Influence of Source Shape on Semi-Airborne Transient Electromagnetic Surveys
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
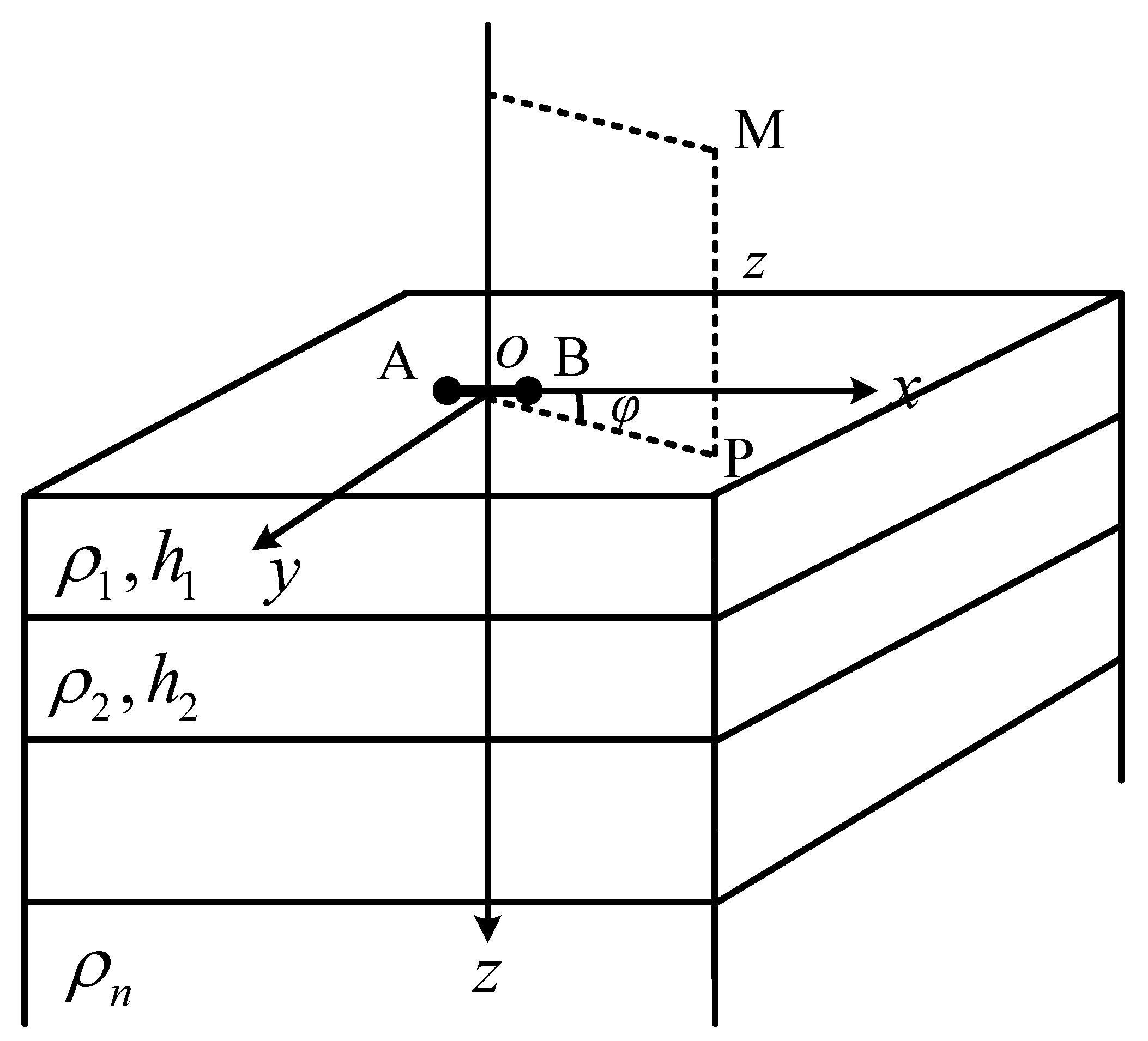
2.1. SATEM 1D Modeling
2.2. SATEM 3D Modeling
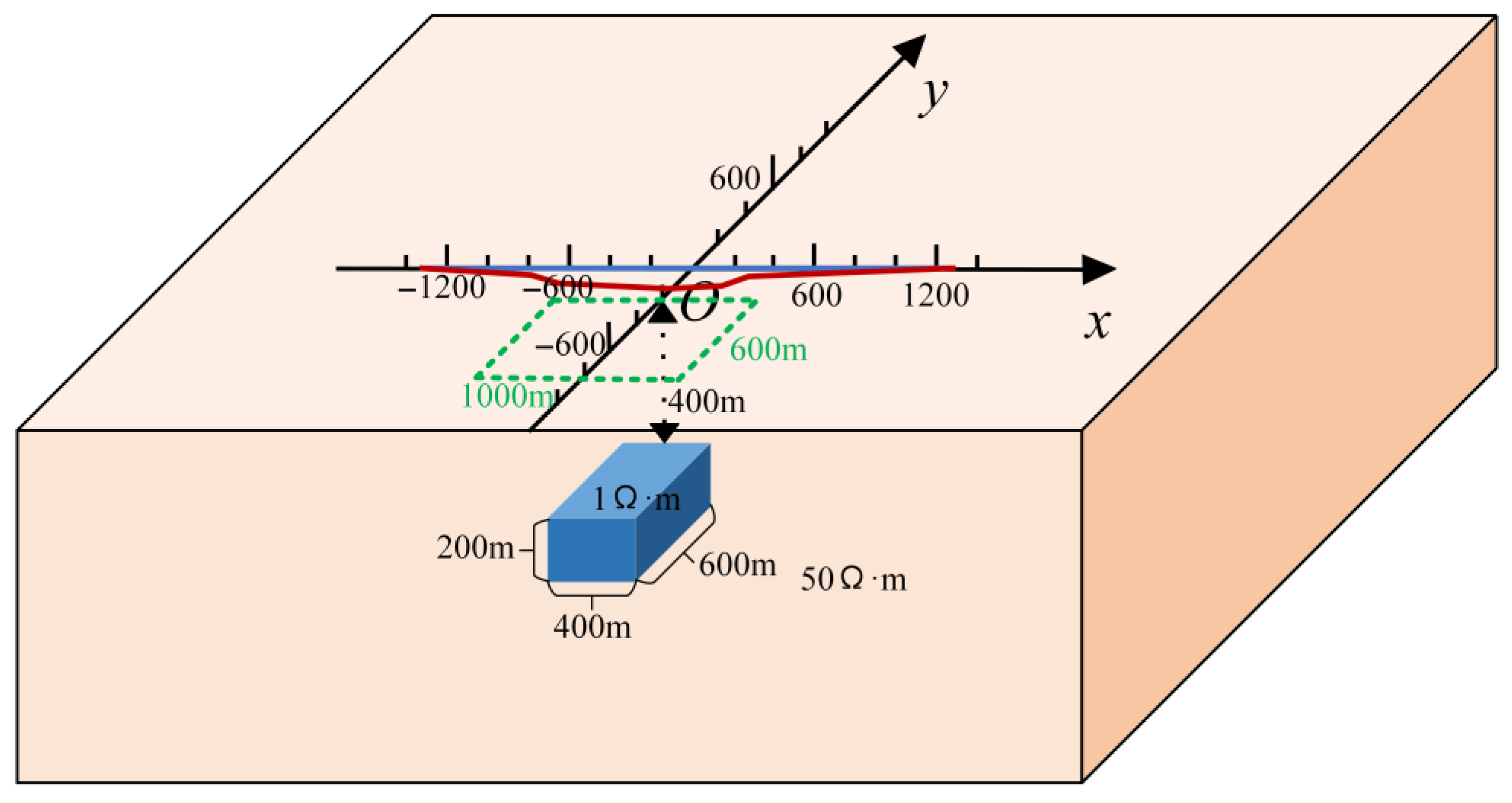
2.3. SATEM Model
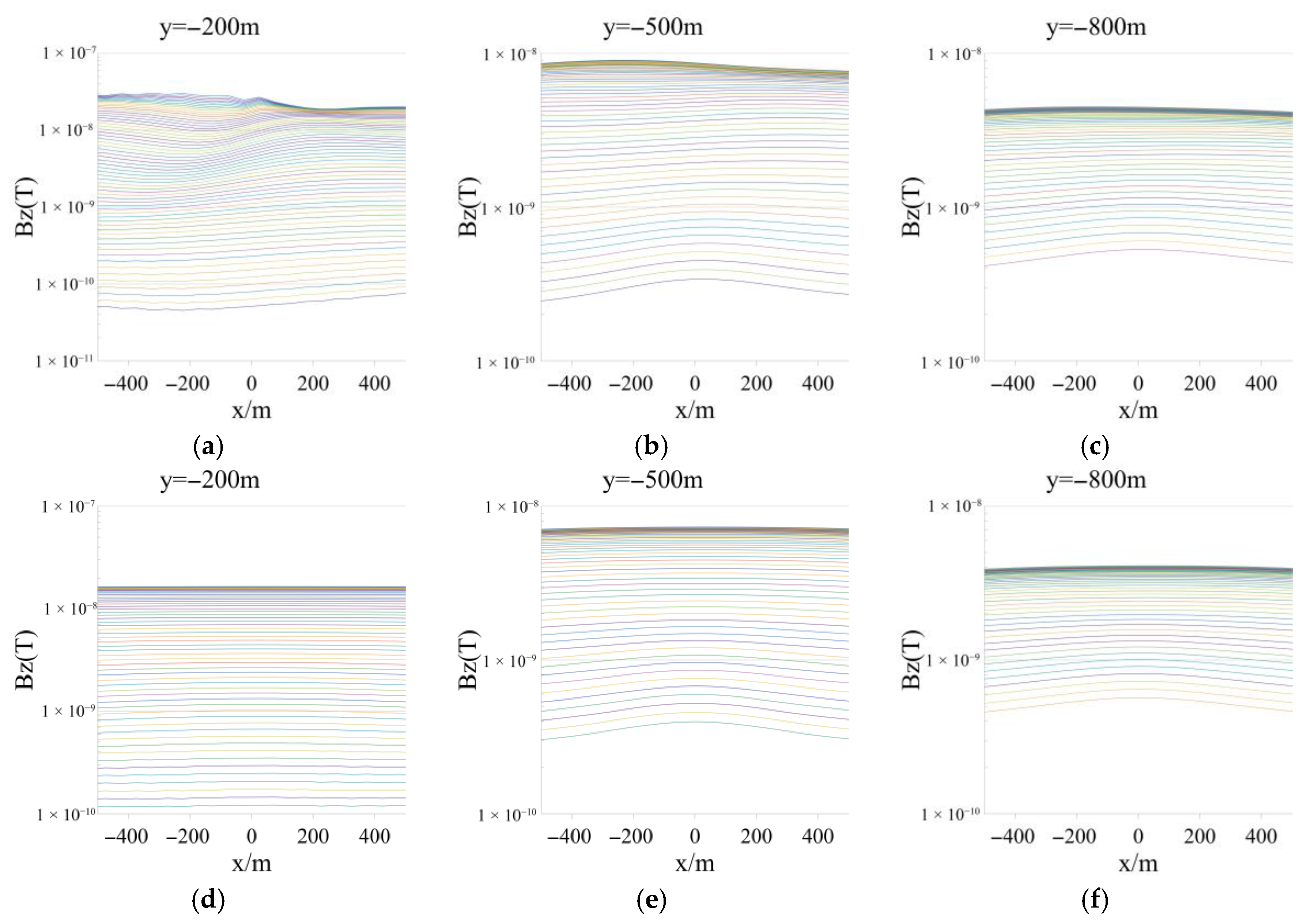
3. Results
3.1. Half-Space Model
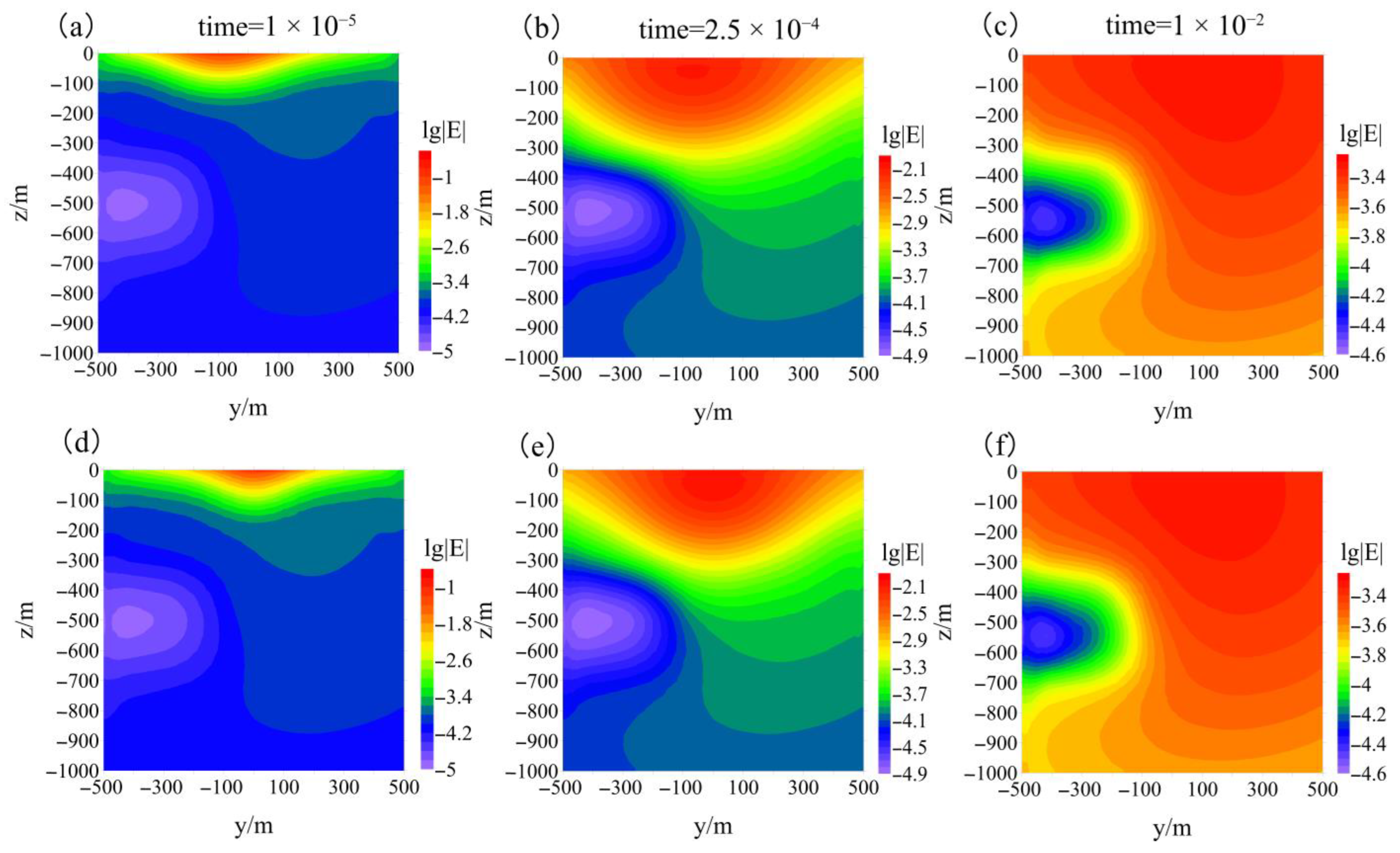
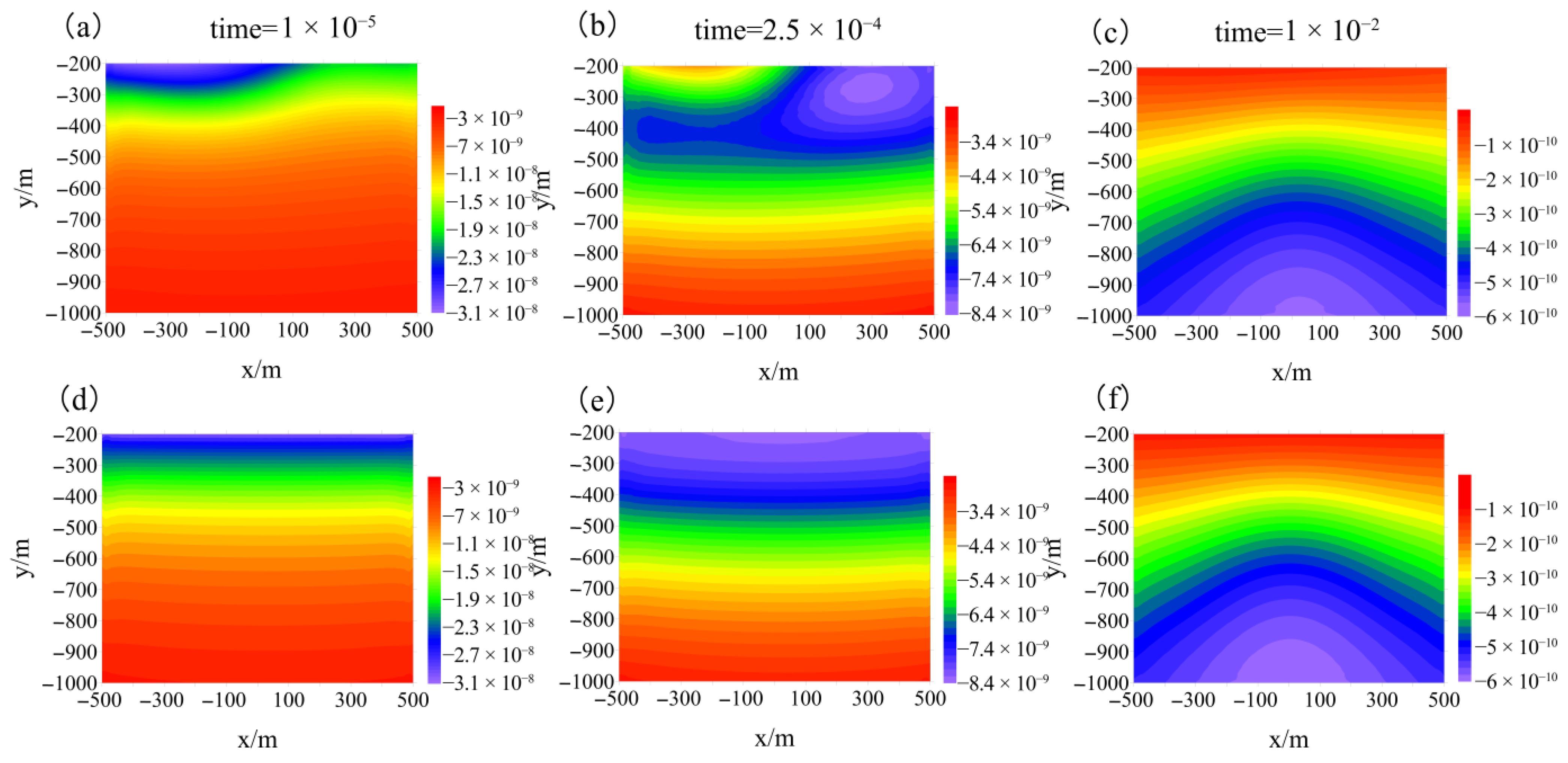
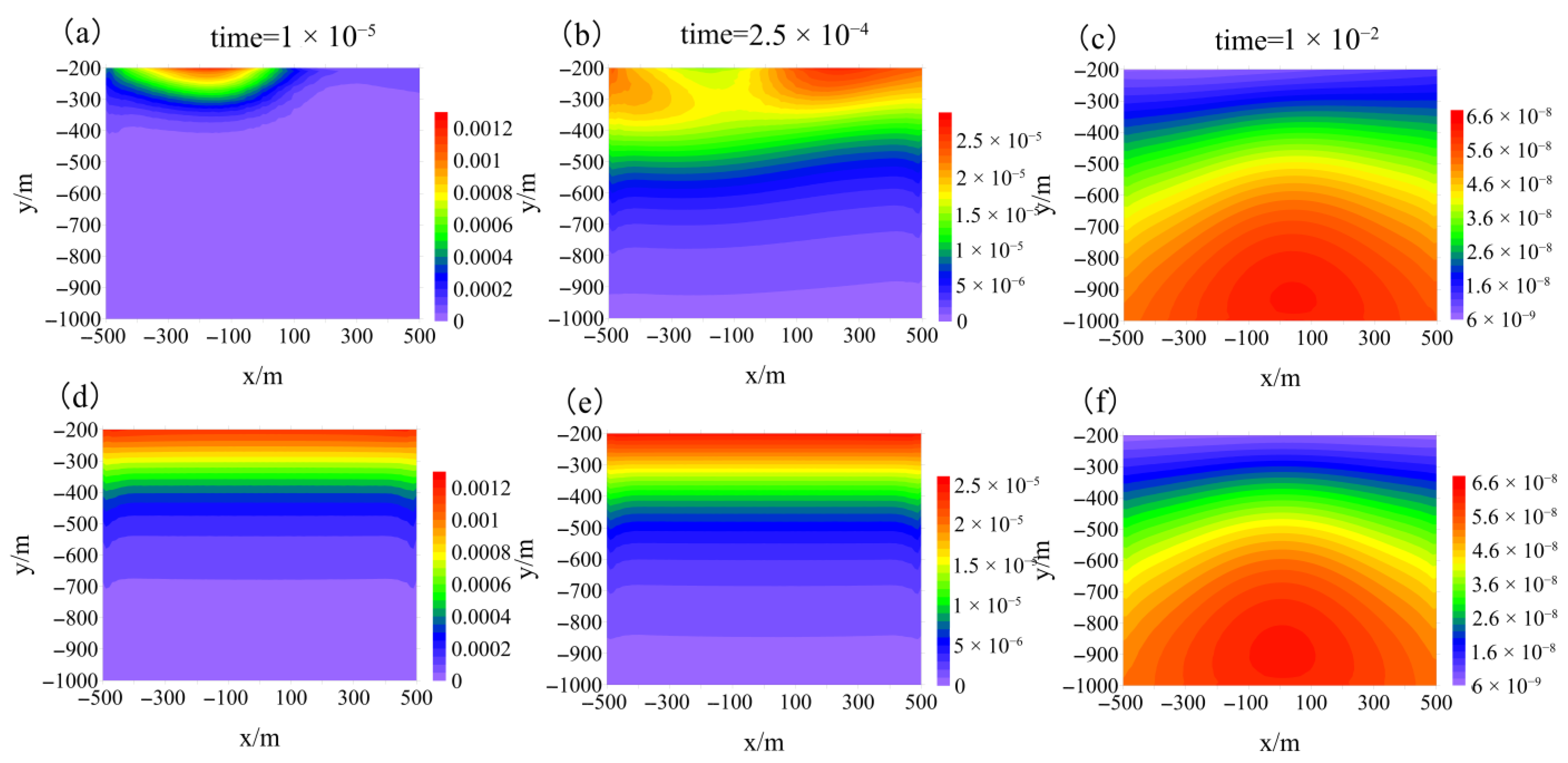
3.1.1. Electric Fields in the Earth
3.1.2. Magnetic Fields in the Air
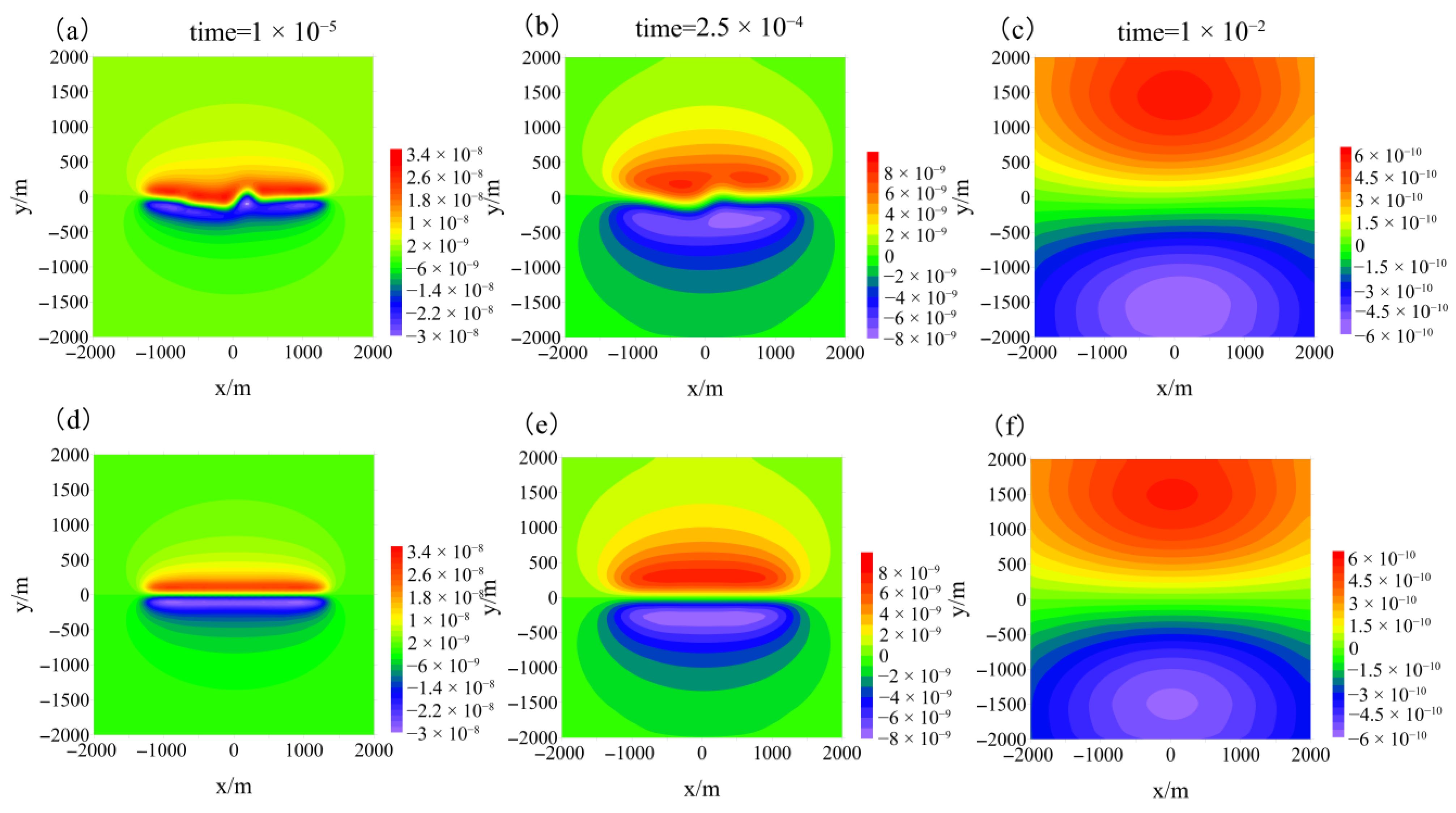
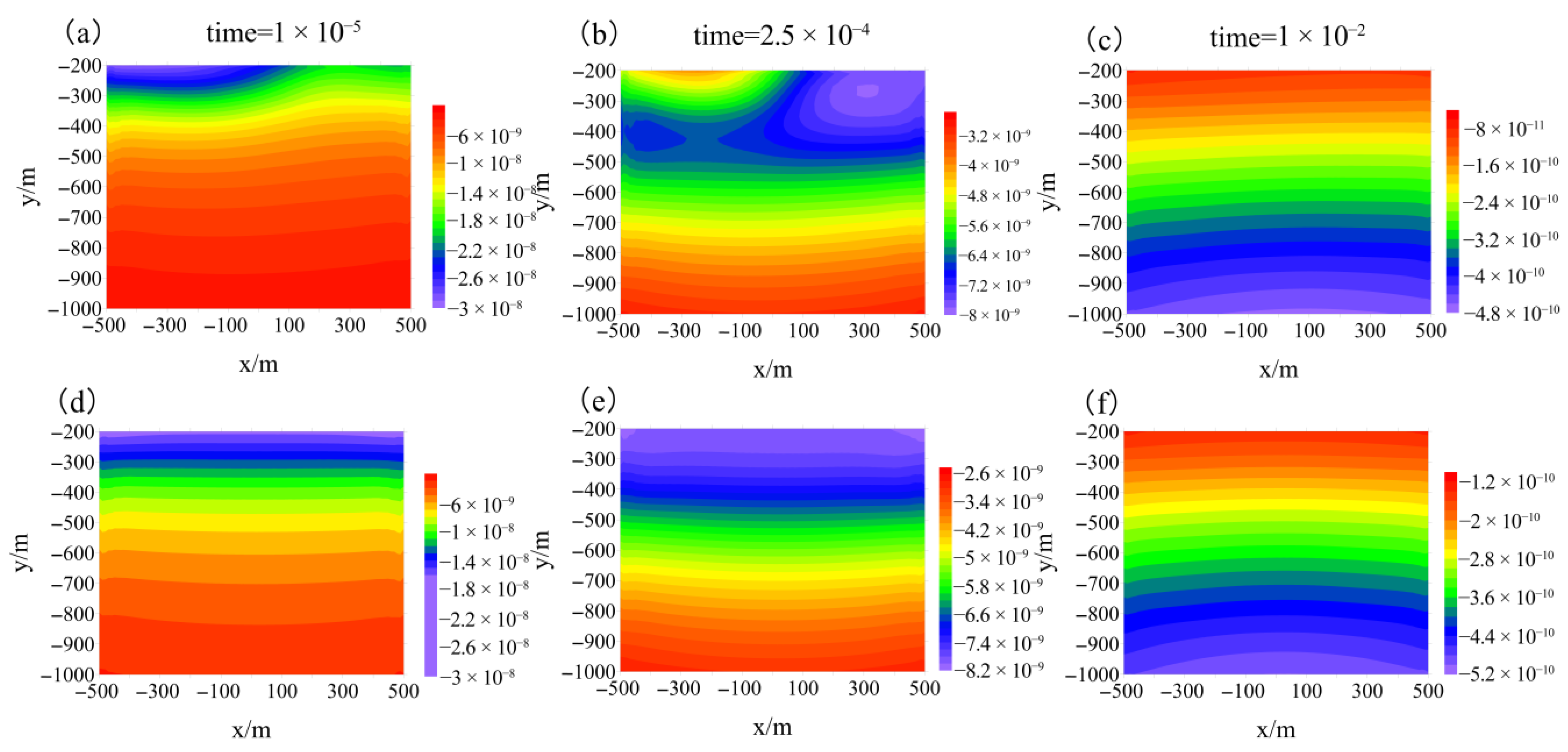
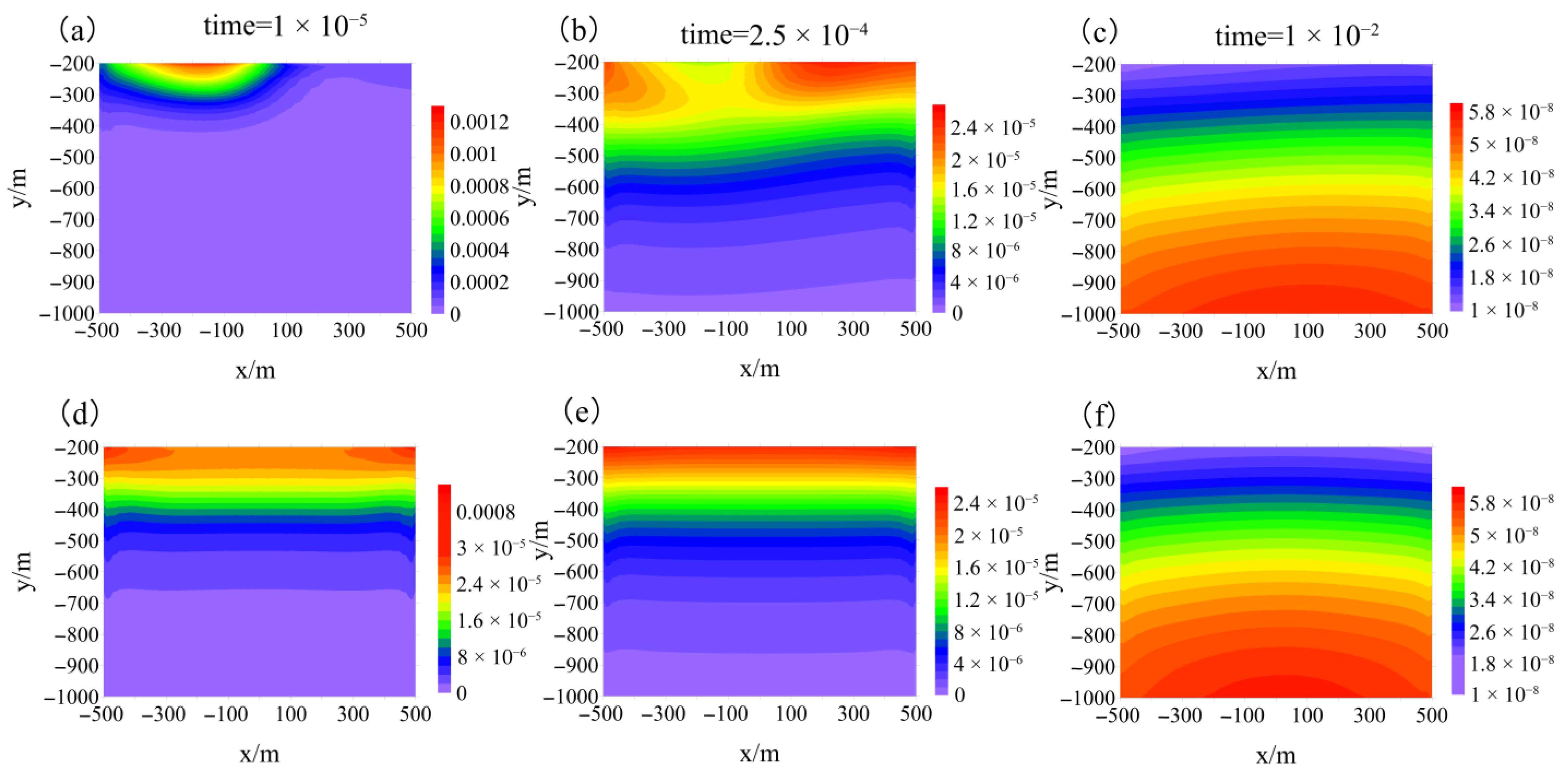
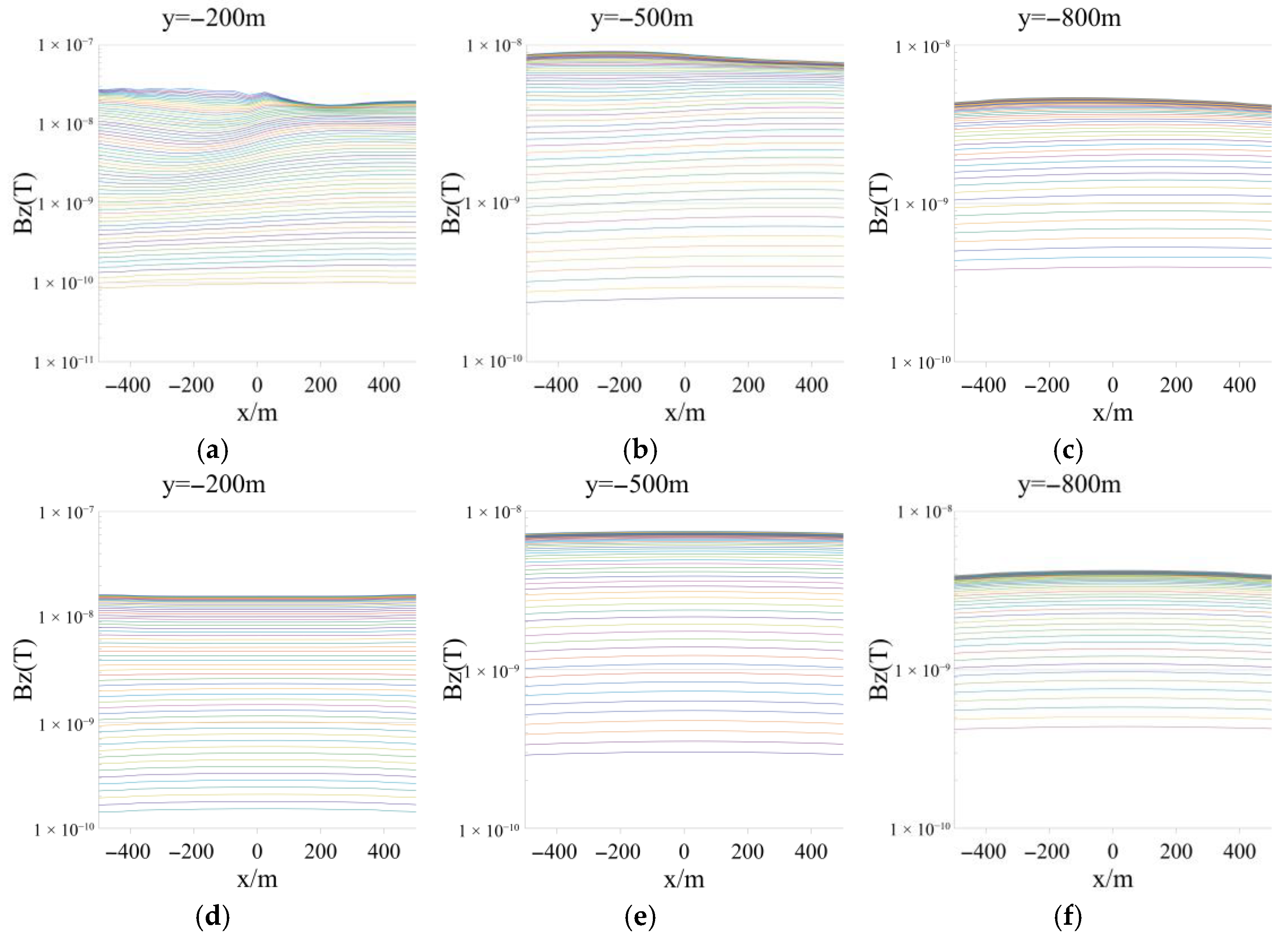
3.2. 3D Model
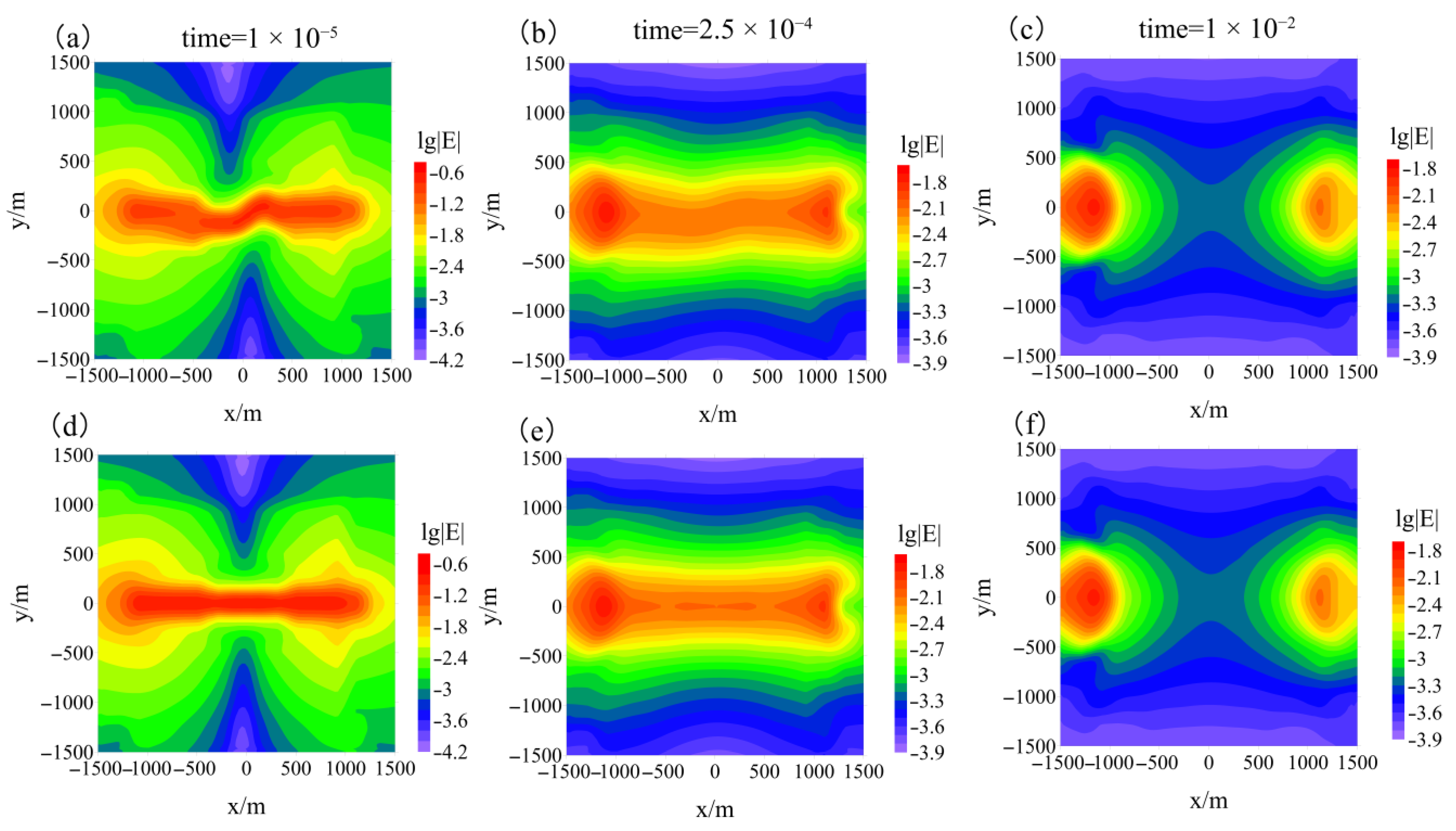
3.2.1. Electric Fields in the Earth
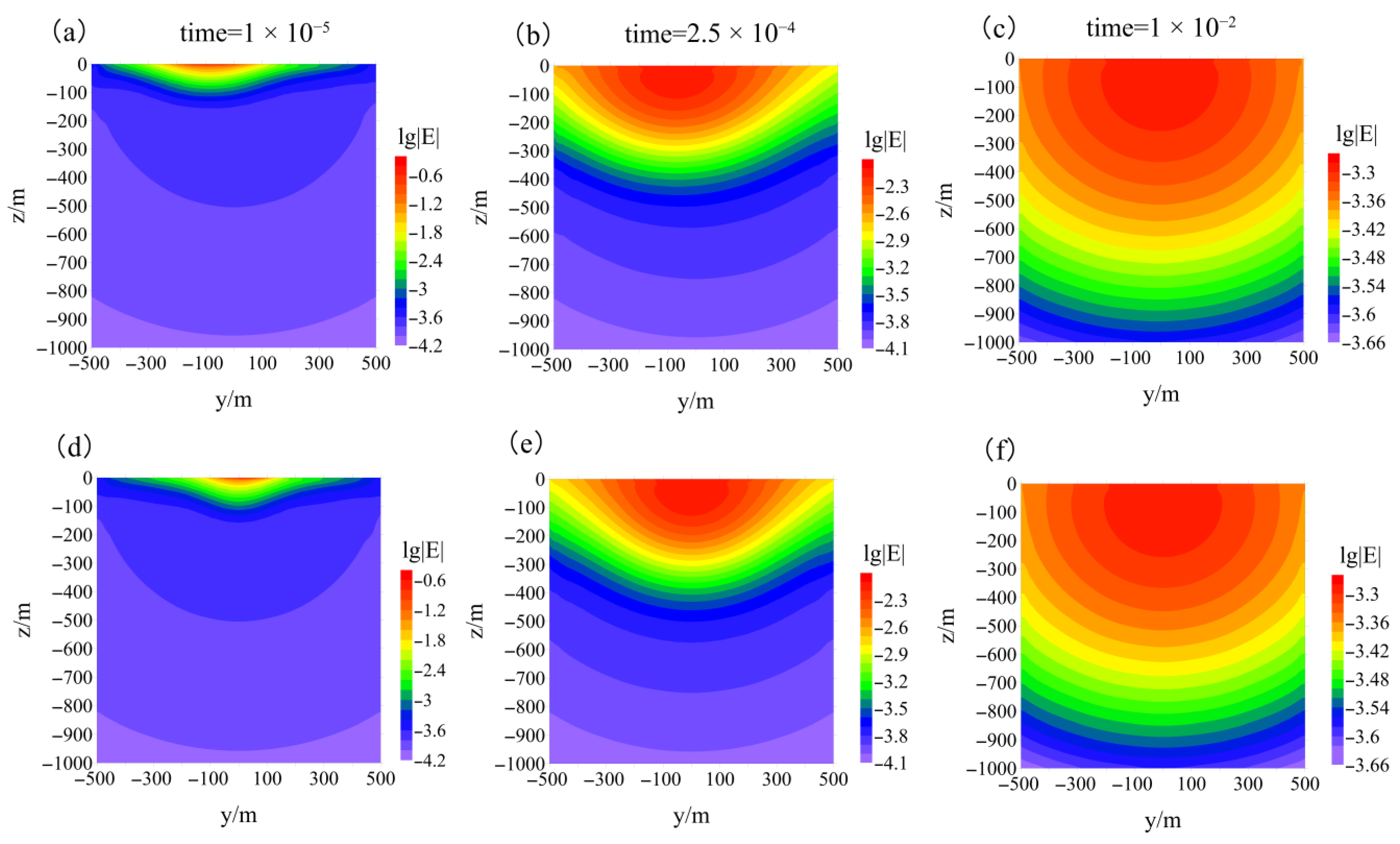
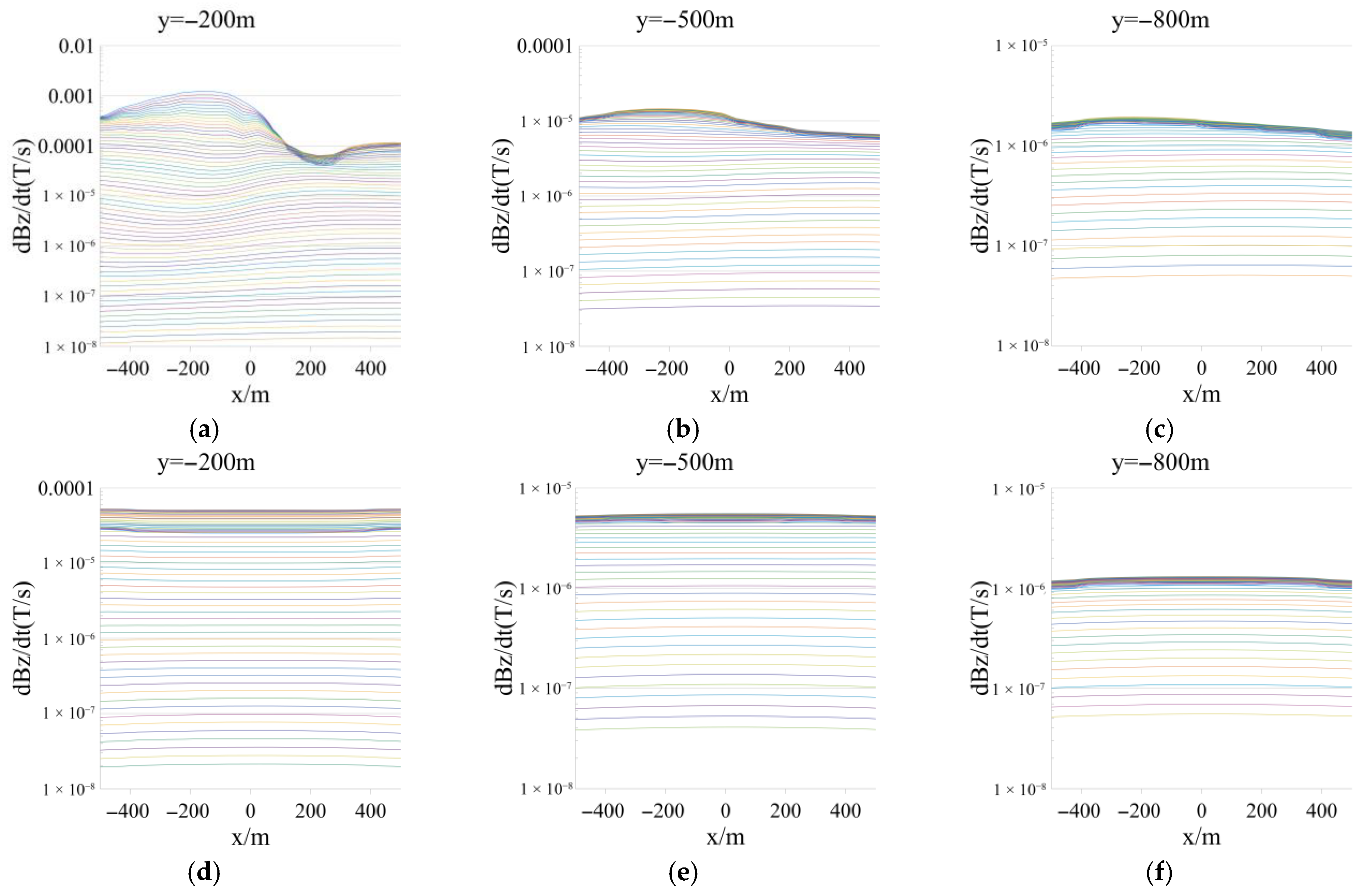
3.2.2. Magnetic Fields in the Air
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, X.; Rao, L.-T.; Luan, X.-D.; Shi, J.-J.; Wang, Y.-B. Design and Development of a Semiairborne Transient Electromagnetic System. Geophysics 2024, 89, E255–E266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Zhang, S. Comparison of Semi-Airborne Transient Electromagnetic Data from Double-Line and Single-Line Grounded-Wire Sources. J. Appl. Geophys. 