Abstract
This work identifies crucial operating parameters which most significantly influence the jetting performances of piezostack-driven non-contact dispensers. This is achieved through experimental investigation and statistical analysis. After introducing the configuration and operating principle of the piezoelectric jetting dispenser, an experimental setup is constructed in order to test the jetting performance, such as the dispensed amount. After selecting four significant operating parameters for the light-emitting diode (LED)-packaging process, two levels for each parameter are considered. Subsequently, the weight of a single dispensed dot is measured 100 times, and the average weight and standard deviation are calculated for each experimental set. The results are then statistically analyzed using a commercial software package. Finally, the crucial operating parameters which provide a low average weight and a minimum variation in the weight of a single dispensed dot are identified.
1. Introduction
In order to obtain an accurate delivery of fluid materials such as an epoxide resin or an encapsulant material, fluid dispensing systems are widely applied in many fields, including the semiconductor industry. Thus, fluid dispensing is an important process in the electronic manufacturing industry for areas such as integrated circuit (IC) chip encapsulation, surface mount technology (SMT), and light-emitting diode (LED) packaging [1,2]. Currently, several types of dispensers have been developed and successfully applied in the field. On the basis of the delivery mode of the fluid, dispensers are classified as contact and non-contact, or jetting. With respect to contact-type dispensers, the nozzle, substrate, and dispensed fluid are simultaneously in contact with each other [3,4,5]. It is necessary to maintain the distance between the nozzle and the substrate to obtain good performance, and thus an accurate position control and an increased cycle time are required, and the process is complicated. In order to overcome the limitations of the contact-type dispensers, a new type of dispenser, called a jetting dispenser, was proposed and developed. With respect to the jetting-type dispensers, the fluid is ejected from the nozzle by using the kinetic energy of the needle movement [6,7]. However, the operating frequency is generally limited to 100 Hz because the jetting dispensers are driven by conventional pneumatic and electromagnetic actuators. Furthermore, the minimum droplet size and viscosity of the fluid that is dispensed are also limited.
Recently, piezoelectric jetting dispensers were proposed and developed to satisfy the market demands, including a better performance in terms of smaller size, a higher frequency, and a variety of dispensable fluids. Specifically, the dispensing heads are designed with small sizes and compact structures by adopting the structural merit intrinsic to the small sizes of the piezoelectric actuators. This means that the weight and inertia of the dispensing head are reduced, and thus a high-frequency operation is possible. The fast response time as well as the low power consumption are also important advantages of the piezoelectric jetting dispensers. Wang et al. designed a jetting dispenser with two piezostack actuators and a displacement amplification device [8]. The jetting performance of a single dot was experimentally evaluated on the basis of parameters such as temperature, backpressure, and frequency. Luo and Deng established a dynamic model of a piezoelectric jetting dispenser and evaluated the jetting performance through a computer simulation [9]. Lu et al. proposed a new type of piezoelectric jetting dispenser featuring a piezostack actuator and a cymbal-type displacement amplifier [10]. The dynamic model and governing equation were derived and the performance was evaluated through both simulation and experimentation. Lu et al. also developed a bond-graph model with respect to piezoelectric jetting dispensers and verified the good performance of the proposed dispensing system [11]. Choi et al. proposed various types of piezoelectric jetting dispensers and reported on the control performances of the proposed jetting systems [12,13,14,15]. Nguyen et al. proposed a new type of jetting dispenser featuring a piezostack actuator and a hydraulic displacement magnification mechanism [12,13]. They manufactured the dispenser system and implemented the controller. The dispensing performances, including dispensing velocity and dispensed volume, were evaluated based on the applied control input. Nguyen et al. developed a jetting dispenser configured with a piezostack actuator and a flexible beam-type displacement amplification mechanism [14]. The dispensing performance was evaluated through a computer simulation, and the verification of the results was conducted via experiments. Hong and Jeon proposed a new type of piezoelectric jetting dispenser system actuated by dual piezostack actuators and evaluated its performance [15,16]. After conducting static and modal analyses, the design parameters of the dispenser system were determined, and the dispenser system was manufactured. This was followed by the evaluation of the jetting performances such as the needle stroke. Although several studies have focused on the piezoactuator-driven jetting dispenser, there is a paucity of studies on the identification of crucial operating parameters that significantly influence the jetting performances in a real field.
In order to treat this issue, a dual type of piezostack-driven jetting dispenser for LED packaging is manufactured and tested in this study. The challenges and technical contributions associated with this specific research are summarized as follows:
- (1)
- The effects of practical operating parameters, such as the needle stroke, on the jetting performances are experimentally evaluated. In the test, special attention is required to avoid testing errors since the weight of a single dispensed dot should be repeatedly measured 100 times for each test.
- (2)
- The evaluated results are statistically analyzed to determine the optimal operating parameters that can be directly used in LED-packaging industrial fields. The statistical analysis identifies the effect of each operating parameter on the average and variance of the dispensing amount, and the effect of the interactions with other parameters is also investigated.
In order to complete the above requirements, four main parameters are selected in this study, namely, needle stroke, rising time, open time, and cooling pressure given several practical operating parameters. Each parameter is divided into two levels, and thus sixteen experimental sets are established based on the design of the experiments. Following the measurements, the average and the standard deviation are calculated for each experimental set. From the analyzed results, optimal operating parameters for a minimum average weight and a minimum variation in the weight of a single dispensed dot are identified. It is noted here that the structural configuration of the piezostack-driven jetting dispenser designed and manufactured in this study is essentially the same as that of the jetting dispenser examined in a previous study [15].
2. Dual Piezostack-Driven Jetting Dispenser
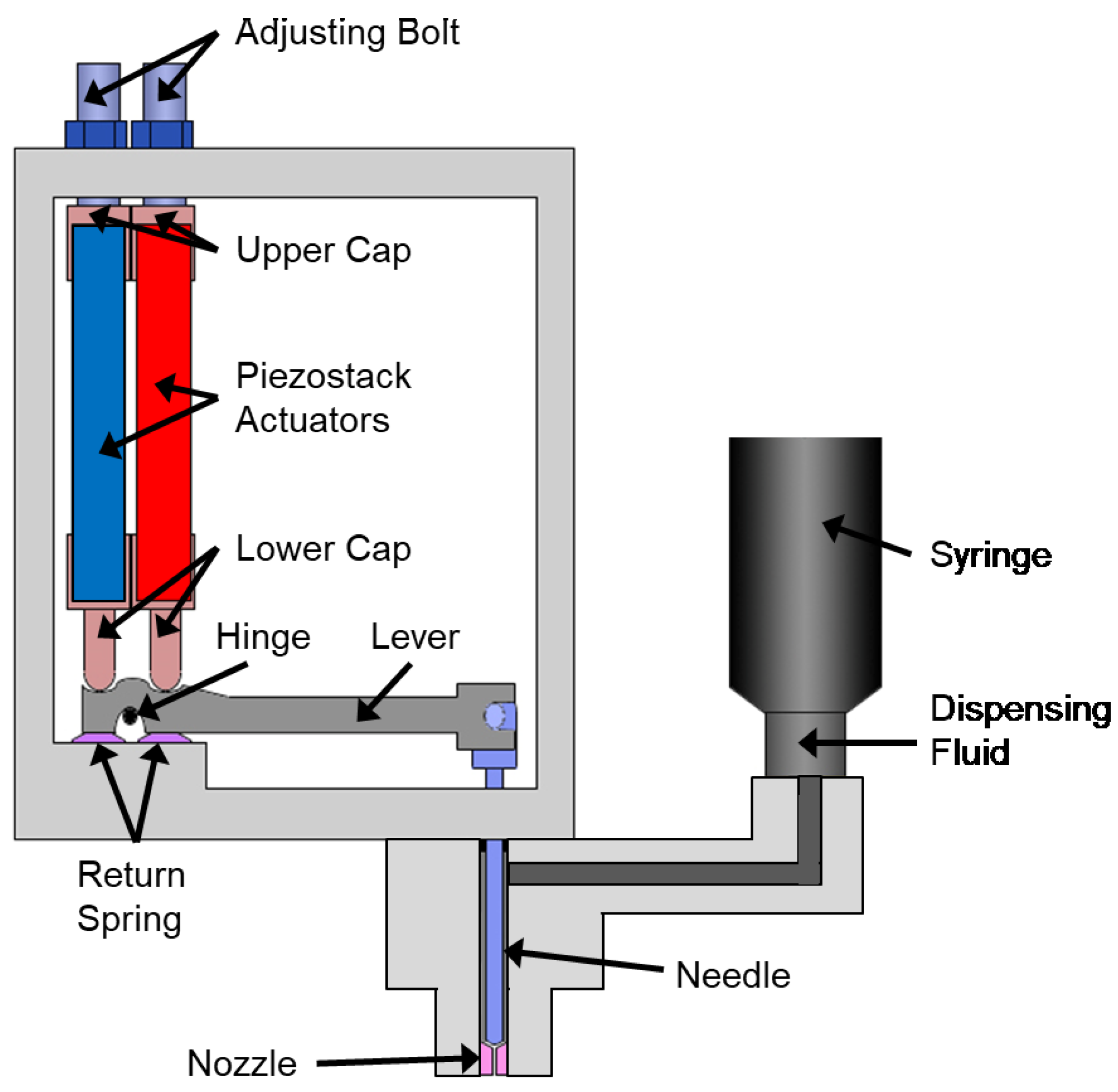
The structural configuration of the proposed piezoelectric jetting dispenser is shown in Figure 1. Two piezo stack actuators are installed in parallel and generate the required force and displacement for fluid jetting. Adjusting bolts are prepared to control the preload of the piezostack actuators. In order to protect the actuators from external shock, upper and lower caps made of stainless steel are attached to the top and bottom of the piezostack actuators. The displacement that is generated by the piezostack actuators, which is normally less than 0.1 mm, is not sufficient for direct fluid jetting. Thus, a displacement amplification device is adopted, based on a lever-hinge mechanism. For amplifying the displacement, the lever is fixed to the hinge and kept in contact with the piezostack actuators by the return springs. When the left-side piezostack is elongated and the right-side piezostack is contracted, the displacement generated by the piezostack actuator makes the lever mechanism rotates counterclockwise, and hence the needle moves upward. In contrast, when the left-side piezostack is contracted and the right-side piezostack is elongated, the lever rotates clockwise, and hence the needle moves downward. The lower caps of the piezostack actuators are in contact with the hinge portion of the displacement amplification device, and disk-type return springs are installed underneath the hinge to recover the initial position of the hinge. The needle of the dispenser is directly connected to the end of the lever part of the displacement amplification device. The design parameters for the dispenser components, such as the lever, hinge, and return spring are given in Table 1 [15]. The proposed piezoelectric jetting dispenser performs fluid jetting through the following four steps:
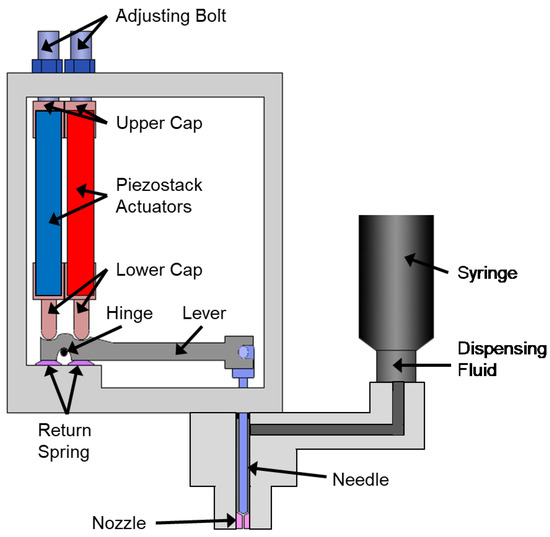
Figure 1.
