WIPP: Wi-Fi Compass for Indoor Passive Positioning with Decimeter Accuracy
Abstract
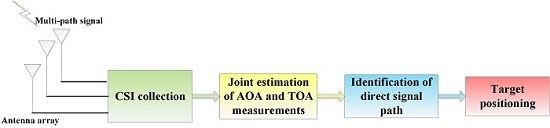
:1. Introduction
- The positioning accuracy of the WIPP is higher than the one by the RADAR system and the conventional system using the AOA solely. In our testbed, the median error of the WIPP is only 0.7 m, while the ones of the other two systems are 2.3 and 1.5 m, respectively.
- Another significant advantage of the WIPP is about the simple system design and low maintenance cost. There is no requirement of fingerprint database construction or hardware modification.
2. Related Works
3. System Description
3.1. Propagation Model Construction
3.2. Angle of Arrival (AOA) Measurement Estimation
3.3. Signal Path Identification
4. Experimental Results
4.1. AOA Measurement Estimation
4.2. Target Location Estimation
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Soubielle, J.; Fijalkow, I.; Duvaut, P.; Bibaut, A. GPS positioning in a multipath environment. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2002, 50, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Qu, L.; Zhao, Q.; Guo, J.; Su, X.; Li, X. Precise point positioning with the beidou navigation satellite system. Sensors 2014, 14, 927–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, X.; Ban, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J. Quantitative analysis to the impacts of imu quality in GPS/INS deep integration. Micromachines 2015, 6, 1082–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahl, P.; Padmanabhan, V.N. Radar: An in-building RF-based user location and tracking system. In Proceedings of the 19th Annual Joint Conference of the IEEE Computer and Communications Societies, Tel Aviv, Israel, 26–30 March 2000; pp. 775–784.
- Park, J.; Charrow, B.; Curtis, D. Growing an organic indoor location system. In Proceedings of the 8th Annual International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications and Services, MobiSys 2010, San Francisco, CA, USA, 15–18 June 2010; pp. 271–284.
- Jiang, Y.F.; Pan, X.; Li, K. ARIEL: Automatic Wi-Fi based room fingerprinting for indoor localization. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Ubiquitous Computing, UbiComp 2012, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 5–8 September 2012; pp. 441–450.
- Zhou, M.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, K.; Tian, Z.; Wang, Y.; He, W. PRIMAL: Page rank-based indoor mapping and localization using gene-sequenced unlabeled WLAN received signal strength. Sensors 2015, 10, 24791–24817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Qiu, F.; Tian, Z.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Q.; He, W. An information-based approach to precision analysis of indoor WLAN localization using location fingerprint. Entropy 2015, 17, 8031–8055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapre, Y.; Mohapatra, P.; Jha, S.; Seneviratne, A. Received signal strength indicator and its analysis in a typical wlan system. In Proceedings of the 38th IEEE Conference on Local Computer Networks, Sydney, Australia, 21–24 October 2013; pp. 304–307.
- Masiero, A.; Guarnieri, A.; Pirotti, F.; Vettore, A. A particle filter for smartphone-based indoor pedestrian navigation. Micromachines 2014, 5, 1012–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, C. A bluetooth/PDR integration algorithm for an indoor positioning system. Sensors 2015, 15, 24862–24885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamazin, M.; Noureldin, A.; Korenberg, M. Robust modeling of low-cost mems sensor errors in mobile devices using fast orthogonal search. J. Sens. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Liu, Y. Pedestrian dead reckoning for marg navigation using a smartphone. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghtadaiee, V.; Dempster, A.G.; Lim, S. Indoor localization using FM radio signals: A fingerprinting approach. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation, Sydney, Australia, 21–23 September 2011; pp. 1–7.
- Sun, G.; Chen, J.; Guo, W.; Liu, K. Signal processing techniques in network-aided positioning: A survey of state-of-the-art positioning designs. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2005, 22, 12–23. [Google Scholar]
- Gezici, S.; Poor, H.V. Position estimation via ultra-wide-band signals. Proc. IEEE 2009, 97, 386–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, B.; Zhao, K.; Rizos, C.; Zheng, Z. An improved algorithm to generate a Wi-Fi fingerprint database for indoor positioning. Sensors 2013, 13, 11085–11096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Lo, A.; Niemegeers, I. A survey of indoor positioning systems for wireless personal networks. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2009, 11, 13–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xenakis, D.; Merakos, L.; Kountouris, M.; Passas, N.; Verikoukis, C. Distance distributions and proximity estimation given knowledge of the heterogeneous network layout. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2015, 14, 5498–5512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xenakis, D.; Kountouris, M.; Merakos, L.; Passas, N.; Verikoukis, C. On the performance of network-assisted device-to-device discovery. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), San Diego, CA, USA, 6–10 December 2015; pp. 1–7.
- Joshi, K.R.; Hong, S.S.; Katti, S. Pinpoint: Localizing interfering radios. In Proceedings of the 10th USENIX Symposium on Networked Systems Design and Implementation, Lombard, IL, USA, 2–3 April 2013; pp. 241–253.
