Seasonal Analysis and Machine Learning-Based Prediction of Air Pollutants in Relation to Meteorological Parameters: A Case Study from Sakarya, Türkiye
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Collection
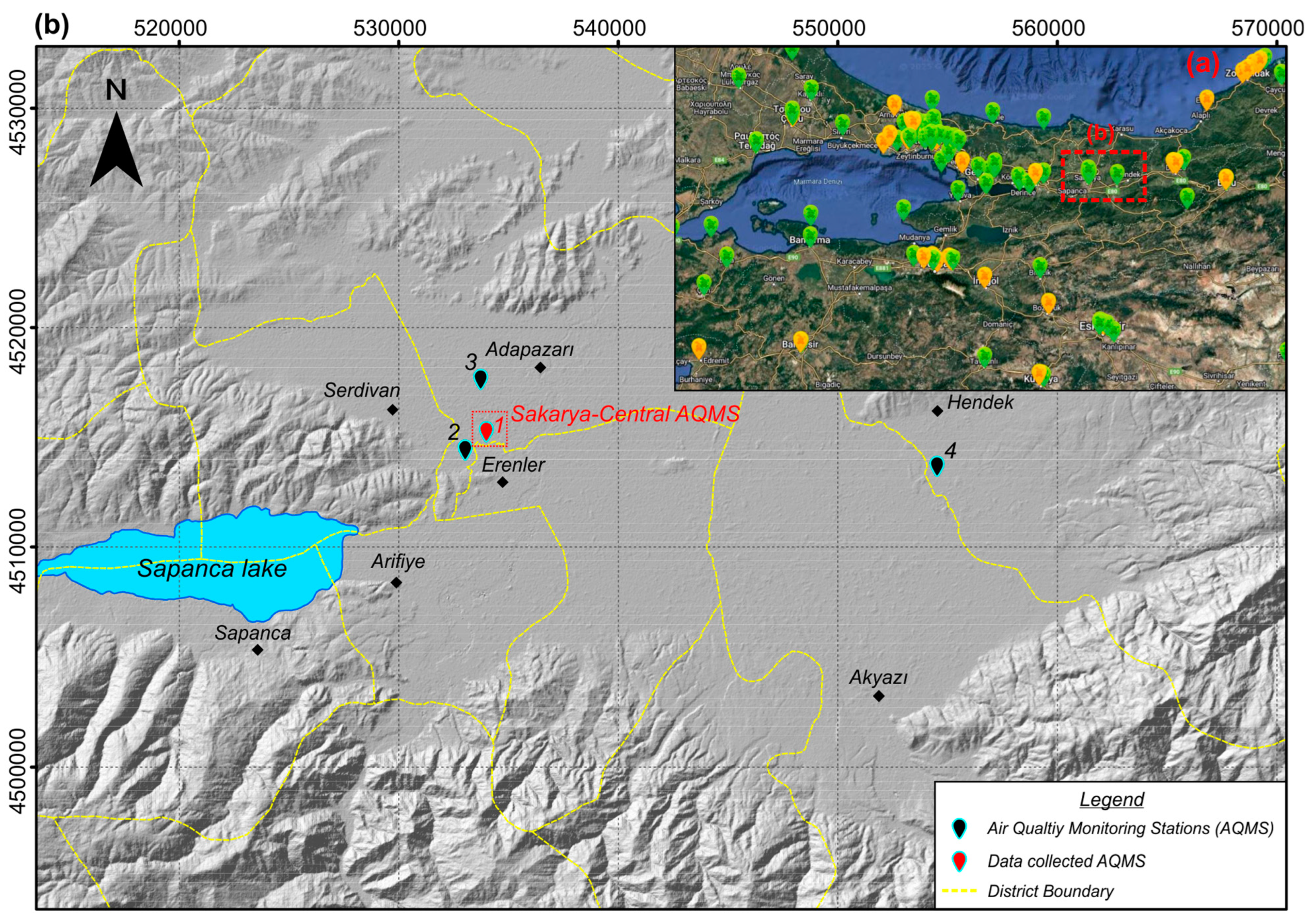
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
3. Methodology
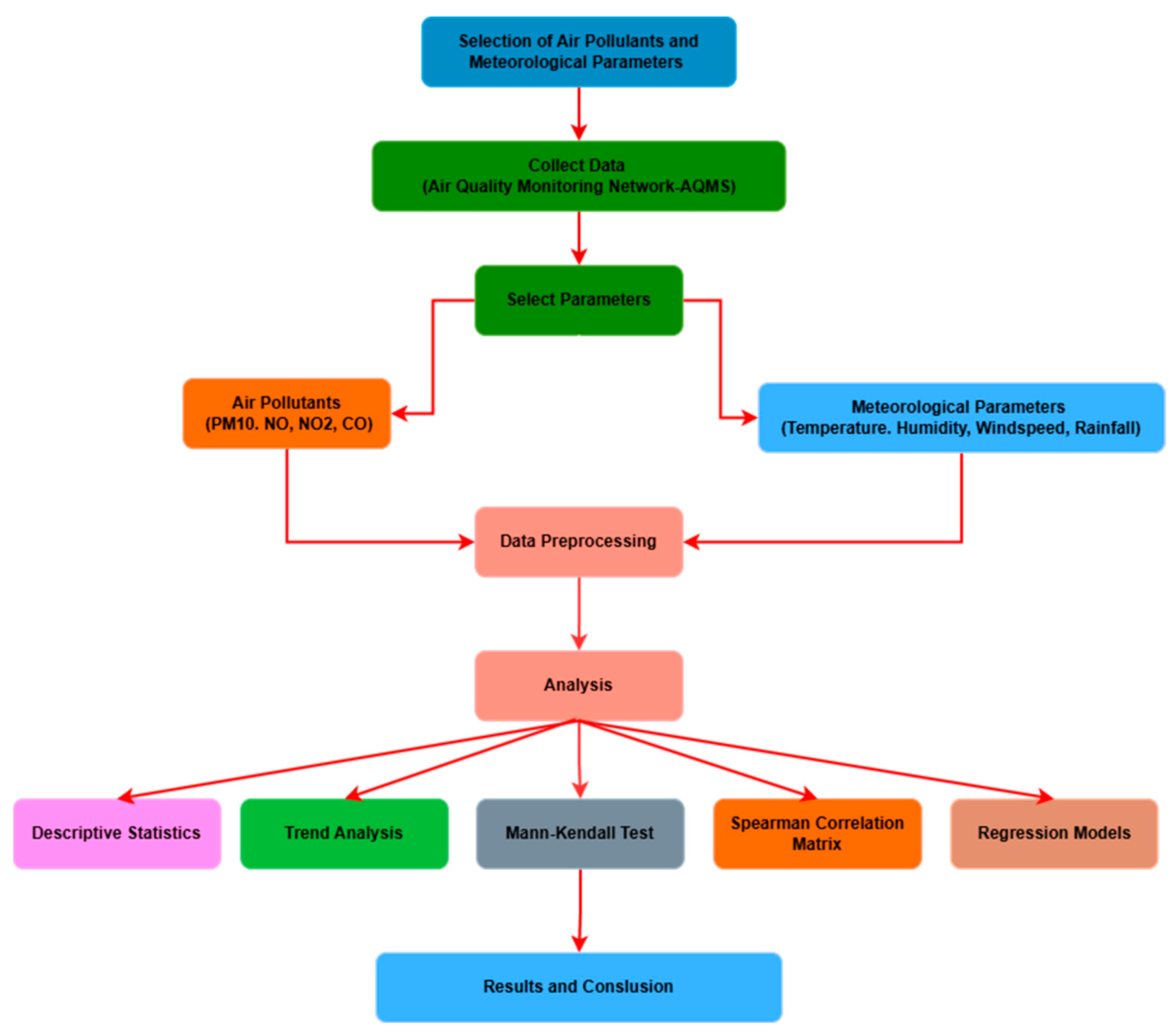
3.1. Analytical Approach
3.2. Statistical and Machine Learning Methods
3.2.1. Descriptive Statistics
3.2.2. Trend Analysis (Mann–Kendall Test)
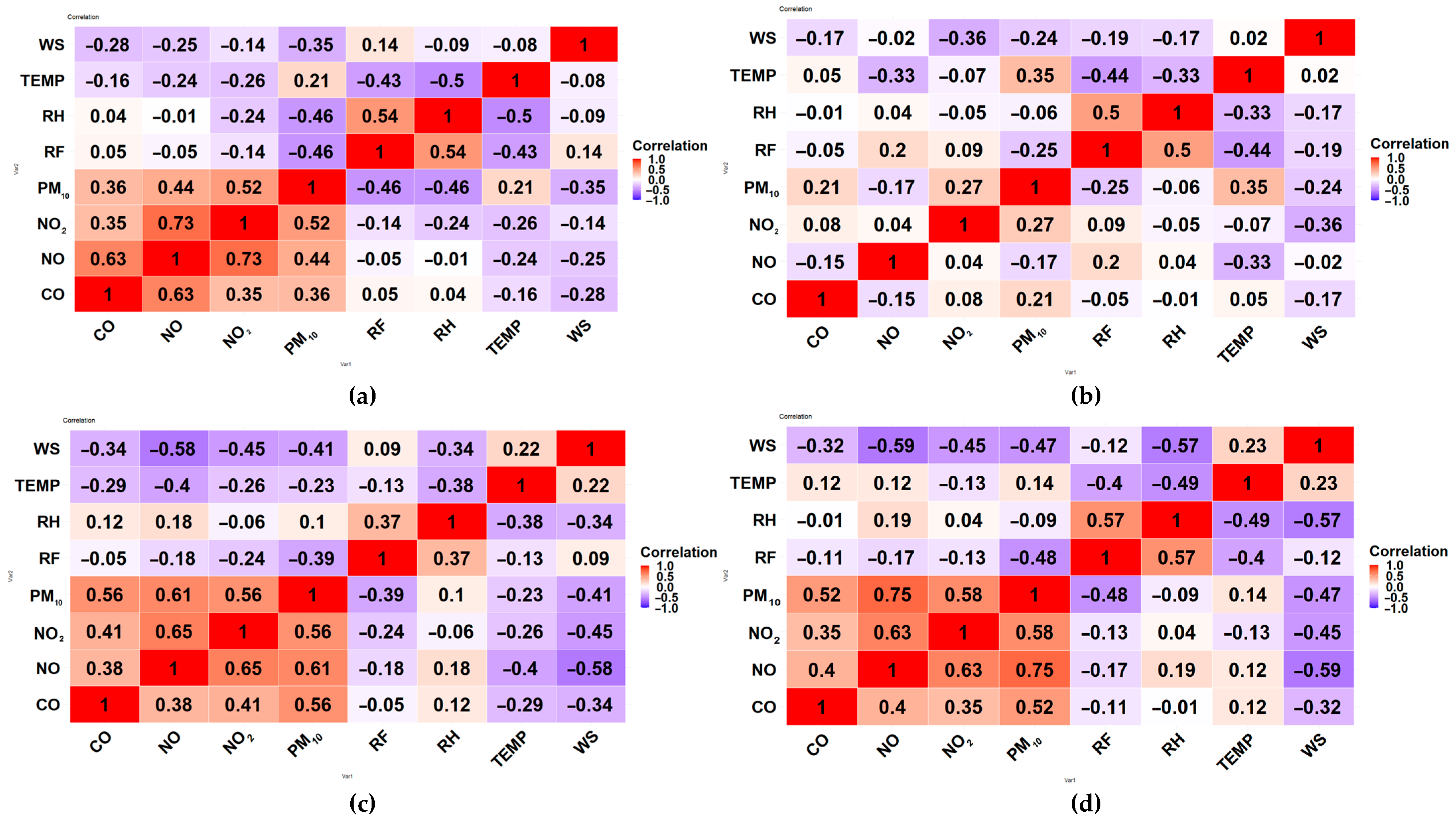
3.2.3. Correlation Analysis
- Positive values indicate a direct relationship.
- Negative values suggest an inverse relationship.
- Values near zero imply no significant association.
3.2.4. Regression Models
MLR
Random Forest (RF) Regression
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Descriptive Statistics and Analysis of Interactions Between Air Pollutants and Meteorological Parameters
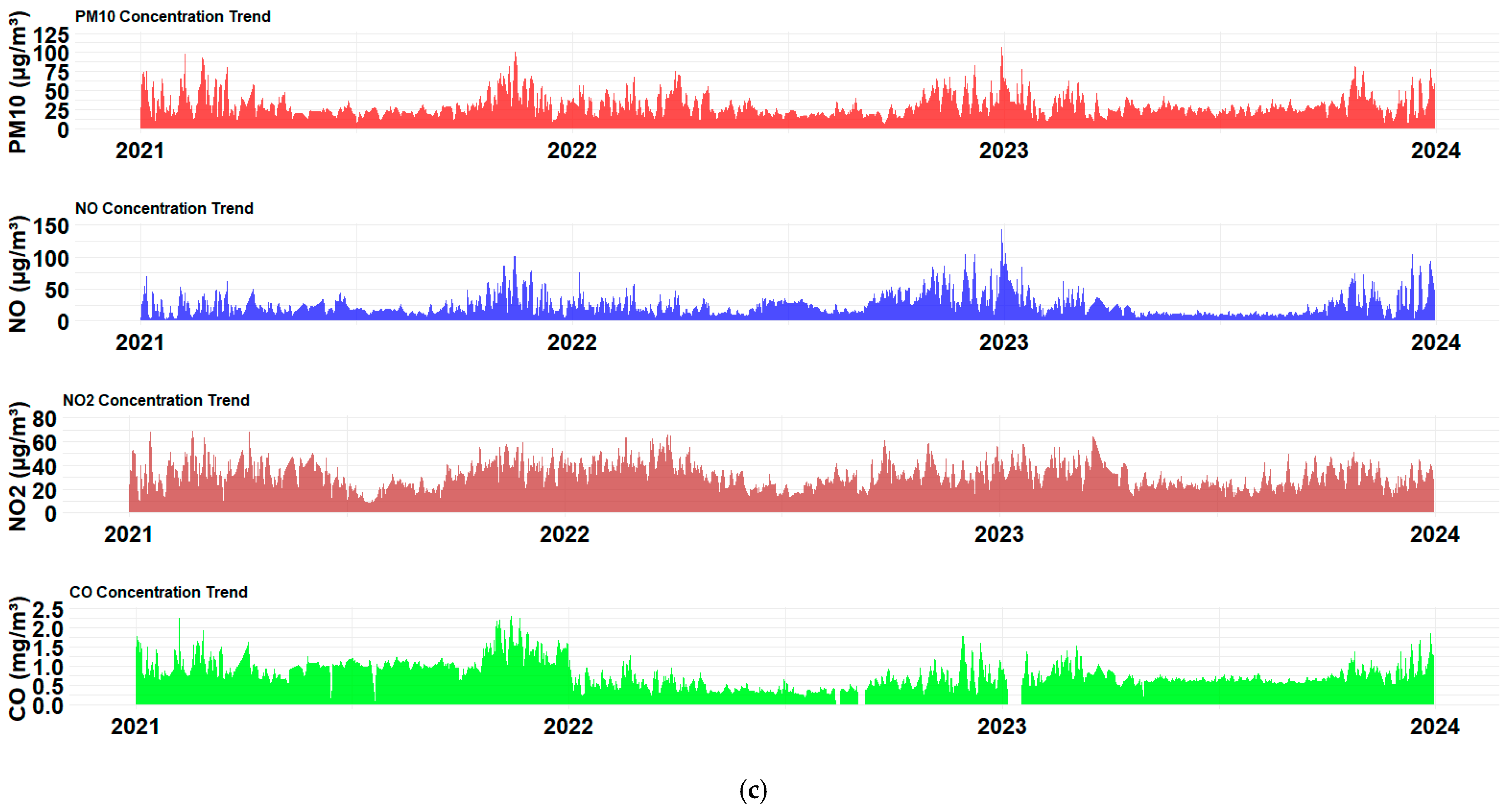
4.2. Temporal Trends and Variations of Air Pollutants and Meteorological Parameters
4.3. Model Comparison for Predicting Air Pollutant Concentrations
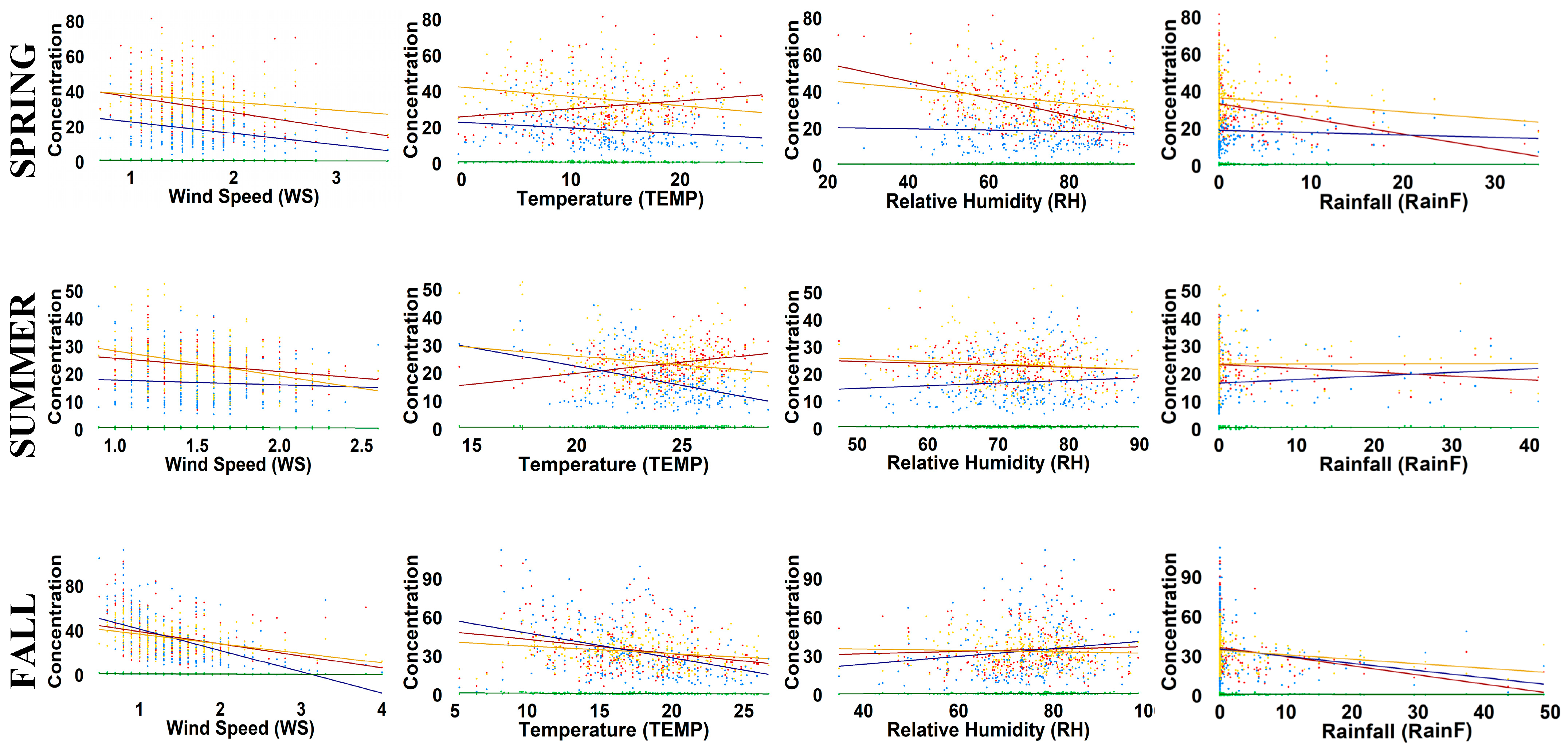
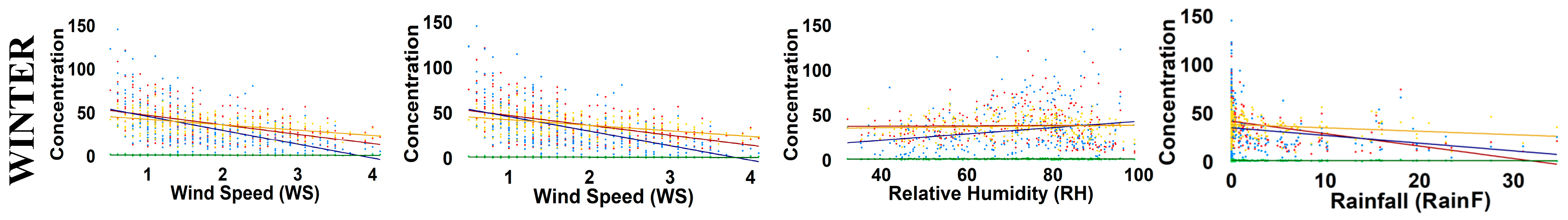
4.4. Seasonal Correlations Between Air Pollutants and Meteorological Parameters
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MLR | Multiple Linear Regression |
| MSE | Mean Squared Error |
| R2 | Coefficient of Determination |
| RainF | Rainfall |
| RF | Random Forest |
| RH | Relative Humidity |
| RMSE | Root Mean Squared Error |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| SE | Standard Error |
| Temp | Temperature |
| WS | Wind Speed |
References
