Featured Application
The proposed method can be used for monitoring the healthy condition of civil structures.
Abstract
Truss-type designs are widely used in civil structures. Despite the fact that they are robust and reliable structures, different kinds of damage can appear. In order to avoid human and economic losses, the development and application of damage-detection methodologies are paramount. In this work, a methodology based on the empirical mode decomposition (EMD) method and the Shannon Entropy Index (SEI) to detect incipient damages associated with corrosion in a 3D 9-bay truss-type bridge is presented. As different EMD methods are presented in literature, the most representative methods are investigated in order to evaluate their performance for this task. To this end, the vibration signals generated in the truss-type bridge at different conditions are analyzed. For the damage condition, four severity levels of simulated corrosion (1 mm, 3 mm, 5 mm, and 8 mm of diameter reduction) generated into the elements of truss-type bridge are considered. Results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposal in terms of detecting corrosion in its very early stage (1 mm of reduction in the element).
1. Introduction
Civil structures represent a pillar in the economy and modern life because they provide protection to people and communication among different countries [1,2]. Among different kinds of civil structures, truss-type designs are one of the most employed structures in the design of civil structures because they offer great benefits such as ease of assembly and light weight. In this regard, this type of design has been used to construct bridges, towers, cranes, roof supports, and building skeletons, among others [3,4,5]. Nevertheless, they suffer continuous degradation or failure during their service life because of excitations produced by human or natural hazards, such as earthquakes, tornadoes, hurricanes, and wind, among others [6,7,8]. Hence, a continuous assessment of their structural integrity, known as structural health monitoring (SHM), is of paramount importance, since any deterioration or failure can be attended to early, in order to avoid potential human and economic losses.
In the past decade, several SHM schemes that make use of experimental procedures such as visual inspections, acoustic emission, ultrasound, laser scanning, and image processing produced by X-rays and thermography, among others, are employed for assessing structural conditions [9,10,11,12,13,14]. However, these procedures require a priori knowledge of the damage location, as well as an easy access to the area to be evaluated, and in certain cases, it is required to temporarily close the structure during its evaluation, which in real-life situations is not always possible [15]. For these reasons, a great deal of research of SHM in recent years has been focused on the development of new procedures based on vibration monitoring, because it has been demonstrated to be capable of detecting damages in hidden areas before they can be identified by visual inspections. Further, a SHM scheme based on vibration monitoring presents the advantages of being low cost and generating a continuous monitoring of structure without interrupting its normal operation [16,17]. The main idea of using a vibration-based SHM scheme is that damage in the structure affects its structural physical characteristics such as mass, stiffness, and damping, among others, producing a change in the measured response, which depends mainly on the severity level of damage. Particularly, the incipient fault produces slight modifications in the properties of the measured signal when they are compared with the ones measured when the structure was in a healthy condition [2]. Hence, a powerful signal processing technique or method capable of estimating subtle features in the measured signals is of vital relevance to detect damage, mainly in its incipient state, in order to schedule the corresponding maintenance in the civil structure.
In recent years, numerous signal processing strategies (SPS) that analyze vibrations to perform damage detection in civil structures have been proposed, among which the Fast Fourier transform (FFT) and its variants known as frequency response function (FRF) [18,19,20,21,22], multiple signal classification (MUSIC) [3,23,24,25], Wigner-Ville distribution (WVD) [26,27], and statistical time series models (STSM) [4,28,29,30,31,32] are the most employed. Nevertheless, although good results have been reported using the aforementioned techniques, they present significant limitations. For instance, FFT, and its variation FRF, cannot analyze signals that have non-linearity properties and a non-stationary (NS) nature, which are generally encountered in the measured responses of civil structures. In addition, they cannot adequately analyze noisy signals, producing errors in the estimated results [33,34]. On the other hand, MUSIC method is an efficient tool to analyze noisy signals; however, the number of frequencies that are present in the time signal must be known a-priori, which, in practical terms, is not possible. Moreover, transient signals still cannot be processed correctly [35]. WVD provides a time-frequency (TF) representation of transient and non-linear signals; however, cross-term items (frequencies not contained into the time-series signal) appear in the representation, affecting the technique’s ability to correctly estimate the instantaneous frequencies related to possible damages in the structure [36]. STSM models such as AR (autoregressive), MA (moving average), or ARMA (autoregressive moving average), among others, are used mainly to model the behavior of time signals with linear or time-invariant properties; however, they present problems when modeling noisy and non-linear (NL) structural responses, which are generally measured in structural responses [37]. In order to lessen the problems encountered when using the aforementioned techniques, other SPS are employed for monitoring structure conditions, such as wavelet transform (WT) [2,38,39,40,41,42,43] and blind source separation (BSS) [44,45]. In particular, WT is a TF strategy designed to handle non-linear and non-stationary signals. Unfortunately, to ensure the best possible results using WT, an appropriate selection of wavelet mother, as well as the decomposition level, is of vital importance to correctly monitor the structure’s condition [46,47]. The BSS method is a relative new signal processing technique employed for monitoring structure conditions, which is capable of exposing features that are blended together in the measured response; nevertheless, it still presents problems in the analysis of signals with non-stationary properties [48].
In recent years, empirical mode decomposition (EMD)-based methods have been introduced for SHM of simple beams or few structural elements [28,49,50,51,52] and system identification [53,54,55,56]. EMD-based methods are capable of analyzing NL and NS time series signals according to their frequency information [57], making them suitable tools for detecting damage in a structure, since the measured signals include non-linear and non-stationary properties. It must be noted that the aforementioned works have employed the EMD methods in civil structures to identify modal parameters such as natural frequencies, damping ratios, and modal shapes, among others, and to detect mainly consolidated damages (damage levels from moderate to high), requiring a high quantity of computational resources, because several indices such as energy, kurtosis, skewness, among others, are employed, as well as a high number of sensors; in several cases, sensors are placed next to damage, which is unrealistic in real-life situations. In addition, it should be noted that some of the aforementioned works make modifications to EMD methods in an attempt to overcome limitations, such as the capability of dealing with noisy signals, or improving the decomposition of the signal. While the obtained results from the adapted techniques are good, the resulting algorithms are application-specific, which might lead to sub-optimal results if the algorithms are not used for the specific application for which they were designed. Hence, it is evident that more effort for proposing low-complex and efficient methodologies based on the EMD methods, i.e., Ensemble-EMD (EEMD), and Complete-EEMD (CEEMD), without specific personalization, and few sensors for damage detection into civil structures mainly incipient damages (light damage level), a condition that slightly modifies the features into the measured signal, are still required.
Considering the benefits that EMD methods can generate in a vibration-based SHM scheme, in this article, a methodology based on both the EMD method and the Shannon Entropy Index (SEI) for detecting incipient damages in a 3D 9-bay truss-type bridge is presented. The most representative EMD-methods, i.e., EMD, EEMD, and CEEMD, are investigated in order to evaluate their performance for this task. In order to evaluate the effectiveness of the proposal, an exhaustive experimentation by considering four damage-severity levels produced by corrosion is carried out. The damages are generated in the elements reducing their diameters by 1 mm, 3 mm, 5 mm, and 8 mm, respectively; these values represent a reduction in stiffness from 10% to 66%, overcoming the recent work proposed by An et al. [58] and Blachowski et al. [5], whose proposals are only capable of identifying a reduction of stiffness starting from 24% to 40% in experimental cases. Results demonstrate that the EMD method coupled with SEI is capable of detecting corrosion at a very early stage (1 mm of reduction in element), regardless of the damage location, without complex or sophisticated modifications to the EMD method.
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Empirical Mode Decomposition (EMD)
Proposed by Huang et al. [59], the EMD method is a suitable SPS to analyze time signals with NL, transient, and NS properties. EMD can decompose a time signal in a set of frequency bands known as intrinsic mode functions (IMFs). To obtain an IMF, it must satisfy two conditions: a) the number of zero crossings and extrema into the time signal have to be either equal or different at most by one, and b) the average value of the upper and the lower envelopes must be equal zero.
In order to obtain each IMF, a method known as the “sifting process” is carried out; this method is described below:
- Detect the extrema points (local maximum and minimum points) of the original time signal .
- Connect the points estimated in (1), employing cubic-splines in order to obtain an upper- and lower-envelope. The average of both envelopes is assigned as , and it is subtracted from the original time signal to obtain a new time signal as follows:If does not satisfy the previous conditions (a) and (b), steps (1) and (2) are repeated until satisfies both conditions; then, is considered as the first IMF, defined as:
- Once the first frequency band or has been obtained, the signal is subtracted from the original time signal to calculate the residue signal as follows:
- Check if is a monotonic function, which would indicate that no more IMFs can be extracted. If is not a monotonic function, it has to be treated as the original time signal and repeat the steps (1) to (3) in order to estimate the other IMFs. The process is finished when becomes a monotonic function.