Structural configuration of the piezostack-driven jetting dispenser.

Table 1.
Design parameters of the jetting dispenser components.
- (1)
- Rising Stage: The lever rotates in a counterclockwise direction and the needle moves upward when the left- and right-side piezostack actuators are elongated and contracted, respectively. Subsequently, the fluid in the syringe begins to fill the empty space in the dispenser head.
- (2)
- Open Stage: The position of the needle is maintained by applying the proper control input voltage to obtain perfect filling of the dispensing fluid.
- (3)
- Falling Stage: The lever rotates in a clockwise direction and the needle moves downward when the left- and right-side piezostack actuators are contracted and elongated, respectively. The needle penetrates the fluid and dispenses it through the nozzle of the head by using the impact energy.
- (4)
- Closed Stage (delay): The position of the needle remains lowered until the next jetting operation.
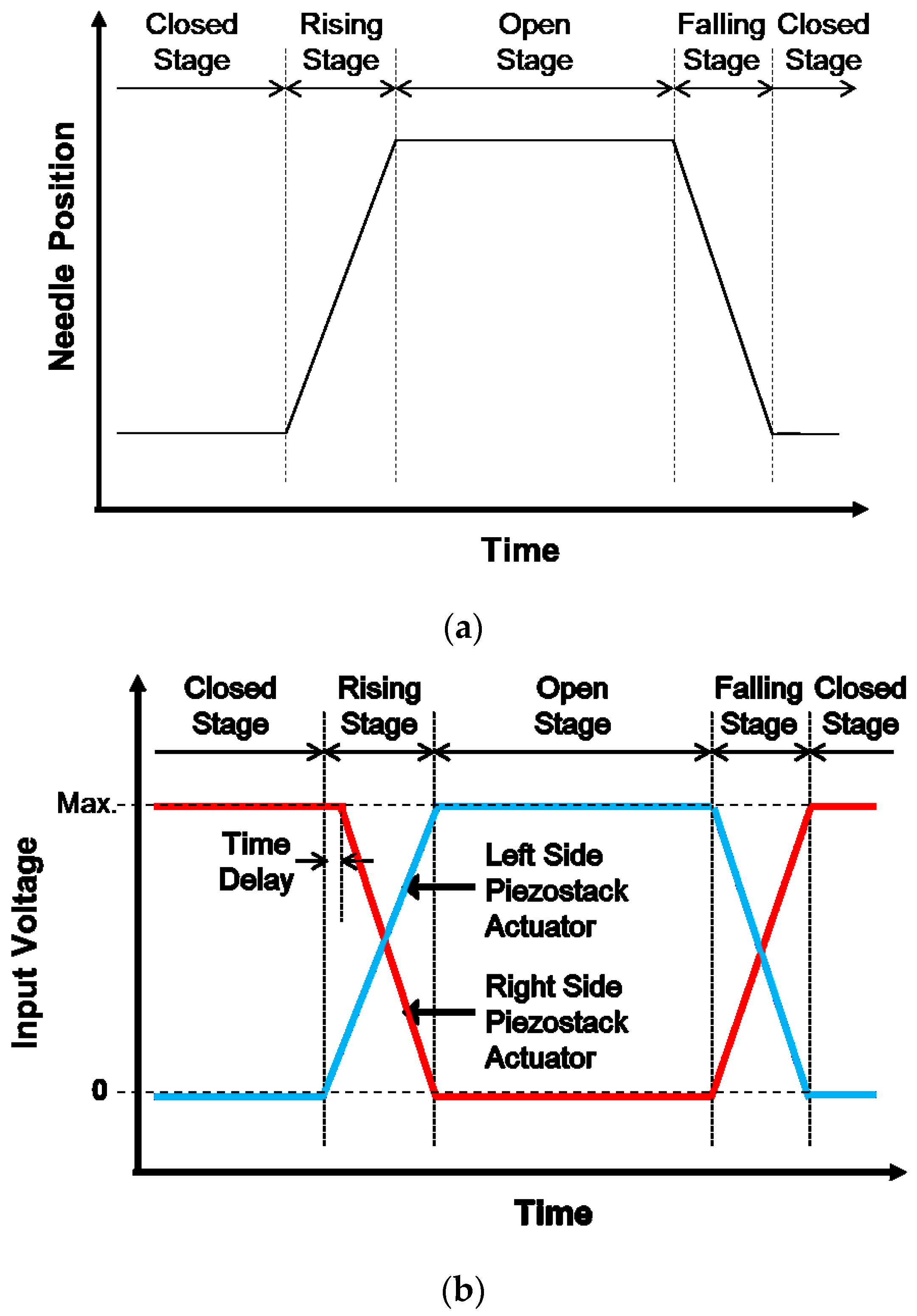
The schematics of the needle position and input voltage profiles are shown in Figure 2a,b, respectively. As shown in Figure 2b, since unidirectional piezoelectric actuators are used in this study, the voltage from 0 to maximum voltage can be applied as the input, and hence it is not necessary to apply offset voltage. The implemented controller controls the time for the rising, open, falling, and closed stages as well as the operating frequency and the stroke of the needle by controlling the input voltage to the piezostack actuators. A sudden voltage application can cause an overshoot, and an excessive overshoot can degrade the accurate performance of the dispenser system. This should be carefully considered from the stage of an appropriate selection of the piezoelectric actuator. The overshoot can be reduced by reducing the magnitude of the input voltage per unit time [17,18]. In this work, to prevent overshoot, the loading rate of the input voltage is reduced by dividing the input voltage into small steps (digitized), and the time per step is 5.8 μs. In order to obtain a rise of time of 2 ms, 340 steps are required, and the voltage is increased by 0.4 V per step, so that a maximum of 135 V can be applied. This control strategy is programmed in the controller and experimentally realized.
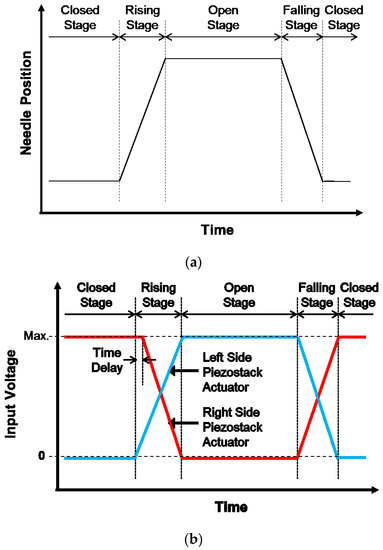
Figure 2.
Operating process for the jetting. (a) Needle position; (b) input voltages.
It is ideal that both piezostack actuators are operated symmetrically. However, the behavior of each piezoelectric actuator is not exactly symmetrical because of the hysteresis of the piezoelectric actuator [19,20]. This behavior occurs even though the input voltages for each actuator are perfectly symmetrical. When two piezoelectric actuators are driven at the same time, the load can be increased in the piezoelectric actuators because of the difference of displacement caused by the hysteresis characteristics of the piezoelectric actuators, and this phenomenon can damage and break the piezoelectric actuators. In this work, the hysteresis characteristics of the piezoelectric actuator are compensated by the open-loop method, applying a time delay to the input signal. When the displacement of the dwindling (contracted) piezostack is smaller than the displacement of the lengthening (elongated) piezostack during these stages, both the piezostack actuators are always subjected to compressive forces induced by the return spring. Because the piezostack actuator can bear some compressive force, this state is acceptable for operating the jetting dispenser system. Therefore, as shown in Figure 2b, the input for the dwindling piezostack actuator has a 30 μs time delay compared to the input for the lengthening piezostack. Since the digitized step size of the input voltage is 5.8 μs, in order to create the 30 μs delay in the input signal to the dwindling piezostack actuator, the input for the dwindling piezostack actuator is applied after five digital units relative to the input for the lengthening piezostack actuator. This directly means that both piezostack actuators will always be compressed and will be not impacted by the lever. This control strategy is programmed in the microprocessor and experimentally realized. In addition, a piezoelectric actuator model having a small difference between the rising time and the falling time is selected for the effective operation of the proposed control strategy. Details on the control algorithms were given in the previous study [15].
