Investigation on Eddy Current Sensor in Tension Measurement at a Resonant Frequency
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Model
2.1. LR Model
2.2. LRC Model
3. Finite Element Analysis
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
4.1. Experimental Setup
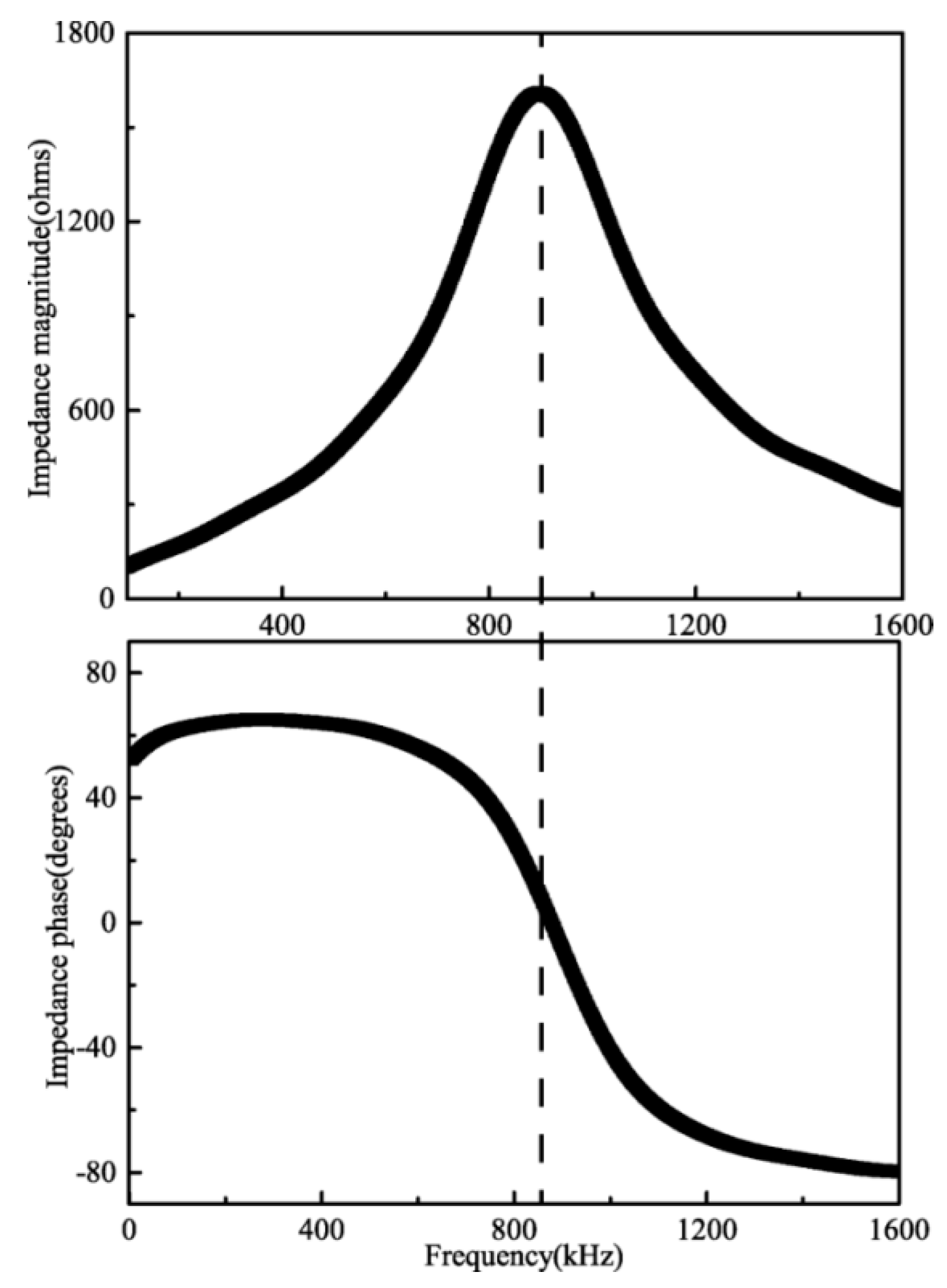
4.2. Sensor Performance at the Resonant Frequency
4.2.1. Impedance Magnitude
4.2.2. Impedance Phase
4.3. The Influence of Sleeve Structure on Sensor Performance
4.3.1. Correlation Coefficient
4.3.2. Relative Sensitivity Coefficient
5. Conclusions and Future Work
- (1)
- A novel sensor was designed, analyzed, and experimentally verified on 45# carbon steel with diameter of 12 mm. Compared with the traditional tension measurement methods, the eddy current sensor with a single-coil structure has the advantages of smaller size, lower cost, easier installation and less mutual interference.
