State of the Art and Trends Review of Smart Metering in Electricity Grids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Trends of the Smart Metering Systems
2.1. Architecture of a Smart Metering System
- A Smart Metering device, Smart Meter (SM);
- A data gathering device, Data Concentrator (DC);
- A communication system used for data flow;
- A centralized management and control system, Control Center (CC).
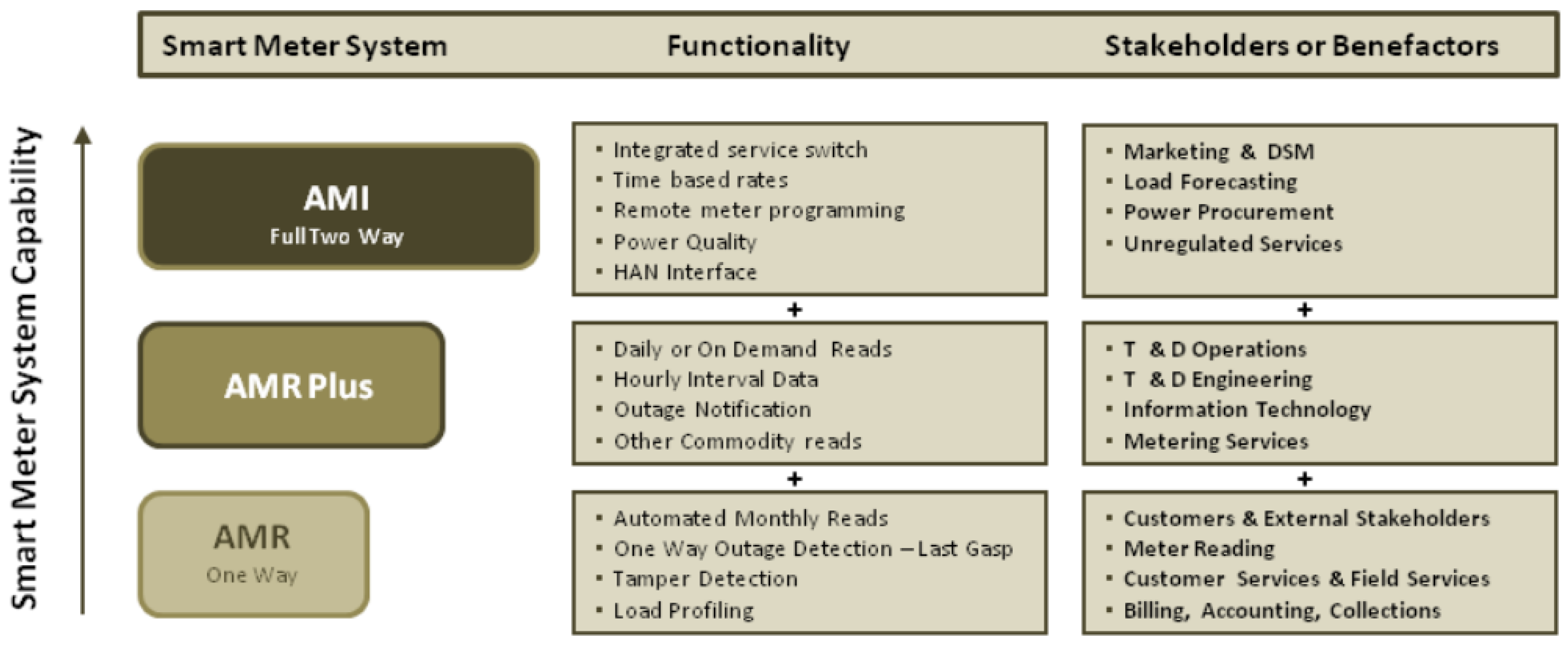
2.1.1. Smart Meter
- Remote reading
- Bidirectional communication
- Support of advanced tariff systems and billing applications
- Remote energy supply control.
2.1.2. Data Concentrator
2.1.3. Communication System
2.1.4. Control Centre
2.2. Considerations for a Smart Metering System
2.3. Smart Metering Applications
- Electricity signal quality:
- DG and DS control:
- Billing:
- Demand Response:
- HAN applications:
- Anti-fraud techniques:
3. Smart Metering Technologies
4. Development of Smart Metering Worldwide
4.1. Europe
4.2. America
4.2.1. The United States
- Systems integration: the introduction of outage and distribution management systems provides enhanced outage management and restoration services as well as improved distribution system and device monitoring.
