Electrically Tunable Propagation Properties of the Liquid Crystal-Filled Terahertz Fiber
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Design of the THz LC-MOF
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Parameter Dependence of Bandgaps
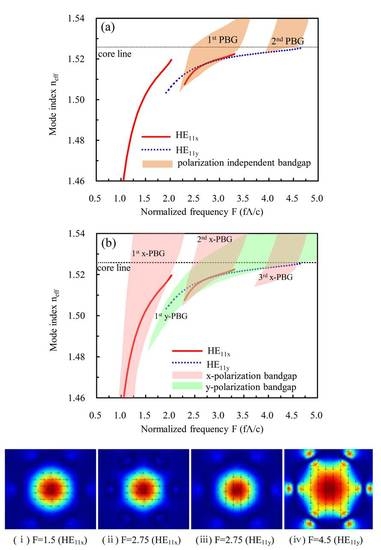
3.2. Polarization Dependence of the Electrically Tunable Bandgaps
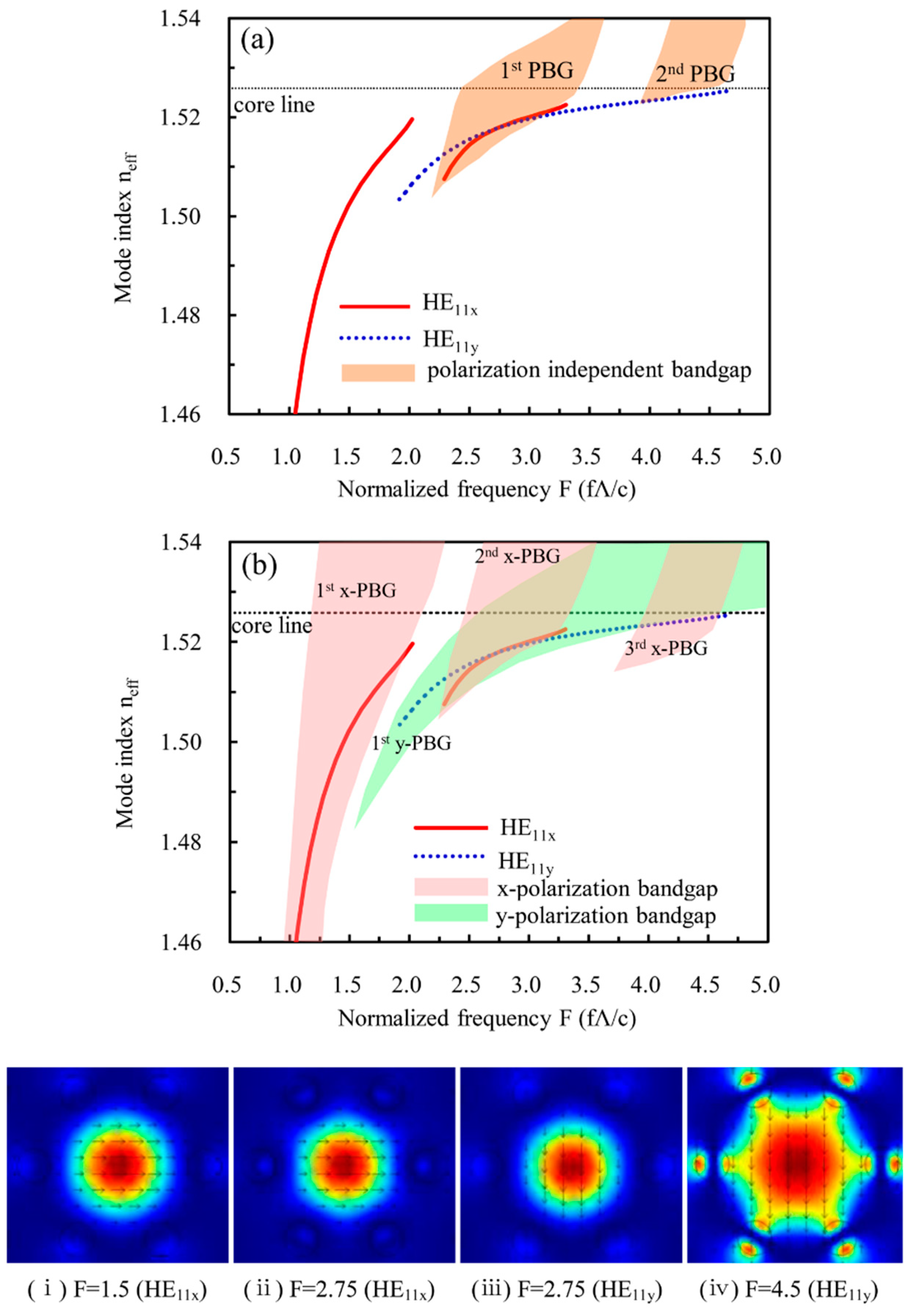
3.3. Guided-Mode Properties of the Designed THz LC-MOF
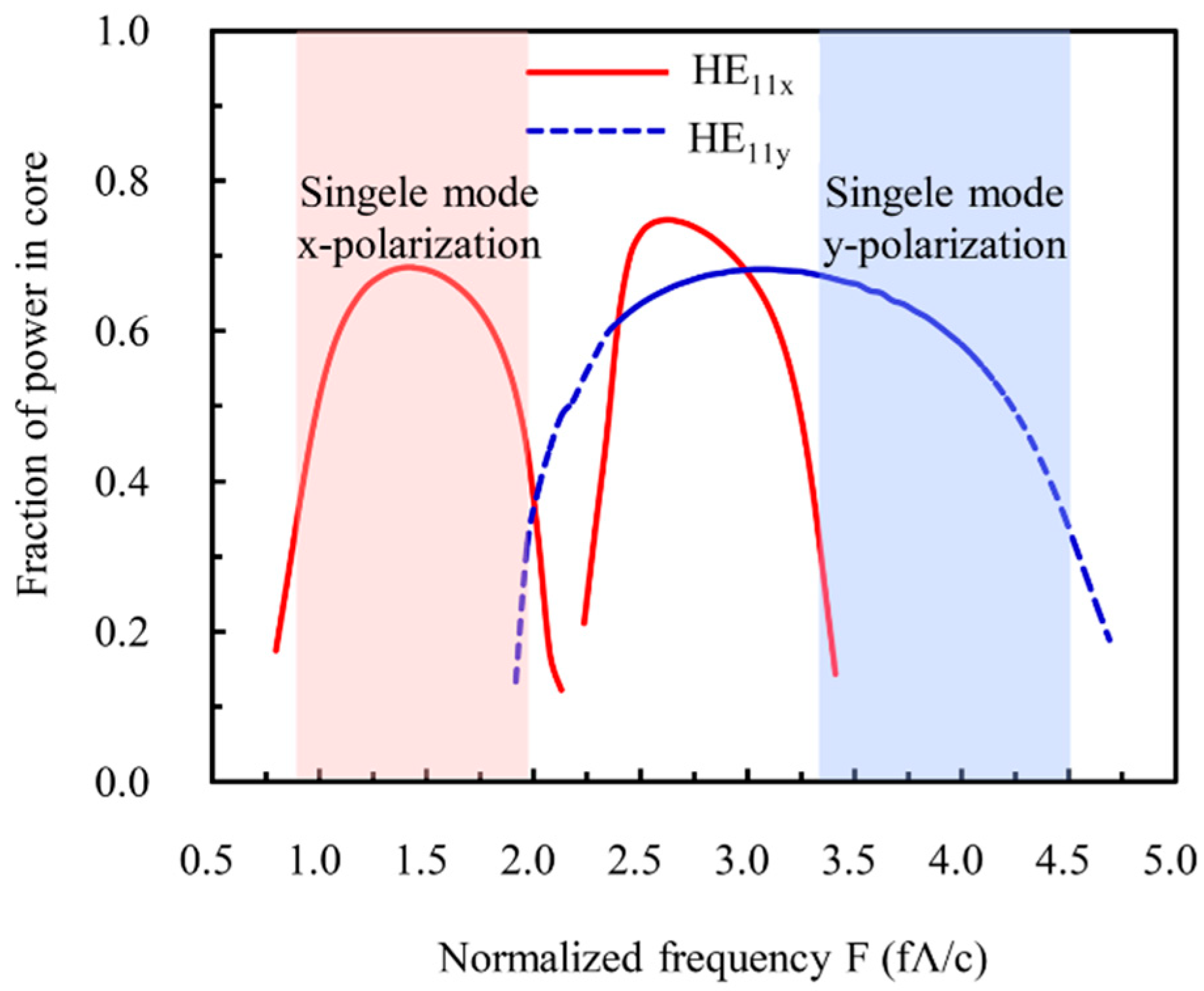
3.4. Electrically Tunable Confinement Loss of the Designed THz LC-MOF
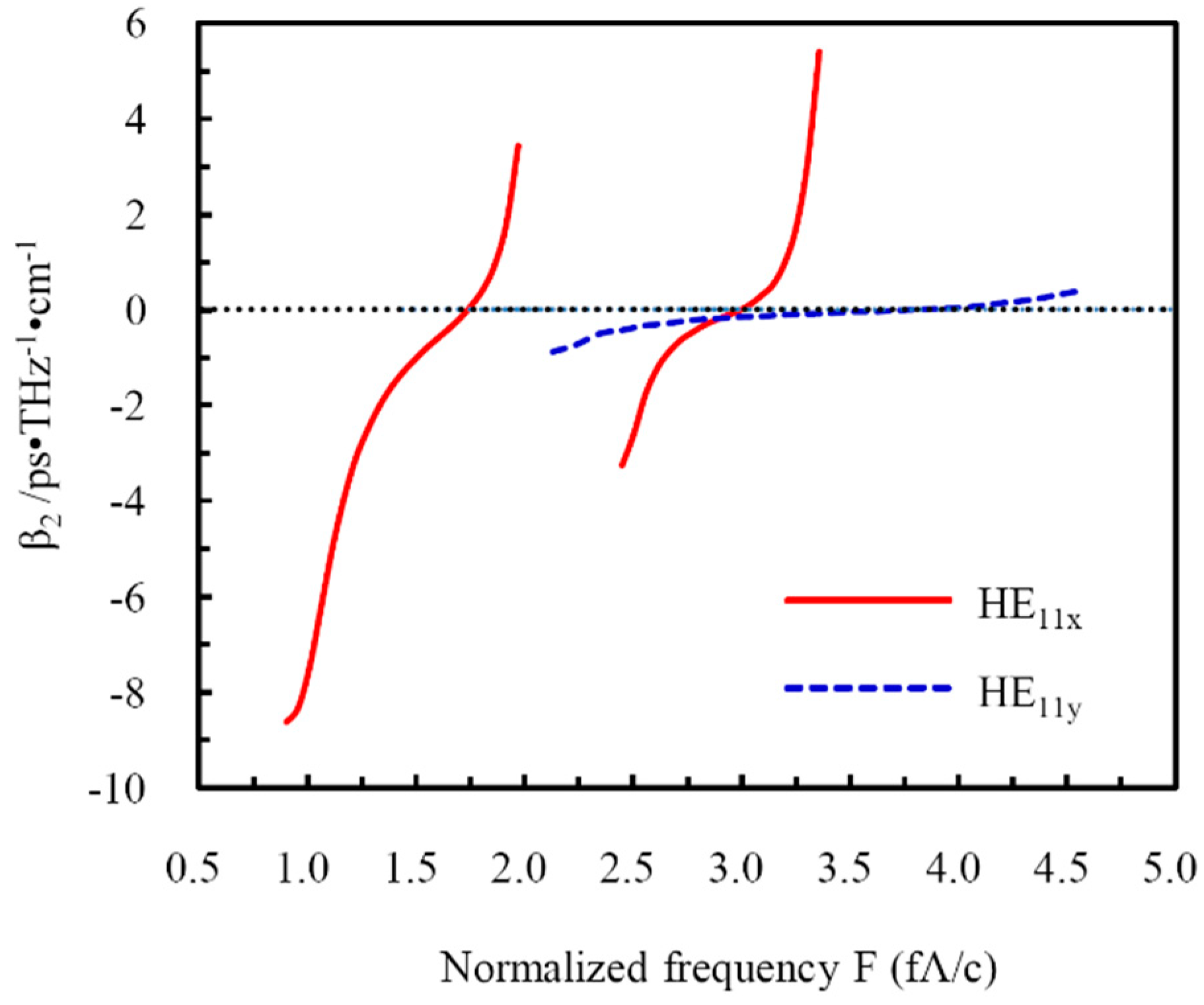
3.5. Dispersion Properties of the Designed THz LC-MOF
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jacobsen, R.H.; Mittleman, D.M.; Nuss, M.C. Chemical recognition of gases and gas mixtures with terahertz waves. Opt. Lett. 1996, 21, 2011–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, M.M.; Cheville, R.A. Transmission terahertz waveguide-based imaging below the diffraction limit. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 221107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Q.; Grischkowsky, D. Waveguide terahertz time-domain spectroscopy of nanometer water layers. Opt. Lett. 2004, 29, 1617–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federici, J.; Moeller, L. Review of terahertz and subterahertz wireless communications. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 111101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Mittleman, D.M. Metal wires for terahertz wave guiding. Nature 2004, 432, 376–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendis, R.; Grischkowsky, D. Plastic ribbon THz waveguides. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 88, 4449–4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Park, H.; Cho, M.; Kim, J. Terahertz pulse propagation in a plastic photonic crystal fiber. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 80, 2634–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, D.S.; Argyros, A.; Leon-Saval, S.G. Reducing the size of hollow terahertz waveguides. J. Lightwave Technol. 2011, 29, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atakaramians, S.; Shahraam, A.V.; Monro, T.M.; Abbott, D. Terahertz dielectric waveguides. Adv. Opt. Photonics 2013, 5, 169–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, K.; Rasmussen, H.K.; Jepsen, P.U.; Bang, O. Porous-core honeycomb bandgap THz fiber. Opt. Lett. 2011, 36, 666–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, K.; Rasmussen, H.K.; Adam, A.J.; Planken, P.C.; Bang, O.; Jepsen, P.U. Bendable, low-loss Topas fibers for the terahertz frequency range. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 8592–8601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanarian, G. Optical properties of cyclic olefin copolymers. Opt. Eng. 2001, 40, 1024–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ung, B.; Mazhorova, A.; Dupuis, A.; Rozé, M.; Skorobogatiy, M. Polymer microstructured optical fibers for terahertz wave guiding. Opt. Express 2011, 19, B848–B861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.Y.; Yu, C.P.; Chang, H.C.; Chen, H.W.; Li, Y.T.; Pan, C.L.; Sun, C.K. Terahertz air-core microstructure fiber. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 064105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, T.T.; Broeng, J.; Hermann, D.S.; Bjarklev, A. Optical devices based on liquid crystal photonic bandgap fibres. Opt. Express 2003, 11, 2589–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyros, A.; Birks, T.A.; Leon-Saval, S.G.; Cordeiro, C.M.B.; Russell, P.S.J. Guidance properties of low-contrast photonic bandgap fibres. Opt. Express 2005, 13, 2503–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, R.P.; Hsieh, C.F.; Pan, C.L.; Chen, C.Y. Temperature-dependent optical constants and birefringence of nematic liquid crystal 5CB in the terahertz frequency range. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 093523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, T.R.; Chen, C.Y.; Pan, R.P.; Pan, C.L. Electrically controlled room temperature terahertz phase shifter with liquid crystal. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2004, 14, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkeskjold, T.T.; Lægsgaard, J.; Bjarklev, A.; Hermann, D.S.; Broeng, J.; Li, J.; Gauza, S.; Wu, S.T. Highly tunable large-core single-mode liquid-crystal photonic bandgap fiber. Appl. Opt. 2006, 45, 2261–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noordegraaf, D.; Scolari, L.; Lægsgaard, J.; Alkeskjold, T.T.; Tartarini, G.; Borelli, E.; Bassi, P.; Li, J.; Wu, S.T. Avoided-crossing-based liquid-crystal photonic-bandgap notch filter. Opt. Lett. 2008, 33, 986–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Chan, C.C. Effect of liquid crystal alignment on bandgap formation in photonic bandgap fibers. Opt. Lett. 2007, 32, 1989–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, G.B.; Shum, P.; Hu, J.J.; Xu, X.; Gong, Y.D. Polarization-dependent bandgap splitting and mode guiding in liquid crystal photonic bandgap fibers. J. Lightw. Technol. 2008, 26, 3650–3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, N.A. Effective area of photonic crystal fibers. Opt. Express 2002, 10, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouwmans, G.; Pureur, V.; Betourne, A.; Quiquempois, Y.; Perrin, M.; Bigot, L.; Douay, M. Progress in solid core photonic bandgap fibers. Opt. Quant Electron. 2007, 39, 949–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, X.H.; Wang, L.L. Fabrication and experimental observation of monolithic multi-air-core fiber array for image transmission. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 7703–7708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, W.; Wei, L.; Alkeskjold, T.T.; Bjarliev, A.; Bang, O. Thermal tunability of photonic bandgaps in liquid crystal infiltrated microstructured polymer optical fibers. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 19356–19364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zografopoulos, D.C.; Kriezis, E.E.; Tsiboukis, T.D. Photonic crystal-liquid crystal fibers for single-polarization or high-birefringence guidance. Opt. Express 2006, 14, 914–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkeskjold, T.T.; Bjarklev, A. Electrically controlled broadband liquid crystal photonic bandgap fiber polarimeter. Opt. Lett. 2007, 32, 1707–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiku, M.N.O. Numerical Techniques in Electromagnetics, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh, K.; Koshiba, M. Leakage loss and group velocity dispersion in air-core photonic bandgap fibers. Opt. Express 2003, 11, 3100–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, F.; George, A.K.; Hedley, T.D.; Pearce, G.J.; Bird, D.M.; Knight, J.C.; St. J. Russell, P. All-solid photonic bandgap fiber. Opt. Lett. 2004, 29, 2369–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Alkeskjold, T.T.; Bjarklev, A. Electrically tunable bandpass filter using solid-core photonic crystal fibers filled with multiple liquid crystals. Opt. Lett. 2010, 35, 1608–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.R.; Hsiao, V.K.S. Photoactive photonic liquid crystal fiber polarization switches. Opt. Fiber. Technol. 2013, 19, 623–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, I.C. Liquid Crystals: Physical Properties and Nonlinear Optical Phenomena, 1st ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, Y.; Yang, B.; Lee, B.; Seo, H.S.; Choi, S.; Oh, K. Electrically controllable long-period liquid crystal fiber gratings. IEEE Photonic Technol. 