3. Design of the Experimental Test
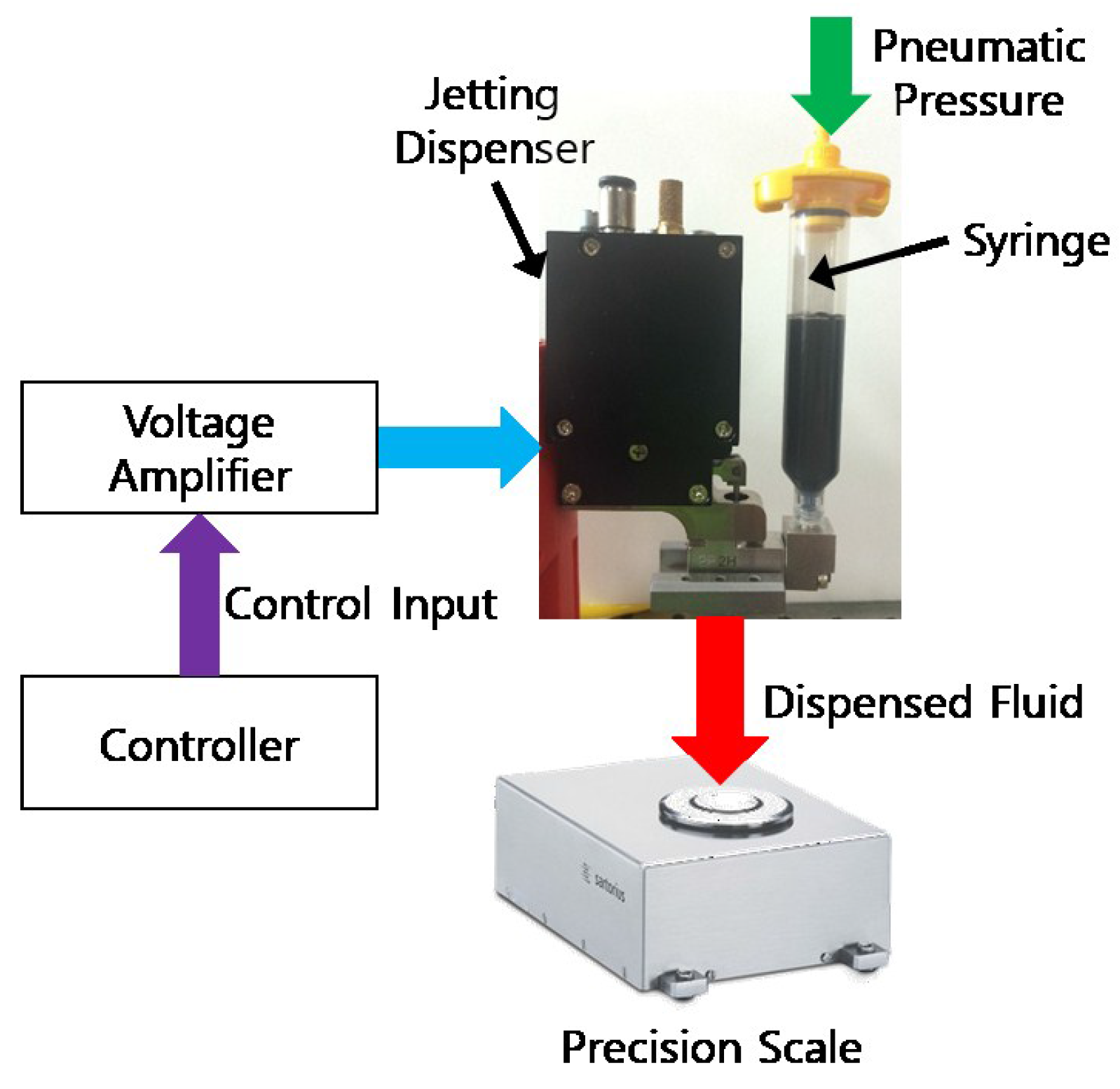
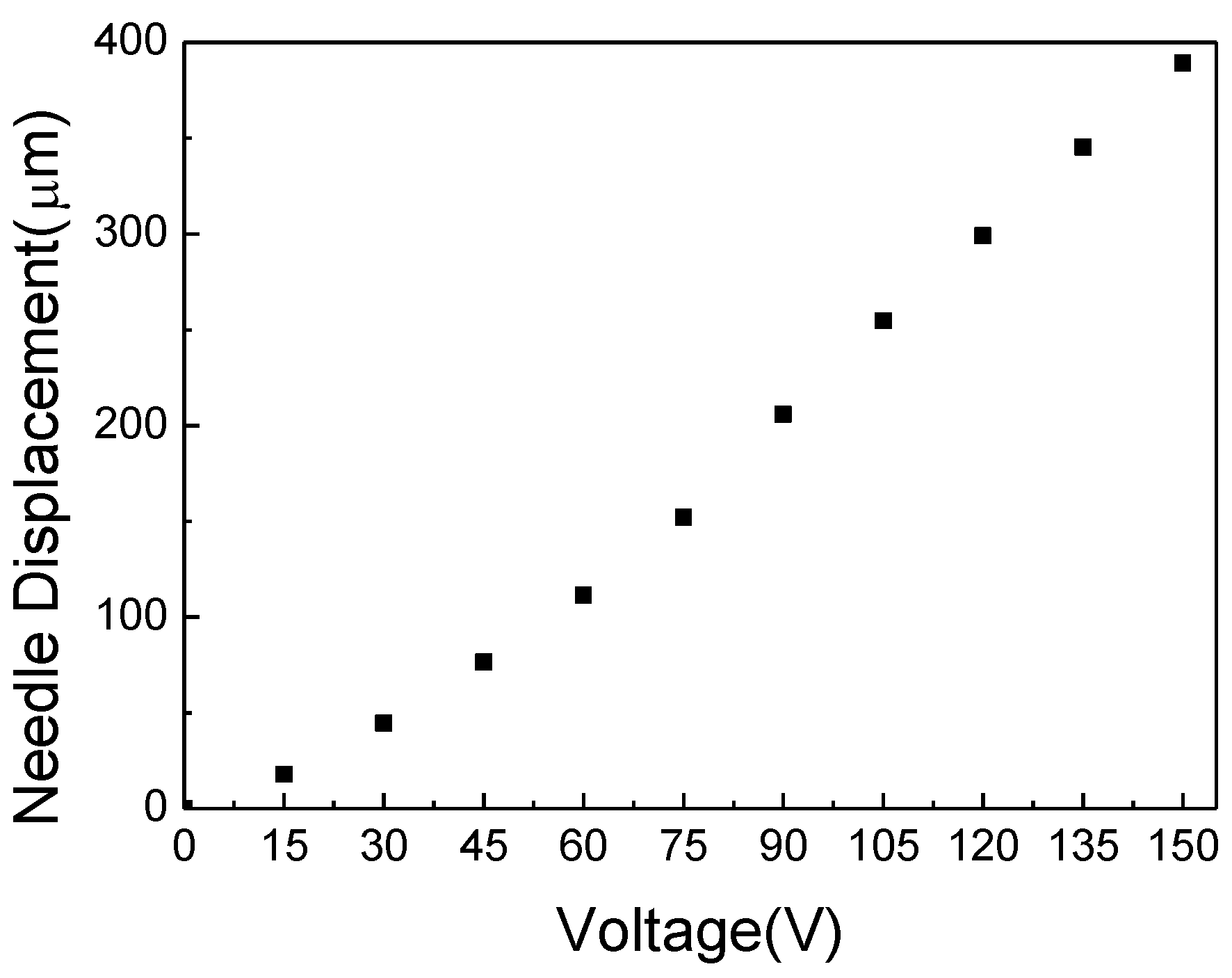
The experimental setup is established as shown in Figure 3 to demonstrate the performance characteristics of the proposed piezoelectric jetting dispenser while considering various operating parameters. The piezoelectric actuator AE0505D44D40DF (TOKIN Corp., Miyagi, Japan) is selected, and the specification of the piezoelectric actuator provided by the manufacturer are given in Table 2. The displacement of the needle according to the input voltage is measured by increasing the input voltage from 0 V to 150 V by 15 V. The measured displacement is presented in Figure 4, and the maximum displacement of the needle is about 390 μm at an input voltage of 150 V. The displacements for 120 V and 135 V input voltages are 300 μm and 345 μm, respectively, thus larger than the minimum displacement for effective dispensing, 300 μm [15]. The weight of a single jetted dot is measured by using a precision balance, WZA245-NC (SARTORIUS Corp., Göttingen, Germany). The maximum measurable weight and the measurement resolution are 240 g and 0.01 mg, respectively. In order to create jetting parameters that are similar to those required in industrial applications, a mixture of 85% silicone (OE-6630, DOW CORNING, Auburn, MI, USA), that is widely used in LED applications, and 15% yellow phosphor–yttrium–aluminum garnet (YAG, NICHIA Corp., Tokushima, Japan) is used as the dispensing fluid. The material properties of the dispensing fluid are listed in Table 3.
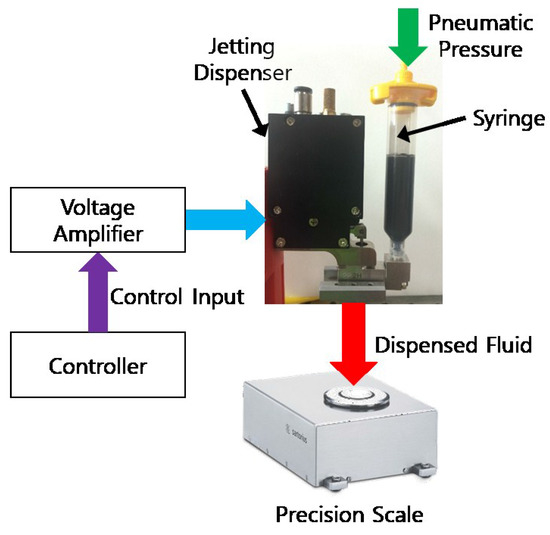
Figure 3.
Experimental setup for the jetting test.

Table 2.
Specifications of the piezoelectric actuator.
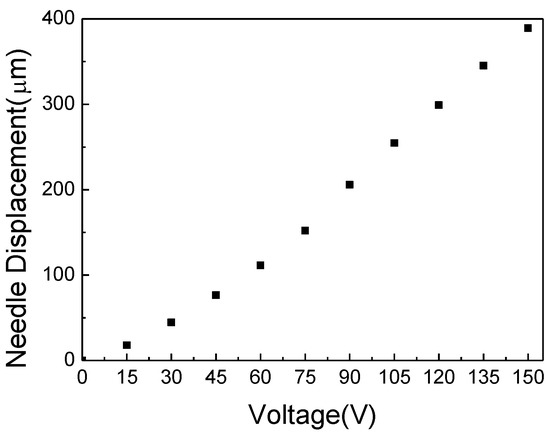
Figure 4.
Measured needle displacement according to the input voltage.

Table 3.
Material properties of the dispensed fluid.