- Meng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Hao, J.; Tao, F.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S. Association between ambient air pollution and daily hospital visits for cardiovascular diseases in Wuhan, China: A time-series analysis based on medical insurance data. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2022, 33, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandotiya, B. Air Pollution, Health and Perception; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbaoma, O.; Ogunkeyede, A.; Adebayo, A.; Otolo, S.; Ikpinima, M. Geostatistical analysis for monitoring and modelling atmospheric pollutants. J. Geogr. Environ. Earth Sci. Int. 2022, 26, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, W.; Yu, M.; Liu, L.; Alam, N.; Gao, Q.; Wang, T. Dynamic relationship between meteorological conditions and air pollutants based on a mixed copula model. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 2611–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Yu, J.; Qin, Y. Spatial distribution of air pollution and its relationship with meteorological factors: A case study of 31 provincial capitals in China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2023, 32, 2513–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Wang, B.; Huang, S. Impacts of meteorological conditions on PM2.5 and PM10 pollution in Zhengzhou, China. E3S Web Conf. 2021, 257, 03025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Yuan, Q.; Li, T.; Shen, H.; Zhang, L. The relationships between PM2.5 and meteorological factors in China: Seasonal and regional variations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Critto, A.; Torresan, S.; Gao, Q. The temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of air pollution index and meteorological elements in Beijing, Tianjin, and Shijiazhuang, China. