Driver Fatigue Detection System Using Electroencephalography Signals Based on Combined Entropy Features
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Entropy-Based Feature Extraction
2.1.1. Spectral Entropy
2.1.2. Approximate Entropy
- (1)
- Considering a time series t(i) of length L, a set of m-dimensional vectors are obtained according to the sequence order of t(i):
- (2)
- is the distance between two vectors and , defined as the maximum difference values between the corresponding elements of two vectors:
- (3)
- For a given calculate the number of of any vectors that are similar to within r as . Then, for ,
- (4)
- where is the number of vectors that are similar to , subject to the criterion of similarity .
- (5)
- Define the function as:
- (6)
- Set m = m + 1, and repeat steps (1) to (5) to obtain and , then:
- (7)
- The approximate entropy can be expressed as:
2.1.3. Sample Entropy
- (1)
- For a given , calculate the number of , of any vector , similar to within s as . Then, for ,
- (2)
- where is the number of vectors that are similar to subject to the criterion of similarity .
- (3)
- Define the function as:
- (4)
- Set m = m + 1, and repeat steps (1) to (3) to obtain and , then
- (5)
- The sample entropy can be expressed as:
2.1.4. Fuzzy Entropy
- (1)
- Set a L-point sample sequence: ;
- (2)
- The phase-space reconstruction is performed on v(i) according to the sequence order, and a set of m-dimensional vectors are obtained as . The reconstructed vector can be written as:where , and is the average value described as the following equation:
- (3)
- , the distance between two vectors and , is defined as the maximum difference values between the corresponding elements of two vectors:
- (4)
- According to the fuzzy membership function , the similarity degree between two vectors and is defined as:where the fuzzy membership function is an exponential function, while n and s are the gradient and width of the exponential function, respectively.
- (5)
- Define the function :
- (6)
- Repeat the steps from (1) to (4) in the same manner, a set of (m + 1)-dimensional vectors can be reconstructed according to the order of sequence. Define the function:
- (7)
- The fuzzy entropy can be expressed as:
2.2. Fisher-Based Distance Metric
2.3. Support Vector Machine (SVM)
2.4. Performance Evaluation
3. Experiment and Results
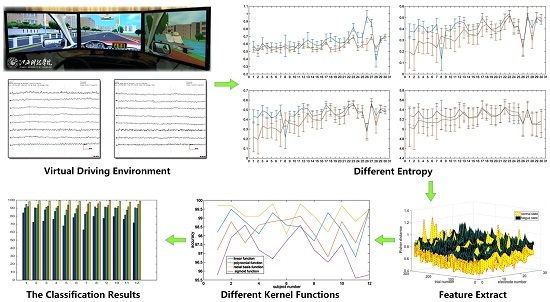
3.1. Data Source
3.2. Entropy Function Selection
3.3. Classification Result
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Logothetis, N.K.; Pauls, J.; Augath, M.; Trinath, T.; Oeltermann, A. Neurophysiological investigation of the basis of the fMRI signal. Nature 2001, 412, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naseer, N.; Hong, K.-S. fNIRS-based brain-computer interfaces: A review. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2015, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.J.; Hong, M.J.; Hong, K.-S. Decoding of four movement directions using hybrid NIRS-EEG brain-computer interface. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.J.; Hong, K.-S. Passive BCI based on drowsiness detection: An fNIRS study. Biomed. Opt. 2015, 6, 4063–4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, M.; Schmidt, E.A.; Kincses, W.E.; Fritzsche, M.; Bruns, A.; Aufmuth, C.; Bogdan, M.; Rosenstiel, W.; Schrauf, M. EEG alpha spindle measures as indicators of driver fatigue under real traffic conditions. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2011, 122, 1168–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, R.; Singh, K. Drowsiness Detection based on EEG Signal analysis using EMD and trained Neural Network. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2013, 10, 157–161. [Google Scholar]
