The Effects of Cu-doped TiO2 Thin Films on Hyperplasia, Inflammation and Bacteria Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Cu-doped TiO2 Thin Films Preparation

2.3. Surface Morphology Characterization
2.4. Nitric Oxide (NO) Release in Vitro
2.5. Isolation and Culture of HUASMC
2.6. HUASMC Morphology and Proliferation
2.7. HUASMC Migration
2.8. Morphology of Macrophages
2.9. Anti-Bacterial Performance Assay
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Surface Characterization


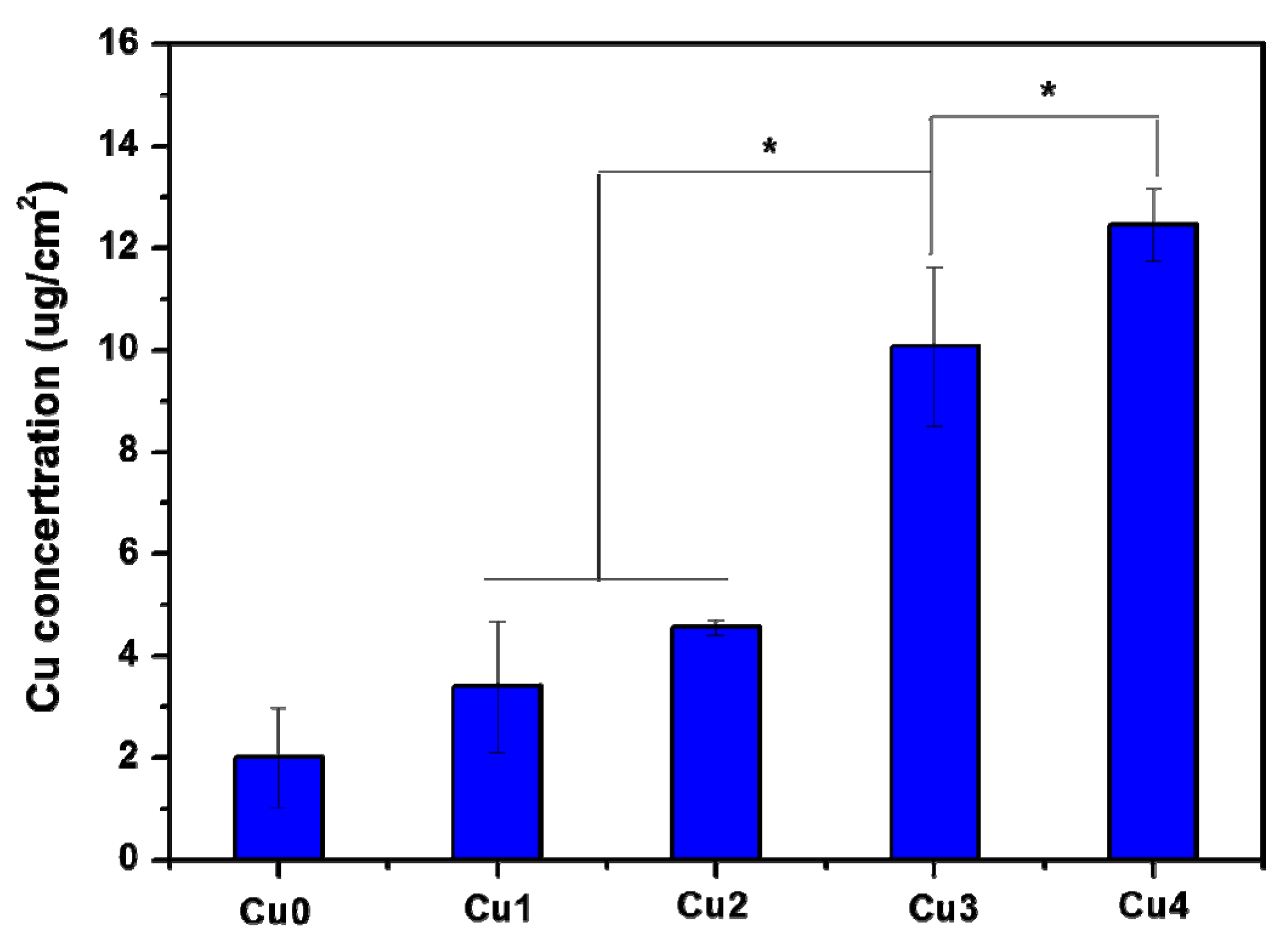
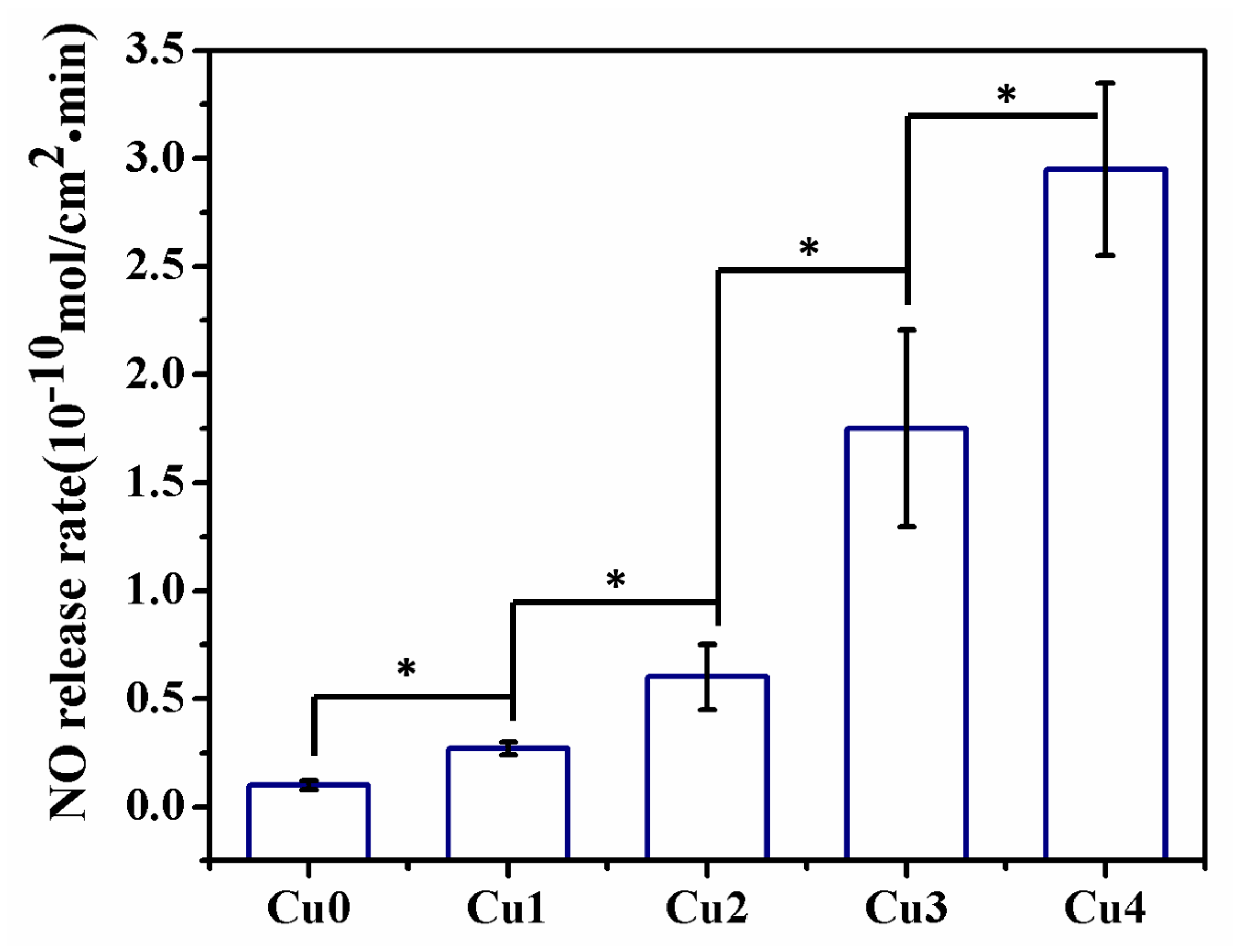
3.2. Nitric Oxide Release in Vitro
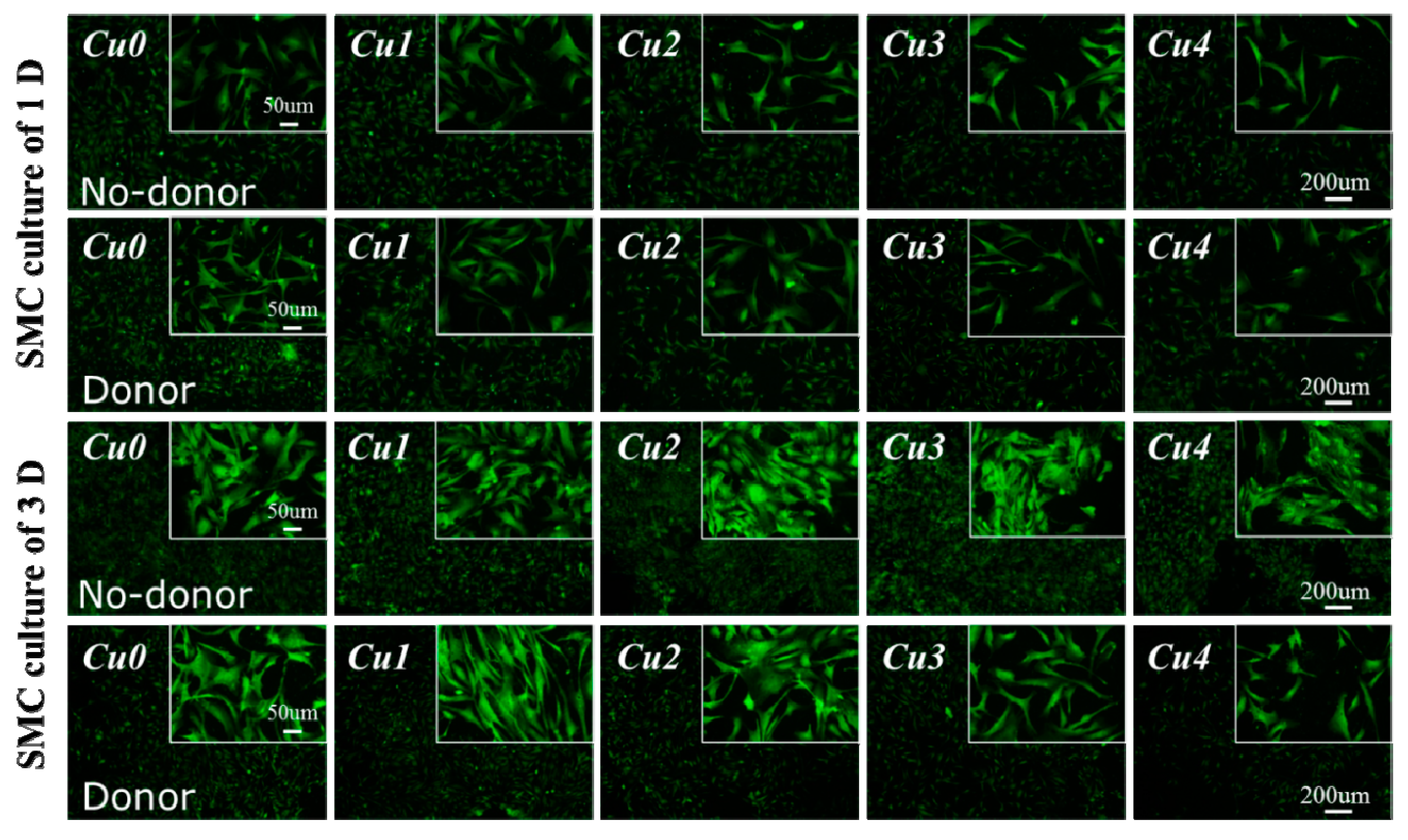
3.3. SMC Attachment and Proliferation

3.4. HUASMC Migration

3.5. Attachment and Morphology of Macrophages


3.6. Antibacterial Experimental Results

4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Williams, D.F. On the mechanisms of biocompatibility. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 2941–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratner, B.D. New ideas in biomaterials science—A path to engineered biomaterials. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1993, 27, 837–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serruys, W.P.; Silber, S.; Garg, S.; van Geuns, R.J.; Richardt, G.; Buszman, E.P. Comparison of Zotarolimus-Eluting and Everolimus-Eluting Coronary Stents. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jukema, W.J.; Ahmed, A.N.T.; Verschuren, J.W.J.; Quax, H.A.P. Restenosis after PCI. Part 2: Prevention and therapy. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2012, 9, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, E.A. Antiplatelet therapy after coronary stenting: For how long? Lancet 2013, 382, 1684–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, S.; Megson, L.I.; Ludlam, A.C.; Fox, A.K.; Newby, E.D. Preserved endothelial vasomotion and fibrinolytic function in patients with acute stent thrombosis or in-stent restenosis. Thromb. Res. 2003, 111, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cushman, M.; Cornell, A.; Folsom, R.A.; Wang, L.; Tsai, Y.M.; Polak, J.; Tang, Z.H. Associations of the β-fibrinogen Hae III and factor VIII Val34Leu gene variants with venous thrombosis. Thromb. Res. 2007, 121, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogita, M.; Miyauchi, K.; Jiang, M.; Kasai, T.; Tsuboi, S.; Naito, R.; Konishi, H.; Dohi, T.; Yokoyama, T.; Okazaki, S.; et al. Circulating soluble LR11, a novel marker of smooth muscle cell proliferation, is enhanced after coronary stenting in response to vascular injury. Atherosclerosis 2014, 237, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfisterer, M.; Brunner-La, R.H.P.; Buser, P.T.; Rickenbacher, P.; Hunziker, P.; Mueller, C. Late clinical events after clopidogrel discontinuation may limit the benefit of drug-eluting stents: An observational study of drug-eluting versus bare-metal stents. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 48, 2584–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenstein, E.L.; Anstrom, K.J.; Kong, D.F.; Shaw, L.K.; Tuttle, R.H.; Mark, D.B. Clopidogrel use and long-term clinical outcomes after drug-eluting stent implantation. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2007, 297, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, N.A. Restenosis following implantation of bare metal coronary stents: Pathophysiology and pathways involved in the vascular response to injury. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2006, 58, 358–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woods, T.C.; Marks, A.R. Drug-eluting stents. Annu. Rev. Med. 2004, 55, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, A.R.; Halliday, A.C.; Miller, M.A.; Diver, A.L.; Dakin, S.R.; Montgomery, J.; McBride, W.M.; Kennedy, S.; McClure, D.J.; Robertson, E.K.; et al. Reducing In-Stent Restenosis: Therapeutic Manipulation of miRNA in Vascular Remodeling and Inflammation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 65, 2314–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, M.; Baruch, R.; Kaplan, E.; Mittelman, M.; Aviram, G.; Siegman-Igra, Y. Coronary stent bacterial infection with multiple organ septic emboli. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2005, 16, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.H.; Shen, L.H.; He, B. Moving with and beyond CANTOS: How to put out the fire of inflammation in atherosclerosis? Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 195, 45–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitiello, L.; Spoletini, I.; Gorini, S.; Pontecorvo, L.; Ferrari, D.; Ferraro, E.; Stabile, E.; Caprio, M.; Sala, A. Microvascular inflammation in atherosclerosis. IJC Metab. Endocr. 