- Once the process is stopped, the original time signal is decomposed into intrinsic modes, IMFs, and the last residue as follows:
2.2. Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition (EEMD)
The EEMD method is known as a noise-assisted method, introduced by Wu and Huang [60], for decomposing noisy time signals into their fundamental components. It is based on the following steps:
- Generate new time signals mixing the original time signal and different white-noise series as follows:where represents the number of trials.
- Decompose the new time signals generated in (1) using the EMD method described in Section 2.1.
- Compute a true IMF, indexed with , as followswhere the IMF indexed with for the trial is represented by . It is recommended that the number of trials be as large as possible in order to obtain a suitable result.
2.3 Complete Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition (CEEMD)
Introduced by Torres et al. [57], the CEEMD method is known for being a variation of the EEMD method. On one hand, in the EEMD method, a residue for each trial is estimated. On the other hand, in the CEEMD method is obtained as a unique first residue , which is described by:
where is a frequency band or true IMF estimated in a similar manner to the EEMD method. So, an ensemble of plus different realizations is performed to estimate the second frequency ban or true . The near residue is estimated as . This process has to be recurrent until all the frequency bands or true IMFs are calculated.
2.4. Shannon Entropy (SE)
The SE index (SEI), a nonlinear measurement in dynamic signals, provides a measurement of the average information contents associated with the data randomness encountered in a signal or event [61]. SEI can vary from 0 to the number of bits of the analog-digital converter (ADC) employed to measure the input time signal, e.g., an ADC of 8 bits allows SEI values from 0 to 8, where a low value indicates that a low level of randomness in the signal; on the other hand, a high SEI value indicates that a high level randomness in the analyzed signal is present. Hence, the SEI can be a useful tool to show changes in the measured signals associated with the structure condition.
SEI of a time signal is calculated as follows:
where denotes the values of a random signal with possible outcomes , can be taken, represents the probability of in the signal x, and is the binary logarithm.
3. Methodology
Vibration-based SHM has become an important topic in civil and structural engineering because vibrations have been demonstrated to be sensitive to changes produced by damage in civil structures, even when that damage is located in internal areas. Hence, vibration analysis is considered a powerful tool for assessing the integrity of civil structures.
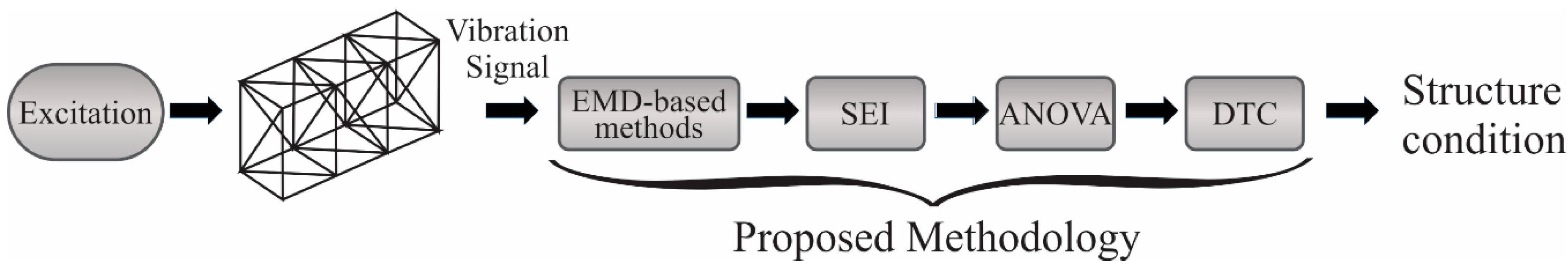
Figure 1 shows a schematic diagram of the proposed methodology for evaluating structure conditions in order to identify if the structure is healthy or presents damage produced by corrosion. It is based on four steps. In step 1, the vibrational response of the structure produced by a forced excitation (electrodynamic shaker) is analyzed or decomposed by three EMD methods, i.e., the EMD, EEMD, and CEEMD methods. In step 2, the decompositions or frequency bands (IMFs) estimated by EMD methods are processed by SEI, a nonlinear measure, to identify features to be used for damage detection. In step 3, the calculated SEI values for each IMF of the three EMD methods are evaluated using the ANOVA (analysis of variance) method, a statistical analysis, in order to determine the most discriminating values for assessing structural conditions. In step 4, the selected SEI values are classified using a decision tree classifier (DTC) in order to assess the condition of the bridge in an automatic way.
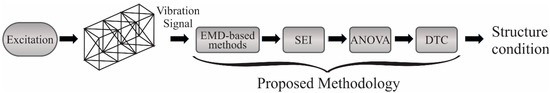
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the proposed methodology.
4. Experimentation
4.1. Experimental Setup
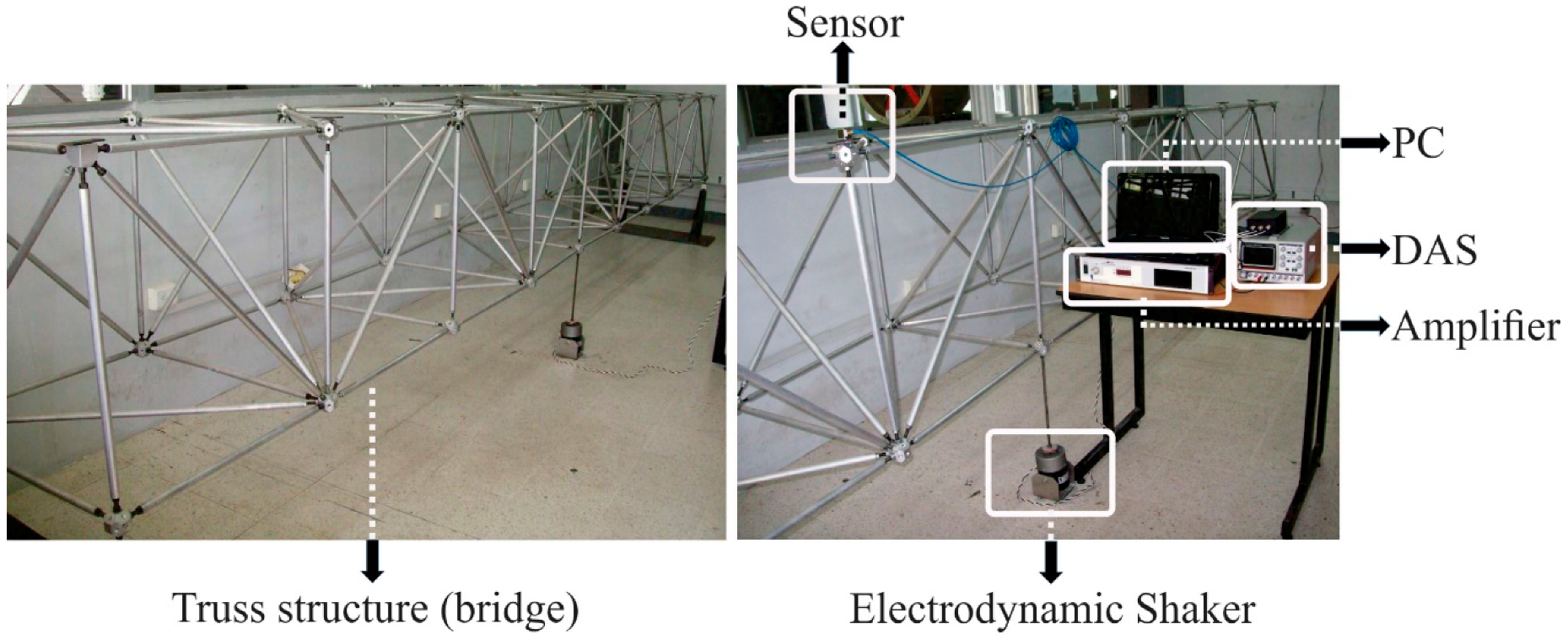
In order to validate the efficiency and usefulness of the proposal, the experimental data of a 9-bay, 162-member truss structure in a bridge style, located at Autonomous University of Queretaro, campus San Juan del Rio, are employed for assessing the healthy condition of the bridge, as well as its damage condition produced by corrosion with different levels of severity. Figure 2 shows the experimental setup. The bridge is made of aluminum and has the following dimensions: 6.4 m length, 0.71 m height, and 0.71 m width. It is subjected to white noise produced by an electrodynamic shaker from Labworks model ET-126B powered by a Labworks Model PA-138 linear power amplifier in order to simulate low-intensity ambient vibrations, i.e., a real-life situation [2], for assessing the bridge’s state. A tri-axis accelerometer, Ax, Ay, and Az, from KISTLER model 8395A placed on the four bay is used to measure the vibrational response of the bridge. It measures ±10 g with a resolution of 400 mV/g and a bandwidth from 0 to 1000 Hz. The vibration signals measured by the sensor are stored and sent to a PC using a data acquisition system (DAS) from National Instruments model NI-USB-6001 with a 14-bit resolution analog-to-digital converter (ADC). A sampling frequency of 200 Hz is set into the DAS, since the excitation presents a bandwidth from 0 to 100 Hz. It is important to mention that ambient vibrations are in this bandwidth or of low frequency [2]. The acquisition time for each test is 20 s, which results in 4000 samples. The experiment is repeated forty times for each condition (healthy and corrosion to different levels of damage i.e., 1 mm, 3 mm, 5 mm, and 8 mm (a total of 1480 tests) in order to generate statistical information.