- (2)
- This paper proposes a novel approach to tension measurement in ferromagnetic materials based on the impedance change of an eddy current sensor at the resonant frequency. In six repetitive experiments, the results show that the impedance parameters are efficient for estimating the tension. In all cases, the correlation coefficient reaches to 0.974 and the sensitivity coefficients are 2.581 ohms/kN in impedance magnitude analysis and 0.443 kHz/kN in impedance phase analysis, respectively.
- (3)
- In order to improve sensor performance, a sleeve structure was presented. Both finite element simulations and experimental results match well with the theoretical analysis, which indicates that the utilization of a sleeve structure remarkably improves sensor sensitivity and correlation coefficient.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, H.N.; Li, D.S.; Ren, L.; Yi, T.H.; Jia, Z.G.; Li, K.P. Structural health monitoring of innovative civil engineering structures in Mainland China. Struct. Monit. Maint. 2016, 3, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aflatooni, M.; Chan, T.H.T.; Thambiratnam, D.P. Condition monitoring and rating of bridge components in a rail or road network by using SHM systems within SRP. Struct. Monit. Maint. 2015, 2, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, M.J.; Yoo, H.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Cho, M.Y. Development of a wireless sensor network system for suspension bridge health monitoring. Autom. Constr. 2012, 21, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.F.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, Y.; Or, S.W.; Fan, K.Q.; Tang, Z.F. Smart elasto-magneto-electric (EME) sensors for stress monitoring of steel structures in railway infrastructures. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 2011, 12, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.Q.; Shi, Z.; Beck, J.L.; Li, H.; Hou, T.Y. Identification of time-varying cable tension forces based on adaptive sparse time-frequency analysis of cable vibrations. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2016, 24, e1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumitro, S.; Jarosevic, A.; Wang, M.L. Elasto-magnetic sensor utilization on steel cable stress measurement. In Proceedings of the First FIB Congress, Concrete Structures in the 21th Century, Osaka, Japan, 13–19 October 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.H.; Liu, J.; Zhou, D.; Huang, S.L. Using PVDF piezoelectric film sensors for in situ measurement of stayed-cable tension of cable-stayed bridges. Smart Mater. Struct. 1999, 8, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Lloyd, G.M.; Wang, M.L. Effects of temperature and corrosion thickness and composition on magnetic measurements of structural steel wires. NDT E Int. 2004, 37, 525–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, J.; Wang, M.L.; Shin, S.W.; Yun, C.B.; Jung, H.J.; Kim, J.T.; Eem, S.H. Field application of elasto-magnetic stress sensors for monitoring of cable tension force in cable-stayed bridges. Smart Struct. Syst. 2013, 12, 465–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Wang, M.L.; Lloyd, G.M. Measuring and modeling of corrosion in structural steels using magnetoelastic sensors. Smart Mater. Struct. 2005, 14, S24–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumitro, S.; Wang, M.L. Sustainable structural health monitoring system. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2005, 12, 445–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricken, W.; Schoenekess, H.C.; Becker, W.J. Improved multi-sensor for force measurement of pre-stressed steel cables by means of the eddy current technique. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2006, 129, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenekess, H.C.; Ricken, W.; Becker, W.J. Method to Determine Tensile Stress Alterations. IEEE Sens. J. 2007, 7, 1200–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricken, W.; Liu, J.; Beck, W.J. GMR and eddy current sensor in use of stress measurement. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2001, 91, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.; Kumar Kaushik, B.; Chakraborty, R. A novel E-shaped coil for eddy current testing. Sens. Rev. 2013, 33, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.D.; Huang, S.L.; Chen, W.M.; Jiang, J.S. Study of a steel strand tension sensor with difference single bypass excitation structure based on the magneto-elastic effect. Smart Mater. Struct. 2008, 17, 025019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.F.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, Y.; Or, S.W.; Fan, K.Q.; Tang, Z.F. Steel stress monitoring sensor based on elasto-magnetic effect and using magneto-electric laminated composite. