The Importance of Dunnian Runoff in Atlantic Forest Remnants: An Integrated Analysis Between Machine Learning and Spectral Indices
Abstract
1. Introduction
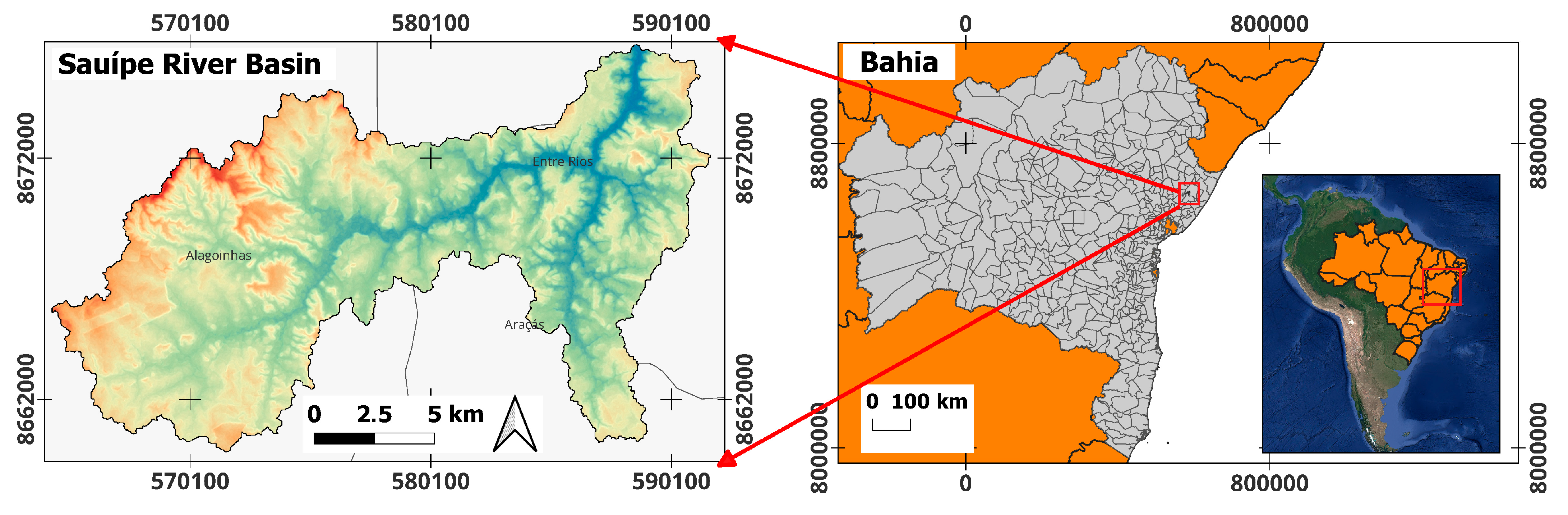
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Random Forest
2.2.2. Spectral Indices: NDVI and NDWI
3. Results
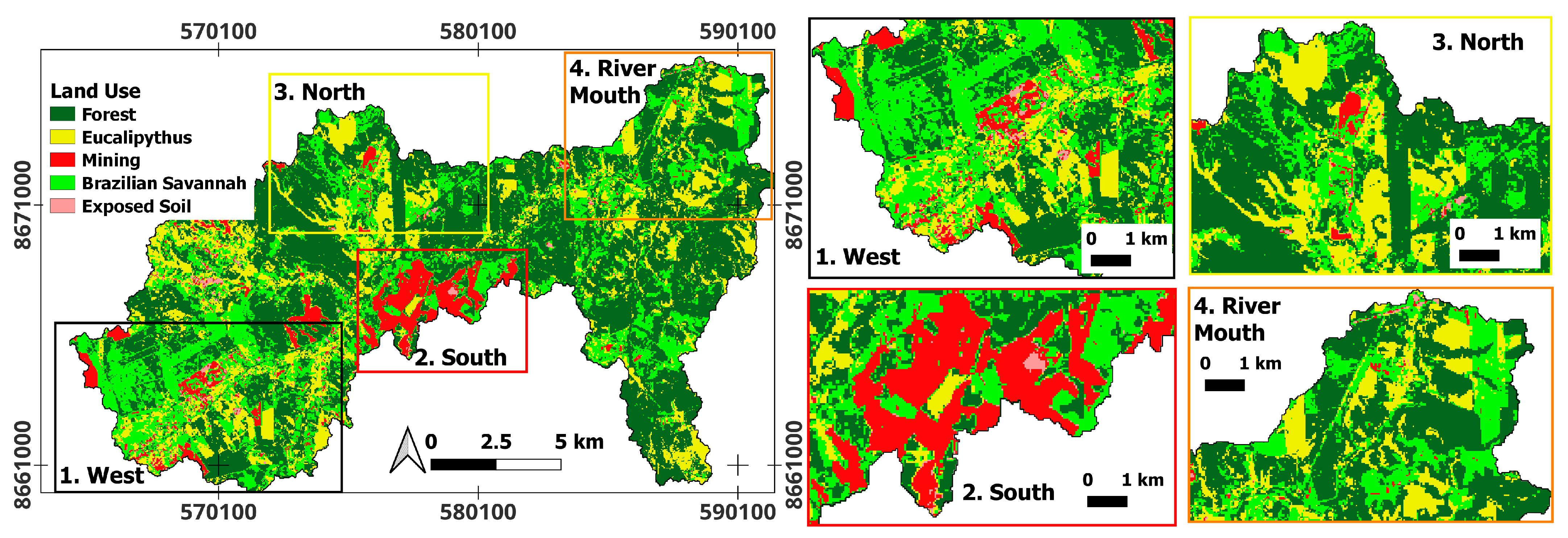
3.1. Classificatory Machine Learning: Random Forest
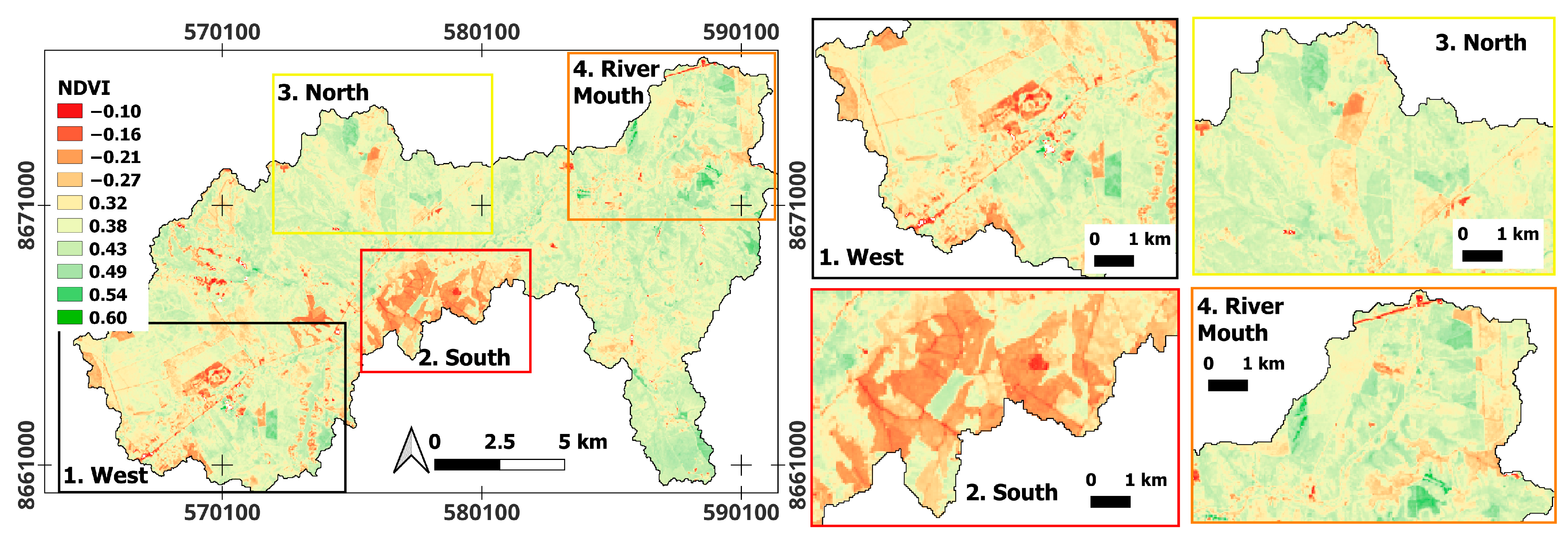
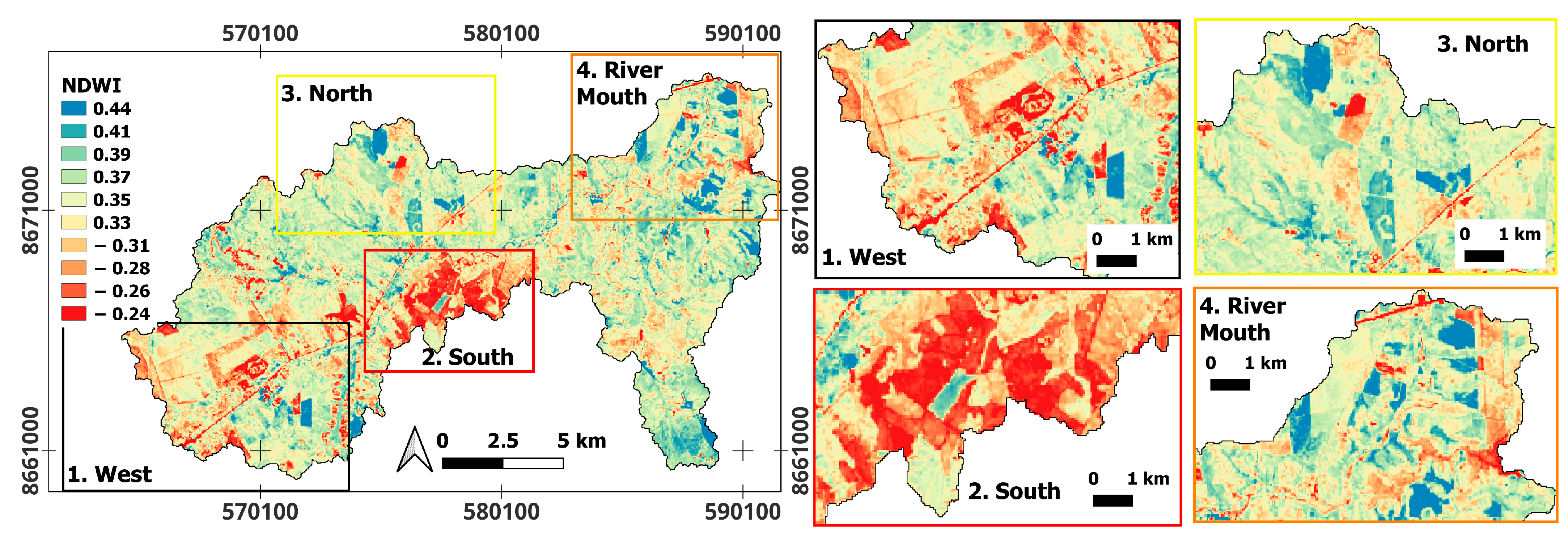
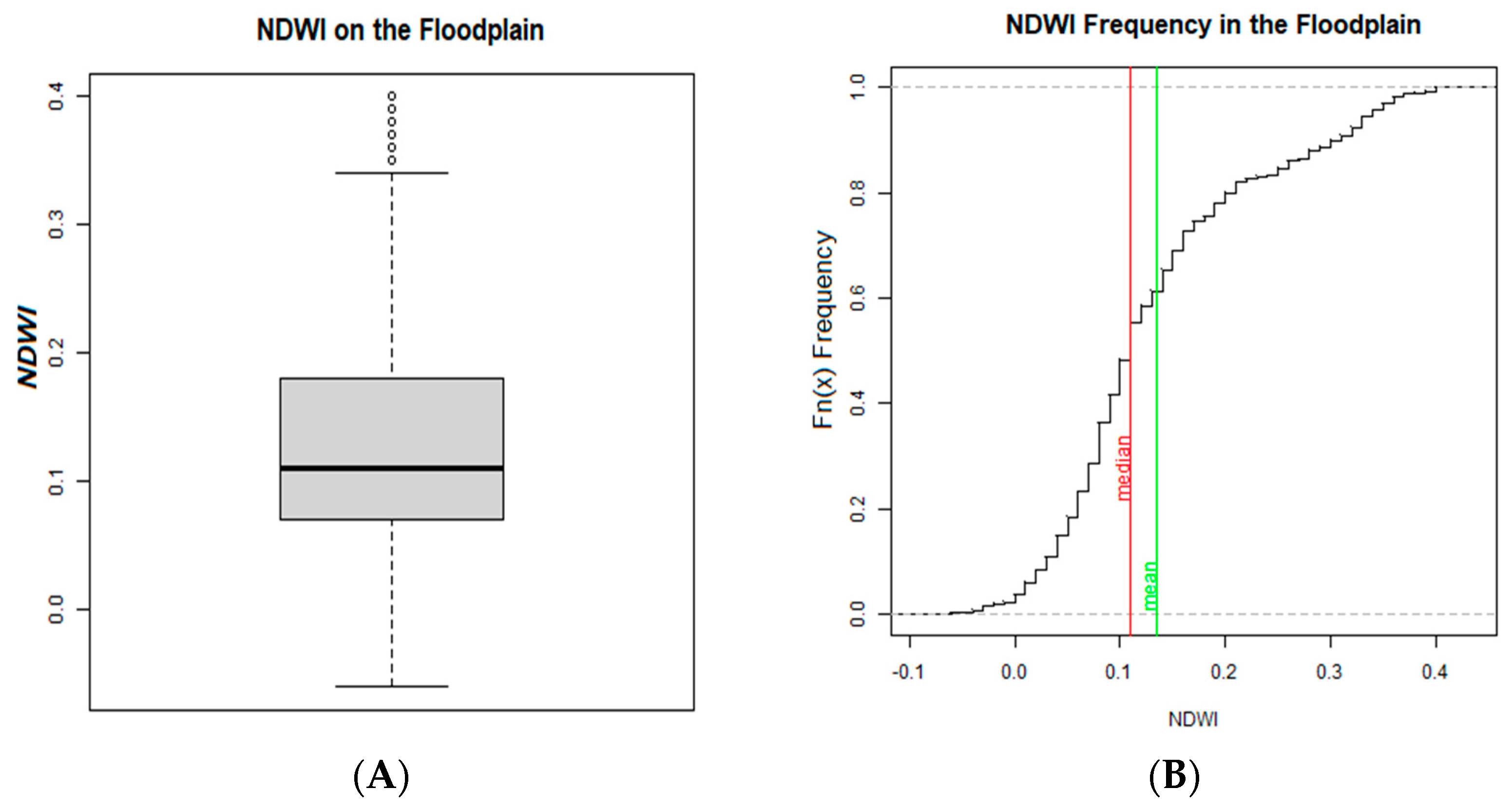
3.2. NDVI and NDWI Spectral Indices
4. Discussion
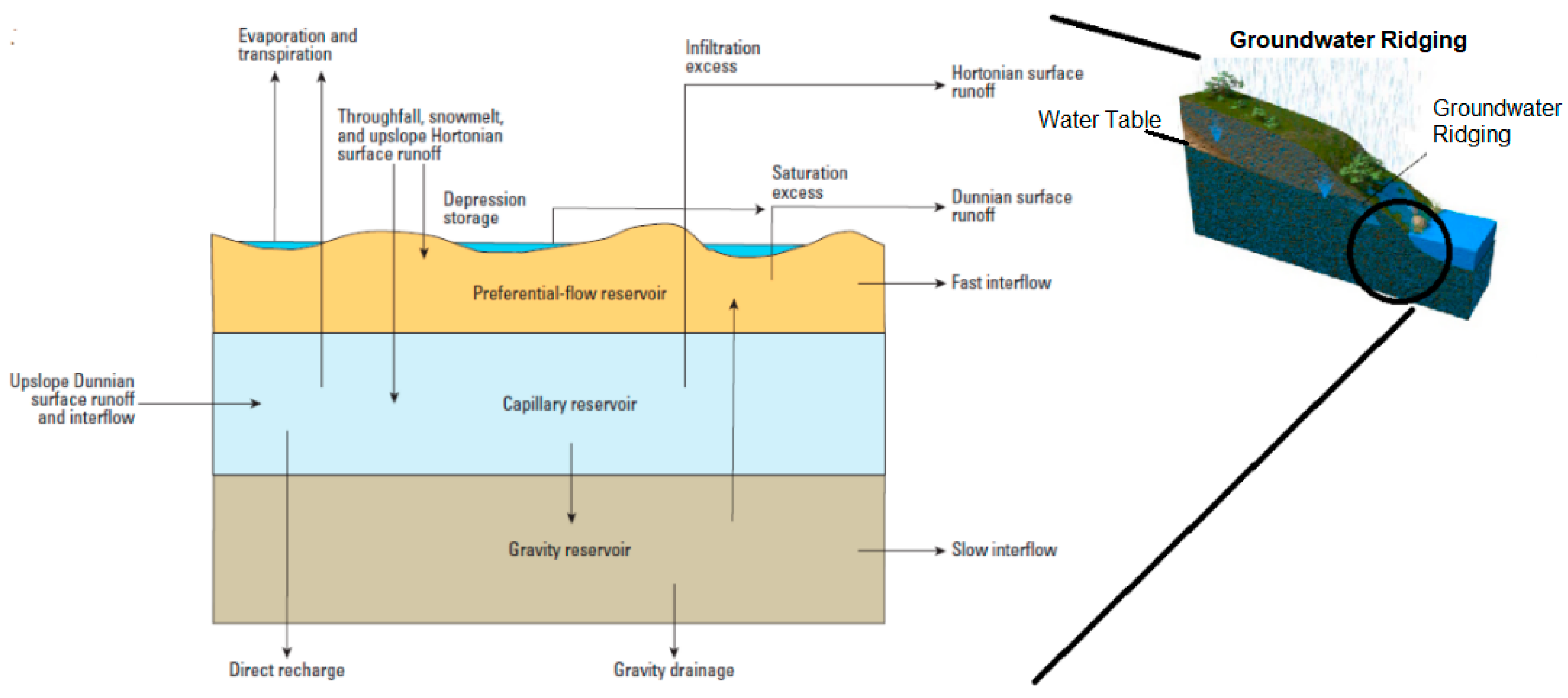
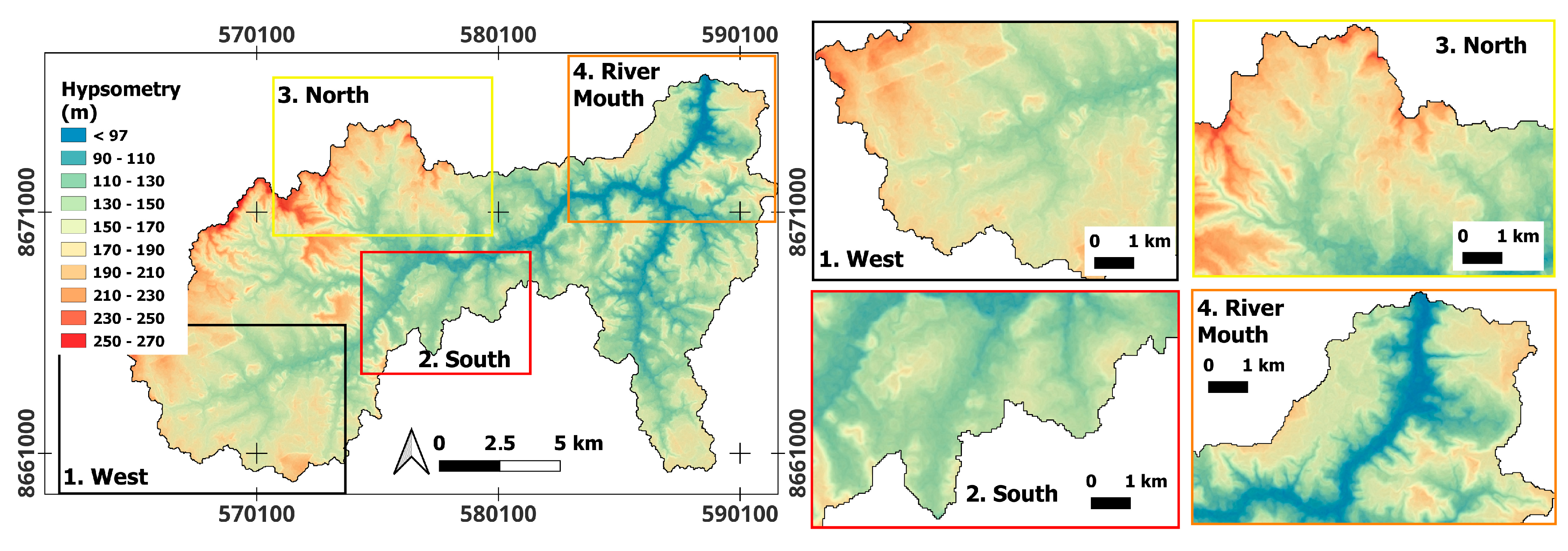
4.1. Topographic Control of Hortonian and Dunnian Flow
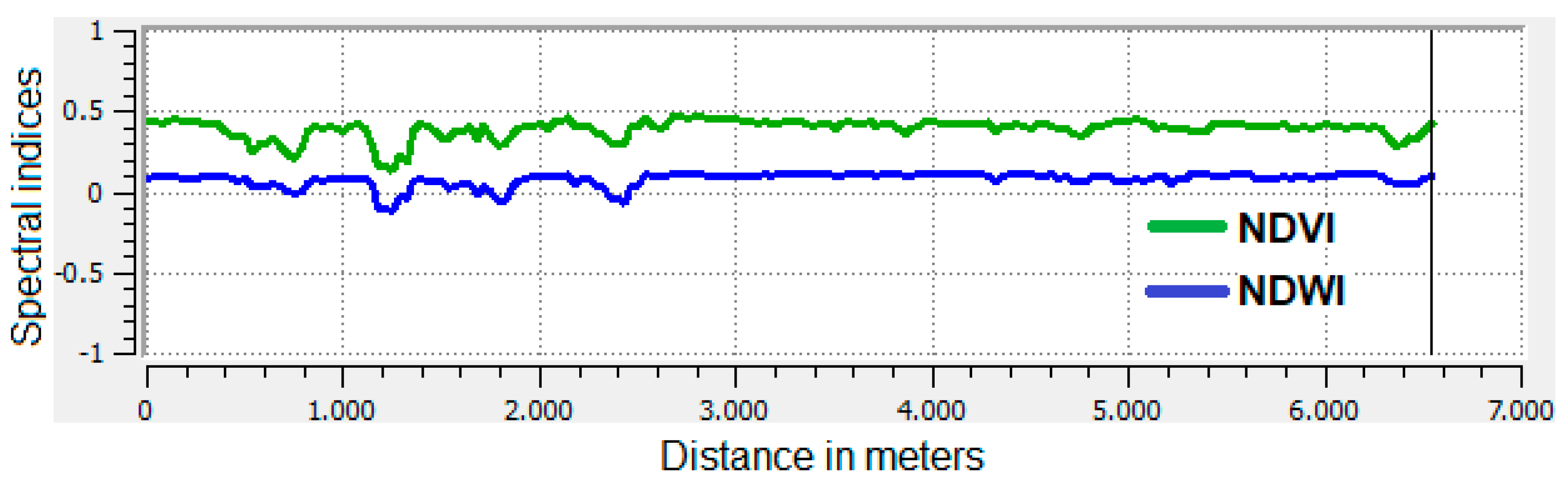
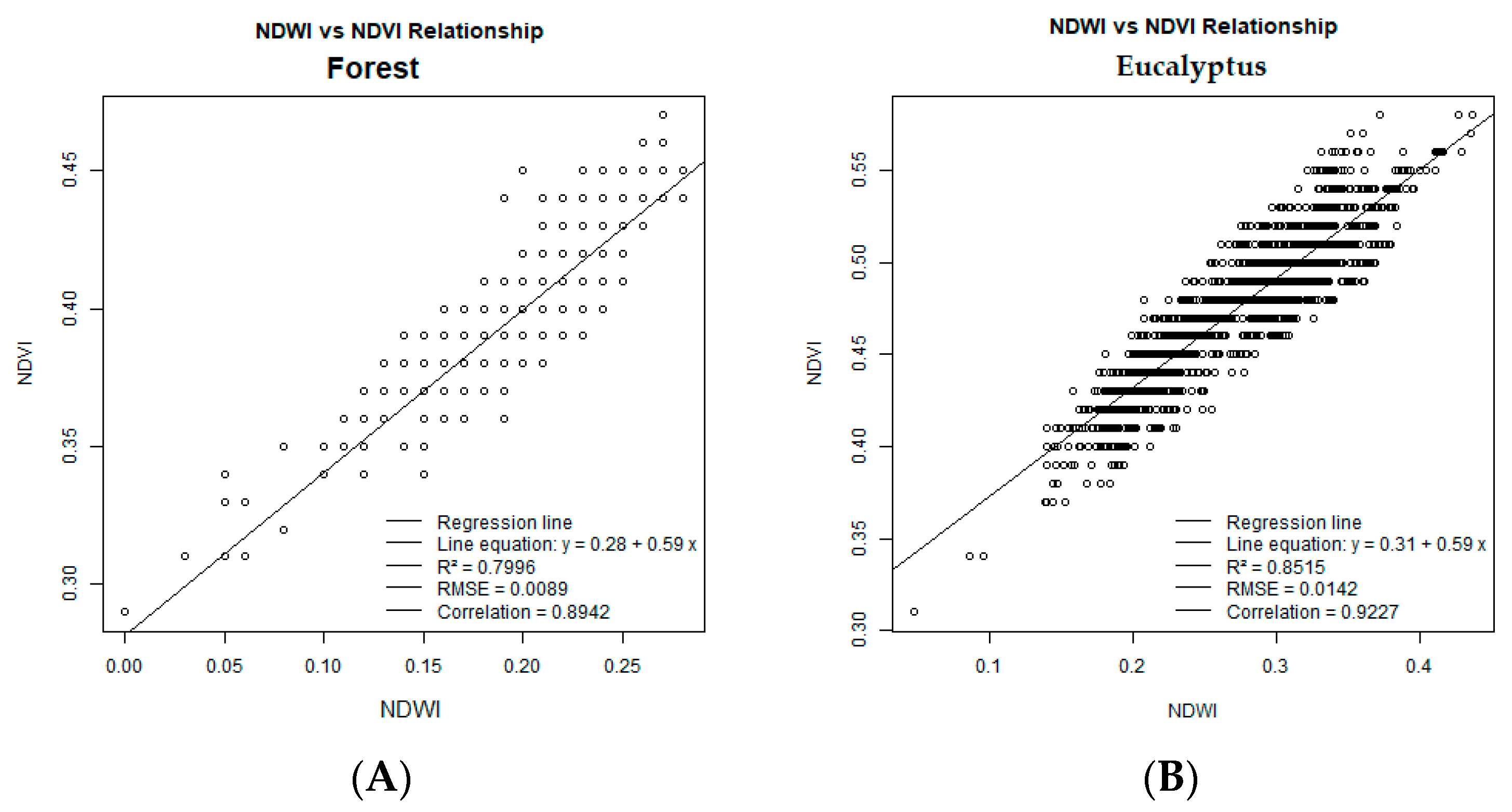
4.2. Dunnian Runoff: Relationships Between NDVI and NDWI in Forested Areas
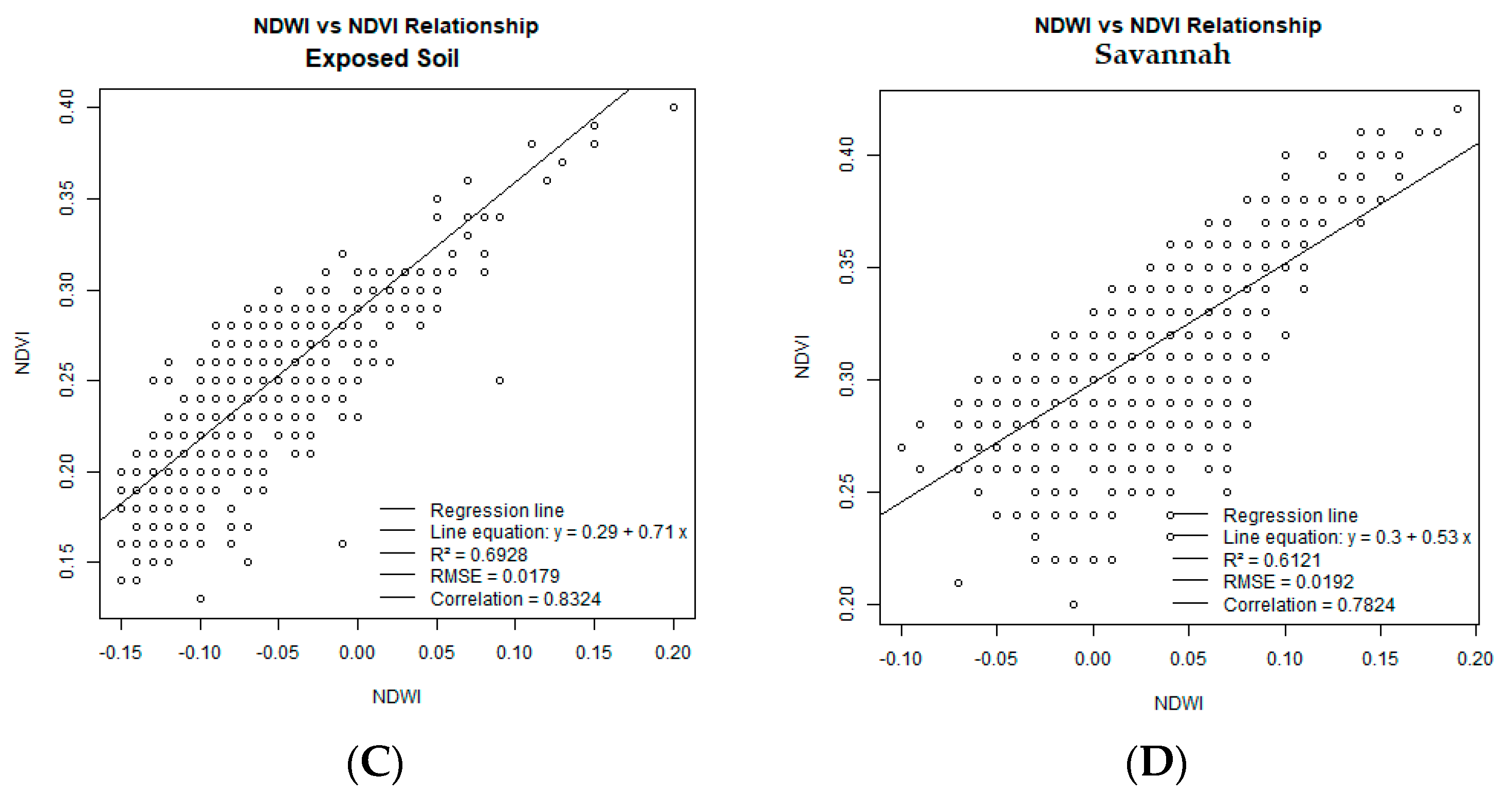
4.3. Dunnian Runoff: Relationship Between NDVI and NDWI for Forest, Eucalyptus, Savanna, and Exposed Soil
4.4. Limitations and Uncertainties of the Models
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- SOS Mata Atlântica. Available online: https://www.sosma.org.br/causas/mata-atlantica (accessed on 23 September 2024).
- Mohebalian, P.M.; Lopez, L.N.; Tischner, A.B.; Aguilar, F.X. Deforestation in South America’s Tri-National Paraná Atlantic Forest: Trends and Associational Factors. For. Policy Econ. 2022, 137, 102697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.R.; Akter, S.; Marandi, A.; Schüth, C. A Simple and Robust Wetland Classification Approach by Using Optical Indices, Unsupervised and Supervised Machine Learning Algorithms. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2021, 23, 100569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, R.C.; Finlayson, C. Global Wetland Outlook: State of the World’s Wetlands and Their Services to People, 1st ed.; Ramsar Convention Secretariat: Gland, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Jin, Z.; Michishita, R.; Cai, J.; Yue, T.; Chen, B.; Xu, B. Dynamic Monitoring of Wetland Cover Changes Using Time-Series Remote Sensing Imagery. Ecol. Inform. 