Overview of 3D Micro- and Nanocoordinate Metrology at PTB
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Instrumentation Developments
2.1. Upgrade of a Nanomeasuring and Nanopositioning Machine (NMM)
- The geometry of the corner mirror has been improved to fix samples better so that the stress introduced into the optical component due to the sample fixing is greatly minimized. In addition, the height of the mirrors has been increased so as to allow higher objects (up to 22 mm).
- The interferometers and the angle sensors have been improved for easier adjustment, better thermal behaviour and better stability.
- A new motorized spring mechanism has been installed for the weight compensation of the motion stage. As a result, the heat generation of the z-driving motors is greatly reduced, allowing much better temperature stabilization.
- All the control electronics have been upgraded. They now have an increased servo frequency response up to 1 kHz for better stage control performance.
- An improved instrument chamber for better thermal and acoustic insulation and an improved vibration damping stage are applied.
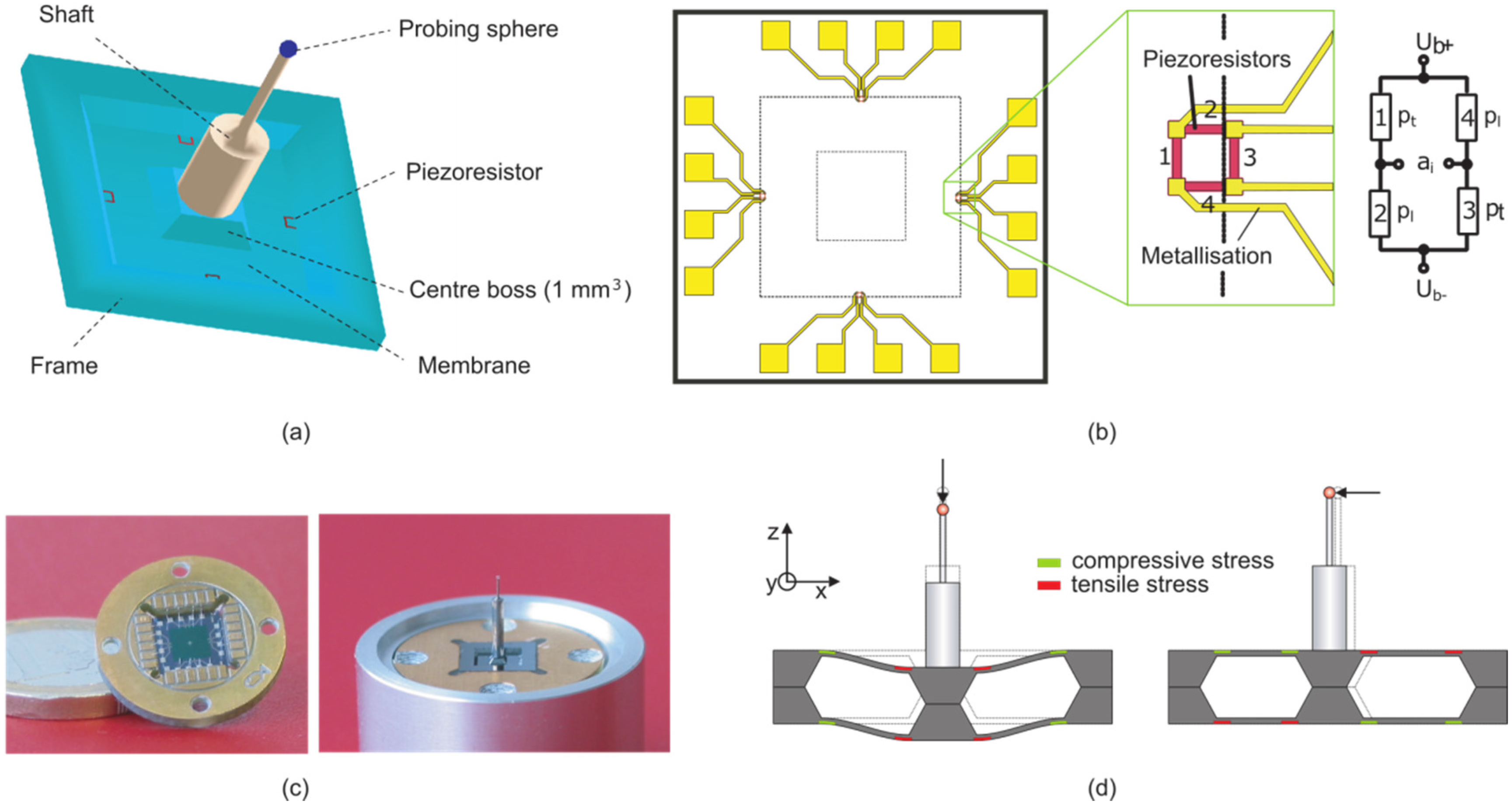
2.2. Boss-Membrane Piezoresistive Microprobe
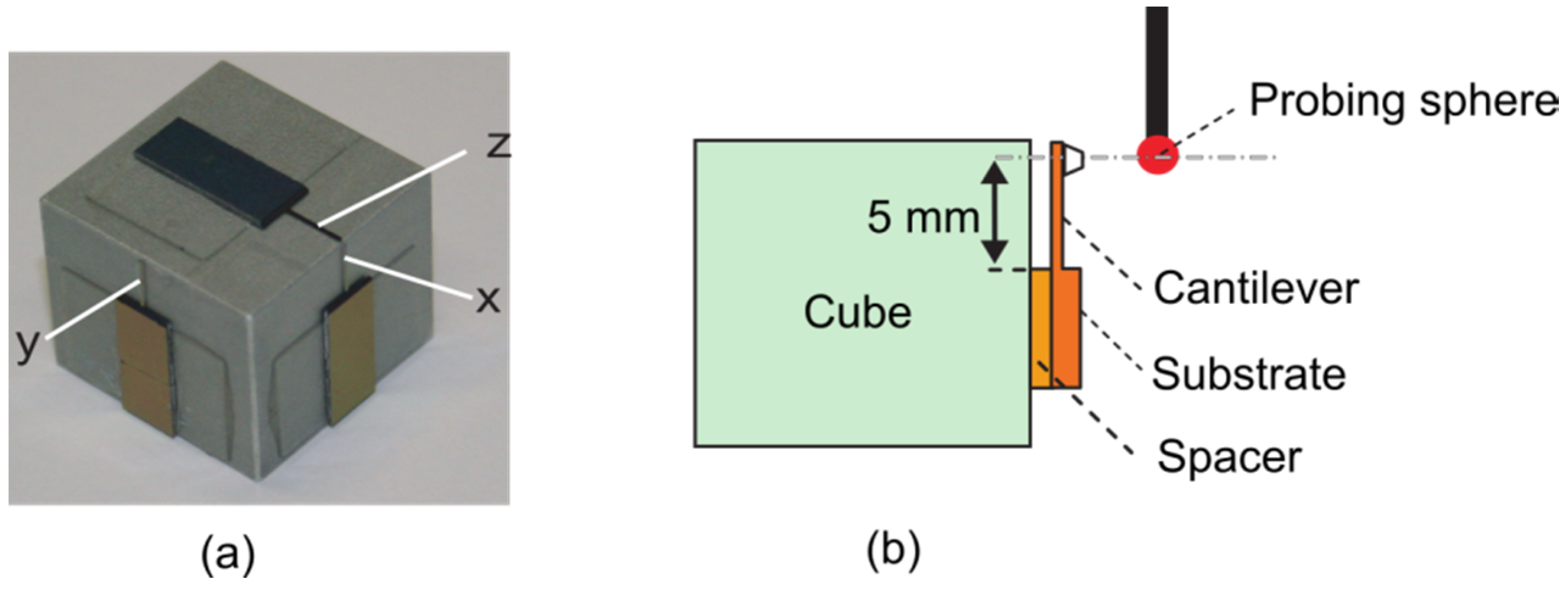
2.3. 3D Tactile-Optical (Fibre) Probe
- -
- Single point probing (ISO 10360-5): P = 0.25 µm (probe diameter 250 µm), P = 0.5 µm (probe diameter 40 µm and 100 µm); and
- -
- Scanning (ISO 10360-4): THN = 1.5 µm (probe diameter 250 µm), THN = 2 µm (probe diameter 40 µm and 100 µm).