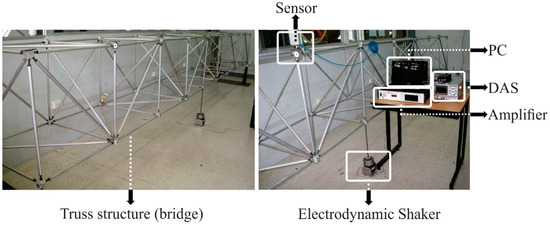
Figure 2.
Experimental setup.
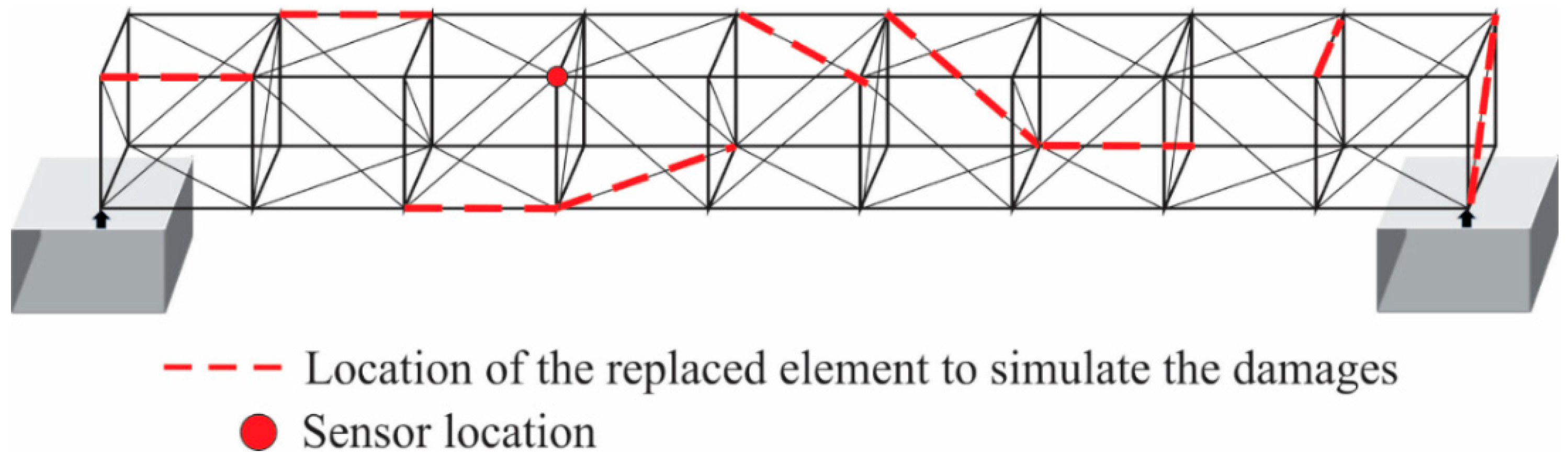
Initially, the vibration signals of the healthy bridge are acquired by using the sensor placed in the four-bay of the structure, as shown in Figure 3; then, the proposed methodology is applied to each axis of the vibration signals (Ax, Ay, and Az), where the nonlinear index (SEI), one for each axis and for each test of the healthy structure, are obtained. Next, the different levels of corrosion are applied to the bridge, and the measured vibration signals are proceeded by the proposal to estimate the nonlinear indices that allow us to estimate the structure’s condition. In this sense, in the first-bay, one of the elements is replaced by another with damage. By using the same location, the elements with different levels of damage are applied. This procedure is repeated for all the bays of the bridge, and their respective nonlinear indices are obtained. It is important to mention that the location of elements with damage is selected randomly in each bay with the aim of demonstrating that the proposal can detect damage regardless of the location of the damaged element. Figure 3 shows the location of the damaged elements applied to the bridge. It is also important to note that only one sensor is required to detect the damage regardless of the damage location, demonstrating the usefulness and effectiveness of the proposed technique.
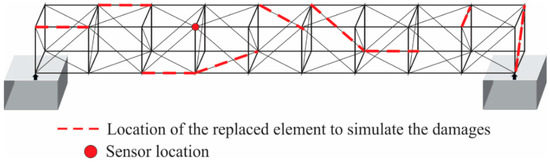
Figure 3.
Location of the bar elements with different damages applied to the bridge.
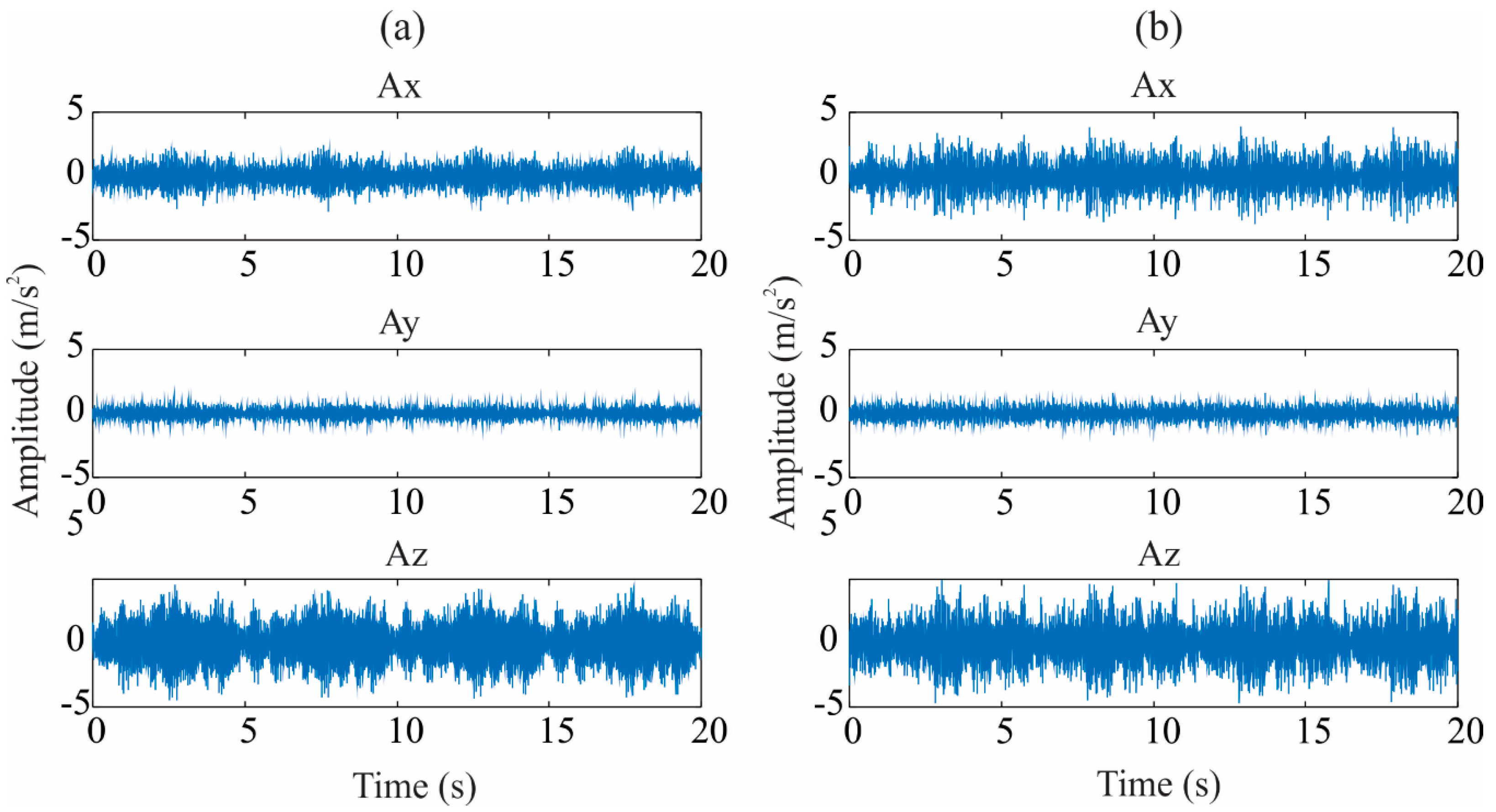
To exemplify the process, Figure 4 illustrates the measured vibration signal for healthy conditions and incipient damage produced in the first-bay (1 mm of reduction in the diameter of the bar element) in the all directions (Ax, Ay, and Ay), respectively. This figure shows that specific differences related to the structure’s condition between the healthy and corrosion-damaged segments cannot be readily observed. Hence, a method capable of revealing differences between a healthy and a damaged structure is presented here.