It is necessary to evaluate the accuracy and precision of the jetted amount of fluid with respect to the operating parameters to identify the performance characteristics of the proposed piezoelectric jetting dispenser. The important operating parameters can be broadly divided into two parts. One includes the factors associated with the operation of the piezoelectric actuator, such as the needle stroke, rise time, open time, cooling temperature, and the other includes the factors for the dispensing equipment, such as the syringe pneumatic pressure, nozzle diameter, nozzle temperature, and so on. As a first step, in order to evaluate these factors at practical operating conditions, four parameters that are directly related to the piezoelectric actuators are selected in this work. In the proposed non-contact jetting dispenser, the actuating characteristics of the piezoelectric actuators are extremely important to achieve high jetting performance. It is assumed that each parameter displays two levels, and the operating parameter combinations are listed in Table 4. The two levels of each parameter were determined from the following criteria that are frequently considered in practical working conditions. When the displacement of 30 μm that occurs at the maximum 150 V input of the piezoelectric actuator is 100%, then 90% and 80% are selected as the stroke parameters by considering the durability. The piezoelectric actuators operate at one cycle of rising, open, falling, and closing, and 10 ms are required for a cycle, thus the operating frequency of 100 Hz is considered. Subsequently, the rising time and the opening time are set to 2 or 3 ms by considering the falling time of 0.1 ms and the closing time in the range of 3 ms to 5 ms. Two levels of 138 kPa (20 psi) and 207 kPa (30 psi) are considered for the cooling pressure of the piezoelectric actuator on the basis of the capacity of the pneumatic device for air cooling in the piezoelectric actuator. The falling time, temperature of the nozzle, and air pressure of the syringe are fixed at 0.1 ms, 35 °C, and 310 kPa, respectively. Additionally, the operating frequency is set to 100 Hz, and the inner diameter of the nozzle is set to 0.3 mm. The four parameters and their two levels are considered, and therefore sixteen experimental sets are prepared, based on full factorial design. The designed experimental sets and their corresponding operating parameters are listed in Table 5.

Table 4.
Main parameters and their levels.

Table 5.
Designed experimental sets.
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Average Weight
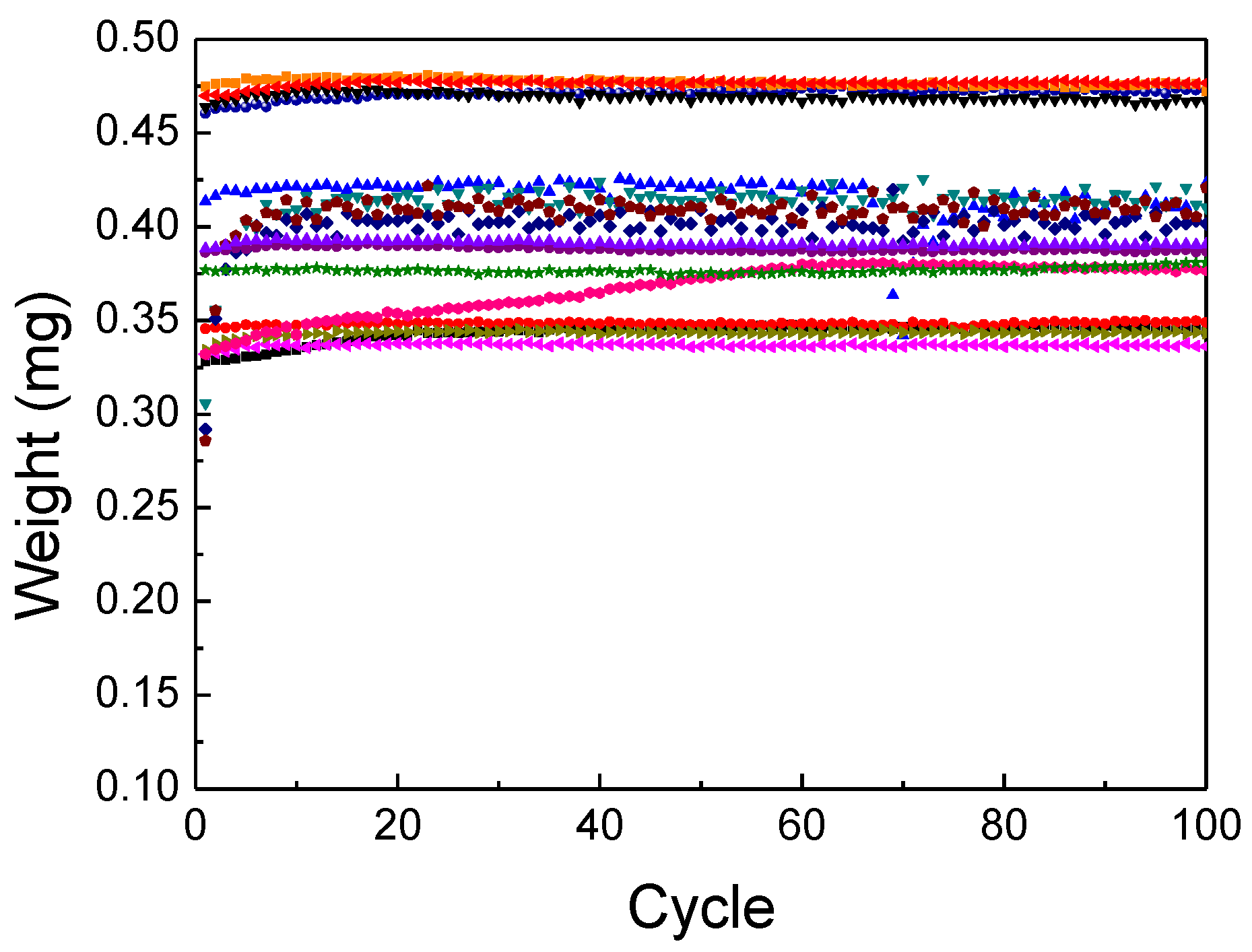