2.4. AFM-Based 3D Probes
3. Calibration Artefacts
3.1. Microforce Calibration Standard
3.2. 3D Aztec Artefact
3.3. Micro-Contour Standard
3.4. Microgear Standard
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hansen, H.N.; Carneiro, K.; Haitjema, H.; De Chiffre, L. Dimensional micro and nanometrology. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2006, 55, 721–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattsson, L. Metrology of micro-components—A real challenge for the future. In Proceedings of the 5th International Seminar on Intelligent Computation in Manufacturing Engineering (CIRP ISME ’06), Ischia, Italy, 25–28 July 2006; pp. 547–552.
- Multi-Sensor Metrology for Microparts in Innovative Industrial Products. EMRP Project. Available online: https://www.ptb.de/emrp/microparts-project.html (accessed on 8 April 2016).
- Peggs, G.N.; Lewis, A.J.; Oldfield, S. Design for a compact high-accuracy CMM. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 1999, 48, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, M.M.P.A.; Rosielle, P.C.J.N.; Schellekens, P.H.J. Design of a high-precision 3D-coordinate measuring machine. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 1998, 47, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Riel, M.; Moers, T. Nanometer uncertainty for a micro price. Mikroniek 2010, 50, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Jäger, G.; Manske, E.; Hausotte, T.; Büchner, H.J. Laserinterferometrische Nanomessmachinen. In Sensoren und Messsysteme 2000. VDI Berichte 1530; VDI Verlag: Düsseldorf, Germany, 2000; pp. 271–278. [Google Scholar]
- Ruijl, T.A.M. Ultra Precision Coordinate Measuring Machine—Design, Calibration and Error Compensation. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität Darmstadt, Darmstadt, Germany, 1 May 2001. [Google Scholar]
- ISARA 400 ULTRAPRÄZISIONS-KOORDINATENMESSMASCHINE, Precision Engineering BV. Available online: http://www.ibspe.de/category/isara-400-ultraprazisions-koordinatenmessmaschine.htm (accessed on 8 April 2016).
- Cao, S.; Brand, U.; Kleine-Besten, T.; Hoffmann, W.; Schwenke, H.; Bütefisch, S.; Büttgenbach, S. Recent developments in dimensional metrology for microsystem components. Microsyst. Technol. 2002, 8, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küng, A.; Meli, F.; Thalmann, R. Ultraprecision micro-CMM using a low force 3D touch probe. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2007, 18, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werth VideoCheck® UA, Werth Messtechnik GmbH. Available online: http://www.werth.de/de/unser-angebot/produkte-nach-kategorie/koordinatenmessgeraete/fuer-labor-und-messraum/werth-videocheck-ua.html (accessed on 8 April 2016).
- UMAP Vision System Type2 Ultra UMAP404. Mitutoyo Corporation. Available online: http://ecatalog.mitutoyo.com/UMAP-Vision-System-TYPE2-Series-364-Micro-Form-Measuring-System-C1577.aspx (accessed on 8 April 2016).
- Fan, K.C.; Fei, Y.T.; Yu, X.F.; Chen, Y.J.; Wang, W.L.; Chen, F.; Liu, Y.S. Development of a low cost micro-CMM for 3D micro/nano measurements. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pril, W.O. Development of High Precision Mechanical Probes for Coordinate Measuring Machines. Ph.D. Thesis, Eindhoven University of Technology, Eindhoven, The Netherlands, December 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Bütefisch, S.; Dauer, S.; Büttgenbach, S. Silicon three-axial tactile sensor for the investigation of micromechanical structures. In Proceedings of the 9th International Trade Fair and Conference for Sensors Transducers and Systems, Nürnberg, Germany, 18–20 May 1999; Volume 2, pp. 321–326.