2022, 197, 104538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becken, M.; Kotowski, P.O.; Schmalzl, J.; Symons, G.; Brauch, K. Semi-Airborne Electromagnetic Exploration Using a Scalar Magnetometer Suspended below a Multicopter. First Break 2022, 40, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Di, Q.; Lei, D.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, J.; Xue, G. The Optimal Survey Area of the Semi-Airborne TEM Method. J. Appl. Geophys. 2020, 172, 103884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Sun, H. Characteristic Analysis and Optimal Survey Area Definition for Semi-Airborne Transient Electromagnetics. J. Appl. Geophys. 2020, 180, 104134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steuer, A.; Smirnova, M.; Becken, M.; Schiffler, M.; Günther, T.; Rochlitz, R.; Yogeshwar, P.; Mörbe, W.; Siemon, B.; Costabel, S.; et al. Comparison of Novel Semi-Airborne Electromagnetic Data with Multi-Scale Geophysical, Petrophysical and Geological Data from Schleiz, Germany. J. Appl. Geophys. 2020, 182, 104172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotowski, P.O.; Becken, M.; Rochlitz, R.; Schmalzl, J.; Ueding, S.; Tolksdorf, P.; Wilhelm, A.; Symons, G. Semi-Airborne Electromagnetic Exploration of Deep Sulfide Deposits with UAV-Towed Magnetometers—Part 1: Processing Modeling. Geophysics 2025, 90, 1–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochlitz, R.; Günther, T.; Kotowski, P.O.; Becken, M. Semi-Airborne Electromagnetic Exploration of Deep Sulfide Deposits with UAV-Towed Magnetometers—Part 2: Inversion Resolution Analysis. Geophysics 2025, 90, 1–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mörbe, W.; Yogeshwar, P.; Tezkan, B.; Kotowski, P.; Thiede, A.; Steuer, A.; Rochlitz, R.; Günther, T.; Brauch, K.; Becken, M. Large-Scale 3D Inversion of Semi-Airborne Electromagnetic Data—Topography and Induced Polarization Effects in a Graphite Exploration Scenario. Geophysics 2024, 89, B339–B352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnova, M.; Juhojuntti, N.; Becken, M.; Smirnov, M. Exploring Kiruna Iron Ore Fields with Large-Scale, Semi-Airborne, Controlled-Source Electromagnetics. First Break 2020, 38, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidenko, Y.; Hallbauer-Zadorozhnaya, V.; Bashkeev, A.; Parshin, A. Semi-Airborne UAV-TEM System Data Inversion with S-Plane Method—Case Study over Lake Baikal. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Li, X.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, J.; Qi, Z.; Li, W.; Li, H. The Application of Multi-Grounded Source Transient Electromagnetic Method in the Detections of Coal Seam Goafs in Gansu Province, China. J. Geophys. Eng. 2021, 18, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Sun, N.; Qi, Z.; Cao, H.; Li, X. The Application of GATEM in Tunnel Geologic Risk Survey Based on Complex Terrain. Geophysics 2024, 89, B453–B465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.S.; Annan, A.P.; McGowan, P.D. A Comparison of Data from Airborne, Semi-airborne, and Ground Electromagnetic Systems. Geophysics 2001, 66, 1379–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunderson, B.M.; Newman, G.A.; Hohmann, G.W. Three-dimensional Transient Electromagnetic Responses for a Grounded Source. Geophysics 1986, 51, 2117–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streich, R.; Becken, M. Electromagnetic Fields Generated by Finite-Length Wire Sources: Comparison with Point Dipole Solutions: EM Fields Generated by Finite-Length Wire Sources. Geophys. Prospect. 2011, 59, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-Y.; Xue, G.-Q.; Cui, J.-W. Analysis on the influence from the shape of electric source TEM transmitter. Prog. Geophys. 2015, 30, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-H.; Huang, Q.-H. 1D forward modeling and inversion algorithm for grounded galvanic source TEM sounding with an arbitrary horizontal wire. Prog. Geophys. 2018, 33, 1515–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Xue, G.; Hou, D.; Lu, Y. An Investigation of the Effect of Source Geometry on Grounded-Wire TEM Surveying with Horizontal Electric Field. J. Environ. Eng. Geophys. 2018, 23, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Weng, A.; Wang, X.; Zou, Z.; Tang, Y.; Wang, T. Source Shape Impact on Controlled Source EM Surveys. J. Appl. Geophys. 2019, 171, 103858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, S.; Rochlitz, R.; Günther, T. Optimizing Semi-Airborne Electromagnetic Survey Design for Mineral Exploration. Minerals 2023, 13, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Farquharson, C.G.; Zhou, J.; Li, X. A Rational Krylov Subspace Method for 3D Modeling of