2014, 24, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Pal, S. Mapping Wetland Habitat Health in Moribund Deltaic India Using Machine Learning and Deep Learning Algorithms. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2024, 24, 667–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatun, R.; Talukdar, S.; Pal, S.; Kundu, S. Measuring Dam Induced Alteration in Water Richness and Eco-Hydrological Deficit in Flood Plain Wetland. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 285, 112157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singha, P.; Pal, S. Modelling Wetland Eco-Hydrological State and Its Role on Ecosystem Service Potentiality. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhard, B.; Kandziora, M.; Hou, Y.; Müller, F. Ecosystem Service Potentials, Flows and Demands-Concepts for Spatial Localisation, Indication and Quantification. Landsc. Online 2014, 34, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; De Groot, R.; Sutton, P.; Van Der Ploeg, S.; Anderson, S.J.; Kubiszewski, I.; Farber, S.; Turner, R.K. Changes in the Global Value of Ecosystem Services. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2014, 26, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keddy, P.; Gaudet, C.; Fraser, L.H. Effects of Low and High Nutrients on the Competitive Hierarchy of 26 Shoreline Plants. J. Ecol. 2000, 88, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajwa-Kuligiewicz, A.; Bojarczuk, A. Streamflow Response to Catastrophic Windthrow and Forest Recovery in Subalpine Spruce Forest. J. Hydrol. 2024, 634, 131078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.-N.-D.; Nguyen, B.Q.; Grodzka-Łukaszewska, M.; Sinicyn, G.; Lakshmi, V. The Role of Reservoirs under the Impacts of Climate Change on the Srepok River Basin, Central Highlands of Vietnam. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1304845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.R.; Akter, S. Analysis of Landcover Change in Southwest Bengal Delta Due to Floods by NDVI, NDWI and K-Means Cluster with Landsat Multi-Spectral Surface Reflectance Satellite Data. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2017, 8, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenhuis, T.S.; Mukundan, R.; Tilahun, S.A. Overland Flow. In Encyclopedia of Soils in the Environment, 2nd ed.; Goss, M.J., Oliver, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2023; pp. 287–293. ISBN 978-0-323-95133-3. [Google Scholar]