- Li, R.J.; Fan, K.C.; Miao J, W.; Huang, Q.X.; Tao, S. An analogue contact probe using a compact 3D optical sensor for micro/nano coordinate measuring machines. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2014, 25, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.L.; Chiu, C.Y. Development of a low-cost nanoscale touch trigger probe based on two commercial DVD pick-up heads. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2007, 18, 1831–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alblalaihid, K.; Kinnell, P.; Lawes, S.; Desgaches, D.; Leach, R. Performance Assessment of a New Variable Stiffness Probing System for Micro-CMMs. Sensors 2016, 16, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bos, E.J.C. Aspects of tactile probing on the micro scale. Precis. Eng. 2011, 35, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauza, M.B.; Hocken, R.J.; Smith, S.T.; Woody, S.C. Development of a virtual probe tip with an application to high aspect ratio microscale features. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2005, 76, 095112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claverley, J.D.; Leach, R.K. Development of a three-dimensional vibrating tactile probe for miniature CMMs. Precis. Eng. 2013, 37, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, H.; Katsuki, A.; Sajima, T.; Suematsu, T. Study of a vibrating fibre probing system for 3-D micro-structures: Performance improvement. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2014, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guijun, J.; Schwenke, H.; Trapet, E. Opto-tactile sensor. Qual. Eng. 1998, 7–8, 40–43. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Neuschaefer-Rube, U.; Bremer, H.; Hopp, B.; Christoph, R. Recent developments of the 3D fibre probe. In Proceedings of the 11th Laser Metrology for Precision Measurement and Inspection in Industry, Tsukuba, Japan, 2–5 September 2014.
- Cui, J.; Chen, Y.; Tan, J. Improvement of dimensional measurement accuracy of microstructures with high aspect ratio with a spherical coupling fibre probe. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2014, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Hsu, H.Y.; Kong, L.X.; Wedding, A.B. Development of a contact probe incorporating a Bragg grating strain sensor for nano coordinate measuring machines. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2009, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oiwa, T.; Nishitani, H. Three-dimensional touch probe using three fibre optical displacement sensors. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2004, 15, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Li, J.; Feng, K.; Tan, J. Three-dimensional fibre probe based on orthogonal micro focal-length collimation for the measurement micro parts. Opt Express 2015, 23, 26386–26398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weckenmann, A.; Hoffmann, J.; Schuler, A. Development of a tunnelling current sensor for a long-range nano-positioning device. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2008, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michihata, M.; Takaya, Y.; Hayashi, T. Nano position sensing based on laser trapping technique for flat surfaces. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2008, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claverley, J.D.; Leach, R.K. A review of the existing performance verification infrastructure for micro-CMMs. Precision Engineering 2015, 39, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verein Deutscher Ingenieure. VDI/VDE 2617 Blatt 12.1 Genauigkeit von Koordinatenmessgeräten—Kenngrößen und Deren Prüfung—Annahme—und Bestätigungsprüfungen für Koordinatenmessgeräte zum Taktilen Messen von Mikrogeometrien; Beuth Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2011. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- International Organization for Standardization. ISO 10360-2:2009-Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS)—Acceptance and Reverification Tests for Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM)—Part 2: CMMs Used for Measuring Linear Dimensions; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Thalmann, R.; Meli, F.; Küng, A. State of the art of tactile micro coordinate metrology. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, G.; Bütefisch, S.; Pohlenz, F.; Danzebrink, H.-U. A high precision micro/nano CMM using piezoresistive tactile probes. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2009, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buetefisch, S.; Dai, G.; Danzebrink, H.-U.; Koenders, L.; Solzbacher, F.; Orthner, M.P. Novel design for an ultra high precision 3D micro probe for CMM applications. In Proceedings of the Eurosensors XXIV Conference, Linz, Austria, 5–8 September 2010.