The dispenser jets 100 times for each run, and the weight of a single jetted dot is measured each time. The measured results are shown in Figure 5. Subsequently, the average weight and standard deviation of the results for each run are calculated and summarized in Table 6. The average weight of a single jetted dot ranges widely from 0.337 g (0.001 standard deviation, 5th run) to 0.477 g (0.002 standard deviation, 12th run) with respect to the operating parameter set. The measured results are analyzed by using a commercial statistical software package, Minitab (trial version 17 Minitab Inc., State College, PA, USA), and the level of significance is set to 0.1 (10%).
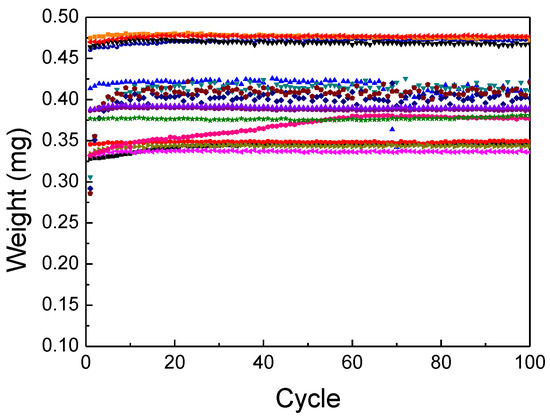
Figure 5.
Measured weight of a single dispensed dot.

Table 6.
Average weight and standard deviation of the experimental results.
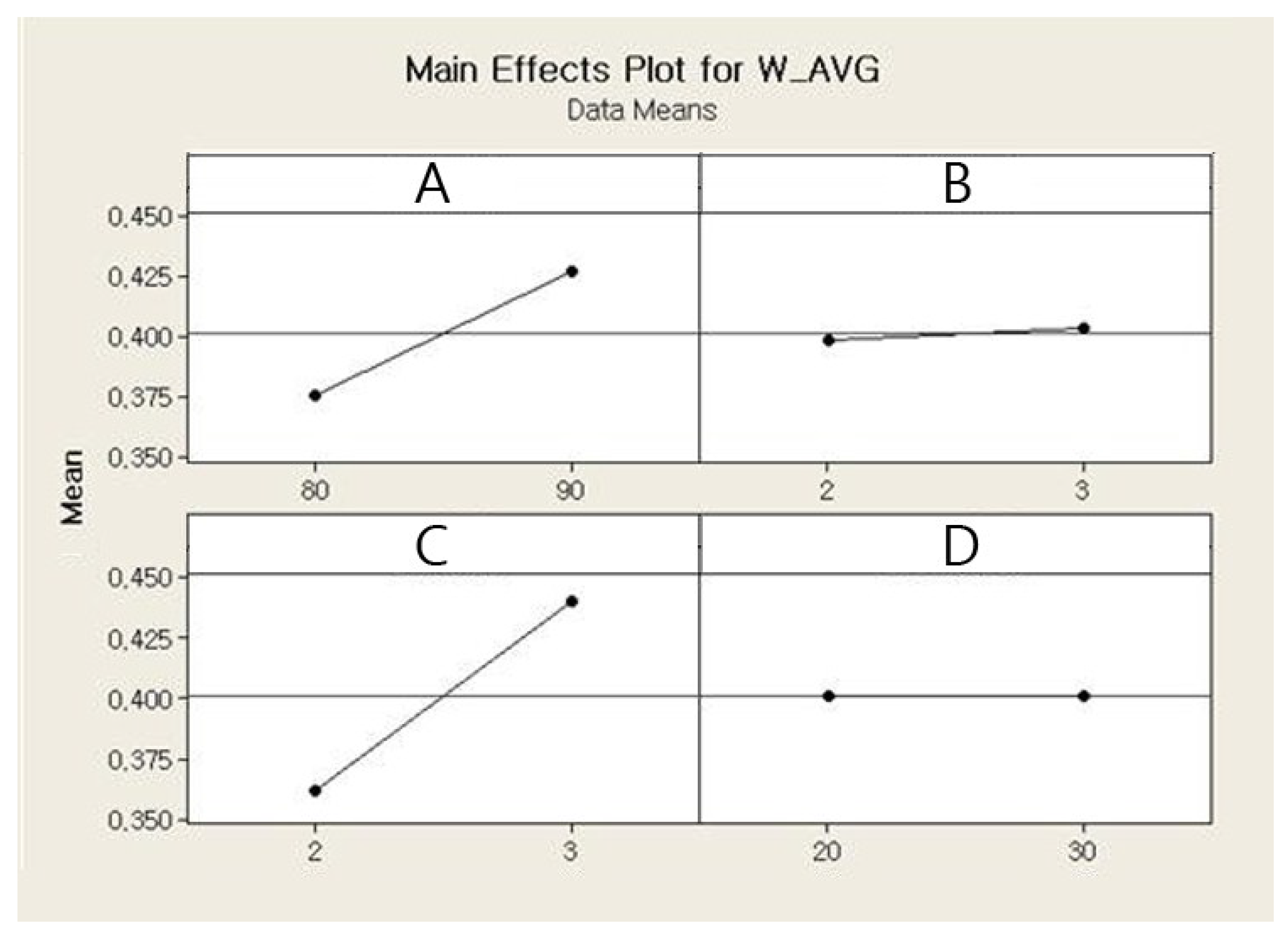
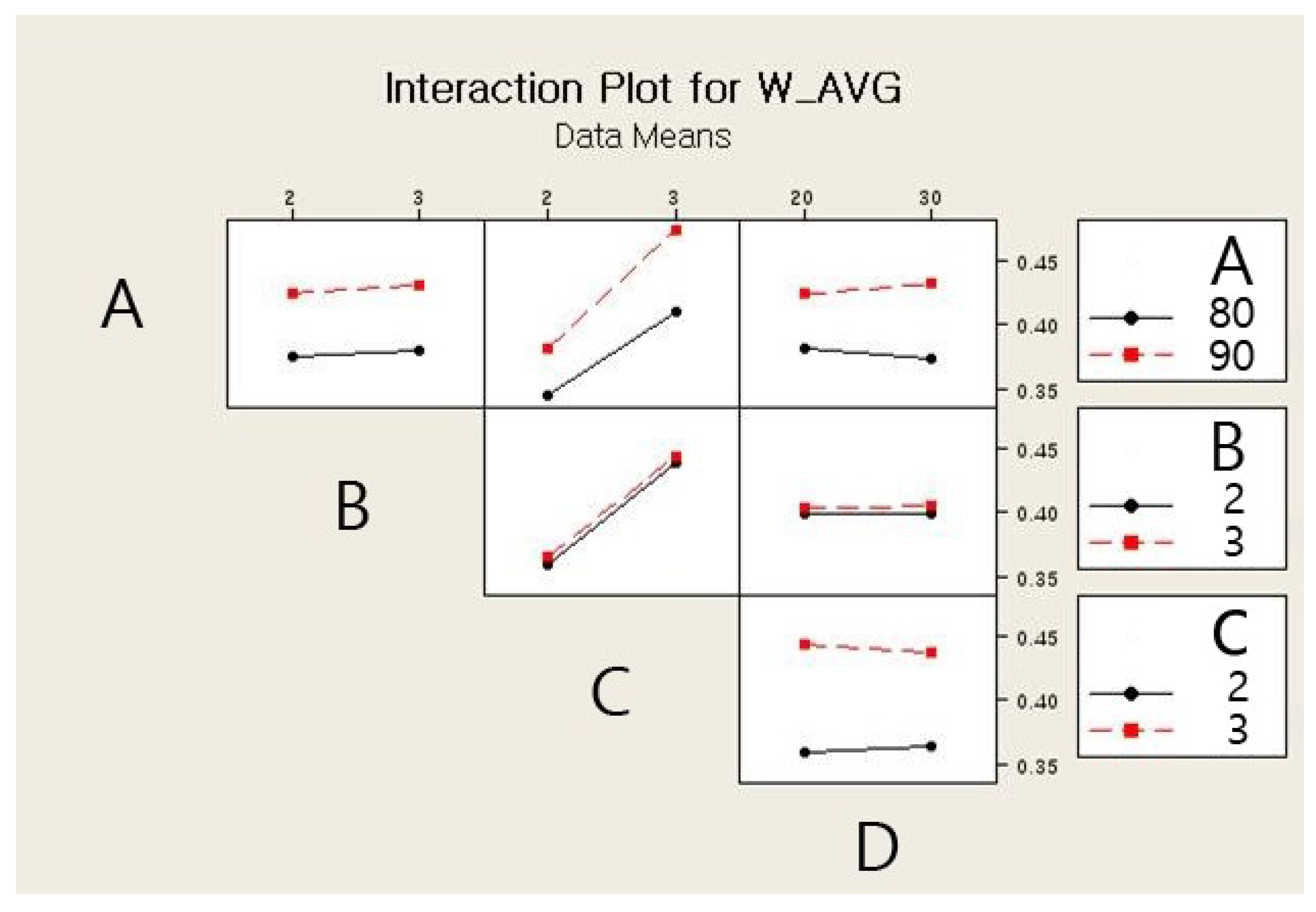
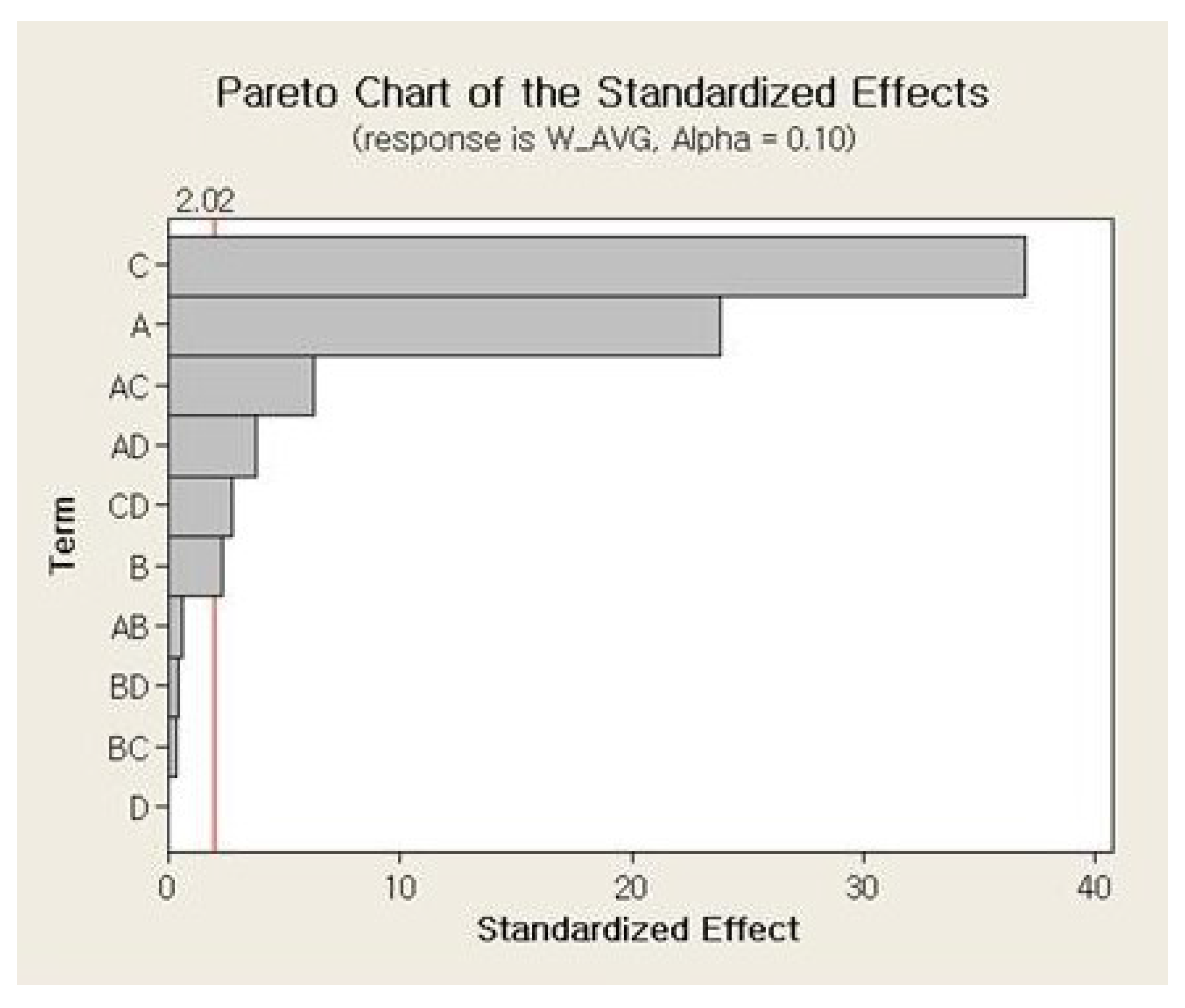
The main effects and the interaction effects plots for the average weight of a single jetted dot are depicted in Figure 6 and Figure 7, respectively. For the main effects plot, the parameters with a steep slope display a significant effect and the parameters with a gentle slope display a small effect on the average weight of a single jetted dot. As shown in Figure 6, the needle stroke (A) and open time (B) are evidently associated with a high effect on the average weight of a single jetted dot, and the rising time (C) and cooling pressure (D) exhibit a low effect on the average weight of a single jetted dot. The average weight of a single jetted dot decreases with decreases in the needle stroke and open time. With respect to the interaction effects plot, the two parameters exhibit a high interaction effect when the two lines cross each other, whereas the parameters do not display any interaction effect when the two lines are parallel. The six interaction effects for the four parameters, AB, AC, AD, BC, BD, and CD, are plotted in Figure 7. As shown in Figure 7, the parameters exhibit small interaction effects on the average weight of a single jetted dot. The Pareto chart clearly explains the effectiveness of each parameter and is shown in Figure 8. It is noted here that any parameter with a bar that extends beyond the vertical red line (significant reference line) is potentially important. With the Minitab Software, the reference line for statistical significance is determined on the basis of the significance level and the Lenth’s method [21]. As shown in Figure 8, open time and needle stroke are the main parameters associated with a significant effect, and the rising time is also a main parameter with a low effect. The interactions stroke–open time, stroke–cooling pressure, and open time–cooling pressure are meaningful parameters, although their effect is very low for the average weight of a single jetted dot.
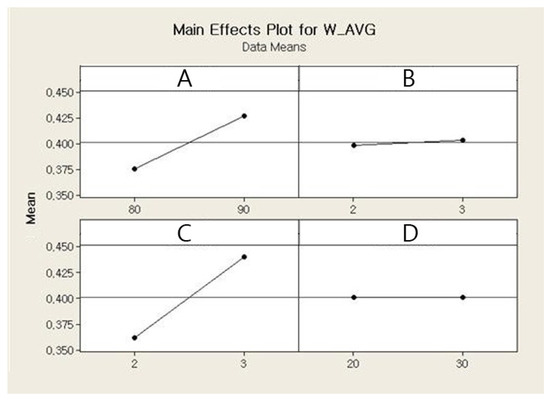
Figure 6.
Main effects plot for the average weight.