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2018, 14, 710–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodor, Z.; Bodor, K.; Keresztesi, Á.; Szép, R. Major air pollutants seasonal variation analysis and long-range transport of PM10 in an urban environment with specific climate condition in Transylvania (Romania). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 38181–38199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okimiji, O.; Techato, K.; Simon, J.; Tope-Ajayi, O.; Okafor, A.; Aborisade, M.; Phoungthong, K. Spatial pattern of air pollutant concentrations and their relationship with meteorological parameters in coastal slum settlements of Lagos, Southwestern Nigeria. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gao, J.; Che, F.; Yang, X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, L.; Xiang, Y.; Li, H. Summertime response of ozone and fine particulate matter to mixing layer meteorology over the North China Plain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 14715–14733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Xu, Q.; Wang, W.; Luo, Y.; Tao, L.; Gao, Q.; Guo, J.; Chen, S.; et al. PM2.5 spatiotemporal variations and the relationship with meteorological factors during 2013–2014 in Beijing, China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, J. Exploring the relationship between air pollution and meteorological conditions in China under environmental governance. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Z.; Wu, F.; Xu, X.; Yang, J.; Liu, L. Mechanism of spatiotemporal air quality response to meteorological parameters: A national-scale analysis in China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Wang, S.; Zhao, W.; Xu, X.; Zhang, W.; Arshad, A. Investigating the relationship between air pollutants and meteorological parameters using satellite data over Bangladesh. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, K.; Xu, X. Evaluation of the influence between local meteorology and air quality in Beijing using generalized additive models. Atmosphere 2021, 13, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Cao, H.; Chen, Y.; Wu, C.; Hong, T.; Fan, H. Spatial and temporal characteristics of air quality and air pollutants in 2013 in Beijing. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 13996–14007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xue, W.; Lei, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, S.; Ren, Z.; Huang, Q. Impact of meteorological conditions on PM2. 5 pollution in China during winter. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Sabbah, I.; Kwak, H.; Prasad, A.; Lee, W.; Kafatos, M. Studying air pollutants origin and associated meteorological parameters over Seoul from 2000 to 2009. Adv. Meteorol. 2015, 2015, 704178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eduk, A.; Leo, C.; Andrew, A.; Mudiaga, C. Prediction and modeling of dry seasons air pollution changes using multiple linear regression model: A case study of Port Harcourt and its environs, Niger Delta, Nigeria. Int. J. Environ. Agric. Biotechnol. 