- Integration of new resources: SMs position the grid as platform for the integration of distributed energy resources (DG, DS, EVs, microgrids, etc.).
- Operational savings: remote activities (reading, connection/disconnection) and the reduction of energy theft are some financial benefits of SMs.
- New customer services: SMs have enabled services to end-users such as automated budget assistance and bill management tools, energy use notifications, smart pricing, and demand response programs.
4.2.2. Canada
4.2.3. Latin America
4.3. Asia-Pacific
4.3.1. China
4.3.2. Japan
4.3.3. Australia
4.3.4. India
4.4. Other Regions
5. Challenges to be Addressed in the Near Future
- Gain the trust and confidence of consumers. An intensive communication effort is required to convince customers about three key aspects: understanding their rights as consumers, the benefits of installing SMs, and their participation in demand response programs.
- Achieve an innovative energy services market. Synergies with the ICT sector will be fundamental for promoting an innovative energy services market.
- Protection of sensitive data. The European Commission and the member states will have to assess the need for specific data privacy and security framework legislation.
- Management of data. Utilities and the ICT sector will have to work together and explore the possibilities of data management.
- Functions of SMs. Technical and commercial interoperability in Smart Metering will enable member states to identify common means of achieving cost efficiencies and ensure fit-for-purpose in their rollout.
- Long-term economic assessment of costs and benefits. A review of the critical parameters used and assumptions made in national rollouts will help to refine technology choices.
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The History of Making the Grid Smart. Available online: http://ethw.org/The_History_of_Making_the_Grid_Smart#The_History_of_Making_the_Grid_Smart (accessed on 1 June 2015).
- Sensor Monitoring Device, Patent US 3842208 A. Available online: http://www.google.com/patents/US3842208 (accessed on 3 June 2015).
- Directive 2012/27/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 25 October on energy efficiency, amending Directives 2009/125/EC and 2010/30/EU and repealing Directives 2004/8/EC and 2006/32/EC, 2012/27/EU. Official Journal of the European Union. L315/1. 2012. Available online: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=celex%3A32012L0027 (accessed on 10 June 2015).
- Jaewoo, K.; Jaiyong, L.; Jaeho, K.; Jaeseok, Y. M2M service platforms: Survey, issues, and enabling technologies. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2014, 16, 61–76. [Google Scholar]
- López, G.; Moreno, J.; Amarís, H.; Salazar, F. Paving the road toward Smart Grids through large-scale advanced metering infrastructures. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2015, 120, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.R.; Oo, A.M.T.; Ali, A.B.M.S. Evolution of smart grid and some pertinent issues. In Proceedings of the 20th Australasian Universities Power Engineering Conference (AUPEC), Christchurch, New Zealand, 5–8 December 2010; Volume 6, pp. 5–8.
- Farhangi, H. The path of the smart grid. IEEE Power Energy Mag. 2010, 8, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edison Electric Institute. Smart Meters and Smart Meter Systems: A Metering Industry Perspective. 2011. Available online: http://www.eei.org/issuesandpolicy/grid-enhancements/documents/smartmeters.pdf (accessed on 6 January 2016).
- Murat, K.; Pipattanasomporn, M.; Rahman, S. Communication network requirements for major smart grid applications in HAN, NAN and WAN. Comput. Netw. 2014, 67, 74–88. [Google Scholar]
- Depuru, S.S.S.R.; Wang, L.; Devabhaktuni, V. Smart meters for power grid: Challenges, issues, advantages and status. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 2736–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun-Hao, L.; Ansari, N. The progressive Smart Grid System from both power and communications aspects. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2012, 14, 799–821. [Google Scholar]
- Mohassel, R.; Fung, A.; Mohammadi, A.F.; Raahemifar, K. A survey on advanced metering infrastructure. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2014, 63, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBM Software. Managing Big Data for Smart Grids and Smart Meters. White Paper. 2012. Available online: http://www-935.ibm.com/services/multimedia/Managing_big_data_for_smart_grids_and_smart_meters.pdf (accessed on 3 January 2016).
- Diamantoulakis, P.D.; Kapinas, V.M.; Karagiannidis, G.K. Big data analytics for dynamic energy management in smart grids. Big Data Res. 2015, 2, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Aparicio, J.; Tas, N.; Loiacono, M.; Rosca, J. Assessing communications technology options for smart grid applications. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications (SmartGridComm), Brussels, Belgium, 17–20 October 2011; pp. 126–131.