2000, 12, 519–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, B.; Liao, C.; Song, J.; Yang, K.; Wang, G.; Wang, Q.; Yin, G.; Zhou, J. Compact tunable multibandpass filters based on liquid-filled photonic crystal fibers. Opt. Lett. 2014, 39, 2148–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieweg, N.; Born, N.; Al-Naib, I.; Koch, M. Electrically Tunable Terahertz Notch Filters. J. Infrared Milli. Terahz. Waves 2012, 33, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litchinitser, N.M.; Steinvurzel, P.E.; Eggleton, B.J.; White, T.P.; McPhedran, R.C.; Sterke, C.M. Application of an ARROW model for designing tunable photonic devices. Opt. Express 2004, 12, 1540–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, G.; Ping, S.; Yu, X.; Hu, J.J.; Wang, G.; Gong, Y. Polarization dependent guiding in liquid crystal filled photonic crystal fibers. Opt. Commun. 2008, 281, 1598–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, D.; Mu, C.; Li, B.; Yang, J. Electrically Tunable Propagation Properties of the Liquid Crystal-Filled Terahertz Fiber. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2487. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122487
Wang D, Mu C, Li B, Yang J. Electrically Tunable Propagation Properties of the Liquid Crystal-Filled Terahertz Fiber. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(12):2487. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122487
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Doudou, Changlong Mu, Baihong Li, and Jing Yang. 2018. "Electrically Tunable Propagation Properties of the Liquid Crystal-Filled Terahertz Fiber" Applied Sciences 8, no. 12: 2487. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122487
APA StyleWang, D., Mu, C., Li, B., & Yang, J. (2018). Electrically Tunable Propagation Properties of the Liquid Crystal-Filled Terahertz Fiber. Applied Sciences, 8(12), 2487. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122487