2018, 3, 899–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Zhu, T.; Fang, Y.; Li, Y.; Han, Y.; Wu, Y.; Hu, M.; Wang, J. The role of meteorological conditions and pollution control strategies in reducing air pollution in Beijing during APEC 2014 and Victory Parade 2015. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 13921–13940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ma, N. Research on air quality prediction method based on GA-BP model. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Application and Information Security (ICCAIS 2021), Wuhan, China, 18–19 December 2021; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2022; Volume 12260, pp. 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, X.; Chen, Z.; Zeng, G.; León, T.; Liang, J.; Huang, G.; Gao, Z.; Jiao, S.; He, X.; et al. Land use regression models coupled with meteorology to model spatial and temporal variability of NO2 and PM10 in Changsha, China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 116, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.M. Improved Air Quality Forecasting-Based on Machine Learning and Multivariate Regression Techniques. Interciencia 2024, 35, 2–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.M. Assessment of Improved Artificial Neural Network Models for Urban Air Quality Forecasting by Transboundary Pollutants. Interciencia 2025, 36, 47–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, M.; Aulakh, I. Meteorological factors correlation with air pollutants: A case study in Delhi. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. 2023, 14, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vani, P.C.; Sahoo, B.C.; Paul, J.C.; Sahu, A.P.; Mohapatra, A.K.B. Trend analysis in gridded rainfall data using Mann-Kendall and Spearman’s Rho tests in Kesinga Catchment of Mahanadi River Basin, India. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2023, 180, 4339–4353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Meng, Y.; Lou, E.; Li, Y. Analysis of global temperature influencing factors based on Spearman correlation coefficient method and grey correlation theory. Highlights Sci. Eng. Technol. 2023, 48, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Mei, G.; Izzo, S. Revealing influence of meteorological conditions on air quality prediction using explainable deep learning. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 50755–50773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, A.; Roy Chowdhury, I. Investigating the association between air pollutants’ concentration and meteorological parameters in a rapidly growing urban center of West Bengal, India: A statistical modeling-based approach. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2023, 9, 2877–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabello-Torres, R.J.; Estela, M.A.P.; Sánchez-Ccoyllo, O.; Romero-Cabello, E.A.; Ávila, F.F.G.; Castañeda-Olivera, C.A.; Valdiviezo-Gonzales, L.; Eulogio, C.E.Q.; Cruz, A.R.H.D.L.; López-Gonzales, J.L. Statistical modeling approach for PM10 prediction before and during confinement by COVID-19 in South Lima, Perú. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamić, L.; Gašparović, M.; Kaplan, G. Developing PM2.5 and PM10 prediction models on a national and regional scale using open-source remote sensing data. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
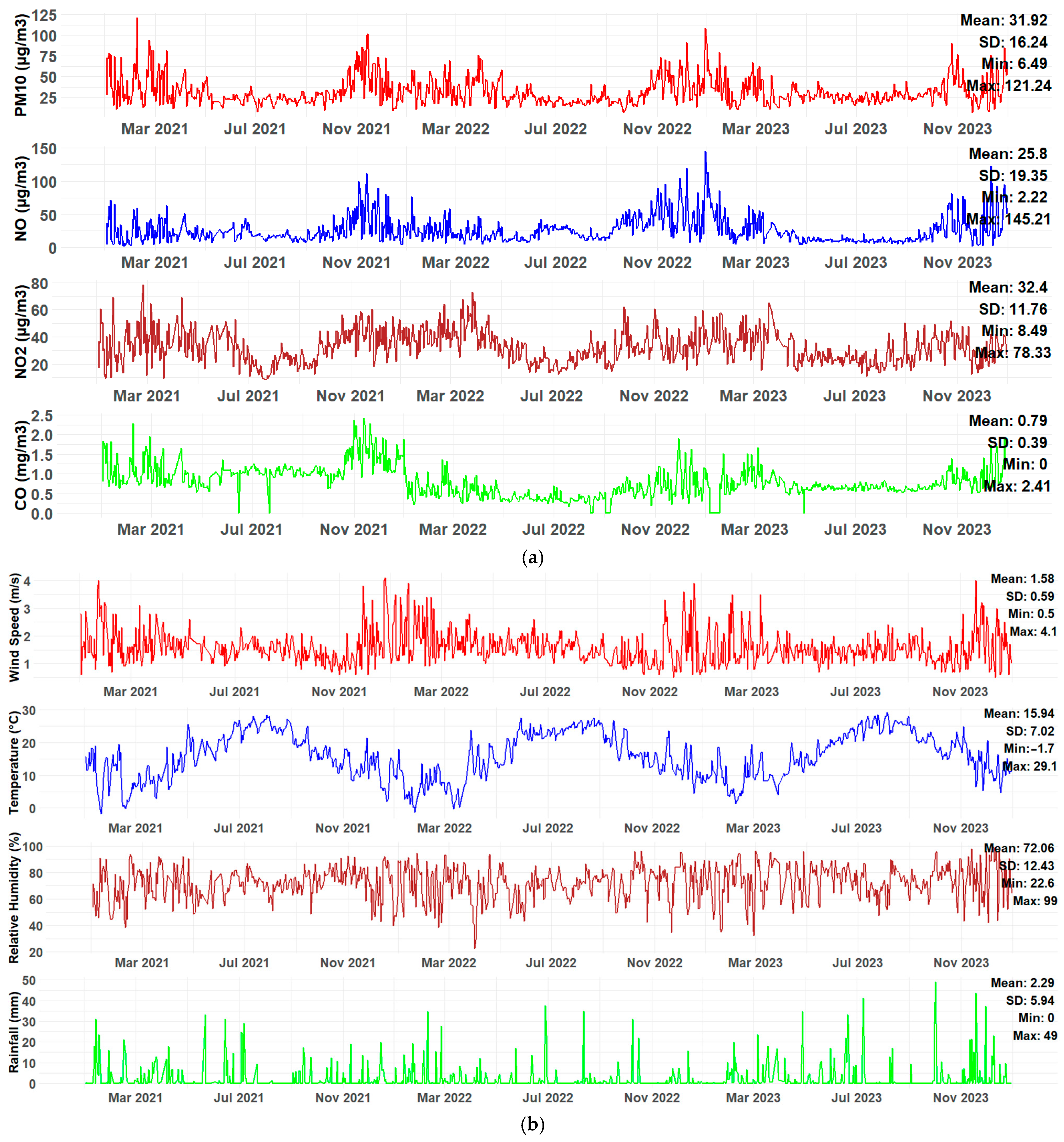