- Tortolero, A. The Three Pillars for an Efficient AMI Operation. Schneider Electric White Paper. 2014. Available online: http://www.schneider-electric.com/solutions/sg/en/med/679458530/application/pdf/2400_998-2095-06-09-14ar1_en.pdf (accessed on 4 January 2016).
- Assessment of Demand Response and Advanced Metering. Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC), 2008. Available online: https://www.ferc.gov/legal/staff-reports/12-20-12-demand-response.pdf (accessed on 15 October 2015).
- Gao, C.; Redfern, M.A. A Review of Voltage Control in Smart Grid and Smart Metering Technologies on Distribution Networks. In Proceedings of the Universities′ 46th International Power Engineering Conference (UPEC), Soest, Germany, 5–8 September 2011.
- U.S. Department of Energy. Application of Automated Controls for Voltage and Reactive Power Management. Smart Grid Investment Grant Program; 2012. Available online: https://www.smartgrid.gov/files/VVO_Report_-_Final.pdf (accessed on 4 January 2016). [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Department of Energy. Regulators: What the Smart Grid Means to You and the People You Represent. Available online: http://www.smartgridinformation.info/pdf/1212_doc_1.pdf (accessed on 26 September 2015).
- Grigoras, G.; Scarlatache, F. Use of data from smart meters in optimal operation of distribution systems. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Optimization of Electrical and Electronic Equipment (OPTIM), Suceava, Romania, 22–24 May 2014.
- Dong, X.; Hongxing, W.; Tianmiao, W.; Suibing, Z. A Smart Metering system for monitoring electricity of building based on wireless network. In Proceedings of the 10th IEEE International Conference on Industrial Informatics (INDIN), Hangzhou, China, 25–27 May 2012.
- Depuru, S.; Lingfeng, W.; Devabhaktuni, V. A conceptual design using harmonics to reduce pilfering of electricity. In Proceedings of the Power and Energy Society General Meeting, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 25–29 July 2010.
- Xiang, W.; St-Hilaire, M.; Kunz, T. Roadmap of Future Smart Grid, Smart Home, and Smart Appliances. Carleton University: Canada, 2011. Available online: http://www.csit.carleton.ca/~msthilaire/Tech_Report/2011-SmartGridRoadMap.pdf (accessed on 14 December 2015).
- Lipošcak, Z.; Boškovic, M. Survey of Smart Metering Communication Technologies. In Proceedings of the EUROCON, Zagreb, Croatia, 1–4 July 2013.
- Parikh, P.P.; Kanabar, M.G.; Sidhu, T.S. Opportunities and challenges of wireless communication technologies for smart grid applications. In Proceedings of the Power and Energy Society General Meeting, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 25–29 July 2010; pp. 1–7.
- Kirkpatrick, K.; Gohn, B. Smart Grid Networking and Communications; Research Report; Pike Research: Boulder, CO, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gungor, V.; Sahin, D.; Kocak, T.; Ergüt, S.; Buccella, C.; Cecati, C.; Hancke, G. Smart Grid Technologies: Communications Technologies and Standards. 2011. Available online: http://repository.up.ac.za/bitstream/handle/2263/18406/Gungor_Smart(2011).pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 4 January 2016).
- Accenture. The Role of Communication Technology in Europe′s Advanced Metering Infrastructure. Technical Paper. 2014. Available online: https://www.accenture.com/us-en/insight-role-communication-technology-europe-advanced-metering.aspx (accessed on 26 December 2015).
- The Commission for Energy Regulation. Electricity Smart Metering Technology Trials Findings Report. 2011. Available online: https://www.ucd.ie/t4cms/Electricity%20Smart%20Metering%20Technology%20Trials%20Findings%20Report.pdf (accessed on 27 December 2015).
- IEEE 802.15 Wireless Personal Area Networks. Available online: https://standards.ieee.org/about/get/802/802.15.html (accessed on 27 September 2015).
- Lu, B.; Gungor, V.C. Online and remote energy monitoring and fault diagnostics for industrial motor systems using wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electr. 2009, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisco. A Standardized and Flexible IPv6 Architecture for Field Area Networks. White Paper. 2014. Available online: https://www.cisco.com/web/strategy/docs/energy/ip_arch_sg_wp.pdf (accessed on 7 January 2016).
