Tensile Properties of Granite Under Cyclic Thermal Shock and Loading
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Equipment and Scheme
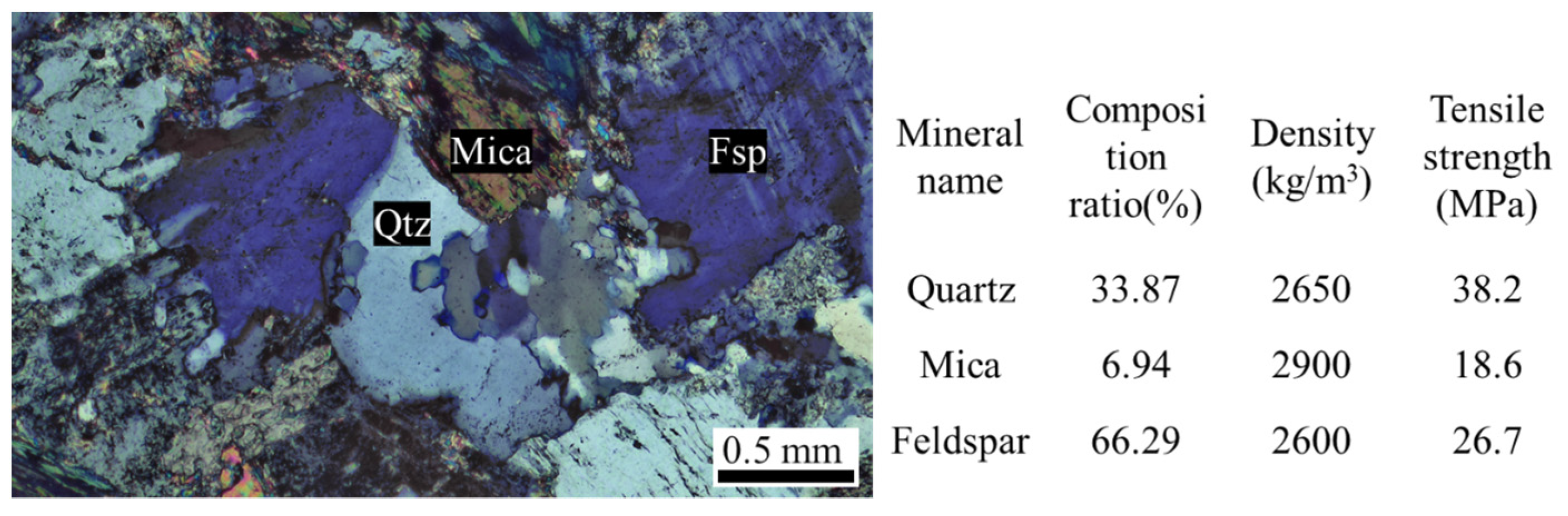
2.1. Specimen Preparation
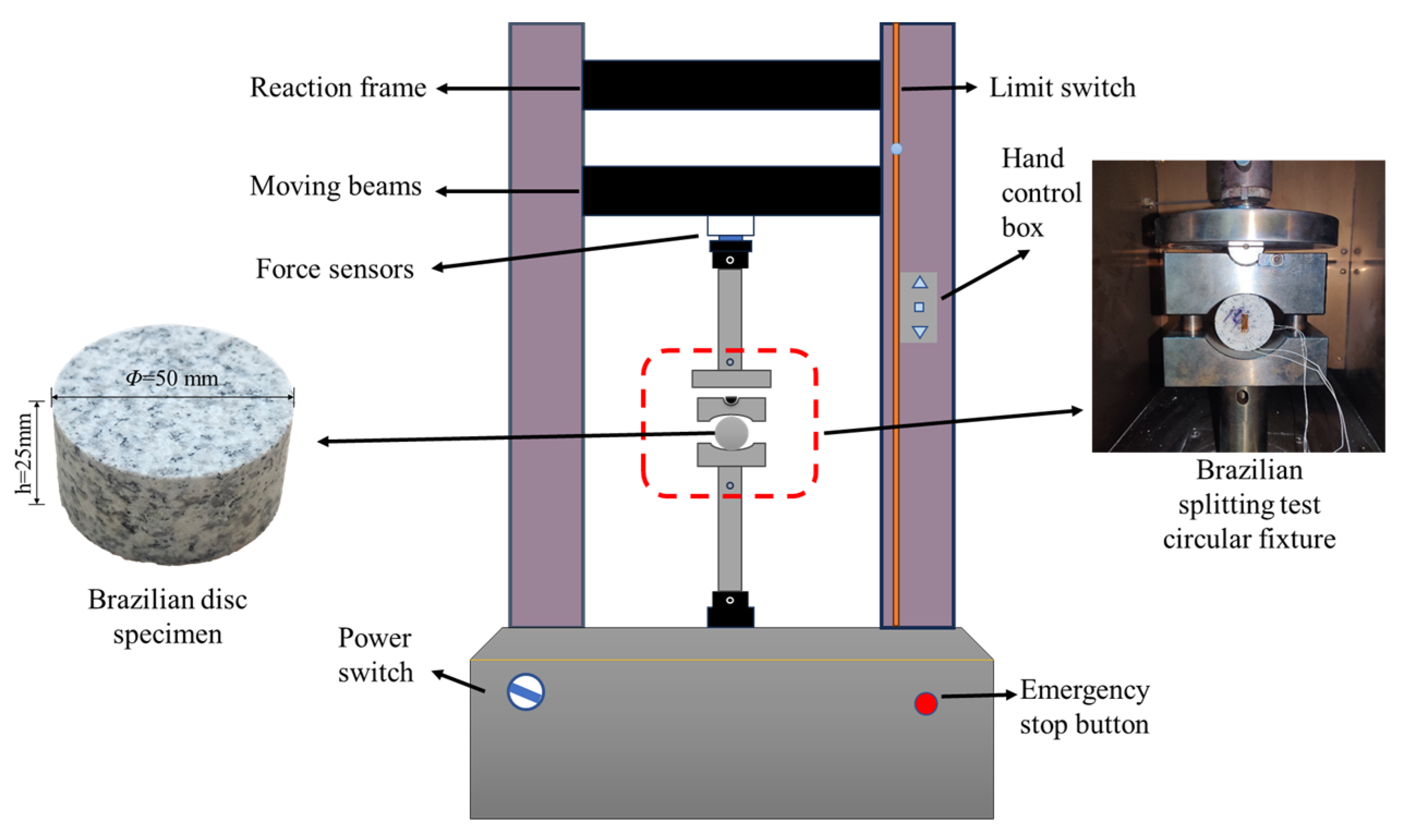
2.2. Experimental Equipment
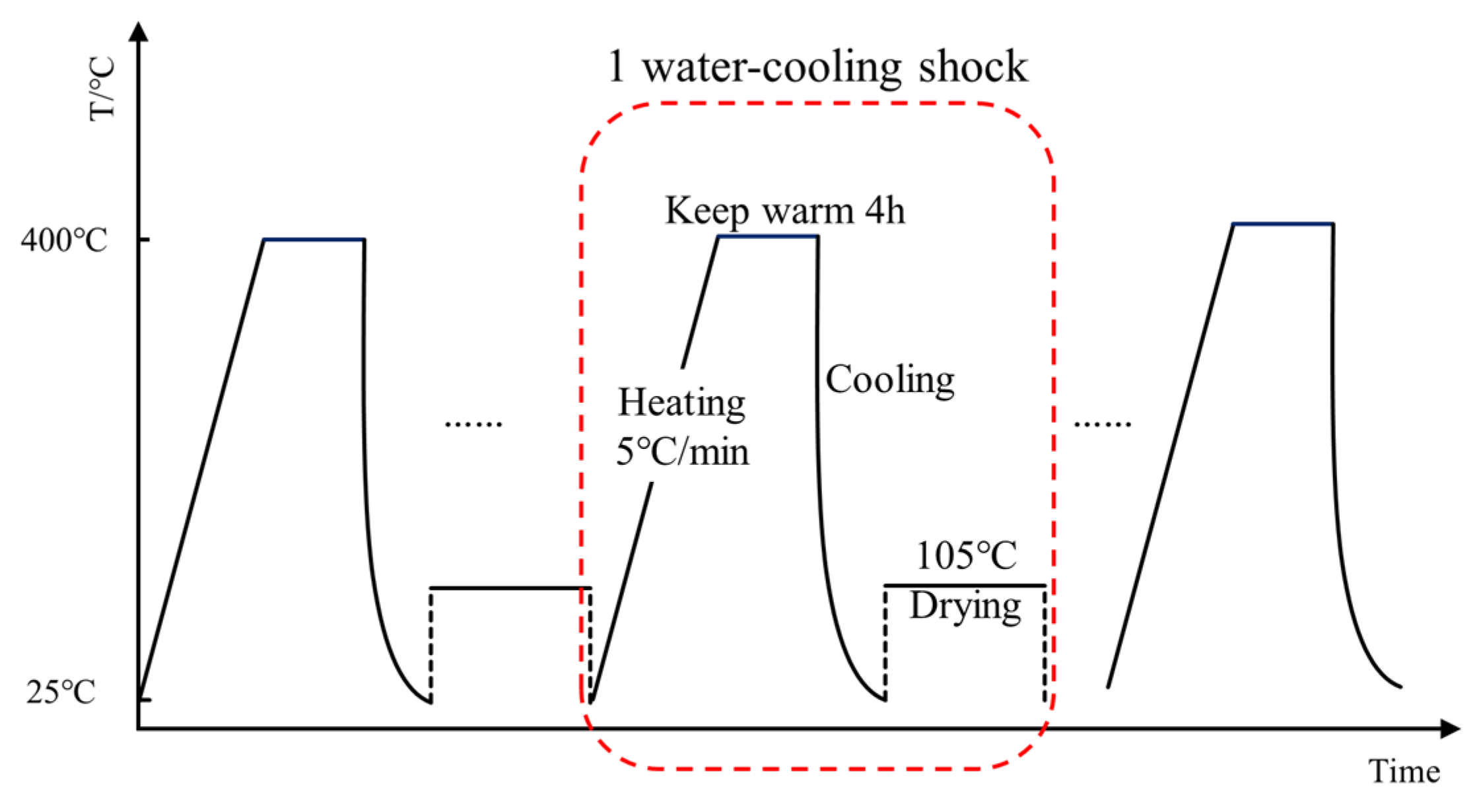
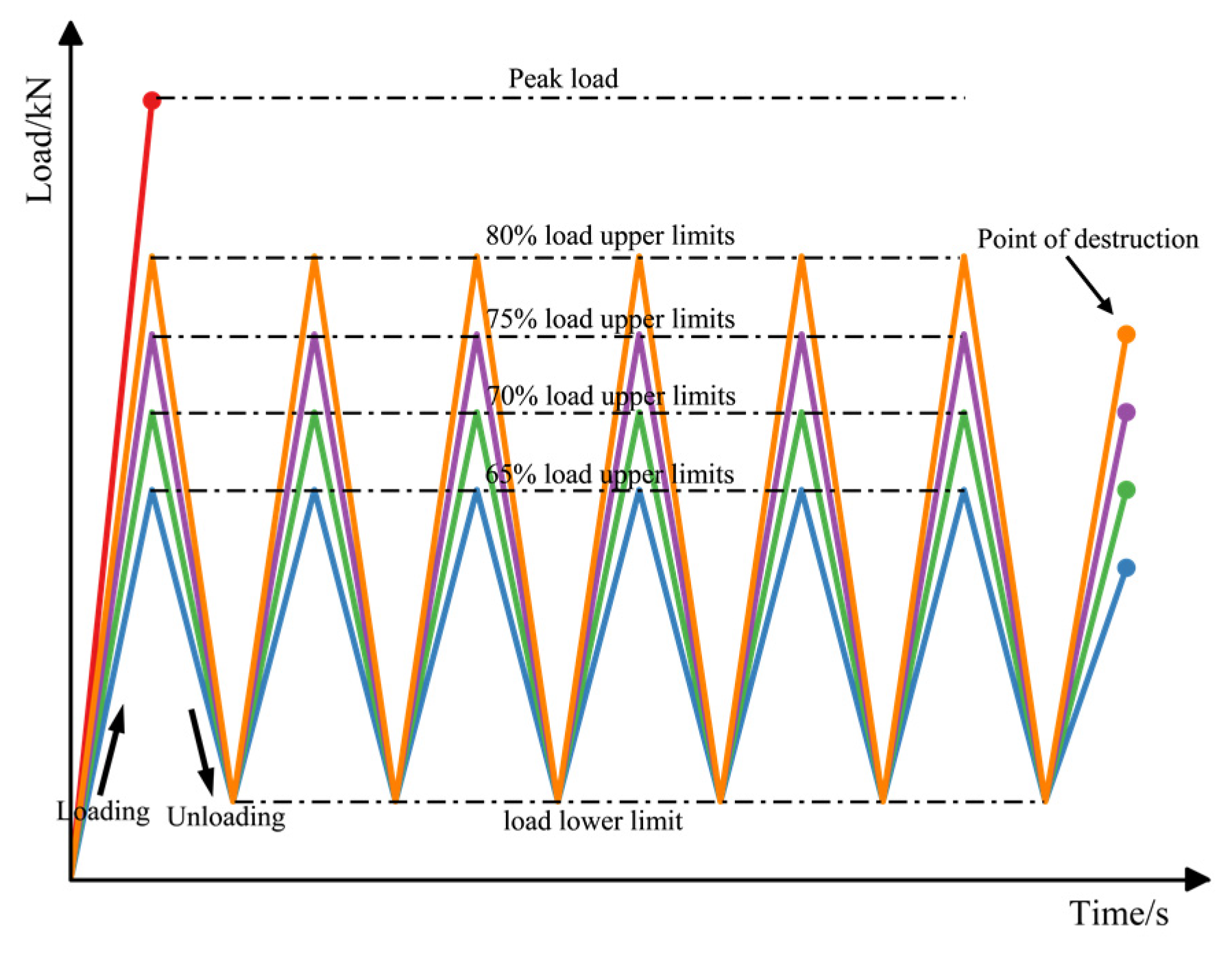
2.3. Experimental Steps
3. Test Results and Analysis
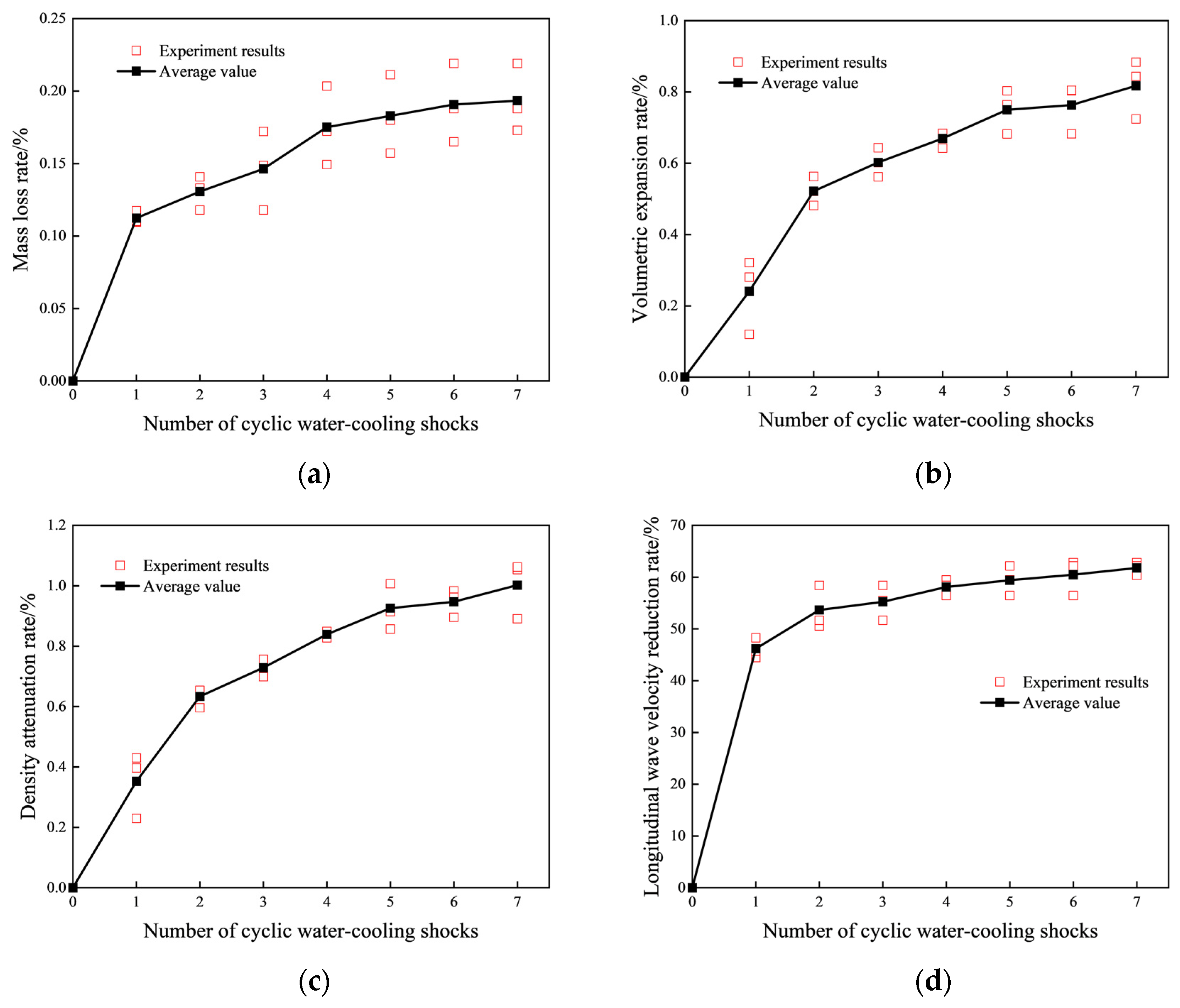
3.1. Physical Parameter Variations
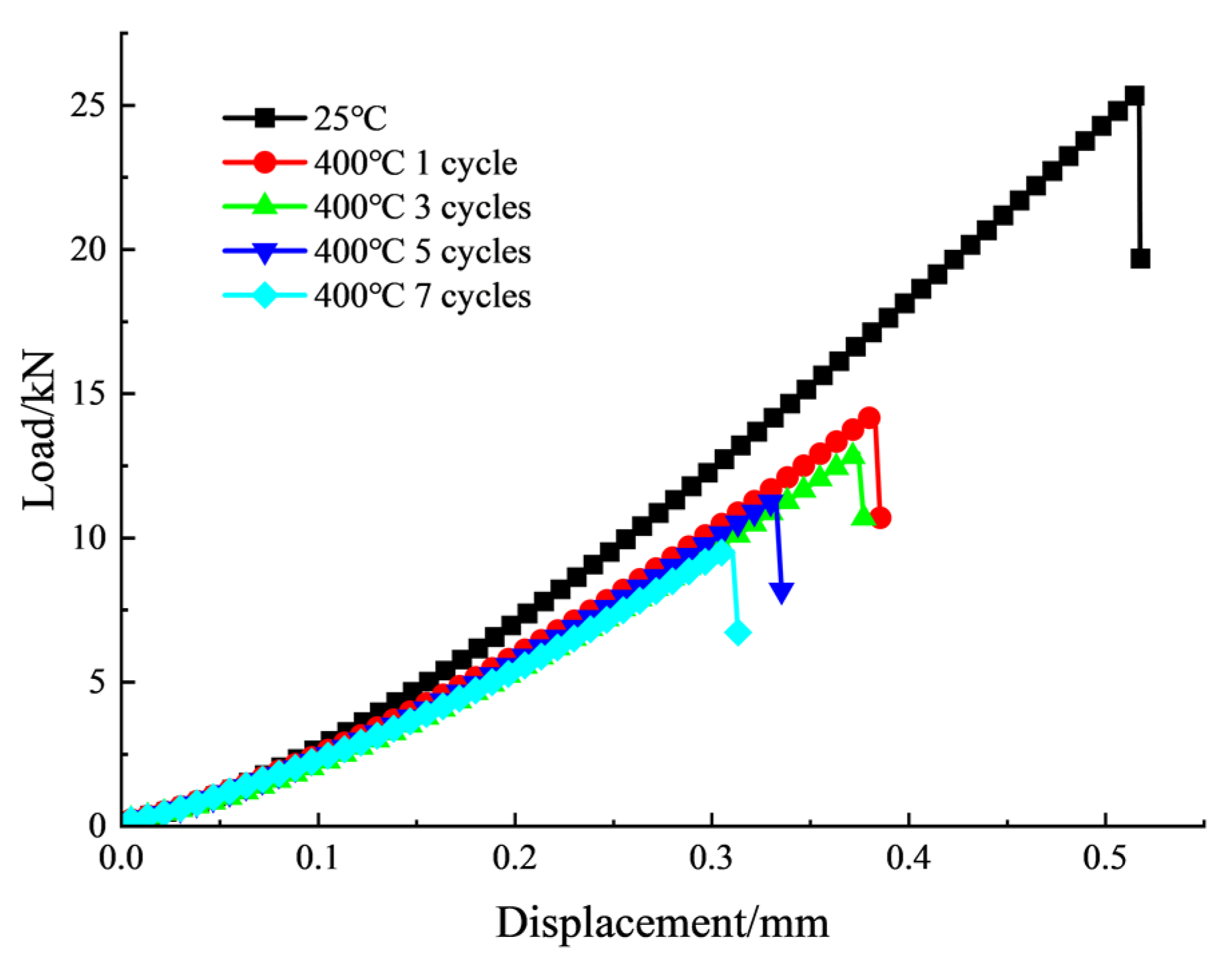
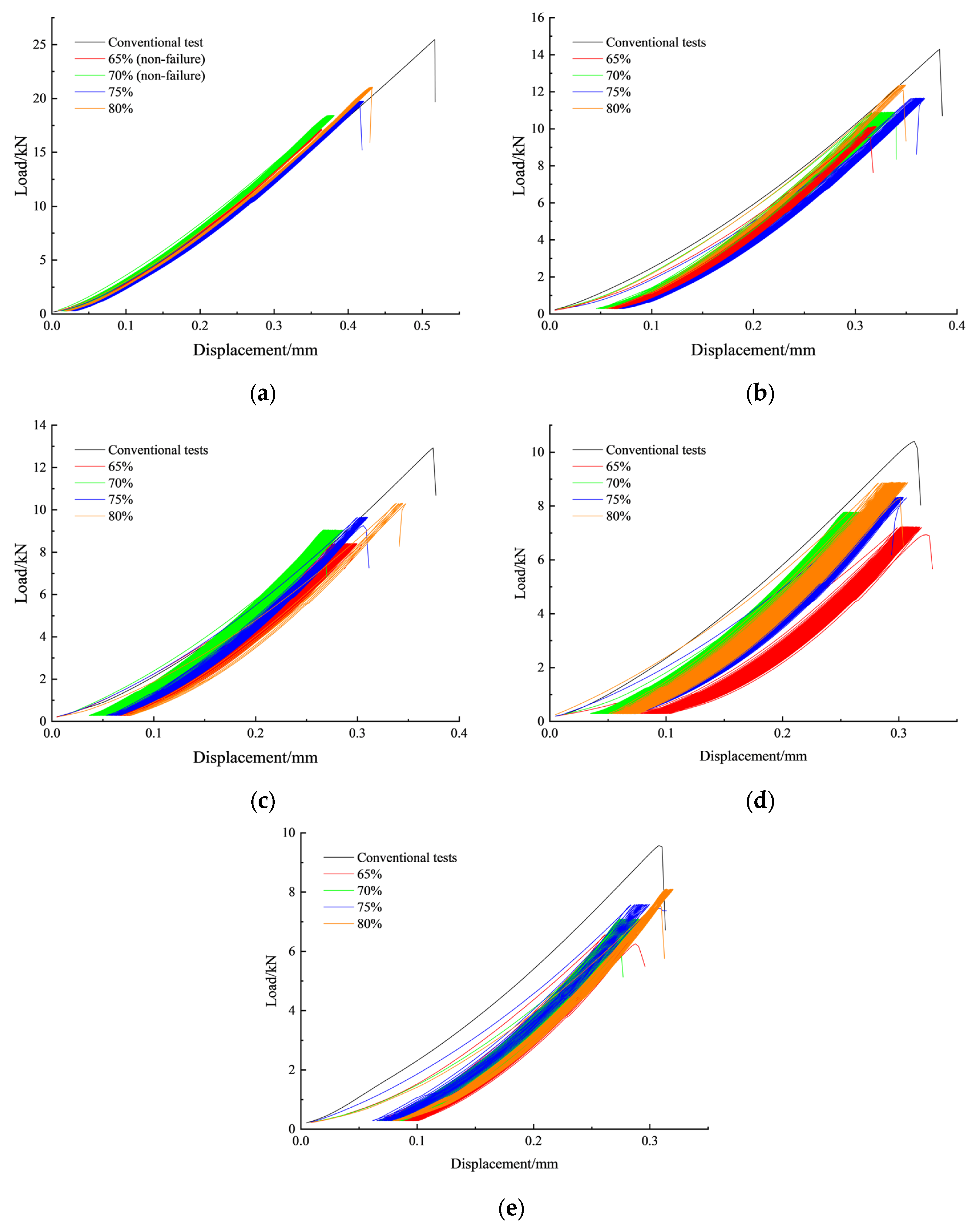
3.2. Load–Displacement Curve
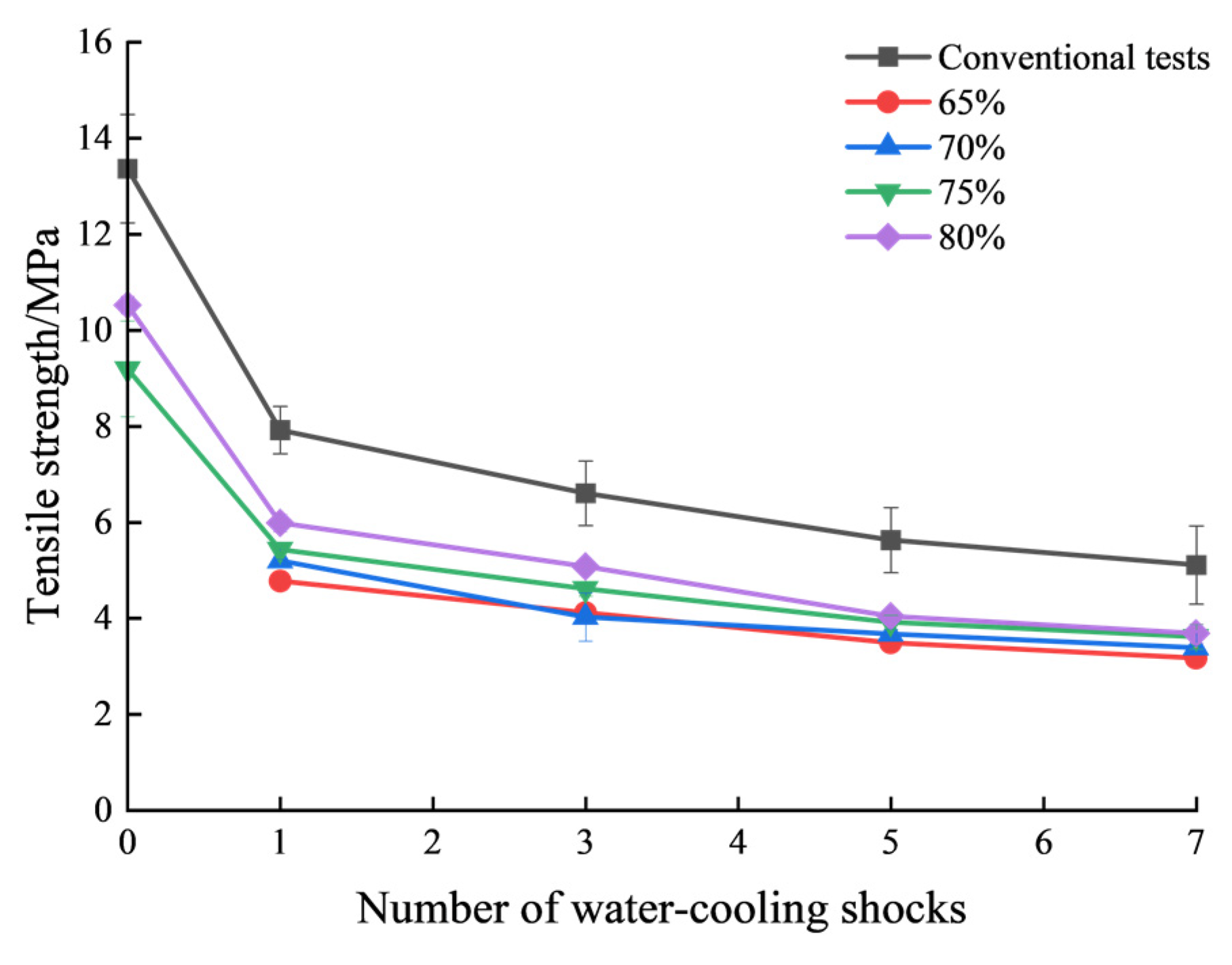
3.3. Tensile Strength
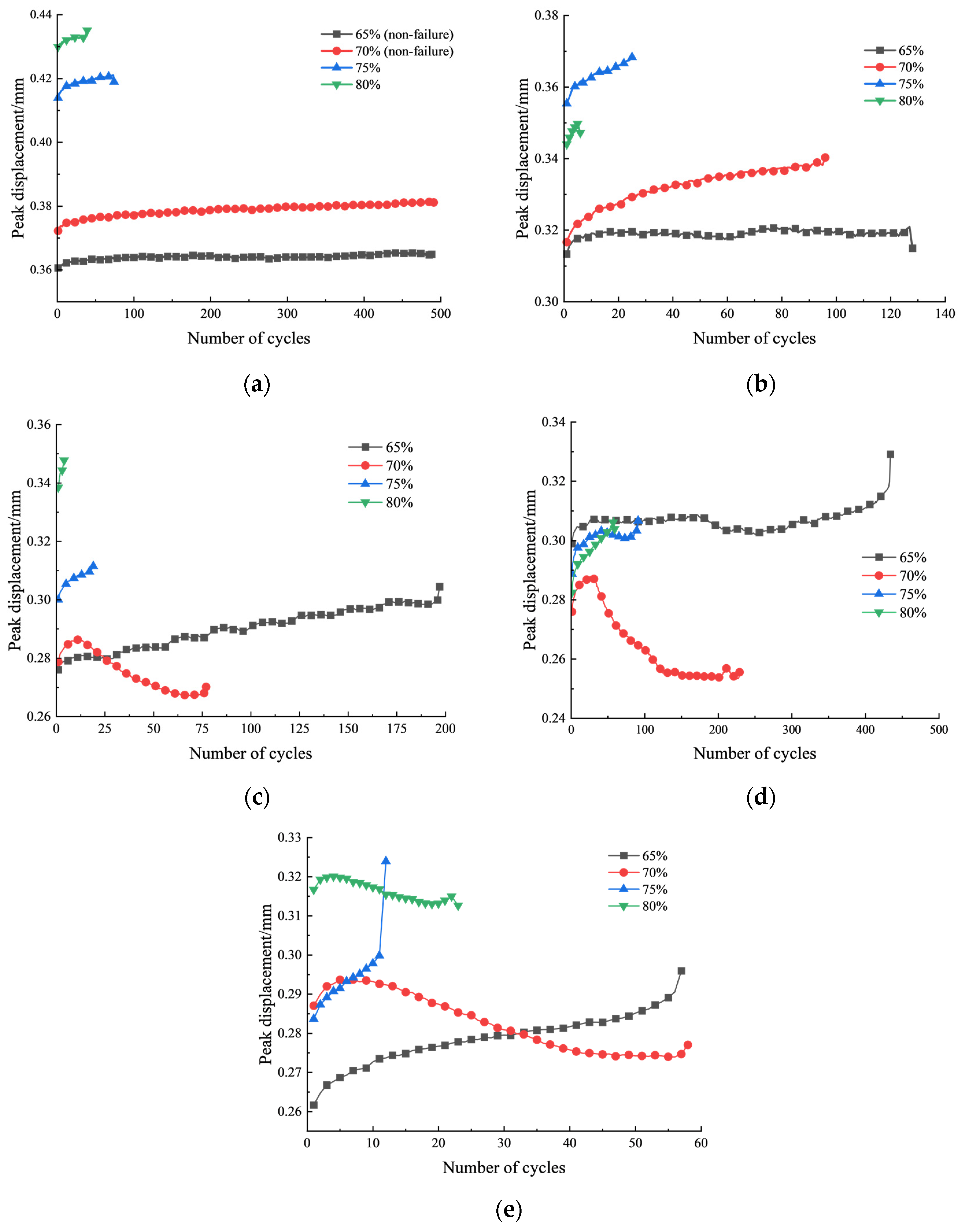
3.4. Cyclic Loading-Unloading Peak Displacement
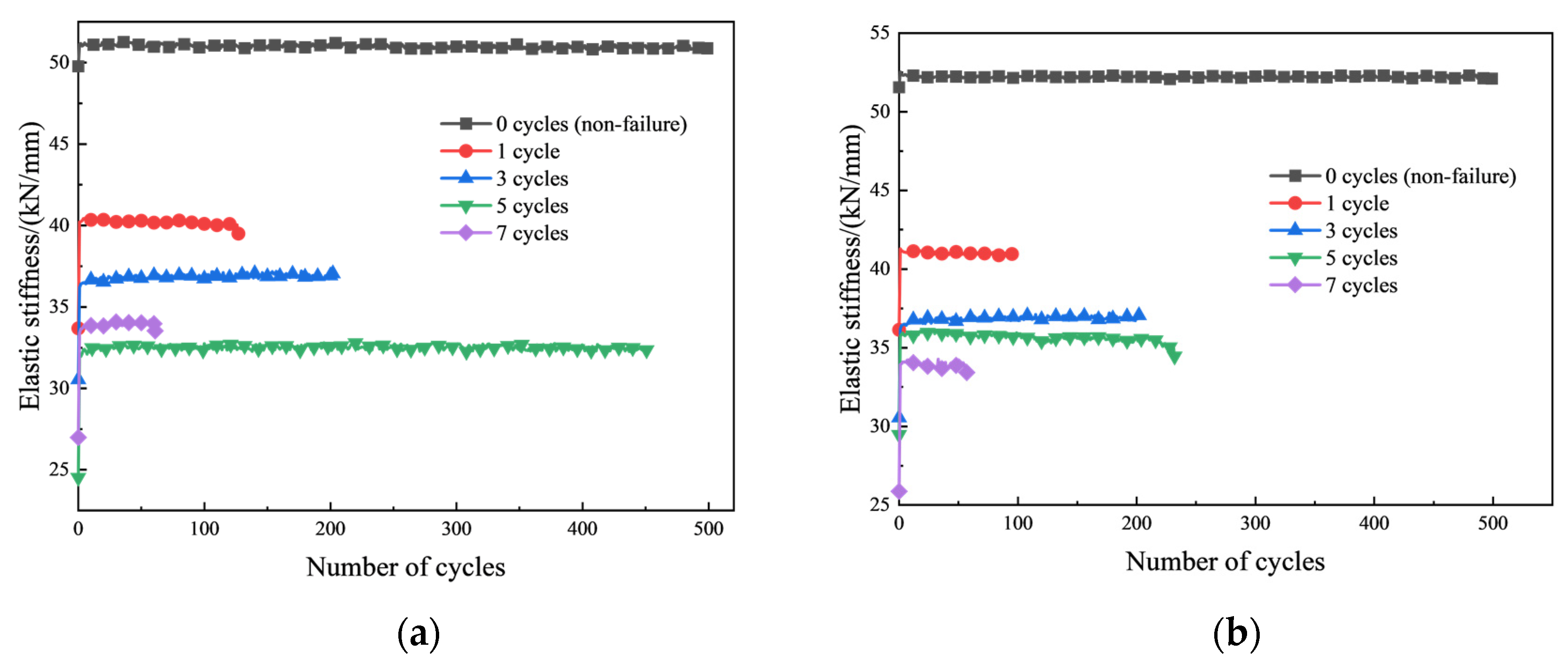
3.5. Elastic Stiffness
4. Failure Characteristics Analysis
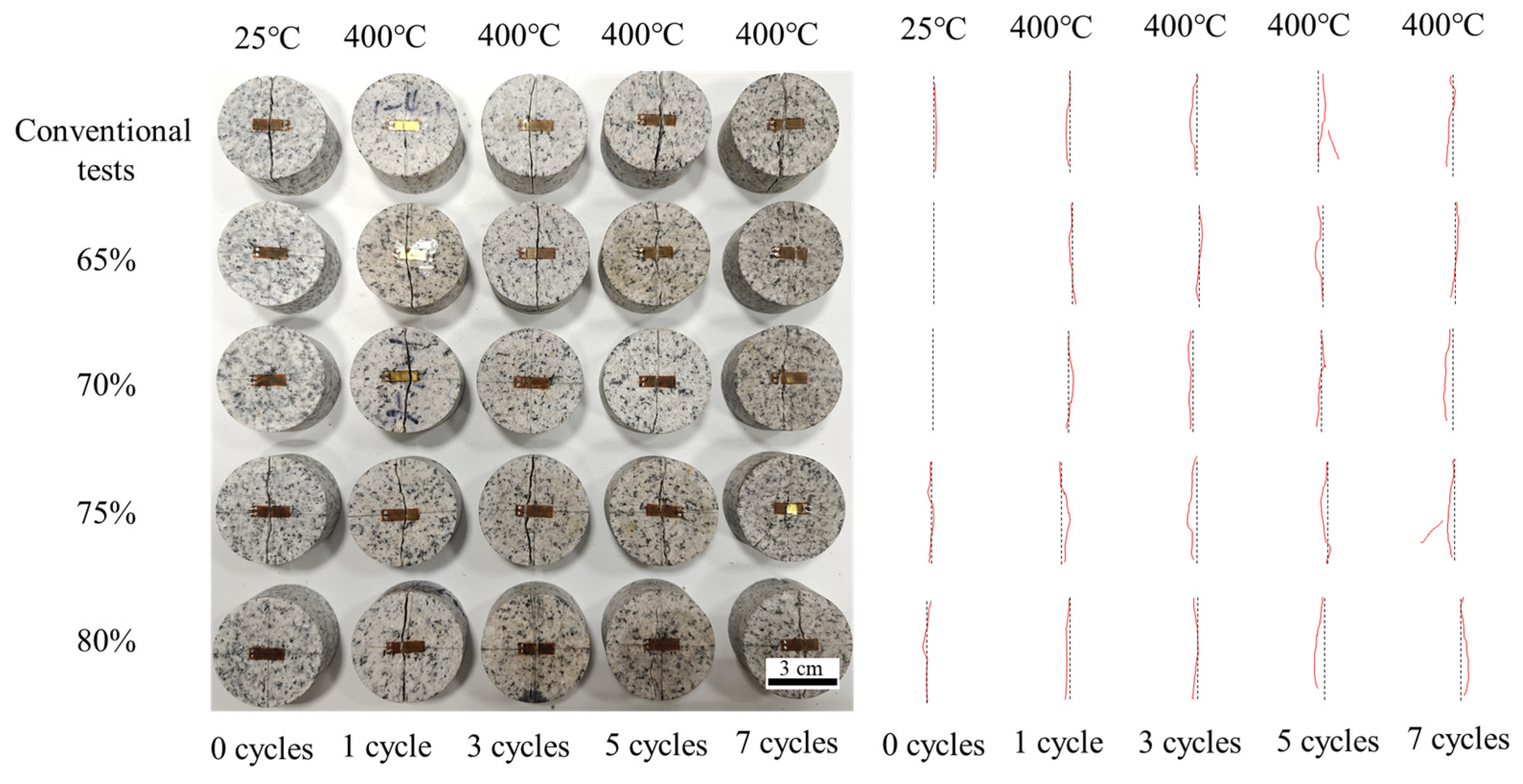
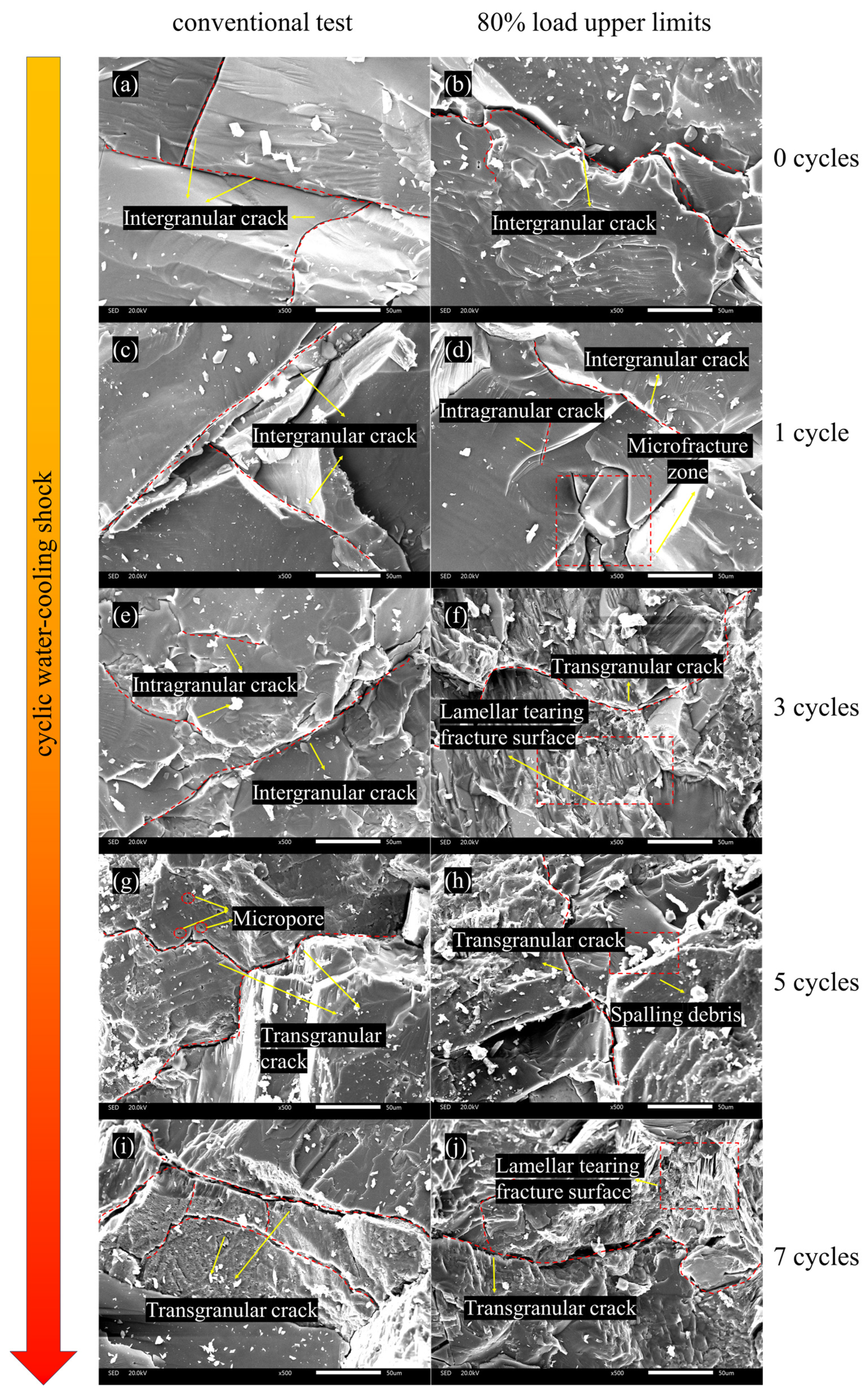
4.1. Macroscopic Failure Characteristics
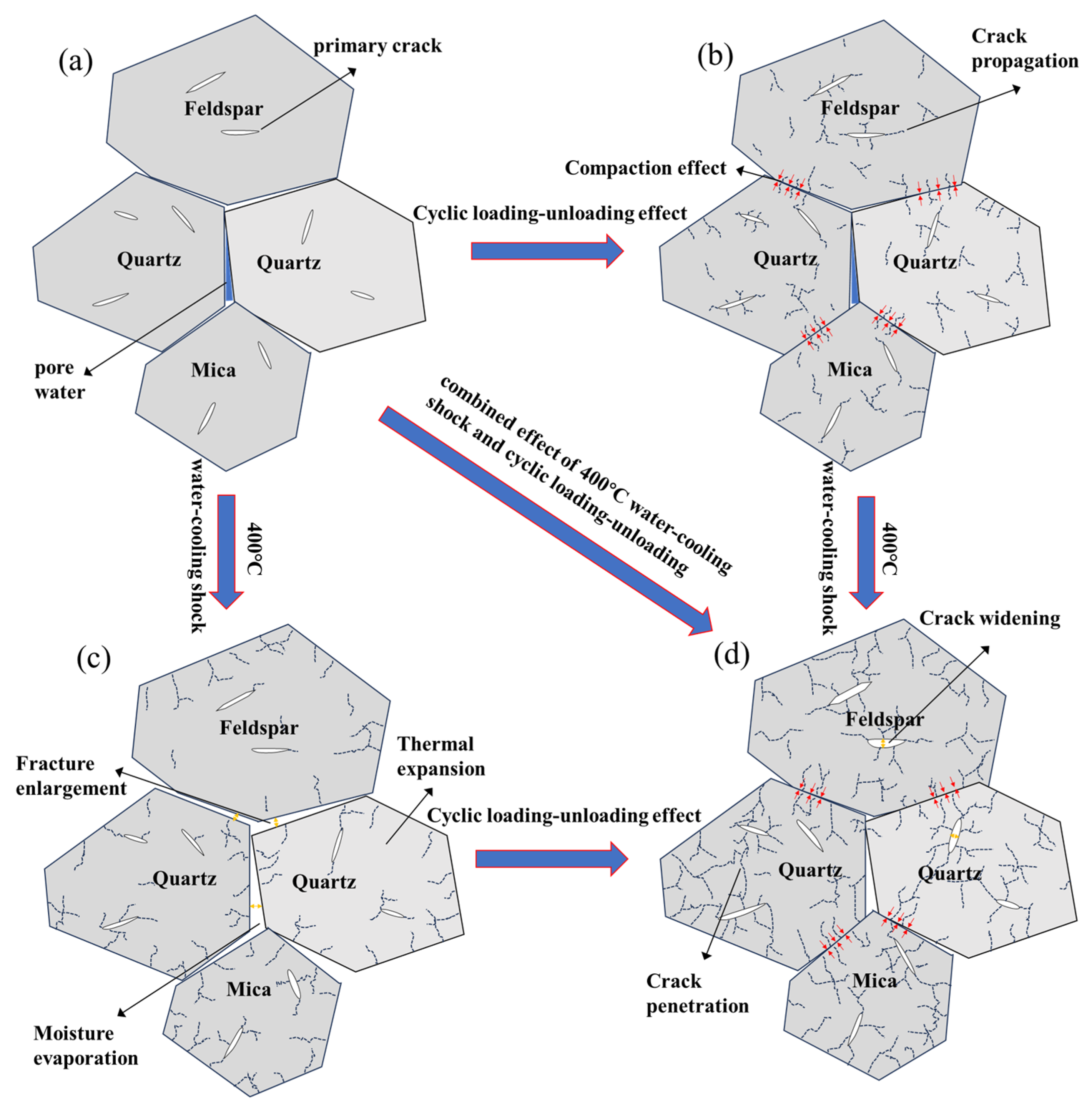
4.2. Microscopic Damage Mechanism Analysis
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
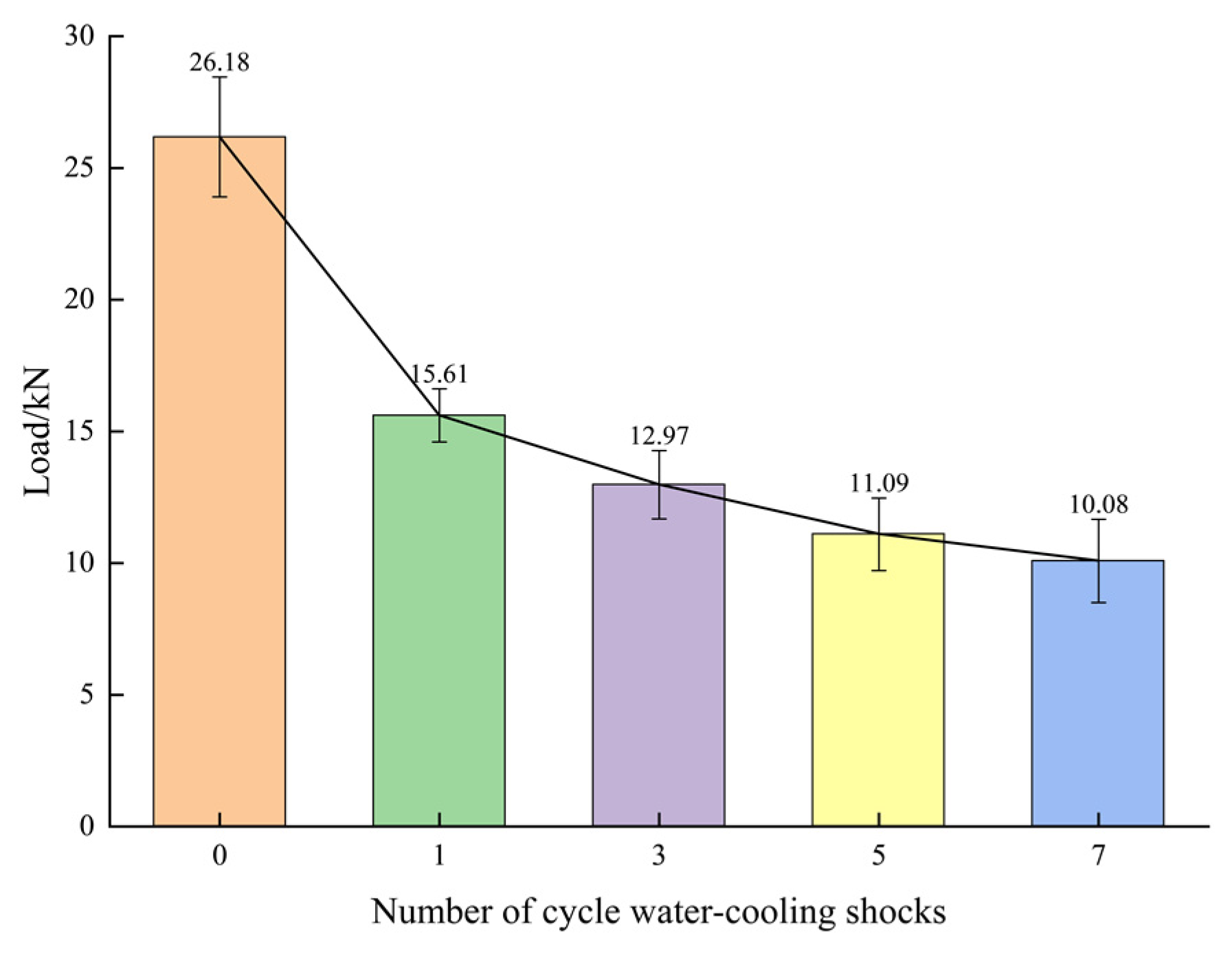
- For granite subjected to cyclic water-cooling shock at 400 °C, an increase in shock cycles leads to mass loss, volume expansion, density reduction, and a decrease in P-wave velocity. The most significant changes occur after the first quenching, after which the variation trends gradually stabilize. With the increasing number of water-cooling shock cycles, the tensile strength gradually decreases, while the rate of decrease diminishes progressively.
- The tensile strength of granite in cyclic loading-unloading Brazilian splitting tests decreases progressively with increasing water-cooling shock cycles. Additionally, the tensile strength under cyclic loading-unloading conditions is significantly lower than that in conventional Brazilian splitting tests. As the preset load upper limit decreases, the tensile strength also exhibits a declining trend.