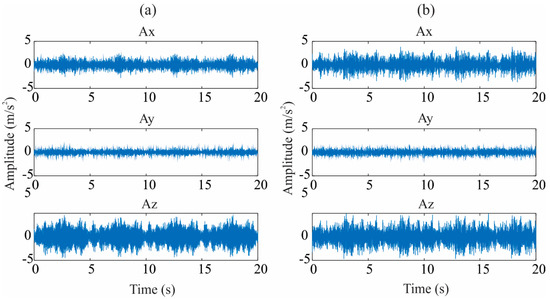
Figure 4.
Measured vibration signals in Ax, Ay, and Az for (a) healthy condition and (b) incipient damage in first-bay.
4.2. Study Cases
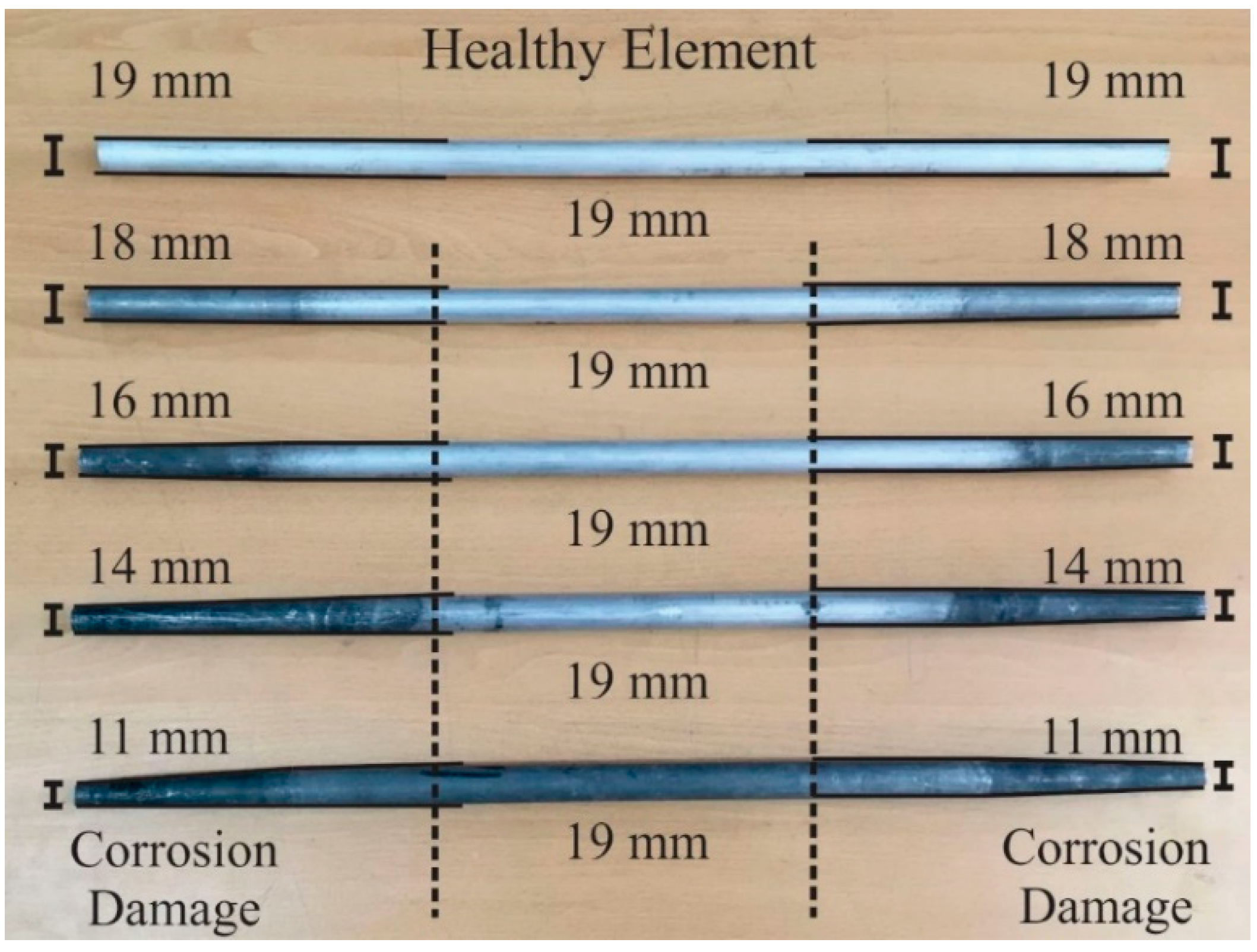
Corrosion is considered one of the main mechanisms that can damage a civil structure, especially truss structures. It is characterized by degrading the materials, mainly metals, that constitute a structure, resulting in weakness of the structural members, which can produce the collapse of the structure in certain cases; hence, corrosion identification in its early stage is of vital importance [62]. Corrosion can take years to degrade the material; hence, in order to accelerate the process, the bar element extremes of the bridge were immersed in hydrochloric acid, generating external corrosion damage. The corrosion damage was produced gradually in the bar element with the aim of observing the behavior of a bridge under four levels of damage. The healthy element presents a diameter of 19 mm. The damaged elements present reductions in their diameters of 1 mm, 3 mm, 5 mm, and 8 mm, representing incipient, light, moderate, and severe levels of damage respectively (see Figure 5). It should be pointed out that the damage levels are selected considering the minimum and maximum amount of diameter reduction that can be induced without compromising the member integrity, and ensuring a uniformly-distributed separation [3,5,58,63].
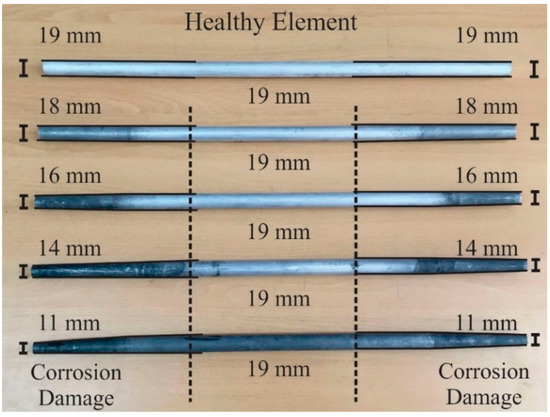
Figure 5.
Bar element with a healthy condition (19 mm of diameter in all sections) and bar elements with the different levels of corrosion (1 mm, 3 mm, 5 mm, and 8 mm of reduction in the diameter).
5. Results
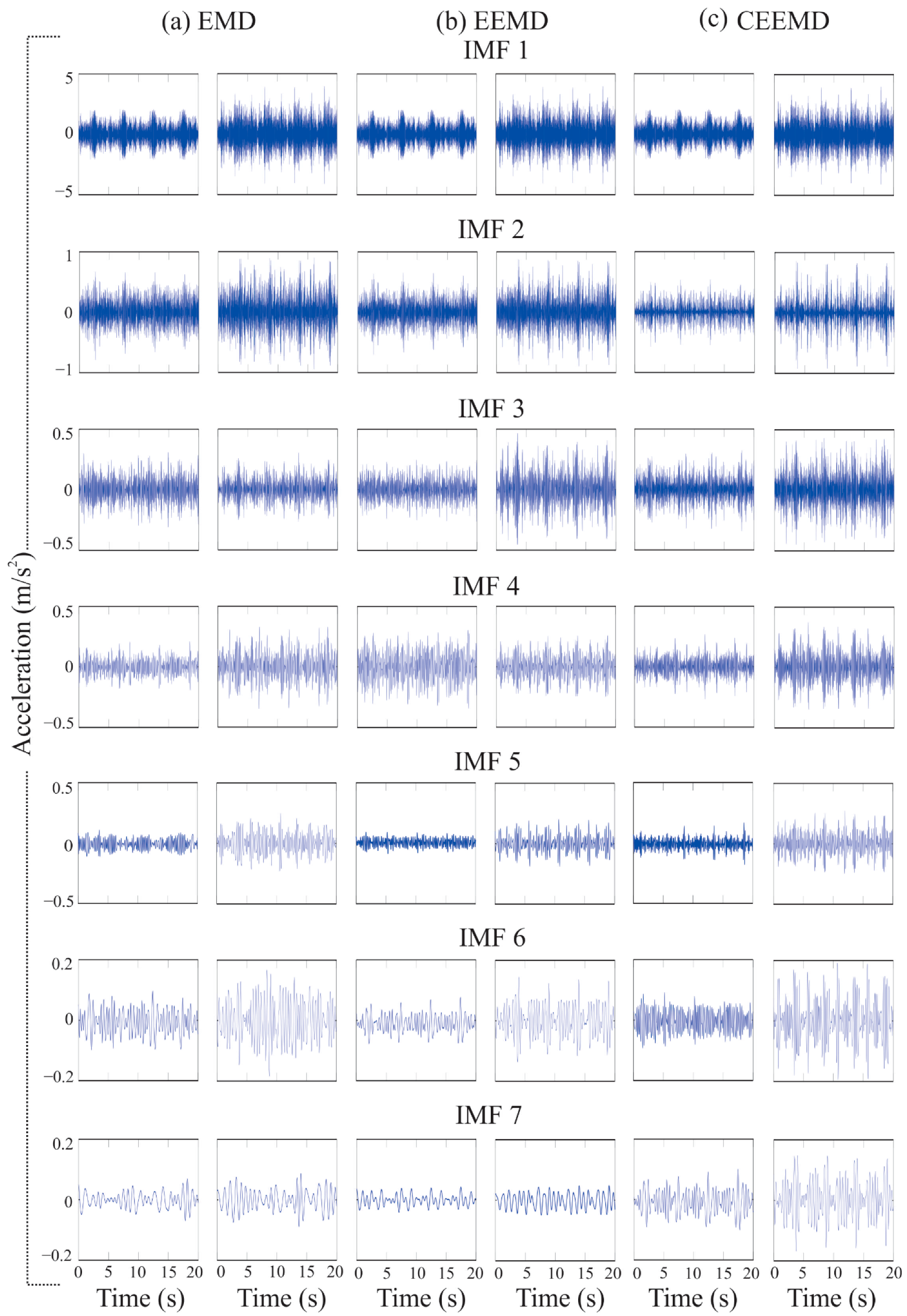
Following the proposed steps in the methodology, the measured vibration response of the bridge under different levels of damage is decomposed into its different frequency bands or IMFs using the three EMD-based methods. Figure 6 shows the first seven IMFs obtained for healthy and incipient damage conditions in Ax, respectively, using the EMD, EEMD, and CEEMD methods. From these figures, it is evident that there are not significant visual differences in the obtained IMFs using the three EMD-based methods; thus, it is necessary to perform a statistical analysis in order to determine both the method and the IMF that can provide the most discriminate information, since this condition will allow us to determine the structure’s condition in the most accurate way. It is important to mention that the same situation (no visible differences) is found in the remaining axis (Ay and Az).
