 291.05–294.45 | 0.02–0.03 | 50 |
| Mondal [9] | water | 293.00–333.00 | 0.02–0.21 | 20 |
| Shaw et al. [11] | water | 297.05–312.25 | 0.25–1.96 | 3 |
| Cox et al. [13] | water | 298.15–323.15 | 0.00–0.12 | 19 |
| Zhou et al. [14] | water | 273.15–373.15 | 10.00–300.00 | 45 |
| Saadallah et al. [15] | water | 293.15–353.15 | 0.00–12.00 | 45 |
| (mol/kg) | ||||
| Fox [25] | 0.50–3.22 | 298.00–308.00 | 1+ | 6 |
| Millero et al. [45] | 0.01–6.00 | 278.15–298.15 | 1+ | 17 |
| Xia et al. [7] | 2.90–6.00 | 313.15–393.15 | 0.30–37.00 | 90 |
| Zimmermann et al. [10] | 0.49–4.28 | 298.15 | 0.00–0.30 | 37 |
| Cox et al. [13] | 1.00 | 298.15–323.15 | 0.03–0.12 | 19 |
| (mol/kg) | ||||
| Fox [25] | 0.00–0.05 | 298.00–308.00 | 1+ | 12 |
| Hudson [27] | 0.50–4.40 | 298.00–308.00 | 1+ | 43 |
| Cox et al. [13] | 0.05–1.00 | 298.15–323.15 | 1.00 | 19 |
| (mol/kg) | ||||
| Fox [25] | 0.50–3.22 | 298.00–308.00 | 1 | 12 |
| Hudson [27] | 0.13–1.41 | 293.15–313.15 | 1+ | 23 |
| Rumpf and Maurer [46] | 0.50–1.00 | 313.15–393.15 | 1.00–28.00 | 65 |
| T-P Coefficient | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| c1 | 0.13245076 × 102 | −0.11148943 × 101 | 0.2296582 × 10−4 |
| c2 | −0.69839713 × 10−4 | 0.18138955 × 10−4 | |
| c3 | −0.34267139 × 104 | 0.17449283 × 103 | |
| c4 | 0.48022032 × 10−7 | −0.69223494 × 10−7 | |
| c1 | 0.14460352 × 101 | 0.46735219 × 101 | |
| c2 | −0.019673290 × 10−5 | −0.079666020 × 10−5 | |
| c3 | −0.27249399 × 103 | −0.68220367 × 103 | |
| * | * | ||
| c1 | 1.6528428 × 10−1 | −1.152724 × 10−2 | |
| c2 | 1.4572839 × 10−4 | ||
| * | * | ||
| c1 | −5.513825 × 10−1 | 4.2222945 × 10−3 | |
| c2 | 1.0502705 × 10−3 | −4.44659191 × 10−5 | |
| c3 | 1.3349619 × 102 | ||
| c4 | −1.9361945 × 10−4 | ||
| c5 | 8.9529014 × 10−7 | ||
| c6 | −3.5780857 × 10−10 |
| References | T (K) | P (bar) | msalt (mol/kg) | Nd | AAD (%) | MAD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bunsen [23] | 273.00–313.00 | 1+ | 0 | 41 | 3.58 | 16.39 |
| Sims [24] | 281.20–323.20 | 1+ | 0 | 22 | 2.65 | −6.77 |
| Fox [25] | 298.20–308.20 | 1+ | 0 | 2 | 3.62 | −5.76 |
| Simth and Parkhurst [26] | 278.20–333.20 | 0.20–1.60 | 0 | 8 | 4.72 | −7.39 |
| Hudson [27] | 283.15–363.15 | 1+ | 0 | 42 | 2.91 | −5.43 |
| Maass and Maass [29] | 283.20–300.20 | 0.00–3.50 | 0 | 29 | 2.53 | −5.67 |
| Campbell and Maass [30] | 298.15–383.15 | 0.14–4.50 | 0 | 55 | 6.95 | −15.82 |
| Morgan and Maass [31] | 273.00–298.00 | 0.00–1.20 | 0 | 22 | 6.75 | −16.90 |
| Conrad and Beuschlein [32] | 298.20 | 0.40–1.00 | 0 | 6 | 2.03 | −3.03 |
| Young [34] | 373.00–423.00 | 1.70–7.20 | 0 | 9 | 6.30 | 13.72 |
