3D Bioprinting Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Neural Tissues Using a Novel Lab-on-a-Printer Technology
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Culture and Expansion of NPCs
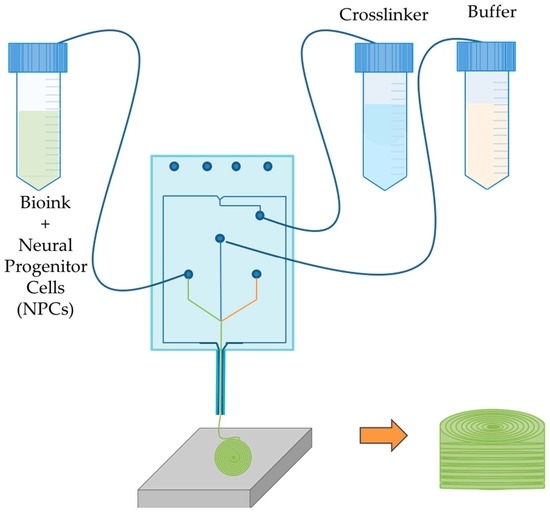
2.2. Bioprinting Process
2.3. Culture of Bioprinted Constructs
2.4. Cell Viability
2.4.1. Viability Assay
2.4.2. Flow Cytometry
2.5. Immunocytochemistry
3. Results
3.1. Bioprinted NPCS in Cylindrical Constructs
3.2. Cell Viability
3.3. Protein Expression of 3D Bioprinted Neural Tissues
3.3.1. Flow Cytometry
3.3.2. Immunocytochemistry
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maitin, I.B.; Cruz, E. Current Diagnosis & Treatment: Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Spinal Cord Injury. Available online: http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/spinal-cord-injury (accessed on 2 November 2018).
- Fehlings, M.G.; Vaccaro, A.R.; Ditunno, J.; Vaccaro, A.R.; Rossignol, S.; Burns, A. Essentials of Spinal Cord Injury: Basic Research to Clinical Practice; Thieme Medical Publishers, Incorporated: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, R.; Singh, M.; Kumar, K.; Jahanavi, V.M.; Jena, R.; Munivenkatappa, A.; Bhandarkar, P.; Agrawal, A. Understanding the Presentations and Patterns of Traumatic Spinal Cord Injuries to Develop the Data Collection Format. Indian J. Neurotrauma 2017, 14, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-W.; Huang, Y.-P.; Pan, S.-L. Spinal Cord Injury Is Related to an Increased Risk of Multiple Sclerosis: A Population-Based, Propensity Score-Matched, Longitudinal Follow-Up Study. J. Neurotrauma 2015, 32, 655–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cox, A.; Varma, A.; Banik, N. Recent Advances in the Pharmacologic Treatment of Spinal Cord Injury. Metab. Brain Dis. 2015, 30, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temenoff, J.S.; Mikos, A.G. Biomaterials: The Intersection of Biology and Materials Science; Pearson/Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2008; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, M.; Willerth, S.M. 3-D Bioprinting of Neural Tissue for Applications in Cell Therapy and Drug Screening. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2017, 5, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Zhai, P.; Chen, X.; Schreyer, D.J.; Sun, X.; Cui, F. Bioengineered Scaffolds for Spinal Cord Repair. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2011, 17, 177–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, G.; Cui, X. Three-dimensional bioprinting in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Biotechnol. Lett. 2016, 38, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mothe, A.J.; Tator, C.H. Advances in stem cell therapy for spinal cord injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 3824–3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nandoe Tewarie, R.S.; Hurtado, A.; Bartels, R.H.; Grotenhuis, A.; Oudega, M. Stem Cell-Based Therapies for Spinal Cord Injury. J. Spinal Cord Med. 2009, 32, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y. Induced pluripotent stem cells, new tools for drug discovery and new hope for stem cell therapies. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2009, 2, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.-Y.; Weick, J.P.; Yu, J.; Ma, L.-X.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Thomson, J.A.; Zhang, S.-C. Neural differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells follows developmental principles but with variable potency. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4335–4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hospodiuk, M.; Dey, M.; Sosnoski, D.; Ozbolat, I.T. The bioink: A comprehensive review on bioprintable materials. Biotechnol. Adv. 2017, 35, 217–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.; Douglas, S.; Michelle Willerth, S. Mechanically stable fibrin scaffolds promote viability and induce neurite outgrowth in neural aggregates derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, I.-Y.; Seo, S.-J.; Moon, H.-S.; Yoo, M.-K.; Park, I.-Y.; Kim, B.-C.; Cho, C.-S. Chitosan and its derivatives for tissue engineering applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2008, 26, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasnim, N.; De la Vega, L.; Kumar, S.A.; Abelseth, L.; Alonzo, M.; Amereh, M.; Joddar, B.; Willerth, S.M. 3D Bioprinting Stem Cell Derived Tissues. Cell. Mol. Bioeng. 2018, 11, 219–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mandrycky, C.; Wang, Z.; Kim, K.; Kim, D.-H. 3D bioprinting for engineering complex tissues. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tasoglu, S.; Demirci, U. Bioprinting for stem cell research. Trends Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bsoul, A.; Cretu, E.; Walus, K. Lab-on-a-printer platform technology. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Miniaturized Systems for Chemistry and Life Sciences, Gyeongju, Korea, 25–29 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lab-On-A-Printer. Available online: https://www.aspectbiosystems.com/technology (accessed on 20 September 2018).