- Under cyclic loading-unloading, the initial peak displacement increases with the preset load upper limit. However, at five shock cycles, no clear trend is observed due to the transition of granite from brittle to ductile behavior. As the preset load upper limit increases, the number of cycles required for failure decreases. The elastic stiffness of granite initially increases with the number of loading-unloading cycles, then stabilizes before eventually decreasing. Moreover, with increasing water-cooling shock cycles, the overall elastic stiffness shows a decreasing trend. In the early stages of cyclic loading and unloading during the Brazilian splitting test, a competitive mechanism exists between damage accumulation and compaction effects in granite. When the number of water-cooling shock cycles is low, damage accumulation dominates; however, after five cycles, the compaction effect becomes the prevailing mechanism.
- With an increasing number of cyclic water-cooling shocks, macro-fracture patterns in granite transition from straight to curved cracks. SEM observations reveal that microcracks become more numerous and wider with additional shock cycles. Under cyclic loading-unloading, the microcrack width further increases, and the fracture surface becomes rougher.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Takleh, H.R.; Zare, V.; Mohammadkhani, F.; Sadeghiazad, M. Proposal and thermoeconomic assessment of an efficient booster-assisted CCHP system based on solar-geothermal energy. Energy 2022, 246, 123360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, M.; Jing, Z.; Feng, C.; Li, M.; Chen, C.; Zou, X.; Zhou, Y. Review on heat extraction systems of hot dry rock: Classifications, benefits, limitations, research status and future prospects. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 196, 114364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, H.; Wu, S.; Liu, L.; Huang, L.; Zhu, B.; Sun, Y.; Liu, E. Progress on heat transfer in fractures of hot dry rock enhanced geothermal system. Energy Eng. 2021, 118, 797–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, K.F.; Zappone, A.; Kraft, T.; Deichmann, N.; Moia, F. A survey of the induced seismic responses to fluid injection in geothermal and CO2 reservoirs in Europe. Geothermics 2012, 41, 30–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, F.; Sun, F.; Lü, H.; Wang, C.; Wu, H.; Zhou, X. Hydraulic fracturing-induced seismicity at the hot dry rock site of the gonghe basin in China. Acta Geol. Sin.-Engl. Ed. 2021, 95, 1835–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Dai, C.