- Dunne, T. Relation of Field Studies and Modeling in the Prediction of Storm Runoff. J. Hydrol. 1983, 65, 25–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunne, T.; Black, R.D. An Experimental Investigation of Runoff Production in Permeable Soils. Water Resour. Res. 1970, 6, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, J.M.; Jefferson, J.L.; Constantine, P.G.; Maxwell, R.M. Global Spatial Sensitivity of Runoff to Subsurface Permeability Using the Active Subspace Method. Adv. Water Resour. 2016, 92, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornberger, G.M.; Raffensperger, J.P.; Wiberg, P.L.; Eshleman, K.N. Elements of Physical Hydrology; Edition Unstated; Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1998; ISBN 978-0-8018-5857-4. [Google Scholar]
- dos Santos, P.V. Impactos ambientais causados pela perfuração em busca do petróleo. Cad. Grad.-Ciênc. Exatas Tecnol. Unit 2012, 1, 153–163. [Google Scholar]
- Zakia, M.J.B.; Ferraz, F.F.B.; Righetto, A.M.; de Paula Lima, W. Delimitação da zona ripária em uma microbacia. Rev. Agrogeoambiental 2009, 1, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendiondo, E.M.; Tucci, C.E.M. Escalas hidrológicas II: Diversidade de processos na bacia vertente. Hydrol. Scales II Divers. Process. Hillslope 1997, 2, 81–100. [Google Scholar]
- Siefert, C.A.C.; Santos, I.D. Mecanismos de geração de escoamento e áreas hidrologicamente sensíveis: Uma abordagem hidrogeomorfológica para delimitação de áreas de preservação permanente. Ra’e Ga 2012, 24, 227–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyman, D.R. Throughflow on Hillslopes and Its Relation to the Stream Hydrograph. Int. Assoc. Sci. Hydrology. Bull. 1970, 15, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USGS. Precipitation Runoff Modeling System (PRMS) as Part of an Integrated Hydrologic Model for the Osage Nation, Northeastern Oklahoma, 1915–2014; Scientific Investigations Report; USGS: Reston, VA. USA, 2020.