| Parameters | Min | Max | Mean | Median | SD | SE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM10 (µg/m3) | 6.49 | 121.24 | 31.92 | 27.14 | 16.24 | 0.51 |
| NO (µg/m3) | 2.22 | 145.21 | 25.8 | 20 | 19.35 | 0.60 |
| NO2 (µg/m3) | 8.49 | 78.33 | 32.4 | 31.32 | 11.76 | 0.37 |
| CO (mg/m3) | 0 | 2.41 | 0.79 | 0.71 | 0.39 | 0.01 |
| WS (m/s) | 0.5 | 4.1 | 1.58 | 1.5 | 0.59 | 0.02 |
| TEMP (°C) | −1.7 | 29.1 | 15.94 | 16 | 7.02 | 0.22 |
| RH (%) | 22.6 | 99 | 72.06 | 73.5 | 12.43 | 0.39 |
| RainF (mm) | 0 | 49 | 2.30 | 0 | 5.94 | 0.19 |
| Statistics | PM10 | NO | NO2 | CO |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tau value | 0.000563 | −0.0235 | −0.0879 | −0.167 |
| z-value | −9.14 × 10−5 | −9.36 × 10−5 | −9.95 × 10−5 | −0.00010675 |
| p-value | 0.97854 | 0.25939 | 2.54 × 10−5 (<0.01) | 1.32 × 10−15 (<0.01) |
| Sen’s slope | 3.11771 × 10−5 | −0.001506558 | −0.005354839 | −0.0003175113 |
| Pollutants | Models | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF | MLR | |||||
| R2 | MSE | RMSE | R2 | MSE | RMSE | |
| PM10 | 0.78 | 68.56 | 8.28 | 0.36 | 162.9 | 12.76 |
| NO | 0.71 | 139.48 | 11.81 | 0.32 | 217.6 | 14.75 |
| NO2 | 0.65 | 49.14 | 7.01 | 0.5 | 67.7 | 8.23 |
| CO | 0.39 | 0.02 | 0.31 | 0.18 | 0.13 | 0.36 |
| Meteorological Parameters | Seasons | PM10 | NO | NO2 | CO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WS | Spring | −0.35 | −0.25 | −0.14 | −0.28 |
| Summer | −0.24 | −0.024 | −0.36 | −0.17 | |
| Fall | −0.41 | −0.58 | −0.45 | −0.34 | |
| Winter | −0.47 | −0.59 | −0.45 | −0.32 | |
| Temperature (TEMP) | Spring | 0.21 | −0.24 | −0.27 | −0.16 |
| Summer | 0.35 | −0.33 | −0.07 | 0.054 | |
| Fall | −0.23 | −0.4 | −0.26 | −0.29 | |
| Winter | 0.14 | 0.12 | −0.13 | 0.12 | |
| RH | Spring | −0.46 | −0.006 | −0.24 | 0.04 |