- Vanderveen, M.C.; van der Veen, A.-J.; Paulraj, A. Estimation of multipath parameters in wireless communications. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1998, 46, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.; Singh, G.; Sarkar, I. Study of DOA estimation using music algorithm. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2015, 6, 594–603. [Google Scholar]
- Pahlavan, K.; Akguel, F.O.; Heidari, M.; Hatami, A.; Elwell, J.M.; Tingley, R.D. Indoor geolocation in the absence of direct path. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2006, 13, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Molisch, A.F. Indirect path detection based on wireless propagation measurements. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2012, 11, 4482–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, L.; Zhuang, W. Non-line-of-sight error mitigation in TDOA mobile location. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference, San Antonio, TX, USA, 25–29 November 2001; pp. 680–684.
- Cong, L.; Zhuang, W. Nonline-of-sight error mitigation in mobile location. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2005, 4, 560–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangas, A.; Wigren, T. Angle of arrival localization in LTE using mimo pre-coder index feedback. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2013, 17, 1584–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Gil, S.; Katabi, D.; Rus, D. Accurate indoor localization with zero start-up cost. In Proceedings of the ACM 10th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, Maui, HI, USA, 7–11 September 2014; pp. 483–494.
- Xiong, J.; Jamieson, K. Arraytrack: A fine-grained indoor location system. In Proceedings of the 10th USENIX Symposium on Networked Systems Design and Implementation, Lombard, IL, USA, 2–5 April 2013; pp. 71–84.
- Tzur, A.; Amrani, O.; Wool, A. Direction finding of rogue Wi-Fi access points using an off-the-shelf mimo-ofdm receiver. Phys. Commun. 2015, 17, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halperin, D.; Hu, W.; Sheth, A.; Wetherall, D. Tool release: Gathering 802.11n traces with channel state information. ACM SIGCOMM Comput. Commun. Rev. 2011, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhede, M.H.; Ganage, D. Performance analysis of music algorithms for evaluation of coherent and non-coherent signals. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2015, 4, 2274–2278. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, J.; Johnson, J.; Sun, D. High resolution angular spectrum estimation techniques for terrain scattering analysis and angle of arrival estimation. In Proceedings of the 1st ASSP Workshop Spectral Estimation, Hamilton, ON, Canada, 17–18 August 1981; pp. 134–139.
- Pillai, S.U.; Kwon, B.H. Forward/backward spatial smoothing techniques for coherent signal identification. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1989, 37, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guvenc, I.; Chong, C.-C.; Watanabe, F.; Inamura, H. Nlos identification and weighted least-squares localization for UWB systems using multipath channel statistics. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2007, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbachin, A.; Oppermann, I.; Denis, B. Ml time-of-arrival estimation based on low complexity UWB energy detection. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference on Ultra-Wideband, Waltham, MA, USA, 24–27 September 2006; pp. 599–604.
- Decarli, N.; Dardari, D.; Gezici, S.; D’Amico, A.A. LOS/NLOS detection for UWB signals: A comparative study using experimental data. In Proceedings of the 5th IEEE International Conference on Wireless Pervasive Computing, Modena, Italy, 5–7 May 2010; pp. 169–174.
- Sen, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, K.-H.; Congdon, P. Avoiding multipath to revive inbuilding wifi localization. In Proceedings of the ACM 11th Annual International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services, Taipei, Taiwan, 25–28 June 2013; pp. 249–262.
- ElGammal, M.; Eltoweissy, M. Location-aware affinity propagation clustering in wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Wireless and Mobile Computing, Networking and Communications, Waltham, Marrakech, Morocco, 12–14 October 2009; pp. 471–475.
- Caso, G.; de Nardis, L.; di Benedetto, M.-G. A mixed approach to similarity metric selection in affinity propagation-based wifi fingerprinting indoor positioning. Sensors 2015, 15, 27692–27720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, M.; Pu, Q.; Xu, K.; Huang, X. Location fingerprint discrimination maximization for indoor WLAN access point optimization using fast discrete water-filling. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), San Diego, CA, USA, 6–10 December 2015; pp. 1–6.
- Tian, Z.; Fang, X.; Zhou, M.; Li, L. Smartphone-based indoor integrated wifi/mems positioning algorithm in a multi-floor environment. Micromachines 2015, 6, 347–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

















| Error Performance | WIPP | RADAR | AOA Solely |
|---|---|---|---|
| RMSEs | 0.7 m | 2.3 m | 1.5 m |
| 50% errors | 0.5 m | 2 m | 1.5 m |
| 70% errors | 1.2 m | 3 m | 2 m |
| 90% errors | 2 m | 5 m | 3 m |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Tian, Z.; Zhou, M.; Li, Z.; Wu, Z.; Jin, Y. WIPP: Wi-Fi Compass for Indoor Passive Positioning with Decimeter Accuracy. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/app6040108
Zhang Z, Tian Z, Zhou M, Li Z, Wu Z, Jin Y. WIPP: Wi-Fi Compass for Indoor Passive Positioning with Decimeter Accuracy. Applied Sciences. 2016; 6(4):108. https://doi.org/10.3390/app6040108
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhenyuan, Zengshan Tian, Mu Zhou, Ze Li, Zipeng Wu, and Yue Jin. 2016. "WIPP: Wi-Fi Compass for Indoor Passive Positioning with Decimeter Accuracy" Applied Sciences 6, no. 4: 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/app6040108
APA StyleZhang, Z., Tian, Z., Zhou, M., Li, Z., Wu, Z., & Jin, Y. (2016). WIPP: Wi-Fi Compass for Indoor Passive Positioning with Decimeter Accuracy. Applied Sciences, 6(4), 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/app6040108