- Santos, I. Monitoramento e Modelagem de Processos Hidrogeomorfológicos: Mecanismos de Geração de Escoamento e Conectividade Hidrológica. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Federal de Santa Catarina, Florianópolis, SC, Brazil, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Elsenbeer, H. Hydrologic Flowpaths in Tropical Rainforest Soilscapes—A Review. Hydrol. Process. 2001, 15, 1751–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.-N.-D.; Lakshmi, V. Enhancing Human Resilience against Climate Change: Assessment of Hydroclimatic Extremes and Sea Level Rise Impacts on the Eastern Shore of Virginia, United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 947, 174289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, J.M.D.C.; Matos, M.R.B.D. Litoral Norte da Bahia: Caracterização Ambiental, Biodiversidade e Conservação; Edufba: Salvador, Brazil, 2021; ISBN 978-85-232-1456-2. [Google Scholar]
- Esquivel, M.S. A Zona Costeira dos Municípios do Litoral Norte e Entorno da Baía de Todos os Santos—Estado da Bahia: Implicações para a Gestão Ambiental; Universidade Federal da Bahia: Salvador, Brazil, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- INMET. Instituto Nacional de Meteorologia. SISDAGRO. Available online: https://sisdagro.inmet.gov.br/sisdagro/app/monitoramento/bhs (accessed on 29 May 2024).
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăguţ, L. Random Forest in Remote Sensing: A Review of Applications and Future Directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, M.; Mather, P.M. Support Vector Machines for Classification in Remote Sensing. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 1007–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, A.E.; Warner, T.A.; Fang, F. Implementation of Machine-Learning Classification in Remote Sensing: An Applied Review. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 2784–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, M. Random Forest Classifier for Remote Sensing Classification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzberg, S.L. C4.5: Programs for Machine Learning by J. Ross Quinlan. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, Inc., 1993. Mach. Learn. 