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, D.; Shao, J.; Hu, D. Experimental investigations on the tensile behaviour of granite after heating and water-cooling treatment. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2021, 80, 5909–5920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Yang, S.; Wang, R.; Xie, J.; Tian, N.; Tian, H.; Zheng, J.; Jiang, G.; Dou, B. Experimental investigation on the physical-thermal properties of Nanan granite after air and water cooling for deep geothermal heat extraction. Renew. Energy 2024, 223, 119963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wang, W.; Tang, J.; Guo, Q.; Liu, Y. Fracture Initiation and Propagation in the Hot Dry Rock Subject to the Cyclic Injection Hydraulic Fracturing Treatment. Geofluids 2023, 2023, 8859177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Xu, T.; Moore, J.; Feng, B.; Liu, Y.; McLennan, J.; Yang, Y. Investigation of the effect of different injection schemes on fracture network patterns in hot dry rocks-A numerical case study of the FORGE EGS site in Utah. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2022, 97, 104346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, E.; Martin, C. Fracture initiation and propagation in intact rock—A review. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2014, 6, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Tian, H.; Dou, B.; Zheng, J.; Chen, J.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, H. Macroscopic and microscopic experimental research on granite properties after high-temperature and water-cooling cycles. Geothermics 2021, 93, 102079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Peng, H.-W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, G.-W. Mechanical test of granite with multiple water–thermal cycles. Geotherm. Energy 2021, 9, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Tian, H.; Mei, G.; Jiang, G.; Dou, B. Experimental investigation on physical and mechanical properties of thermal cycling granite by water cooling. Acta Geotech. 2020, 15, 1881–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Jing, H.; Yin, Q.; Ding, S.; Zhang, J. Mechanical characteristics of granite after heating and water-cooling cycles. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2020, 53, 2015–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Jing, H.; Yin, Q.; Han, G. Experimental study on the damage of granite by acoustic emission after cyclic heating and cooling with circulating water. Processes 2018, 6, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Sun, Q. Effects of quenching cycle on tensile strength of granite. Géotechnique Lett. 2018, 8, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahraman, E. Investigation of the effects of two different cooling treatments on the physico-mechanical and microstructural properties of granite after high temperatures. Geomech. Geophys. Geo-Energy Geo-Resour. 2022, 8, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Lyu, C.; Lin, J.; Wang, L.; Cao, Y.-H. Experimental investigation of physical and tensile mechanical properties of granite after different heating and cooling treatments. Q. J. Eng. Geol. Hydrogeol. 2024, 57, qjegh2023-2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Gao, F.; Cai, C.; Du, M.; Wang, Z.; Huo, L.; Bai, Y. Effect of different cooling treatments on the tensile properties and fracture modes of granite heated at different temperatures. Nat. Resour. Res. 2022, 31, 817–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erarslan, N.; Williams, D.J. Investigating the Effect of Cyclic Loading on the Indirect Tensile Strength of Rocks. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2011, 45, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erarslan, N.; Alehossein, H.; Williams, D.J. Tensile Fracture Strength of Brisbane Tuff by Static and Cyclic Loading Tests. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2013, 47, 1135–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Qiu, B.; Gao, J.; Du, X. A real-time visual investigation on microscopic progressive fatigue deterioration of granite under cyclic loading. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2023, 56, 5133–5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, F.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, S.; Li, K.; Ma, S. Effect of Cyclic Loading on Mode I Fracture Toughness of Granite under Real-Time High-Temperature Conditions. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Z.; Xue, Y.; Li, Z.; Su, M.; Kong, F.; Bai, C. Damage characteristics of granite under hydraulic and cyclic loading–unloading coupling condition. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2022, 55, 1393–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Y.; Zhou, M. A thorough investigation of the dynamic properties of granite under cyclic loading. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 12514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Guo, Y.; Chang, X.; Jin, P.; Hu, Y. Effects of temperature and increasing amplitude cyclic loading on the mechanical properties and energy characteristics of granite. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2022, 81, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieniawski, Z.; Hawkes, I. Suggested methods for determining tensile strength of rock materials. Int. J. Rock Mech. 1978, 15, 99–103. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Zhao, J.; Hu, D.; Shao, J.; Sheng, Q. Evolution of bulk compressibility and permeability of granite due to thermal cracking. Géotechnique 2019, 69, 906–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, P.; Xue, F.; Xue, M. Experimental investigation on the macro-and micromechanical properties of water-cooled granite at different high temperatures. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 17149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, X. Effect of Thermal Treatment on the Physical and Mechanical Properties of Sandstone: Insights from Experiments and Simulations. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2022, 55, 3171–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhu, J.; Qu, H.; Zhou, T.; Zhou, C. An experimental investigation on fatigue characteristics of granite under repeated dynamic tensions. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2022, 158, 105185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, M.; Basu, A. Evaluation of ring test with reference to deformation rate and specimen geometry in assessing the tensile behaviors of granite. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2025, 185, 105973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.; Wu, J.; Zhu, C.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Jing, H.; Xie, J. The role of multiple heating and water cooling cycles on physical and mechanical responses of granite rocks. Geomech. Geophys. Geo-Energy Geo-Resour. 