- Lu, S.C.; Wu, Q.; Seah, W.K. Quality of Service Provisioning for Smart Meter Networks Using Stream Control Transport Protocol; School of Engineering and Computer Science, Victoria University of Wellington: Wellington, New Zealand, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Koay, B.S.; Cheah, S.; Sng, Y.; Chong, P.; Shum, P.; Tong, Y. Design and implementation of bluetooth energy meter. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Information, Communications & Signal Processing, Singapore, Singapore, 15–18 December 2003; pp. 1474–1477.
- Ancillotti, E.; Bruno, R.; Conti, M. The role of communication systems in smart grids: Architectures, technical solutions and research challenges. Comput. Commun. 2013, 36, 1665–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE 802.11™ Wireless LANs. Available online: http://standards.ieee.org/about/get/802/802.11.html (accessed on 15 August 2015).
- Victorian AMI Rollout-Legislative and Regulatory Framework. 2008. Available online: http://www.smartmeters.vic.gov.au/about-smart-meters/reports-and-consultations/advanced-metering-infrastructure-cost-benefit-analysis/2.-background (accessed on 26 December 2015).
- Energy Networks Association. Pilots and Trials Report on Smart Metering and Related Matters. 2012. Available online: http://www.aemc.gov.au/getattachment/6a455547-4851-4a86-b83c-385be12f967d/Energy-Networks-Association-Pilots-and-trials-repo.aspx (accessed on 6 January 2016). [Google Scholar]
- Gungor, V.C.; Sahin, D.; Kocak, T.; Ergut, S.; Buccella, C.; Cecati, C.; Hancke, G.P. Smart grid technologies: Communication technologies and standards. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2011, 7, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, S.; Lys, T. Next generation Narrowband (under 500 kHz) Power Line Communications (PLC) standards. Communications 2015, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gungor, V.C.; Sahin, D.; Kocak, T.; Ergüt, S. Smart Grid Communications and Networking; Türk Telekom Technical Report-11316-01; Türk Telekom: Altındağ, Turkey, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- IEC 62056-31:1999 Withdrawn. https://webstore.iec.ch/publication/20273 (accessed on 9 September 2015).
- Electa. Study on Smart Meters from the Angles of the Consumer Protection and the Public Service Obligations. 2010. Available online: http://economie.fgov.be/nl/binaries/201010smartMeters_ELECTA_FINAL_REPORT_tcm325-117779.pdf (accessed on 4 January 2016). [Google Scholar]
- Strother, N.; Lockhart, B. Smart Meters. Smart Electric Meters, Advanced Metering Infrastructure, and Meter Communications: Global Market Analysis and Forecasts; Navigant Research: Boulder, CO, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Alejandro, L.; Blair, C.; Bloodgood, L.; Khan, M.; Lawless, M.; Meehan, D.; Schneider, P.; Tsuji, K. Global Market for Smart Electricity Meters: Government Policies Driving Strong Growth. Working Paper; US International Trade Commission, 2014. Available online: https://www.usitc.gov/publications/332/id-037smart_meters_final.pdf (accessed on 28 December 2015). [Google Scholar]
- Northeast Group, LLC. Brazil Smart Grid: Market Forecast (2012–2022). 2012. Available online: http://www.northeast-group.com/reports/Brazil_Smart_Grid_Market_Forecast_2012-2022_Brochure_Northeast_Group_LLC.pdf (accessed on 28 December 2015).
- Li, D.; Hu, B. Advanced metering standard infrastructure for smart grid. In Proceedings of the 2012 China International Conference on Electricity Distribution (CICED), Shanghai, China, 10–14 September 2012; pp. 1–4.
- ABI Research. Smart Electricity Meters to Total 780 Million in 2020. 2015. Available online: https://www.abiresearch.com/press/smart-electricity-meters-to-total-780-million-in-2/ (accessed on 3 January 2016).
- Status Review of Regulatory Aspects of Smart Metering. Council for European Energy Regulators (CEER), 2013. Available online: http://www.ceer.eu/portal/page/portal/EER_HOME/EER_PUBLICATIONS/CEER_PAPERS/Customers/2013/7-1_C13-RMF-54-05-Status_Review_of_Regulatory_Aspects_of_Smart_Metering_FOR_PUBLICATION.pdf (accessed on 27 October 2015).
- Benchmarking Smart Metering Deployment in the EU-27 with a Focus on Electricity. European Commission, 2014. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/energy/en/topics/markets-and-consumers/smart-grids-and-meters (accessed on 15 October 2015).