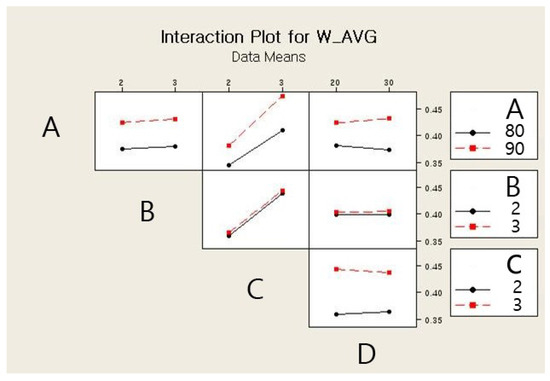
Figure 7.
Interaction effects plot for the average weight.
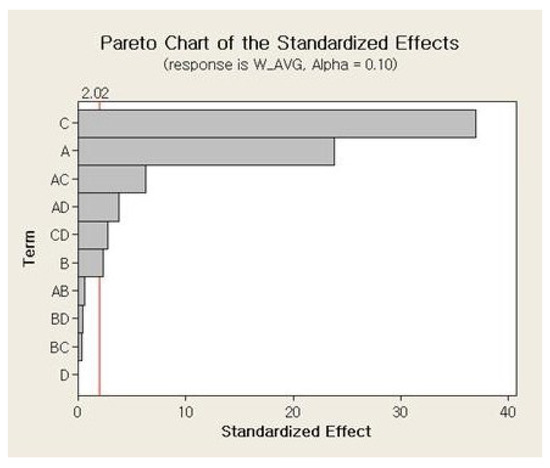
Figure 8.
Pareto chart for the average weight.
The effects and estimated coefficients for the average weight of a single jetted dot are listed in Table 7. The p-value for each term is tested considering the null hypothesis in which the coefficient is equal to zero (no effect). A low p-value (less than 0.1 in this work) indicates that the null hypothesis can be rejected. In other words, a predictor that has a low p-value is likely to be a meaningful addition to the regression model because the changes in the predictor’s value are related to the changes of the response variable. Conversely, a larger p-value (higher than 0.1 in this work) suggests that the changes in the predictor are not associated with the changes of the response [21]. Then, any parameter in the table with a p-value lower than 0.1 is an important parameter that affects the average weight, because the level of significance is set to 0.1. Table 7 shows the effective parameters with a shaded background, and the results are exactly in accordance with those of the effects plots shown in Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8. The column ‘Effect’ denotes the vertical distance between two points in Figure 6 and Figure 7. The column ‘Coefficient’ is the same as half of the column ‘Effect’, and the values are the coefficients in the regression equation. The column ‘t’ is obtained by dividing the ‘Coefficient’ with the ‘SE Coefficient’. The values of column ‘t’ are shown in the Pareto chart in Figure 8. A high magnitude of ‘t’ indicates that the parameter displays a high effect. Thus, it is concluded that the most effective method to minimize the weight of a single jetted dot involves reducing the needle stroke and the open time, and this significantly affects the average weight with a high t-value. In Table 6, a run order of 1, 2, 5, and 6, with low needle stroke and low open time displays a lower average value when compared with other run orders. The average values for the run orders 9, 10, 13, and 14 slightly increased because of the higher needle stroke when compared to the run orders 1, 2, 5, and 6. However, the average values for the run orders 3, 4, 7, and 8 sharply increased because of the higher open time when compared to the run orders 1, 2, 5, and 6. The effects and estimated coefficients are reinterpreted with only the meaningful parameters, and the result is depicted in Table 8. The coefficients in the third column in Table 8 are used to express the regression model to estimate the average weight of a single dot as follows:

Table 7.
Effects and estimated coefficients for the average weight.

Table 8.
Effects and estimated coefficients for the average weight with the meaningful parameters.
4.2. Weight Variation
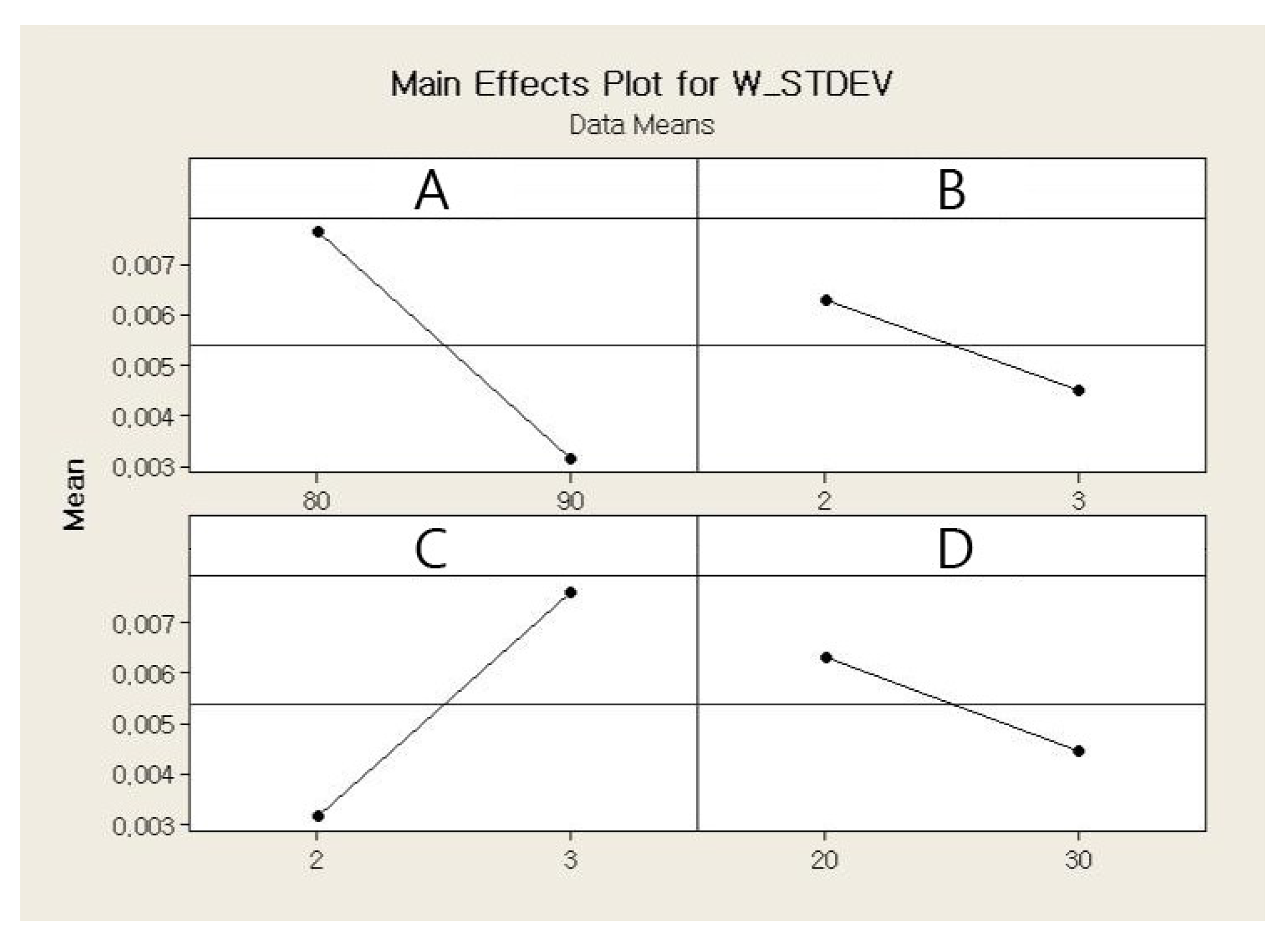
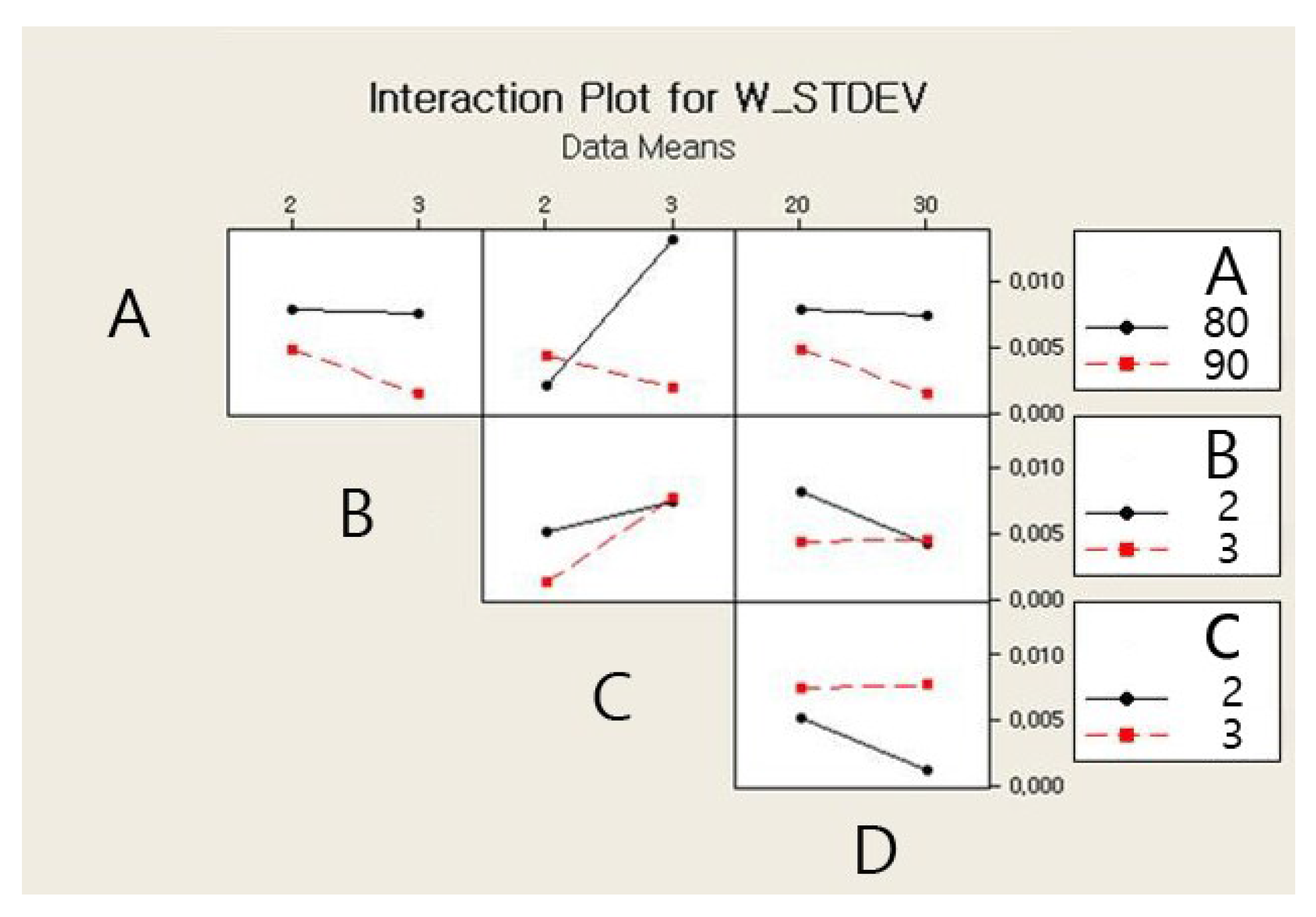