1994, 16, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-Learn: Machine Learning in Python. Mchine Learn. Python 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Chandramohan, K.; Elayapillai, P.; Vijayalakshmi, G.; Kaliraj, S. Chapter 43—Evaluating the Relation of NDVI, NDWI, SMI, and LAI to Land and Soil Degradation Processes—A Case Study of Virudhunagar District, Tamil Nadu, India. In Remote Sensing of Soils; Dharumarajan, S., Kaliraj, S., Adhikari, K., Lalitha, M., Kumar, N., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 689–697. ISBN 978-0-443-18773-5. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Tang, L.; Wang, H. An Improved Approach for Monitoring Urban Built-up Areas by Combining NPP-VIIRS Nighttime Light, NDVI, NDWI, and NDBI. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 328, 129488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Weng, C.; Lu, Q.; Feng, T.; Zhang, L. Automatic Labelling and Selection of Training Samples for High-Resolution Remote Sensing Image Classification over Urban Areas. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 16024–16044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montandon, L.M.; Small, E.E. The Impact of Soil Reflectance on the Quantification of the Green Vegetation Fraction from NDVI. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 1835–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B. NDWI—A Normalized Difference Water Index for Remote Sensing of Vegetation Liquid Water from Space. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 58, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.E.; Amorim, G.; Grigio, A.M.; Paranhos, A.C. Comparative Analysis of Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) Methods in Continental Wetland. Anuário Instituto Geociências (Ufrj. Impresso) 2018, 41, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congalton, R.G. Assessing Landsat Classification Accuracy Using Discrete Multivariate Analysis Statistical Techniques. Photogramm. Eng. 1983, 49, 1671–1678. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfield, G.H. A Coefficient of Agreement as a Measure of Thematic Classification Accuracy. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1986, 2, 223–227. [Google Scholar]