2014, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, T.A.; Mensah, G.A.; Alexander, R.W.; Anderson, J.L.; Cannon, R.O.; Criqui, M. Markers of inflammation and cardiovascular disease application to clinical and public health practice: A statement for healthcare professionals from the centers for disease control and prevention and the American Heart Association. Circulation 2003, 107, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mombelli, A. Microbiology and antimicrobial therapy of peri-implantitis. Periodontology 2002, 28, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, F.; AlGhamdi, A.S.T.; Ahmed, A.; Mikami, T.; Ahmed, H.B.; Tenenbaum, H.C. Clinical efficacy of antibiotics in the treatment of peri-implantitis. Int. Dent. J. 2013, 63, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diebold, U. The surface science of titanium dioxide. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2003, 48, 53–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.A.; Yang, P.; Zhang, K.; Ren, H.L.; Huang, N. Preparation of SiO2/TiO2 and TiO2/TiO2 micropattern and their effects on platelet adhesion and endothelial cell regulation. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sec. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 2013, 307, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.J.; Li, C.H.; Yang, P.; Li, J.A.; Huang, N. Fabrication of micro-patterned titanium dioxide nanotubes thin film and its biocompatibility. J. Eng. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Chen, J.; Xiang, L.J.; Xu, Y.; Yang, P.; Li, J.A.; Wu, J.J.; Huang, N. Fabrication of 3D TiO2 micromesh on silicon surface and its effects on platelet adhesion. Mater. Lett. 2014, 132, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.J.; Li, J.A.; He, Z.K.; Wu, J.J.; Yang, P.; Huang, N. Design and construction of TiO2 nanotubes in microarray using two-step anodic oxidation for application of cardiovascular implanted devices. Micro Nano Lett. 2015, 10, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, O.; Ghaderi, E. Photocatalytic Reduction of Graphene Oxide Nanosheets on TiO2 Thin Film for Photoinactivation of Bacteria in Solar Light Irradiation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 20214–20220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, O.; Ghaderi, E. Flash Photo Stimulation of Human Neural Stem Cells on Graphene/TiO2 Heterojunction for Differentiation into Neurons. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 10316–10326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhavan, O. Lasting antibacterial activities of Ag-TiO2/Ag/a-TiO2 nanocomposite thin film photocatalysts under solar light irradiation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 336, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, B.; Huang, L.; Fang, Y.Q.; Guo, R.W.; Yin, Y.G.; Zhao, X.H. Transplantation of endothelial progenitor cells overexpressing endothelial nitric oxide synthase enhances inhibition of neointimal hyperplasia and restores endothelium-dependent vasodilatation. Microvasc. Res. 2011, 81, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamawaki, H.; Kameshima, S.; Usui, T.; Okada, M.; Hara, Y. A novel adipocytokine, chemerin exerts anti-inflammatory roles in human vascular endothelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 423, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delledonne, M.; Xia, Y.; Dixon, R.A.; Lamb, C. Nitric oxide functions as a signal in plant disease resistance. Nature 1998, 394, 585–588. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Broughton, G.; Janis, J.E.; Attinger, C.E. The basic science of wound healing. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2006, 117, 12S–34S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizk, M.; Witte, M.B.; Barbul, A. Nitric oxide and wound healing. World J. Surg. 2004, 28, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isenberg, J.S.; Ridnour, L.A.; Espey, M.G.; Wink, D.A.; Roberts, D.A. Nitric oxide in wound-healing. Microsurgery 2005, 25, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dicks, A.P.; Williams, D.L.H. Generation of nitric oxide from S-nitrosothiols using protein-bound Cu2+ sources. Chem. Biol. 1996, 3, 655–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.L.H. The chemistry of S-nitrosothiols. Acc. Chem. Res. 1999, 32, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, B.K.; Kim, Y.K.; Park, K.W.; Lee, W.H.; Choi, J.W. Surface plasmon resonance immunosensor for the detection of Salmonella typhimurium. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2004, 19, 1497–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignarro, L.J.; Balestrieri, M.L.; Napoli, C. Nutrition, physical activity, and cardiovascular disease: An update. Cardiovasc. Res. 2007, 73, 326–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radomski, M.V.; Latham, C.A.T. Occupational Therapy for Physical Dysfunction; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Li, J.A.; Yao, L.F.; Li, L.H.; Yang, P.; Huang, N. Preparation and characterization of Cu-doped TiO2 thin films and effects on platelet adhesion. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 261, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.J.; Li, J.A.; Wu, F.; He, Z.K.; Yang, P.; Huang, N. Effect of micropatterned TiO2 nanotubes thin film on the deposition of endothelial extracellular matrix: For the purpose of enhancing surface biocompatibility. Biointerphases 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, R.F.; Tang, L.L.; Zhong, S.; Yang, Z.L.; Wang, J.; Weng, Y.J.; Tu, Q.F.; Jiang, C.X.; Huang, N. In vitro investigation of enhanced hemocompatibility and endothelial cell proliferation associated with quinone-rich polydopamine coating. ASC Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 1704–1714. [Google Scholar]
- Wink, D.A.; Cook, J.A.; Kim, S.Y.; Vodovotz, Y.; Pacelli, R.; Krishna, M.C. Superoxide modulates the oxidation and nitrosation of thiols by nitric oxide-derived reactive intermediates chemical aspects involved in the balance between oxidative and nitrosative stress. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 11147–11151. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, J.A.; Zhang, K.; Xu, Y.; Chen, J.; Yang, P.; Zhao, Y.C.; Zhao, A.S.; Huang, N. A novel co-culture model of HUVECs and HUASMCs by hyaluronic acid micro-pattern on titanium surface. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2014, 102, 1950–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.A.; Zhang, K.; Yang, P.; Liao, Y.Z.; Wu, L.L.; Chen, J.L.; Zhao, A.S.; Li, G.C.; Huang, N. Research of smooth muscle cells response to fluid flow shear stress by hyaluronic acid micro-pattern on a titanium surface. Exp. Cell Res. 2013, 319, 2663–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.C.; Yang, P.; Qin, W.; Maitz, M.F.; Zhou, S.; Huang, N. The effect of coimmobilizing heparin and fibronectin on titanium on hemocompatibility and endothelialization. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 4691–4703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, H.L.; Bae, I.H.; Lim, S.K.; Song, T.I.; Lee, H.; Muthiah, M.; Namgung, R.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, D.G.; Ahn, Y.; et al. Suppression of post-angioplasty restenosis with an Akt1 siRNA-embedded coronary stent in a rabbit model. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 8548–8556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.; Ren, K.F.; Wang, J.L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, B.L.; Zheng, S.M.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Ji, J. Surface-mediated functional gene delivery: An effective strategy for enhancing competitiveness of endothelial cells over smooth muscle cells. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 3345–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, S. Alternative activation of macrophages. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grass, G.; Rensing, C.; Solioz, M. Metallic copper as an antimicrobial surface. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 1541–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, J.; Yang, P.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, N. The Effects of Cu-doped TiO2 Thin Films on Hyperplasia, Inflammation and Bacteria Infection. Appl. Sci. 2015, 5, 1016-1032. https://doi.org/10.3390/app5041016
Li L, Xu Y, Zhou Z, Chen J, Yang P, Yang Y, Li J, Huang N. The Effects of Cu-doped TiO2 Thin Films on Hyperplasia, Inflammation and Bacteria Infection. Applied Sciences. 2015; 5(4):1016-1032. https://doi.org/10.3390/app5041016
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Linhua, Ying Xu, Zhi Zhou, Jiang Chen, Ping Yang, Youhe Yang, Jing’an Li, and Nan Huang. 2015. "The Effects of Cu-doped TiO2 Thin Films on Hyperplasia, Inflammation and Bacteria Infection" Applied Sciences 5, no. 4: 1016-1032. https://doi.org/10.3390/app5041016
APA StyleLi, L., Xu, Y., Zhou, Z., Chen, J., Yang, P., Yang, Y., Li, J., & Huang, N. (2015). The Effects of Cu-doped TiO2 Thin Films on Hyperplasia, Inflammation and Bacteria Infection. Applied Sciences, 5(4), 1016-1032. https://doi.org/10.3390/app5041016