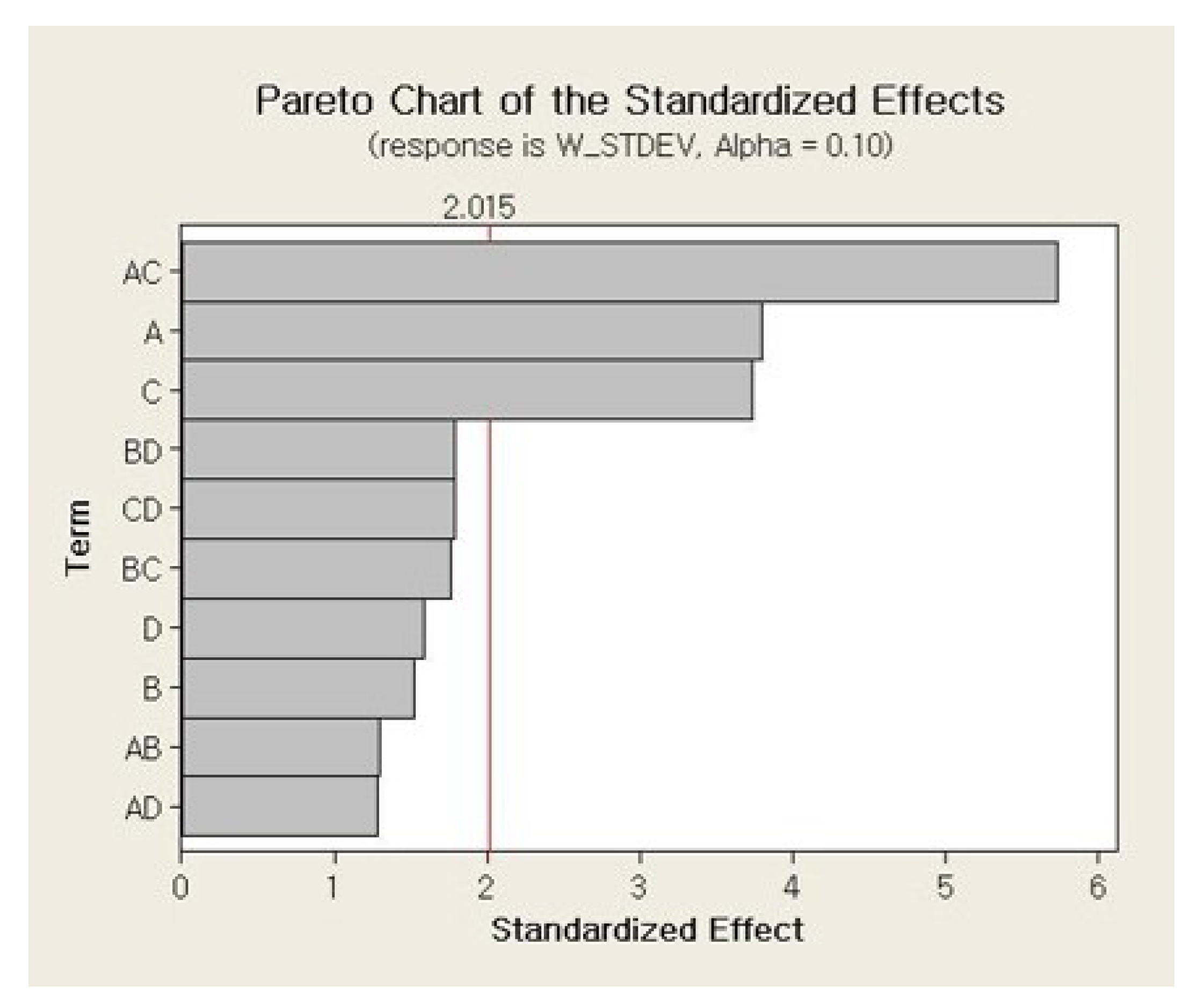
The main and interaction effects plots for the standard deviation of the weight of a single jetted dot are shown in Figure 9 and Figure 10, respectively. As shown in Figure 9, all four parameters exhibit steep slopes, and thus it appears that all parameters significantly affect the weight variation of a single jetted dot. The six interaction effects for the four parameters, AB, AC, AD, BC, BD, and CD, are plotted in Figure 10. As shown in Figure 10, the stroke–open time, rising time–open time, and rising time–cooling pressure significantly affect the weight variation. The Pareto chart of the standard deviation of the weight is shown in Figure 11. However, it is observed from the Pareto chart that only the needle stroke and the open time are the main effective parameters, and the stroke–open time is the only effective interaction parameter. These results are verified in the table of the effects and estimated coefficients for the standard deviation, as shown in Table 9. The effective parameters include the needle stroke, the open time, and the stroke–open time with a p-value lower than 0.1 and are denoted by a shaded background. The results in Figure 11 and Table 9 indicate that the interaction of the needle stroke–open time displays the highest effect on the variation of the weight of a single jetted dot. With respect to the low needle stroke and low open time, the run orders of 1, 2, 5, and 6 in Table 6 display a lower standard deviation value when compared with the other run orders. With respect to the higher open time, the standard deviations for the run orders 3, 4, 7, and 8 rapidly increase. However, with respect to a higher needle stroke, the standard deviations for the run orders 9, 10, 13, and 14 are unchanged compared to those of the run orders 1, 2, 5, and 6 with the exception of the run order 9. These results are also observed in the interaction effects plot in Figure 10. The variation is reanalyzed with only the effective parameters, and the result is shown in Table 10. A regression model is constructed to estimate the standard deviation of the average weight of a single jetted dot as follows, by using the coefficients in the third column in Table 10.
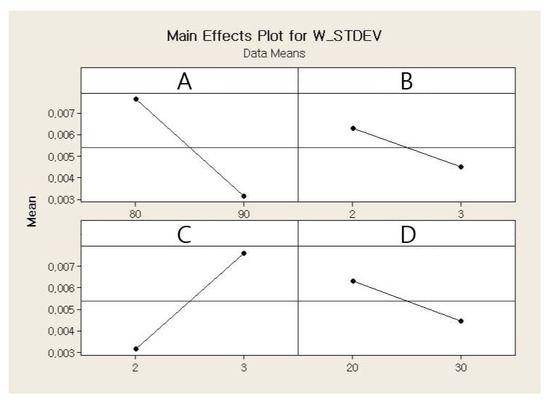
Figure 9.
Main effects plot for the variation in weight.
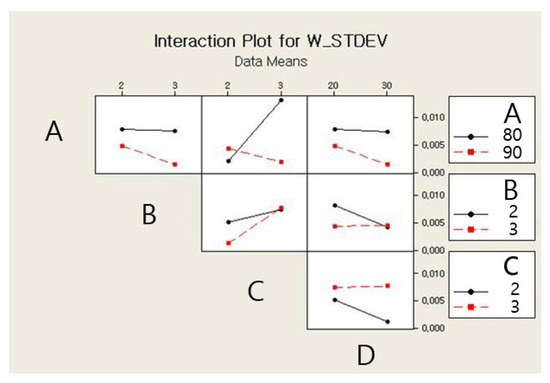
Figure 10.
Interaction effects plot for the variation in weight.
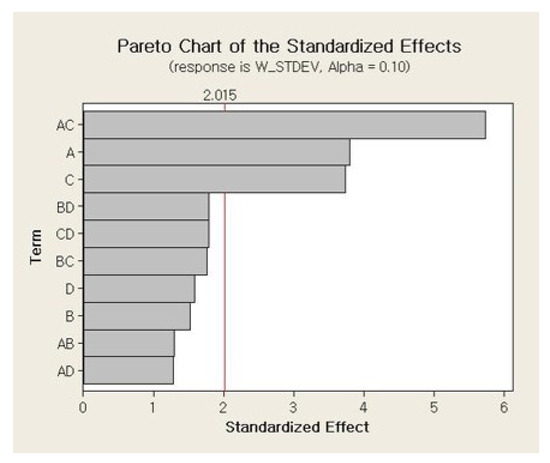
Figure 11.
Pareto chart for the variation in weight.

Table 9.
Effects and estimated coefficients for the weight variation.

Table 10.
Effects and estimated coefficients for the weight variation with the meaningful parameters.
This is similar to the conclusions for the average weight, and it is concluded that the reduction of the needle stroke and the open time is the most effective method to minimize the variation in the weight of a single jetted dot.