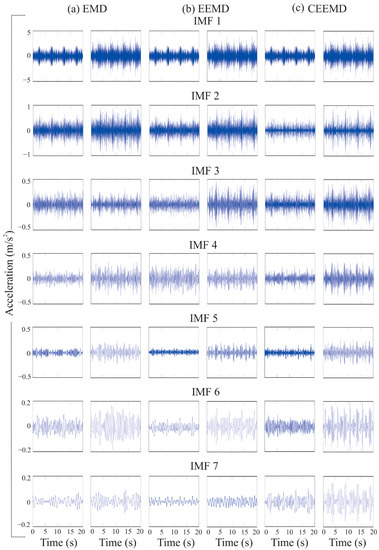
Figure 6.
The first seven IMFs obtained for the healthy and incipient damage conditions (damage located in first-bay) in Ax, respectively using (a) EMD, (b) EEMD and (c) CEEMD methods.
To perform the statistical analysis, the SEI values of all IMFs for each structure condition are obtained; then, the one-way ANOVA is used to obtain the p-value, which is the probability that the there are no significant differences between two sets of data. In general terms, the lower the p-value, the better the differentiation between the two groups. In this way, the IMF 1 fused with SEI that has the lowest p-value can be considered as the one that is the most discriminant for determining the structure’s condition. Table 1 summarizes the p-values computed by the three EMD methods for the first 7 IMFs of each axis. It is worth mentioning that the SEI values obtained by IMF 1 for all the three methods have the lowest p-value. Moreover, it is should be also noted that the three EMD methods have very closely p-values.

Table 1.
P-values estimated by one-way ANOVA for different EMD methods and IMFs.
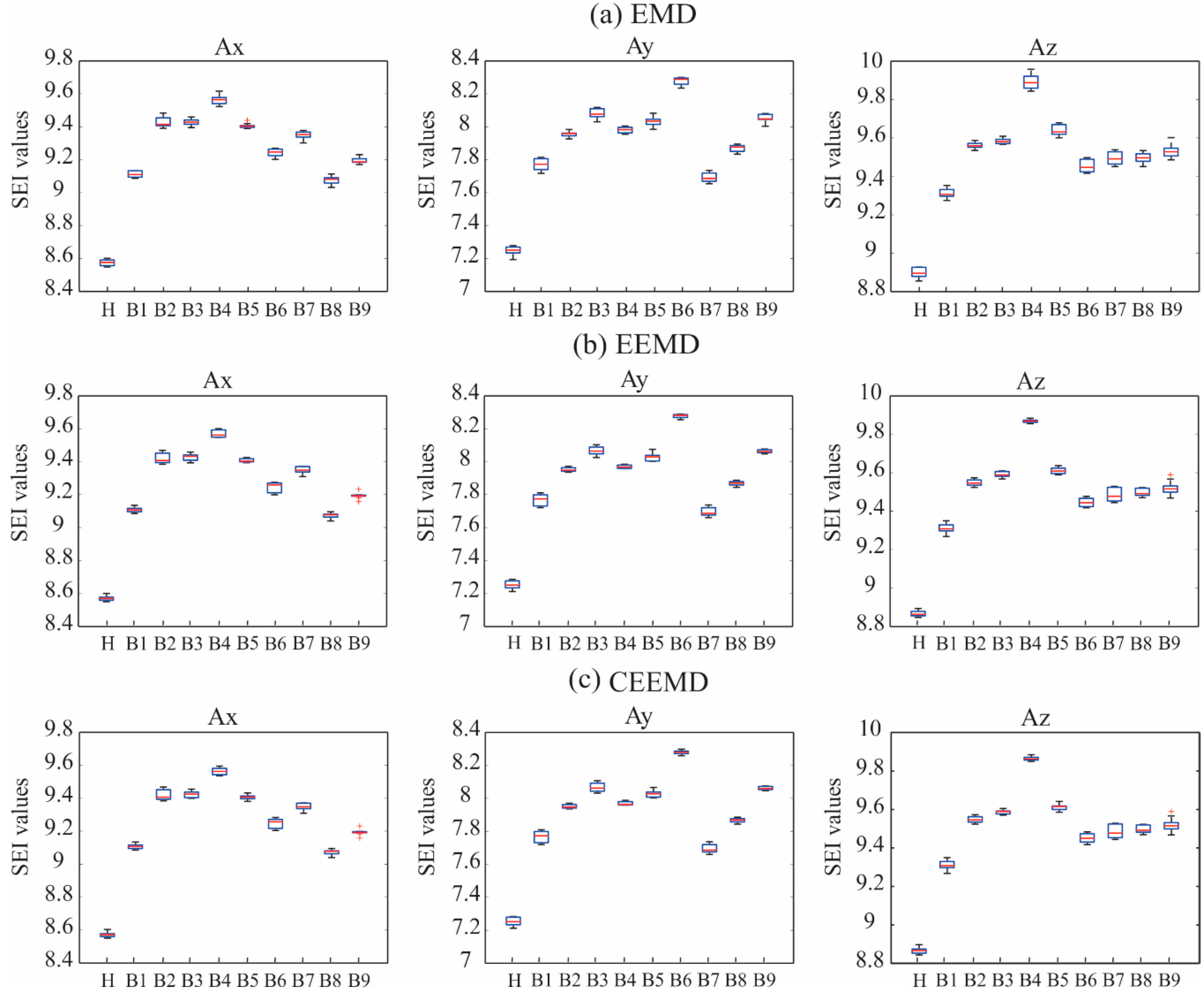
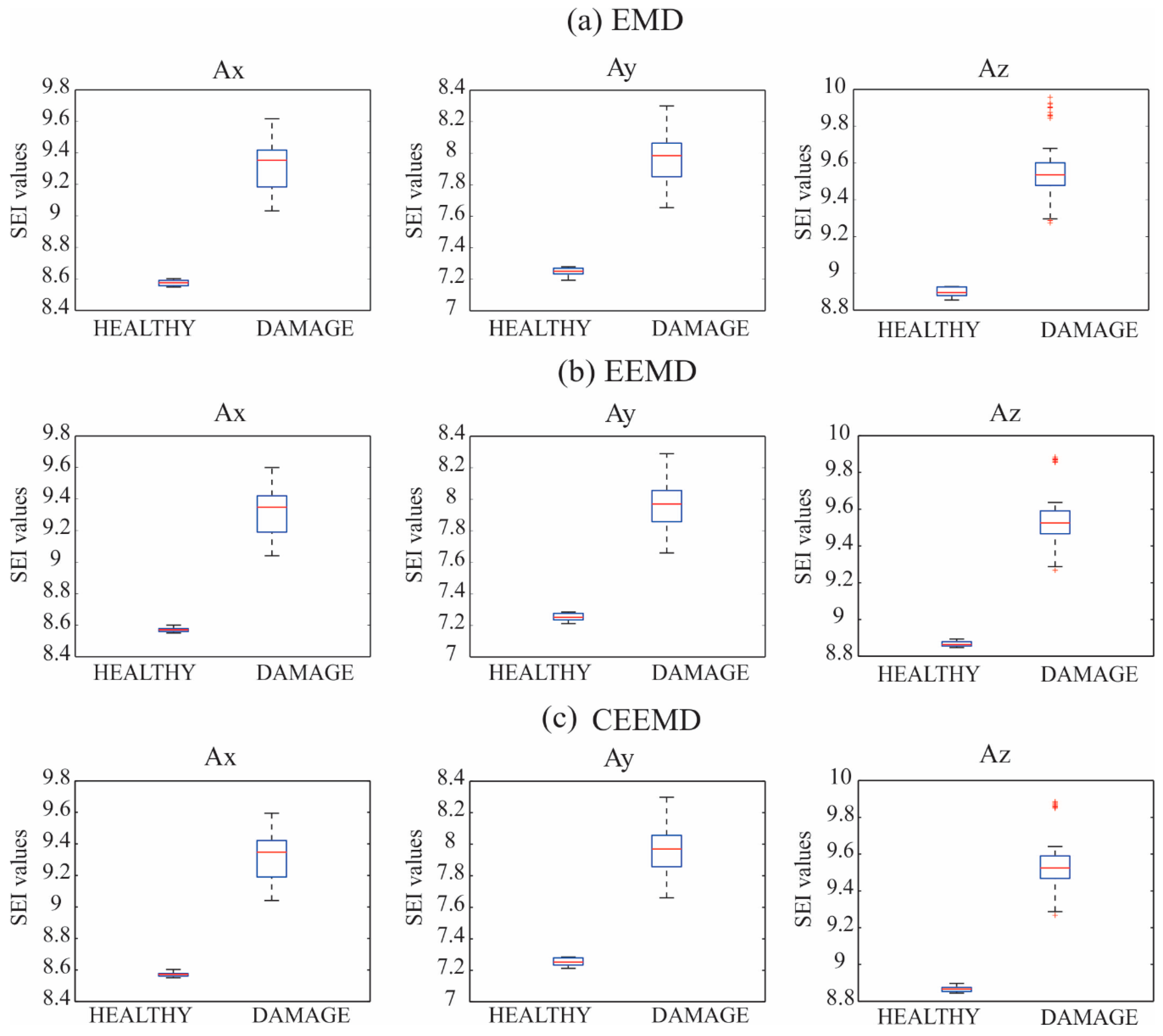
Figure 7 shows graphically the SEI values for the healthy (H) and the incipient damage condition encountered in each bay using the IMF 1 for Ax, Ay, and Az, and the three EMD methods, respectively. It is possible to observe that the three EMD-based methods estimate similar results, as all the box plots follow the same pattern, thereby justifying that the EMD method is suitable for the decomposition of the signals. Figure 8 shows the distribution of the estimated SEI values of the healthy condition and incipient damage using the IMF 1 for Ax, Ay, and Az, and the three EMD methods, respectively; however, in this case the SEI values calculated by IMF 1 for each axis and each bay of the incipient damage have been joined in order to show that the EMD fused with SEI is capable of detecting damage in the bridge regardless of the damage localization.