- Commission Staff Working Document, “Cost-benefit analyses & state of play of Smart Metering deployment in the EU-27”, COM(2014) 356 final. 2014. Available online: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:52014SC0189&from=EN (accessed on 16 October 2015).
- Executive Summary; Berg Insight: Göteborg, Sweden, 2013.
- USmart Consumer Project. European Smart Metering Landscape Report. 2014. Available online: http://www.escansa.es/usmartconsumer/documentos/USmartConsumer_Landscape_2014_Final_pr.pdf (accessed on 28 December 2015).
- Realizing the Full Potential of Smart Metering. Accenture′s Digitally Enabled Grid Program. Available online: https://www.accenture.com/us-en/~/media/Accenture/Conversion-Assets/DotCom/Documents/Global/PDF/Industries_9/Accenture-Smart-Metering-Report-Digitally-Enabled-Grid.pdf (accessed on 20 September 2015).
- Gerwen, R.; Jaarsma, S.; Wilhite, R. Smart Metering; KEMA: Arnhem, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- House of Commons-Energy and Climate Change Committee. Smart meter roll-out-Fourth Report of Session 2013–2014. 2013. Available online: http://www.publications.parliament.uk/pa/cm201314/cmselect/cmenergy/161/161.pdf (accessed on 18 November 2015).
- Duplex, J.; Gosswiller, S.; Fagnoni, S. A better knowledge of electricity consumption for residential customers through the Linky smart meter. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference and Exhibition on Electricity Distribution (CIRED 2013), Stockholm, Sweden, 10–13 June 2013; pp. 1–4.
- DNV GL. Smart Grid Data Communication: Accelerating Results in Spain. 2014. Available online: http://www.dnvkema.com/Images/SG%20Data%20Communications%20Lab%20Madrid%20A4_070714.pdf (Accessed on 4 January 2016).
- Bayar, T. Will Germany Reject Smart Meters? Available online: http://www.renewableenergyworld.com/articles/2013/09/will-germany-reject-smart-meters.html (accessed on 26 December 2015).
- Federal Energy Regulatory Commission. Assessment of Demand Response and Advanced Metering. 2015. Available online: http://www.ferc.gov/legal/staff-reports/2015/demand-response.pdf (accessed on 28 December 2015). [Google Scholar]
- Institute for Electric Innovation. Edison Foundation. Utility-Scale Smart Meter Deployments: Building Block of the Evolving Power Grid. Report. 2014. Available online: http://www.edisonfoundation.net/iei/Documents/IEI_SmartMeterUpdate_0914.pdf (accessed on 26 December 2015).
- PG & E SmartMeter Program Overview. 2008. Available online: http://www.edisonfoundation.net/iei/Documents/PGE_SmartMeter_Overview.pdf (accessed on 28 December 2015).
- Park, E.; Callahan, S. PG & E SmartMeter Project (AMI)—The Intelligent Network. 2006. Available online: http://info.publicintelligence.net/SmartMeter2.pdf (accessed on 26 December 2015).
- Nanne, Y. Southern California Edison Smart Meter Deployment. 2014. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/8872228/SCE_Smart_Meter_Deployment_A_Case_Study_of_Thematic_Implementation (accessed on 27 December 2015).
- U.S. Department of Energy. Case Study-Florida Power & Light. 2012. Available online: https://www.smartgrid.gov/files/FPLcasestudy.pdf (accessed on 27 December 2015). [Google Scholar]
- Greer, J. Oncor Smart Texas-Focus on Smart Meters. Available online: http://www.oncor.com/EN/Documents/Ways%20to%20Save/Advanced%20Meters/Focus%20on%20Newsletter.pdf (accessed on 29 December 2015).
- U.S. Department of Energy. Case Study—Center Point. 2013. Available online: https://www.smartgrid.gov/files/CenterPoint_Case_Study.pdf (accessed on 29 December 2015). [Google Scholar]
- Monitoring Report Smart Meter Deployment and TOU Pricing. 2011. Available online: http://www.ontarioenergyboard.ca/OEB/_Documents/SMdeployment/Monthly_Monitoring_Report_June2011.pdf (accessed on 4January 2016).
- The Global Smart Grid Federation Report. 2012. Available online: https://www.smartgrid.gov/files/Global_Smart_Grid_Federation_Report.pdf (accessed on 26 December 2015).