2021, 7, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, S.; Khamehchiyan, M.; Taheri, A.; Nikudel, M.R.; Zalooli, A.; Sadeghi, E. The effect of cyclic loading parameters on the physical, mechanical, and microcracking behavior of granite. Eng. Geol. 2024, 332, 107475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Feng, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wan, Z. Experimental investigation on thermal cracking, permeability under HTHP and application for geothermal mining of HDR. Energy 2017, 132, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, S.; Pan, P.-Z.; Hou, W.; He, B.; Yu, P. Stress intensity factor evolution considering fracture process zone development of granite under monotonic and stepwise cyclic loading. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2022, 273, 108727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Dong, Y.-H.; Xu, Z.-F.; Zhou, P.-P.; Wang, L.-H.; Tong, S.-Q.; Duan, R.-Q. Granite microcracks: Structure and connectivity at different depths. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2016, 124, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, C.L. Deformation of partially molten granite: A review and comparison of experimental and natural case studies. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2001, 90, 60–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Chang, X.; Guo, Y.; Yang, H.; Guo, W.; Hu, Y. Fatigue of granite subjected to cyclic loading at various temperatures: Experimental insights from deformation and energy conversion. Geomech. Geophys. Geo-Energy Geo-Resour. 2022, 8, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, T.; Wu, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, C.; Wu, B. Determination of double-K fracture toughness parameters of thermally treated granite using notched semi-circular bending specimen. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2020, 226, 106865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Roquete, M.; Kou, S.; Lindqvist, P.-A. Characterization of rock heterogeneity and numerical verification. Eng. Geol. 2004, 72, 89–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Kusuda, H.; Kusaka, E.; Mabuchi, M. Crack growth in Westerly granite during a cyclic loading test. Eng. Geol. 2011, 117, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairhurst, C.; Hudson, J.A. Draft ISRM suggested method for the complete stress-strain curve for intact rock in uniaxial compression. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 1999, 36, 279–289. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Gao, L.; Wu, J.; Zhu, C.; Chen, S.; Zhuo, X. Effects of cyclic heating and water cooling on the physical characteristics of granite. Energies 2020, 13, 2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, L.; Heap, M.J.; Baud, P.; Schmittbuhl, J. Quantification of microcrack characteristics and implications for stiffness and strength of granite. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2017, 100, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K.; Luo, X.; Liu, M.; Liu, X.; Zhou, J. Understanding the evolution mechanism and classification criteria of tensile-shear cracks in rock failure process from acoustic emission (AE) characteristics. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2024, 296, 109864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.-J.; Hou, X.; Yuan, J.-Q.; Wang, S.-F.; Zhao, C.-H. Thermal cracking characteristics of high-temperature granite suffering from different cooling shocks. Int. J. Fract. 2020, 225, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.-H.; Fang, L.; Qiu, X.; Lin, H.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Qiao, Q. Effect of heating–water cooling cycle treatment on the pore structure and shear fracture characteristics of granite. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2023, 286, 109263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, H.; Wu, J.; Dahal, S.; Joo, T.; Garg, N. Automated estimation of cementitious sorptivity via computer vision. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 9935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabir, B.; Wild, S.; O’farrell, M. A water sorptivity test for martar and concrete. Mater. Struct. 1998, 31, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, F.; Lin, Z.; Wang, T. Experimental study on effects of cyclic loading paths on cracking behavior and fracture characteristics of granite. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2024, 295, 109761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Yang, P.; Liu, S.; Zeng, S. Impact dynamic characteristics and constitutive model of granite damaged by cyclic loading. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zuo, J.; Sun, Y.; Wen, J. The effects of thermal treatments on the fatigue crack growth of Beishan granite: An in situ observation study. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2021, 80, 1541–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Number of Water-Cooling Shock Cycles | Average Tensile Strength of Conventional Splitting/MPa | Preset Load Upper Limit/% | Number of Cyclic Loading and Unloading Cycles | Tensile Strength of Cyclic Brazilian Splitting /MPa | Reduction Amplitude/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 13.37 | 65 | 500 | - | - |
| 70 | 500 | - | - | ||
| 75 | 78 | 9.19 | 31 | ||
| 80 | 39 | 10.52 | 21 | ||
| 1 | 7.92 | 65 | 128 | 4.78 | 40 |
| 70 | 96 | 5.20 | 34 | ||
| 75 | 25 | 5.43 | 31 | ||
| 80 | 6 | 5.98 | 24 | ||
| 3 | 6.61 | 65 | 202 | 4.11 | 38 |
| 70 | 87 | 4.03 | 39 | ||
| 75 | 18 | 4.61 | 30 | ||
| 80 | 4 | 5.08 | 23 | ||
| 5 | 5.63 | 65 | 452 | 3.49 | 38 |
| 70 | 233 | 3.67 | 35 | ||
| 75 | 94 | 3.91 | 31 | ||
| 80 | 60 | 4.04 | 28 | ||
| 7 | 5.11 | 65 | 62 | 3.17 | 38 |
| 70 | 58 | 3.38 | 34 | ||
| 75 | 23 | 3.61 | 29 | ||
| 80 | 12 | 3.68 | 28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Liu, S.; Lv, C.; Xu, S. Tensile Properties of Granite Under Cyclic Thermal Shock and Loading. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4385. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084385
Zhang Y, Zhang F, Liu S, Lv C, Xu S. Tensile Properties of Granite Under Cyclic Thermal Shock and Loading. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(8):4385. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084385
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yiming, Fan Zhang, ShengYuan Liu, Congcong Lv, and Siming Xu. 2025. "Tensile Properties of Granite Under Cyclic Thermal Shock and Loading" Applied Sciences 15, no. 8: 4385. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084385
APA StyleZhang, Y., Zhang, F., Liu, S., Lv, C., & Xu, S. (2025). Tensile Properties of Granite Under Cyclic Thermal Shock and Loading. Applied Sciences, 15(8), 4385. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084385