- Foody, G.M. Explaining the Unsuitability of the Kappa Coefficient in the Assessment and Comparison of the Accuracy of Thematic Maps Obtained by Image Classification. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 239, 111630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.C.G.; Trevisan, G.d.M. Comparação da classificação de ocupação do solo do município de frederico westphalen-rs, utilizando os métodos isodata e distância mínima. Nativa 2019, 7, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, A.D.; Fernande, J.C. Detecção Remota; Edições Técnicas; Lidel: Lisboa, Portugal, 2004; ISBN 978-972-757-292-2. [Google Scholar]
- Mather, P.; Tso, B. Classification Methods for Remotely Sensed Data, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-0-429-19202-9. [Google Scholar]
- Helldén, U.; Stern, M. Monitoring land degradation in southern Tunisia: A test of LANDSAT imagery and digital data. Environ. Sci. Geogr. 1980, 1, 1601–1611. [Google Scholar]
- Ashok, A.; Rani, H.P.; Jayakumar, K.V. Monitoring of Dynamic Wetland Changes Using NDVI and NDWI Based Landsat Imagery. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2021, 23, 100547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, R.E. Analysis of Runoff-Plat Experiments with Varying Infiltration-Capacity. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1939, 20, 693–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lei, T.W.; Zhao, J.; Yuan, C.P.; Fan, Y.T.; Qu, L.Q. Effects of Rainfall Intensity and Antecedent Soil Water Content on Soil Infiltrability under Rainfall Conditions Using the Run Off-on-out Method. J. Hydrol. 2011, 396, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Rode, M.; Borchardt, D. Examining Runoff Generation Processes in the Selke Catchment in Central Germany: Insights from Data and Semi-Distributed Numerical Model. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2016, 7, 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, J.C. 4.3 Pedogenesis with Respect to Geomorphology. In Treatise on Geomorphology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 27–43. ISBN 978-0-08-088522-3. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, M.S.L.D.; Oliveira Neto, M.B.D. Latossolos Amarelos—Portal Embrapa. Available online: https://www.embrapa.br/agencia-de-informacao-tecnologica/territorios/territorio-mata-sul-pernambucana/caracteristicas-do-territorio/recursos-naturais/solos/latossolos-amarelos (accessed on 5 April 2024).