- Auditor General of Ontario, Smart Metering Initiative. 2015. Available online: http://www.auditor.on.ca/en/reports_en/en14/311en14.pdf (accessed on 3 January 2016).
- BC Hydro. Smart Metering & Infrastructure Program. Business Case. 2014. Available online: https://www.bchydro.com/content/dam/BCHydro/customer-portal/documents/projects/smart-metering/smi-program-business-case.pdf (accessed on 2 January 2016).
- Hydro-Québec. Next-Generation Meters Project. 2013. Available online: http://meters.hydroquebec.com/media/exportpdf/HQ_project.pdf (accessed on 6 January 2016).
- PR Newswire. Mexico Smart Grid Market to Reach $8.3 Billion. 2011. Available online: http://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/mexico-smart-grid-market-to-reach-83-billion-by-2020-131504898.html (accessed on 27 December 2015).
- PV Magazine. Smart Meter Market Is Hotting Up in China. 2013. Available online: http://www.pv-magazine.com/news/details/beitrag/smart-meter-market-is-hotting-up-in-china_100011272/#axzz3wLSfQBW1 (accessed on 26 December 2015).
- Asian Power. Metering India Smartly. 2012. Available online: http://asian-power.com/sites/default/files/asianpower/print/APMay_2013_lr_12.pdf (accessed on 7 January 2016).
- China′s Power Sector, Smart Grid Strategy and Investment Climate. 2011. Available online: http://nebula.wsimg.com/edf018e665a3fcef0fac9ba08f4b75e0?AccessKeyId=1A0D9A575B761BCFC58F&disposition=0&alloworigin=1 (accessed on 7 January 2016).
- China Tests a Small Smart Electric Grid. MIT Technology Review. 2013. Available online: http://www.technologyreview.com/news/510171/china-tests-a-small-smart-electric-grid/ (accessed on 7 January 2016).
- Global Smart Meter Unit Shipments Will Peak; Navigant Research: Boulder, CO, USA, 2013.
- SAIC. Smart Grid around the World-Selected Country Overviews. 2011. Available online: https://www.eia.gov/analysis/studies/electricity/pdf/intl_sg.pdf (accessed on 4 January 2016). [Google Scholar]
- Moore, K. Overview of the Victorian Smart Meter Program. 2015. Available online: http://www.mbie.govt.nz/info-services/sectors-industries/energy/electricity-market/nz-smart-grid-forum/meeting-6/case-study-victorian-smart-meter-rollout.pdf (accessed on 26 December 2015). [Google Scholar]
- Goswami. Smart Metering: Energizing India. 2012. Available online: http://www.dqindia.com/smart-metering-energizing-india/ (accessed on 22 December 2015).
- Alexander, B. Smart Meters, Demand Response and “Real Time” Pricing: Too Many Questions and Not Many Answers. 2007. Available online: http://www.narucmeetings.org/Presentations/Dynamic%20Pricing%20NARUC%202007.ppt (accessed on 16 October 2015).
- Bartak, G.F.; Abart, A. EMI of Emissions in the Frequency Range 2 kHz–150 kHz. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Electricity Distribution (CIRED), Stockholm, Sweden, 10–13 June 2013.