- Wali, M.K.; Murugappan, M.; Ahmmad, B. Wavelet Packet Transform Based Driver Distraction Level Classification Using EEG. Math. Probl. Eng. 2013, 3, 841–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, A.G.; Orosco, L.; Laciar, E. Automatic detection of drowsiness in EEG records based on multimodal analysis. Med. Eng. Phys. 2014, 36, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resalat, S.N.; Saba, V. A practical method for driver sleepiness detection by processing the EEG signals stimulated with external flickering light. Signal Image Video Process. 2015, 9, 1151–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, K.; Park, H.K.; Kwon, D.H.; Kim, Y.T.; Cho, S.N.; Cho, H.J.; Peterson, B.S.; Jeong, J. Decreased cortical complexity in methamphetamine abusers. Psychiatry Res. 2012, 201, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.P.; Sriraam, N.; Benakop, P.G.; Jinaga, B.C. Entropies based detection of epileptic seizures with artificial neural network classifiers. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 3284–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Pachori, R.B.; Acharya, U.R. Application of entropy measures on intrinsic mode functions for the automated identification of focal electroencephalogram signals. Entropy 2015, 17, 669–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Crowcroft, J.; Zhang, J. Automatic epileptic seizure detection in EEGs based on optimized sample entropy and extreme learning machine. J. Neurosci. Methods 2012, 210, 132–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannathal, N.; Choo, M.L.; Acharya, U.R.; Sadasivan, P. Entropies for detection of epilepsy in EEG. Comput. Methods Progr. Biomed. 2005, 80, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azarnoosh, M.; Nasrabadi, A.M.; Mohammadi, M.R.; Firoozabadi, M. Investigation of mental fatigue through EEG signal processing based on nonlinear analysis. Symb. Dyn. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2011, 44, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. ACM SIGMOBILE Mob. Comput. Commun. Rev. 2001, 5, 3–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fell, J.; Röschke, J.; Mann, K.; Schäffner, C. Discrimination of sleep stages: A comparison between spectral and nonlinear EEG measures. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1996, 98, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pincus, S.M. Approximate entropy as a measure of system complexity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 2297–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richman, J.S.; Moorman, J.R. Physiological time-series analysis using approximate entropy and sample entropy. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2000, 278, H2039–H2049. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Wang, Z.; Xie, H.; Yu, W. Characterization of surface EMG signal based on fuzzy entropy. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2007, 15, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Zhuang, J.; Yu, W.; Wang, Z. Measuring complexity using FuzzyEn, ApEn, and SampEn. Med. Eng. Phys. 2009, 31, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wu, G.; Zhu, Y. Analysis of Affective Effects on Steady-State Visual Evoked Potential Responses. Intell. Auton. Syst. 2013, 12, 757–766. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, L.; Zeng, Q.; Lin, L.; Guo, Z.; Liu, Z.; Xiong, H.; Liu, S. Noninvasive prostate cancer screening based on serum surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy and support vector machine. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 091104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güler, I.; Ubeyli, E.D. Multiclass support vector machines for EEG-signals classification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2007, 11, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subasi, A.; Gursoy, M.I. EEG signal classification using PCA, ICA, LDA and support vector machines. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 8659–8666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, K.Q.; Li, X.P.; Ong, C.J.; Shao, S.Y.; Wilder-Smith, E.P. EEG-based mental fatigue measurement using multi-class support vector machines with confidence estimate. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2008, 119, 1524–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orrù, G.; Pettersson-Yeo, W.; Marquand, A.F.; Sartori, G.; Mechelli, A. Using support vector machine to identify imaging biomarkers of neurological and psychiatric disease: A critical review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2012, 36, 1140–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrett, D.; Peterson, D.A.; Anderson, C.W.; Thaut, M.H. Comparison of linear, nonlinear, and feature selection methods for EEG signal classification. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2003, 11, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schölkopf, B.; Smola, A.J. Learning with Kernels: Support Vector Machines, Regularization, Optimization, and Beyond; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.C.; Lin, C.J. LIBSVM: A library for support vector machines. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2011, 2, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.W.; Hsieh, C.J.; Chang, K.W.; Ringgaard, M.; Lin, C.J. Training and testing low-degree polynomial data mappings via linear SVM. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2010, 11, 1471–1490. [Google Scholar]
- Azar, A.T.; El-Said, S.A. Performance analysis of support vector machines classifiers in breast cancer mammography recognition. Neural Comput. Appl. 2014, 24, 1163–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.F.; Mu, Z.D.; Wang, P. Multi-feature authentication system based on event evoked electroencephalogram. J. Med. Imaging Health Inform. 2015, 5, 862–870. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, Z.D.; Hu, J.F.; Min, J.L. EEG-Based Person Authentication Using a Fuzzy Entropy-Related Approach with Two Electrodes. Entropy 2016, 18, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Z.D.; Hu, J.F.; Yin, J.H. Driving Fatigue Detecting Based on EEG Signals of Forehead Area. Int. J. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 2016, 1750011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.H.; Hu, J.F.; Mu, Z.D. Developing and evaluating a Mobile Driver Fatigue Detection Network Based on Electroencephalograph Signals. Healthc. Technol. Lett. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, H.; Fu, R. Automated detection of driver fatigue based on entropy and complexity measures. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2014, 15, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khushaba, R.N.; Kodagoda, S.; Lal, S.; Dissanayake, G. Driver drowsiness classification using fuzzy wavelet-packet-based feature-extraction algorithm. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 58, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.H.; Xu, S.L.; Rong, J.; Zhang, X.J. Discrimination threshold of driver fatigue based on Eletroencephalography sample entropy by Receiver Operating Characteristic curve Analysis. J. Southwest Jiaotong Univ. 2013, 43, 178–183. [Google Scholar]
- Acharya, U.R.; Fujita, H.; Sudarshan, V.K.; Koh, J.E. Application of entropies for automated diagnosis of epilepsy using EEG signals: A review. Knowl. Based Syst. 2015, 88, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Entropies | Acc | Sp | Sn | MCC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SpectralEn | 75.00 | 78.00 | 72.00 | 47.08 |
| ApproxEn | 87.25 | 84.05 | 87.50 | 73.57 |