| Summer | −0.058 | 0.036 | −0.048 | −0.007 | |
| Fall | 0.097 | 0.18 | −0.059 | 0.12 | |
| Winter | −0.093 | 0.19 | 0.044 | −0.009 | |
| RainF | Spring | −0.46 | −0.05 | −0.14 | 0.045 |
| Summer | −0.25 | 0.2 | 0.093 | −0.054 | |
| Fall | −0.39 | −0.18 | −0.24 | −0.051 | |
| Winter | −0.48 | −0.18 | −0.13 | −0.11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eren, B.; Serat, S.; Arifoglu, Y.D.; Ozdemir, S. Seasonal Analysis and Machine Learning-Based Prediction of Air Pollutants in Relation to Meteorological Parameters: A Case Study from Sakarya, Türkiye. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4551. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084551
Eren B, Serat S, Arifoglu YD, Ozdemir S. Seasonal Analysis and Machine Learning-Based Prediction of Air Pollutants in Relation to Meteorological Parameters: A Case Study from Sakarya, Türkiye. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(8):4551. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084551
Chicago/Turabian StyleEren, Beytullah, Samiullah Serat, Yasemin Damar Arifoglu, and Serkan Ozdemir. 2025. "Seasonal Analysis and Machine Learning-Based Prediction of Air Pollutants in Relation to Meteorological Parameters: A Case Study from Sakarya, Türkiye" Applied Sciences 15, no. 8: 4551. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084551
APA StyleEren, B., Serat, S., Arifoglu, Y. D., & Ozdemir, S. (2025). Seasonal Analysis and Machine Learning-Based Prediction of Air Pollutants in Relation to Meteorological Parameters: A Case Study from Sakarya, Türkiye. Applied Sciences, 15(8), 4551. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084551