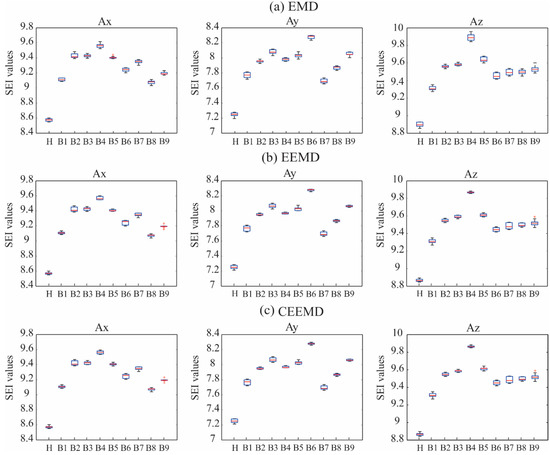
Figure 7.
Distribution of the estimated SEI values for the healthy (H) and the incipient damage condition for each bay (B) using the IMF 1 for Ax, Ay, and Az, and the (a) EMD, (b) EEMD, and (c) CEEMD methods, respectively.
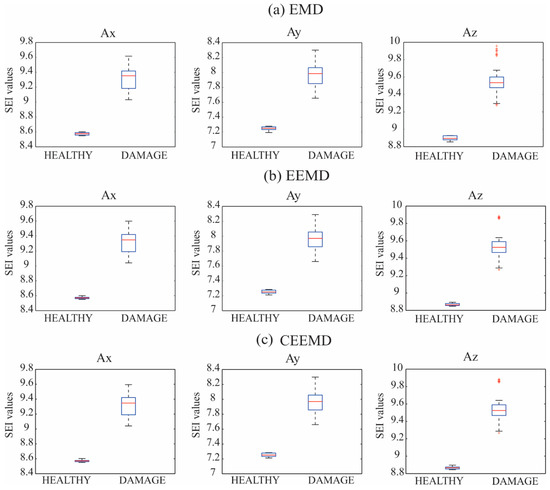
Figure 8.
Distribution of the estimated SEI values for the healthy and the incipient damage condition joining all the estimated SEI values for all the bays using the IMF 1 for Ax, Ay, and Az, and the (a) EMD, (b) EEMD, and (c) CEEMD methods, respectively.
Based on ANOVA results and Figure 7 and Figure 8, the EMD method fused with SEI is capable of identifying incipient damage; the other two EMD methods (EEMD and CEEMD methods) can be discarded for this task because they are more computationally-intensive, as mentioned in Section 2. In this way, the computational load used in the proposed methodology is kept at a minimum. Therefore, the IMF 1 in the x-direction (Ax), obtained using the EMD method, is selected as the most discriminant IMF.
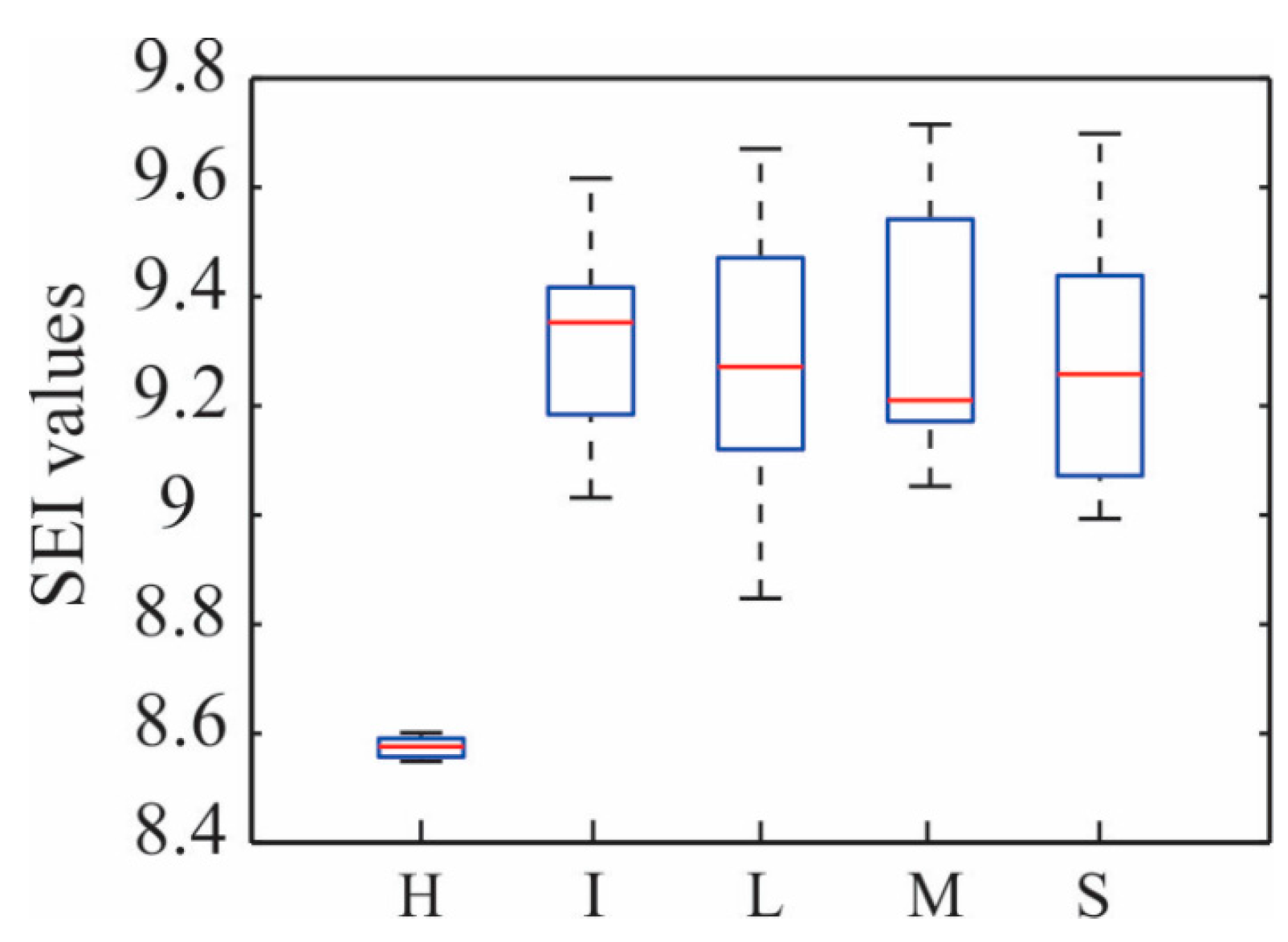
Once selected as the most useful method for evaluating the structure condition, it is used to verify its efficiency under other levels of damage such as moderate, high, and severe, which are represented by a reduction of diameter in the bar element of 3 mm, 5 mm, and 8 mm, respectively. Figure 9 illustrates the distribution of the SEI values estimated by using the IMF1 and Ax for healthy condition and for all the damage levels of corrosion treated in this work (1 mm (I: incipient), 3 mm (L: light), 5 mm (M: moderate), and 8 mm (S: severe) of reduction in the bar element diameter). Observing this figure, the obtained SEI values for the healthy condition and different levels of damage are completely separated, allowing us to identify different levels of damage regardless of its location.