| SampleEn | 89.75 | 84.50 | 91.00 | 78.66 |
| FuzzyEn | 93.50 | 92.50 | 91.50 | 85.02 |
| CombinedEn | 98.75 | 97.50 | 96.00 | 93.51 |
| No. | SpectralEn | ApproxEn | SampleEn | FuzzyEn | CombinedEn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 84.2108 | 90.3983 | 94.8875 | 91.8033 | 98.3625 |
| 2 | 72.4208 | 90.4583 | 90.1075 | 94.4533 | 99.2325 |
| 3 | 73.9208 | 87.8983 | 91.1175 | 92.4733 | 98.8825 |
| 4 | 76.0708 | 85.9283 | 90.3975 | 92.4933 | 99.6925 |
| 5 | 67.9408 | 80.9783 | 87.7875 | 94.0633 | 99.3725 |
| 6 | 78.2808 | 83.2783 | 89.3975 | 93.2733 | 98.8725 |
| 7 | 62.9308 | 82.4783 | 85.4575 | 95.3433 | 97.5425 |
| 8 | 79.6808 | 91.6483 | 89.9775 | 95.4333 | 98.0625 |
| 9 | 77.2308 | 91.5383 | 90.7775 | 93.4333 | 99.6925 |
| 10 | 79.5308 | 90.4383 | 89.8175 | 92.3833 | 98.6825 |
| 11 | 76.0208 | 81.4883 | 87.5675 | 91.7333 | 97.7025 |
| 12 | 71.7608 | 90.4683 | 89.7075 | 95.1133 | 98.9025 |
| No. | T5 | TP7 | TP8 | FP1 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | Fatigue | Variation | Normal | Fatigue | Variation | Normal | Fatigue | Variation | Normal | Fatigue | Variation | |
| 1 | 0.507 | 0.655 | 0.148↑ | 0.63 | 0.62 | 0.010↓ | 0.353 | 0.579 | 0.226↑ | 0.19 | 0.674 | 0.484↑ |
| 2 | 0.694 | 0.819 | 0.125↑ | 0.519 | 0.683 | 0.164↑ | 0.633 | 0.672 | 0.039↑ | 0.518 | 0.568 | 0.050↑ |
| 3 | 0.737 | 0.682 | 0.055↓ | 0.811 | 0.696 | 0.115↓ | 0.751 | 0.625 | 0.126↓ | 0.712 | 0.632 | 0.080↓ |
| 4 | 0.845 | 0.507 | 0.338↓ | 0.946 | 0.551 | 0.395↓ | 0.582 | 0.588 | 0.006↑ | 0.68 | 0.778 | 0.098↑ |
| 5 | 0.46 | 0.559 | 0.099↑ | 0.454 | 0.53 | 0.076↑ | 0.438 | 0.551 | 0.113↑ | 0.541 | 0.578 | 0.037↑ |
| 6 | 0.653 | 0.499 | 0.154↓ | 0.643 | 0.485 | 0.158↓ | 0.543 | 0.38 | 0.163↓ | 0.695 | 0.430 | 0.265↓ |
| 7 | 0.762 | 0.731 | 0.031↓ | 0.607 | 0.552 | 0.055↓ | 0.71 | 0.674 | 0.036↓ | 0.697 | 0.597 | 0.100↓ |
| 8 | 0.597 | 0.624 | 0.027↑ | 0.592 | 0.41 | 0.182↓ | 0.672 | 0.645 | 0.027↓ | 0.679 | 0.626 | 0.053↓ |
| 9 | 0.327 | 0.288 | 0.039↓ | 0.477 | 0.291 | 0.186↓ | 0.247 | 0.366 | 0.119↑ | 0.323 | 0.304 | 0.019↓ |
| 10 | 0.765 | 0.774 | 0.009↑ | 0.774 | 0.782 | 0.008↑ | 0.755 | 0.766 | 0.011↑ | 0.799 | 0.776 | 0.023↓ |
| 11 | 0.467 | 0.366 | 0.101↓ | 0.583 | 0.474 | 0.109↓ | 0.561 | 0.547 | 0.014↓ | 0.442 | 0.475 | 0.033↑ |
| 12 | 0.95 | 0.845 | 0.105↓ | 0.843 | 0.752 | 0.091↓ | 0.755 | 0.682 | 0.073↓ | 0.805 | 0.692 | 0.113↓ |
| Research Group | Number of Subjects | Feature Types | Classifier | Adopted Entropy | Acc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhang [37] | 20 | EEG + EOG + EMG | neural network | Approximate | 96.50% |
| Khushaba [38] | 31 | EEG + EOG | The Fuzzy Mutual Information based Wavelet Packet Algorithm | Fuzzy | 95% |
| Zhao [39] | 28 | EEG | Threshold of ROC curve | Sample | 95% |
| This paper | 12 | EEG | SVM (support vector machine) | Combined Entropy | 98.75% |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mu, Z.; Hu, J.; Min, J. Driver Fatigue Detection System Using Electroencephalography Signals Based on Combined Entropy Features. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7020150
Mu Z, Hu J, Min J. Driver Fatigue Detection System Using Electroencephalography Signals Based on Combined Entropy Features. Applied Sciences. 2017; 7(2):150. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7020150
Chicago/Turabian StyleMu, Zhendong, Jianfeng Hu, and Jianliang Min. 2017. "Driver Fatigue Detection System Using Electroencephalography Signals Based on Combined Entropy Features" Applied Sciences 7, no. 2: 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7020150
APA StyleMu, Z., Hu, J., & Min, J. (2017). Driver Fatigue Detection System Using Electroencephalography Signals Based on Combined Entropy Features. Applied Sciences, 7(2), 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7020150