- Takazawa, T.; Croft, G.F.; Amoroso, M.W.; Studer, L.; Wichterle, H.; MacDermott, A.B. Maturation of Spinal Motor Neurons Derived from Human Embryonic Stem Cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neely, M.D.; Litt, M.J.; Tidball, A.M.; Li, G.G.; Aboud, A.A.; Hopkins, C.R.; Chamberlin, R.; Hong, C.C.; Ess, K.C.; Bowman, A.B. DMH1, a Highly Selective Small Molecule BMP Inhibitor Promotes Neurogenesis of hiPSCs: Comparison of PAX6 and SOX1 Expression during Neural Induction. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2012, 3, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Du, Z.-W.; Chen, H.; Liu, H.; Lu, J.; Qian, K.; Huang, C.-L.; Zhong, X.; Fan, F.; Zhang, S.-C. Generation and expansion of highly pure motor neuron progenitors from human pluripotent stem cells. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, B.-Y.; Zhang, S.-C. Differentiation of spinal motor neurons from pluripotent human stem cells. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Vega, L.; Karmirian, K.; Willerth, S.M. Engineering Neural Tissue from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells Using Novel Small Molecule Releasing Microspheres. Adv. Biosyst. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.; Yau, S.-Y.; Sun, L.; Gabers, N.; Bibault, E.; Christie, B.R.; Willerth, S.M. Optimizing Differentiation Protocols for Producing Dopaminergic Neurons from Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells for Tissue Engineering Applications: Supplementary Issue: Stem Cell Biology. Biomarker Insights 2015, 10, BMI-S20064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbay, A.; De La Vega, L.; Nixon, G.; Willerth, S. Guggulsterone-releasing microspheres direct the differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells into neural phenotypes. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 13, 034104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thomas, A.M.; Kubilius, M.B.; Holland, S.J.; Seidlits, S.K.; Boehler, R.M.; Anderson, A.J.; Cummings, B.J.; Shea, L.D. Channel density and porosity of degradable bridging scaffolds on axon growth after spinal injury. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 2213–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghasemi-Mobarakeh, L.; Prabhakaran, M.P.; Morshed, M.; Nasr-Esfahani, M.-H.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospun poly (ɛ-caprolactone)/gelatin nanofibrous scaffolds for nerve tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 4532–4539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, M.P.; Hou, Z.; Propson, N.E.; Zhang, J.; Engstrom, C.J.; Costa, V.S.; Jiang, P.; Nguyen, B.K.; Bolin, J.M.; Daly, W. Human pluripotent stem cell-derived neural constructs for predicting neural toxicity. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 12516–12521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Joung, D.; Truong, V.; Neitzke, C.C.; Guo, S.Z.; Walsh, P.J.; Monat, J.R.; Meng, F.; Park, S.H.; Dutton, J.R.; Parr, A.M. 3D Printed Stem-Cell Derived Neural Progenitors Generate Spinal Cord Scaffolds. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1801850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Tomaskovic-Crook, E.; Lozano, R.; Chen, Y.; Kapsa, R.M.; Zhou, Q.; Wallace, G.G.; Crook, J.M. Functional 3D neural mini-tissues from printed gel-based bioink and human neural stem cells. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 1429–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Q.; Tomaskovic-Crook, E.; Wallace, G.G.; Crook, J.M. 3D bioprinting human induced pluripotent stem cell constructs for in situ cell proliferation and successive multilineage differentiation. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1700175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Name | Letter Code | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Negative | N+ | CHIR, SB, LDN |
| Puro | P+ | Puro + CHIR, SB, LDN |
| RA | R+ | RA+ CHIR, SB, LDN |
| Puro and RA | PR+ | Puro and RA+ CHIR, SB, LDN |
| Puro and RA | PR− | Puro and RA |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De la Vega, L.; A. Rosas Gómez, D.; Abelseth, E.; Abelseth, L.; Allisson da Silva, V.; Willerth, S.M. 3D Bioprinting Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Neural Tissues Using a Novel Lab-on-a-Printer Technology. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2414. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122414
De la Vega L, A. Rosas Gómez D, Abelseth E, Abelseth L, Allisson da Silva V, Willerth SM. 3D Bioprinting Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Neural Tissues Using a Novel Lab-on-a-Printer Technology. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(12):2414. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122414
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe la Vega, Laura, Diego A. Rosas Gómez, Emily Abelseth, Laila Abelseth, Victor Allisson da Silva, and Stephanie M. Willerth. 2018. "3D Bioprinting Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Neural Tissues Using a Novel Lab-on-a-Printer Technology" Applied Sciences 8, no. 12: 2414. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122414
APA StyleDe la Vega, L., A. Rosas Gómez, D., Abelseth, E., Abelseth, L., Allisson da Silva, V., & Willerth, S. M. (2018). 3D Bioprinting Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Neural Tissues Using a Novel Lab-on-a-Printer Technology. Applied Sciences, 8(12), 2414. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122414