- Christoph, R.; Neumann, H.J. Multisensor Coordinate Metrology; Verlag Moderne Industrie: München, Germany, 2007; ISBN 978-3-937889-66-5. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, G.; Haeßler-Grohne, W.; Hueser, D.; Wolff, H.; Fluegge, J.; Bosse, H. New developments at Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt in three-dimensional atomic force microscopy with tapping and torsion atomic force microscopy mode and vector approach probing strategy. J. Micro/Nanolithogr. MEMS MOEMS 2012, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, G.; Wolff, H.; Danzebrink, H.U. Atomic force microscope cantilever based microcoordinate measuring probe for true three-dimensional measurements of microstructures. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Critical Dimension Re-Entrant Tip, Team Nanotec. Available online: http://www.team-nanotec.de/index.cfm?contentid=10&shopAction=showProductDetails&id=399 (accessed on 9 April 2016).
- Frühauf, J.; Gärtner, E.; Brand, U.; Doering, L. Silicon springs for the calibration of the force of hardness testing instruments and tactile profilometers. In Proceedings of the 4th EUSPEN International Conference, Glasgow, UK, 31 May–2 June 2004; pp. 362–363.
- Küng, A.; Meli, F. Comparison of three independent calibration methods applied to an ultra-precision micro-CMM. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference—European Society for Precision Engineering and Nanotechnology, Bremen, Germany, 20–24 May 2007; Volume 1, pp. 230–233.
- Chao, Z.X.; Tan, S.L.; Xu, G. Evaluation of the volumetric length measurement error of a micro-CMM using a mini sphere beam. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Laser Metrology, Machine Tool, CMM and Robotic Performance, Uxbridge, MA, USA, 30 June–2 July 2009; pp. 48–56.
- Neuschaefer-Rube, U.; Neugebauer, M.; Ehrig, W.; Bartscher, M.; Hilpert, U. Tactile and optical microsensors: Test procedures and standards. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2008, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischer, J.; Buchholz, I.; Härtig, F.; Dai, G. Mikroverzahnungsprüfkörper μ-DBA für evolventische Profillinienabweichungen. Tech. Mess. 2008, 75, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedmann, A.; Kniel, K.; Dunovska, V.; Härtig, F.; Klemm, M. Rückführung von Mikroverzahnungsmessungen. In VDI-Berichte Band 2236; VDI Verlag: Düsseldorf, Germany, 2014; pp. 199–212. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Dunovska, V.; Krause, M.; Kniel, K. Messung von Mikroverzahnung—Entwicklung von Verfahren zur Eignungsprüfung von Messgeräten für die Mikroverzahnungsmessung, Forschungsvereinigung Antriebstechnik e.V. (FVA)—Arbeitskreis Messtechnik, Abschlussbericht zu Forschungsvorhaben Nr. 567 II, Heft 1144; Forschungsvereinigung Antriebstechnik e.V. (FVA): Frankfurt, Germany, 2015. (In German) [Google Scholar]











| RCV (µm) | RCC (µm) | A (°) | H (µm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UIF | 2.0 | 2.0 | 0.15 | 1.0 |
| UF25 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.1 | 0.5 |
| Δm | 1.2 | 0.4 | 0.05 | 0.2 |
| En | 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.2 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dai, G.; Neugebauer, M.; Stein, M.; Bütefisch, S.; Neuschaefer-Rube, U. Overview of 3D Micro- and Nanocoordinate Metrology at PTB. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/app6090257
Dai G, Neugebauer M, Stein M, Bütefisch S, Neuschaefer-Rube U. Overview of 3D Micro- and Nanocoordinate Metrology at PTB. Applied Sciences. 2016; 6(9):257. https://doi.org/10.3390/app6090257
Chicago/Turabian StyleDai, Gaoliang, Michael Neugebauer, Martin Stein, Sebastian Bütefisch, and Ulrich Neuschaefer-Rube. 2016. "Overview of 3D Micro- and Nanocoordinate Metrology at PTB" Applied Sciences 6, no. 9: 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/app6090257
APA StyleDai, G., Neugebauer, M., Stein, M., Bütefisch, S., & Neuschaefer-Rube, U. (2016). Overview of 3D Micro- and Nanocoordinate Metrology at PTB. Applied Sciences, 6(9), 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/app6090257