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 07E516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Duan, Y.F.; Or, S.W.; Zhao, Y. Smart elasto-magneto-electric (EME) sensors for stress monitoring of steel cables: Design theory and experimental validation. Sensors 2014, 14, 13644–13660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.F.; Zhang, R.; Dong, C.Z.; Luo, Y.Z.; Or, S.W.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, K.Q. Development of Elasto-Magneto-Electric (EME) Sensor for In-Service Cable Force Monitoring. Int. J. Struct. Stab. Dyn. 2016, 16, 1640016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.T.; Yang, T.; Du, P.A. A new eddy current displacement measuring instrument independent of sample electromagnetic properties. NDT E Int. 2012, 48, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Javier, G.M.; Jaime, G.G.; Ernesto, V.S. Non-destructive techniques based on eddy current testing. Sensors 2011, 11, 2525–2565. [Google Scholar]
- Theodoulidis, T.; Wang, H.T.; Tian, G.Y. Extension of a model for eddy current inspection of cracks to pulsed excitations. NDT E Int. 2012, 47, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.Y.; Zhao, Z.X.; Baines, R.W. The research of inhomogeneity in eddy current sensors. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 1998, 69, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sophian, A.; Tian, G.Y.; Taylor, D.; Rudlin, J. Electromagnetic and eddy current NDT: A review. Insight 2001, 43, 302–306. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, J.W.; Tian, G.Y.; Barrans, S. Residual magnetic field sensing for stress measurement. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2007, 135, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhu, S.G.; Tian, G.Y.; Wang, H.T.; Wilson, J.; Wang, X. Stress measurement using magnetic Barkhausen noise and metal magnetic memory testing. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2010, 21, 055703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.Q.; Wang, J.; He, Y.Z.; Chen, D.W.; Li, K. Influence of metallic shields on pulsed eddy current sensor for ferromagnetic materials defect detection. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2016, 248, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Li, A.Q.; Li, W.R.; Shen, S. Wind-Induced Fatigue Analysis of High-Rise Steel Structures Using Equivalent Structural Stress Method. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, W.S.; Baek, J. Impedance-Based Non-Destructive Testing Method Combined with Unmanned Aerial Vehicle for Structural Health Monitoring of Civil Infrastructures. Appl. Sci. 2016, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Su, Y.; Zhang, L.; Bi, J.; Luo, J. Magnetoelastic Effect-Based Transmissive Stress Detection for Steel Strips: Theory and Experiment. Sensors 2016, 16, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]












| Parameters | Inductance | Resistance | Capacitance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Values | 176.5 μH | 1.8 ohms | 182.9 pF |
| Statistics | Mean Value | Variance | Coefficient of Variation (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 kN | loading | 1610 | 2.27 | 0.14 |
| unloading | 1607 | 1.53 | 0.10 | |
| 3 kN | loading | 1600 | 1.49 | 0.09 |
| unloading | 1596 | 1.07 | 0.07 | |
| 6 kN | loading | 1590 | 0.94 | 0.06 |
| unloading | 1588 | 1.11 | 0.07 | |
| 9 kN | loading | 1583 | 1.07 | 0.07 |
| unloading | 1580 | 0.90 | 0.06 | |
| 12 kN | loading | 1577 | 1.57 | 0.10 |
| unloading | 1575 | 0.94 | 0.06 | |
| 15 kN | loading | 1567 | 1.70 | 0.11 |
| unloading | 1567 | 1.70 | 0.11 | |
| Correlation Coefficient | Sleeve Structure | Non-Sleeve Structure | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loading | Unloading | Loading | Unloading | |
| Impedance magnitude | 0.991 | 0.986 | 0.981 | 0.982 |
| Impedance phase | 0.989 | 0.996 | 0.977 | 0.974 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiu, C.; Ren, L.; Li, H. Investigation on Eddy Current Sensor in Tension Measurement at a Resonant Frequency. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7060538
Xiu C, Ren L, Li H. Investigation on Eddy Current Sensor in Tension Measurement at a Resonant Frequency. Applied Sciences. 2017; 7(6):538. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7060538
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiu, Chengzhu, Liang Ren, and Hongnan Li. 2017. "Investigation on Eddy Current Sensor in Tension Measurement at a Resonant Frequency" Applied Sciences 7, no. 6: 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7060538
APA StyleXiu, C., Ren, L., & Li, H. (2017). Investigation on Eddy Current Sensor in Tension Measurement at a Resonant Frequency. Applied Sciences, 7(6), 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7060538