| 2012/148/EU Recommendation |
|---|
| Consumer |
| Provide readings directly to the consumer and/or any third party. |
| Update the readings frequently enough to use energy saving schemes. |
| Metering Service Operator |
| Allow remote reading by the operator. |
| Provide bidirectional communication for maintenance and control. |
| Allow frequent enough readings to be used for networking planning. |
| Commercial Service Issues |
| Support advanced tariff system. |
| Allow remote ON/OFF control supply and/or flow or power limitation. |
| Security and Data Protection |
| Provide secure data communications. |
| Fraud prevention and detection. |
| Distributed Generation |
| Provide consumed, generated, and reactive metering data. |
| Planning Aspects | |
|---|---|
| Technological | Election of the most suitable technology according the final end |
| Implementation of software | |
| Physical aspects | Resilience and strength |
| Communication | Type of network (wired, wireless, hybrid) |
| Range of network | |
| Bandwidth | |
| Quality of signal | |
| Security & privacy | |
| Costs | Costs of devices |
| Costs of communication network infrastructure | |
| Maintenance | |
| Customers | Service providing |
| Access to personal data | |
| Wireless | Data Rate | Frequency Bands | Distance | Advantages | Drawbacks | Deployments/Projects | |
| RF- Mesh | - | 902–928 MHz | Depends on hops | Coverage can be increased with multiple hops. Ad hoc communication links formed dynamically. | Tends to be a proprietary offering. Performance decreases over long distances. | Most rollouts in USA | |
| Cellular | 3G–4G | 60–240 kbps | 824–894 MHz 1900 MHz | Up to 50 km | Wide-range coverage Low maintenance Low power consumption High flexibility | Individual connections are expensive. Moderate bit rates | China Southern Power Grid (CHN) Smart Grid Smart City (AUS) Essential Energy (AUS) |
| GSM | 14.4 kbps max. | 900–1800 MHz | 1–10 km | Telegestore (IT) | |||
| GPRS | 170 kbps max. | 900–1800 MHz | 1–10 km | PRICE-GEN (ES) Eandis and Infrax (BE) Linky (FR) | |||
| IEEE 802.15 Group | ZigBee | 20–250 kbps | 868 MHz/915 MHz/2.4 GHz | 10–1000 m | Low cost Low power consumption | Low bit rates Security issues (specially Bluetooth) | Energy Demand Research Project, EDRP (UK) National Smart Metering Programme, NSMP (IRL) |
| 6LoWPAN | |||||||
| Bluetooth | 721 kbps | 2.4–2.4835 GHz | 1–100 m | ||||
| IEEE 802.11 Group | Wi-Fi | 54 Mbps max. | 2.4 GHz/5.8 GHz | Up to 100 m | High degree of reliability and availability | Affected by surrounding emitting devices | CMP AMI (US) National Smart Metering Programme, NSMP (IRL) |
| Enhanced Wi-Fi | 54 Mbps max. | 2.4 GHz | |||||
| IEEE 802.11 n | 600 Mbps max. | 2.4 GHz | |||||
| IEEE 802.16 | WiMAX | 70 Mbps | 1.8–3.65 GHz | 50 km | Good performance over larger distances Able to supply thousands of end-users | Higher costs than similar technologies | Victorian Smart Meter Rollout (AUS) |
| Wired | Data Rate | Frequency Bands | Distance | Advantages | Drawbacks | Deployments/Projects | |
| NB-PLC | up to 500 kbps | 3–500 kHz | Several km | Medium already deployed Devices do not depend on batteries. | Power cables are a harsh medium for communications. | Most rollouts in Europe and China Telegestore (IT) Woodruff Electric Cooperative (USA) Pacific Northwest Boulder SmartCityGrid (US) PRICE-GEN (ES) Eandis and Infrax (BE) Linky (FR) Energy Demand Research Project, EDRP (UK) | |
| BB-PLC | Up to several hundred of Mbps | 1.8–250 MHz | Several km | ||||
| xDSL | ADSL | 800 kbps upstream 8 Mbps downstream | From 25 kHz to 1 MHz | 5 km | Medium already deployed Quite high data rates | High maintenance costs Efficiency decreases with distance | PRICE-GEN (ES) Eandis and Infrax (BE) |
| HDSL | 2 Mbps | 3.6 km | |||||
| VHDSL | 15–100 Mbps | 1.5 km | |||||
| Euridis | IEC 62056-31 | 9.6 kbps | 80 MHz–1 GHz | Hundreds m | Low cost Known technology | Low data rates | Wide rollout of SMs in France |
| PON | 155–2.5 Gbps | 500 MHz-km | 60 km | High data rates Noise immunity Good performance over km | High cost | Boulder SmartCityGrid (US) PRICE-GEN (ES) Austin (US) | |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uribe-Pérez, N.; Hernández, L.; De la Vega, D.; Angulo, I. State of the Art and Trends Review of Smart Metering in Electricity Grids. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/app6030068
Uribe-Pérez N, Hernández L, De la Vega D, Angulo I. State of the Art and Trends Review of Smart Metering in Electricity Grids. Applied Sciences. 2016; 6(3):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/app6030068
Chicago/Turabian StyleUribe-Pérez, Noelia, Luis Hernández, David De la Vega, and Itziar Angulo. 2016. "State of the Art and Trends Review of Smart Metering in Electricity Grids" Applied Sciences 6, no. 3: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/app6030068
APA StyleUribe-Pérez, N., Hernández, L., De la Vega, D., & Angulo, I. (2016). State of the Art and Trends Review of Smart Metering in Electricity Grids. Applied Sciences, 6(3), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/app6030068