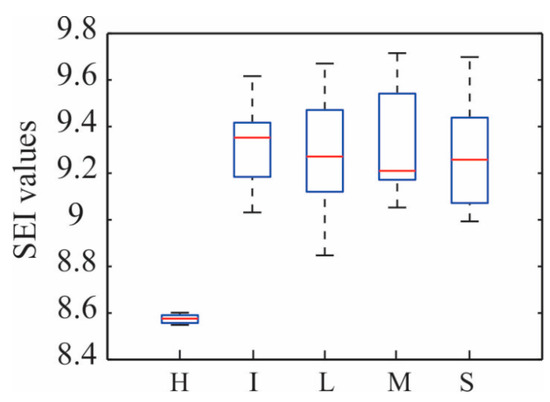
Figure 9.
Distribution of the estimated SEI values using IMF 1 and Ax for healthy condition (H) and for the four levels of corrosion, joining all SEI values estimated by all bays (1 mm (I: incipient), 3 mm (L: light), 5 mm (M: moderate), and 8 mm (S: severe) of reduction in the bar element diameter).
Finally, once all SEI values for the 5 conditions (healthy and four damage levels) have been estimated, and based on one-way ANOVA, two intervals of analysis are established and introduced to the DTC for the automatic evaluation of the structure condition. Interval 1 (healthy condition): 8.4 ≤ SEI ≤ 8.65 and interval 2 (damage condition): 8.69 ≤ SEI ≤ 9.8. Table 2 presents the classification results in form of a confusion matrix, showing that the proposed methodology is efficient and reliable for assessing the structure’s condition, because 100% accuracy is obtained.

Table 2.
Results of the DTC (confusion matrix) based on the estimated intervals using ANOVA of the estimated SCI values for all bays.
It is important to mention that the proposed method can become a useful tool for evaluating the condition of civil structures because (a) it can be considered of low computational complexity, allowing the implantation in hardware such as field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs), digital signal processors (DSPs), etc, (b) it requires only a sensor to determine the structure’s condition, and (c) it detects the presence of incipient damage in the structure regardless of its location, overcoming the recent work proposed by An et al. [58] and Blachowski et al. [5], where their proposals are only capable of identifying damages starting from a moderate level; in addition, they require more than one sensor.
6. Conclusions
This paper proposes a new methodology to perform the SHM in truss-type civil structures. It consists of the integration of the EMD method coupled with SEI to analyze the vibration structure response in order to obtain the features that can determining a given structure’s condition. In this regard, a statistical analysis using the one-way ANOVA is performed to determine the IMF number as well as the axis that has the most discriminate features. The IMFs obtained using three EMD-based methods (EMD, EEMD, and CEEMD) are compared. From Figure 6 and Table 1, it is shown that the three methods estimate very similar results, being also necessary to select the method that has the lowest computational burden [64]. In this way, EMD is the one that uses the fewest resources; therefore it is chosen as the signal processing technique in this proposal. In this way, the computational resources employed are kept at a minimum. On the other hand, the SEI was shown to be an effective and reliable index to detect damage, since an effectiveness of 100% was obtained using a low-complexity DTC. From Table 1, it is seen that IMF 1 has all the information required to detect damage, regardless of its severity. It should be pointed out that IMF 1 is a high-frequency mode; thus, failure is found in the high-frequency region.
The obtained results show that the proposal can detect a reduction of 1 mm in the bar diameter, which is a useful advantage in SHM applications. On the other hand, if the ADC resolution is increased, a more detailed signal can be acquired, which for noisier signals, can be useful; this can allow us to better estimate features using the SEI, possibly resulting in a lower p-value. Further, it must be noted that the proposed method can detect damage regardless its location, which is also a desirable feature, as it can be used in situations where the number of sensors is limited. Thanks to the moderate usage of computational resources, a real-time signal processing platform, such as a field programmable gate array, can be used to implement the proposal, as efficient implementations of the EMD and Shannon entropy methods have been developed [65,66], allowing for the development of the proposed strategy for the continuous assessment of truss structure integrity, by executing the proposal in specific time intervals, and comparing the obtained results with previous ones. Hence, the results presented allow us to affirm that the proposal can be considered as a solid alternative for SHM-based methodologies, where computational resources as well as the number of sensors are limited.
Author Contributions
Methodology: A.M.-G. and C.A.P.-R.; Experiments and Analyzed: M.V.-R., O.C.-A. and A.D.-G. Guided the research, Conception, and Revision: J.P.A.-S.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the Mexican Council of Science and Technology (CONACyT) by the scholarship 304844 and by the SEP-CONACyT CB-2015/254697 project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Qarib, H.; Adeli, H. A new adaptive algorithm for automated feature extraction in exponentially damped signals for health monitoring of smart structures. Smart Mater. Struct. 2015, 24, 125040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiei, M.H.; Adeli, H. A novel machine learning-based algorithm to detect damage in high-rise building structures. Struct. Des. Tall Spec. Build. 2017, 26, e1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osornio-Rios, R.A.; Amezquita-Sanchez, J.P.; Romero-Troncoso, R.J.; Garcia-Perez, A. MUSIC-ANN analysis for locating structural damages in a truss-type structure by means of vibrations. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2012, 27, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.W.; Chang, K.C.; Kitauchi, S.; McGetrick, P.J. A field experiment on a steel Gerber-truss bridge for damage detection utilizing vehicle-induced vibrations. Struct. Health Monit. 2016, 15, 174–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blachowski, B.; An, Y.; Spencer, B.F., Jr.; Ou, J. Axial strain accelerations approach for damage localization in statically determinate truss structures. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2017, 32, 304–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeli, H.; Jiang, X. Intelligent Infrastructure: Neural Networks, Wavelets, and Chaos Theory for Intelligent Transportation Systems and Smart Structures; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.R.; Yan, G.R.; Ou, J.P. Response surface method based on radial basis functions for modeling large-scale structures in model updating. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2013, 28, 210–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amezquita-Sanchez, J.P.; Valtierra-Rodriguez, M.; Adeli, H. Current efforts for prediction and assessment of natural disasters: Earthquakes, tsunamis, volcanic eruptions, hurricanes, tornados, and floods. Sci. Iran. 2017, 24, 2645–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.S.; Lee, H.M.; Adeli, H.; Lee, I. A new approach for health monitoring of structures: Terrestrial laser scanning. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2007, 22, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, T.; Yoshida, J.; Sugiyama, T.; Fujino, Y. Concrete crack detection by multiple sequential image filtering. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2012, 27, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, C.; Turan, O.T. Imaging tools for evaluation of gusset plate connections in steel truss bridges. J. Bridge Eng. 2013, 18, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, J.; Pirskawetz, S.; Zang, A. Detection of crack propagation in concrete with embedded ultrasonic sensors. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2005, 146, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yapar, O.; Basu, P.K.; Volgyesi, P.; Ledeczi, A. Structural health monitoring of bridges with piezoelectric AE sensors. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2015, 56, 150–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, F.; Cegla, F.B. On quantitative corrosion rate monitoring with ultrasound. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 812, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curadelli, R.O.; Riera, J.D.; Ambrosini, D.; Amani, M.G. Damage detection by means of structural damping identification. Eng. Struct. 2008, 30, 3497–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amezquita-Sanchez, J.P.; Adeli, H. Synchrosqueezed wavelet transform-fractality model for locating, detecting, and quantifying damage in smart highrise building structures. Smart Mater. Struct. 2015, 24, 065034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesen, P.; Sadhu, A. Performance of tensor decomposition-based modal identification under nonstationary vibration. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 035024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, P.; Lima, H.; Varum, H.; André, P. Optical fiber sensors for static and dynamic health monitoring of civil engineering infrastructures: Abode wall case study. Measurement 2012, 45, 1695–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.T.; Rahmatalla, S.; Eun, H.C. Damage detection by mixed measurements using accelerometers and strain gages. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 075014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetgul, M.; Senyurek, V.Y.; Uyandik, R.; Tansel, I.N.; Yazicioglu, O. Evaluation of the health of riveted joints with active and passive structural health monitoring techniques. Measurement 2015, 69, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.B.; Radzienski, M.; Kudela, P.; Ostachowicz, W. Fourier spectral-based modal curvature analysis and its application to damage detection in beams. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2016, 84, 763–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Li, D.; Zhang, S.; Ou, J. Analysis of wave motion in one-dimensional structures through fast-Fourier-transform-based wavelet finite element method. J. Sound Vib. 2017, 400, 369–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Adeli, H. Pseudospectra, MUSIC, and dynamic wavelet neural network for damage detection of highrise buildings. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2007, 71, 606–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Yuan, S.; Qiu, L. Multiple damage detection on aircraft composite structures using near-field MUSIC algorithm. Sens. Actuators A 2014, 214, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amezquita-Sanchez, J.P.; Park, H.S.; Adeli, H. A novel methodology for modal parameters identification of large smart structures using MUSIC, empirical wavelet transform, and Hilbert transform. Eng. Struct. 2017, 147, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshan-Ghias, A.; Shamsollahi, M.B.; Mobed, M.; Behzad, M. Estimation of modal parameters using bilinear joint time—Frequency distributions. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2007, 21, 2125–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoubi, A.; Mathews, V.; Harley, J.; Adams, D. Lamb Waves Mode Decomposition Using the Cross-wigner-ville Distribution. In Proceedings of the 10th International Workshop on Structural Health Monitoring, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA, 1–3 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.; Li, Y.; Lai, M. Structural damage detection using empirical-mode decomposition and vector autoregressive moving average model. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2010, 30, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Chong, J.W.; Chon, K.H.; Kim, J. Wavelet-based AR-SVM for health monitoring of smart structures. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 015003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.; Pakzad, S.N. Damage and noise sensitivity evaluation of autoregressive features extracted from structure vibration. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 025007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhu, J.H. Nonlinear damage detection using higher statistical moments of structural responses. Struct. Eng. Mech. 2015, 54, 221–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.C.; Kim, C.W. Modal-parameter identification and vibration-based damage detection of a damaged steel truss bridge. Eng. Struct. 2016, 122, 156–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewuyi, A.P.; Wu, Z. Vibration-based damage localization in flexural structures using normalized modal macrostrain techniques from limited measurements. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2011, 26, 154–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Esmaeily, A.; Melhem, H.G. Signal pattern-recognition for damage diagnosis in structures. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2012, 27, 699–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Perez, A.; Amezquita-Sanchez, J.P.; Dominguez-Gonzalez, A.; Sedaghati, R.; Osornio-Rios, R.A.; Romero-Troncoso, R.J. Fused empirical mode decomposition and wavelets for locating combined damage in a truss-type structure through vibration analysis. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 2013, 14, 615–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanos, P.D.; Giaralis, A.; Politis, N.P. Time-frequency representation of earthquake accelerograms and inelastic structural response records using the adaptive chirplet decomposition and empirical mode decomposition. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2007, 27, 675–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeli, H.; Jiang, X. Dynamic fuzzy wavelet neural network model for structural system identification. J. Struct. Eng. 2006, 132, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Ma, Z.J.; Ren, W.X. Crack detection from the slope of the mode shape using complex continuous wavelet transform. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2012, 27, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, P.R.; Nobrega, E.G. Lamb wave based damage detection and localization using two ring-shaped arrangement of piezo transducers. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2015, 48, 646–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hao, H. Health monitoring of joint conditions in steel truss bridges with relative displacement sensors. Measurement 2016, 88, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Oyadiji, S.O. Damage detection using modal frequency curve and squared residual wavelet coefficients-based damage indicator. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 83, 385–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Tang, J. On time-frequency domain feature extraction of wave signals for structural health monitoring. Measurement 2018, 114, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiei, M.H.; Adeli, H. A novel unsupervised deep learning model for global and local health condition assessment of structures. Eng. Struct. 2018, 156, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musafere, F.; Sadhu, A.; Liu, K. Time-Varying System Identification Using a Hybrid Blind Source Separation Method. In Structural Health Monitoring, Damage Detection & Mechatronics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 7, pp. 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Musafere, F.; Sadhu, A.; Liu, K. Towards damage detection using blind source separation integrated with time-varying auto-regressive modeling. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 015013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.L.; Liu, J.J.; Lai, H.C. Wavelet analysis for identification of damping ratios and natural frequencies. J. Sound Vib. 2009, 323, 130–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodogiannis, V.S.; Amina, M.; Petrounias, I. A clustering-based fuzzy-wavelet neural network model for short-term load forecasting. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2013, 23, 1350024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazra, B.; Sadhu, A.; Roffel, A.J.; Narasimhan, S. Hybrid time-frequency blind source separation towards ambient system identification of structures. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2012, 27, 314–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razi, P.; Esmaeel, R.A.; Taheri, F. Application of a robust vibration-based non-destructive method for detection of fatigue cracks in structures. Smart Mater. Struct. 2011, 20, 115017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, D.; Taheri, F. Damage identification in beams using empirical mode decomposition. Struct. Health Monit. 2011, 10, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.; Chiou, D.; Chen, C.; Liu, M.; Chiang, W.; Huang, P. Sensitivity of initial damage detection for steel structures using the Hilbert-Huang transform method. J. Vib. Control 2012, 19, 857–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, C.; Hao, H.; Li, Z.X. Multi-stage identification scheme for detecting damage in structures under ambient excitations. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 045006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.Y.; Chiang, W.L.; Chen, C.W.; Hsu, W.K.; Lu, L.C.; Chu, T.J. Identification and monitoring of bridge health from ambient vibration data. J. Vib. Control 2010, 17, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Shan, J.; Lu, X. Modal identification of Shanghai World Financial Center both from free and ambient vibration response. Eng. Struct. 2012, 36, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.H.; Chen, C.C.; Jhou, J.W.; Lai, G. A rapidly convergent empirical mode decomposition method for analyzing the environmental temperature effects on stay cable force. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2018, 33, 672–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosh, M.; Sadhu, A.; Vogrig, M. Multisensor-based hybrid empirical mode decomposition method towards system identification of structures. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2018, 25, e2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.E.; Colominas, M.A.; Schlotthauer, G.; Flandrin, P. A Complete Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition with Adaptive Noise. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Prague, Czech Republic, 22–27 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- An, Y.; Błachowski, B.; Zhong, Y.; Hołobut, P.; Ou, J. Rank-revealing QR decomposition applied to damage localization in truss structures. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2017, 24, e1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Liu, H.H. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, N.E. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A noise-assisted data analysis method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2009, 1, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sherrawi, M.H.; Lyashenko, V.; Edaan, E.M.; Sotnik, S. Corrosion as a source of destruction in construction. Int. J. Civ. Eng. Technol. 2018, 9, 306–314. [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Macias, F.J.; Perez-Ramirez, C.A.; Valtierra-Rodriguez, M.; Dominguez-Gonzalez, A.; Amezquita-Sanchez, J.P. Wavelet Transform-Fractal Dimension-Based Methodology for Damage Assessment in Truss Type Structures. In Proceedings of the 43rd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Beijing, China, 29 October–1 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mejia-Barron, A.; Valtierra-Rodriguez, M.; Granados-Lieberman, D.; Olivares-Galvan, J.C.; Escalera-Perez, R. The application of EMD-based methods for diagnosis of winding faults in a transformer using transient and steady state currents. Measurement 2018, 117, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camarena-Martinez, D.; Valtierra-Rodriguez, M.; Garcia-Perez, A.; Osornio-Rios, R.A.; Romero-Troncoso, R.J. Empirical mode decomposition and neural networks on FPGA for fault diagnosis in induction motors. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 908140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabal-Yepez, E.; Valtierra-Rodriguez, M.; Romero-Troncoso, R.J.; Garcia-Perez, A.; Osornio-Rios, R.A.; Miranda-Vidales, H.; Alvarez-Salas, R. FPGA-based entropy neural processor for online detection of multiple combined faults on induction motors. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2012, 30, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).