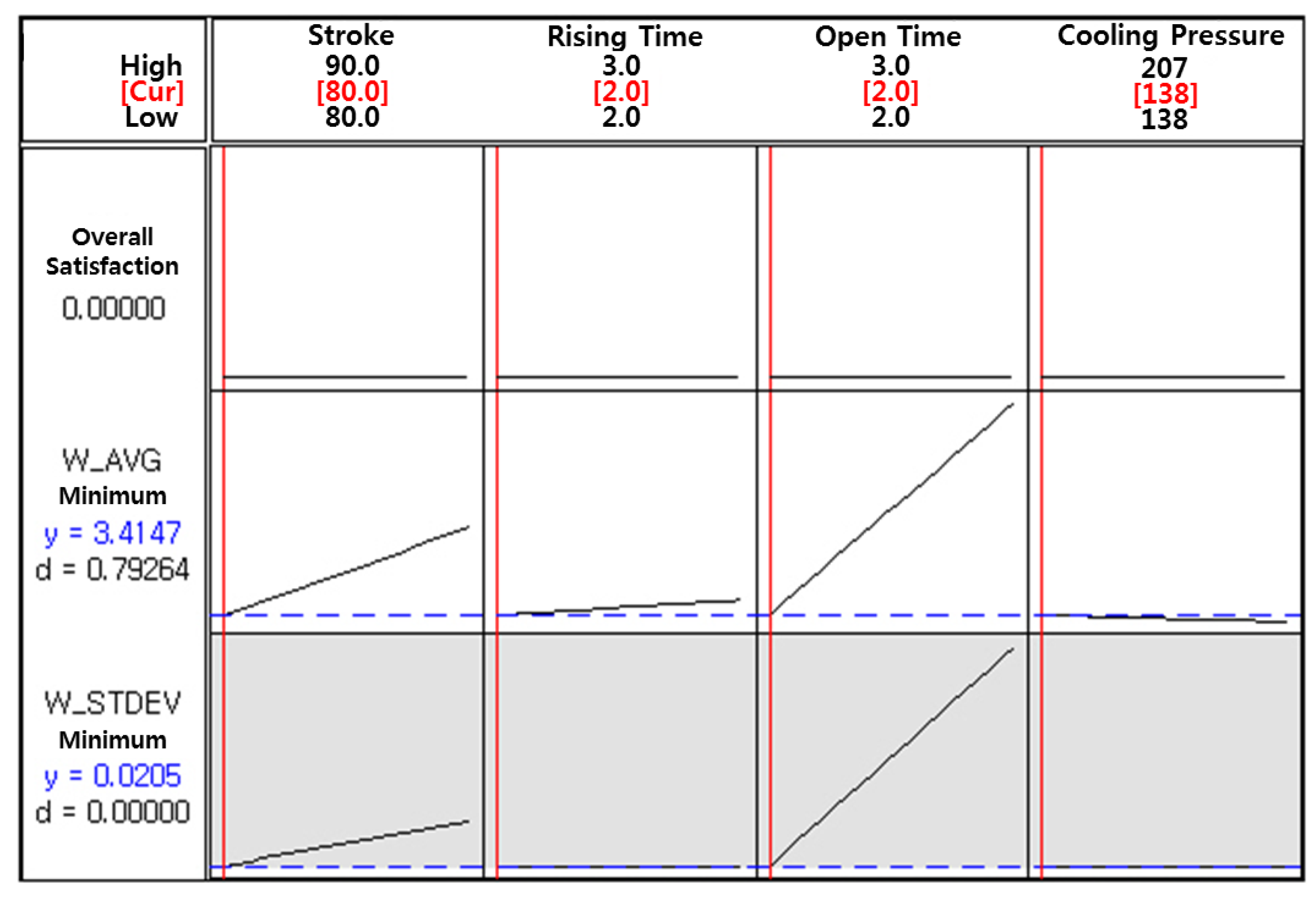
Among the 16 parameter sets, the optimal operating parameters to minimize both the average weight and the standard deviation of the weight of a single jetted dot are obtained and shown in Figure 12. It is observed that an 80% needle stroke, 2 ms rising time, 2 ms open time, and 138 kPa cooling pressure are selected as the optimal operating parameters for the minimum average weight and minimum variation with respect to the weight of a single jetted dot. However, it is observed that the average weight and standard deviation for the run order 1 in Table 6 (the operating parameters are the same as the optimal parameters) are small but not minimum. The values for the run orders 2, 5, and 6, with different rising time and cooling pressure, are lower than those for the run order 1. It is concluded that the average weight and the variation of the weight of a single jetted dot are mainly affected by parameters such as the needle stroke and the open time and not affected by parameters such as the rising time and the cooling pressure.
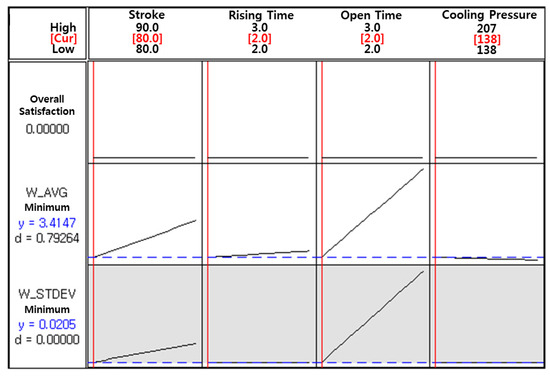
Figure 12.
Optimal parameters for the jetting dispenser.
5. Conclusions
In this study, the effects of various operating parameters on the performance of the piezoelectric jetting dispenser were experimentally tested, and the most crucial parameters that affect the jetting performances were statistically analyzed and identified. First, the structural configuration and operating principles of the piezoelectric jetting dispenser driven by dual piezostack actuators were described. An experimental apparatus was prepared with a precision scale after manufacturing the piezoelectric jetting dispenser. The selection of four primary parameters with two levels for each parameter was followed by constructing sixteen experimental sets based on the design of the experiments. The weight of a single dispensed dot was measured 100 times for each experimental set. Additionally, the average weight and standard deviation were also calculated for each experimental set. Subsequently, the experimental results were statistically analyzed by using a commercial software package. The optimal operating parameters for the minimum average weight and the minimum variation of the weight of a single dispensed dot were determined. It was confirmed that the reduction of the open time is an important parameter that reduces the average weight and the variation of the weight in the dispensed amount. However, it is difficult to increase the opening time so that it is much faster than in the presented condition. The durability of the piezoelectric actuator and the efficiency of the packaging process are considered, and the operating frequency is approximately 100 Hz. Subsequently, the operating cycle of the piezoelectric actuator that is composed of rising, open, falling, and closing is approximately 10 ms. The increment in the open time may reduce the operating frequency and result in an increment of the packing time and a decrease in the efficiency.
The results presented in this work indicated that the needle stroke and the open time are important parameters and, hence, the reduction of the needle stroke and of the open time is the most effective method to obtain a low average weight and a low variation in the weight of a single jetted dot. In other words, it has been confirmed that, as the needle stroke and the opening time are reduced, the discharged amount decreases. Therefore, a new design of the jetting dispenser considering these two most significant parameters can be accomplished in a practical environment, especially for the LED-packaging process industry. It is finally remarked that in the next phase of this study, an experimental investigation will be carried out considering other design parameters, such as the diameter of the nozzle and the operating frequency, besides the needle stroke and the open time considered in this study.
Author Contributions
Jung Woo Sohn analyzed the experimental results and wrote the manuscript; Seung-Bok Choi conceived and designed the research and supervised the projects; all authors provided input for the manuscript and reviewed and approved its final version.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Li, J.; Deng, G. Technology Development and Basic Theory Study of Fluid Dispensing—A Review. In Proceedings of the Sixth IEEE CPMT Conference on High Density Microsystem Design and Packaging and Component Failure Analysis, Shanghai, China, 30 June–3 July 2004; pp. 198–205. [Google Scholar]
- Nguon, B.; Jouaneh, M. Design and Characterization of a Precision Fluid Dispensing Valve. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2004, 24, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.B.; Kai, J. Modeling of Positive-Displacement Fluid Dispensing Process. IEEE Trans. Electron. Packag. Manuf. 2004, 27, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.B. Modeling of Rotary Screw Fluid Dispensing Processes. J. Electron. Packag. 2007, 129, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.P.; Li, H.X.; Ding, H. Modeling and Control of Time-pressure Dispensing for Semiconductor Manufacturing. Int. J. Autom. Comput. 2007, 4, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Hua, Z.; Li, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J. A Jetting System or Chip on Glass Package. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electronic Packaging Technology & High Density Packaging, Beijing, China, 10–13 August 2009; pp. 954–960. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Z.; Deng, G. Design and Modeling of Jet Dispenser Based on Giant Magnetostrictive Material. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electronic Packaging Technology & High Density Packaging, Beijing, China, 10–13 August 2009; pp. 974–979. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Du, J.; Luo, Z.; Du, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Sun, D. Design and Experiment of a Jetting Dispenser Driven by Piezostack Actuator. IEEE Trans. Electron. Packag. Manuf. 2013, 3, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Deng, G. Simulation Analysis of Jetting Dispenser Based on Two Piezoelectric Stacks. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Electronic Packaging Technology (ICEPT), Dalian, China, 11–14 August 2013; pp. 738–741. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.; Liu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Huang, B.; Sun, L. Design and Analysis of a Piezostack Driven Jetting Dispenser for High Viscosity Adhesives. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM), Besacon, France, 8–11 July 2014; pp. 227–232. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.; Liu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhong, M. Bond-graph Model of a Piezostack Driven Jetting Dispenser. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2014, 49, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.H.; Choi, M.K.; Choi, S.B. A New Type of Piezostack-driven Jetting Dispenser for Semiconductor Electronic Packaging: Modeling and Control. Smart Mater. Struct. 2008, 17, 015033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.H.; Choi, M.K.; Yun, B.Y.; Choi, S.B. Design of a Novel Jetting Dispenser Featuring Piezostack and Linear Pump. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2008, 19, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.H.; Choi, S.B.; Kim, J.D. The Design and Control of a Jetting Dispenser for Semiconductor Electronic Packaging Driven by a Piezostack and a Flexible Beam. Smart Mater. Struct. 2008, 17, 065028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.; Hong, S.M.; Choi, M.K.; Choi, S.B. Design and Performance Evaluation of a New Jetting Dispenser System Using Two Piezostack Actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 2015, 24, 015020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.M. Fabrication and Characteristics of Jetting Dispenser with Dual Piezostack Actuators. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Inha University, Busan, Korea, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Uchino, K. Materials Issues in Design and Performance of Piezoelectric Actuators: An Overview. Acta Mater. 1998, 46, 3745–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Tong, L. Design and Testing for Shape Control of Piezoelectric Structures using Topology Optimization. Eng. Struct. 2015, 97, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, C.A.; Kelnberger, A.; Yang, G.Y.; Eitel, R.E.; Shrout, T.R. High Strain Piezoelectric Multilayer Sctuators—A Material Science and Engineering Challenge. J. Electroceram. 2005, 14, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webber, K.G.; Vögler, M.; Khansur, N.H.; Kaeswurm, B.; Daniels, J.E.; Schader, F.H. Review of the mechanical and fracture behavior of perovskite lead-free ferroelectrics for actuator applications. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 063001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minitab 17 Support. Available online: https://support.minitab.com/en-us/minitab/17 (accessed on 5 February 2018).
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).