Grounded Electrical Source Airborne Time-Domain Electromagnetic Data. J. Geophys. Eng. 2019, 16, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haber, E. Computational Methods in Geophysical Electromagnetics; Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-1-61197-379-2. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, W.; Li, X.; Qi, Z. 3D Transient Electromagnetic Modeling Using a Shift-and-Invert Krylov Subspace Method. J. Geophys. Eng. 2018, 15, 1341–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-Y.; Li, X.; Yao, W.-H.; Zhi, Q.-Q.; Li, J. Multi-component full field apparent resistivity definition of multi-source ground-airborne transient electromagnetic method with galvanic sources. Chin. J. Geophys. 2015, 58, 2745–2758. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogi, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Kusunoki, K.; Morikawa, T.; Jomori, N. Development of Grounded Electrical Source Airborne Transient EM (GREATEM). Explor. Geophys. 1998, 29, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogi, T.; Kusunoki, K.; Kaieda, H.; Ito, H.; Jomori, A.; Jomori, N.; Yuuki, Y. Grounded Electrical-Source Airborne Transient Electromagnetic (GREATEM) Survey of Mount Bandai, North-Eastern Japan. Explor. Geophys. 2009, 40, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabighian, M.N.; Macnae, J.C. Time Domain Electromagnetic Prospecting Methods. In Electromagnetic Methods in Applied Geophysics: Volume 2, Application, Parts A and B; Investigations in Geophysics; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 1991; pp. 427–520. ISBN 978-1-56080-022-4. [Google Scholar]
- Mörbe, W.; Rochlitz, R.; Kotowski, P.; Tezkan, B.; Yogeshwar, P. Multi-Source 3D Imaging of a Graphite Deposit Combining Drone-Based Semi-Airborne and Ground-Based Electromagnetics. In Proceedings of the 26th EM Induction Workshop, Beppu, Japan, 7–13 September 2024. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Xue, G.; Chen, W.; Tian, Z. Three-Dimensional Inversion of Semi-Airborne Transient Electromagnetic Data Based on a Particle Swarm Optimization-Gradient Descent Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Cai, H.; Liu, M.; Xiong, Y.; Long, Z.; Li, J.; Hu, X. Three-Dimensional Inversion of Semi-Airborne Transient Electromagnetic Data Based on Finite Element Method. Near Surf. Geophys. 2022, 20, 661–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochlitz, R.; Becken, M.; Günther, T. Three-Dimensional Inversion of Semi-Airborne Electromagnetic Data with a Second-Order Finite-Element Forward Solver. Geophys. J. Int. 2023, 234, 528–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, L.; Xie, J.; Liu, W.; Zhou, J. Influence of Source Shape on Semi-Airborne Transient Electromagnetic Surveys. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4389. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084389
Liu L, Xie J, Liu W, Zhou J. Influence of Source Shape on Semi-Airborne Transient Electromagnetic Surveys. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(8):4389. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084389
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Lei, Jianghai Xie, Wentao Liu, and Jianmei Zhou. 2025. "Influence of Source Shape on Semi-Airborne Transient Electromagnetic Surveys" Applied Sciences 15, no. 8: 4389. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084389
APA StyleLiu, L., Xie, J., Liu, W., & Zhou, J. (2025). Influence of Source Shape on Semi-Airborne Transient Electromagnetic Surveys. Applied Sciences, 15(8), 4389. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084389