- Wang, J.; Cui, C.; Jia, Z.; Liu, M.; Pang, S.; Zhai, K. Analysis of the Responses of Surface Water Resources to Climate Change in Arid and Semi-Arid Area. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 295, 108751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherlink, V. NDVI FAQs: Frequently Asked Questions About the Index. Available online: https://eos.com/blog/ndvi-faq-all-you-need-to-know-about-ndvi/ (accessed on 6 May 2024).
- Barbosa, H.A.; Huete, A.R.; Baethgen, W.E. A 20-Year Study of NDVI Variability over the Northeast Region of Brazil. J. Arid Environ. 2006, 67, 288–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aegro O que são mapas NDVI e como utilizá-los na fazenda. Blog da Aegro 2020. Available online: https://blog.aegro.com.br/ndvi/ (accessed on 13 May 2024).
- Oliveira, M.D.G.S. O Eucalipto no Município de Alagoinhas-ba: Influências na Qualidade de vida da População do Entorno Florestal e no meio Ambiente. Available online: http://famamportal.com.br:8082/jspui/bitstream/123456789/2574/1/Maria%20das%20Gra%c3%a7as%20Santos%20Oliveira.pdf (accessed on 8 November 2023).
- Farrar, T.J.; Nicholson, S.E.; Lare, A.R. The Influence of Soil Type on the Relationships between NDVI, Rainfall, and Soil Moisture in Semiarid Botswana. II. NDVI Response to Soil Moisture. Remote Sens. Environ. 1994, 50, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georganos, S.; Abdi, A.M.; Tenenbaum, D.E.; Kalogirou, S. Examining the NDVI-Rainfall Relationship in the Semi-Arid Sahel Using Geographically Weighted Regression. J. Arid Environ. 2017, 146, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Hao, D.; Huete, A.; Dechant, B.; Berry, J.; Chen, J.M.; Joiner, J.; Frankenberg, C.; Bond-Lamberty, B.; Ryu, Y.; et al. Optical Vegetation Indices for Monitoring Terrestrial Ecosystems Globally. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 477–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, S.M.; Anyamba, A.; Tucker, C.J. Recent Trends in Vegetation Dynamics in the African Sahel and Their Relationship to Climate. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2005, 15, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Qu, J.J. NMDI: A Normalized Multi-Band Drought Index for Monitoring Soil and Vegetation Moisture with Satellite Remote Sensing. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Random 70 | Forest | Eucalyptus | Exposed Soil | Brazilian Savannah | Mining |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forest | 1612 | 7 | 0 | 8 | 0 |
| Eucalyptus | 3 | 1220 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| Exposed Soil | 0 | 0 | 1127 | 0 | 3 |
| Brazilian Savannah | 8 | 0 | 0 | 437 | 1 |
| Mining | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 69 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliveira, A.M.d.; Barros de Matos, M.R.; Figueiredo, M.B.; de Oliveira, L.N.A. The Importance of Dunnian Runoff in Atlantic Forest Remnants: An Integrated Analysis Between Machine Learning and Spectral Indices. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3977. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073977
Oliveira AMd, Barros de Matos MR, Figueiredo MB, de Oliveira LNA. The Importance of Dunnian Runoff in Atlantic Forest Remnants: An Integrated Analysis Between Machine Learning and Spectral Indices. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(7):3977. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073977
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliveira, Alarcon Matos de, Mara Rojane Barros de Matos, Marcos Batista Figueiredo, and Lusanira Nogueira Aragão de Oliveira. 2025. "The Importance of Dunnian Runoff in Atlantic Forest Remnants: An Integrated Analysis Between Machine Learning and Spectral Indices" Applied Sciences 15, no. 7: 3977. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073977
APA StyleOliveira, A. M. d., Barros de Matos, M. R., Figueiredo, M. B., & de Oliveira, L. N. A. (2025). The Importance of Dunnian Runoff in Atlantic Forest Remnants: An Integrated Analysis Between Machine Learning and Spectral Indices. Applied Sciences, 15(7), 3977. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073977