| Beuschlein and Simenson [35] | 296.40–386.15 | 0.12–2.11 | 0 | 51 | 5.44 | −17.55 |
| Rabe and Harris [37] | 303.15–353.15 | 0.09–1.20 | 0 | 39 | 4.79 | −15.76 |
| Tokunaga [39] | 283.15–313.15 | 1+ | 0 | 4 | 3.78 | −6.76 |
| Lavrova and Tudorovskaya [40] | 299.15–363.15 | 1+ | 0 | 5 | 2.04 | 3.48 |
| Douabul and Riley [41] | 278.97–303.25 | 1+ | 0 | 6 | 5.53 | −10.35 |
| Byerley, et al. [42] | 298.15–323.15 | 1+ | 0 | 2 | 11.37 | 15.30 |
| Rumpf and Maurer [43] | 293.14–393.33 | 0.35–25.09 | 0 | 55 | 6.04 | −17.19 |
| Zhou et al. [14] | 273.15–373.15 | 10.00–300.00 | 0 | 34 | 8.11 | −21.46 |
| Saadallah et al. [15] | 293.15–353.15 | 0.00–12.00 | 0 | 36 | 6.98 | −19.08 |
| (mol/kg) | ||||||
| Fox [25] | 298.00–308.00 | 1+ | 0.50–3.22 | 6 | 1.46 | 3.64 |
| Millero et al. [45] | 278.15–298.15 | 1+ | 0.01–6.00 | 17 | 4.52 | −13.96 |
| Xia, et al. [7] | 313.15–393.15 | 0.30–37.00 | 2.90–6.00 | 57 | 5.33 | −14.11 |
| (mol/kg) | ||||||
| Fox [25] | 298.00–308.00 | 1+ | 0.00–0.05 | 12 | 11.53 | −21.56 |
| Hudson [27] | 298.00–308.00 | 1+ | 0.50–4.40 | 43 | 1.28 | −4.6 |
| (mol/kg) | ||||||
| Fox [25] | 298.00–308.00 | 1 | 0.50–3.22 | 12 | 1.46 | 3.64 |
| Hudson [27] | 293.15–313.15 | 1+ | 0.13–1.41 | 18 | 3.45 | −5.73 |
| Rumpf and Maurer [46] | 313.15–393.15 | 1.00–28.00 | 0.50–1.00 | 35 | 6.18 | 18.07 |
| System | Reference | T (K) | P (bar) | (g/kg) | Nd | AAD (%) | MAD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SO2-Seawater | Douabul and Riley [41] | 278.97–303.25 | 1+ | 10.00–40.00 | 24 | 7.48 | 12.75 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, B.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, M.; Mao, S. A Thermodynamic Model for the Solubility of SO2 in Multi-Ion Electrolyte Solutions and Its Applications. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3927. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073927
Feng B, Zhang Z, Xu M, Mao S. A Thermodynamic Model for the Solubility of SO2 in Multi-Ion Electrolyte Solutions and Its Applications. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(7):3927. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073927
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Baoyi, Zequn Zhang, Mei Xu, and Shide Mao. 2025. "A Thermodynamic Model for the Solubility of SO2 in Multi-Ion Electrolyte Solutions and Its Applications" Applied Sciences 15, no. 7: 3927. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073927
APA StyleFeng, B., Zhang, Z., Xu, M., & Mao, S. (2025). A Thermodynamic Model for the Solubility of SO2 in Multi-Ion Electrolyte Solutions and Its Applications. Applied Sciences, 15(7), 3927. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073927